1
Salicylic acid
OH
OH
O
2
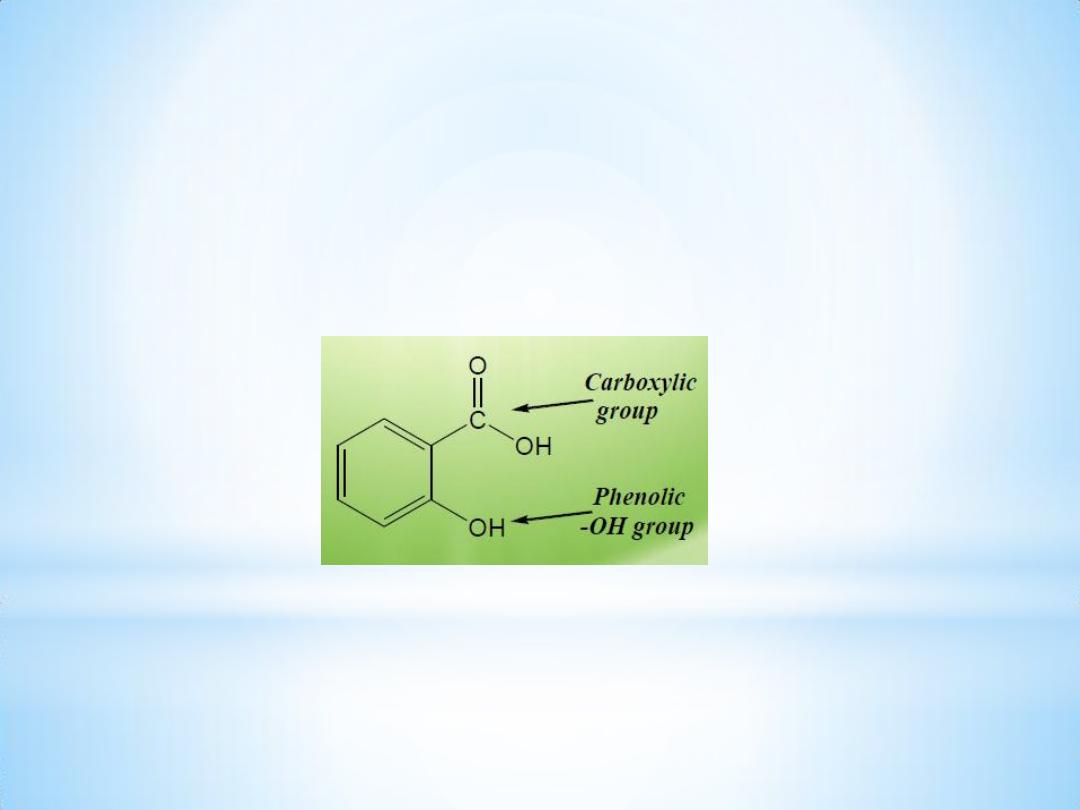
Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid has been known since 1839 and is found in the free
state as salts & esters.
Salicylic acid ( from
Latin salix
)
is a
monohydroxybenzoic acid
.
3
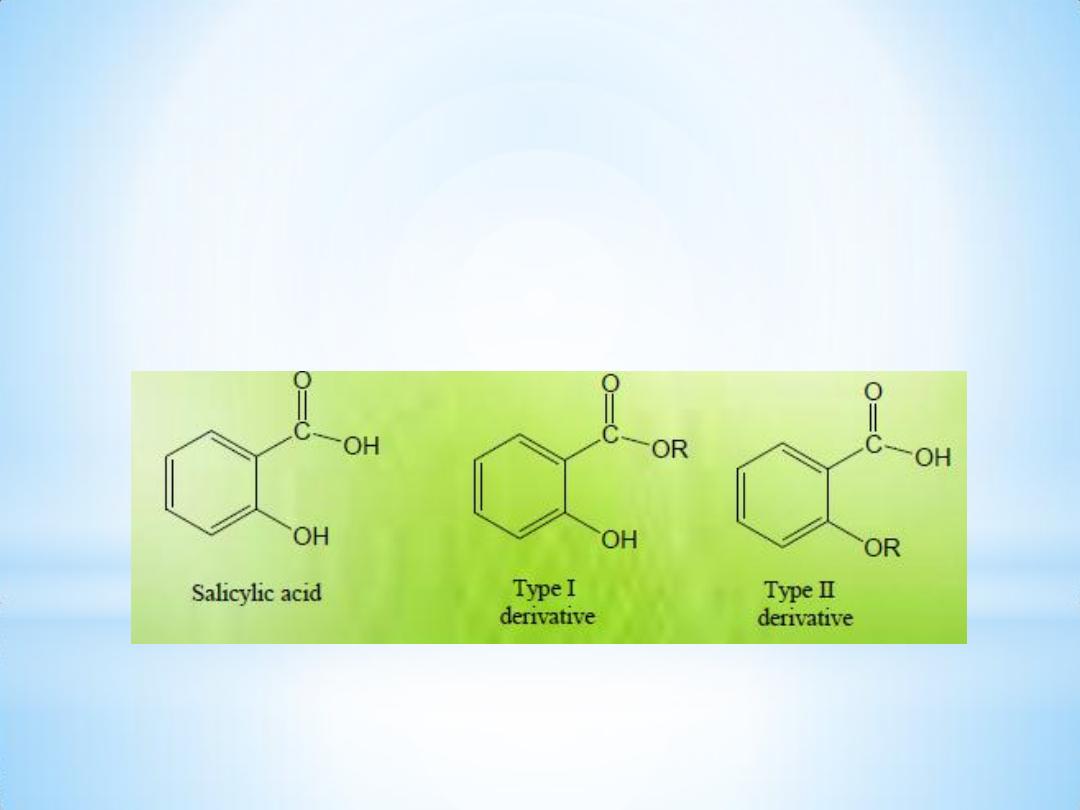
Types of S.A. derivatives:
•
Type I: Represents those that are formed by modifying the
carboxyl group of S.A. , ( e.g. salts, esters or amides ) .
• Type II: Represents those that are derived by substitution on –OH
group of S.A.
4

5
Preparation of S.A.:
1- Kolbe reaction ( industrial method ).
2- Oxidation of salicylaldehyde.
3- Alkaline hydrolysis of ester. Kolbe reaction :-
Kolbe reaction :-
It is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by heating
sodium phenolate ( the sodium salt of phenol ) with CO2 under
pressure (100 atm , 125 °C), then treating the product with sulfuric
acid .
The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is known as
salicylic acid (the precursor to aspirin).
6
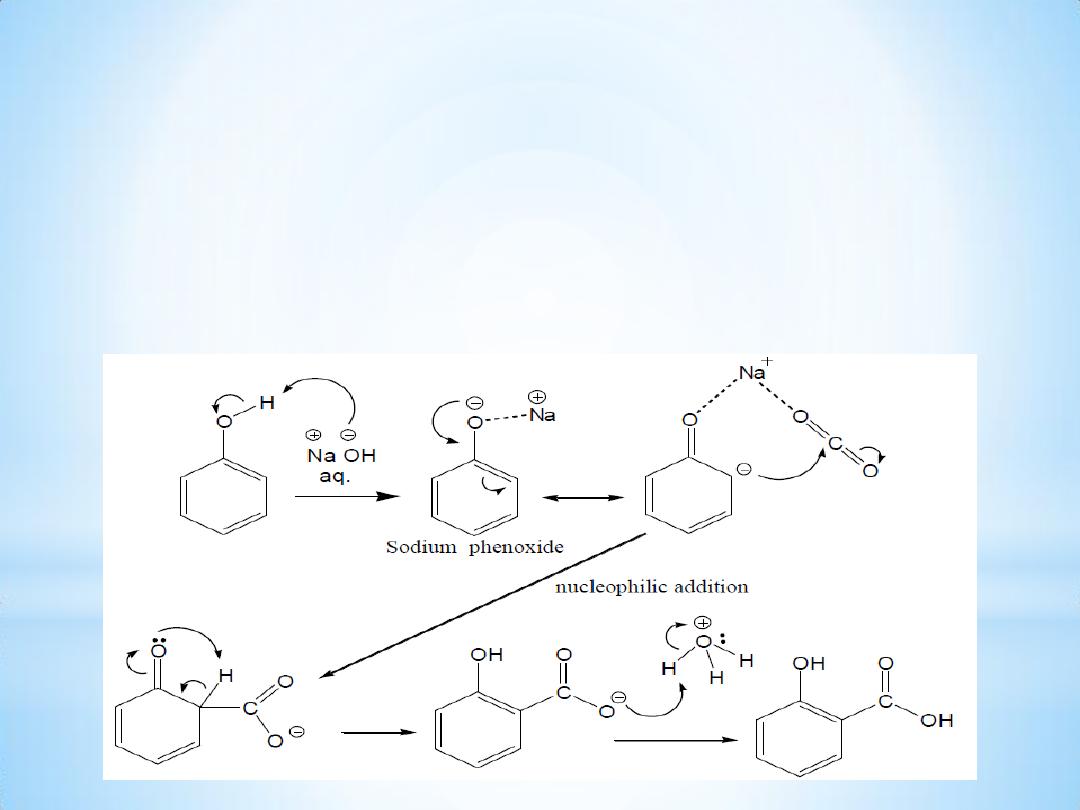
The mechanism of the reaction:
The Kolbe
– Schmitt reaction proceeds via the nucleophile addition
of a phenolate to carbon dioxide to give the salicylate.
The final step is the reaction of the salicylate with acid to form the
desired salicylic acid.

7
2
– oxidation of salicylaldehyde
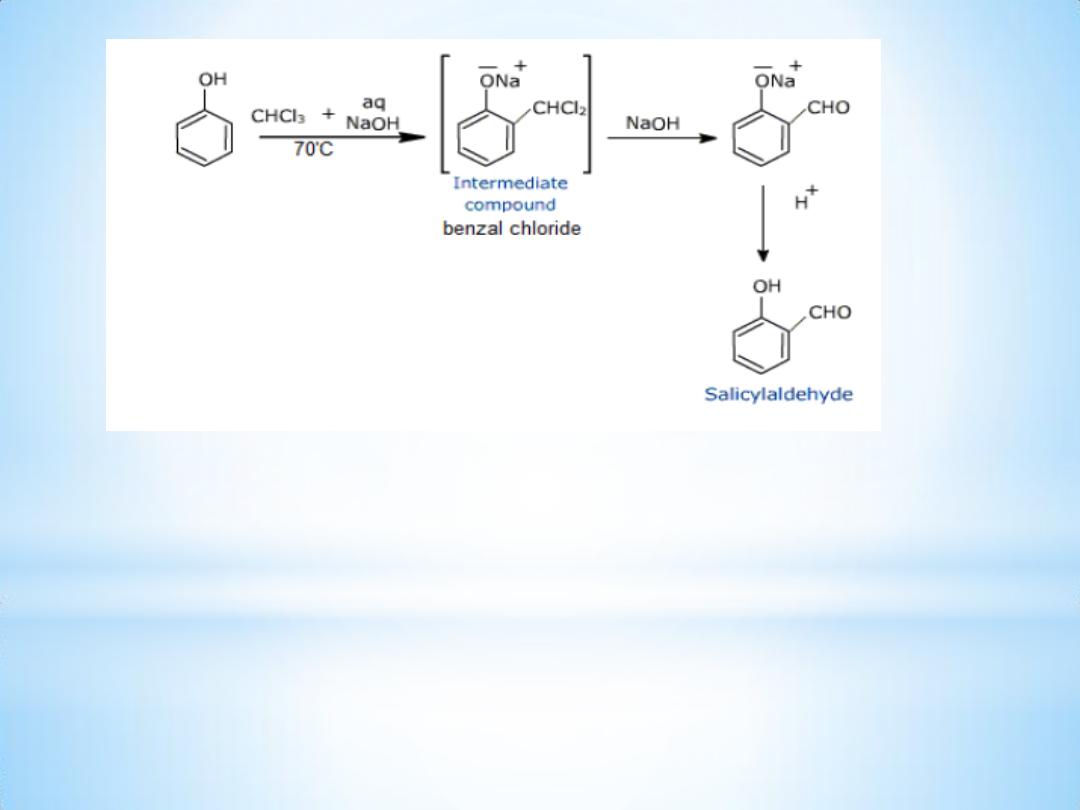
On treating phenol with chloroform in presence of sodium hydroxide
an aldehyde group , a - CHO group, is introduced at ortho position of
benzene ring . This reaction is known as Reimer
– Tiemann reaction.
This results in the formation of o
– hydroxybenzaldehyde
(salicylaldehyde) and p
– hydroxybenzaldehyde .
The ortho isomer being the major product.
8
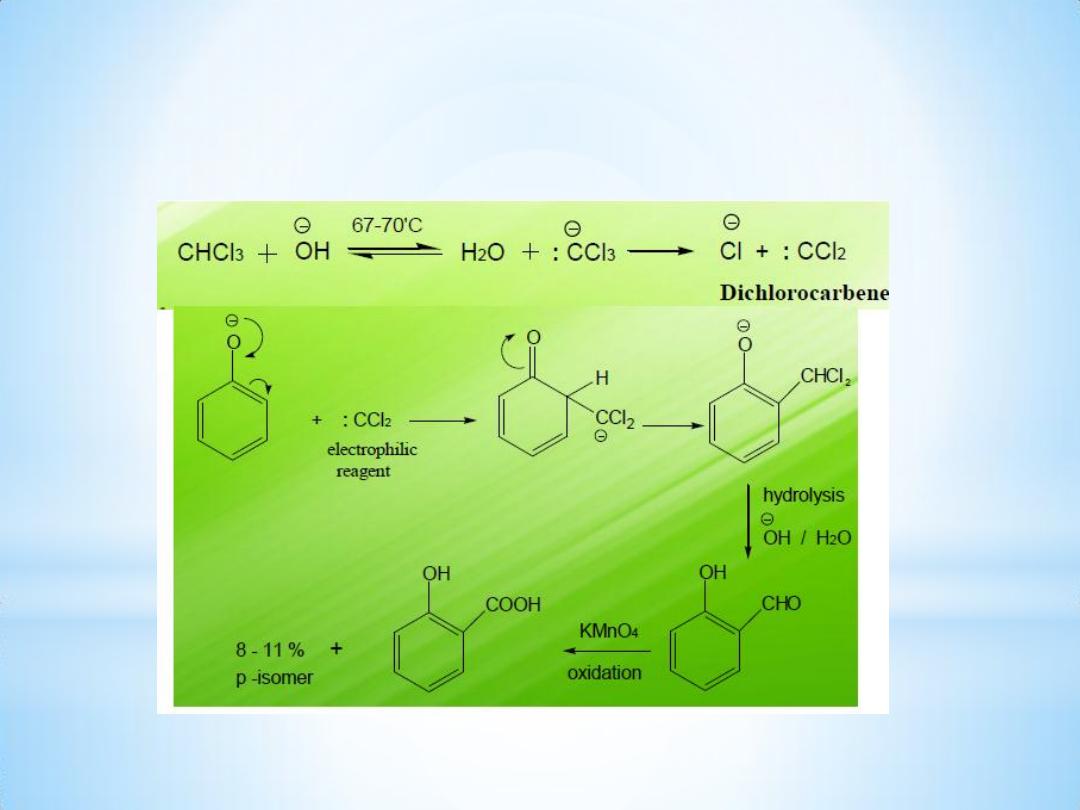
Mechanism of the reaction:
Reimer Tiemann reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
The first step is the generation of electrophile.
9
10
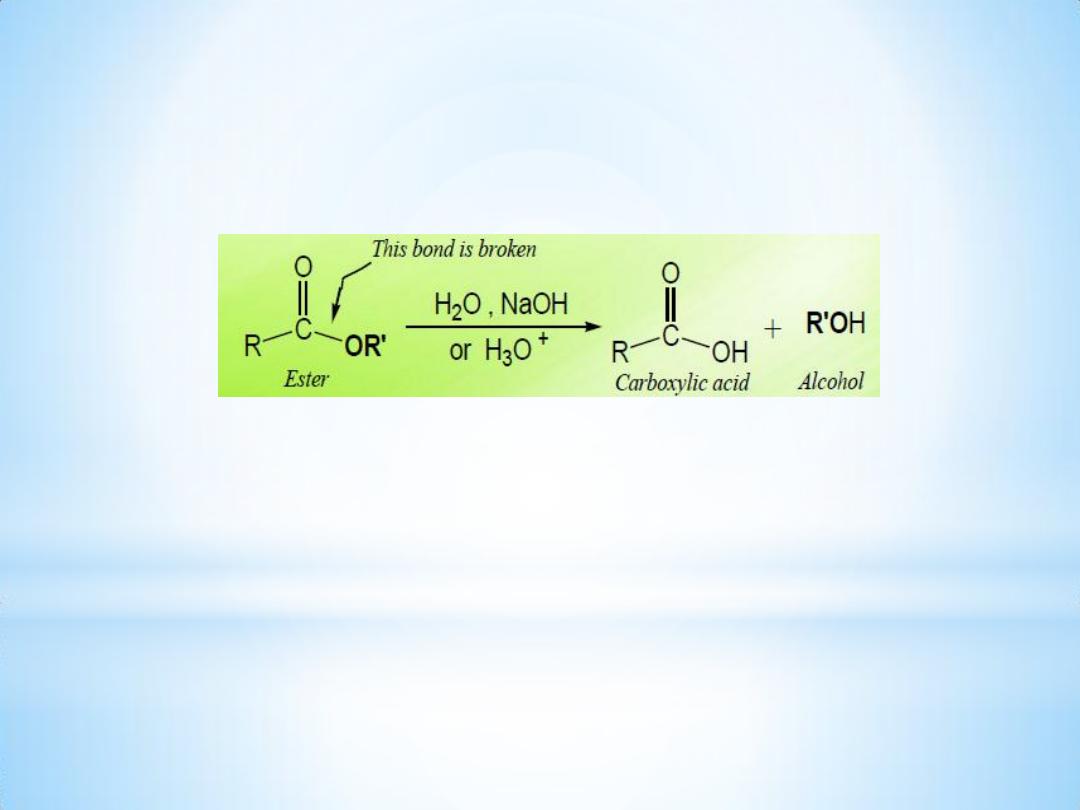
3- Alkaline hydrolysis of ester:
An ester is hydrolyzed either by aqueous base ( Saponification ) or by
aqueous acid, to yield a carboxylic acid plus an alcohol.
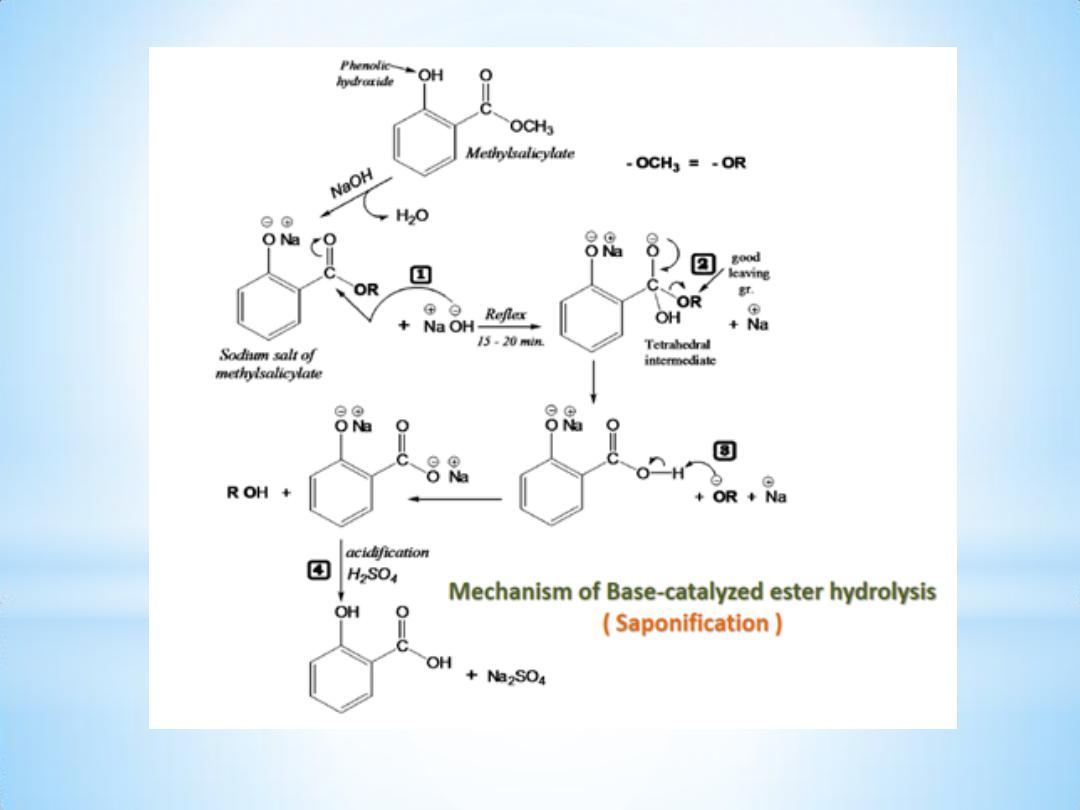
11

12
Name of Experiment : Alkaline Hydrolysis of Ester .
Aim of experiment: Preparation of Salicylic Acid by Alkaline hydrolysis
of Methylsalicylate.
Procedure:
1- Put 2.1 ml of Methylsalicylate in 250 ml boiling flask with few boiling
chips.
2- Add 25ml of 20% aq. NaOH solution & mix ; at this point a white ppt.
appears which will redissolve again by heating .
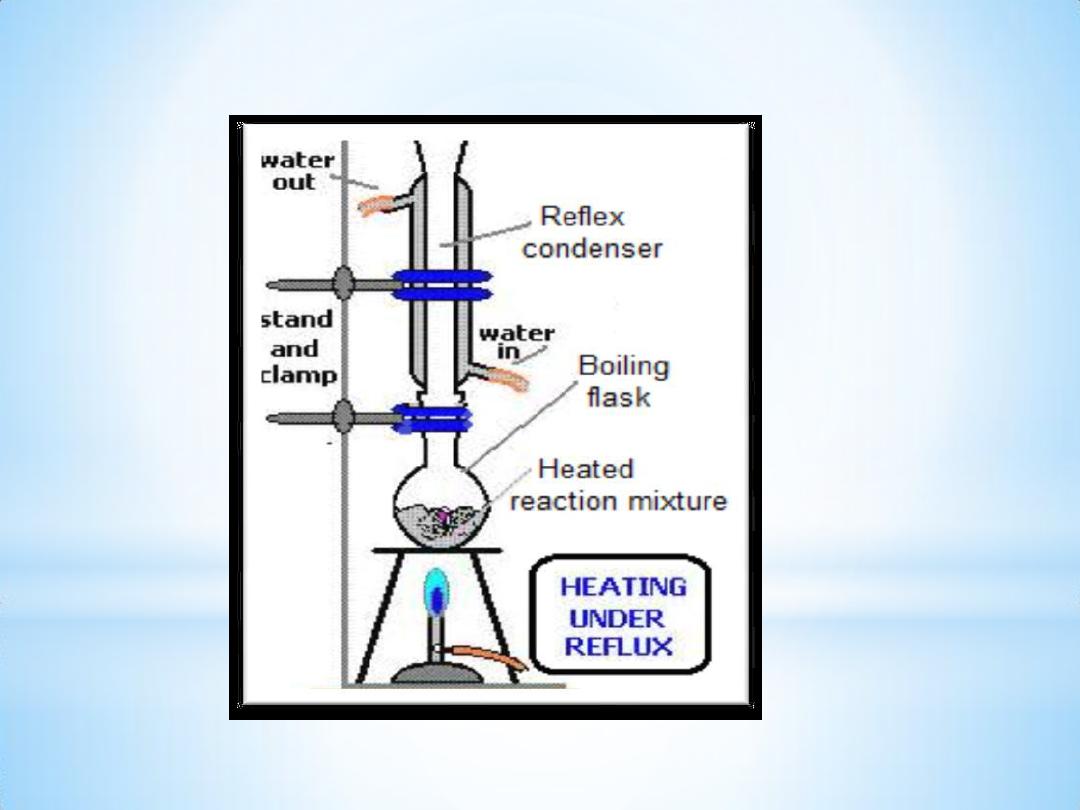
3- Reflex for 15
– 20 min.
4- Stop reflex, cool & transfer the mixture to a beaker.
5- Add 35 ml of dil. H2SO4 to get the acid ( S.A. ppt. ).
6- Further cooling is required then filter & collect the ppt.
7- Recrystallize S.A. from the minimum amount of hot water
13
OCH
3
O
OH
+
2NaOH
Reflux
15-20 min
-H
2
O
O
-
Na
+
O
O
-
Na
+
+ CH
3
OH
O
-
Na
+
O
O
-
Na
+
H
2
SO
4
OH
O
OH
+
Na
2
SO
4
14
