
Nervous tissue
Lab. 7

• Nervous tissue :- is responsible for transport
nervous impulse (motor and sensory impulse),
and it is formed by network more than 100
million
nerve cell
(neurons) ,
nerve fiber
and
nerve ending
, nerve tissue develop from
ectoderm.
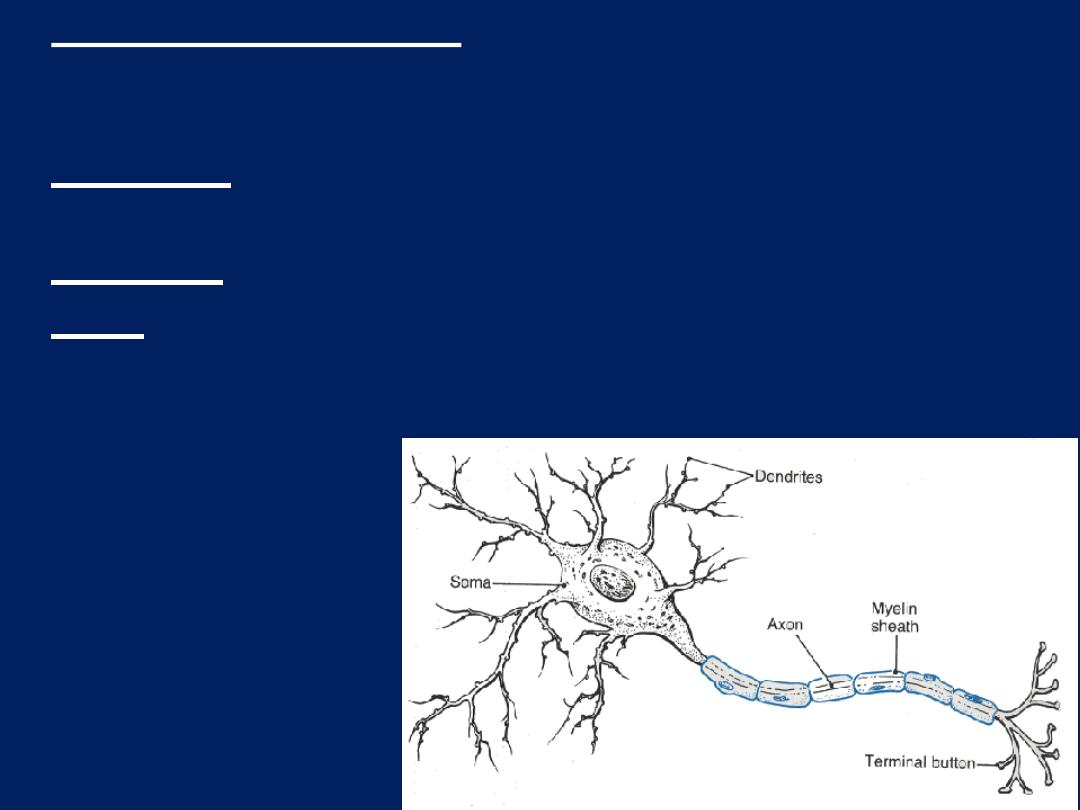
• Nerve cell (neurons):- are responsible for reception
transmission and processing of stimuli and release
neurotransmitters and are consist of:-
• dendrites:- which are multiple elongated processes
specialized for receiving stimuli from environment
• cell body:- perikaryon
• axon:- single process specialized in generating or
conducting nerve impulse to other cells (nerve, muscle,
gland)
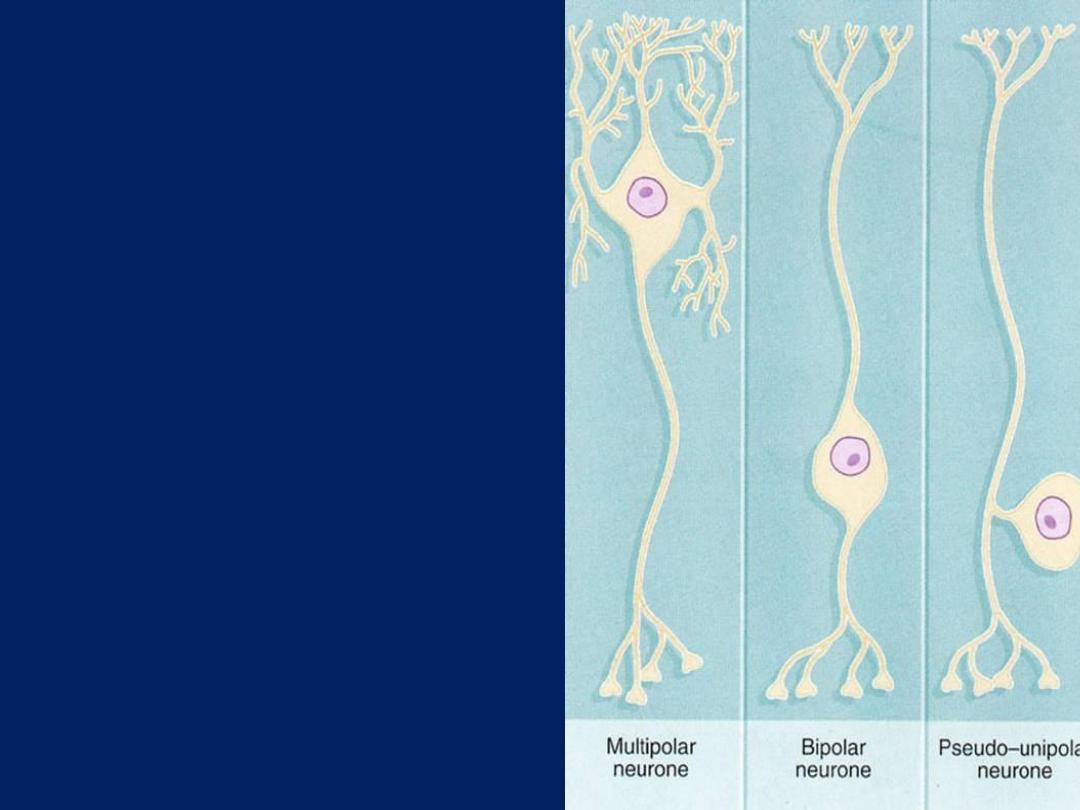
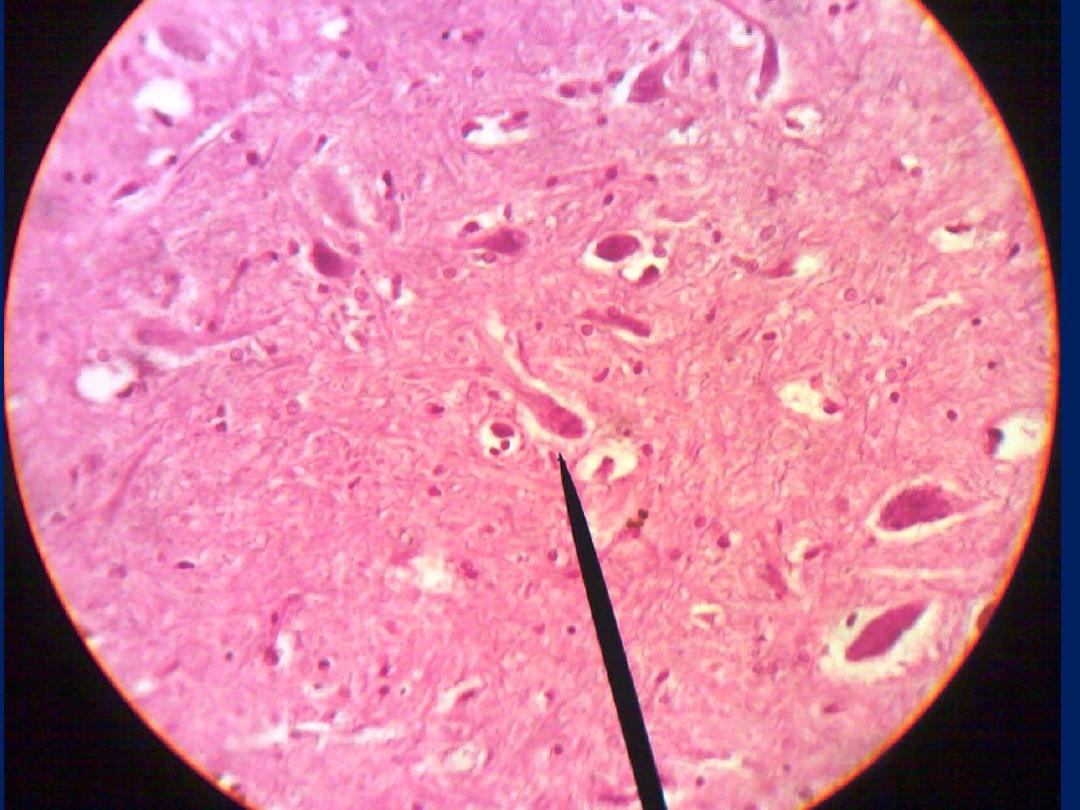
• Nerve cell classified to 3
types according to
numbers of process
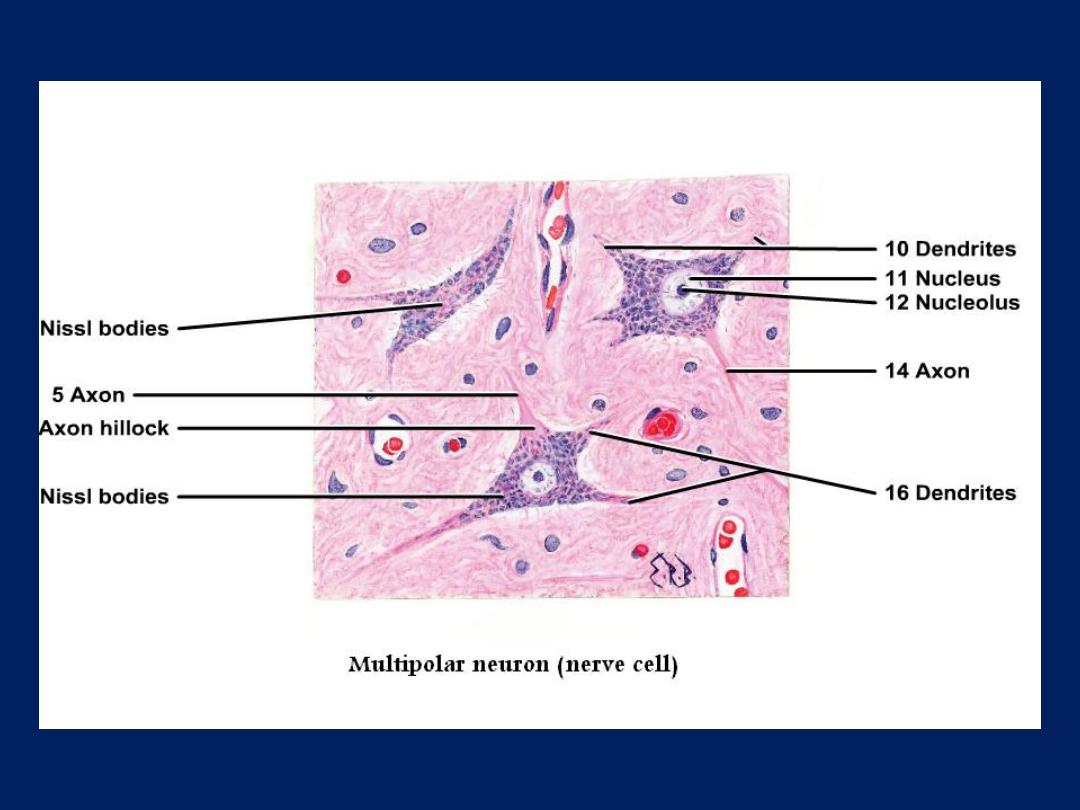
• Multipolar
which have
more than 2 processes.
Most neurons of the
body are multipolar
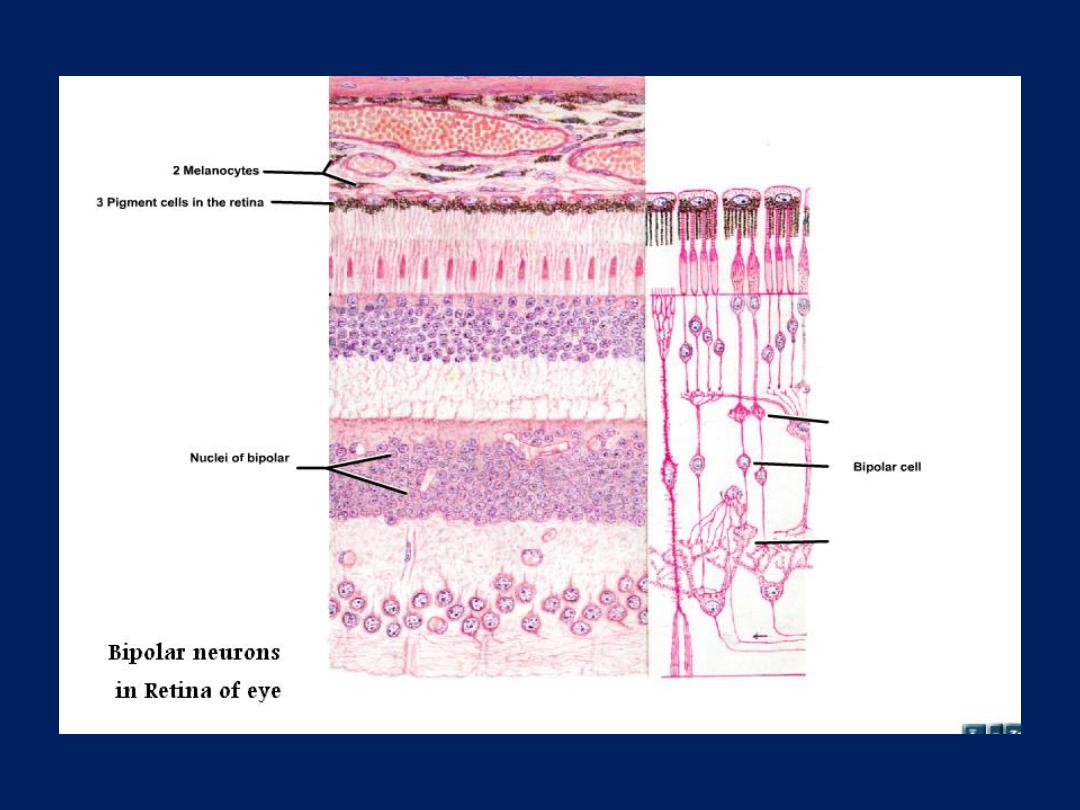
• Bipolar
which have 2
processes.
Found retina
and olfactory mucosa
• Pseudounipolar
which
have single process and
it divide to 2 branches.
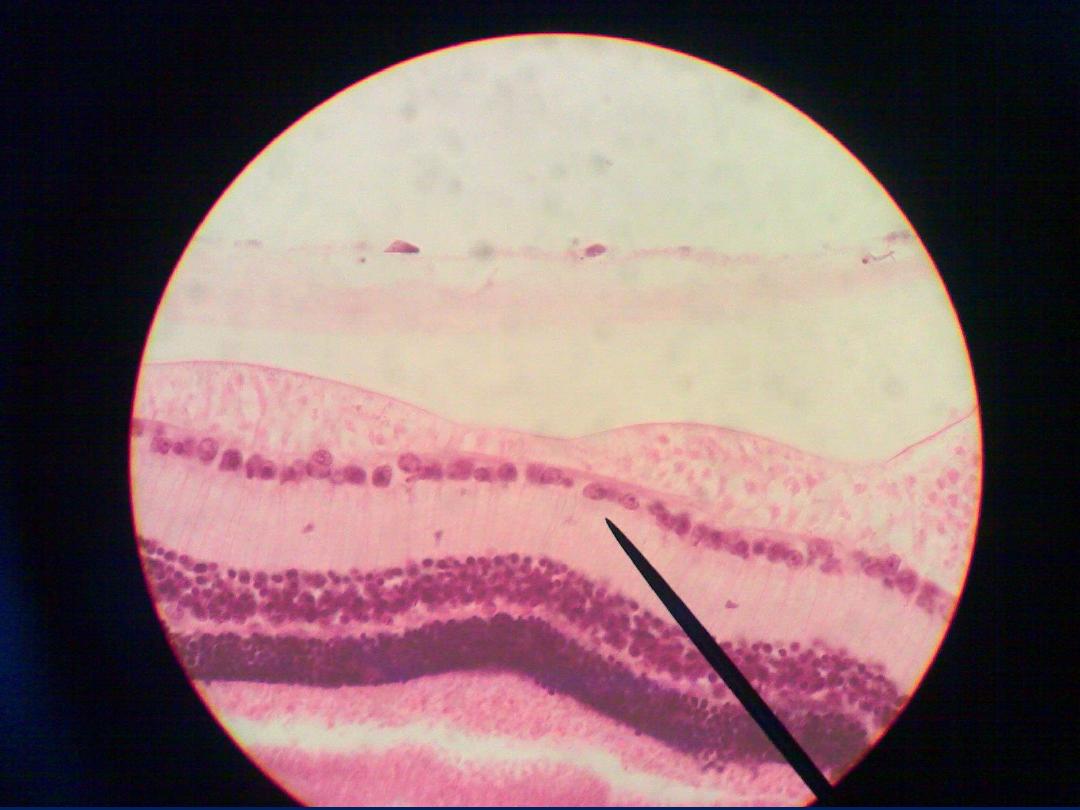
Found spinal ganglia
and cranial ganglia

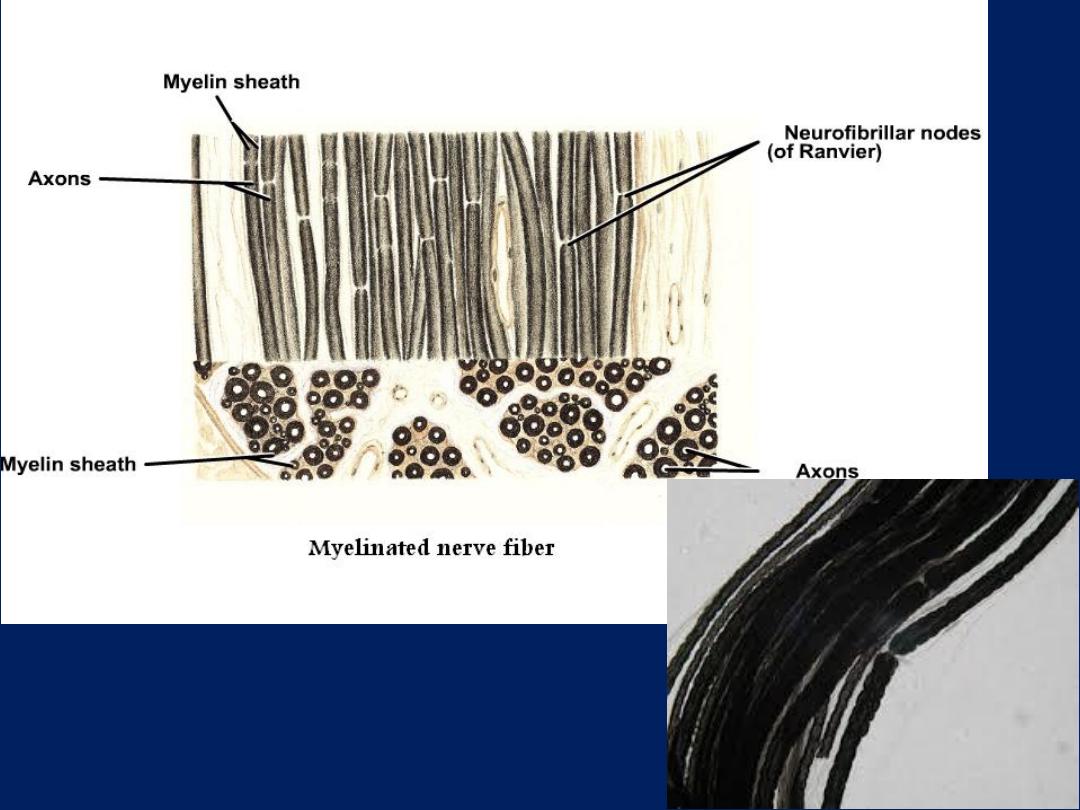
• Fiber:
- consist of axons enveloped by special
sheath of
Schwann cell
. And classified to:-
• Myelinated fibers:
- are the fiber which
enveloped with multilayer
Schwann’s
plasmalema
and unite form myelin sheath and
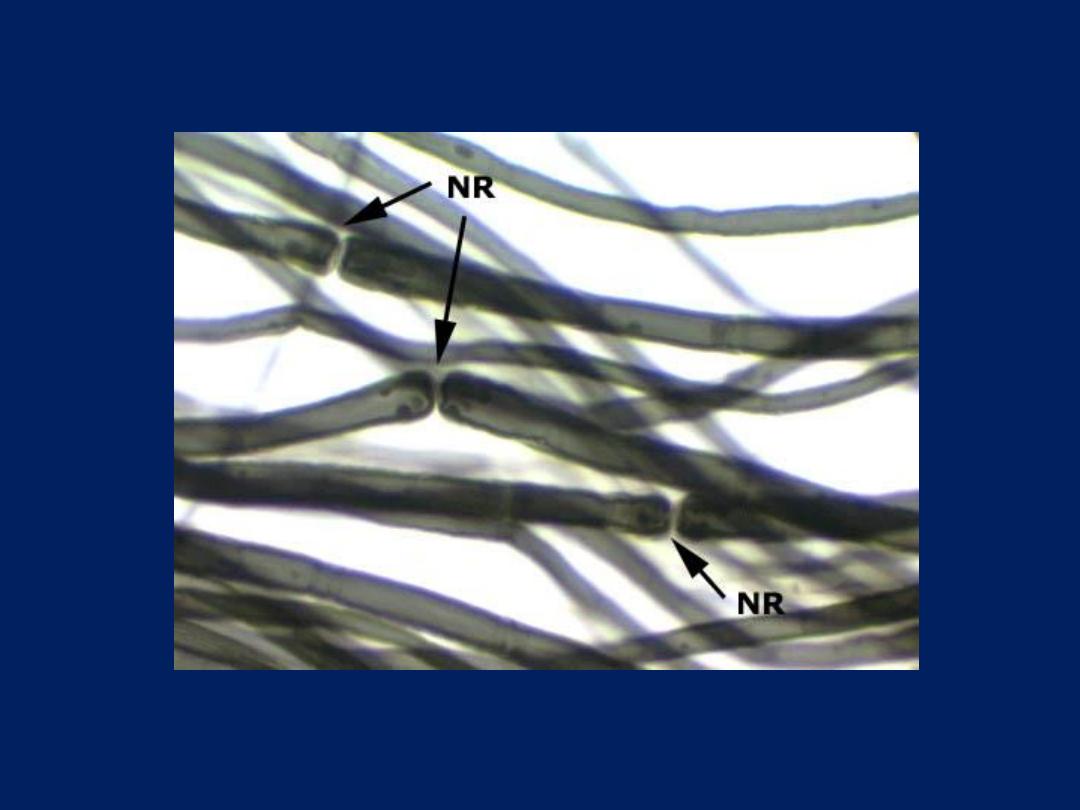
the space between 2 Schwann cell is called
node of Ranvier
.
Found mainly in PNS.
• Un myelinated fibers:
- the axons are
enveloped within simple cleft of Schwann cells
found in CNS.
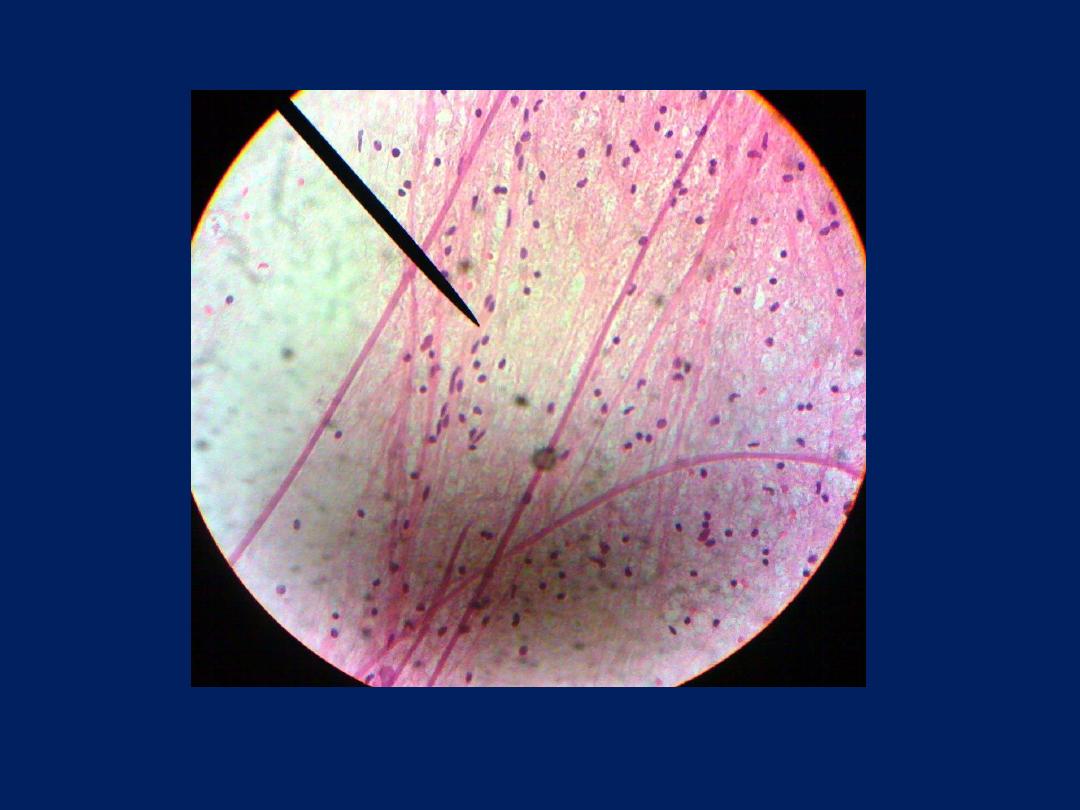

• Nerve ending: -
the nerves end either in
muscle or connective tissue or epithelial tissue.
Therefore they are of two type
sensory nerve
ends
or
motor nerve ending.
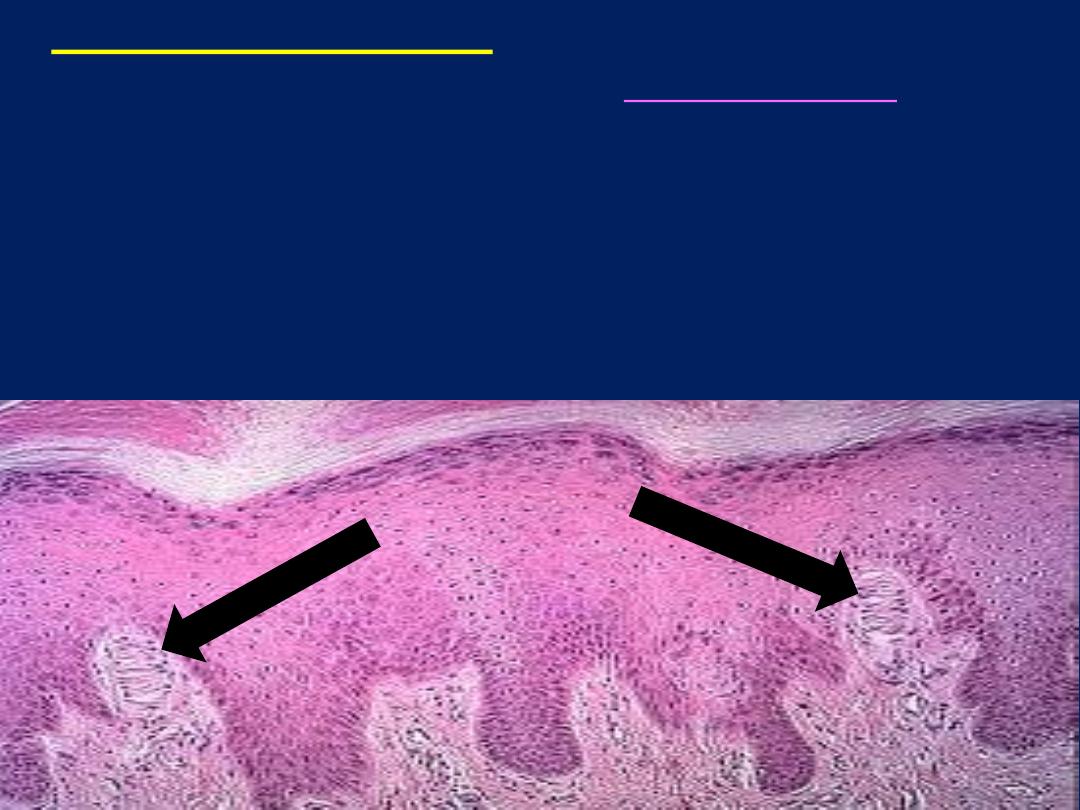
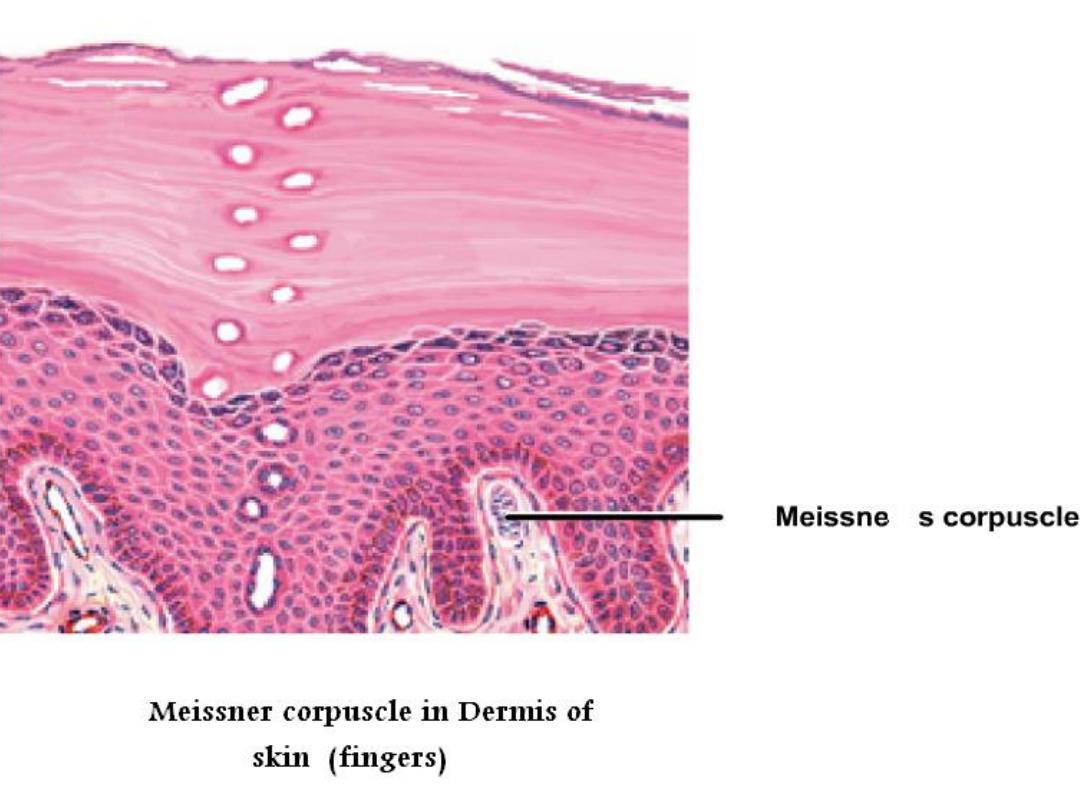
• Meissner corpuscles:-
are small encapsulated
sensory receptors found in the
dermis of skin
(
finger
tip
,
foot
,
eyelid
,
lips
) Meissner corpuscles are oval
shape the receptors consist of delicate collagenous
tissue capsule surrounding a mass of plump, oval cells
arranged transversely and representing specialized
Schwann cells and non myleinated sensory fiber rarify
throughout the cell mass in helical meaner.
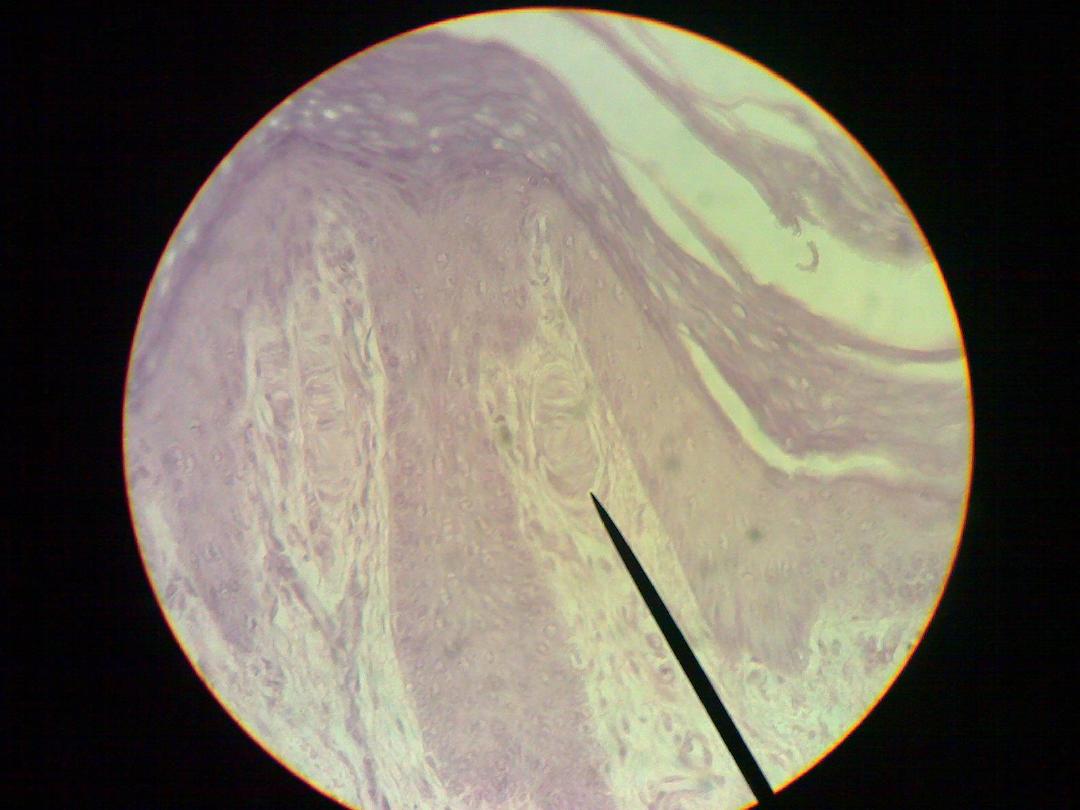

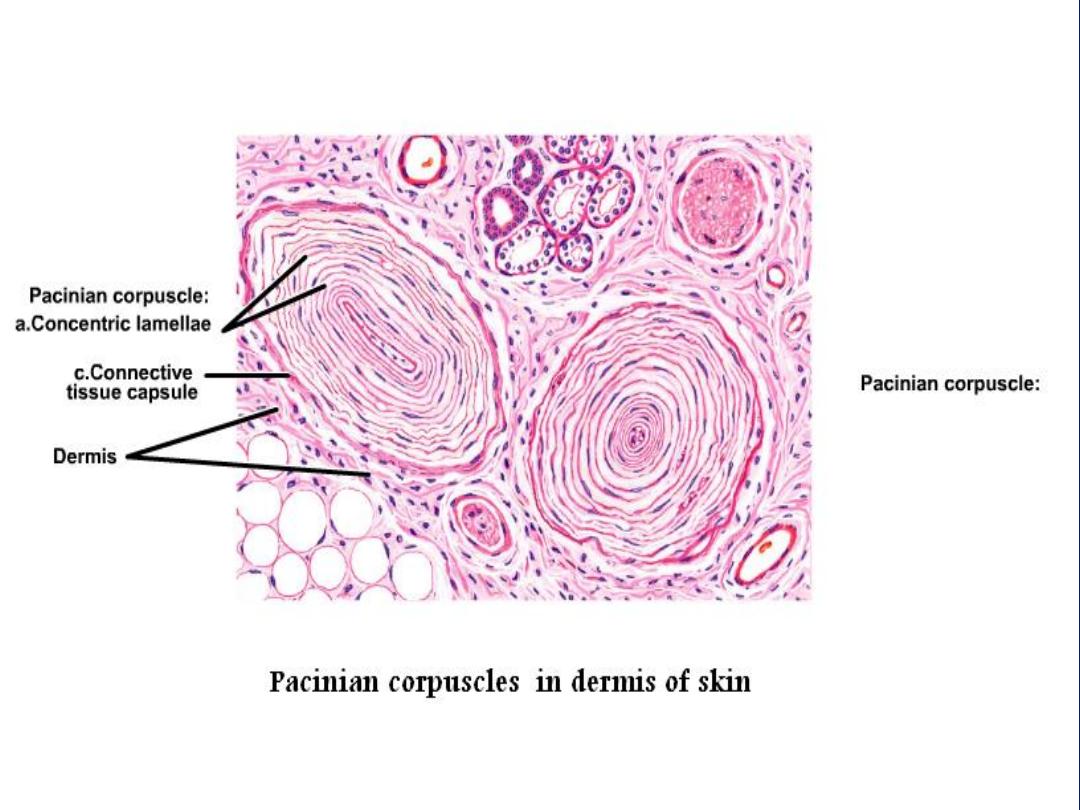
• Pacinian corpuscles: -
large encapsulated sensory
receptor responsive to
pressure
or
coarse touch
,
vibration
and
tension
found in
deep skin layer
,
ligament
. These organs consist of delicate capsule
enclosing many concentric lamellae of flattened cell

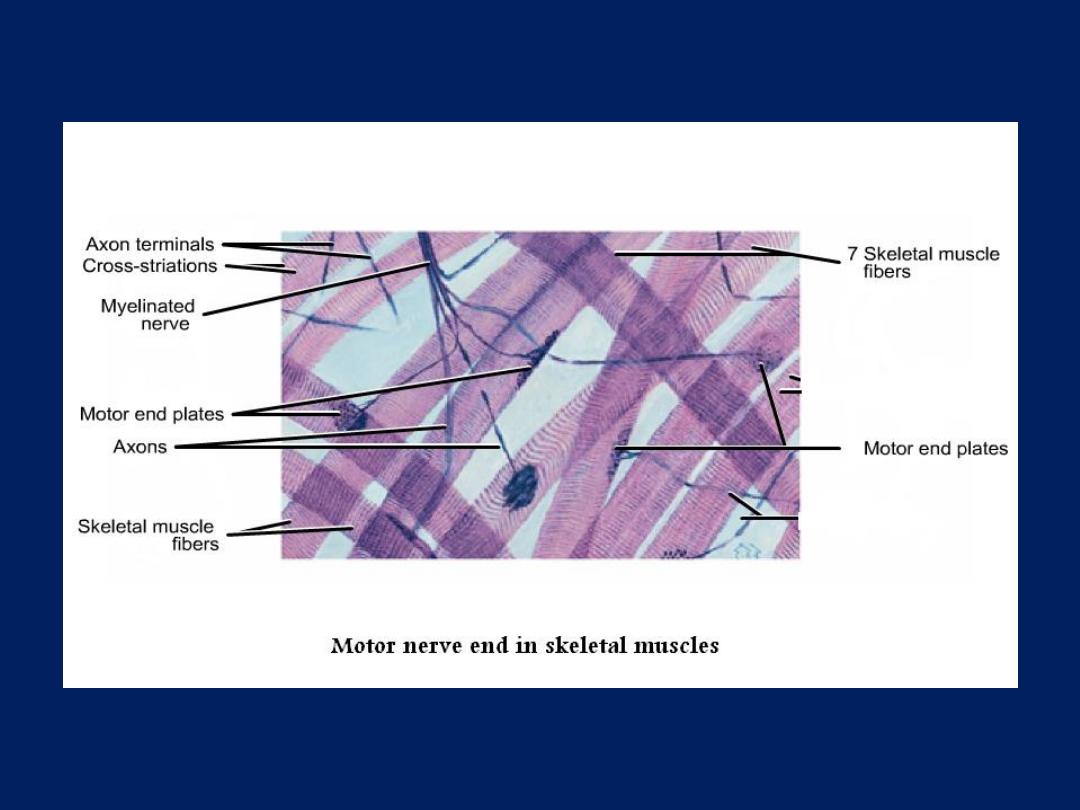
• Motor nerve end: -
in which nerve fiber end
in striated muscles and becomes unmyelinated
and branch and end with dents.

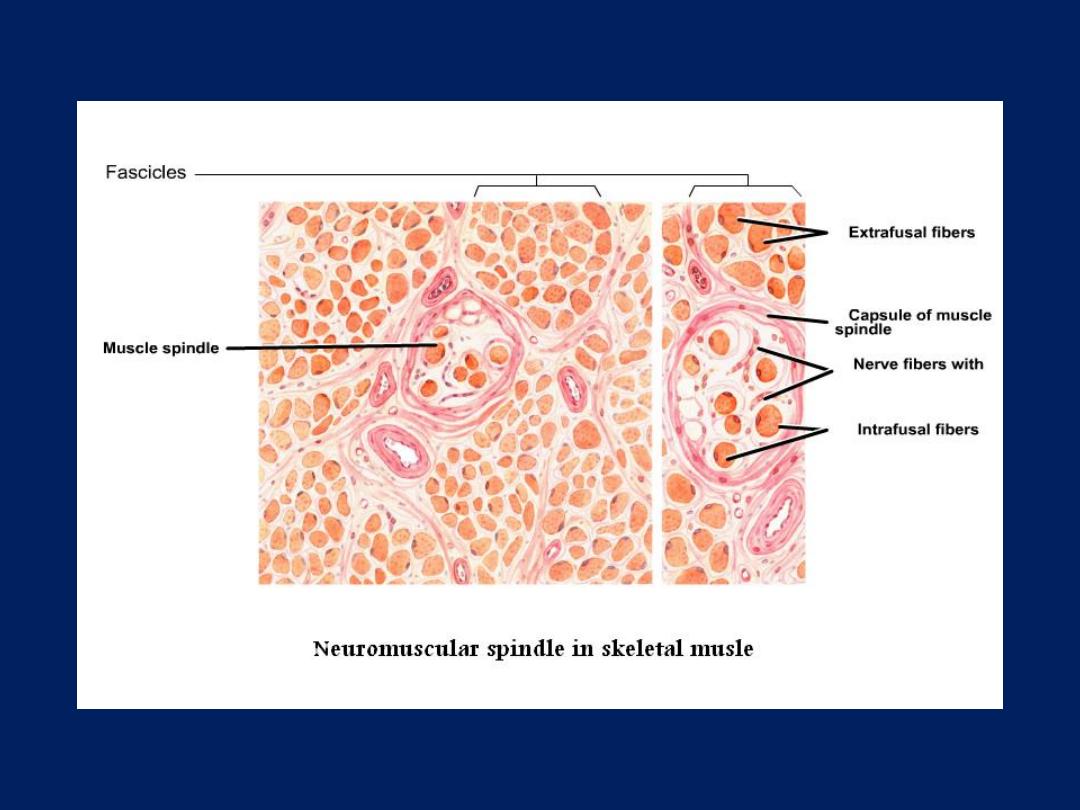
• Neuromuscular spindle: -
stretch receptor
organs within skeletal muscles which are
responsible for regulation of muscle tone via
spinal reflex.
• These organs are encapsulated, lymph filled
fusiform structure. Each spindle contain 2 to
10 modified skeletal muscle fibers called (intra
fusel fibers) which are smaller than skeletal
proper membrane. The intra fusal fibers have a
central non striated area and nuclei tend to
central.

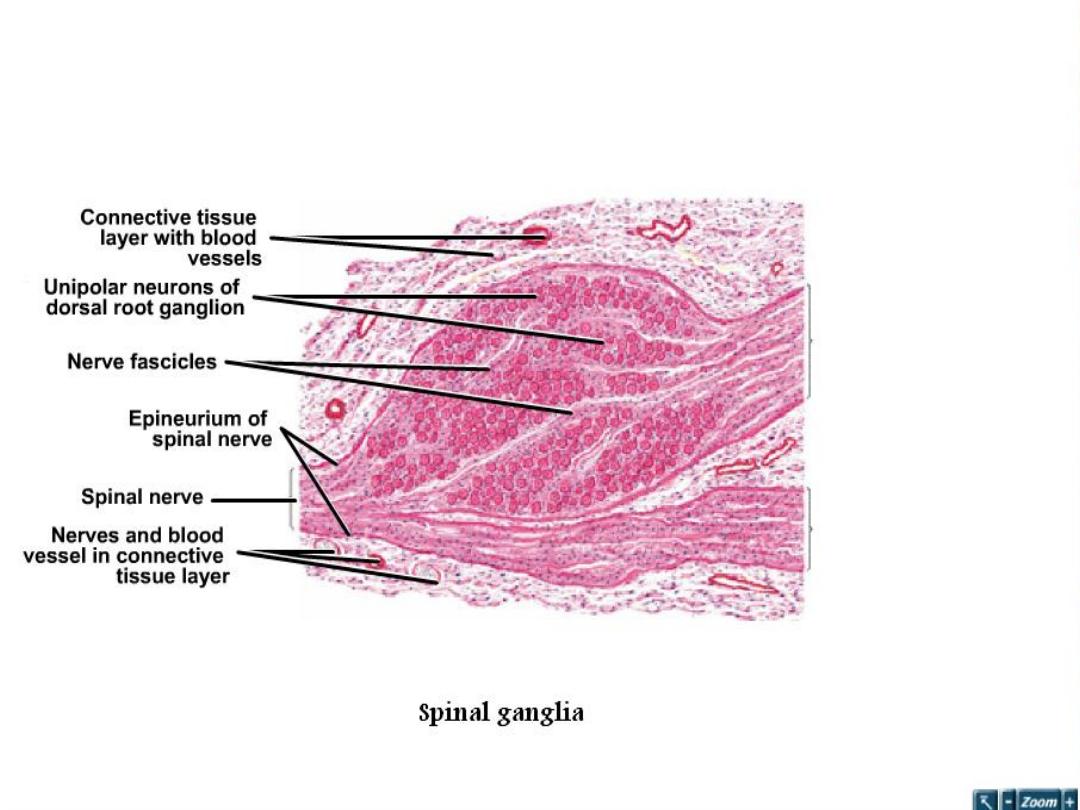
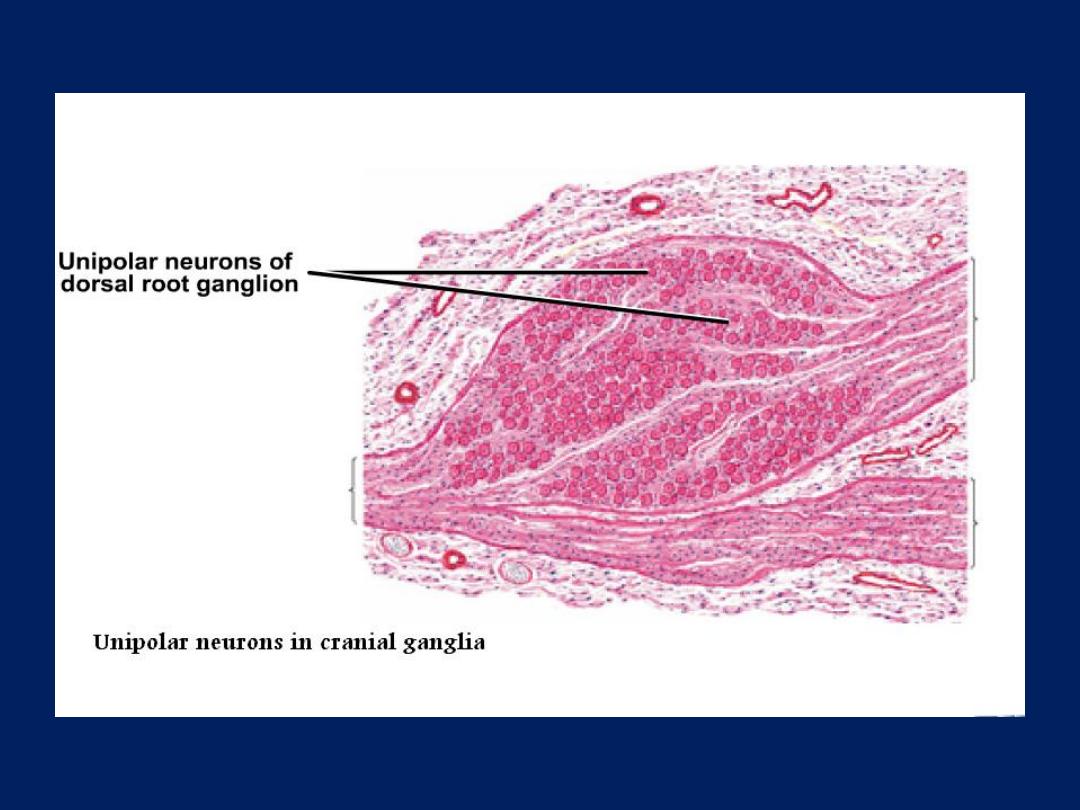
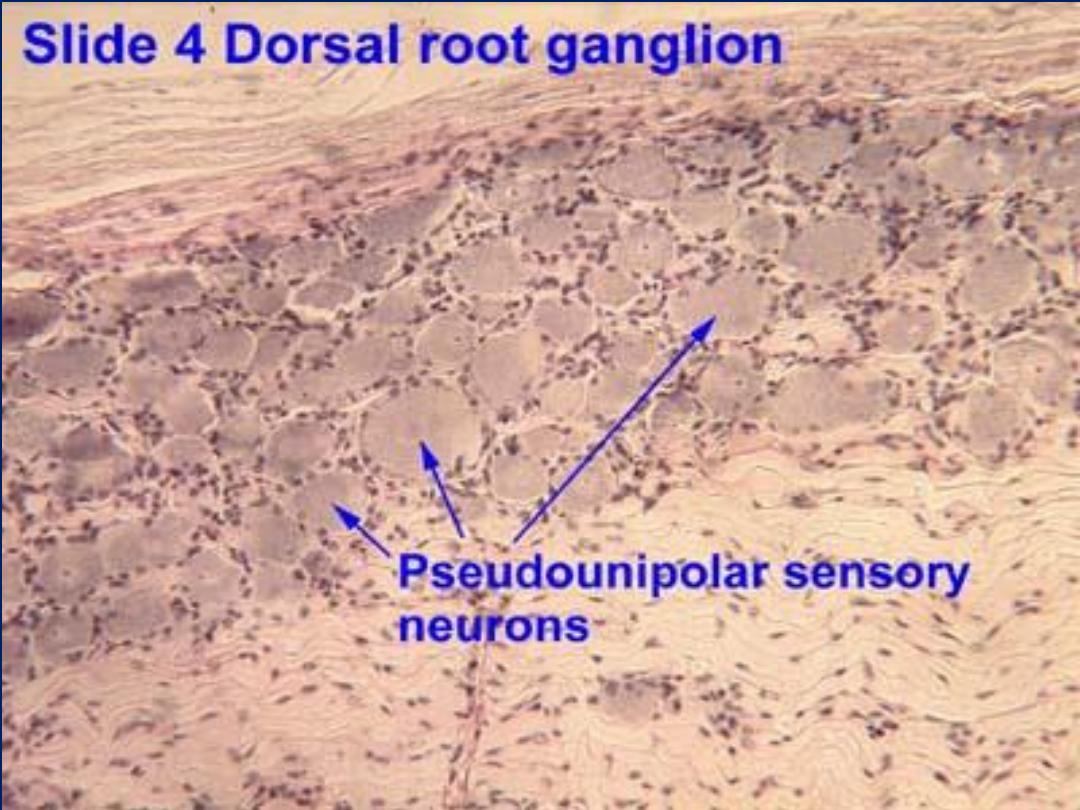
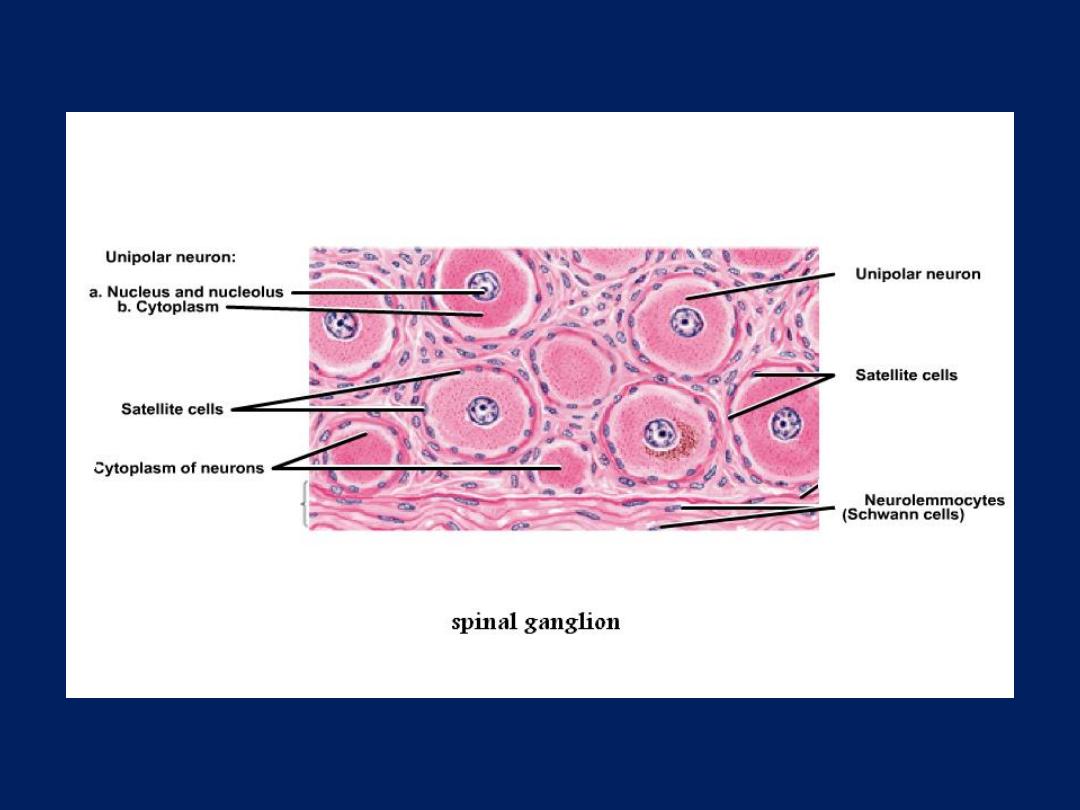
• Spinal ganglion: -
are aggregations of neurons
cell bodies located outside CNS and spinal
ganglia lie on the posterior nerve roots of
spinal cord.
• They contain the cell bodies of primary
sensory neurons which are psendounipolar and
they surrounded by satellite cell (provide
structural and metabolic support ) and there is
fascicle of nerve passing to the center of
ganglion and whole ganglion is encapsulated
by condensed supporting tissue which
continuous with perineural and epineuria
sheaths of the peripheral nerve.

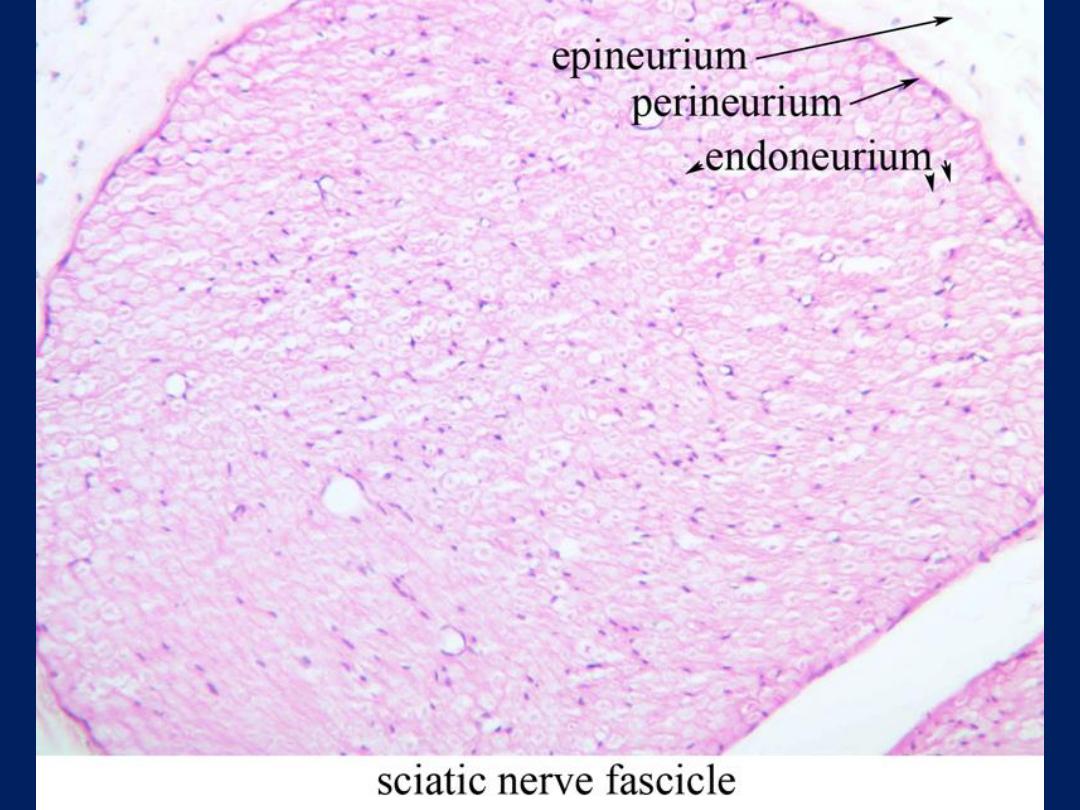
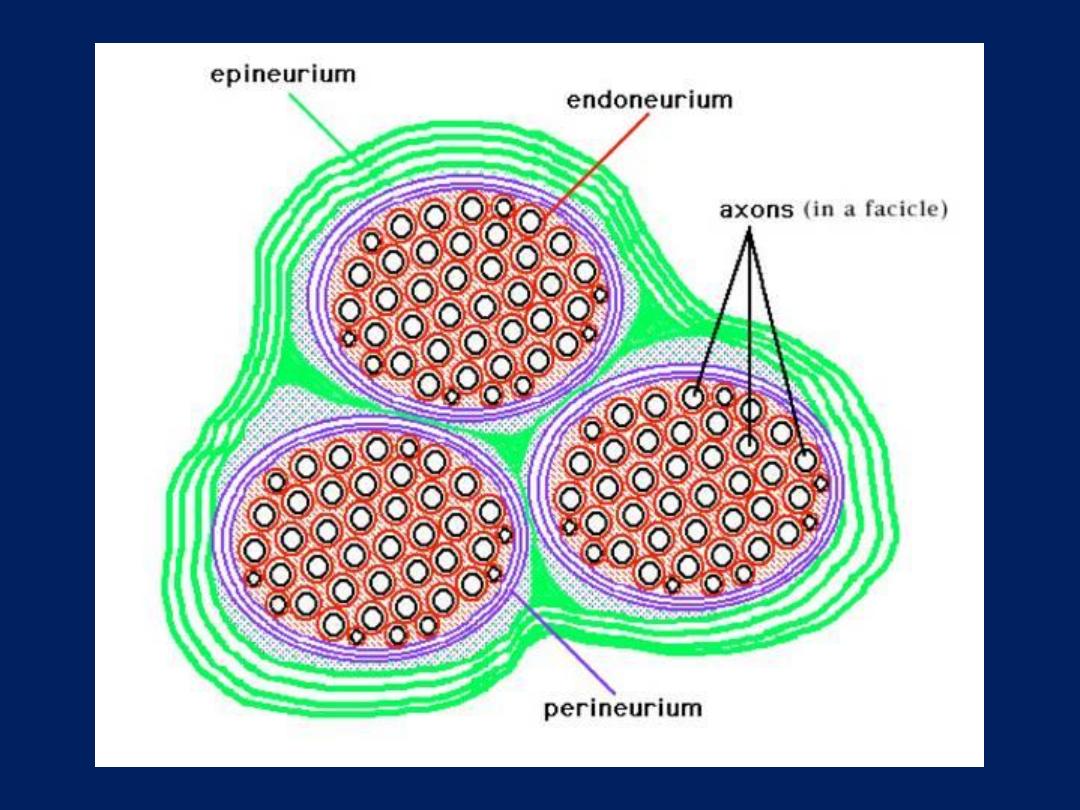
• Nerve trunk: -
nerve fibers grouped in
bundles to form the nerves.
• Nerves have an external fibrous coat of
dense connective tissue called
epineurium
.Which also fills the space
between the bundles of nerve fibers which
called
perineurium
.
• The
endoneurium
consist of a thin layer of
reticular fibers produced by Schwann cells.
• The layers protect the nerve from
aggression and act as barrier to the passage
of macromolecules.

Thank you for Listening
