Muscular tissue

Muscular tissue
Muscular tissue is composed of specialized cells
(fibers) for producing movement of body. We can
classify muscular tissue according to the function
and structure to:
•Skeletal muscle
•Cardiac muscle
•Smooth muscle

Skeletal muscle
• It is striated voluntary muscle.
• It is attached to skeletal backbone.
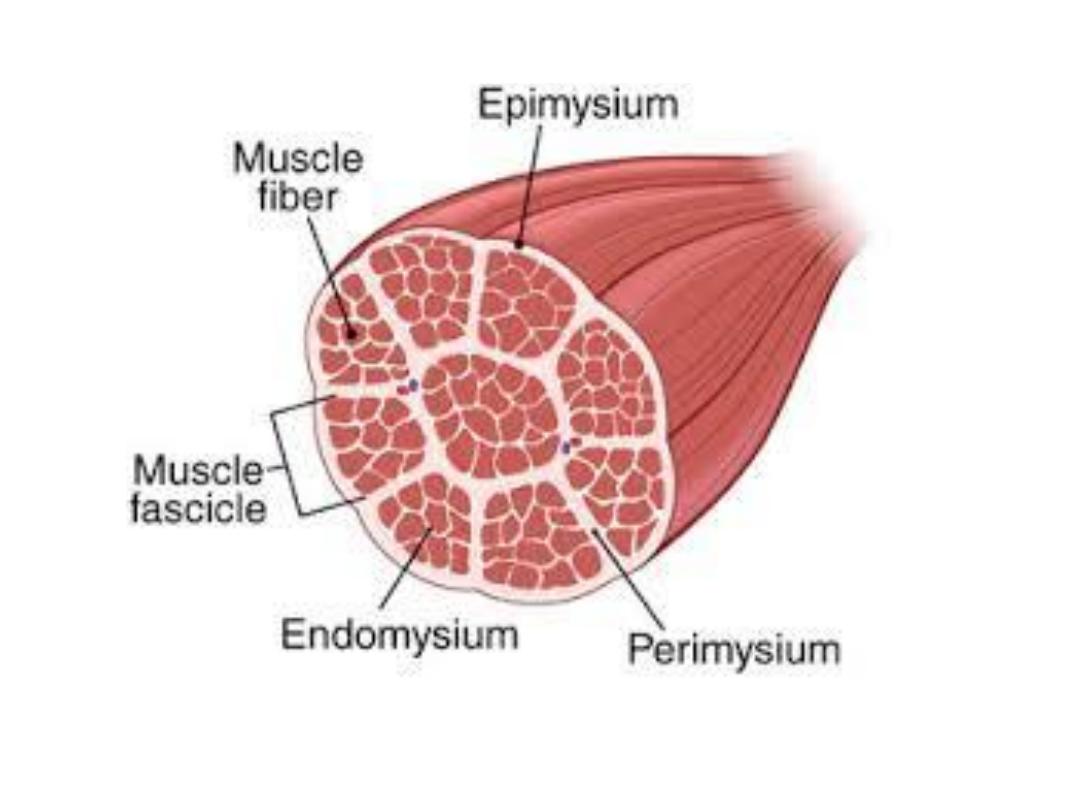
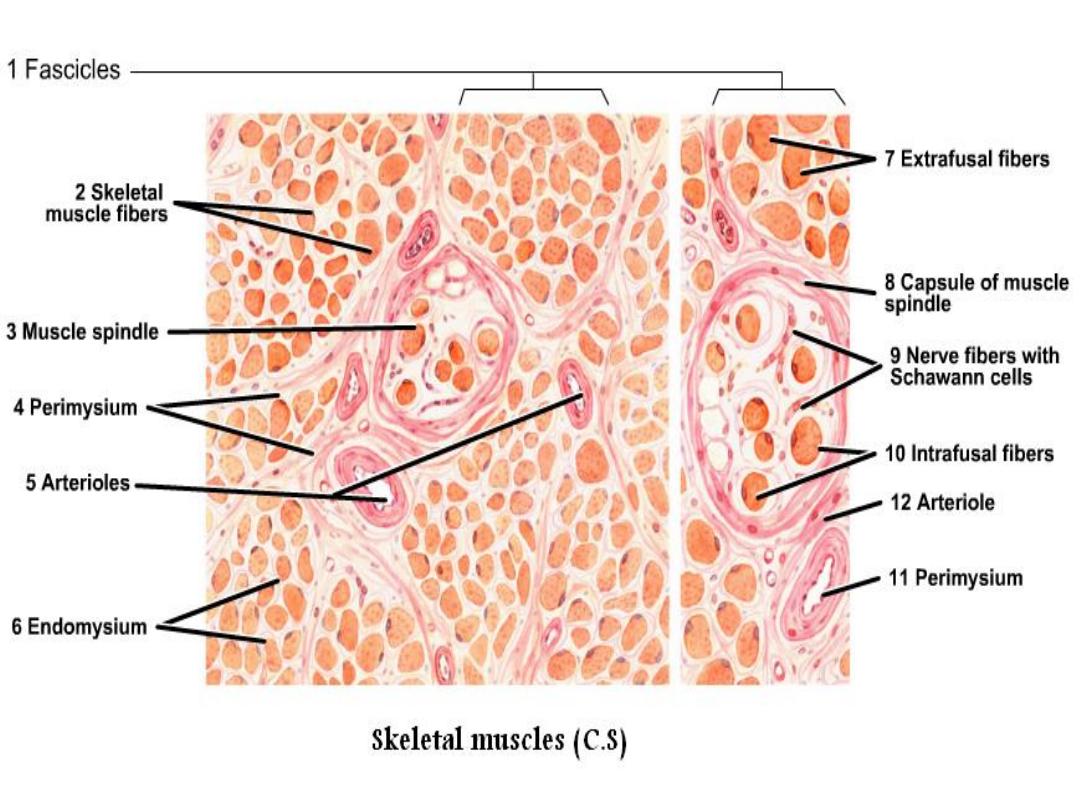
• Each skeletal muscle envelop in a layer of
connective tissue called epimysium within it,
are the muscle fibers arranged in bundles, each
bundle is surrounding by sheath called
perimysium within the fasciculus ,the muscle
fibers covered by sheath called endomysium.
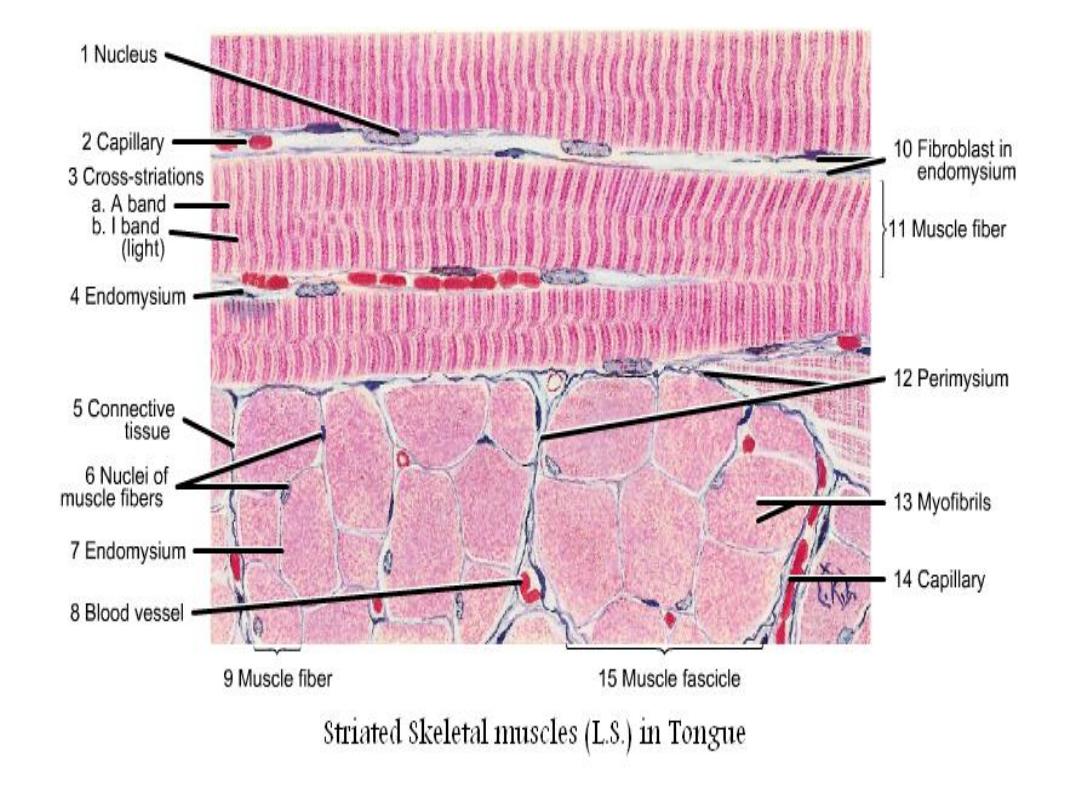
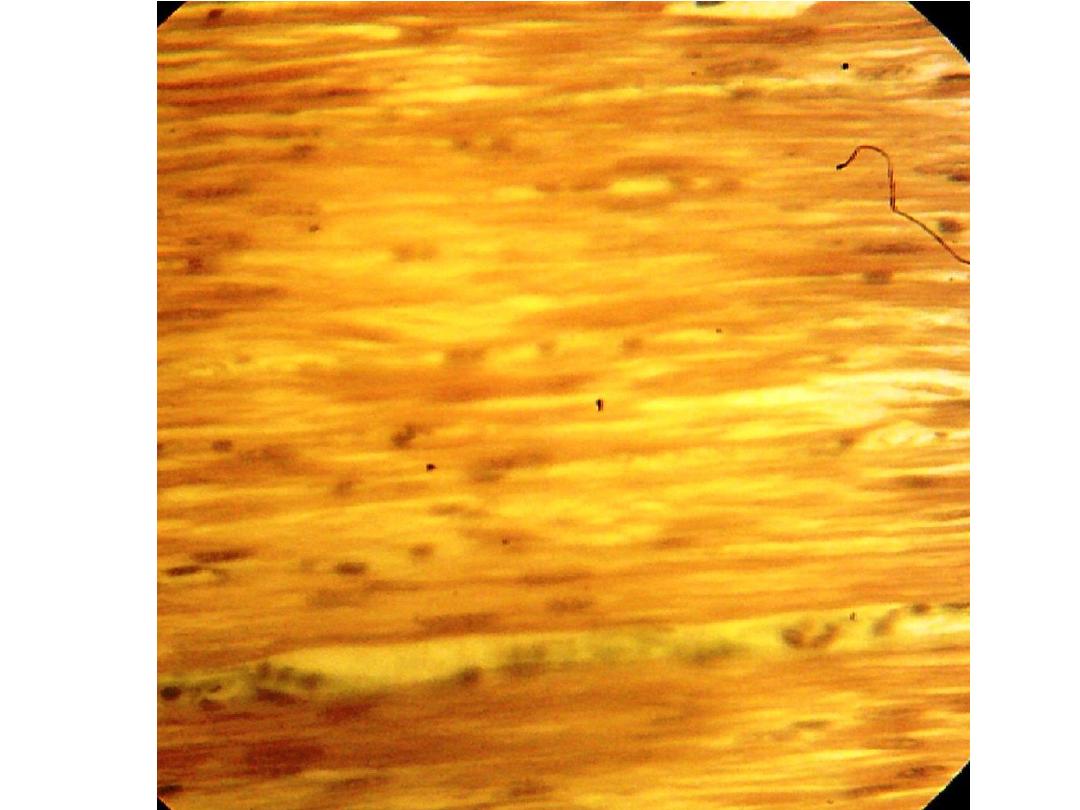
• L.S the muscle fiber show alternating dark A
band (anisotropic), and light I bands (isotropic).
• There is a Z line in the middle of I band.
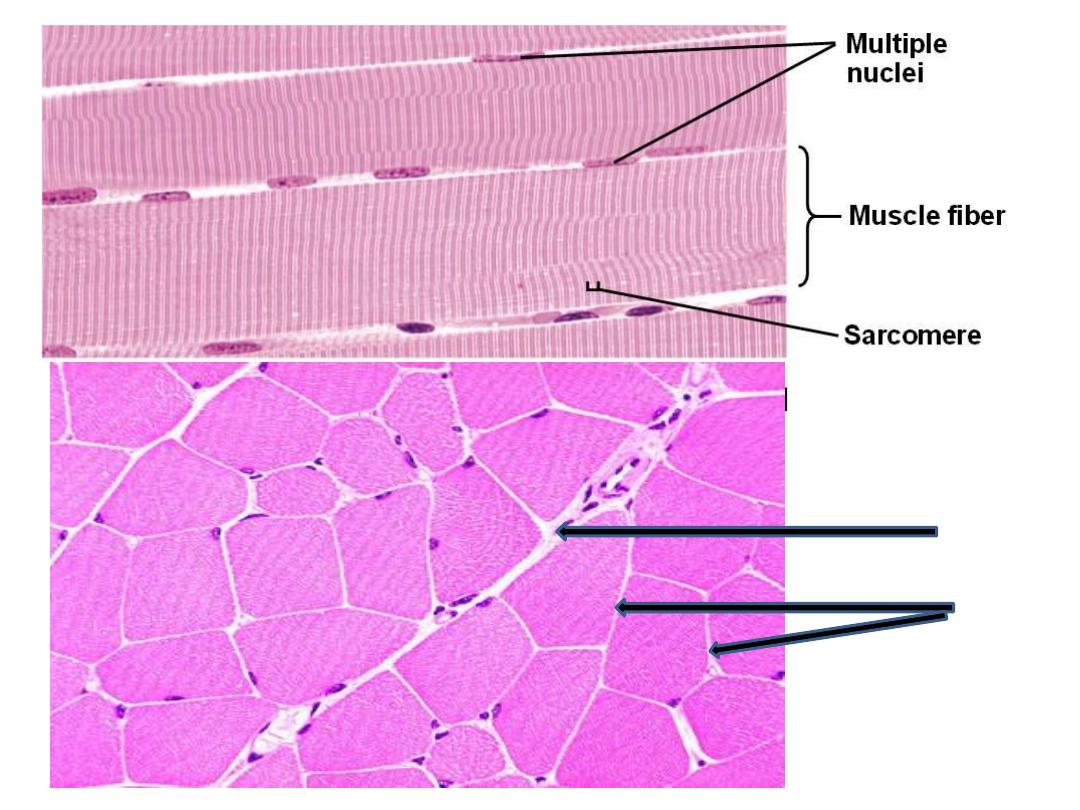
• In general this section of skeletal muscle appears
as cylindrical, parallel bundles with multi-
peripheral nuclei.

• In C.S, the fibers section appears polygonal
to round shape with different diameters. The
myofibrils appear as dots with clear as the
peripheral nuclei.
m
endomysium
perimysium
L.S
C.S

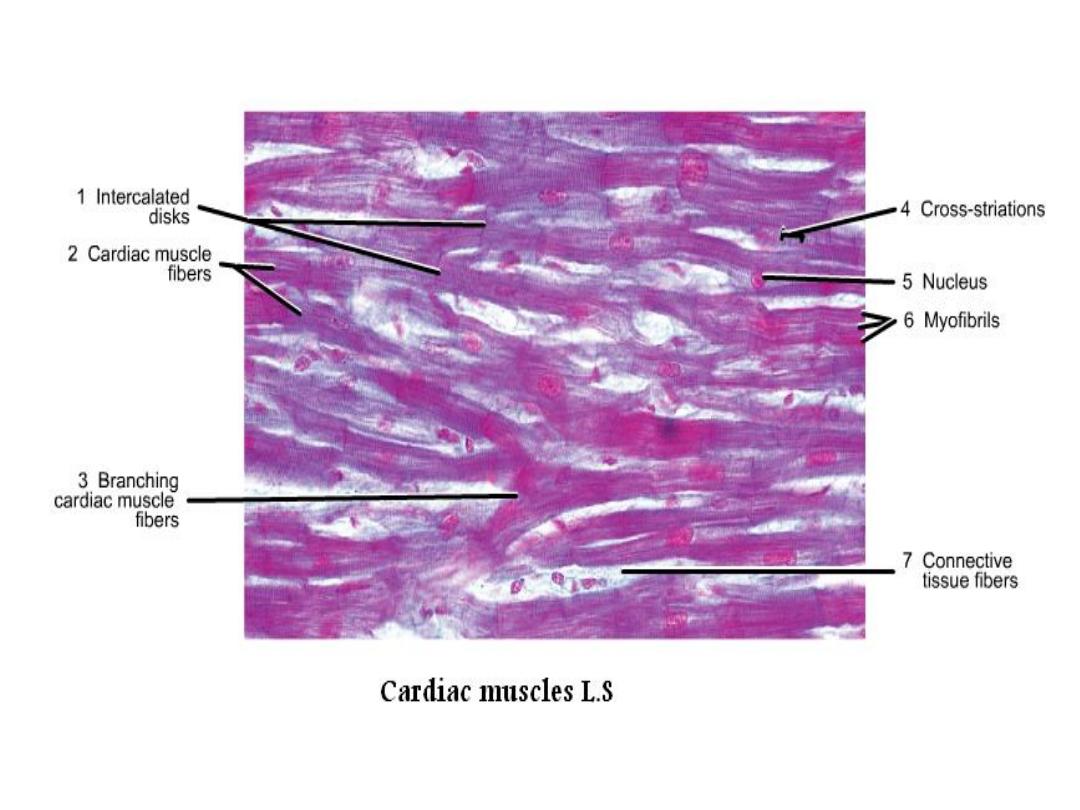
Cardiac muscle
• It is striated, involuntary muscle, contract rhythmically
and automatically.
• It is found only in muscular layer of heart and the roots
of large vessels joining the heart.
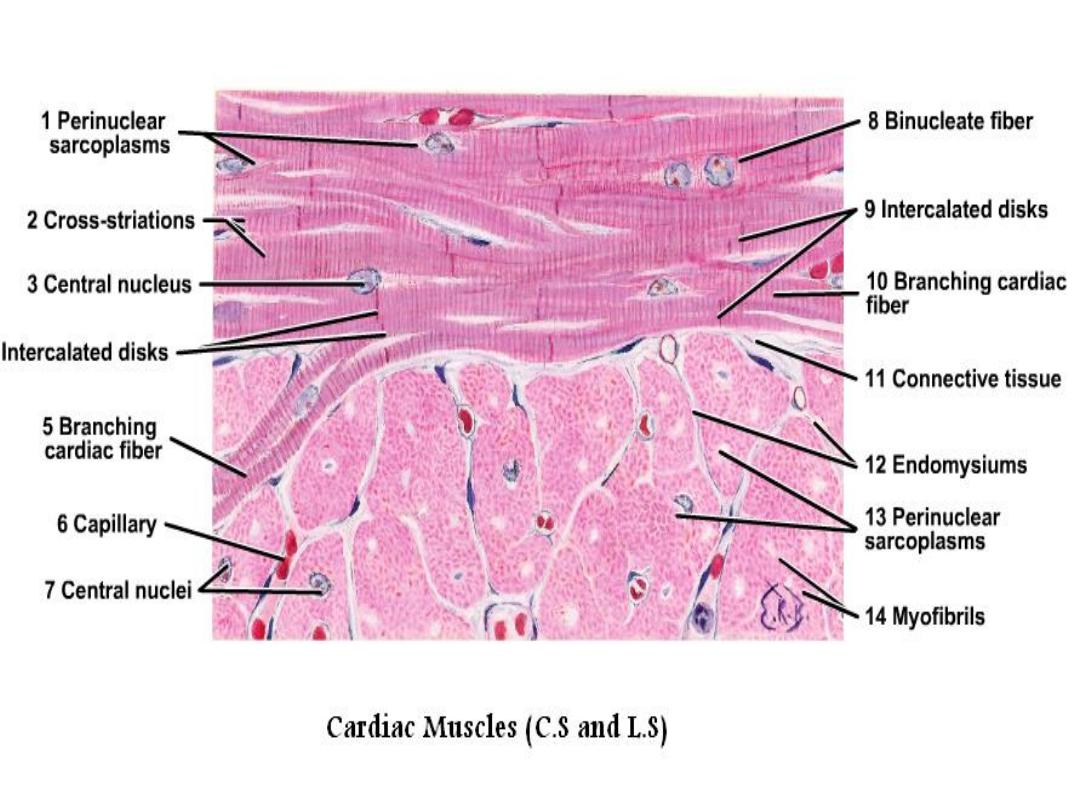
• Cardiac muscle cells have a branched shape so that
each cell is in contact with three of four other cardiac
muscle cells.
• Each cardiac muscle fiber contains a single nucleus and
is striated, because it appears to have light and dark
bands when seen through a microscope.
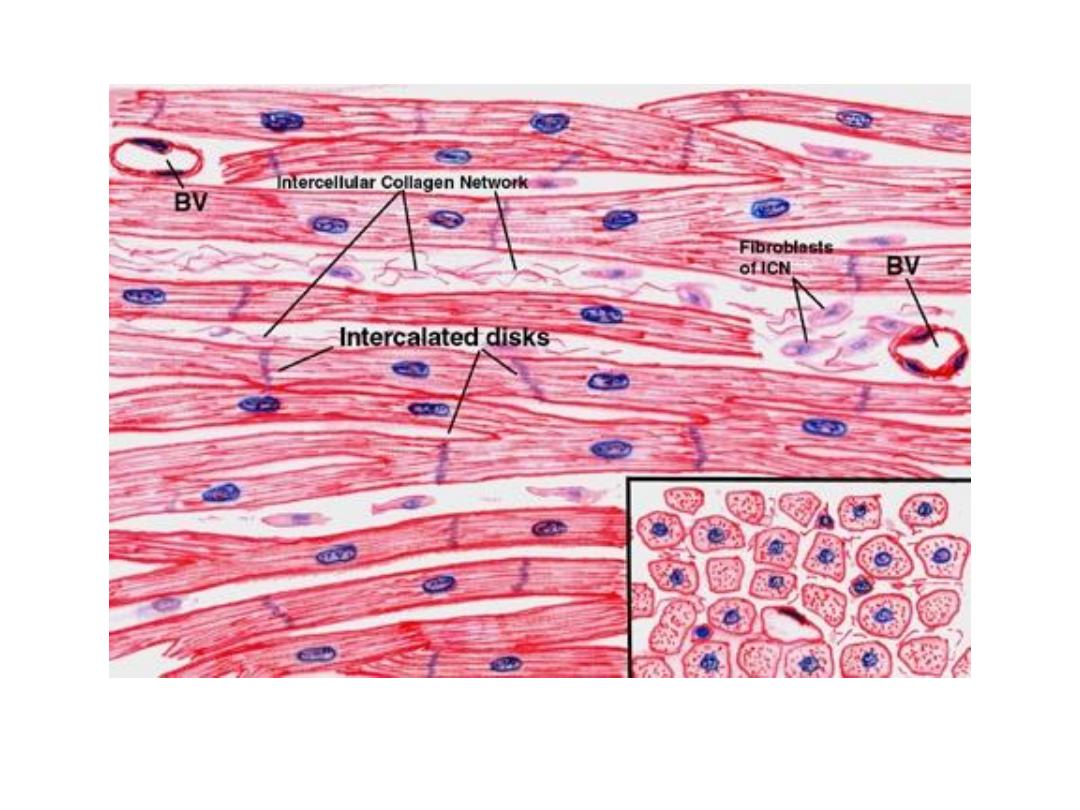
• At the ends of each cell is a region of finger-like
extensions of the cell membrane known as intercalated
disks.
Cardiac muscle
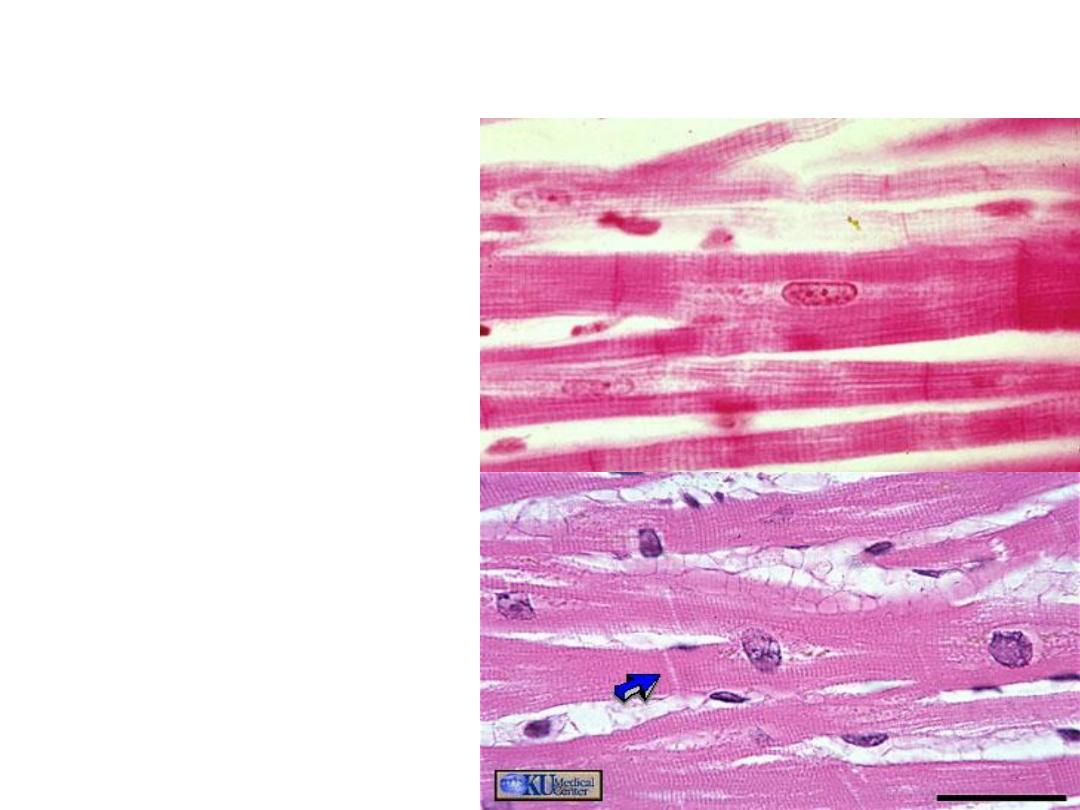
• In L.S. :
the myofibers appear
branched, striated
similar to skeletal
muscle. We can see
the intercalated disk,
the cardiac myofibers
have central, single
nucleus.
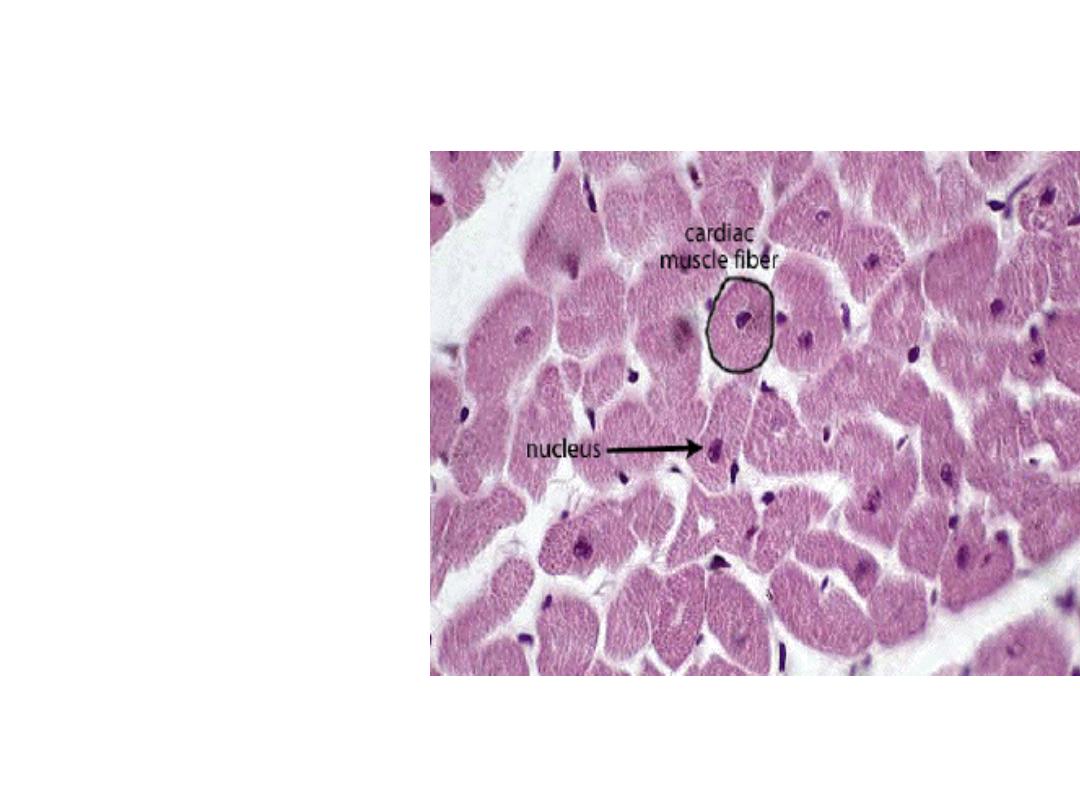
• In C.S. the myofibers
are irregular and
smaller than the section
of skeletal muscles, and
myofibrils are more
rough than myofibrils
in skeletal muscle,
central and single
nucleus in each fiber.

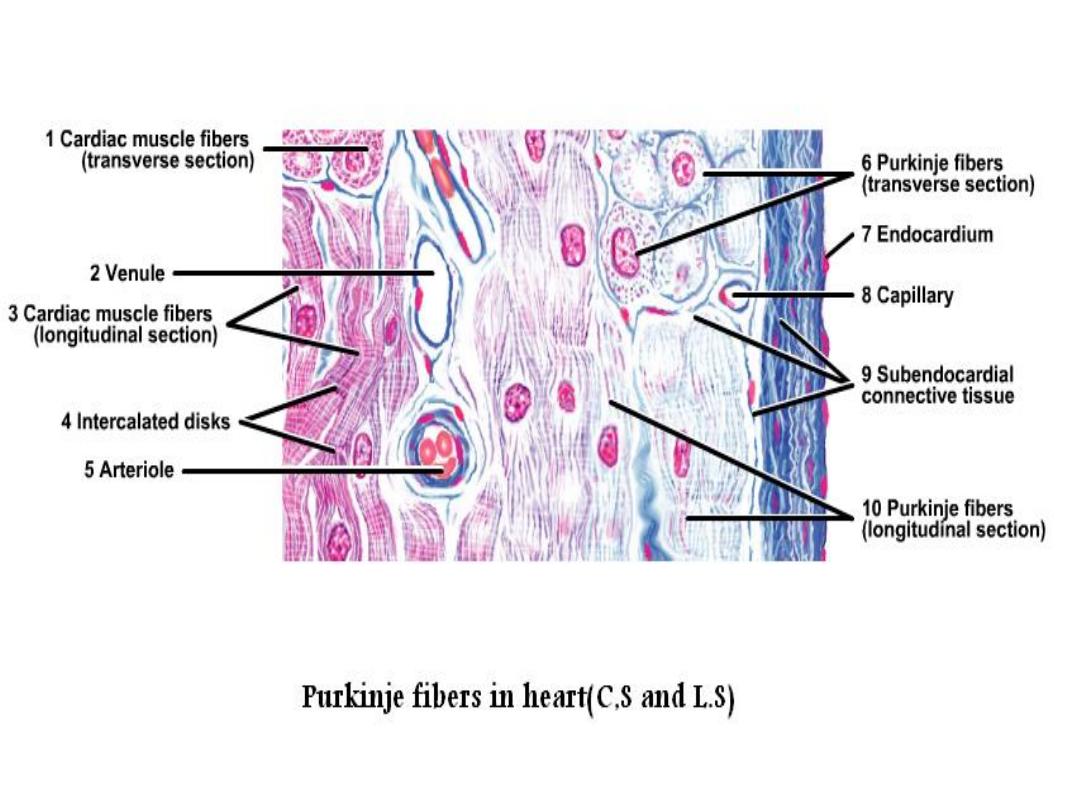
Purkinjie fibers
• They are specialized cardiac muscles.
• They are located just near the endocardium on
the internal surface of the heart.
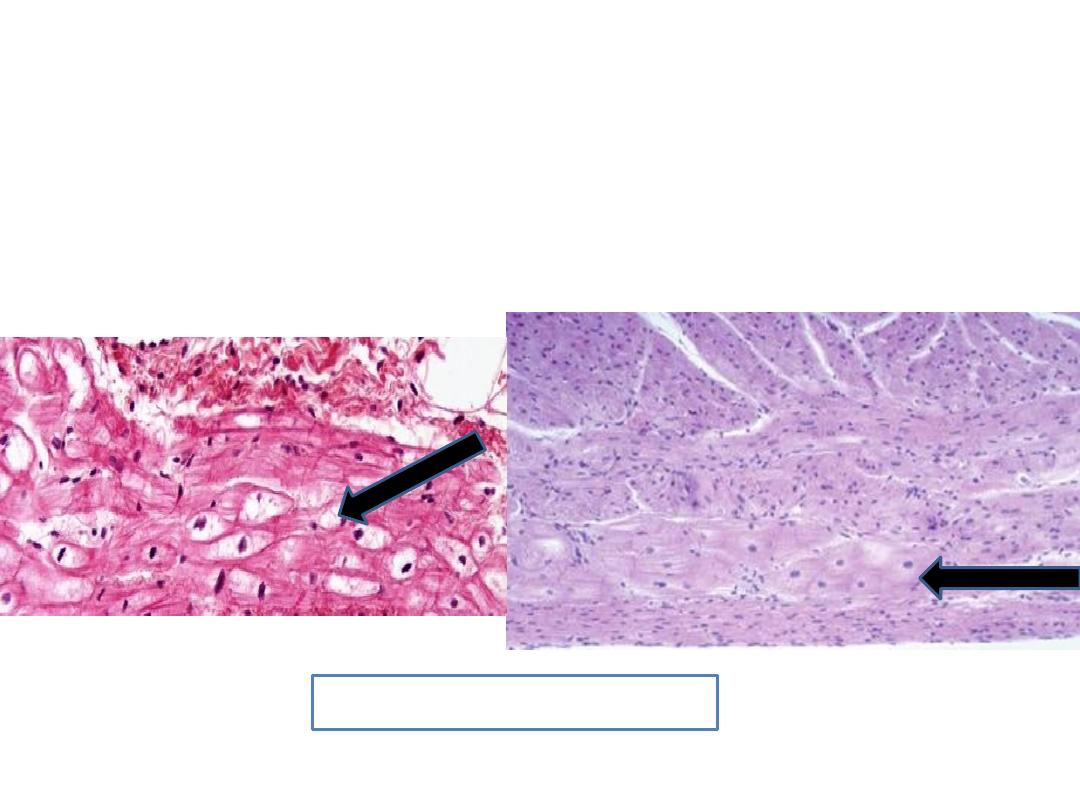
•
L.S. :
when comparing the purkinjie fibers with cardiac fibers, it appear larger, shorter, wide thick
and pale staining (lighter) than cardiac muscles, with central nucleus or binucleated and few
myofibrils which usually are found peripheral position.
Purkinjie fibers
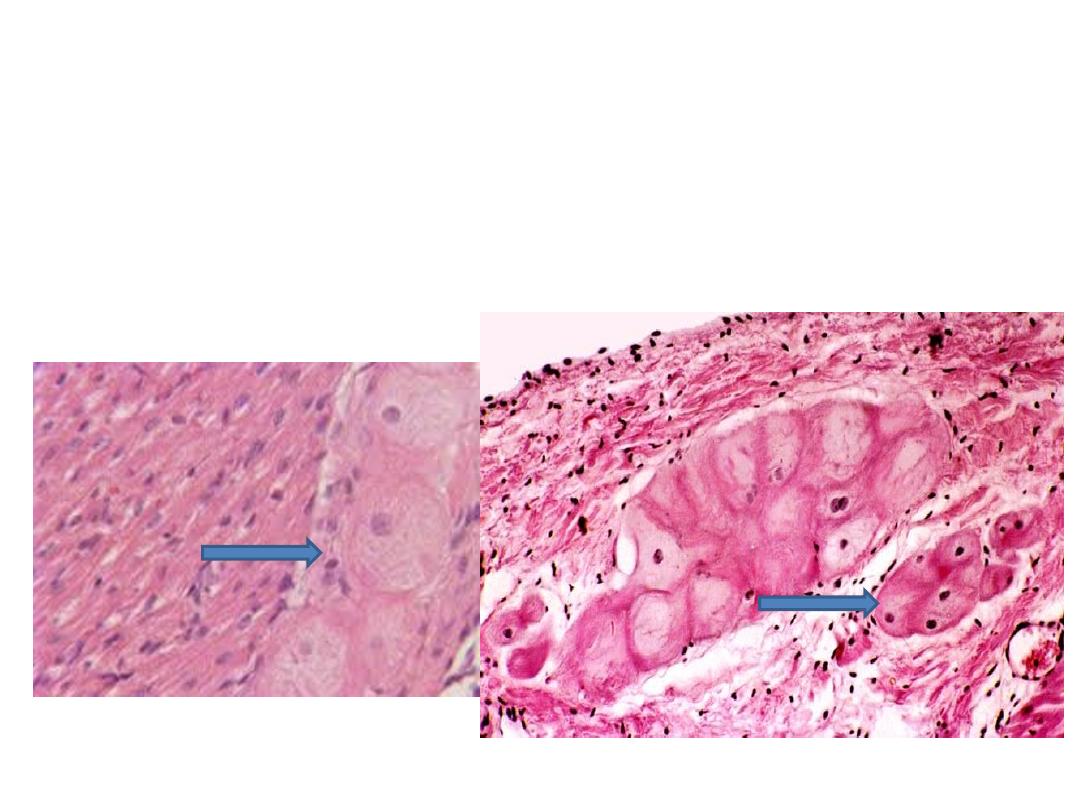
• In C.S., the purkinjie fibers appear as cell
groups (3-4) cells.
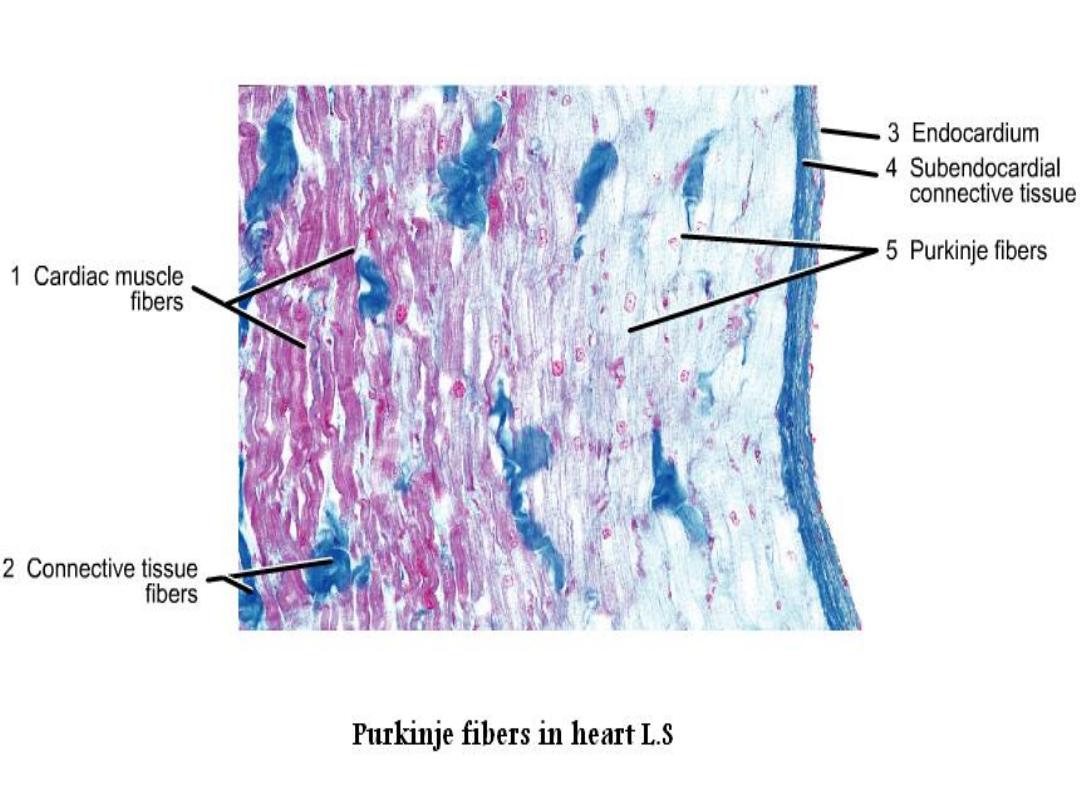
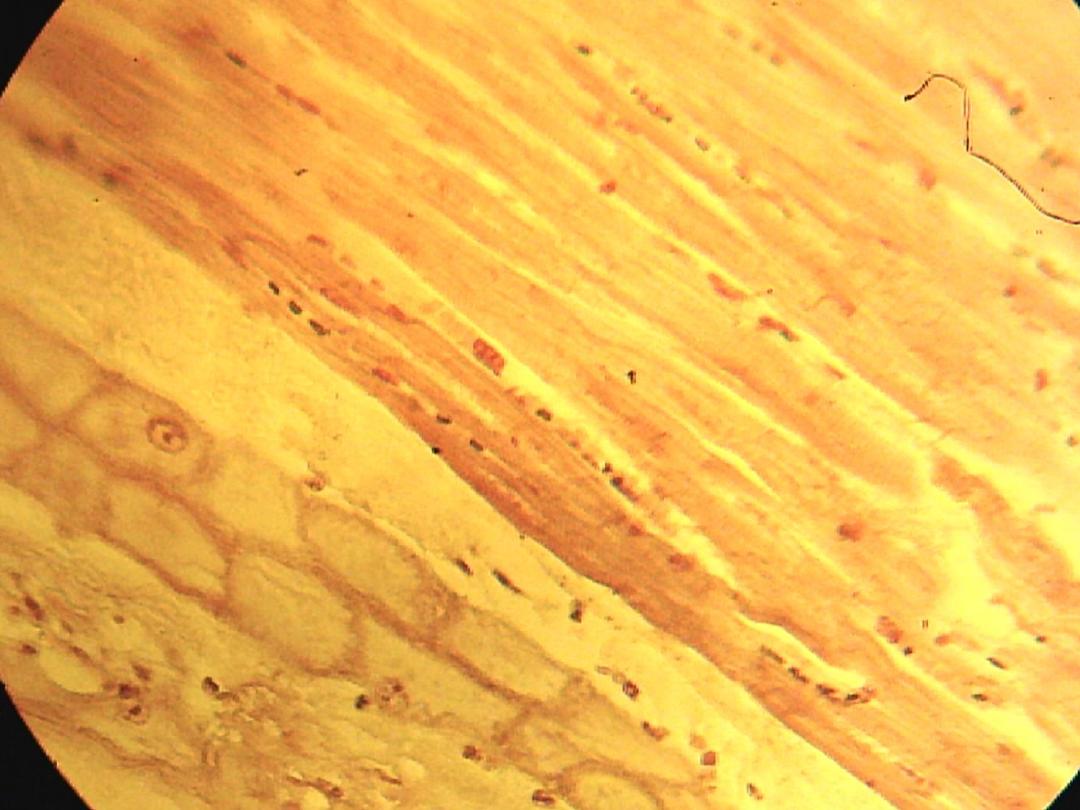
purkinjie fibers
L.S.
C.S.

Smooth muscle:
• It is non-striated, involuntary muscle, with visceral
distribution.
• It is present in the wall of digestive tract from mid-
esophagus to anus, urinary and genital system.
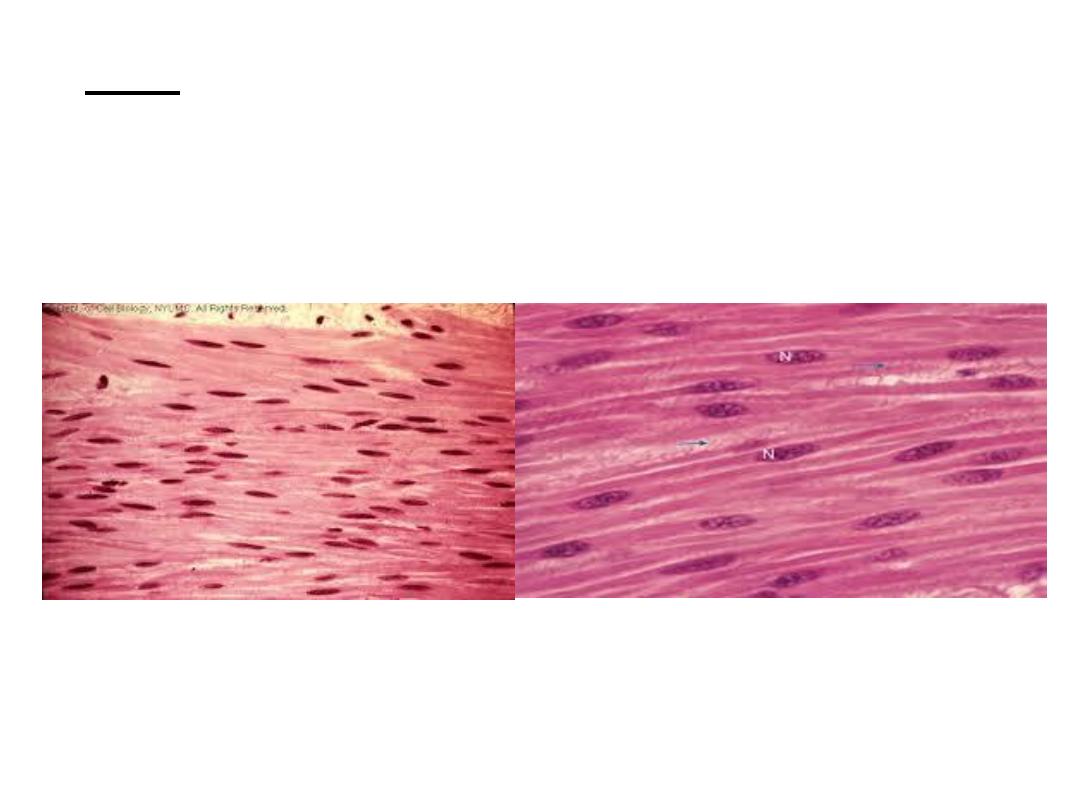
• L.S in smooth muscle, fibers are spindle
shape, with flattened central mononucleus,
cytoplasm called sarcoplasm which contain
many myofibrils.
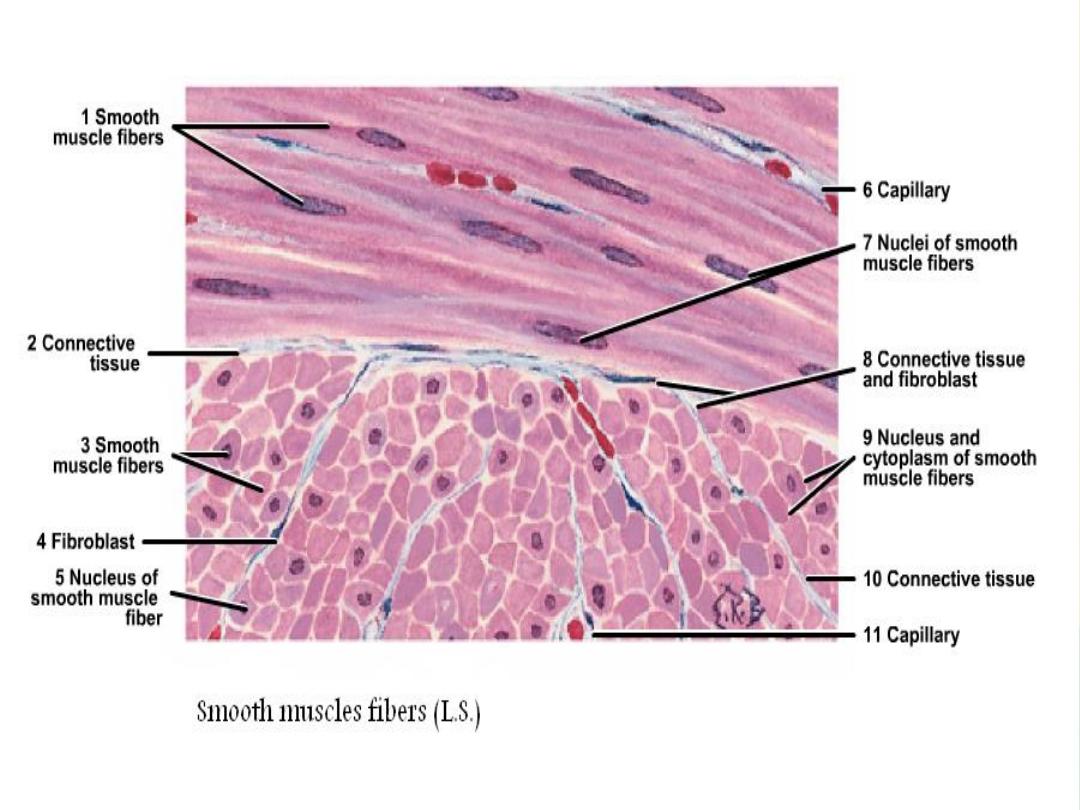
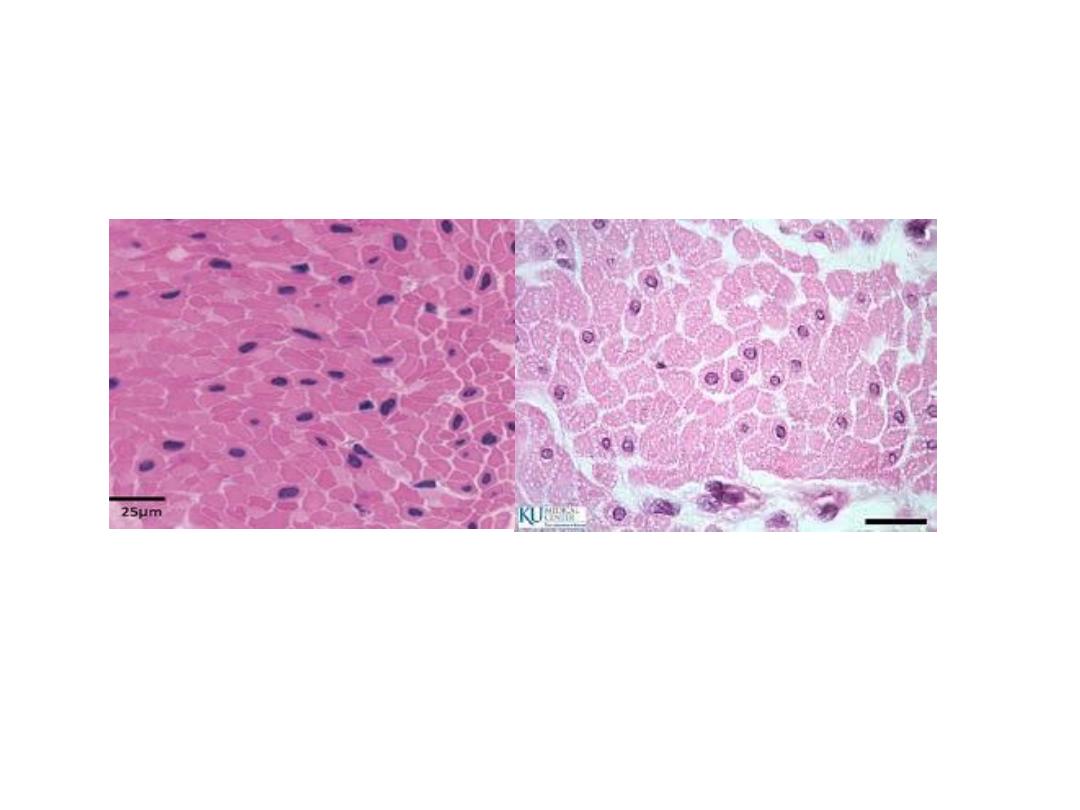
In C.S, the smooth muscle fibers appear different in size, it
may appear wide and narrow and may be with nucleus or
with out nucleus.