
1
Lec.3
Biology
Histology
Connective tissue
Connective tissue is the most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the
body . While some connective tissues are specialized ( bone , blood), all
organs have some amount of connective tissue in them which hold their
parenchyma together.
Connective Tissue is characterized by:
1. Binding and supporting the organs.
2. It is vascular except the cartilage.
3. It is derived from mesoderm layer.
4. It consists of cell immersed in large amount of intercellular substance,
which is formed by cells.
5. Can replicate (healing and repair)
Functions of connective tissues :
• Enclosing and separating organs
• Connecting tissues to one another (ligaments and tendons)
• Supporting and moving ( Joints and cartilage)
• Storing (adipose tissue and bones)
• Cushioning and insulating (adipose tissues)
• Transport and protection (blood)
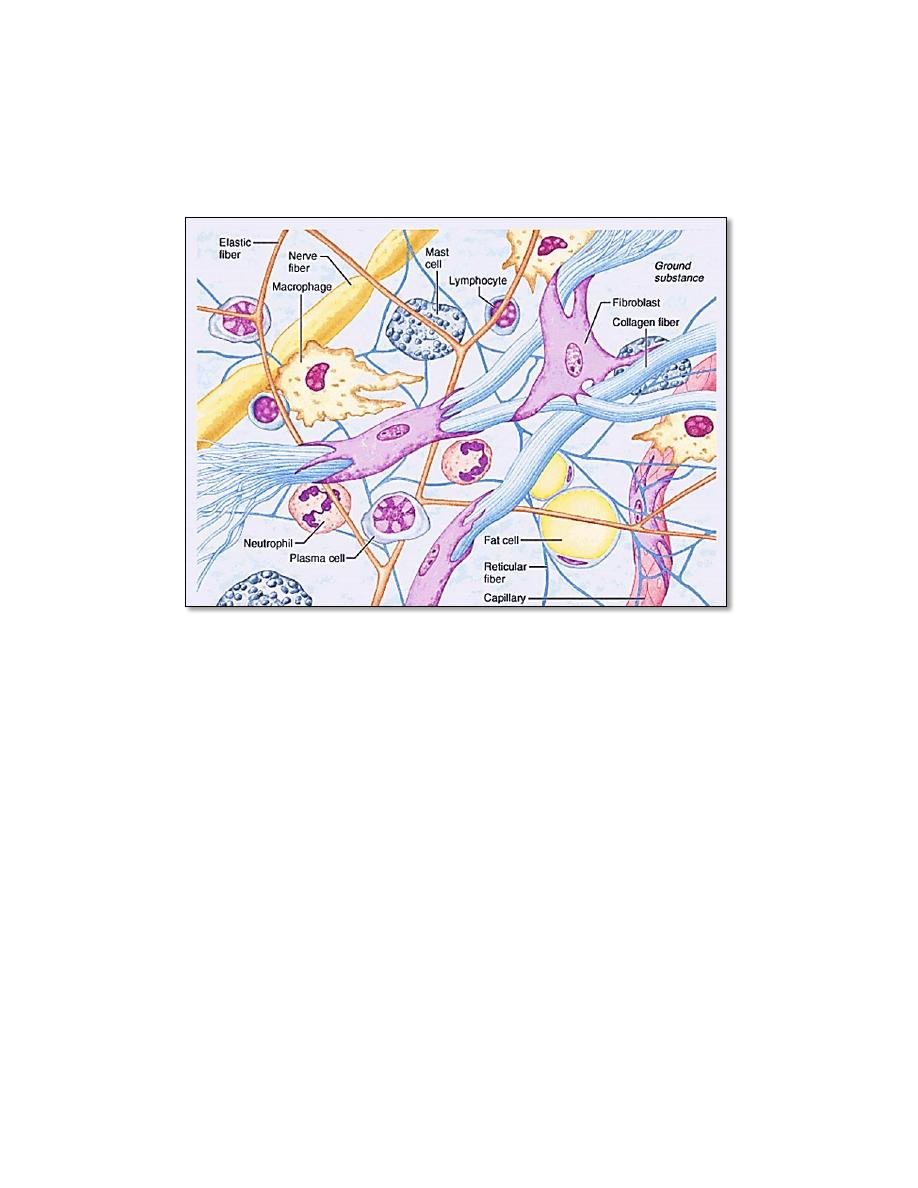
Components of Connective Tissue
1. Extracellular matrix: composed of
ground substance
and fibers.
2. Connective tissue cells.
2
The composition and structure of extracellular matrix determine function
and characteristic of connective tissue.
(Basic elements in a typical connective tissue)
Ground Substance
Ground substance: is a hydrated colorless and transparent, amorphous
material. It is found in all cavities and clefts between the fibers and cells of
connective tissues.
The ground substance may be viscous (as in blood),
semisolid (as in cartilage), or solid (as in bone).
Ground substance supports
cells, binds them together, stores water ,and provides a medium through
which substances are exchanged.
It primarily consists of protein and
carbohydrate molecules and variable amounts of water. The protein and
carbohydrates are mainly present in form of proteoglycans and glycoproteins
(Proteoglycan = Protein core + glycosaminoglycan. Glycoprotein= Protein +
oligosaccharide ). Also present in the ground substance are adhesion proteins
, which are responsible for linking components of the ground substance to
one another and to the surfaces of cells.
3
Fibers:
There are three types of connective tissue fibers:
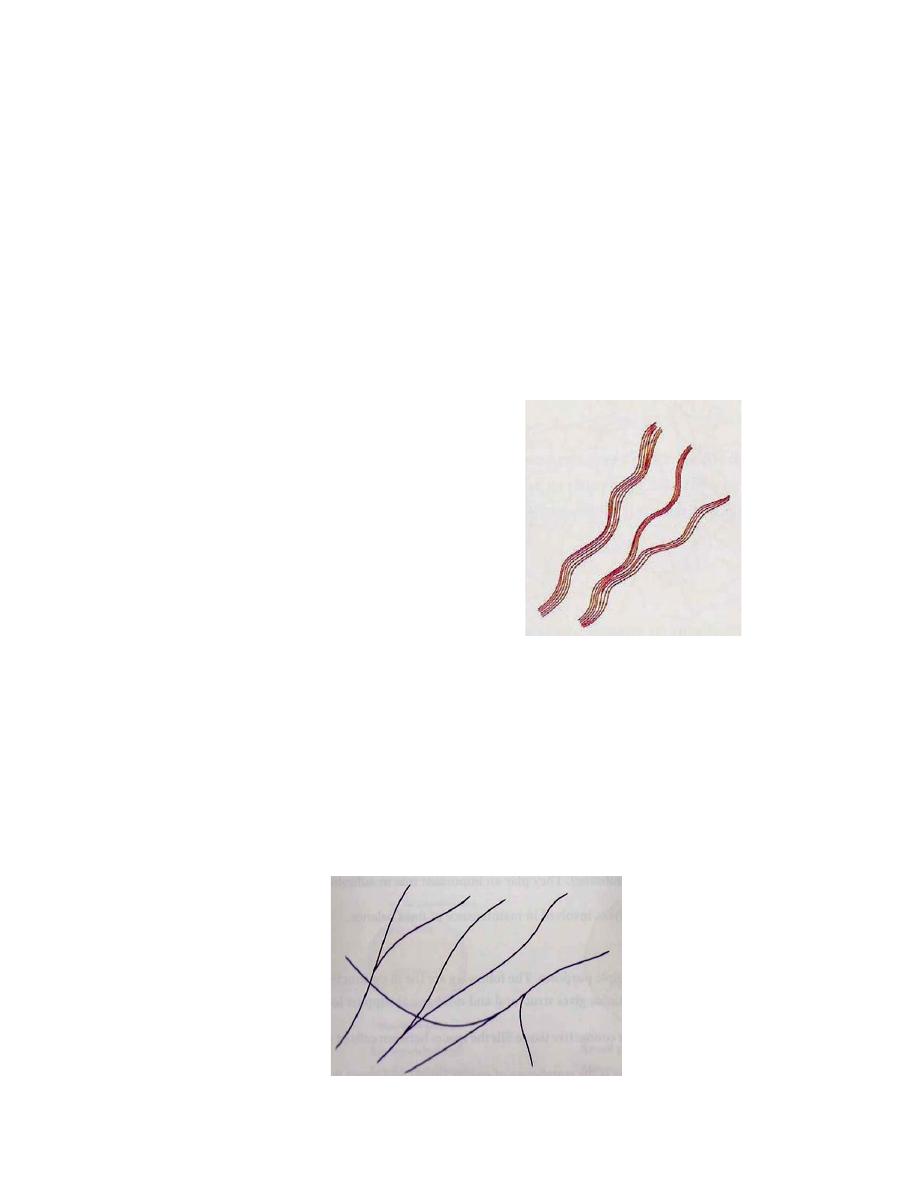
1. Collagen fibers (white fiber):
They are the most numerous and strongest fibers in the body . Collagen
fibers are made of protein called "collagen" and appear as fine clear threads
in fresh preparations. Thus, they are often called “white fibers. They are
formed by fibroblasts. These fibers are straight or wavy, un branched, they
always run parallel to each other forming bundles, which branched and
anastomose.
Found in abundance in bone , cartilage, tendon & ligament.
They function in (1) providing a structural framework and in (2) providing
strength.
Types of Collagen fibers:
•Type 1- bones & tendons
•Type 2- cartilage (hyaline & elastic)
•Type 3- reticular fibers
•Type 4- basement membrane
•Type 5- blood vessels
2. Elastic fibers
Elastic fibers are made of the protein elastin and appear yellow in fresh
preparations. Thus, they are often called “yellow fibers. They are generally
formed by fibroblasts. Elastic fibers are
smaller in diameter than collagen
fibers, branch to form a network within the tissue, found in ligaments and
vocal cords. They function in allowing the tissue to stretch and recoil.

4
3. Reticular fibers
Reticular fibers are made up of collagen but are thinner as compared to
collagen fibers and arranged in branching network of very fine fibers.
Reticular fibers are found around spleen, lymph nodes, red bone marrow,
liver, endocrine glands and kidney. They are associated with special cells
called reticular cells. Like collagen
fibers, they function in (1) providing a
structural framework and in (2) providing strength.
