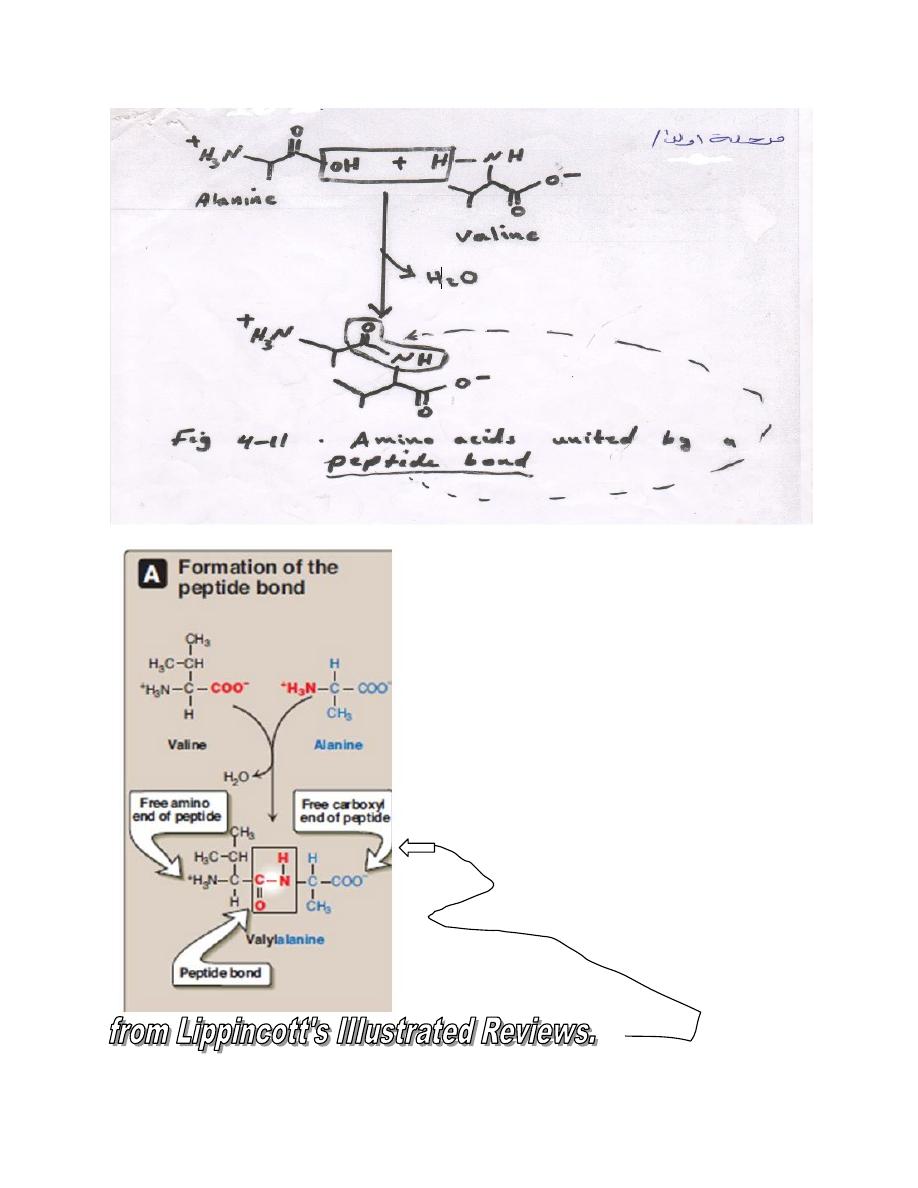

To synthesize peptide bonds, the carboxyl group must first be
activated.
Chemically, this may involve prior conversion to an acid chloride.
Biologically, activation involves initial condensation with ATP, forming
an aminoacyl adenylate.
Peptides
Biomedical important:-
# In endocrinology :- Many major hormones are peptides and may be
given to patients to correct corresponding deficiency states (eg,
administration of insulin to patients with diabetes mellitus).
# In nervous system, either as neurotransmitters or as
neuromodulators.
# certain antibiotics are peptides (eg. Valinomycin and gramicidin A),
L-α Amino acids linked by peptide bond form peptides
Peptide structure are written with the amino terminal residue (the
residue with a free α- amino group) at the left and with the carboxyl
terminal residue (the residue with a free α-carboxyl group) add at the
right.
The peptide has a single free α-amino group and a single free α-
carboxyl group.
Amino acid sequence determine primary structure.
When the number, structure , and order of all of the amino acid
residues in a polypeptide are known, its primary structure has been
determined. Amino acids whose α-carboxyl group participate in the
formation of peptide bond are termed “aminoacyl residue”. These
residue are named by replacing the –ate or –ine ending of free amino
acid by –yl (eg. Alanyl, aspatyl, tyrosyl).Peptide are named as
derivatives of the carboxyl terminal aminoacyl residue. For example,
the tetrapeptide Lys- Leu- Tyr- Glu- is named as a derivation of
glutamine and is called lysyl – leucyl – tyrosyl - glutamine . The –ine
ending on glutamine indicate that it is α-carboxyl group is not involved
in peptide bond formation.
Abbreviations are used to name the amino acids present in peptides
Both three and one-letter abbreviations for the amino acids (table 4-1).
Are used to represent primary structure (fig. 5-2)
Glu-Ala-Lys-Gly-Tyr-Ala
E A K G Y A
(fig. 5-2) three- and one- letter representation of a hexapeptide.
Glu-Lys-(Ala,Gly,Tyr)-His-Ala
Fig. 5-3 A heptapeptide containing a region of uncertainty primary
structure (in parentheses). ﺗﻮﺿﻊ ﺑﯿﻦ ﻗﻮﺳﯿﻦ
Three-letter abbreviation linked by straight lines represent a primary
structure that is known. These lines are omitted for single letter
abbreviations.
Where there is uncertainty about the precise order of a portion of a
polypeptide, the questionable ( )ﻣﺸﻜﻮك ﺑﮫresidues are enclosed in
brackets and separated by commas (fig 5-3).
Many peptides have physiological activity
Animal , plant , and bacteria cells contain a variety of low - molecular –
weight polypeptides (3-100 amino-acyl residues) with profound
physiological activity .
Some , including most mammalian polypeptide hormones , contain only
peptide bonds formed between α -amine and α -carboxyl groups of the
L-α – amino acids of proteins .
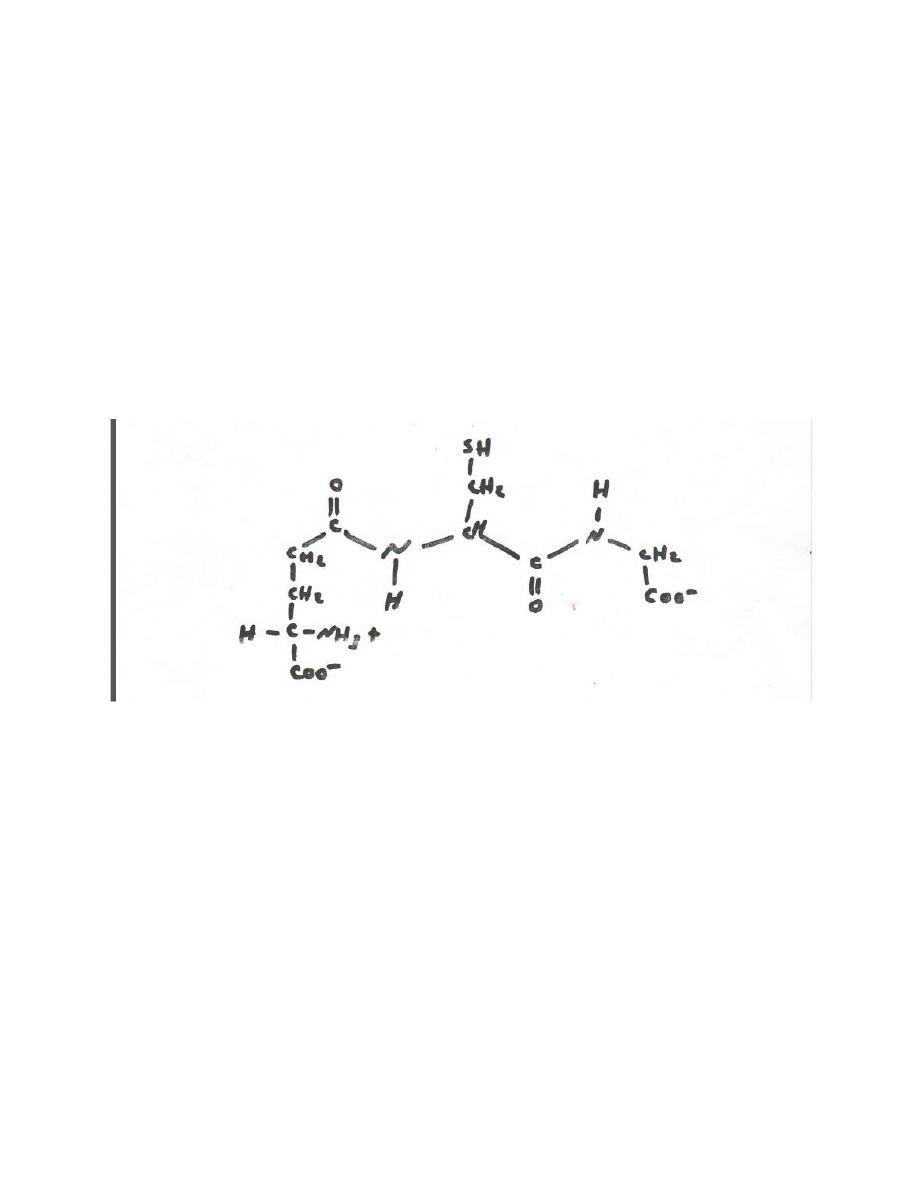
However , additional amine acids or derivatives of the protein amino
acids may also be present . others contain unusual peptides bonds .
for example , in glutathione the amine terminal glutamate is linked to
cysteine by a non-α peptide bond (fig 5-4)
Fig 5-4 glutathione (α- glutamyl – cysteinyl – glycoine) .
Note the non – α peptide bond that links glu to cys.

Proteins ; structure
: p.48
The four orders of protein structure primary, secondary , tertiary and
(for oligomer proteins only) quaternary : primary structure the
sequence of amino acids and location of any disulfide bonds , is
encoded in the genes .
Secondary and tertiary structure , which concern the proteins
conformations permitted by peptide bonds , are dictated by the
primary structure .
Secondary structure describes the folding of polypeptides chains into
multiply hydrogen – bonded motifs such as the a α - helix and the β-
pleated sheet . Combination of these motifs can then form
supersecondary motifs (eg , β-α-β). Tertiary structure concerns the
relationships between secondary structural domains and between
residues for apart in a primary structural sense. Quaternary structure
present only in proteins having two or more polypeptide chains
(oligometric proteins ) describes contact point and other relationships
between these polypeptides or subunits .
While primary structure involves covalent bonds , higher order are
stabilized only by weak forces that include multiple hydrogen bonds
salt (electrostatic) bonds between surface residues , and
nonstoichiometric association of group in the interiors of
protein.Reagent that break noncovalents bonds (eg , urea ) disrupt
secondary , tertiary and quaternary structure with attendant loss of
biologic activity (denaturation). Physical techniques for study of higher
orders protein structure include x-ray crystallography
Peptides can be resolved by chromatography or electrophoresis .
Compostion of * human blood
Total solid , present normal range(mg / 100 )
Albumins (serum) 4.7 -5.7
Globulins (serum) 1.3 – 2.5
A/ G ratio 1.2 – 1.8
(secondary and tertiary structures) plus ultracentrifugation, gel
filtration , and gel electrophorsis (quaternary structure ) .
The close linkage of protein structure and biological function is
illustrated by two fibrous proteins : silk fibroin and collagen.
Protein are classified in many ways
Proteins may be classified on the basis of their solubility , shape ,
biological function , or three dimensional structure. A system in limited
use in clinical biochemistry distinguishes "albumins","Globulin"
,“histones” etc based on their solubility in aqueous salt solution.
Protein may also be classified based on their overall shape. Thus,
Globular proteins (eg , many enzymes ) have compactly folded coiled
polypeptides chains and axial ratios (ratios of length to breadth) of less

than 10 and generally not greater than 3-4 fibrous protein have axial
ratio greater than 10.
Based on their biologic function , proteins might be classified as
enzymes (dehydrogenase, kinases), storage protein (ferritin ,
myoglobin), regulatory protein (DNA, binding protein, peptide
hormones), structural protein (collagen, proteoglycans), protective
protein (blood clotting factors, immunoglobuline), transport protein
(hemoglobin, plasma lipoprotein), and contractile or motile protein
(actin, tubulin).
Specialized system of classification distinguish certain complex protein
of high medical interest thus, plasma lipoproteins are termed ”origin”.
α 1- α2- , or β-lipoprotein based on their electrophoretic mobility at pH
8.6 ,or as VLDL, LDL, HDL, or VHDL (very high density lipoprotein) based
on their sedimentation behavior in an ultracentrifuge. Lipoprotein may
also be classified by immunologic determination of which apoprotein
(A,B,C,D,E,F) are present. Similarities in three-dimensional structure,
revealed primarily by x-ray crystallography, provide a potentially
valuable basis for protein classification. For instance, protein that bind
nucleotides share a nucleotide-binding domain of tertiary structure.
Globular protein contain β-bends
Globular protein the predominant protein type in cytosol are compact
structures because their peptide chain frequently change direction.
