First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 1 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
Carbohydrates
By : Dr.Tamathir Abbas
Definition
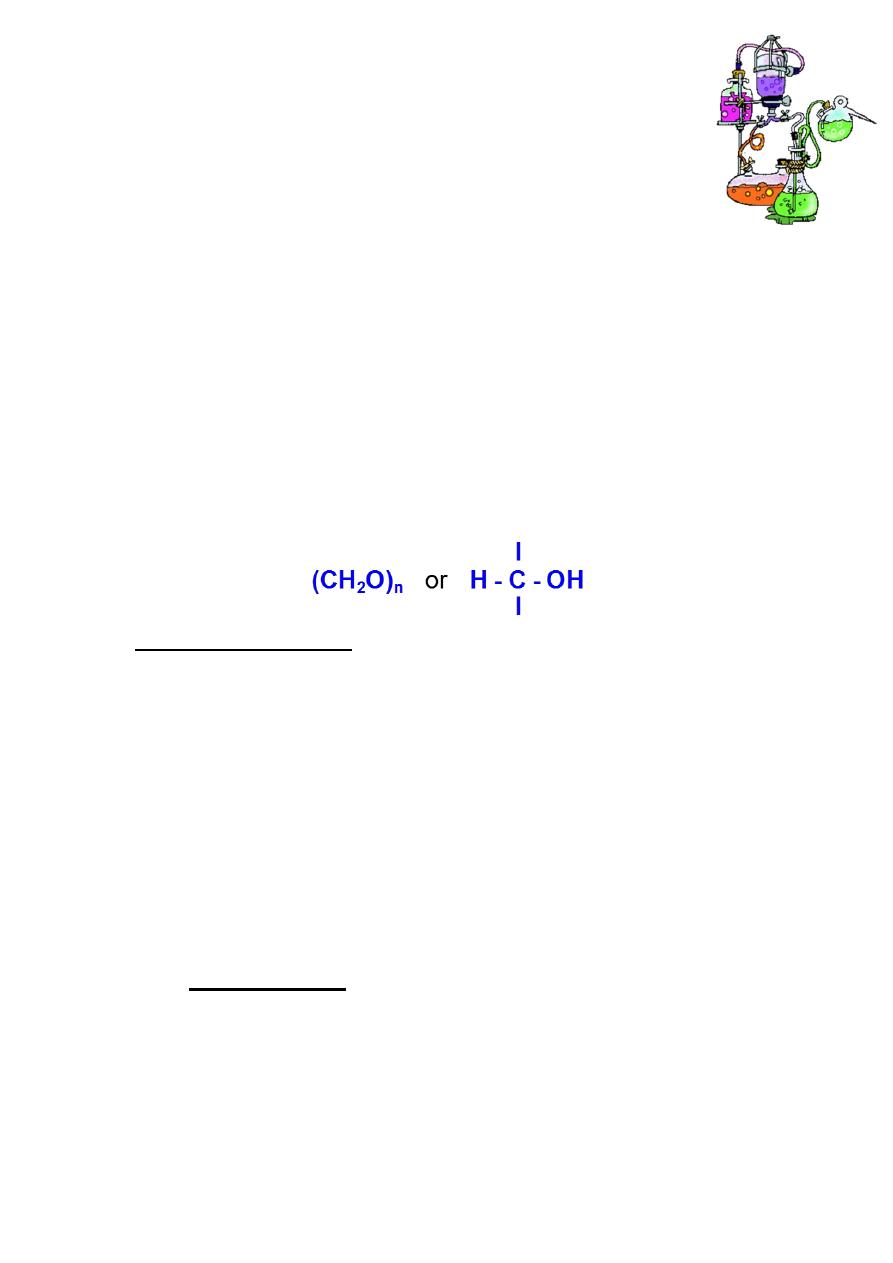
• Organic compounds composed of C, H and O with H and O present in
the same ratio as in water.
• Example: Glucose C
6
H
12
O
6
. [C
m
(H
2
O)
n
]
m, n= where m and n are
integer.
• New definition:
Optically active Polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that
hydrolyze to yield polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
Carbohydrates (glycans) have the following basic composition:
Types of Carbohydrates
1- Monosaccharides - simple sugars with multiple OH groups. Based on
number of carbons (3, 4, 5, 6), a monosaccharide is a triose, tetrose,
pentose or hexose.
2- Disaccharides - 2 monosaccharides covalently linked.
3- Oligosaccharides - a few monosaccharides covalently linked.
4- Polysaccharides - polymers consisting of chains of monosaccharide or
disaccharide units.
• Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates
- Also called “simple sugars”
- Examples: glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose
First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 2 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
Monosaccharides
Physical Characteristics
• State:
Sugars are white, crystalline in shape and with sharp melting points,
while polysaccharides are white amorphous solids.
• Taste:
Sugars have a sweet taste. Polysaccharides are tasteless.
• Solubility:
Monosaccharides are soluble in cold water and hot alcohol.
Polysaccharides are partially soluble in hot water.
Qualitative Analysis Test
• Is concerned with determining the identity of a substance.
• Enables us to detect the presence of things which may be
beyond the reach of our senses.

First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 3 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
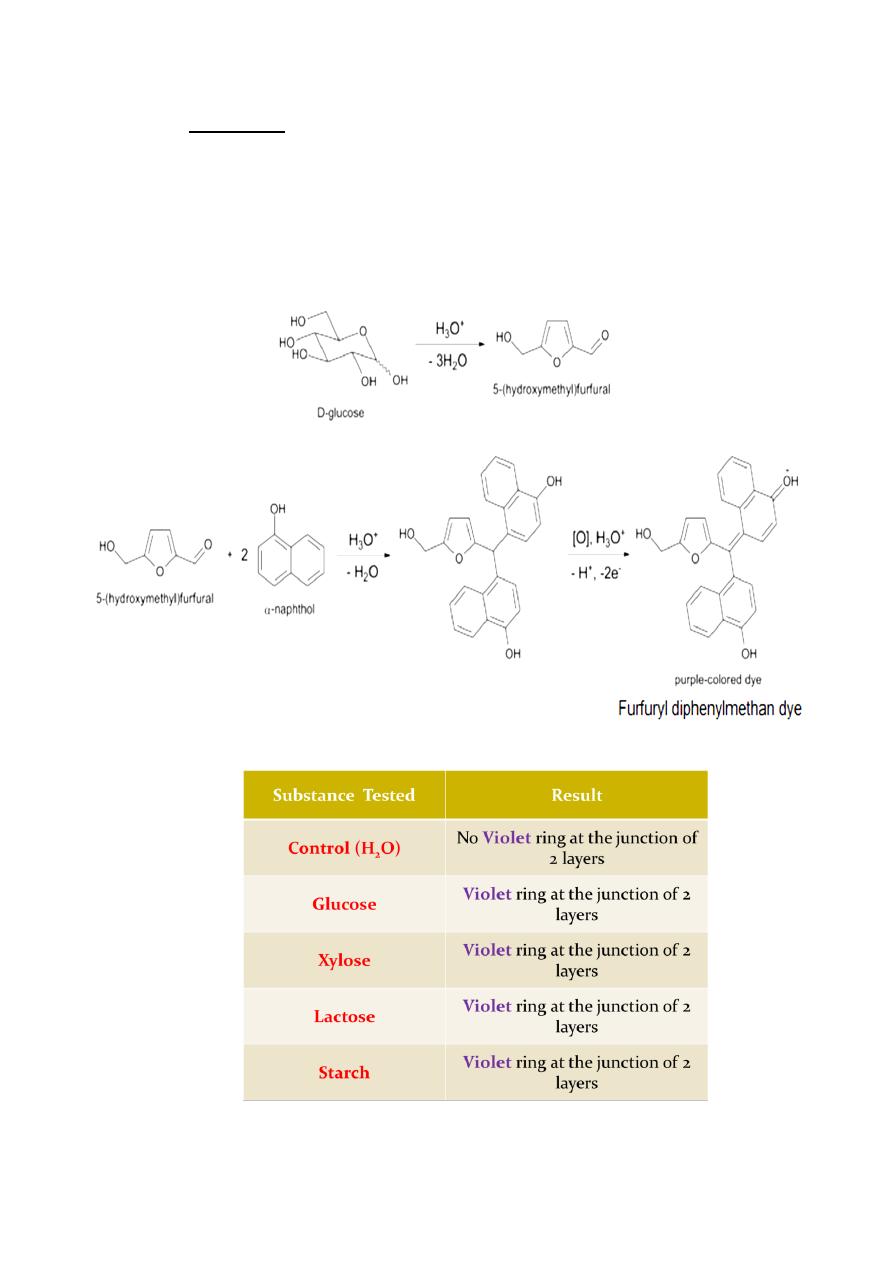
Molisch's Test
The Molisch's test is a general test for the presence of carbohydrates.
Molisch's reagent is a solution of α-naphthol in 95% ethanol. This test is useful
for identifying any compound which can be dehydrated to furfural or
hydroxymethylfurfural in the presence of H
2
SO
4
.
Furfural is derived from the dehydration of pentoses and pentosans, while
hydroxymethylfurfural
is
produced
from
hexoses
and
hexosans.
Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are hydrolyzed to yield their repeating
monomers by the acid.
The alpha-naphthol reacts with the cyclic aldehydes to form purple colored
condensation products. Although this test will detect compounds other than
carbohydrates (i.e. glycoproteins), a negative result indicates the ABSENCE of
carbohydrates.
Molisch's Test
General test for carbohydrates
Rgt.: 5% α-naphthol in EtOH
Procedure: sple. + 2 drps. Molisch rgt., incline test tube, + conc. H
2
SO
4
(+) result: Violet colored ring at the junction or interface of the two
layers: denser H
2
SO
4
on the lower layer and the rgt. and sple. on the
upper layer.
Principle: conc. H
2
SO
4
dehydrates carbohydrates to form furfural
derivatives. This product combines with sulphonated α-naphthol to give a
purple color.
First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 4 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
Generally:
carbohydrate → dehydration product→ violet product
Pentose → furfural → violet product
Hexose → 5-hydroxymethylfurfural → violet product
First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 5 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
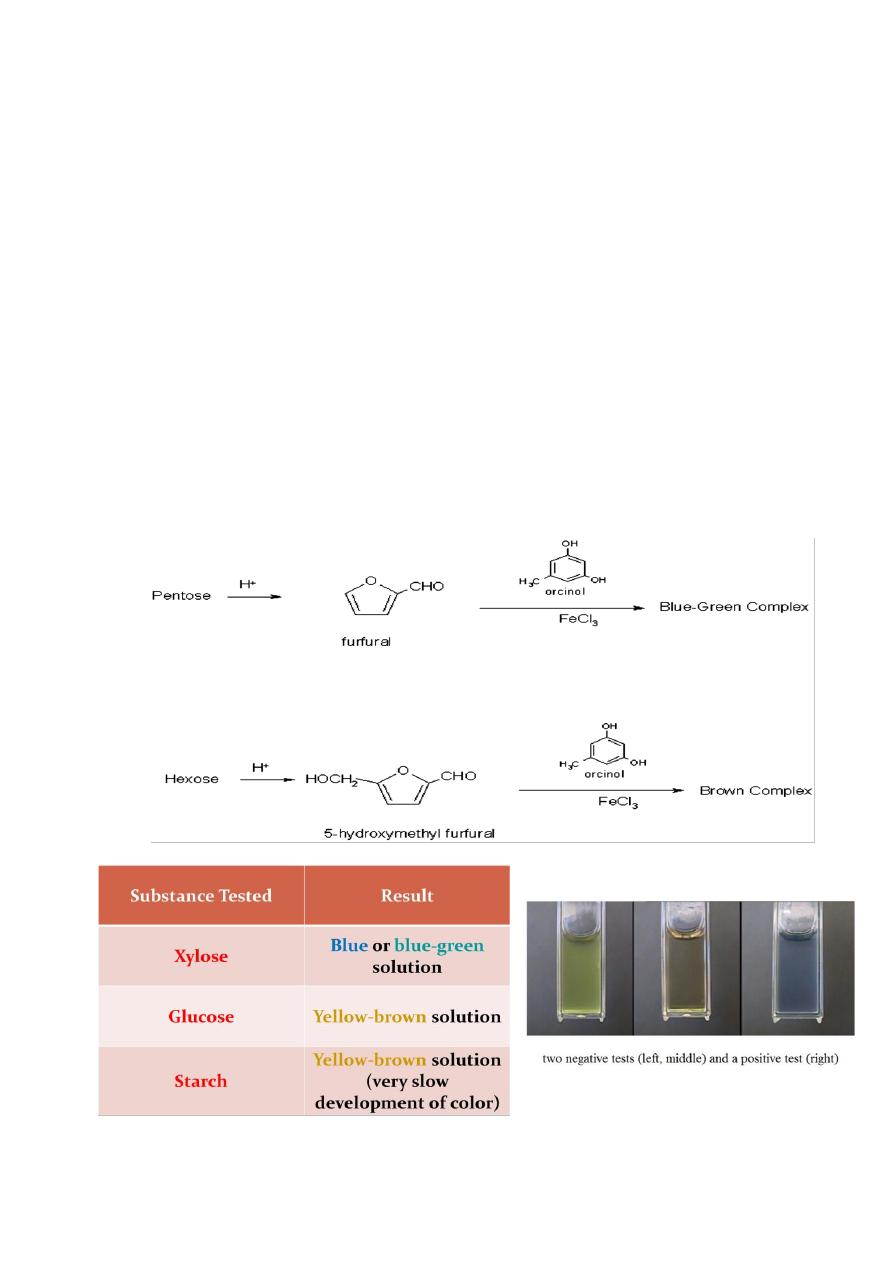
Bial’s Test
Used to distinguish between pentoses and hexoses
Used to determine the presence of pentoses
Rgt.: orcinol in conc. HCl
Procedure: sple. + 5 mL rgt., ∆, + FeCl
3
, ∆
(+) Result: blue-green colored solution, no ppt.
Hexoses may give yellow-brown colored solution. Di- and
polysaccharides may also give similar result but at a much slower rate.
Principle: conc. HCl dehydrates pentoses to form furfural. Furfural then
reacts with orcinol and the condensation agent FeCl
3
to form the blue-
green colored complex.
First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 6 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
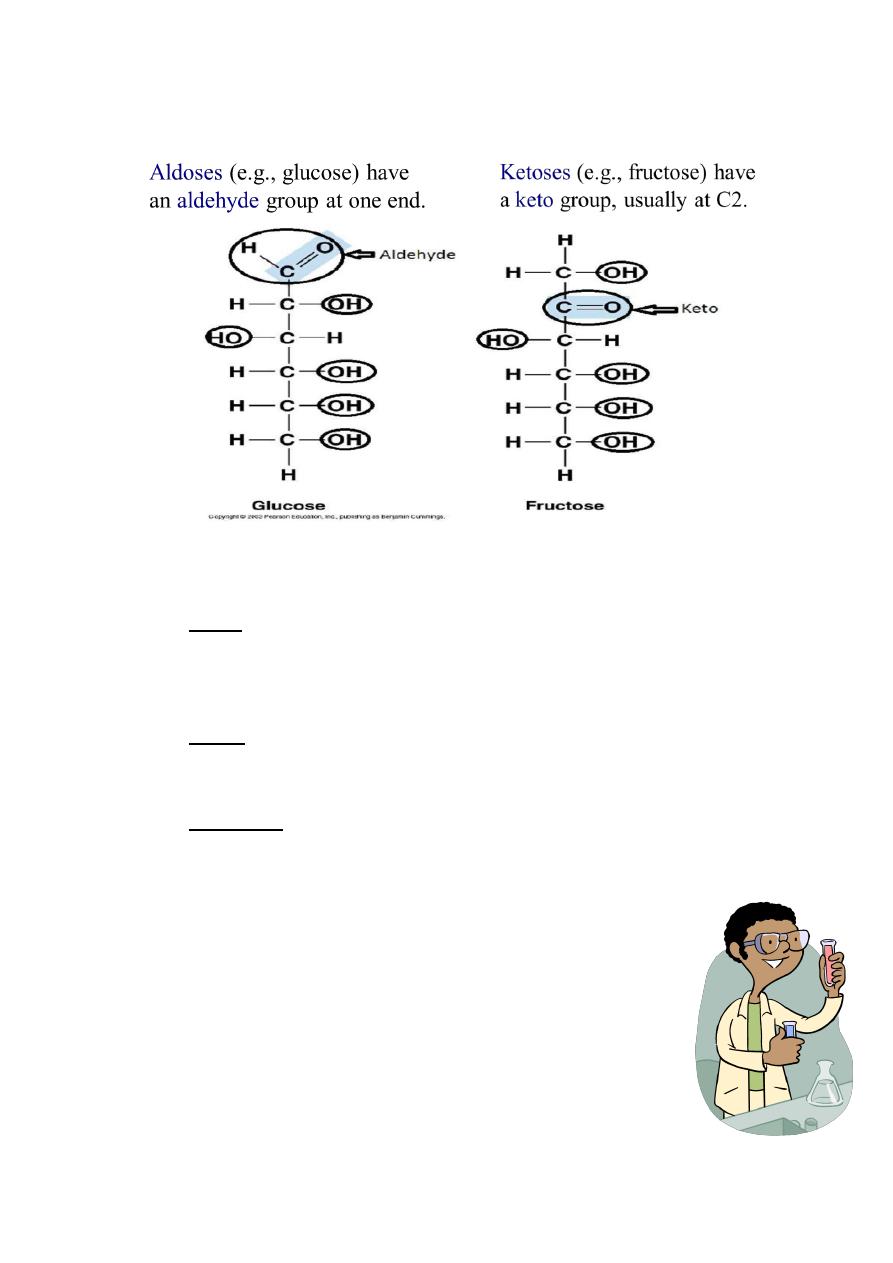
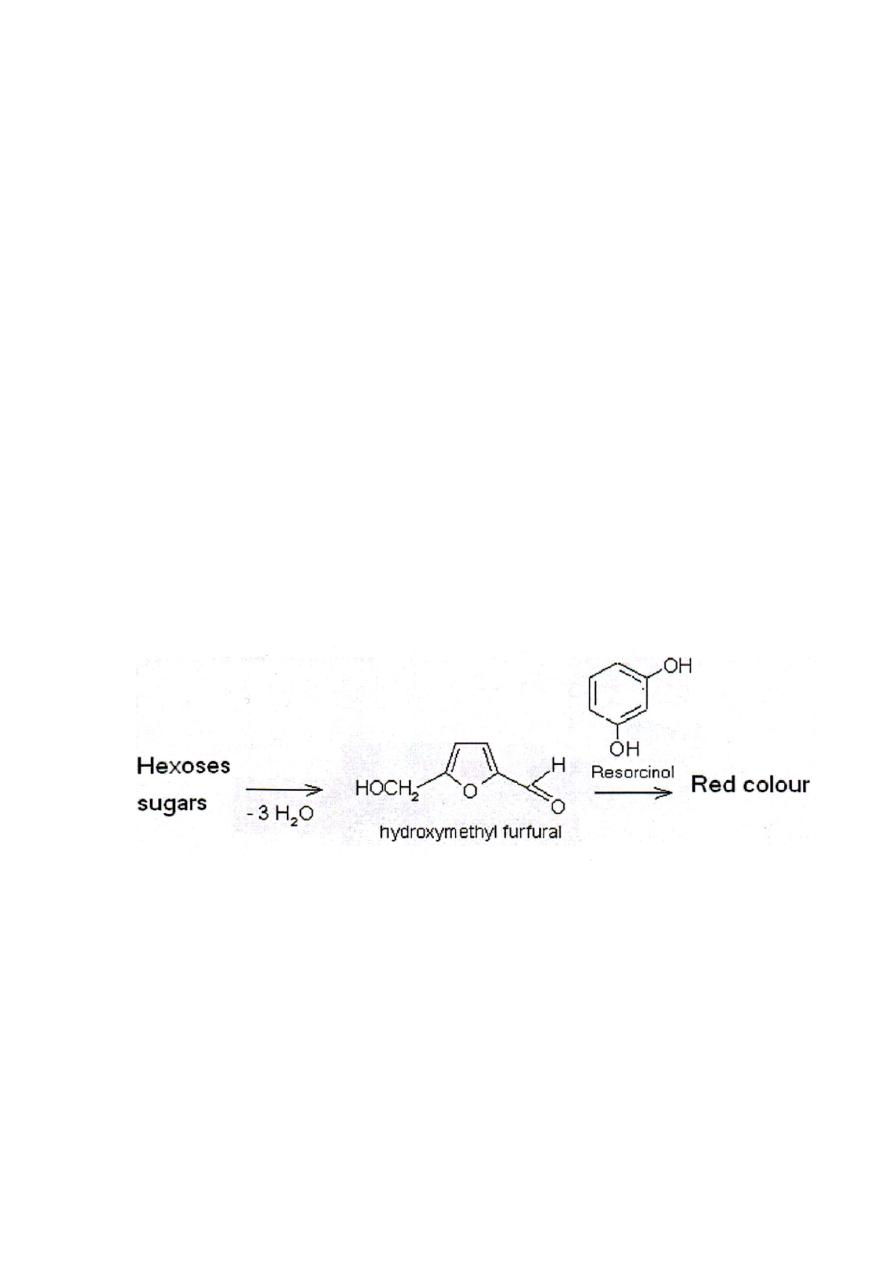
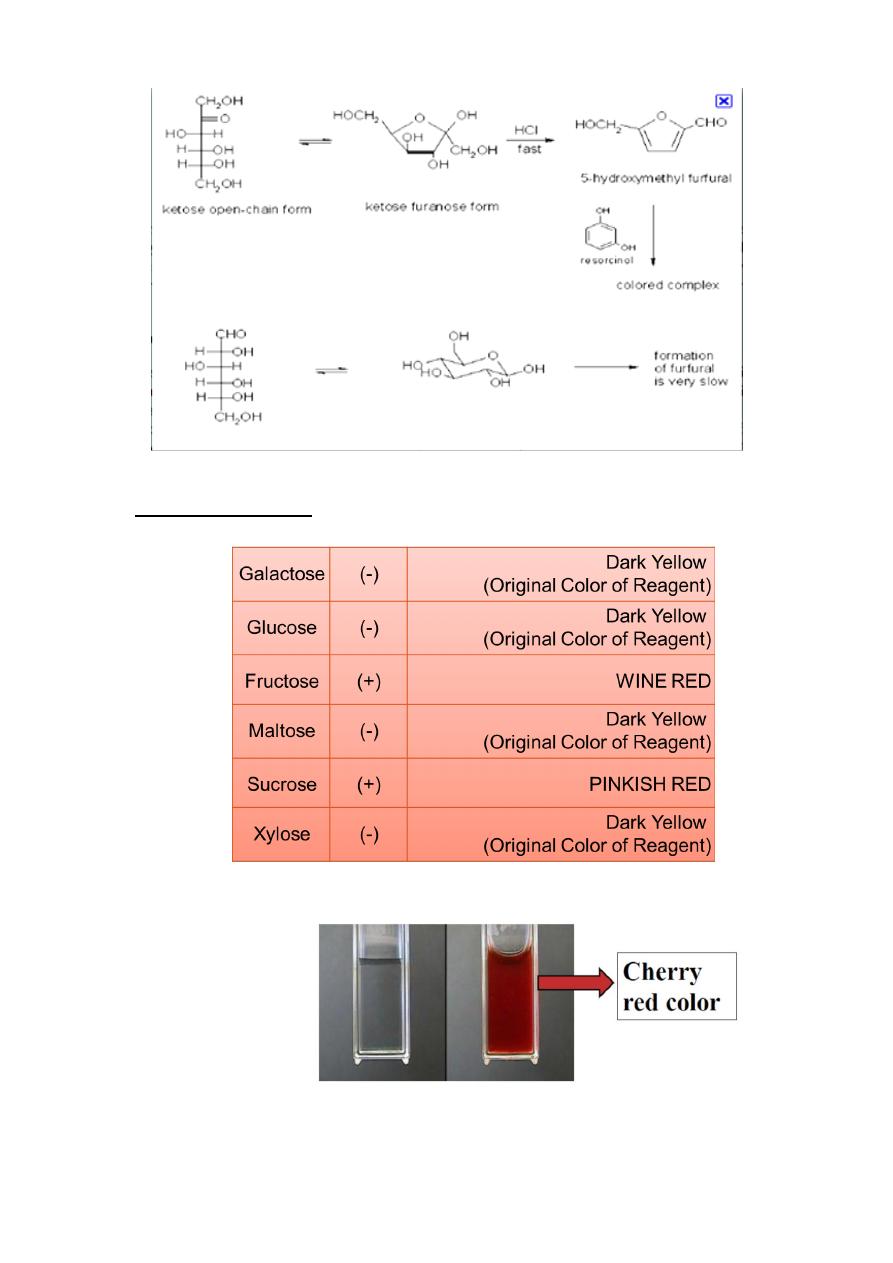
Seliwanoff’s Test
Used to differentiate aldoses from ketoses
A timed color reaction specific for ketoses
Rgt.: resorcinol in HCl
Procedure: sple. + Seliwanoff’s rgt., ∆ for 2 mins.
(+) Result : cherry red colored solution
Aldoses give pink to peach colored solution after 2 mins . of boiling. (-)
Principle: Aldoses generally exist in solution as pyranoses while
ketoses exist as furanoses, hence the ability of ketoses to rapidly
dehydrate to yield furfurals.
Prolonged heating may convert aldoses to ketoses and disaccharides containing
ketoses (such as fructose) may yield the component monosaccharides. They
may then dehydrate to form furfurals.
First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 7 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
results &Discussion
First Class/Practical Medical Chemistry
Page 8 of 8
By : Dr. Tamathir Abass
Reducing Sugars
Have free aldehyde or ketone group that can cause oxidation, hence serve
as reducing agents
Aldehydes can be oxidized to give carboxylic acids in acidic medium
while carboxylate salts in basic medium.
Ketones can also be oxidized when being converted to aldehydes through
keto-enol tautomerization.
Tautomerization – a chemical equilibrium between a keto form and an enol
form. The compounds are said to be tautomers of each other .When aldehydes are
oxidized, they produce carboxylic acids with a number of C the same as with the
parent aldehyde.
When ketones are oxidized in the presence of strong oxidizing agents such as
HNO
3
, KMnO
4
, K
2
Cr
2
O
7
, H
2
SO
4
, they do so in a destructive way that the products
produced are shorter in the number of carbons compared to the parent ketone.
Keto-enol Tautomerization
