
1
4th stage
Surgery
Lec
Dr.ahmad
4/16/2016
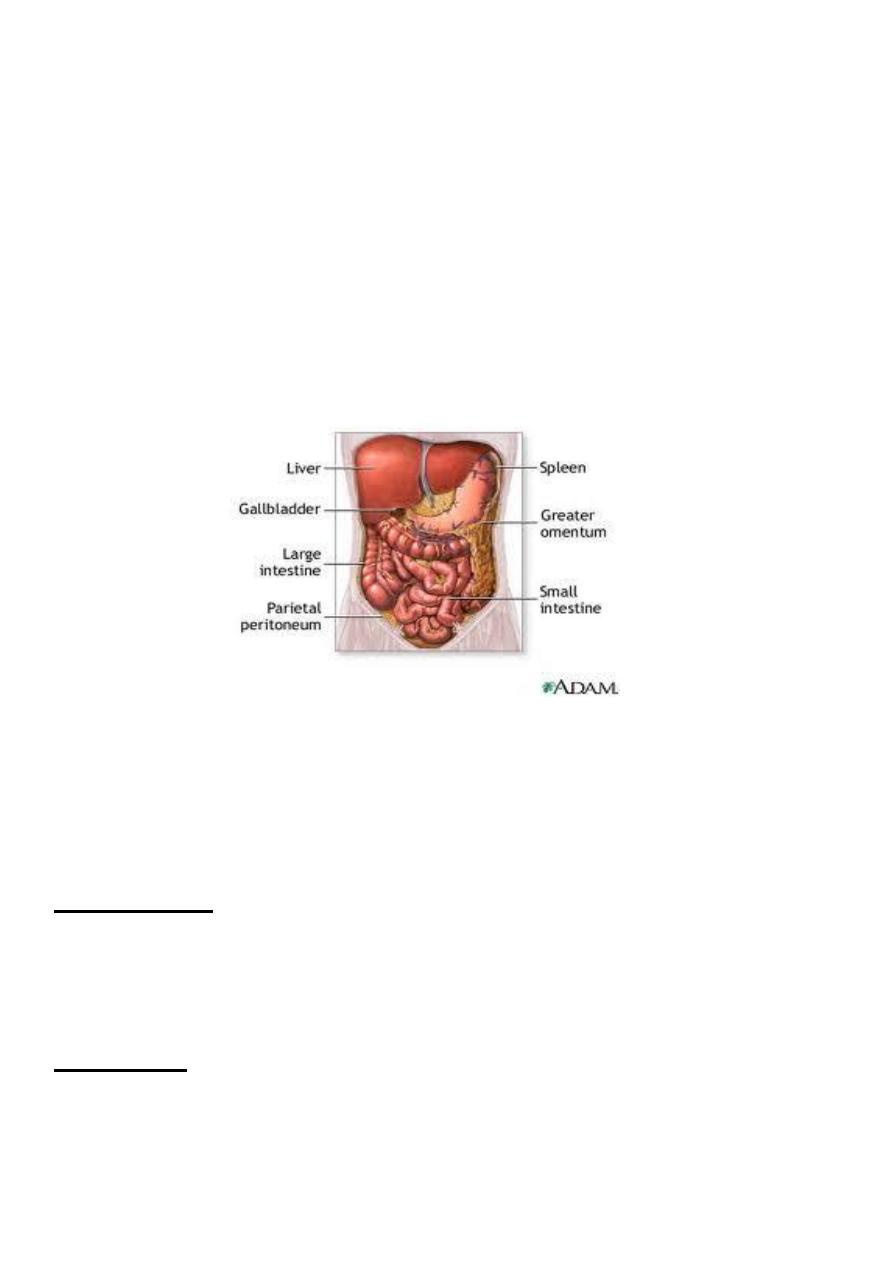
Peritoneum 1
It is a single layer of flat mesothelial cells resting on a bed of loose connective tissue .
Divided to two part :
- parietal
- visceral
Innervations
The parietal is sensitive and innervated by both somatic and visceral afferent nerves.
The anterior parietal is most sensitive.
The visceral receives innervations only from autonomic nervous system and is
reletively insensitive .
Generalised septic peritonitis
Aetiology :m.o like E-coli ,aerobic and unaerobic strep. , bacteroids ,staph and pneumococci.
Source of infection
1- Local spread:
- infected organ: appendicitis
- leaking organ: perforated PU, anastamotic leak, extravasated urine.
2- Direct entry:operation
3- Blood spread:septicemia
4- Primary peritonitis :child,female,unknown .str. And pneumococci.
Pathology
Inflamed area become opaque and fibrin deposit.
Purulent exudate accumilate.
Paralytic ileus as a reflex

2
Fate depends on
1. Virulance of m.o
2. Effect of treatment
3. Resistance of the body
Resolution
Localization: abscess.
Flaring up(generalized)
Septicemia
Factors predispose to generalized peritonitis
1. High virulance m.o
2. Sudden perforation of viscous
3. Persistnt source of infection
4. Stimulation of peristalsis by e,ating,enema
5. Rough handling of localized collection during surgery
6. Immune suppretion (AIDS,STROID,D.M)
7. children ,elderly
Clinical picture
Increase pain at site of pathology with movement .
Vomiting
Abdominal distention
Constipation but in pelvic abscess diarrhoea
Examination
Patient looks ill ,fever ,tachycardia, distressed, avoid movement
Abdominal distention , tenderness ,rebound T.
Negative bowel sounds
Advanced condition leads to sunken eyes , septic shock

3
Investigations
Blood picture
Radiology (gases ,air under diaphragm)
U/S
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Treatment :
- Preoperative :
- NG suction
- I.V. Fluid
- Antibiotics
- Analgesia
-Urinary catheter
- Surgery
UGA
Mid line or paramedian
Pus send for C/S
Dealing with the pathology(appendix,D.U)
Peritoneal toilet
Drainage
-Post operative care
Continue antibiotics
I.V fluid
NG suction
Chart for assessment
Prevent septicemia
4
Localized intraperitoneal abscess
Has better prognosis than generalized peritonitis.
Indicate proper defense mechanism
Common sites of collection
RIF
LIF
Pelvis
Subphrenic and subhepatic.
Iliac abscess
In the RT side : A. Appendicitis ,perforated D.U
In the left side: perforated diverticulitis ,Ca. colon.
In both sides :from genital organs ,perforated DU
Clinical picture
Pain, swelling, hectic temperature ,vomiting,constipation.
O/E :tenderness ,rigidity or gaurding over site of abscess .
Investigation
Blood examination show leukocytosis.
U/S
C T ,MRI
5
Treatment :
Drainage of pus
Controlling the cause
Antibiotic
_ drainage should be done extraperitonealy through muscle cut incision.
_ percutaneous drainage under U/S or CT guide is preferable .
_ appendisectomy (interval)12 weeks
Pelvic abscess
Collection of pus in the recto-vesical pouch or Doglas pouch.
Causes:
- Acute appendicitis
- localization of resolving diffuse peritonitis
- pelvic inflammatary disease in female
Clinical picture
1. Hectic temp.
2. Deep pelvic pain
3. Diarrhea due to irritation of the rectum
4. Burning micturition ,friquency due to bladder irritation.
5. Suprapubic mass.
6. Rectal examination fullness ,tenderness in front of rectum
7. If neglected may rupture to rectum or vagina
Treatment
Drainage ,antibiotics
If abscess is pointing in rectum =trans – rectal
If in vagina = trans- vaginal through the post fornix
If suprapubic mass extraperitoneal drainage
Rectal drainage better than suprapubic drainage
