
Medicine
Dr. Zuhair
Neurology
“
Meningitis
”
Dr. Zuhair
LECTURE 16

Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
3
Meningitis
Objectives
To know about clinical presentation of meningitis and Encephalitis
To know about the common infective organisms responsible meningitis and
encephalitis.
To know about the pathophysiology of meningitis and Encephalitis
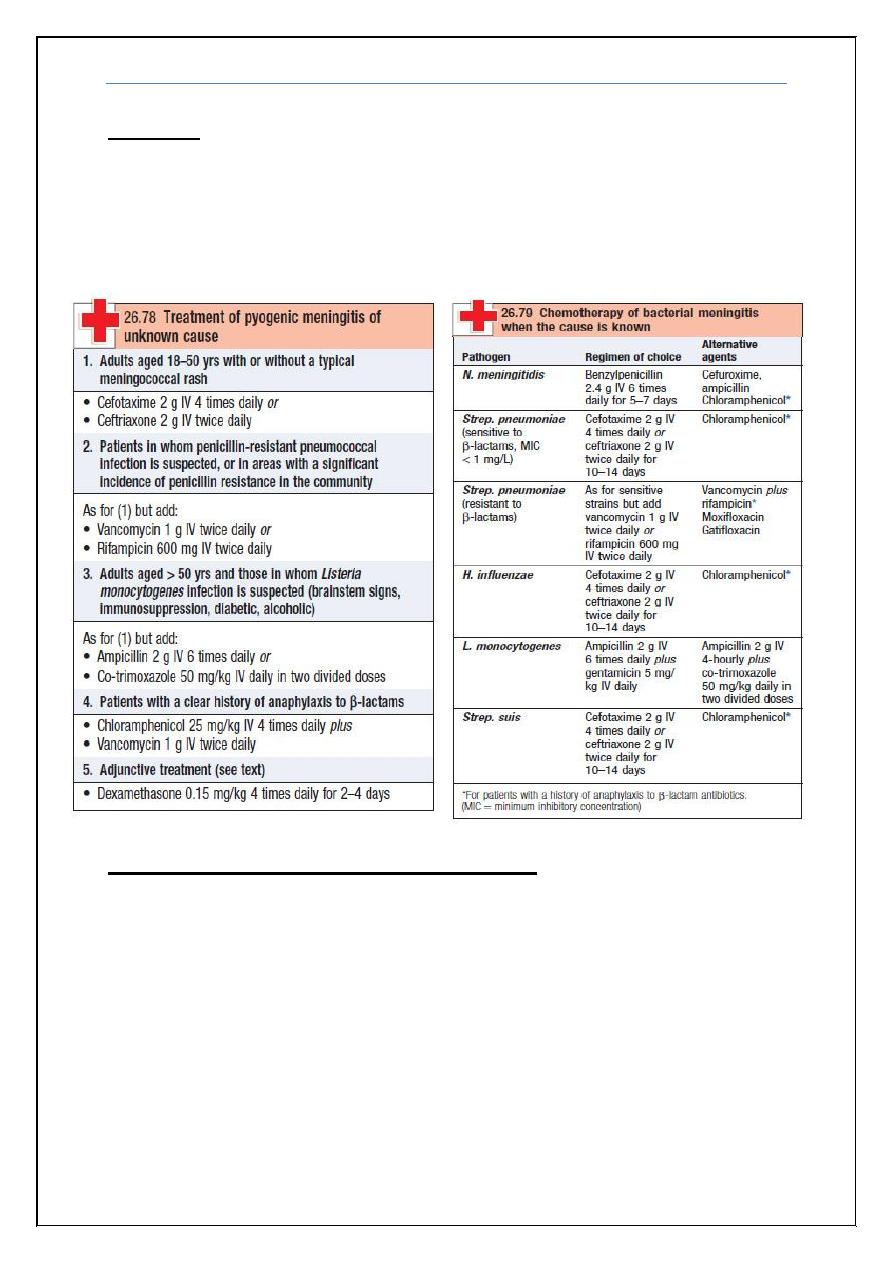
To know how to investigate a patient suspected of intracranial infection
To know the main differential diagnosis of meningitis and of encephalitis
To know about empirical treatment of meningitis and encephalitis
To know about complications of meningitis and Encephalitis
Sites
Meningitis
Encephalitis
Parameningeal: sinusitis, mastoiditis, otitis media, brain abscess and spinal
epidural abscess.
Presentation:
Fever
Headache
Vomiting
Neck pain and signs of meningeal irritation.
Disturbed consciousness
Seizures
Focal neurological manifestations
Manifestations of the causative agent.
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
4
Pathophysiology
Inflammation -> fibrinous exudate -> fibrosis
Subpial Encephalopathy
Increase intracranial pressure
Brain Oedema -> herniation
Vasculitis -> infarcts
Venous sinus thrombosis
Hydrocephalus
Encephalitis -> Direct dysfunction of areas of brain
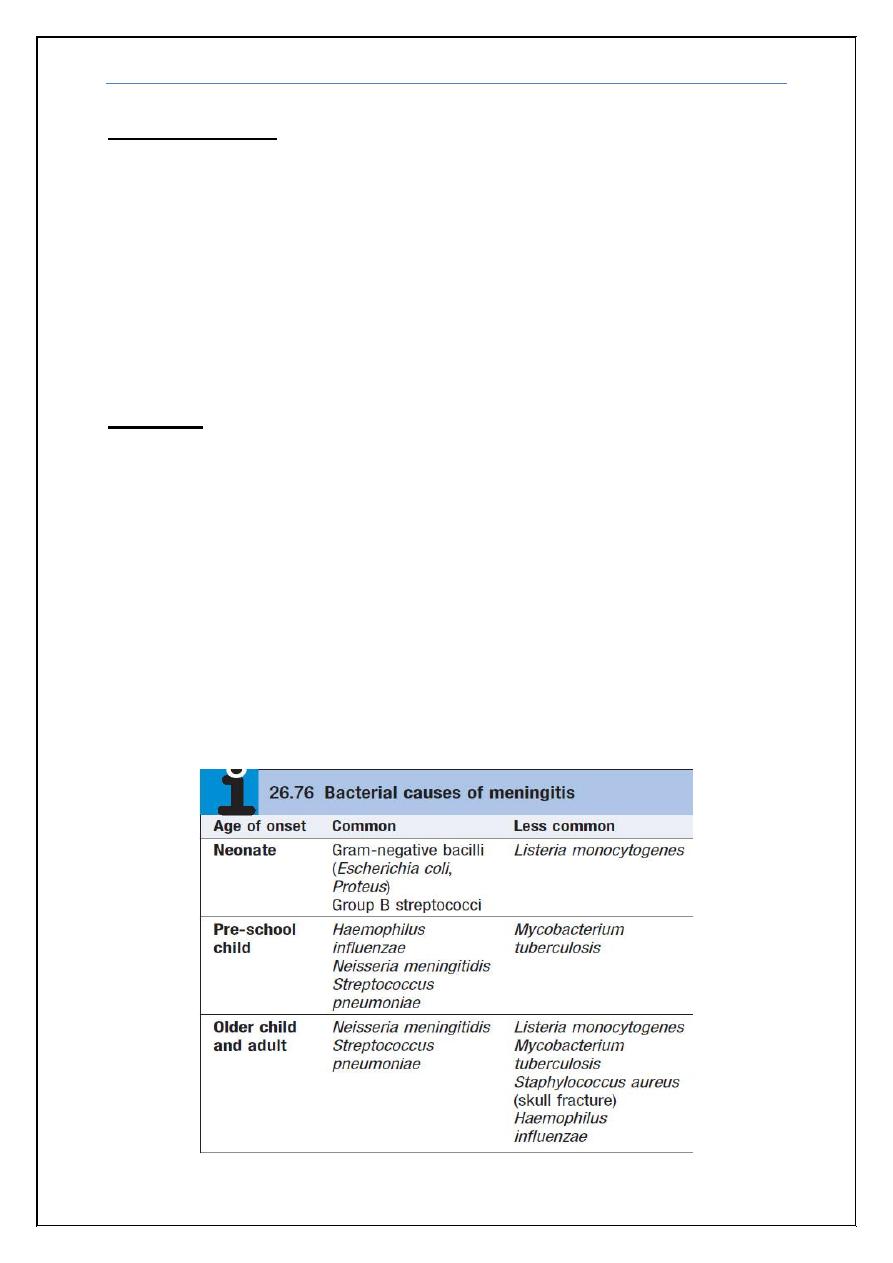
Atiology:
Infective
Bacterial
Acute: Pneumo, Meningo, H.Inf, List.mono
Subacute: TB, Ricketseal and Brucellosis
Viral: H.simplex, V.Z, E.Bar, JC and others
Fungal
Non infective ->
Connective Tissue
Malig: fixed, Leuk, Lymph
Radiation, Chemeical
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
5
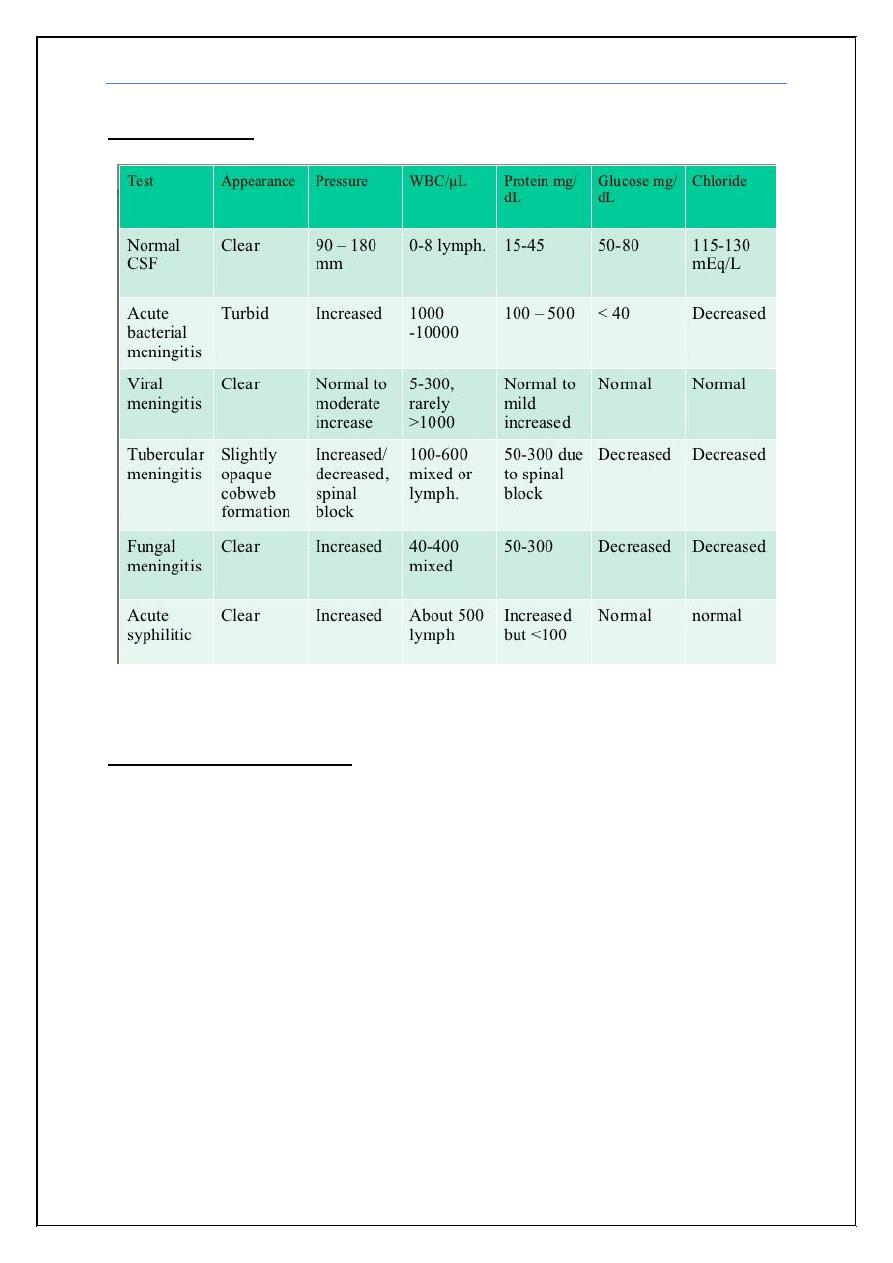
CSF Analysis:
Other CSF parameters:
Manometry
Gram stain
Sereological
Procalcitonin
PCR
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
6
Cases:
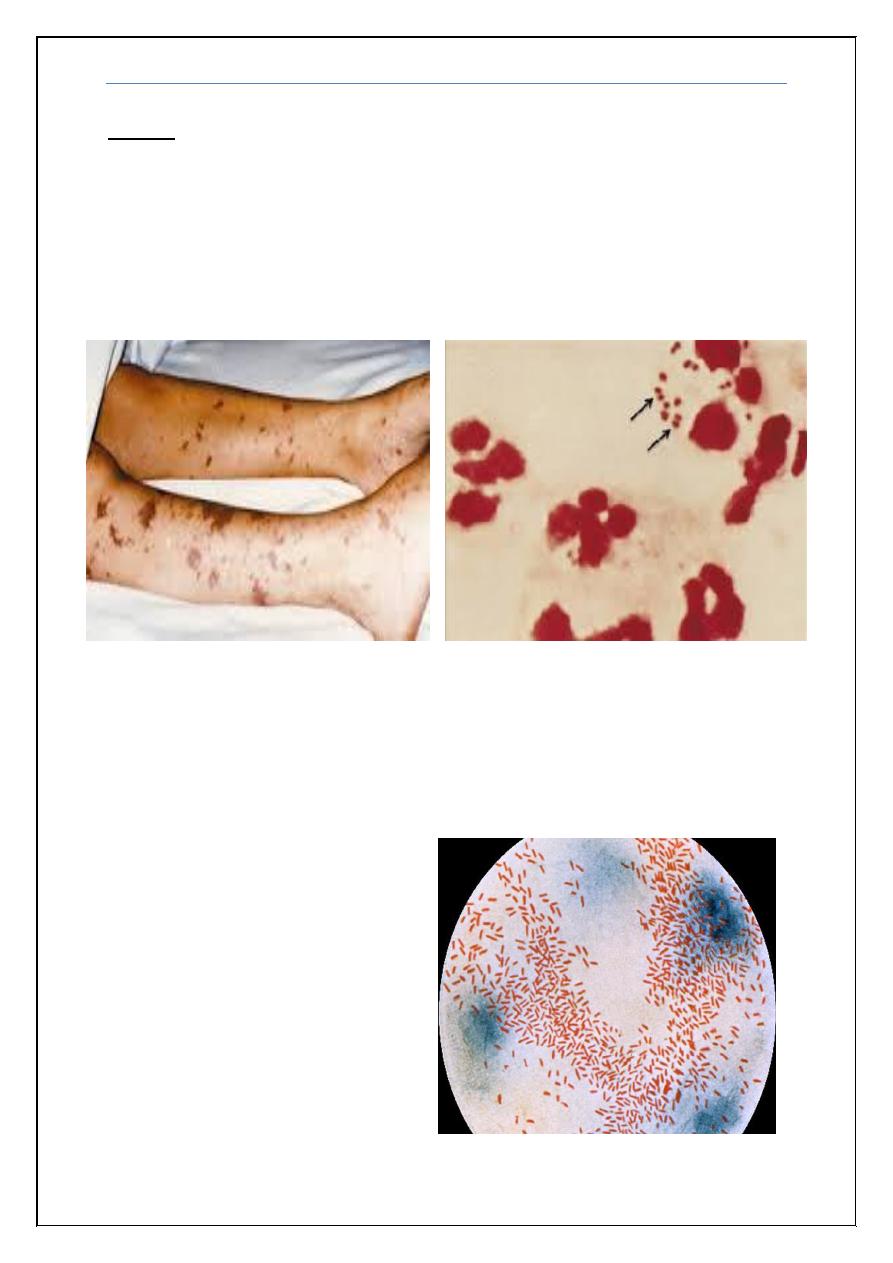
1) 10 years old boy presented with fever headache, photophobia and
vomiting of 3 days duration, was very toxic, history of similar condition
in his brother was noted, which lead to death. O/E Neck stiffness and
Kernig’s sign were positive. CSF: protein 120 mg/dl, sugar 39 mg/dl
(blood 99 mg/dl), cells: 600 WBC, 90% Neutrophils. Gram stain shown
below, also picture of his brother’s condition is shown below:
What is the most likely pathogen?
2) 5 years old boy presented with fever headache and vomiting of 3 days
duration, O/E Neck stiffness and Kernig’s sign were positive. CSF:
protein 120 mg/dl, sugar 39 mg/dl (blood 99 mg/dl), cells: 600 WBC,
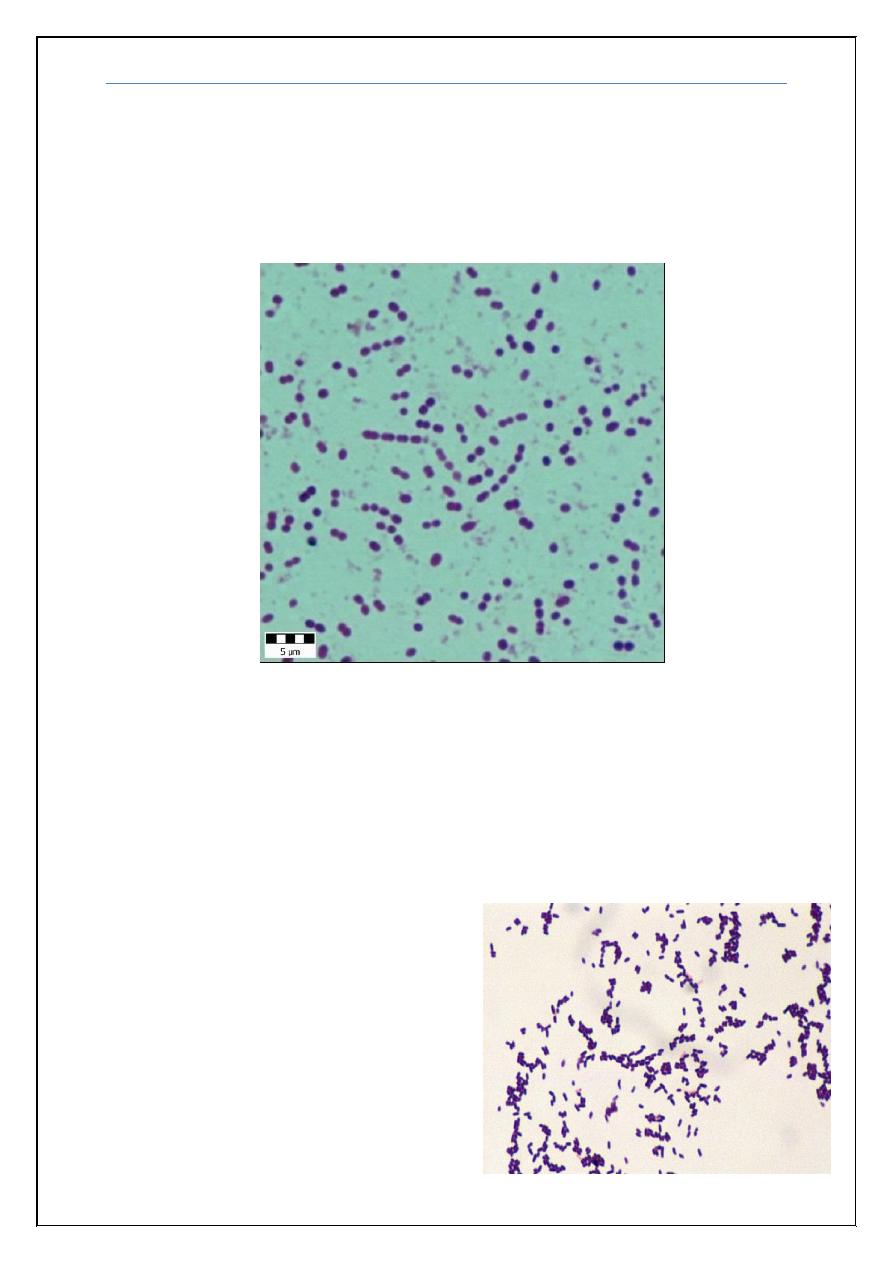
90% Neutrophils. Gram stain shown below:
What is the most likely pathogen?
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
7
3) 35 years old man known thalasemic presented with fever headache and
vomiting of 3 days duration, O/E Neck stiffness and Kernig’s sign were
positive. CSF: protein 200 mg/dl, sugar 39 mg/dl (blood 99 mg/dl), cells:
2600 WBC, 90% Neutrophils. Had a history of splenctomy 1 year ago.
Gram stain shown below:
What is the most likely pathogen?
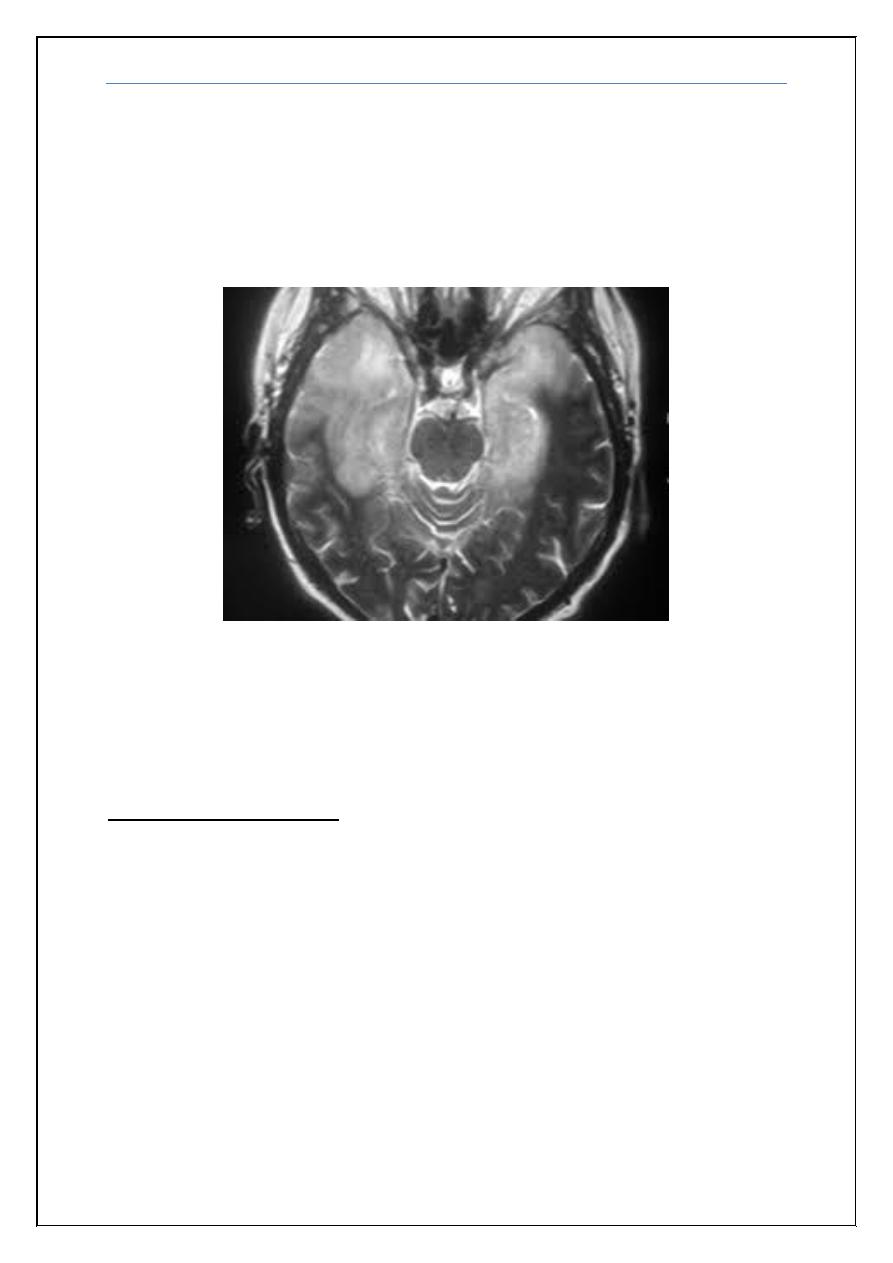
4) 30 years old pregnant lady with fever headache and vomiting of 5 days
duration, with acute onset deterioration in level of consciousnss following
a complaint of double vision.
O/E Neck stiffness and Kernig’s sign were positive. Bilateral VI, and
spastic quadriparesis. CSF: protein 200 mg/dl, sugar 39 mg/dl (blood 99
mg/dl), cells: 300 WBC, 90% Neutrophils.
What is the most likely pathogen?
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
8
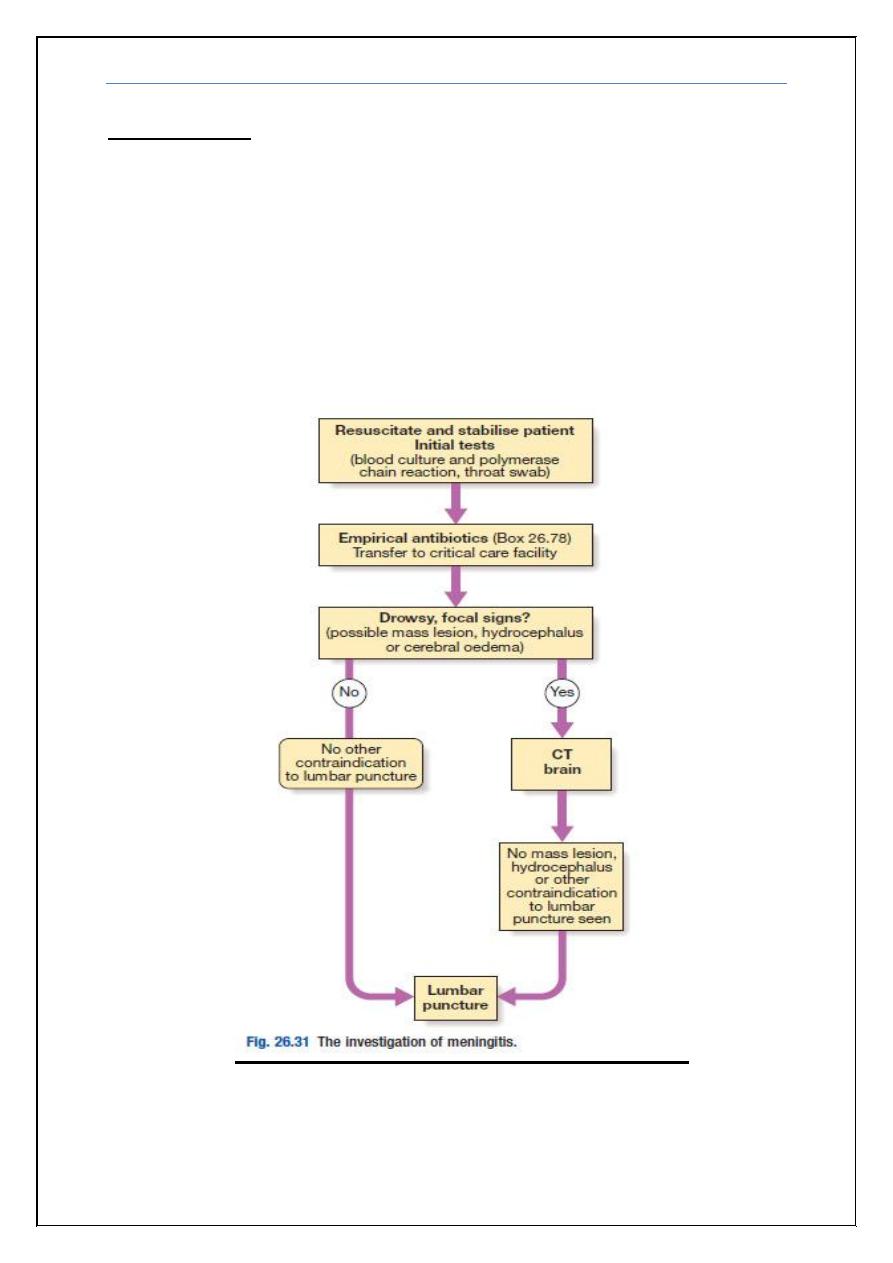
5) 17 years old girl brought to A&E with severe agitation and speaking non
sense, sustained three fits each preceded by abnormal sense of smell for
few seconds. O/E there was mild neck stiffness, Kernig sign was
negative. However she was Dilerious. CSF showed protein 67 mg/dl,
sugar normal, cells 10 WBC, all lymphocytes. Gram stain negative.EEG
reveals bilateral temporal spikes and MRI picture shown below.
What is the diagnosis?
Differential Diagnosis:
Meningitis:
Subarachoid Hemorrhage
Venous Sinus Thrombosis
Encephalitis
Encephalitis
Venous Infarction
Hemorrhagive Leucoencphalitis
Meningitis
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
9
Investigations
CBC & ESR, U&E, LFT, Nasopharyngeal swab, Blood cultures
CXR
CT scan & MRI brain, also for sinuses, otitis media, and other
parameningeal source.
EEG
MRV & MRI
Tuberculin test
HIV screen
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
10
Steroids:
Pyogenic Meningitis: Dexamethason: 4mg q6h iv x 4d
Herpes Simplex encephalitis: Dexamethason 8mg q12h x 4d
TB: 8mg iv q12h x 20 days
Prophylaxis of meningococcal Meningitis:
• Households, close contact (children)
• Rifampicine: po q12h x2d
• <1 year -> 5mg/kg/dose
• >1 year -> 10mg/kg/dose
• Adult: 600mg/dose
OR
• Single dose Ciprofloxacin 500mg
Meningitis Dr. Zuhair
11
Complications:
• Hydrocephalus
• Cranial nerves palsies
• Stroke
• Dementia
• Amnesia
• Aphasias
• Venous sinus thrombosis
• Death
END
