
Surgery
Nephroblastoma (wilms tumor)
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 32
NEPHROBLASTOMA
Nephroblastoma, also known as Wilms tumor, is the most common
solid renal tumor of childhood, accounting for roughly 5% of childhood
cancers.
The peak age for presentation is during the third year of life, and there
is no sex predilection.
they occur in either kidney with equal frequency. In 5% of cases the
tumors are bilateral.
Etiology
Wilms tumor occurs in familial and nonfamilial forms.
the occurrence of a familial Wilms tumor in approximately 1% of
cases.
Karyotypic analyses of Wilms tumor Shows Deletions of WT1, located
on chromosome 11p13
A second Wilms' tumor gene, WT2, has been identified on chromosome
(11p15 ).
Associated
congenital malformations.
Approximately 10% of patients with Wilms tumors have recognized
congenital malformations.
Surgery
Nephroblastoma (wilms tumor)
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 32
TheWAGR syndrome (Wilms, aniridia, genitourinary malformation,
mental retardation),
overgrowth syndromes, such as Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and
isolated hemihypertrophy .
Genitourinary abnormalities such as hypospadias, cryptorchidism, and
renal fusion.
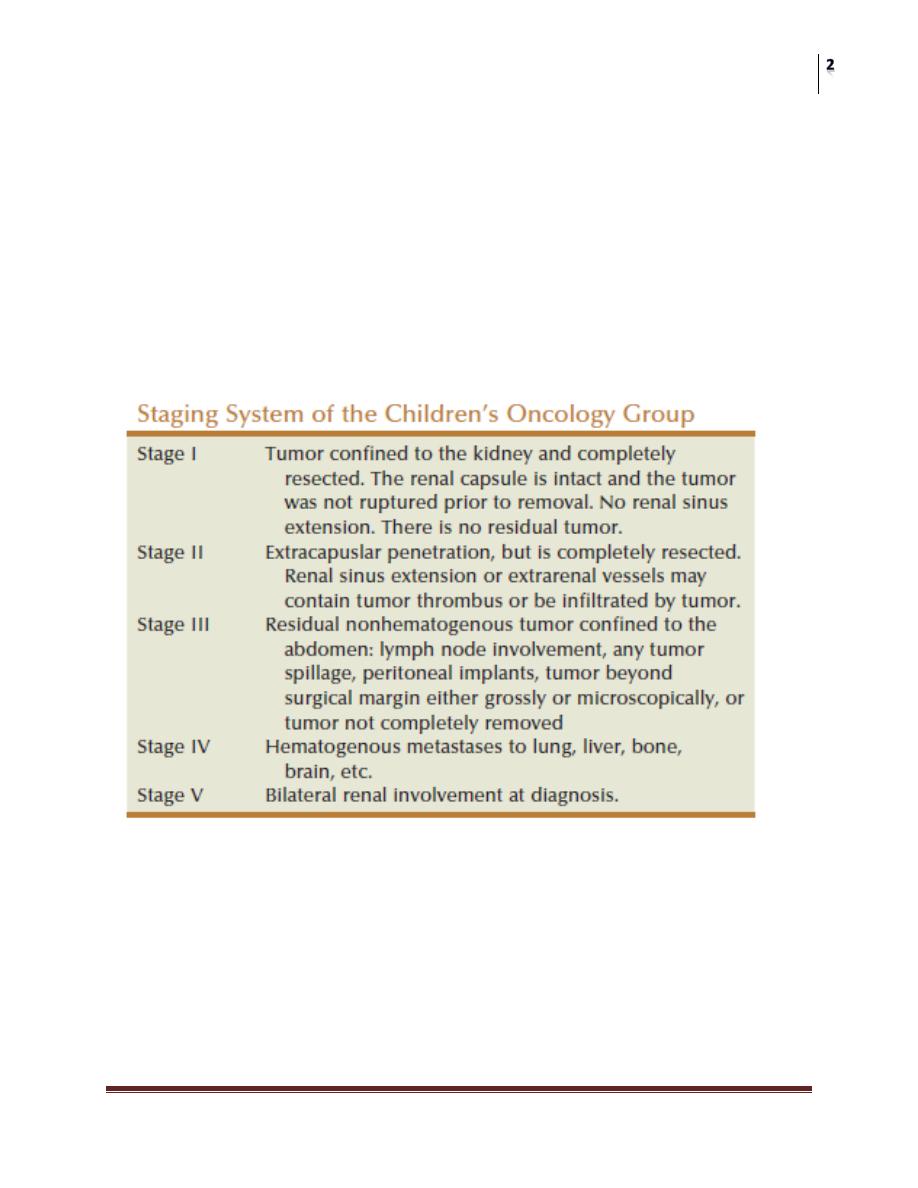
Tumor Staging
The NWTS staging system is most widely used and is based on surgical
and pathologic findings.
Clinical Findings
The diagnosis of Wilms tumor is most commonly made after the
discovery of an asymptomatic mass by a family member or a physician
during a routine physical examination.
Common symptoms at presentation include abdominal pain and
distention, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, fever, and hematuria.
The most common sign is an abdominal mass.
Surgery
Nephroblastoma (wilms tumor)
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 32
Hypertension is seen in 25–60% of cases and is caused by elevated
renin levels
Up to 30% of patients demonstrate hematuria and coagulopathy can
occur in 10%.
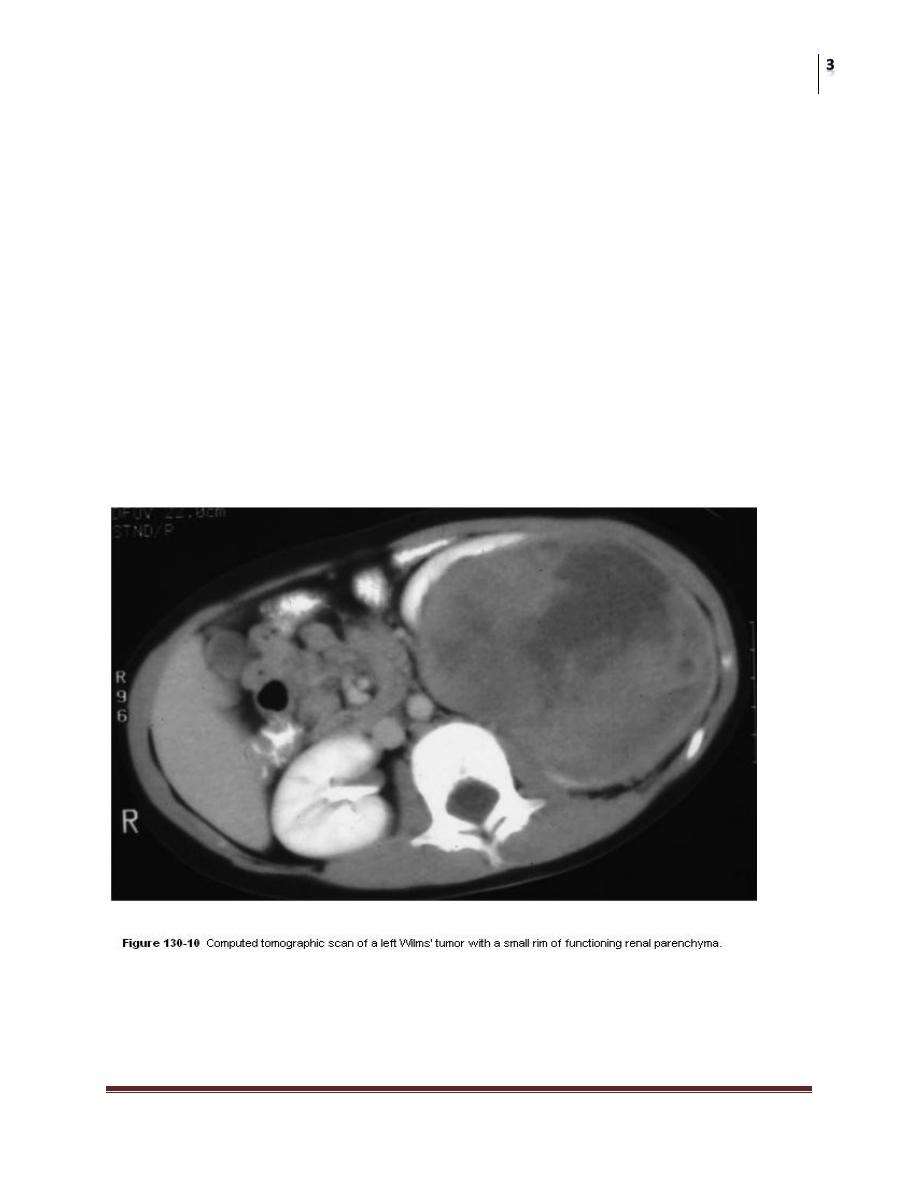
X-RAY IMAGING
Abdominal US and CT scanning are performed initially to evaluate the
mass.
MRI can also provide important information in defining the extent of
tumor into the inferior vena cava, including those with intra cardiac
extension.
Chest x-ray remains the initial examination of choice to evaluate for the
presence of lung metastases.

Surgery
Nephroblastoma (wilms tumor)
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 32
D. NEEDLE BIOPSY
Preoperative biopsy is indicated routinely only in tumors deemed too
large for safe primary surgical resection and for which preoperative
chemotherapy or radiation therapy is Planned.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of a flank mass in a child includes;
Hydronephrosis,
Cystic kidneys,
Intrarenal neuroblastoma,
Mesoblastic nephroma,
Various very rare sarcomas.
Treatment Of Wilms Tumor
A. SURGICAL MEASURES
For patients with unilateral kidney involvement whose tumors are
deemed surgically resectable (tumors not crossing the midline or
involving adjacent visceral organs), radical nephrectomy via a
transabdominal incision is the procedure of choice.
B. CHEMOTHERAPY
favorable histology tumors undergo surgical resection and have
adjuvant chemotherapy with vincristine and dactinomycin
combinations.
Patients with Un favorable tumors are receiving
vincristine,doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide.
C. RADIATION THERAPY
Postoperative radiation is recommended for patients with stage III or
IV disease.

Surgery
Nephroblastoma (wilms tumor)
Dr. Saad Dakhil
Lec. 32
Wilms & Neuroblastoma
In contrast to Wilms tumors, which are typically confined to one side of
the abdomen, neuroblastomas usually cross the midline.
Wilms tumors are intrarenal masses and rarely cause a change in the
axis of the kidney, while neuroblastomas may cause an outward and
downward displacement of the kidney (drooping lily).
Children with neuroblastomas are more likely to present with
metastatic disease, and
these tumors have a higher frequency of calcification observed
radiographically.
neuroblastomas may produce various tumor markers including
vanillylmandelic acid and other catecholamines that are not seen in
patients with Wilms tumor.
