Food safety
Dr. Nadia AzizC.A.B.C.MBaghdad medical collegeobjectives
Describe types of food born diseases and its causesDescribe types of food preservation
Define global warming
Explain different ways of medical wastes disposal
Food safety
The objectives of food processing and preparation are to provide safe and neutrious food to the consumer.The responsibilities for accomplishing this objective lie with every step in the food chain beginning with food production in the farm and continuing through processing, storage, distribution cell and consumption.
Food born diseases 1- Bacterial infection
Salmonellosis: many people are permanent often asymptomatic carriers. Chicken infected with salmonella species can excrete these organisms into the eggs.Shigellosis: Salads are frequently implicated.
Viberiosis: consumption of raw or undercooked shellfish.
E coli: Enterotoxigenic strains are a notable cause of traveler diarrhea
Food born diseases 2-viral infection
Infectious hepatitis: control is achieved by cooking food, stressing personal hygiene and by avoiding shellfish harvested from polluted waters
Enteroviruses: (coxsackie, echo ,Norwalk, rotavirus) foods associated with transmission of viral agents are raw shellfish , vegetables , fruits and salads
Food born diseases 3-parasites
Nematodes (round warm): Ascaris lumbricoides , Enterobius vermicularisProtozoa cause a large number of food born and water born outbreaks each year. Entamoeba histolytica, toxoplasma gondii, giardia lamblia cause dysentery like illness that can be fatal.
Food born diseases
Bacterial IntoxicationStaph. aureus :certain strain produce a heat - stable enterotoxin, 25% of healthy people are carriers
bacillus cereus: heat stable & heat labile enterotoxins
Ch. botulinum: infant botulism is the common form of botulism(6 week- 6 month)
chemical intoxications
chemical hazards are minimally important as etiological agents of food born disease .most human made chemicals associated with food born disease find their way into foods by non intentional means accidental or inadvertent contamination with heavy metals, detergents or sanitizers can occur .
Food born diseases
Food PreservationPreventing growth or activity of microbes with low temperatures, drying, anaerobic conditions, or preservatives can be done.
Killing or injuring microbes with heat, irradiation, or some preservatives is certainly effective.
Food Preservation
Steps to manipulate the microbial growth:
a. Avoid addition of actively growing organisms that found on unclean containers, equipment, and utensils & by reducing contamination.
b. Create unfavorable environmental conditions for growth.
Food Preservation
Unfavorable environmental conditions for growth :Is the most important step of food preservation & done by extremes of temperature , irradiation, low Ph, and by adding inhibitors and preservatives
Food Preservation
Asepsis:Packaging is the most widely used form of asepsis and includes wraps packages, cans, etc.
Food Preservation
Modified atmosphere conditions:altering the atmosphere surrounding the food can be a useful way to control microbes examples: packaging with vacuum , CO2 , N2 , or combinations of inert gases with or without oxygen .
Food Preservation
High temperature preservation :Based on destroying microbes, but may injure certain thermoduric microbes (spore formers usually survive)
Less severe heat processing is pasteurization which usually involves heating at less than 100oC .
Food Preservation
Low temperature preservation :
Refrigeration freezing temperature should be maintained as low as possible for
refrigerated food.
Food Preservation
Drying:Foods can be preserved by removing or binding water. any treatment that lowers water activity can reduce or eliminate growth of micro organisms .
Food Preservation
Preservatives :Inorganic preservatives examples are NaCl , nitrate, nitrite , sulfite and SO2 .
NaCl lowers water activity and causes plasmolysis by with drawing water from cells.
Nitrite and nitrates are curing agents for meats to inhibit C.potulinum under vacuum packaging conditions
Food Preservation
Inorganic preservativessulfur dioxide (SO2) sulfite (so3) bisulfite HSO3 and metabisulfites S2O5 form sulfurous acids which is the anti microbial agents
Food Preservation
Inorganic preservatives
Nitrite can react with secondary and tertiary amines to form potentially carcinogenic nitrosamine during cooking.
Nitrates in high concentrations can results in red blood cell functional impairment.
Sulfating agents likewise can cause adverse respiratory effects to susceptible consumer particularly asthmatics
Food Preservation
Irradiation: non ionizing radiationultraviolet
microwaveinfrared
Food Preservation
ultraviolet are used to disinfect water, surfaces, utensils walls ceilings and floors.ultraviolet will not penetrate opaque materials and is good only for surface decontamination.
infrared has little penetrating power
microwaves have excellent penetrating power
Food Preservation
Fermentation:A number of foods use beneficial microorganisms in the course of their processing.
The sugar in certain food is converted to organic acids, ethanol, or carbon dioxide, these three by- products not only serve as desirable flavors but also provide a significant antimicrobial barrier to pathogens.
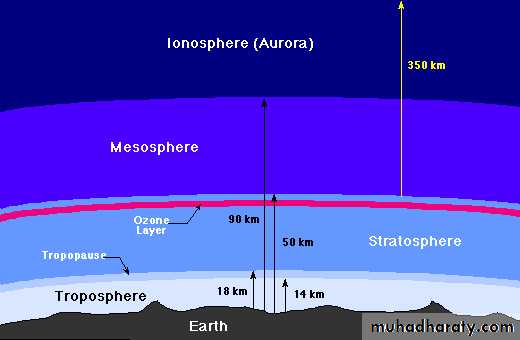
Global warming
Earth mantle of atmosphere acts like a greenhouse, allowing passage of short-wavelength solar radiation into the biosphere, trapping longer wavelength infrared radiation.
Without the greenhouse effect, earth surface temperature would swing from over
500c in strong sunlight to -400c at dawn.
Global warming
The concentration of greenhouse gases in the troposphere has risen rapidly since the beginning of the industrial era because several of these gases, notably carbon dioxide, are products of fossil fuel combustion and other human activities.Global warming
Over 6 billion metric tons of CO2, the principle greenhouse gas, are added to the troposphere annually, increasing amounts every year.Tropical rain forest , the most important carbon sink(a biological system that absorbs carbon emissions, helping to balance negative impacts on earth temperature), are being rapidly depleted often by burning and adds more carbon gases to the greenhouse.
Global warming
Phytoplankton, another important carbon sink, are damaged by increased ultraviolet radiation (UVR) flux from depleting stratosphere ozone.It is estimated by global climate models that the average temperature will rise by about 0.50C in the first half of the twenty-first century.
Global warming
Global warming has direct and indirect adverse effect on health.
heat –wave deaths are dramatic and obvious.
increase incidence and prevalence of water born and vector born disease. Malaria, is expected to be prevalent in temperate zones and in altitudes in tropical and subtropical regions from which it is now absent .
Global warming
The indirect effects of global warming include:A rise in sea –level of up to 50 cm by the year 2050, due to melting of polar and alpine ice-caps and thermal expansion of sea water mass. This will disrupt many coastal ecosystems and perhaps some ocean fisheries.
Anomalous weather emergencies such as catastrophic floods, hurricanes and tornadoes and heat waves.
Global warming
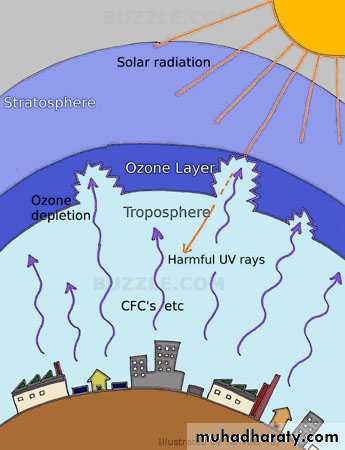
Stratospheric Ozone attenuationThe chlorofluorocarbons (CFCS), a widely used class of chemicals, would permeate the upper atmosphere where they would break down under the influence of solar radiation to produce Chlorine monoxide.
Chlorine monoxide destroys Ozone, each molecule of chlorine monoxide is capable of destroying over 10,000 ozone molecules.
Global warming
Other atmospheric contaminant that destroy stratospheric ozone include other halocarbons and perhaps oxides of nitrogen (in exhaust emissions of high- flying supersonic jet aircraft).Volcanic eruptions sometimes release Chlorine compounds into the atmosphere, so natural as well as human –induced processes can contribute stratospheric ozone attenuation.
Global warming
In 1985, Farman and coworkers observed extensive attenuation (a hall) in the stratospheric ozone layer over Antarctica during the southern hemisphere spring. Seasonal ozone depletion has been observed in the northern hemisphere too.Stratospheric ozone depletion was correlated with increased surface level UVR flux.
Ozone depletion is about 3-4% of total stratospheric ozone and increasing annually.
Global warming
CFCs were widely used as solvents in manufacture of microprocessors for computers, foaming agents in polystyrene packing, and as Freon gas in air conditioners and refrigerators, their supposed chemical inertness made them a popular choice.Global warming
Stratospheric ozone depletion permits greater amount of harmful UVR to enter biosphere, where it has adverse effects on many biological systems and on human health.Global warming
The principal biological effects of increased UVR are disruption of the reproductive capacity and vitality of small and single- celled organisms , notably phytoplankton.Increased UVR also has direct adverse effects on human health, it increases the risk of skin cancer, increases the risk of ocular cataracts, and probably impairs immune function.
Medical Waste Disposal
The primary methods of treatment and disposal of medical waste are:Incineration
Autoclaves
Chemical Disinfection
Microwave
Irradiation
Medical Waste Disposal
AutoclavesAutoclaves are closed chambers that apply both
heat and pressure, and sometimes steam
Chemical Disinfection
primarily through the use of Chlorine products
Medical Waste Disposal
MicrowaveThe microwaves internally heat the waste, rather than applying heat externally, as in an autoclave.
Irradiation
Through exposure of the waste to a cobalt source. The gamma radiation generated by the cobalt source inactivates all microbes that may be present in the waste