Transverse lieoblique lie
Dr HAIDER Al-Shamma’aobjectives
Able to define transverse and oblique lieThe student should be able to diagnose transverse , oblique lie
Should be able to list the causes .
Able to outline the management and justify it
Able to define unstable lie
Able to list the causes
Able to outline the management and can justify it
Objectives continue…
Able to identify fetal causes of abnormal laborAble to outline the management with justification
The student should be able to diagnose cord prolaps
Able to apreciate the risks of cord prolaps
Able to manage the patient with cord prolaps
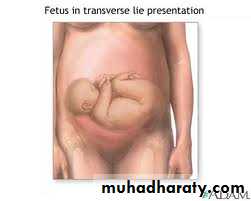
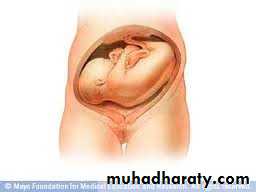
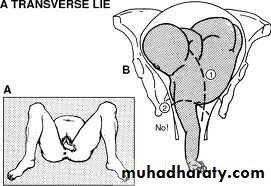
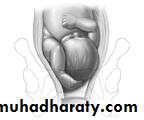
Transverse lie :- occurs when the longitudinal axis of the fetus is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the mother the presenting part is the shoulder ( also named shoulder presentation ).
Oblique lie :- when the head or the breech is slightly higher than the other side
Transverse lieOblique lie
the denominator is the back ( dorsum )
Dorso-anterior is more common than dorso-posteriorIncidence :- 1/250 – 1/500 deliveries
Right acromio-dorsoposteriorCauses of transverse lie
• Multiparity is the most common cause• Prematurity
• Polyhydramnious
• Multiple pregnancy
• Contracted pelvis
• Placenta previa
• Fibroids of the lower segment
• Congenital abnormalities of the uterus as septate and arcuate uterus
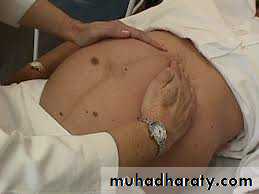
Diagnosis of transverse lie
On abdominal examination:-• The abdomen is asymmetrically distended
• Width more than length
• Fundal height less than expected
• Round heard mass at one iliac fossa , softer breech at the other fossa
• Absent presenting part ( pelvic grip feel empty lower segment
• On p/v examination:-
• Can not feel the presenting part (high)
• Bulging membranes or rupture membranes
• Fetal arm or umbilical cord may prolaps to the vagina
Abdom. Finding T. Lie
Hand prolaps
Mechanism of labor
No mechanism of labor due to very large dimensions of the fetus , in a neglected case lead to fetal death and rupture of the uterus and maternal deathRarely in a small premature dead macerated fetus in a stout mother , the baby may fold on itself and deliver vaginally
Management of transverse lie
• Before labour :-• Manage as breech do ECV *
• During early labor:-
• Before rupture membrane can try ECV
• 3. Advanced labor , failure of ECV or contraindicated ECV :-
• Cesarean section is the safest method even incase of a dead fetus (TLSCS or easier LVCS)
Rarely in advanced neglected case with no facilities of CS
Decapitation by hook or saw , then pull the hand to deliver the trunk then deliver the head by forceps
Cesarean section is safer
Unstable lie
When the fetus changes its axis every visitCauses as t lie
Management :-ECV each visit after 36 weeks
((same contraindication as ECV of breech)
Admission to hospital at 36 weeks
ECV and induction of labor at 38 wks
Elective cs may be performed in selected cases
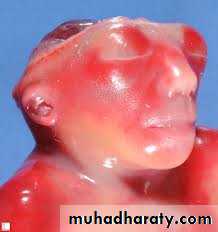
Fetal malformation causes difficult labor
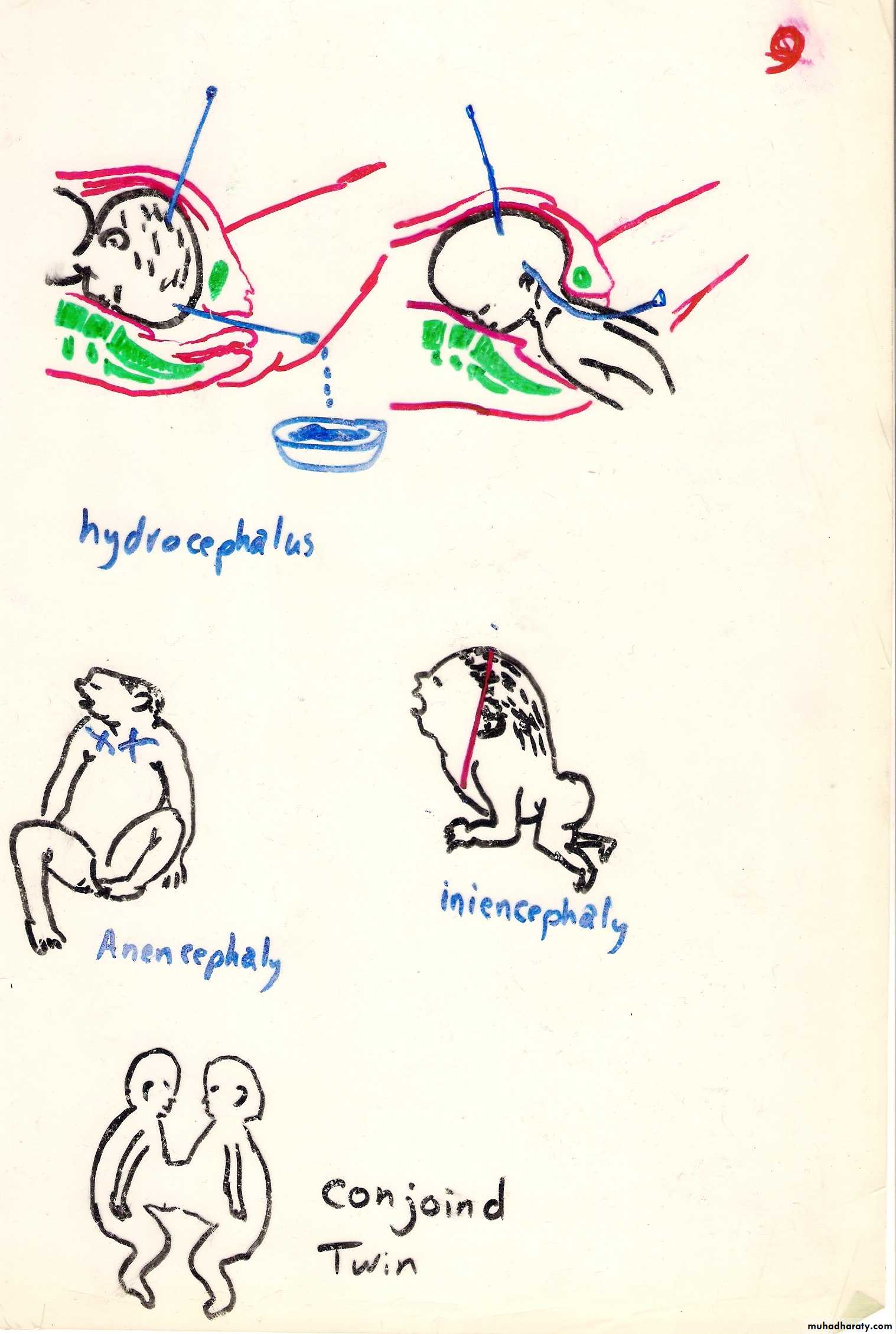
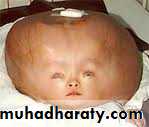
HydrocehalusDiagnosed by U/S
During labor feel widely separated sutures
Big head cause obstructed labor rare in modern practice
Management : terminate pregnancy when the head reaching 9.5 cm by induction of labor or by CS (up to 12cm)
Advanced obstructed labor perforate the head and drain the CSF and deliver vaginally ( rare )
hydrocephalus
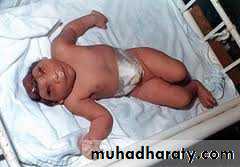
Anencephalus
Absent vault and brain , incompatible with lifeMay cause prolonged pregnancy(>42 wks)
due to irregular shape dilatation is difficult , may need cleidotomy
Anencephalus
anencephalus
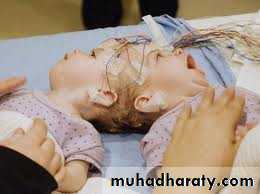
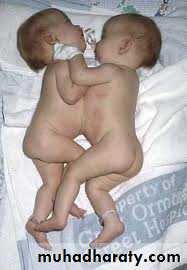
Conjoined twins
Suspected if the twins maintain the same relation to each otherU/S can diagnose the connection
Cause obstructed labor and need CS even that may be difficult !!
Conjoined twins cephalopagus
Thoracopagus
Compound presentation
Head +handHead + foot
Give large and irregular presenting part with risk of cord prolaps
Management:-
Usually corrected spontaneously with progress of head descent
If persistent try to push limb up
CS may be needed
Cord prolaps
Descent of loop of cord through the cervix to the vagina or even outside the vagina when the membranes rupturesCauses
• Malposition malpresentation
• Rupture of the membranes when the head is high
Diagnosis of cord prolaps
Feel soft cord felt below the fetusPulsation can be felt and this mean the fetus is alive
If No pulsation either dead or spasm
Consequences of cord prolaps
Thermal and tactile stimulation cause spasm that interfere with fetal oxygenation fetal hypoxia and death may occur in less than 30 min
Also cord compression between the presenting part and boney pelvis
Treatment of cord prolaps
Steep Trendlingberg position or knee chest position to dis-impact the fetus and reduce cord compressionVaginal pack
Terminate pregnancy by the most rapid method before fetal death
(1st stage C/S) & ( 2nd stage : forceps , vacuum extractor or C/S which ever can deliver first)
Diagram of cord prolaps Mx
prolapsDead fetus alive fetus
Continue labor 1st stage 2nd stageAs no prolaps
CPD no CPD
C/S forceps / vacuum
Thank you