Eczema part 2
• Objectives• Recognize endogenous types of eczema
• Differentiate between exogenous types
• Plan General and specific management of eczema
•40 year old man
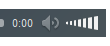
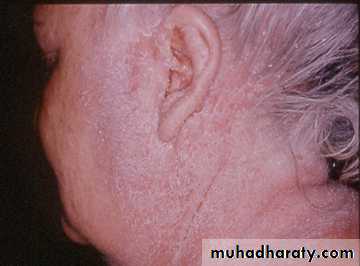
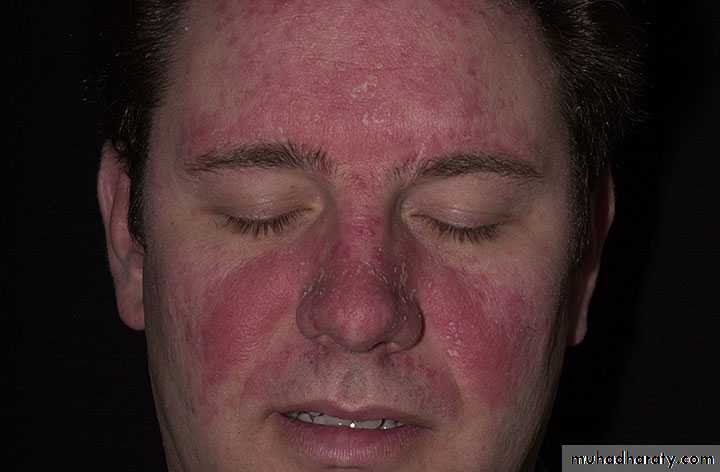
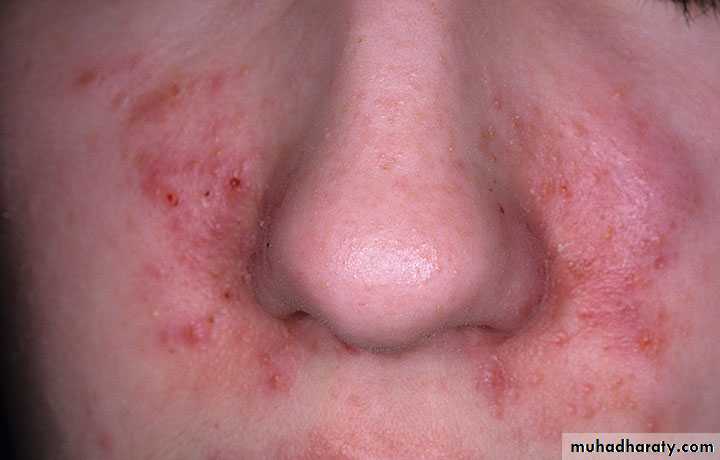
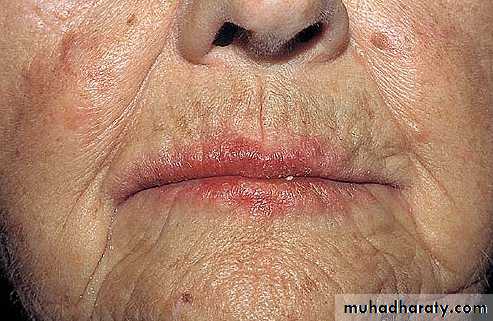
•“Fed-up” with years of dandruff•Recent onset of itchy, red scaling of eyebrows, naso-labial folds
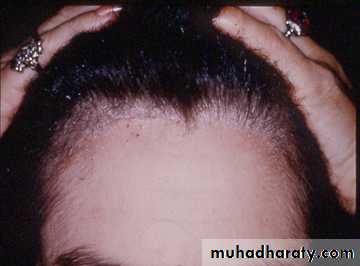
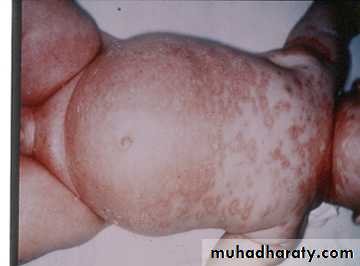
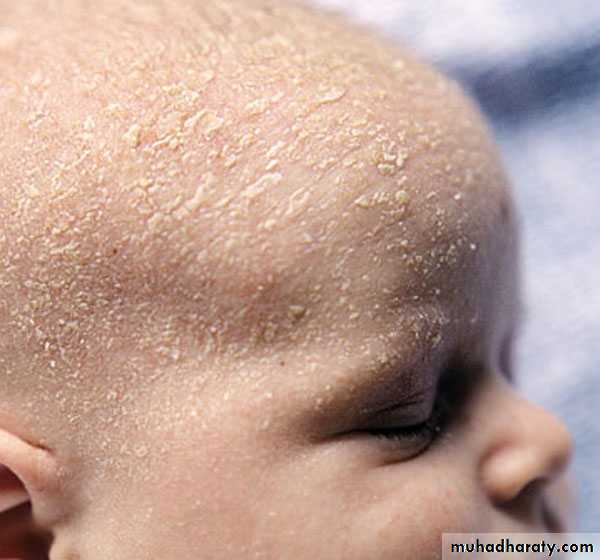
Seborrheic Dermatitis
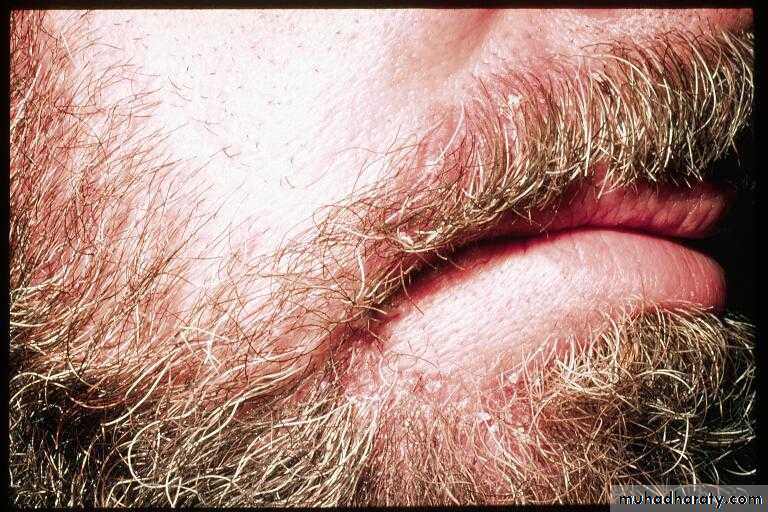
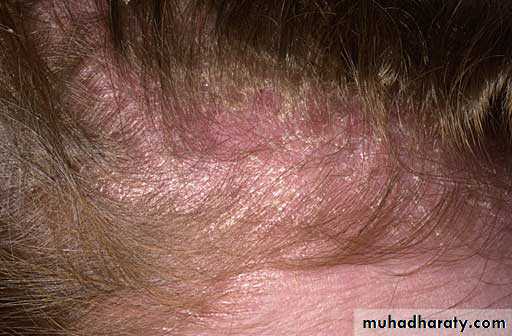
• Chronic, superficial inflammation affecting hairy regions. Most common on scalp, eyebrows, face nasolabial folds• Central chest axillae groin
• White-yellowish greasy scale on erythematous patches or plaques. Indistinct margins. Hair loss uncommon.
• Likely etiology is yeast Pityrosporum ovale
• Common, affects 3-5% of the population
• Cradle Cap is scalp SD common in infants
• Treat with zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, topical steroids
• Acute onset or widespread exacerbation is commonly seen in HIV infection.
sd
sd
SD of scalp and beard
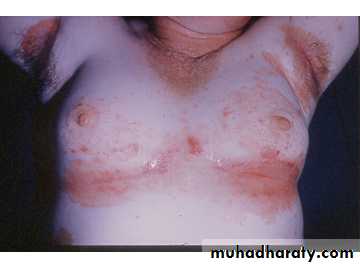
Nummular Eczemachronic disorder of unknown etiology.
Papules and papulovesicles coalesce to form nummular plaques with oozing, crust, and scale.
Most common sites of involvement are upper extremities, including the dorsal hands in women, and the lower extremities in men.
Pathology may show acute, subacute, or chronic eczema
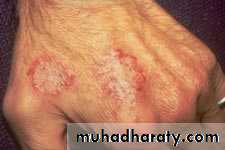
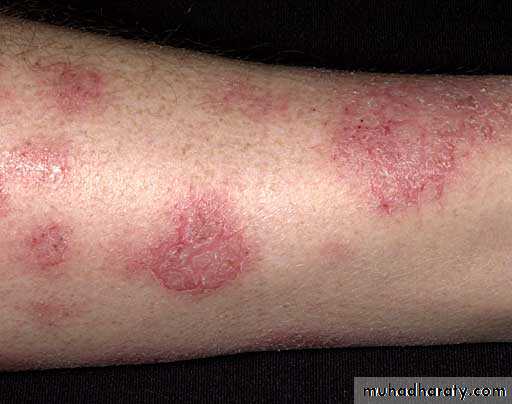
Nummular Eczema
• Oval, coin-shaped, weeping patches with crusted papulovesicles
• Overlaps with Atopic Dermatitis
• Most common on trunk and extremities
• Idiopathic
• Tx: med-high potency steroids, emollients
•75 year old man
•Retirement apartment•Likes to keep clean
•Diuretics
•Itching started on legs and spread to arms and trunk
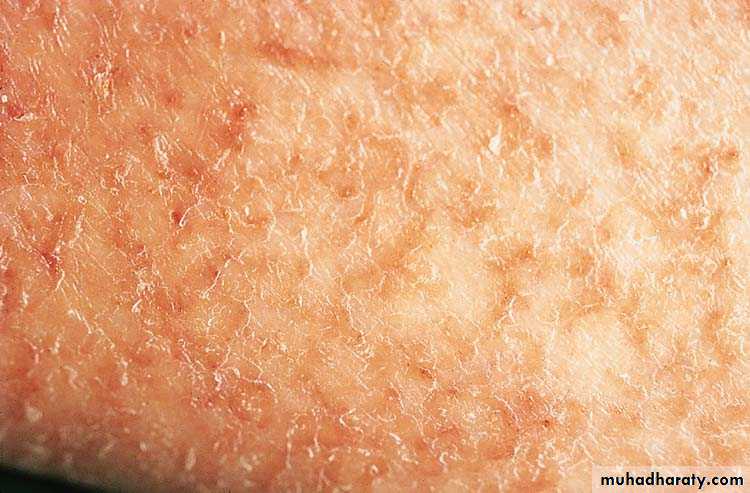
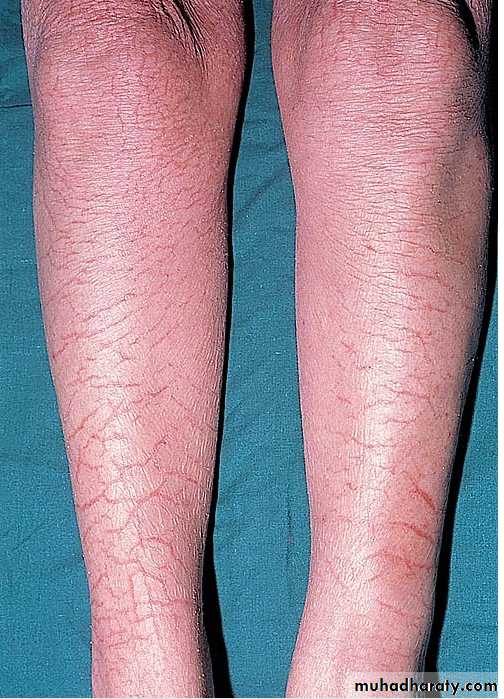
Asteatotic Dermatitis
• Erythematous patches with scaling and fissuring. Markedly dry skin.• Pruritic lesions may have secondary lichenification
• Associated with, anti-androgens, dehydration, malnutrition, neurologic disorders
• Most common on shins, hands, and trunk
• More common in the elderly, M>F
• Tx: topical steroids, anti-histamines, emollients, avoid irritants
Asteatotic Dermatitis
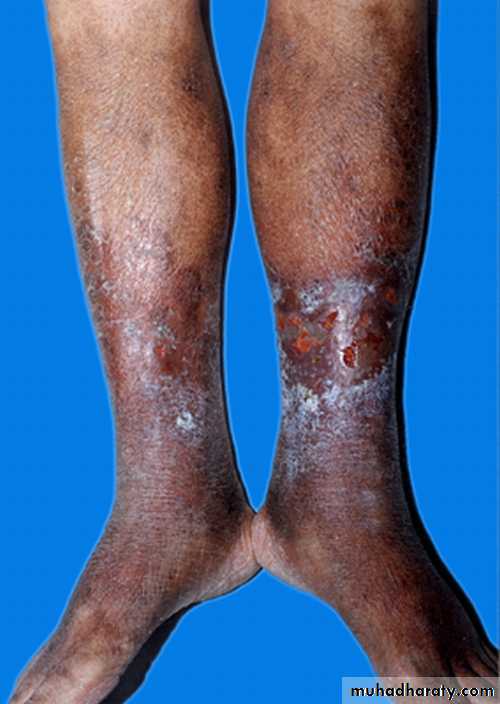
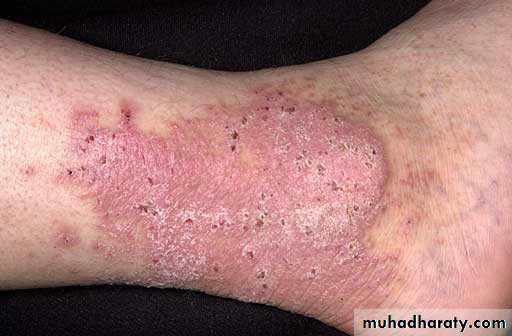
Gravitational Dermatitis
• Increased hydrostatic pressure and capillary damage leads to extravasated fluid and RBCs• Inflammation and deposition of heme results in the eczematous lesions
• Involved skin is hyperpigmented, thickened, scaling, weeping
• Most common site is proximal to the medial malleolus
• Treatment with support hose, leg elevation, weight reduction, topical steroids, treatment of secondary infections
Gravitational Dermatitis
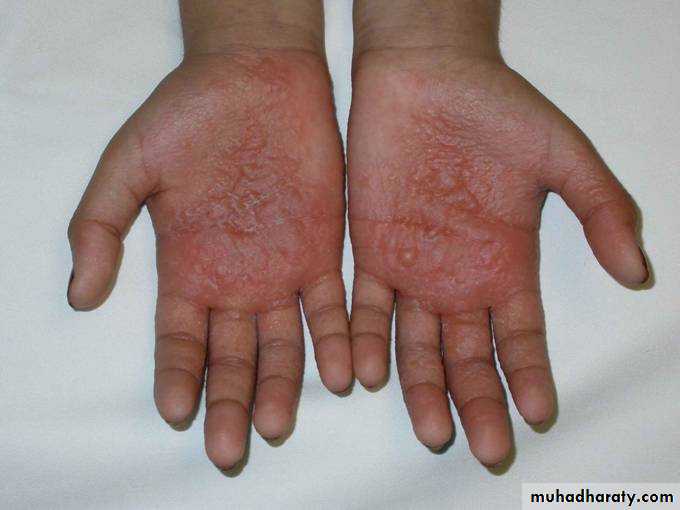
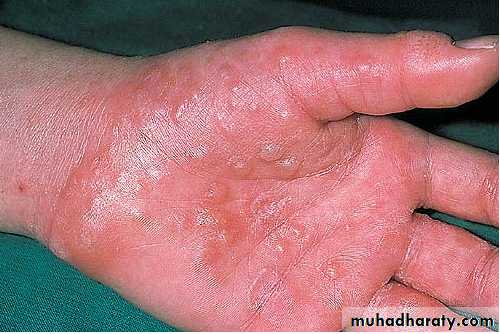
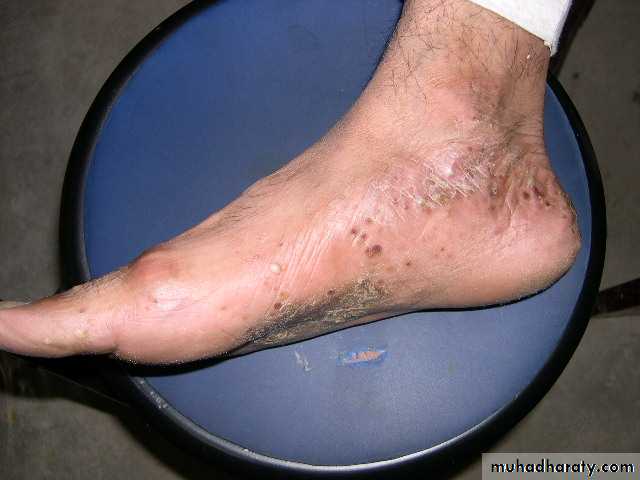
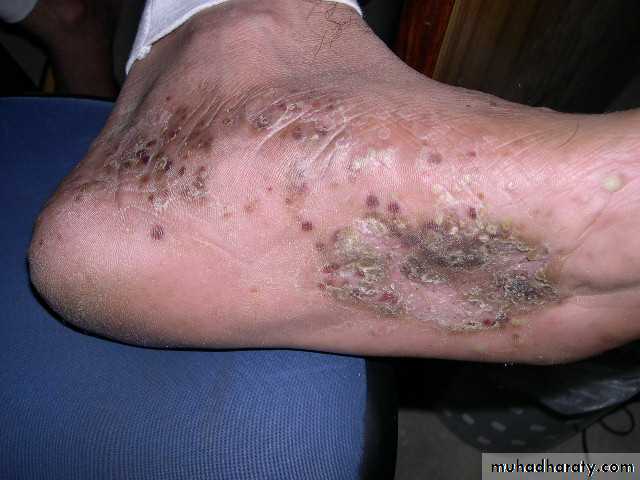
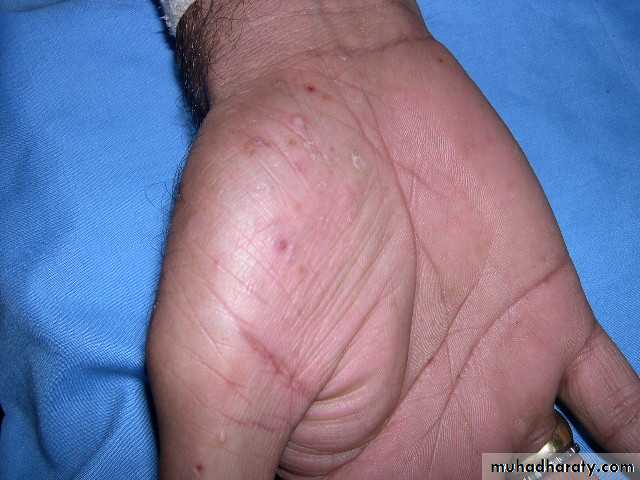
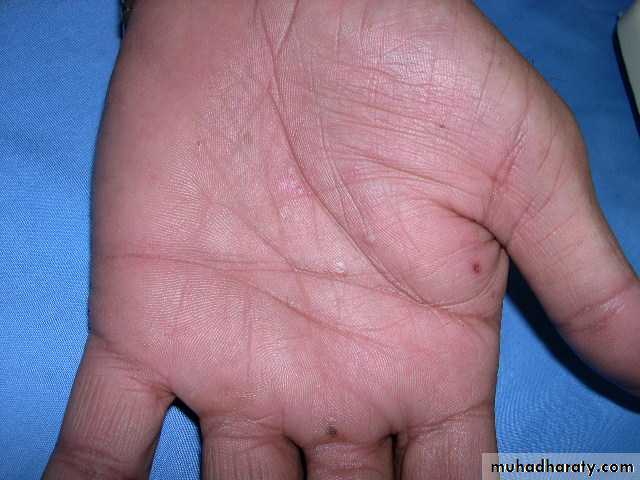
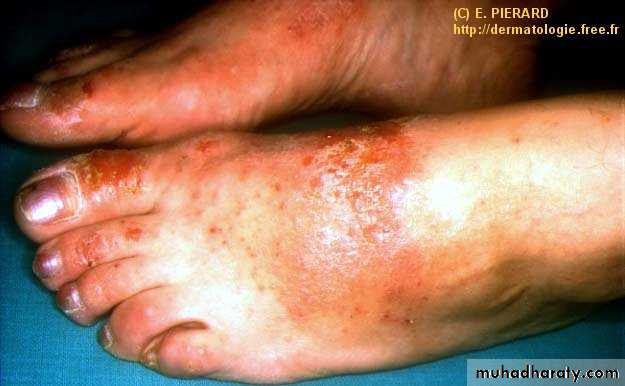
“I can’t do anything with my hands like this!”
pomphylox
pomphylox
Recurrent vesicles and bullae occur on the palms, palmar surface of the fingers and soles, and are very itchy.This form of eczema can occur in atopic eczema and in irritant and contact allergic dermatitis. It can be provoked by heat, stress and nickel ingestion in a nickel-sensitive patient but is often idiopathic
Treatment systemic steroid ,use glass dishes??
Mild form
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
• Chronic lesions due to scratching• Lichenified plaques on posterior neck, extensors of UE and LE, genitals
• Occurs within reach of scratching implement
• Patient’s mood affects course
• Treat with topical or intralesional steroids, cover the area, emotional support
• B. exogenous (environmental )
• 1-occupational d.• 2-irritant contact d.
• 3-allergic contact d.
• 4- infective d.
• 5-photoallergic d.
Contact Dermatitis
• Inflammatory reaction precipitated by an exogenous chemical• Irritant or allergic subtypes
• Very common problem
• Occurs in distribution of contact
• leather – shoe area
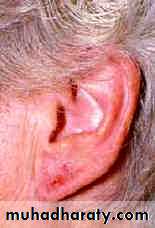
• nickel – earlobes, neck, wrist, peri-umbilical
• Can be eczematous, vesicular
• History is very important!
• Irritant dermatitis
• Detergent acids alkalis
• Industrial
• napkins
• All people affected
• First exposure
Allergic contact dermatitis
some peopleSecond exposure
Elicited after 2 days
Needs cell mediated immunity
Nickel, dichromate (cement) ,rubber
Earlobe wrist
Patch testing
Shoe Leather Dermatitis
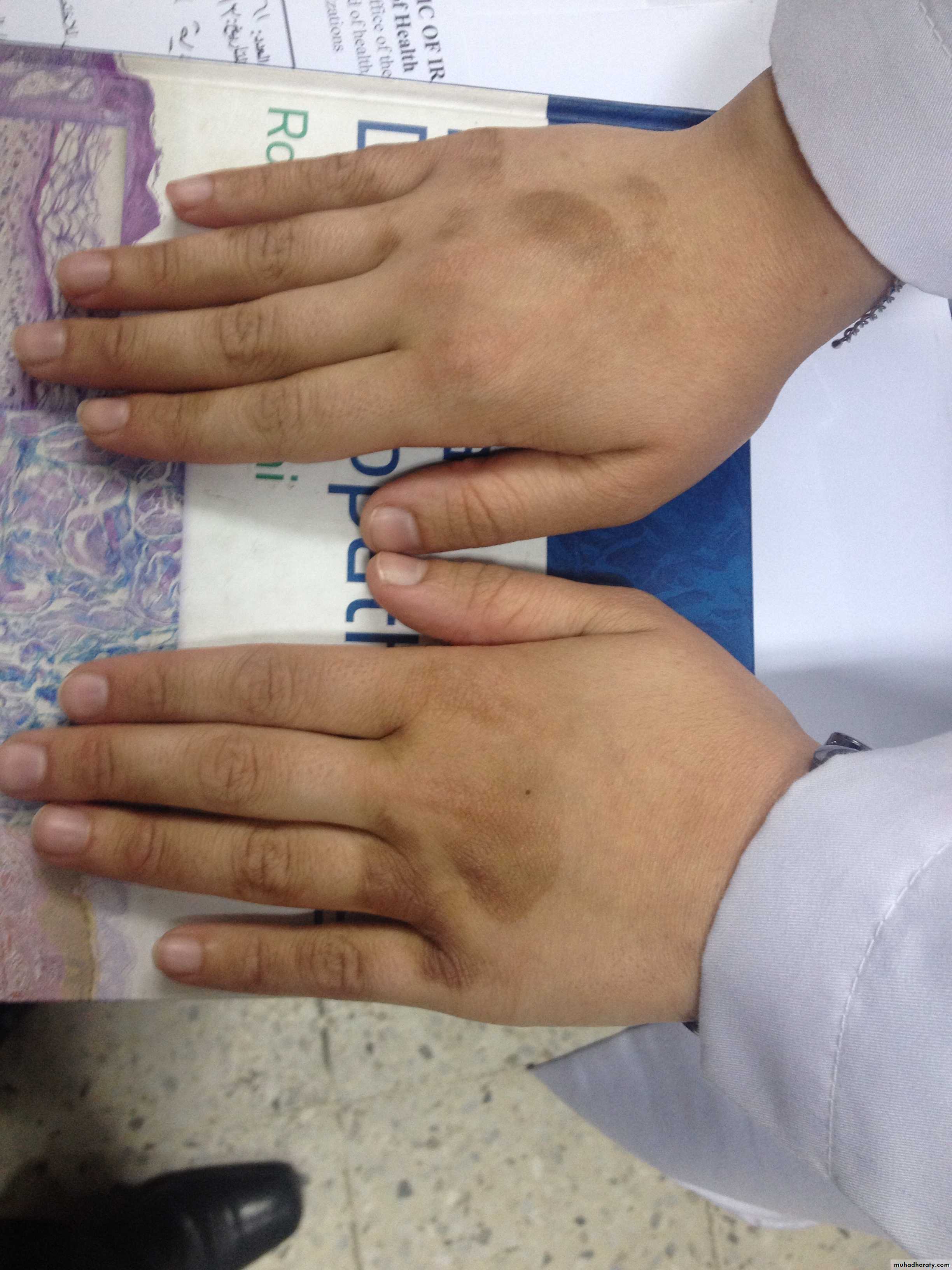
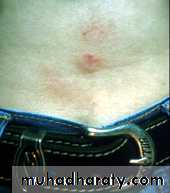
Nickel Allergy from Belt Buckle and Jewelry
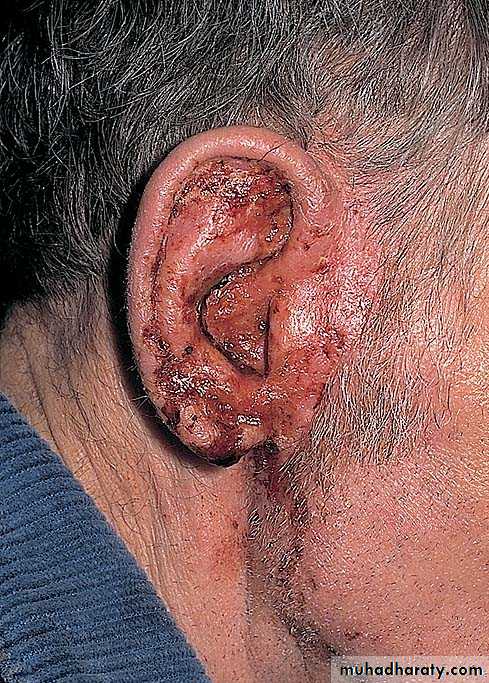
Tooth paste dermatitisEar drop dermatitis
Any question
summaryDifferent presentation of endogenous eczema
Exogenouse eczema with a define cause
Irritant and allergic types