first stage
اساسيات الطب د.هيثم بدر3/4/2015
Professionalism, Humanism& Medical Ethic
What is the thing that attracted you to this field?
What does medical professionalism mean to you?
❶ It is a vocation implies service to others❷ It has a distinctive knowledge base
❸ It determines its own standards and exams.
❹ It has a special relationship with patients.
❺ It has particular ethical principles
4 Hs
Head, Hand & Heart, where is the fourth H?
Professional statusIt has a cognitive base which includes definable attributes
It is the basis of medicine’s social contract with society
Both medicine and society have legitimate expectations- “each of the other”
Medicine’s obligations arise from societal expectations
There are consequences if these expectations are not met
Professional status
Professional Status is Not an Inherent RightIT IS GRANTED BY SOCIETY
Professional statmedicineus is important to
IT CONFERS
Prestige and Respect
Trust
Autonomy in Practice
Physician-Led Regulation
Financial Rewards
Professionalism is beneficial to society
Neither economic incentives,
nor technology,
nor administrative control has proved an effective surrogate for the commitment to integrity evoked in the ideal of professionalism
How we can define medical professionalism?
Constituting those attitudes and behaviors
That place
patient interest above physician Self-interest
Setting and maintaining
standard of competence, integrity, and provide expert advice on a matter of health
Main Characteristics of Professional Conduct (behavior)
(الامانة) ❶ Honesty
(الايثار) ❷ Altruism
(الخدمة) ❸ Service
(الالتزام) ❹ Commitment
(التواصل) ❺ Communication
(الالتزام بالبراعة)❻ Commitment to excellence
(المسؤلية) ❼ Accountability
The behavior of professionalism
“Keep it human.”
الطب مهنة انس×ــــــانية
Humanism Vs. ProfessionalismHumanism (Values)
– denotes an intrinsic set of deep-seated convictions about one’s obligations towards others
• Professionalism (Behaviors)
– Behaving in accordance to a set of normative values and expectations
Humanism Vs. Professionalism
Humanism
– Who you are (when no one is watching)
• Professionalism
– What you do (when every one is watching)
Doing
Professionalism
Professionalism
Experience
Knowledge
Feeling
Expectation
Assumption
Value
Attitude
Beliefs
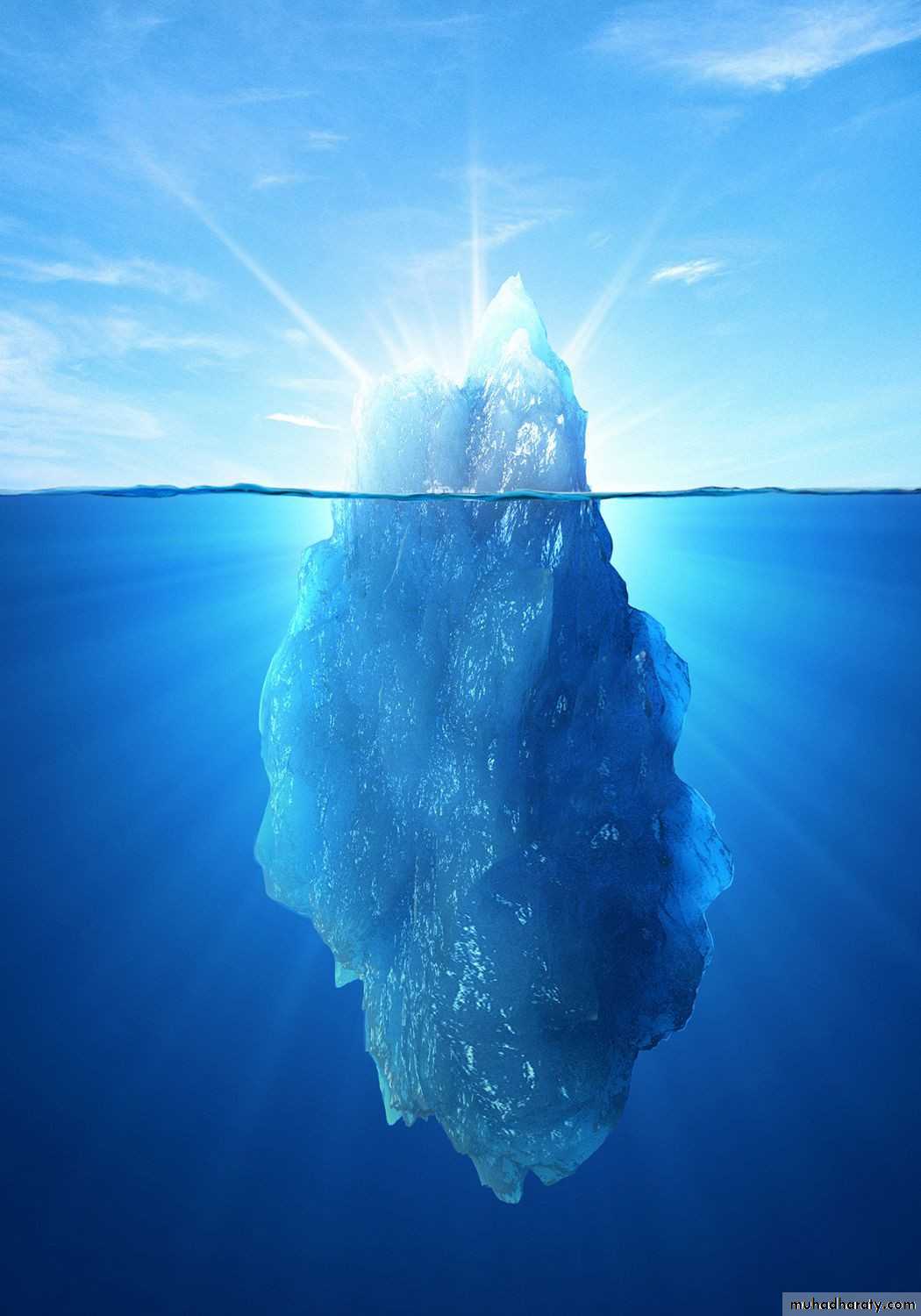
Humanism
Humanism
Iceberg
How can be taught or learned professionalism❶ Role modeling
❷ Role Plays
❸ Simulated Patients
❹ Small group discussions
How can be taught or learned professionalism
How can professionalism be assessed
The assessment of clinical skills/competence/performance
Performance or hands on assessment
Does
Shows howKnows how
Written, Oral or
Computer based assessment Knows....................................................................................................................
The moral duties of doctors
The duty to help, cure
The duty to promote and protect the patient’s health
The duty to confidentiality
The duty to protect the patient’s life
The duty to respect the patient’s autonomy
The duty to protect privacy
The duty to respect the patient’s dignity
The moral rights of the patients
The right to high quality medical service
The right to autonomous choice
The right to decide
The right to be informed
The right to privacy
The right to health education
The right to dignity
Primum non nocere
First, do no harm
Always remember 1st Hippocrates law
Thank you for your nice listening
Edited by / Mohammed J AlRawi
Telegram/first stage of medicineAll the lectures/www.muhadaraty.com