

Contain of the same competent
found in connective tissues, but
there are fewer cells and ground
substance.
Dense connective tissue can be
classified according to the
arrangement of fibers into
:

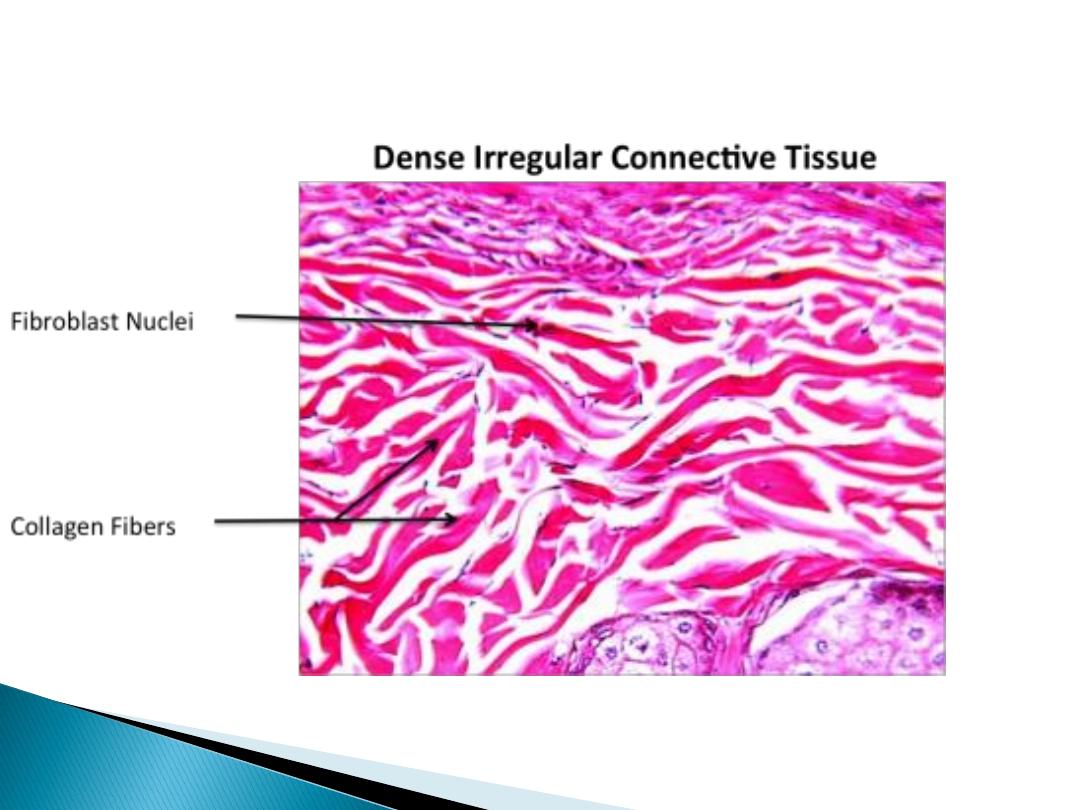
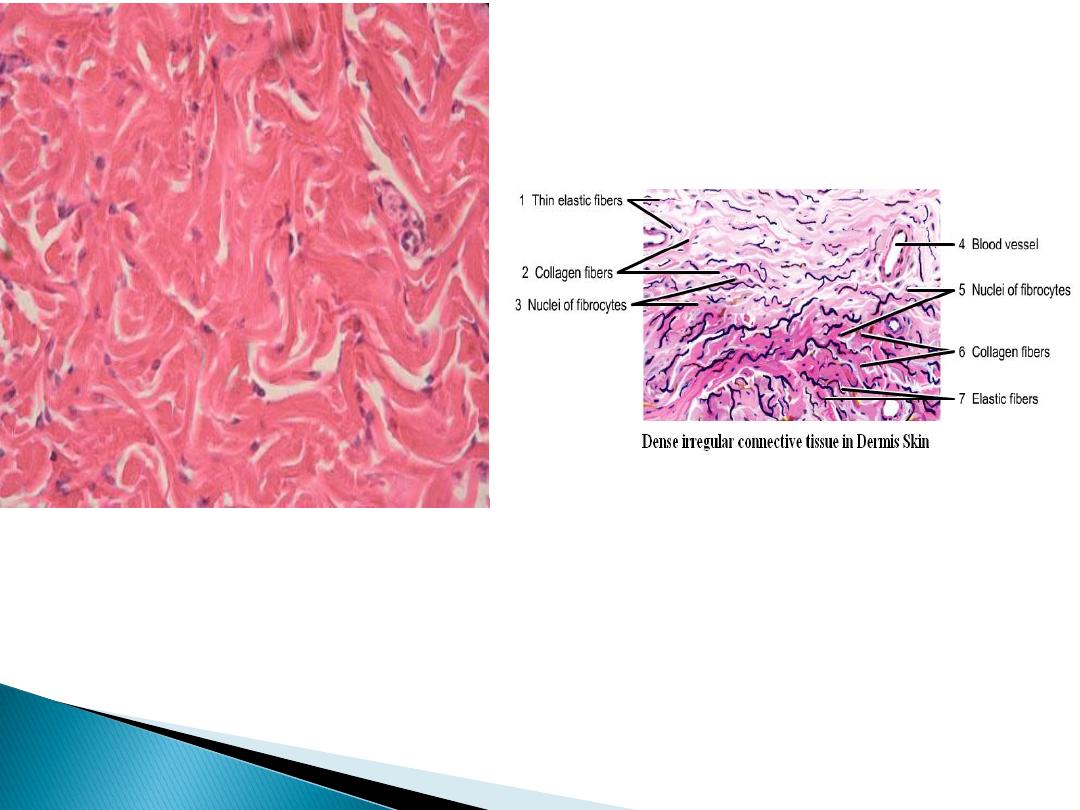
Irregular connective tissue
In this section the collagen fibers are arrange in
bundle, and form three dimensional network to
provide resistance to stress from all directions, it
can be seen in the dermis of skin.
Regular connective tissue
In this section the collagen fibers are arranges in
regular bundles, it's resistant to tension from one
direction, it can be classified according to the
type of fibers to:
Irregular dense con. t.
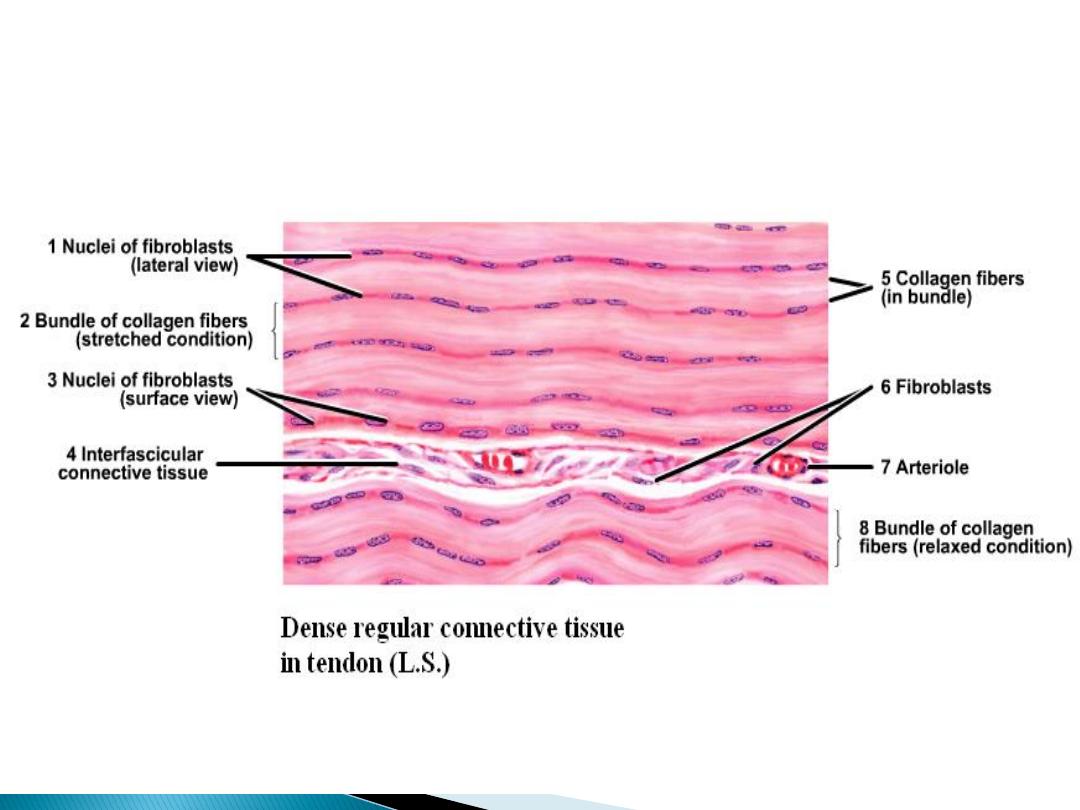
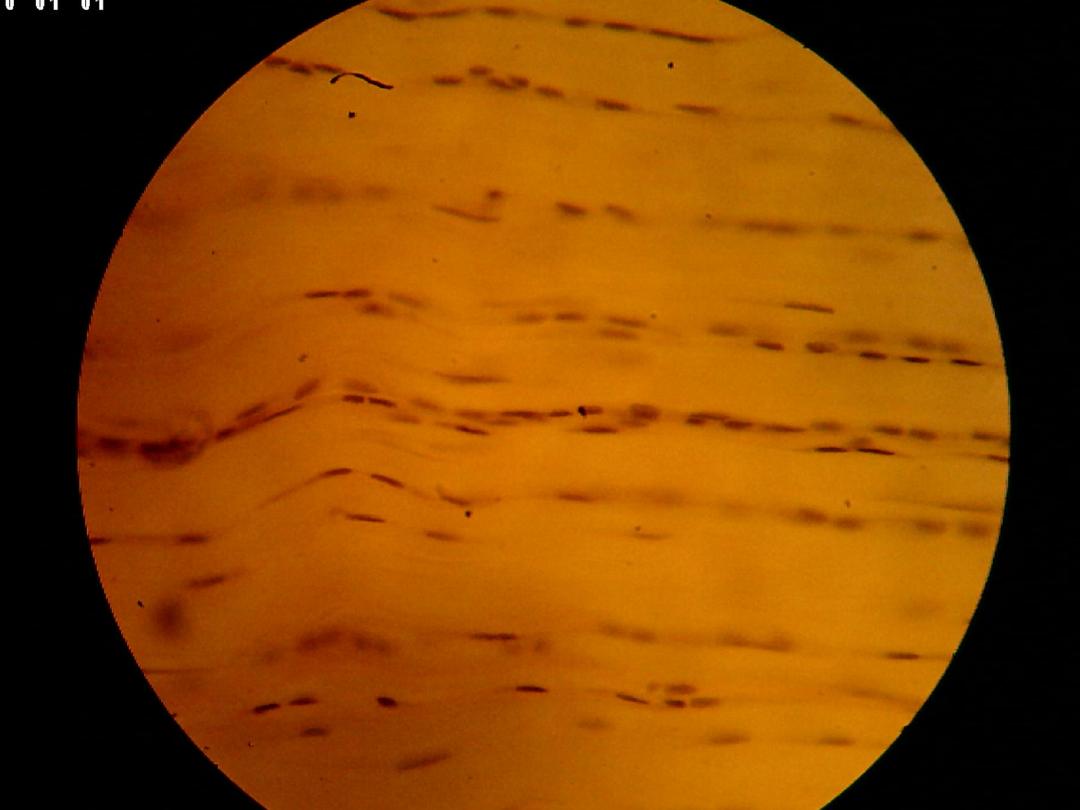
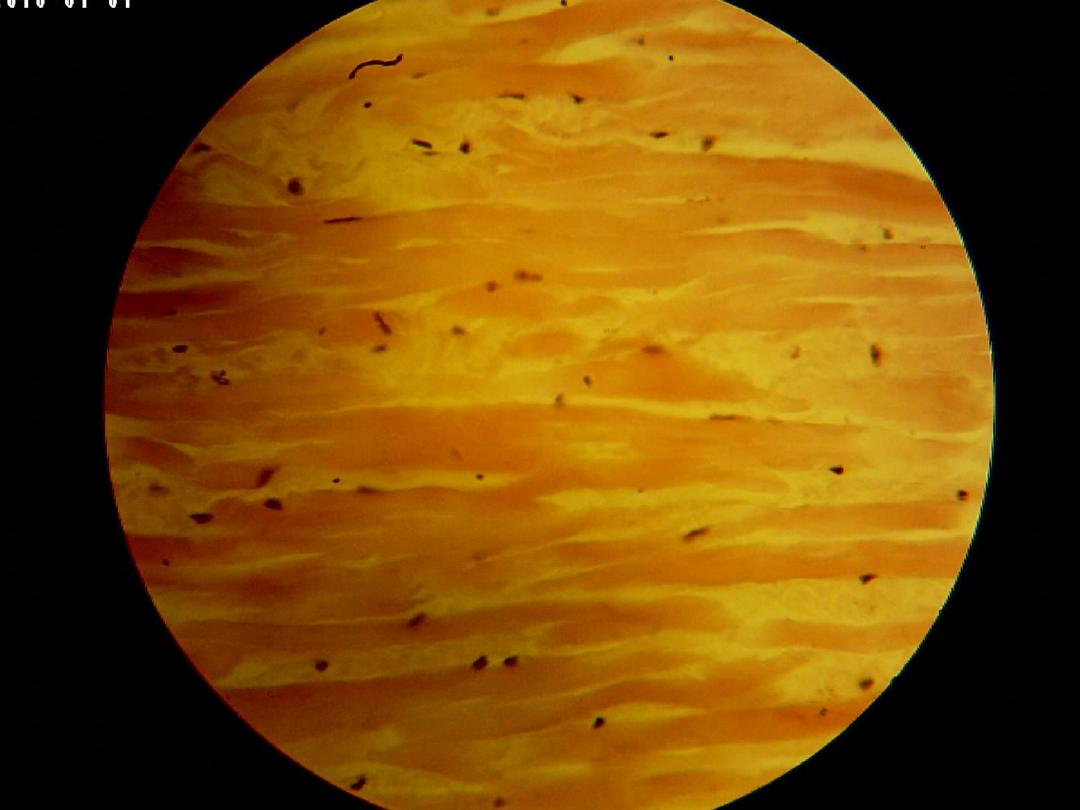
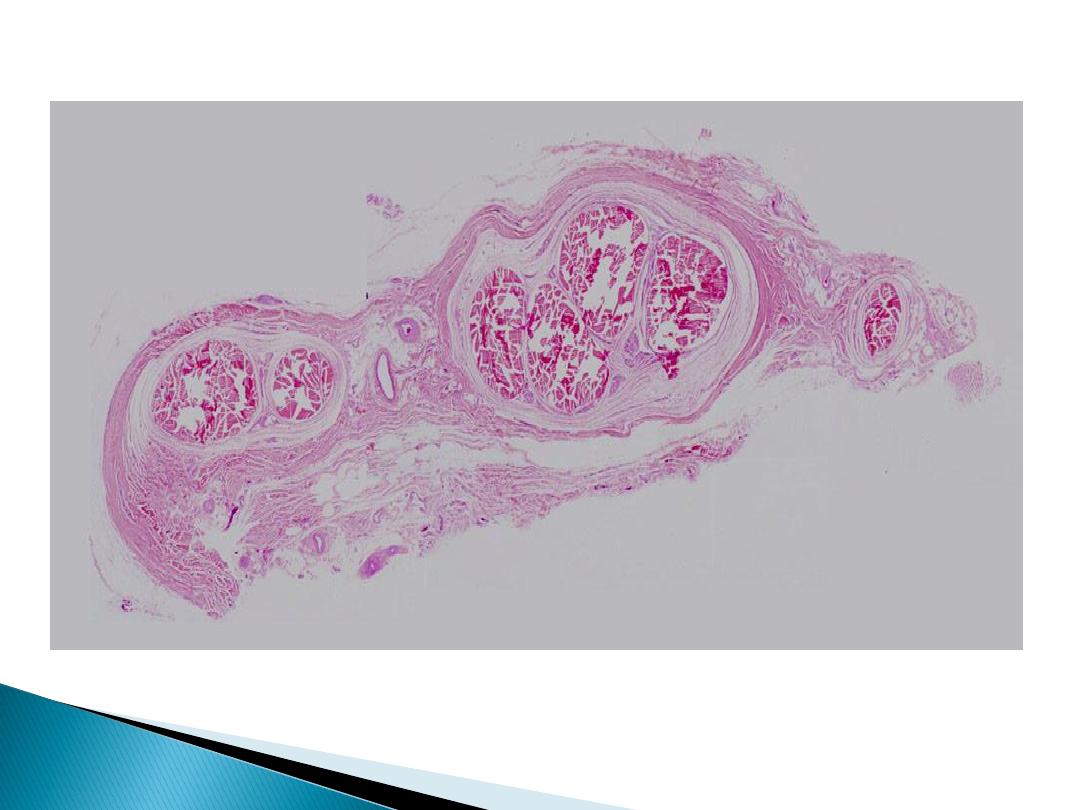
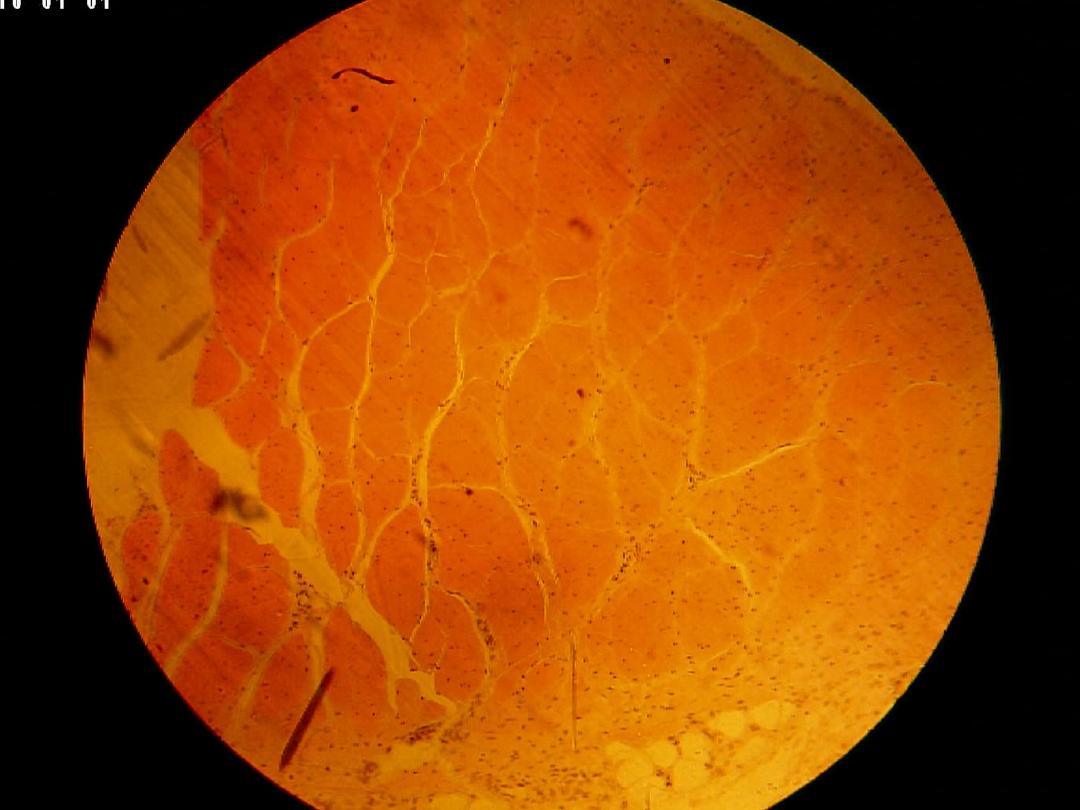
C .S in Tendon (low magnification)
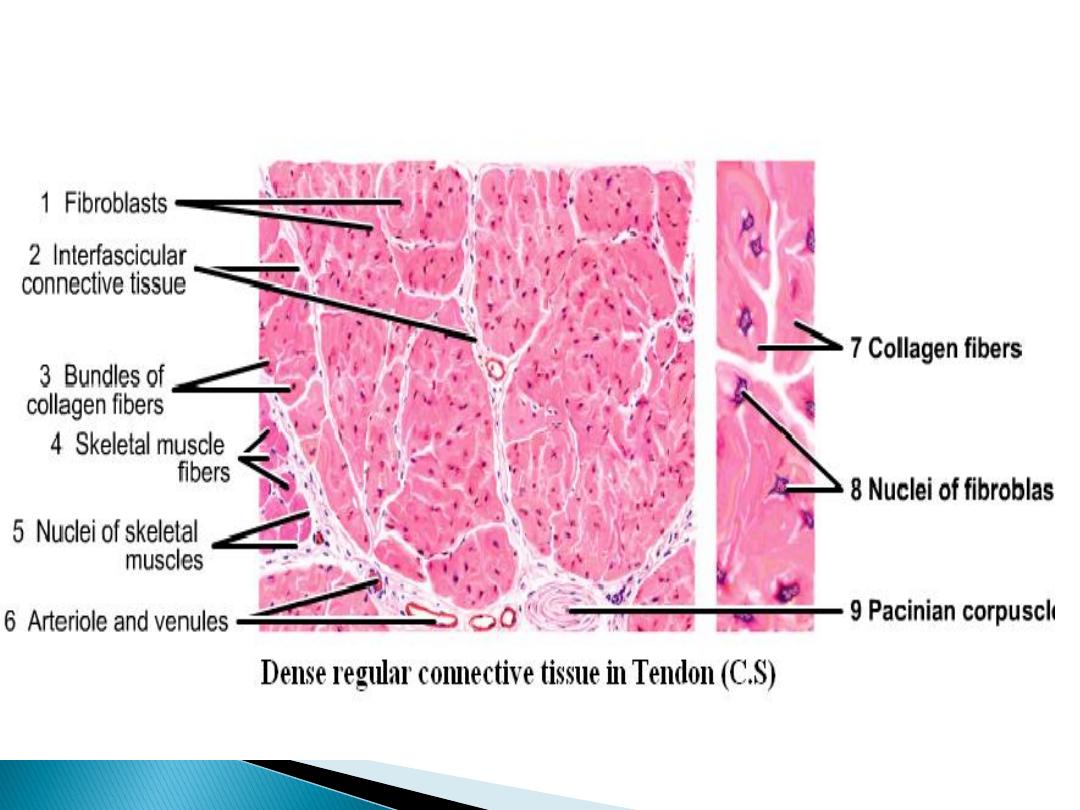
White fibrous connective tissue
Tendons are the most common of the white
fibrous. They have parallel, and closely packed
bundles of collagens (the primary bundles)
separated by small amount of ground substance.
Their fibroblast called tendon cell, contain
elongated nuclei parallel of fibers.
Tendon is surrounded by a sheath of dense con.t.
Called epitendineum, while secondary bundles
covered with peritendineum, and the primary
bundles covered with endotendineum.

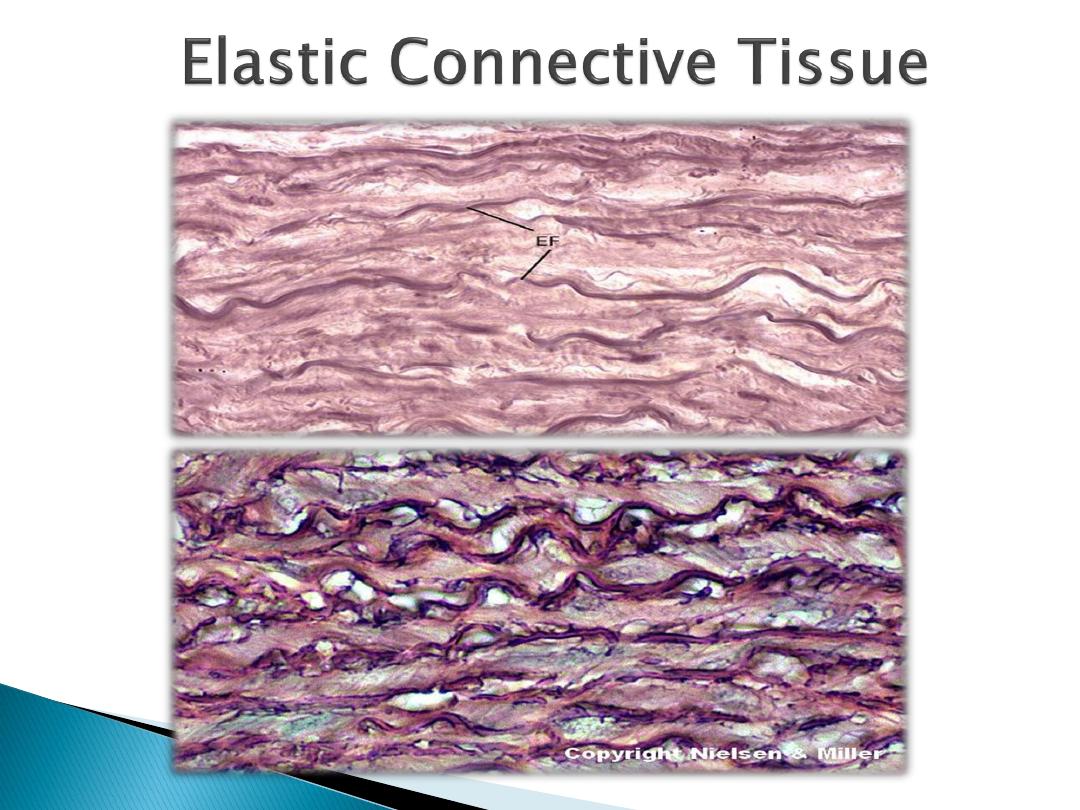
Elastic connective tissue
Is composing of bundles of thick, and parallel
elastic fibers. The space between these fibers
is occupied by thin collagen fibers and
flattened fibroblast. It's called elastic because
it's yellow color and great elastic. It's present
in ligaments of vertebral.

Skeletal con.t.
Cartilage: - consists of cells called
chondrocytes and ground substance contain
chondroitin sulfates.
There are three kinds of cartilage:
Hyaline cartilage
Elastic cartilage
White fibro cartilage

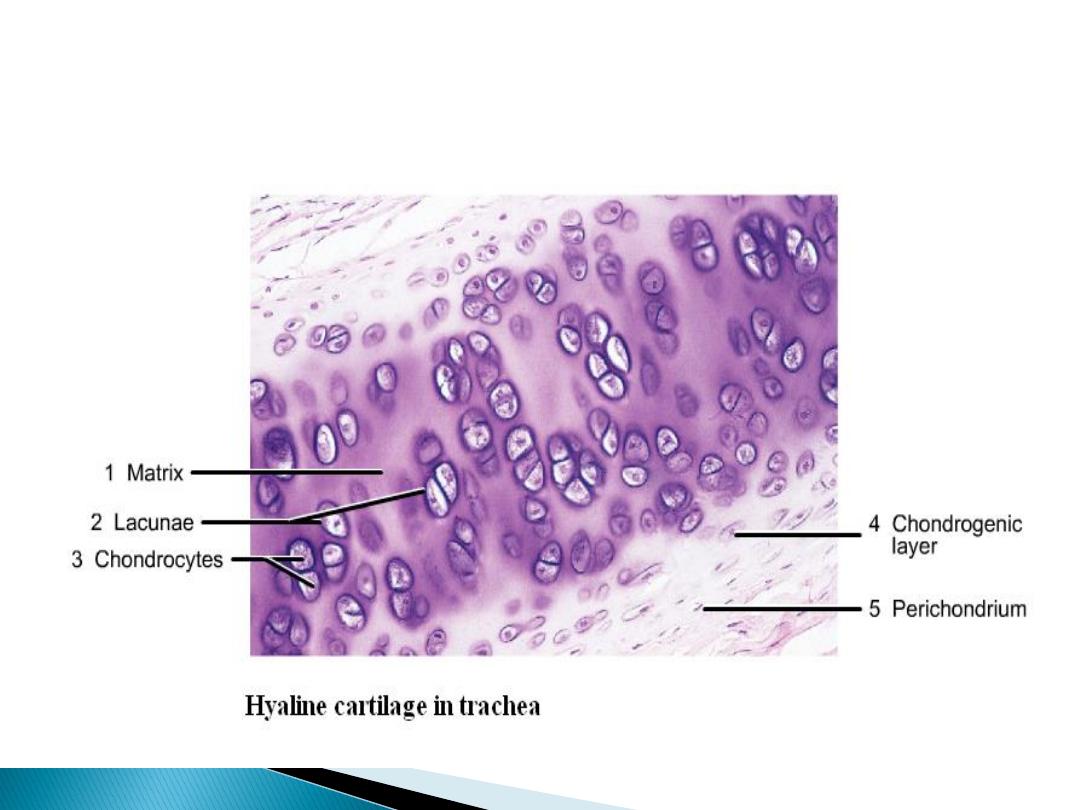
Hyaline cartilage:-
It’s present in the cartilage of nose larynx,
trachea and bronchi also in vertebral ends of rib
Chondrocyte is single or aggregate as groups
called cell nest, it's surrounded with capsule and
it's found with lacuna in ground substance.
Ground substance appears as hyaline (glass) and
contains fewer amounts of white fibers so it is
called hyaline cartilage.
It's surrounded with perichondrium which consist
of two layers to protect and repair the cartilage.
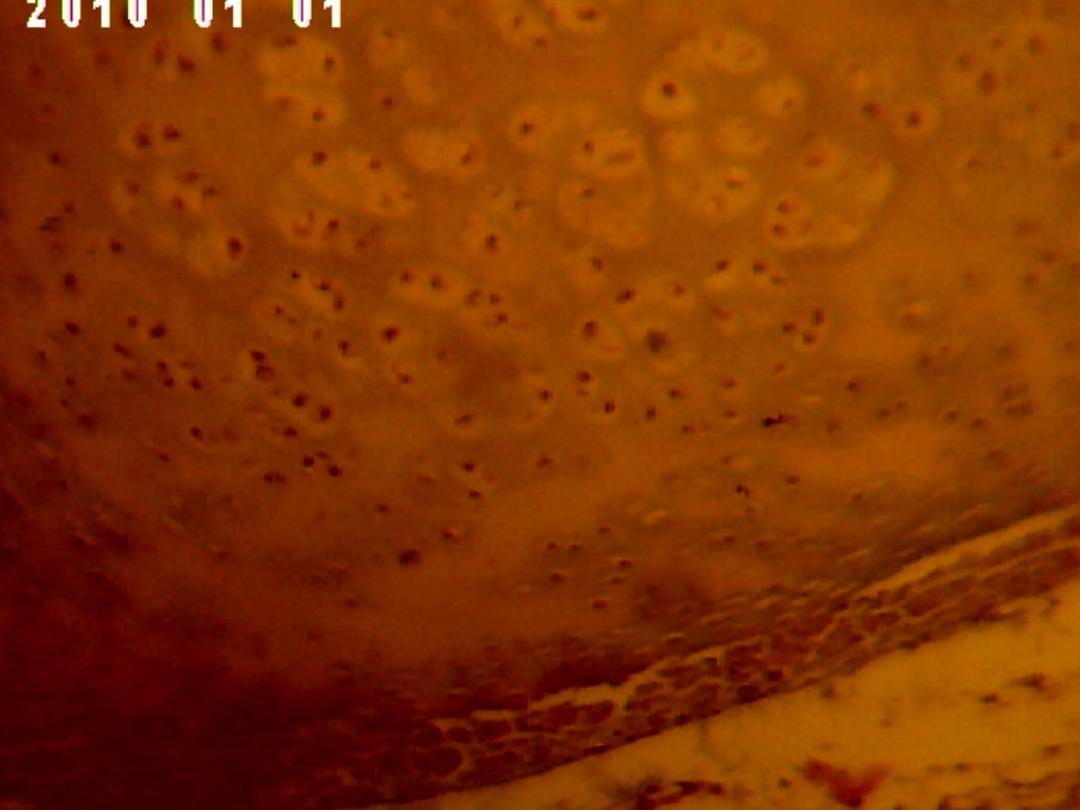

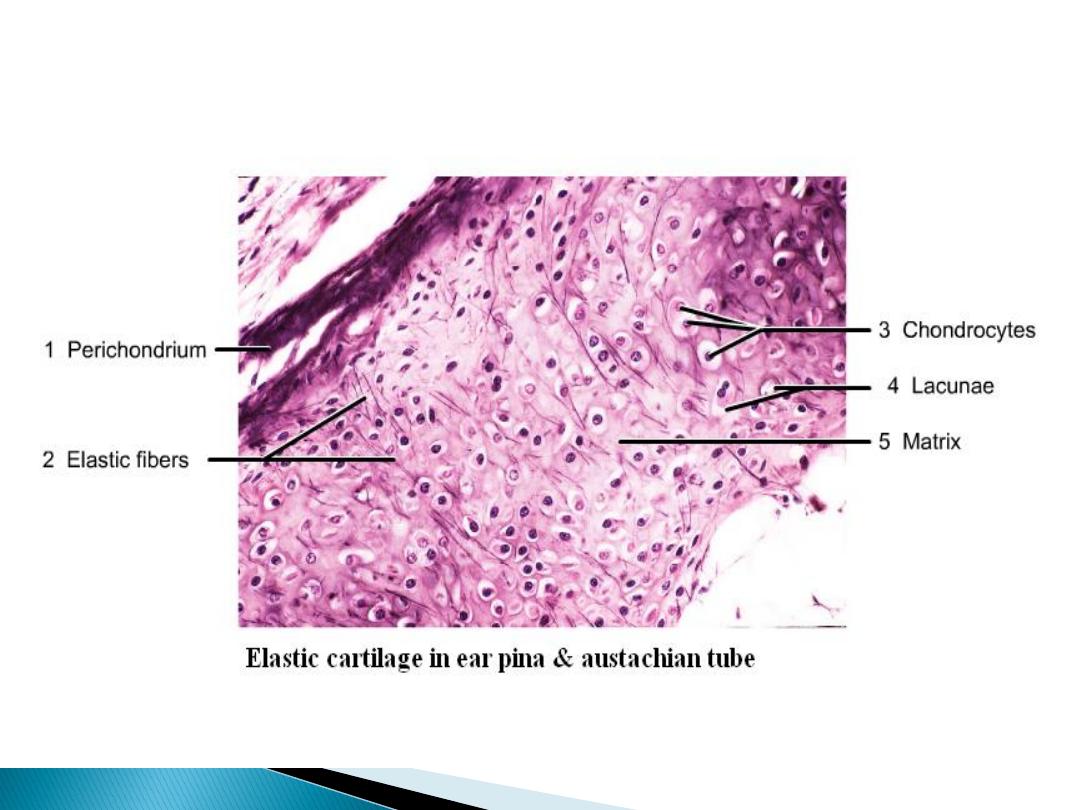
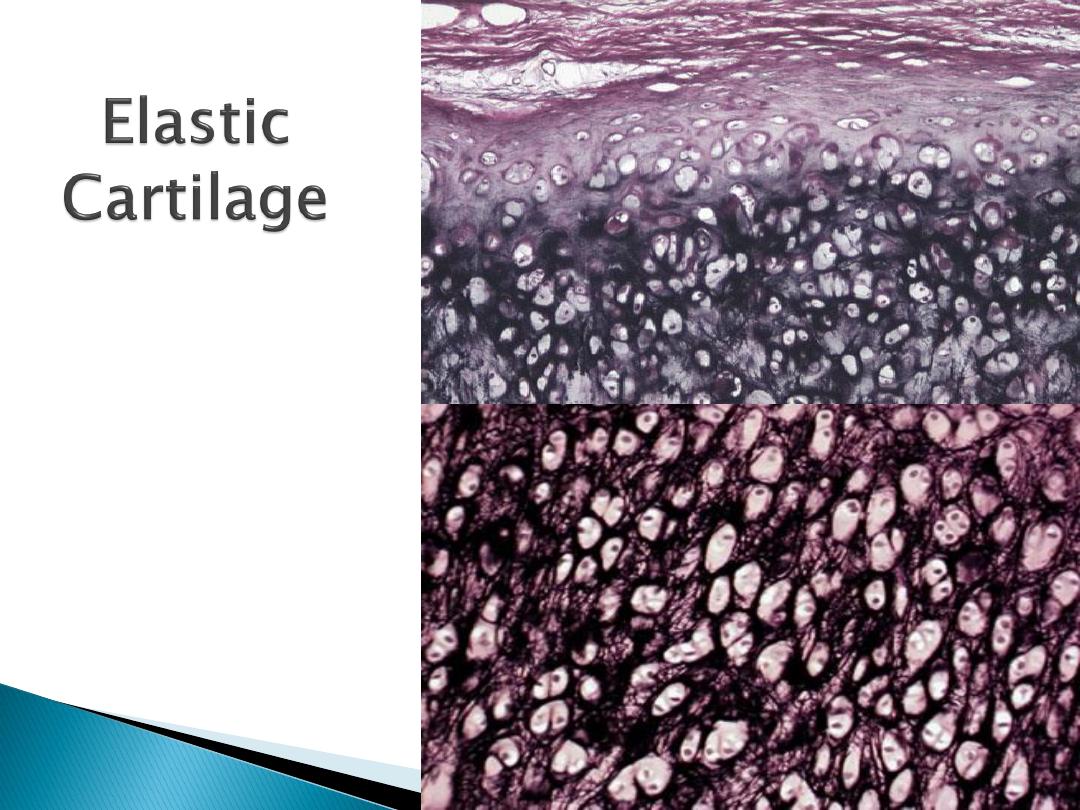
Elastic cartilage:-
It's present in auricle of the ear and Eustachian tube.
It's identical to hyaline cartilage except it contains
bundles of elastic fiber.
Its surrounded with perichondrium
White cartilage:-
Its found in intervertebral disc
Ground substance contains bundles of white fibers in
parallel arrangement.
It's never present in alone but associated with hyaline
cartilage or dense fibrous tissue, because, it lack
perichondrium
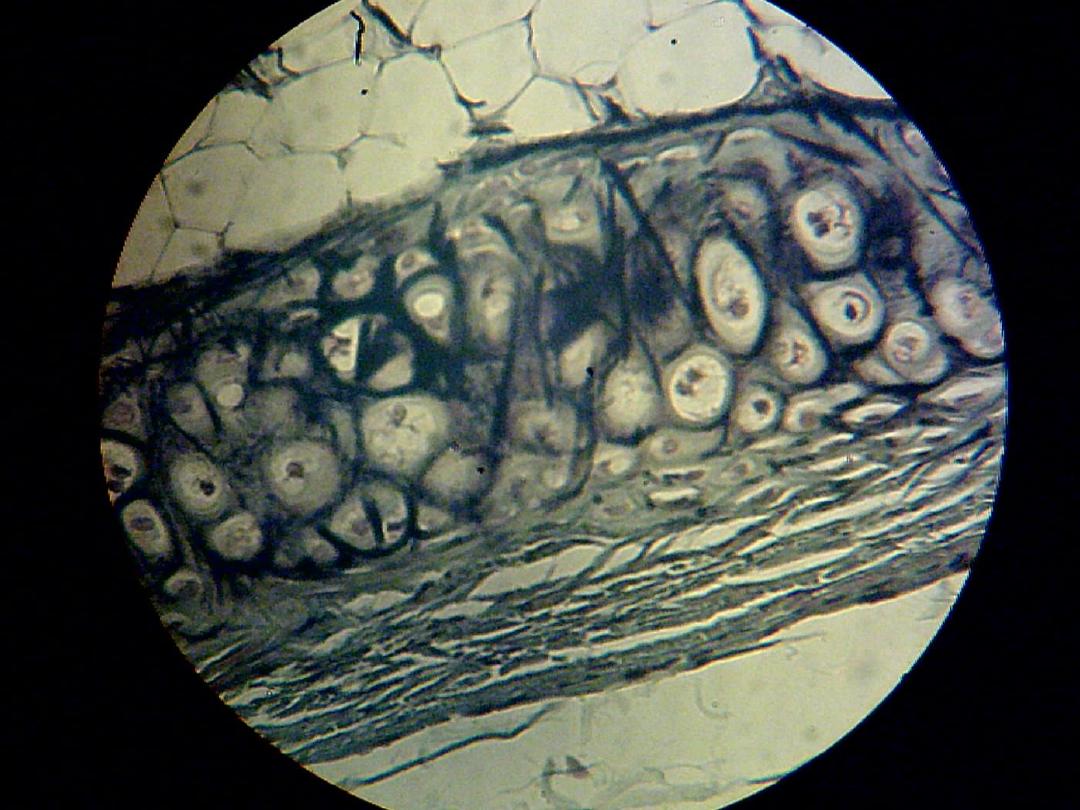
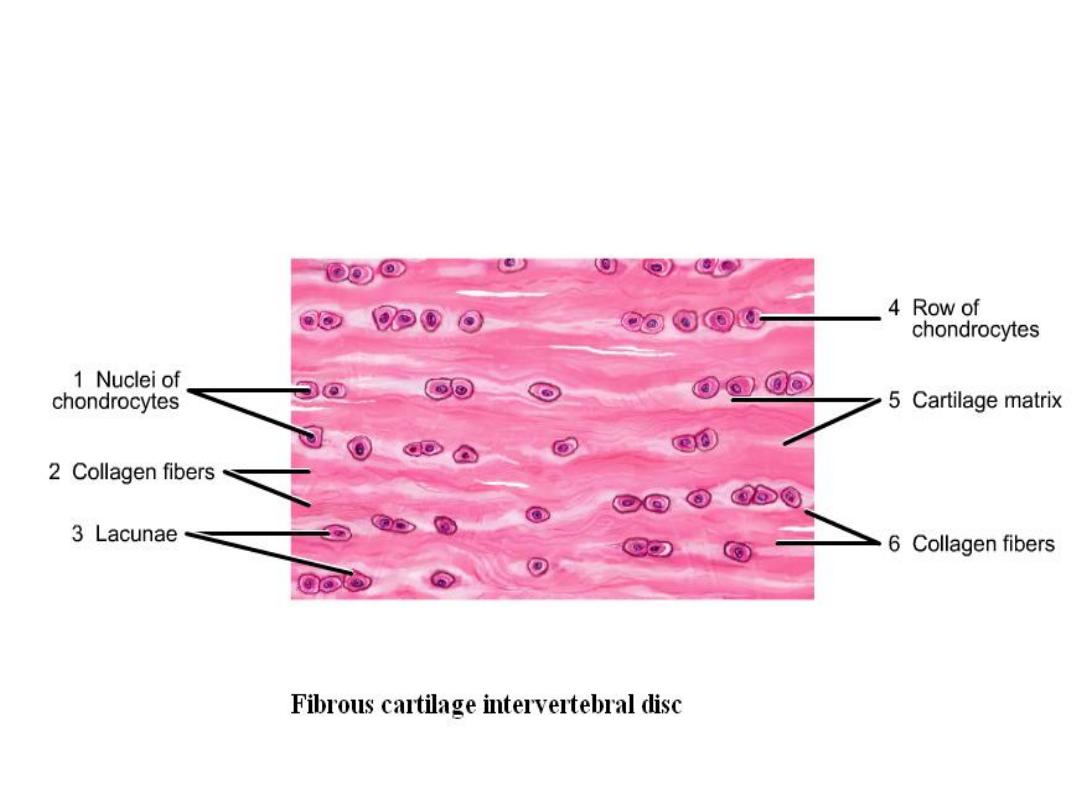
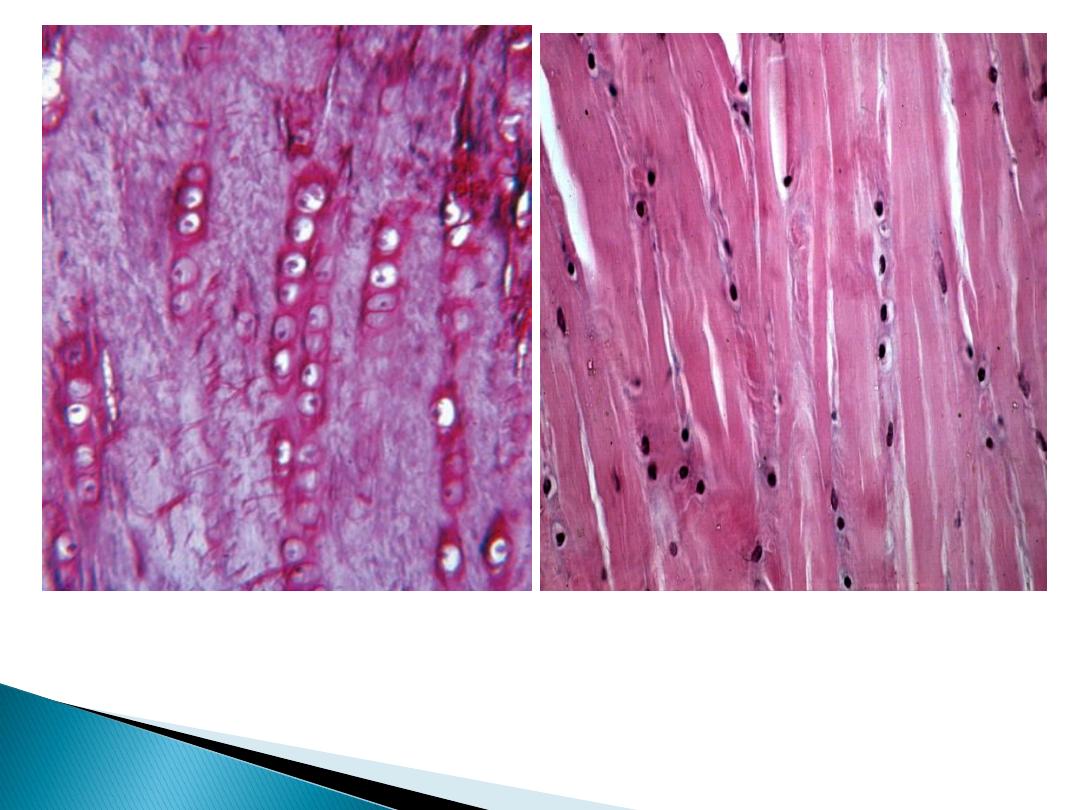
Fibrocartilage

Bone: - is a specialized connective tissue
composed of intercellular calcified material
(bone matrix) and three types of cells:
osteocyte, which found in lacunae within the
matrix; osteoblast, which is multinucleated
giant cell in the matrix called Howship's
lacunae.

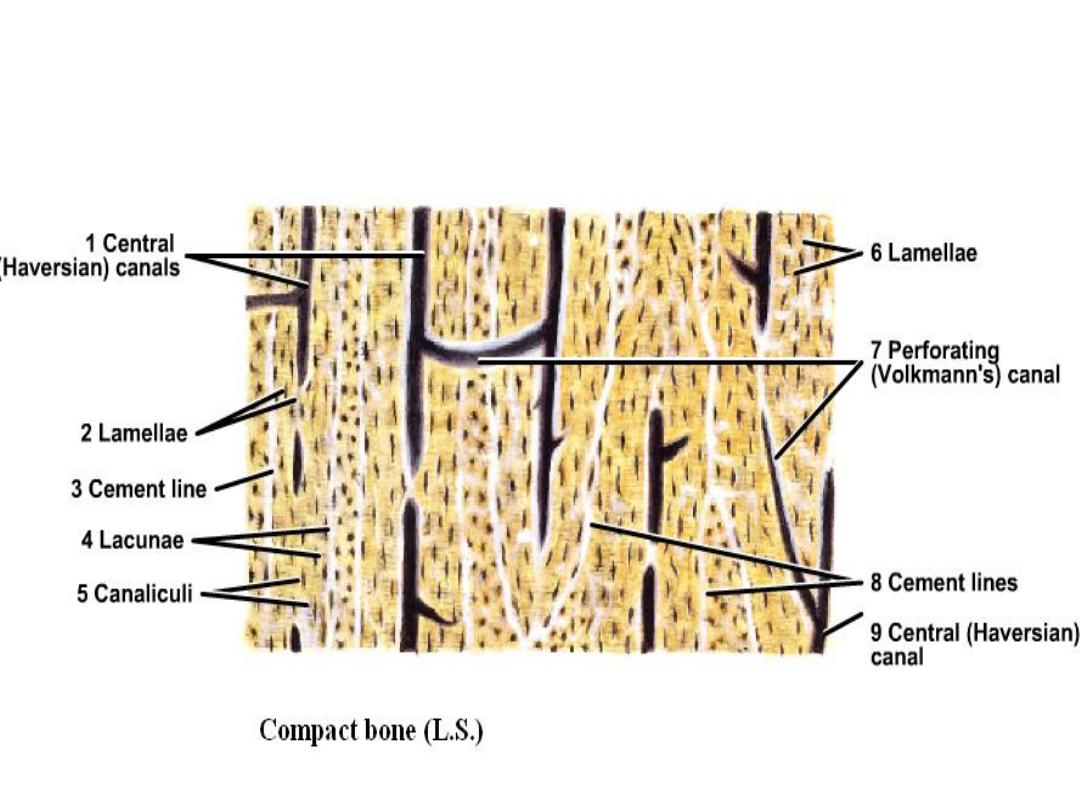
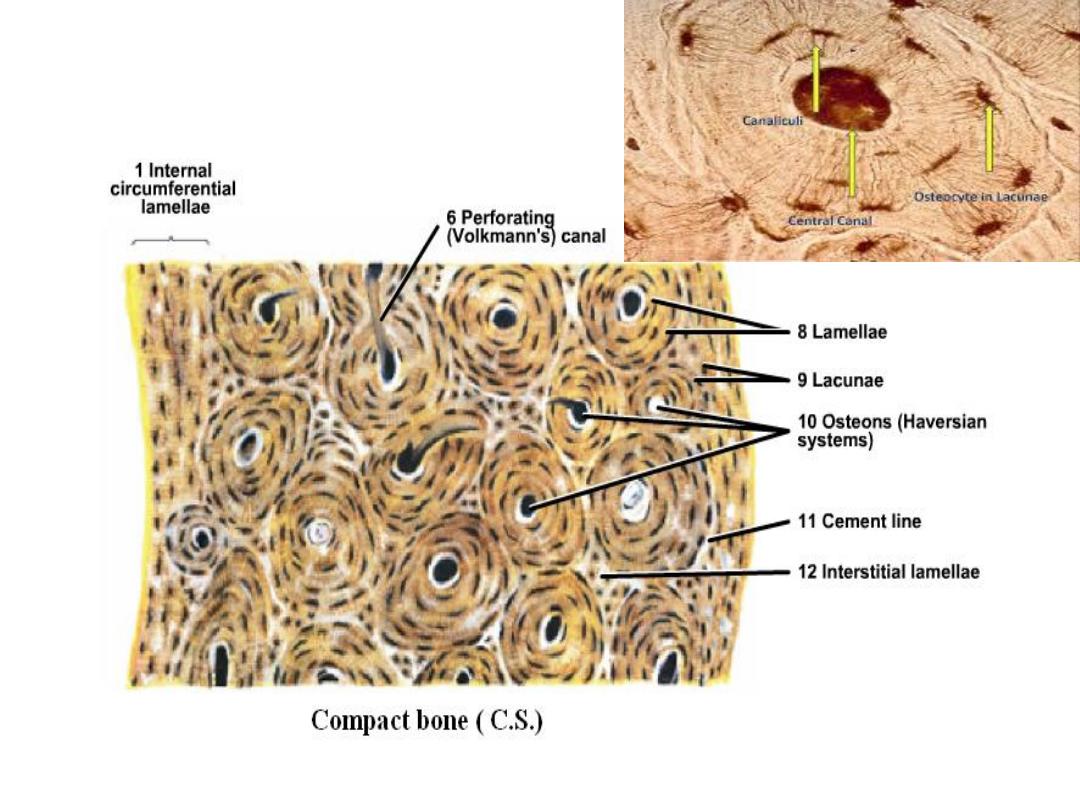
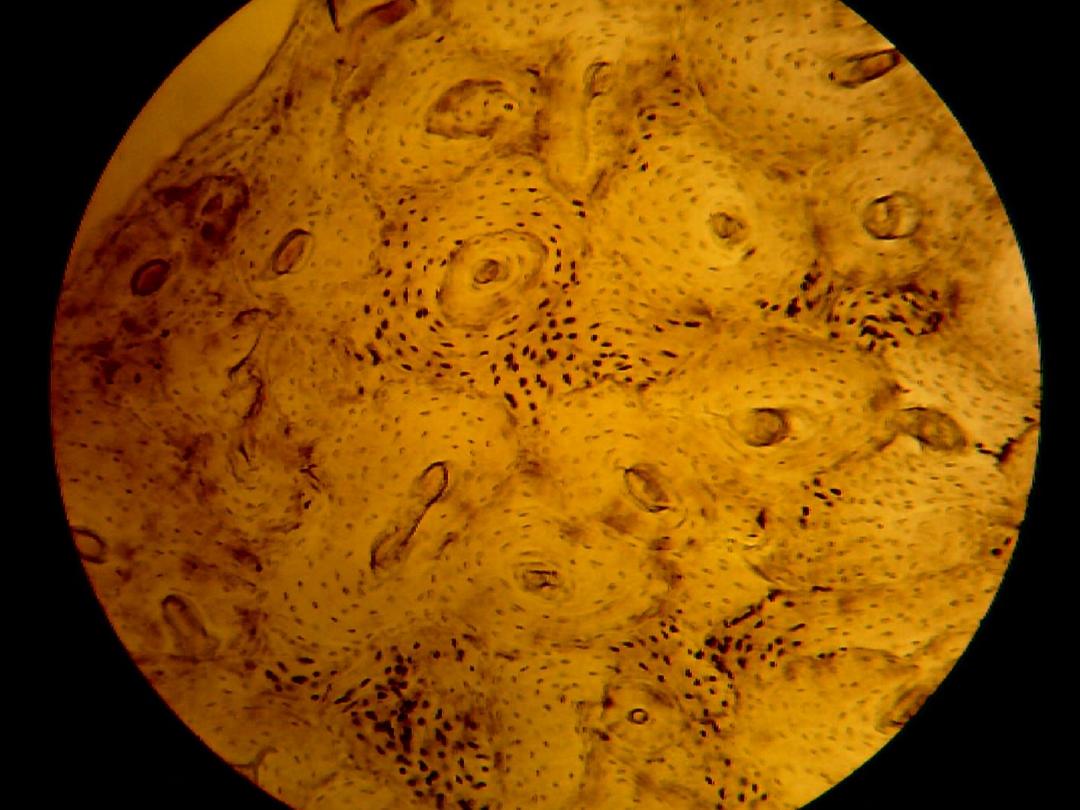
Compact bone
Its shown in long bone diaphysis, in this
section, lamellae is regularly arranged around
Haversian's canal and determined by blood
vessels and nerves, this complex system
called Haversian's system. Haversian's canal
connects with others by Volkmann's canal,
and between Haversian system there are
interstitial lamellae.

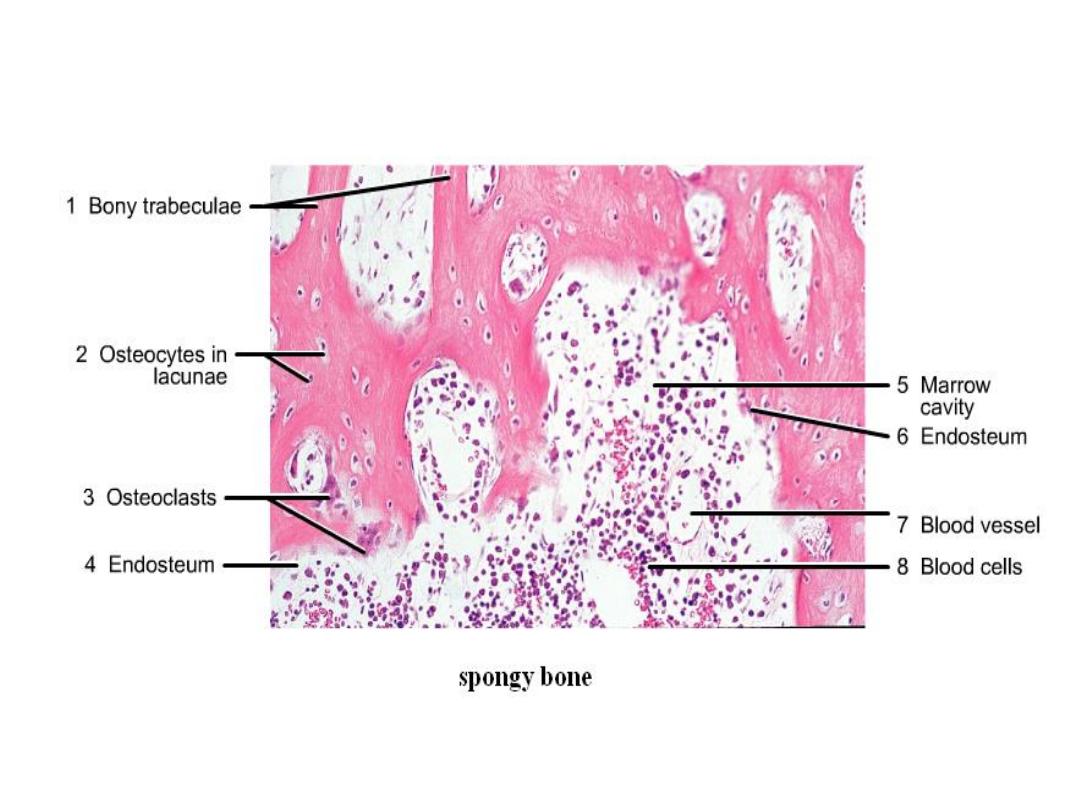
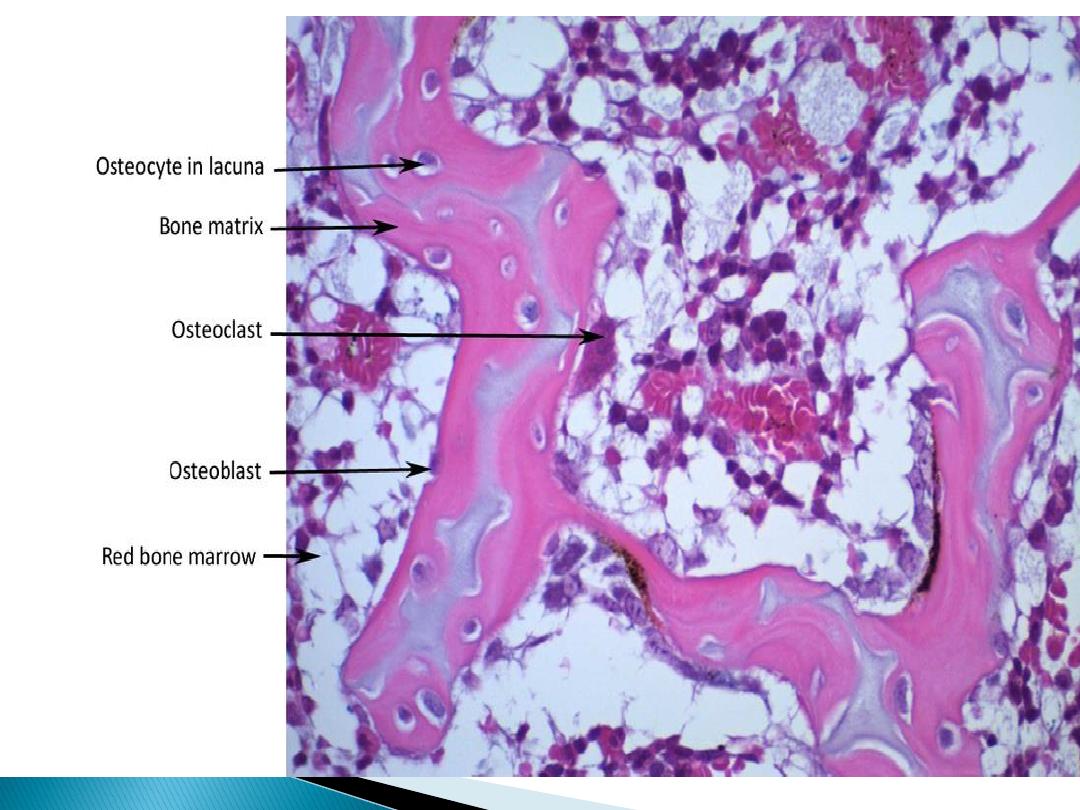
Spongy bone
It's found in bulbous ends of long bones
called epiphysis. Bone matrix appears as
irregular trabeculae spongy, there is cavities
between these trabeculae contain red bone
marrow and three kinds of cells: osteocyte,
osteoblast, and osteoclast.
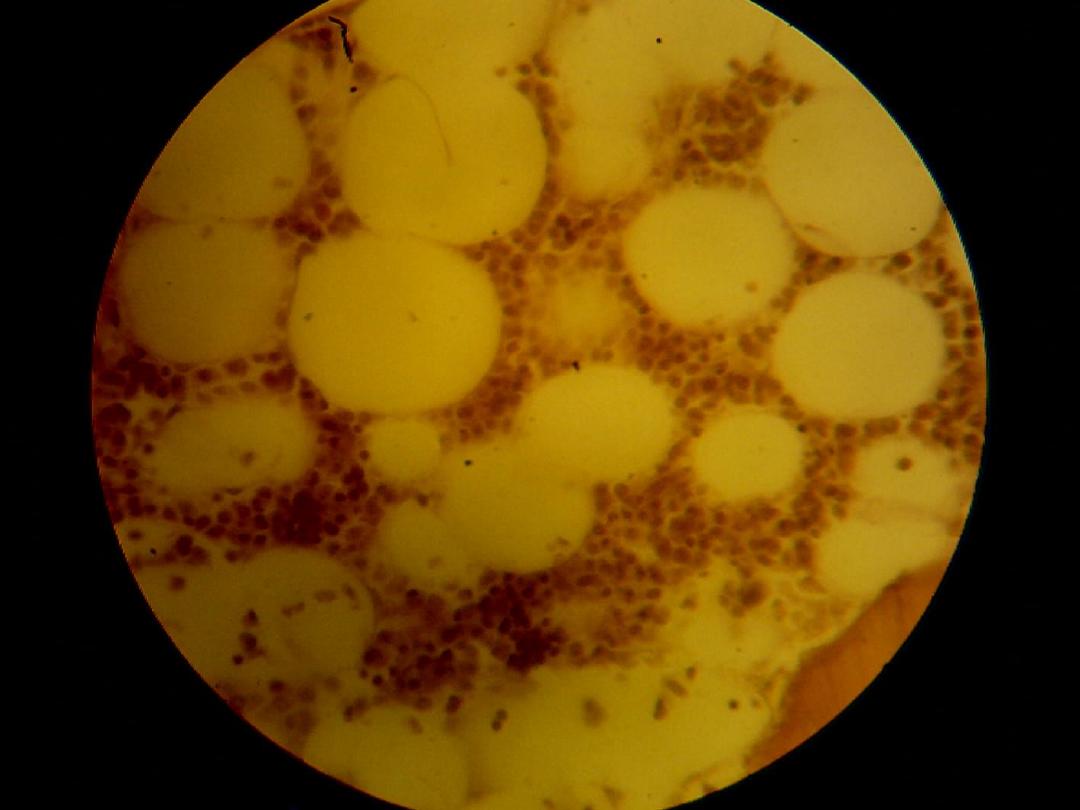
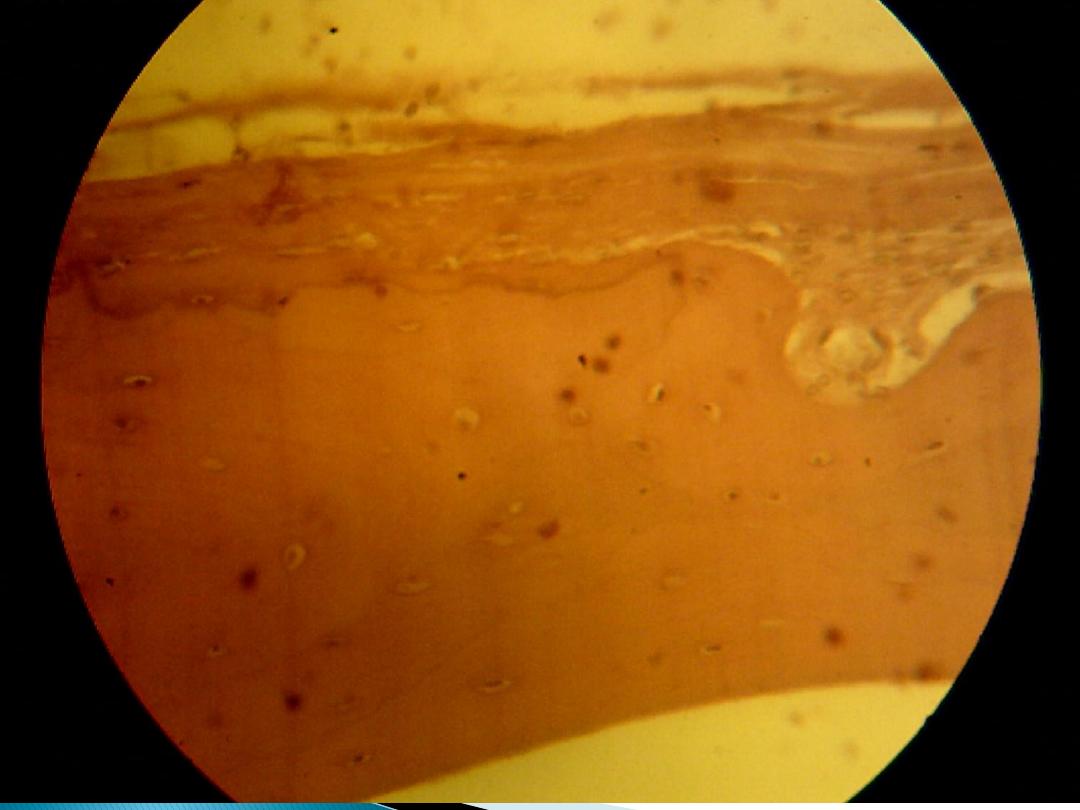

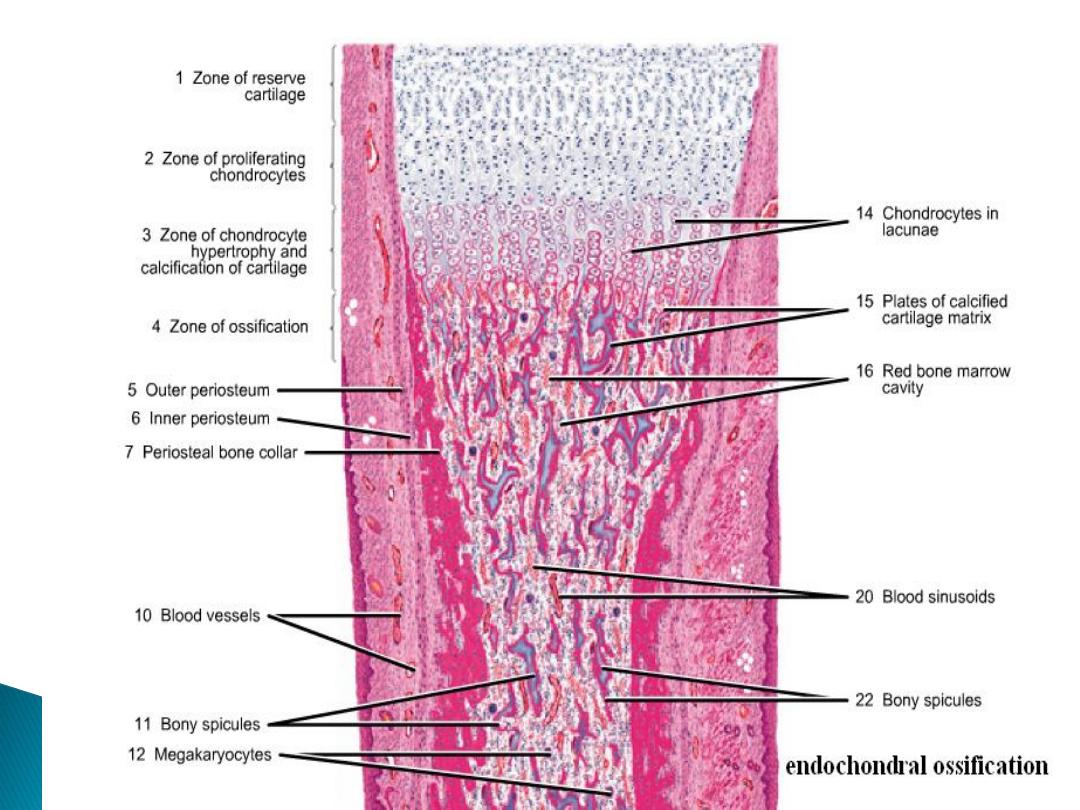
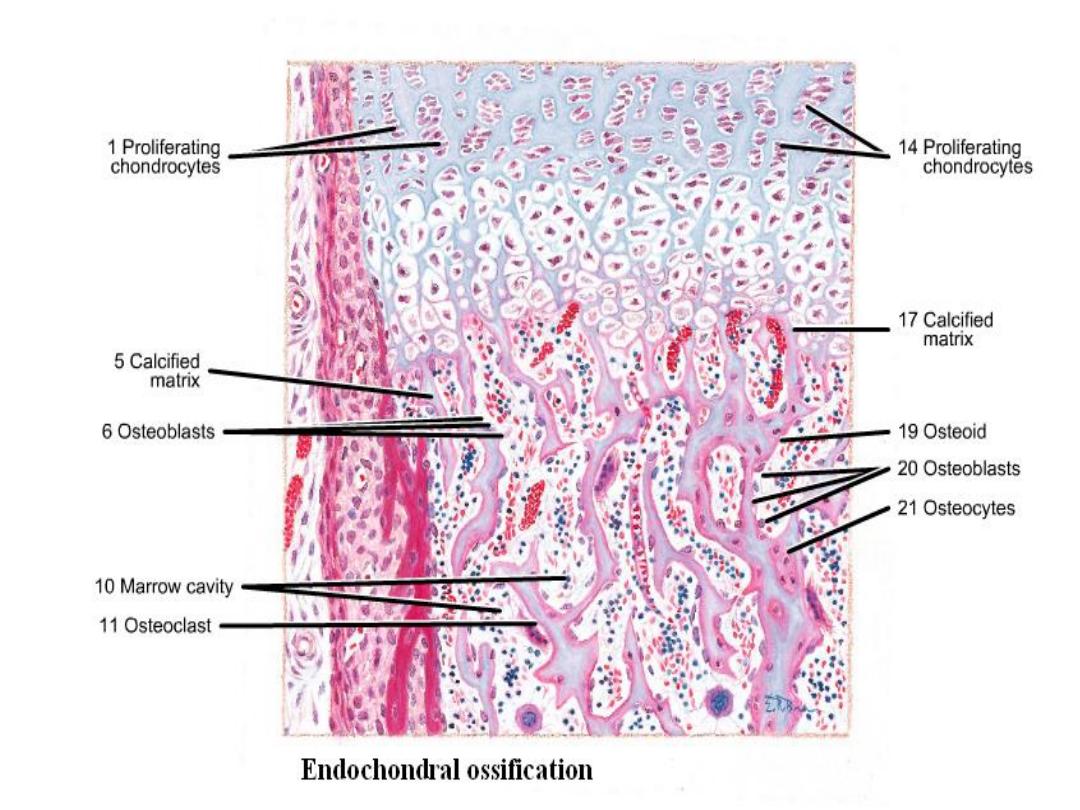
Endochondral ossification:
This type of ossification is responsible for formation of short and long bone:-
Reserve zone: compose of hyaline cartilage, its present nearest to the end of bone.
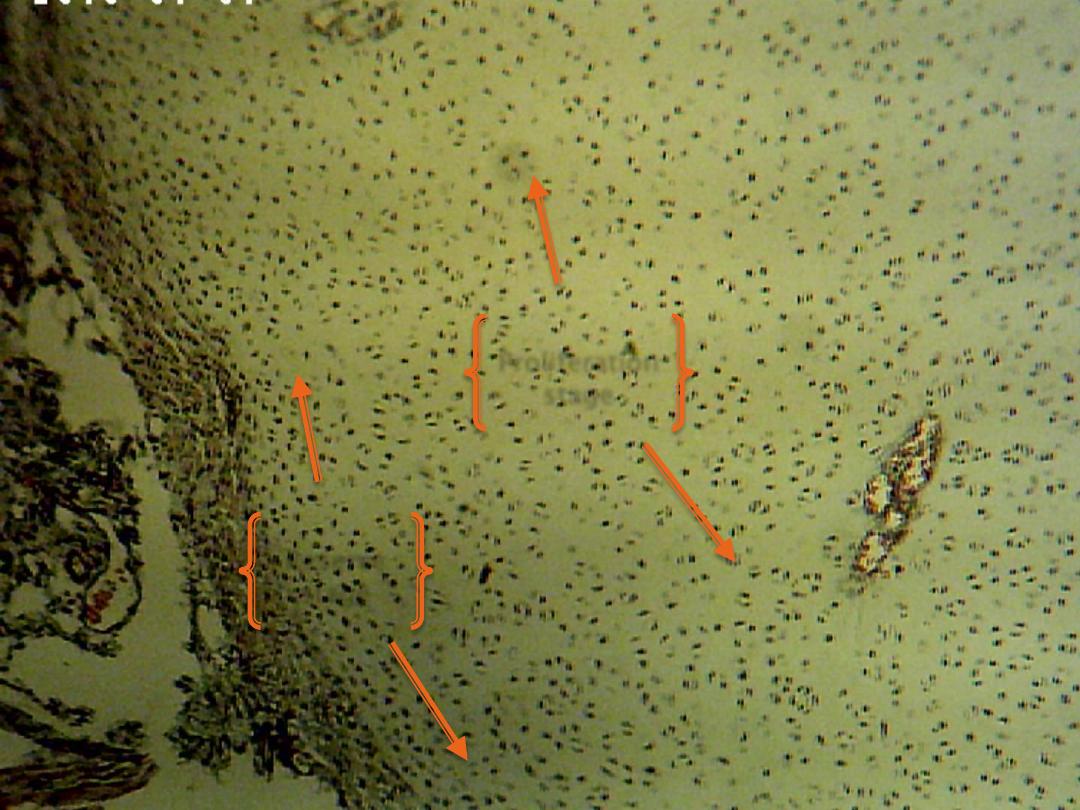
Zone of proliferation: is an active zone showing numerous mitosis, each row
consist of a numbers of flat cells separated by little matrix.
Zone of maturation: mitosis no longer, the cells and lacunae enlarge becoming
cubical in shape.
Zone of calcification: the matrix surrounded the enlarged lacunae and deposition
of mineral within it.
Zone of retrogression (erosion): the cartilage cells die and undergo dissolution;
there are thicker plates of matrix between rows of cells.
Zone of ossification: osteoblasts differentiate from mesenchymal cells of the
marrow tissue.
Zone of resorption: in this zone, the marrow cavity increases in size, owing to
resorption of bone in the center of diaphysis.
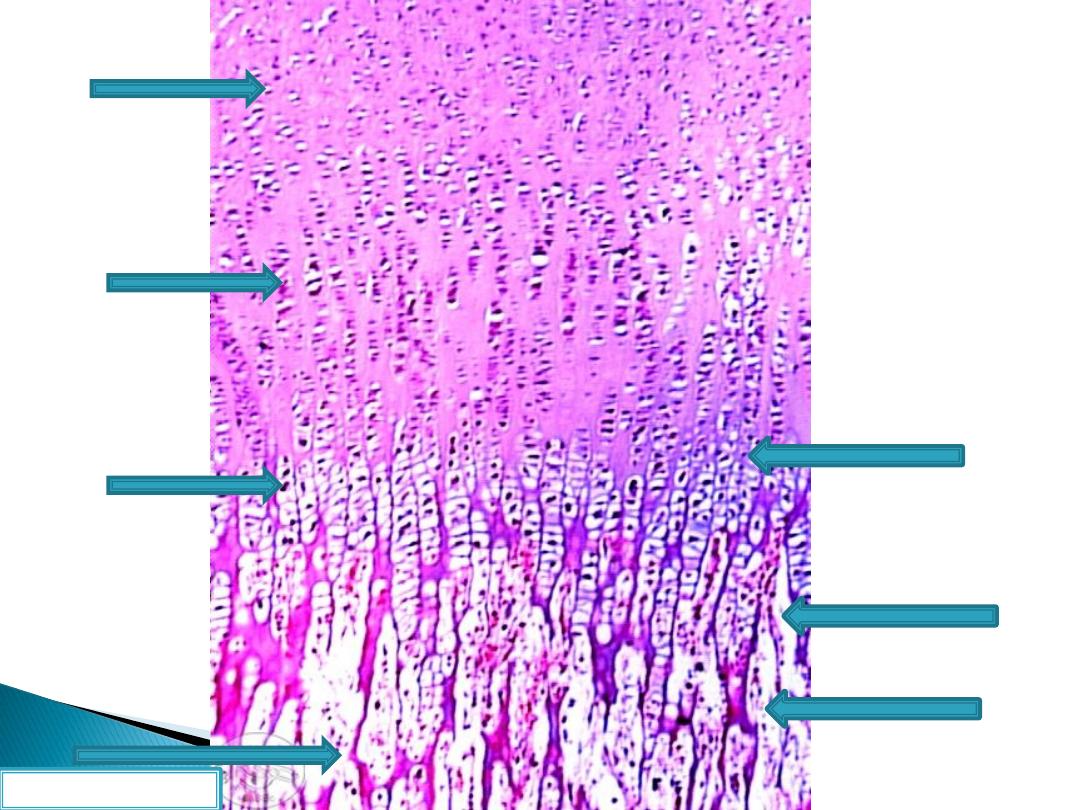
Reserve zone
Proliferation zone
Maturation zone
Calcification zone
Erosion zone
Ossification zone
Resorption zone
Reserve
stage
Proliferation
stage
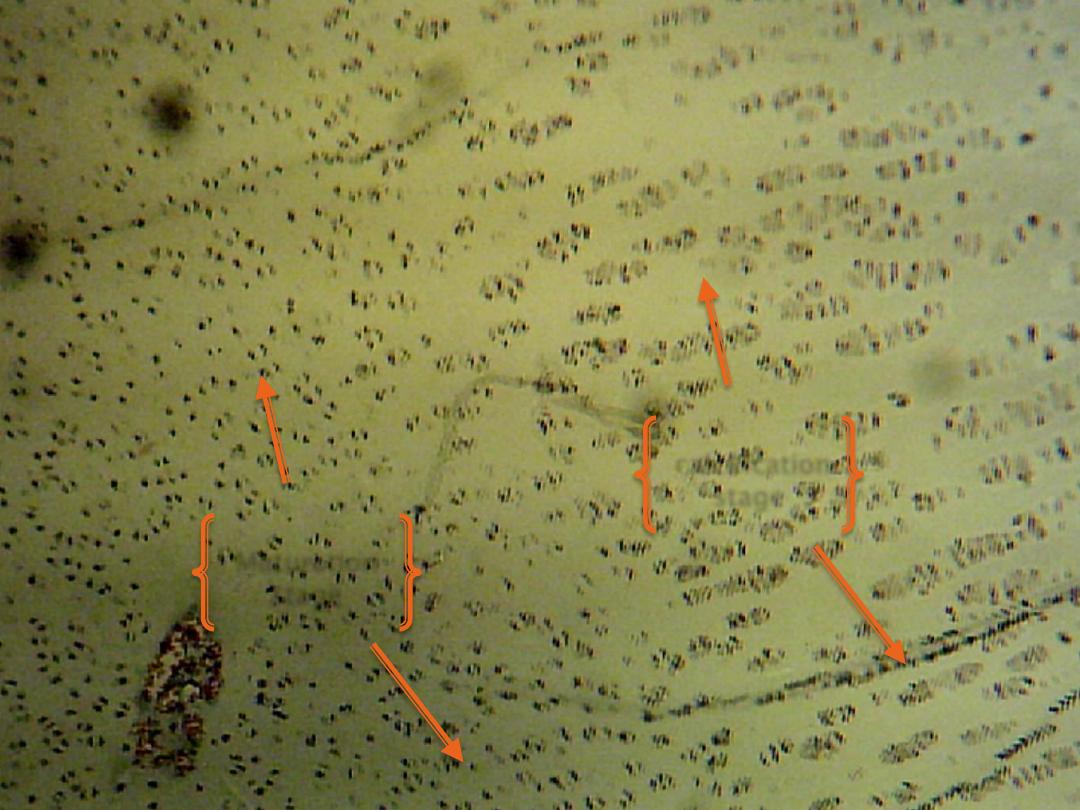
Maturation
stage
calcification
stage

calcification
stage
erosion
stage
ossification
stage
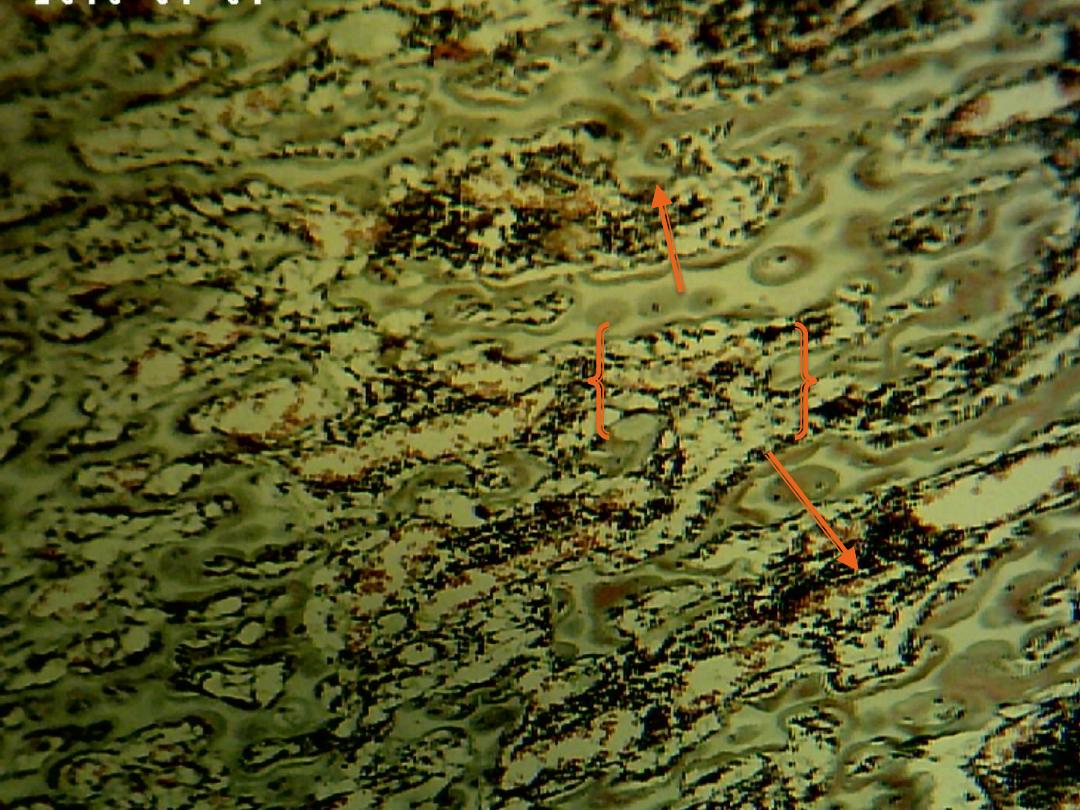
resorption
stage
