Fifth stage
Radiology
Lec-11
د.هديل
5/4/2016
NEURORADIOLOGY OF SPINE
INDICATION OF MRI
for precise localization of the level of a lesion which is difficult to be done from clinical
examination.
ADVANTAGE OVER CT SCAN:
MRI is a direct multiplanar acquisition i.e. can be easily applied in any plane, including optimal
sagittal axis.
SIGNAL INTENSITY:
- The annulus fibrosus, spinal ligaments & dura matter & the cortical bone of the vertebrae
give low signals.
-Epidural & paraspinal fat give high intensity signal.
-The gel of the normal nucleus pulposus of the normal intervertebral discs gives high intensity
signal on T2 weighted image sequences.
-In the normal adult disc, a shelf of annulus causes a low
signal horizontal band resulting in a bilocular appearance
, & with normal aging, the intensity of the signal from the
nuclei decreases.
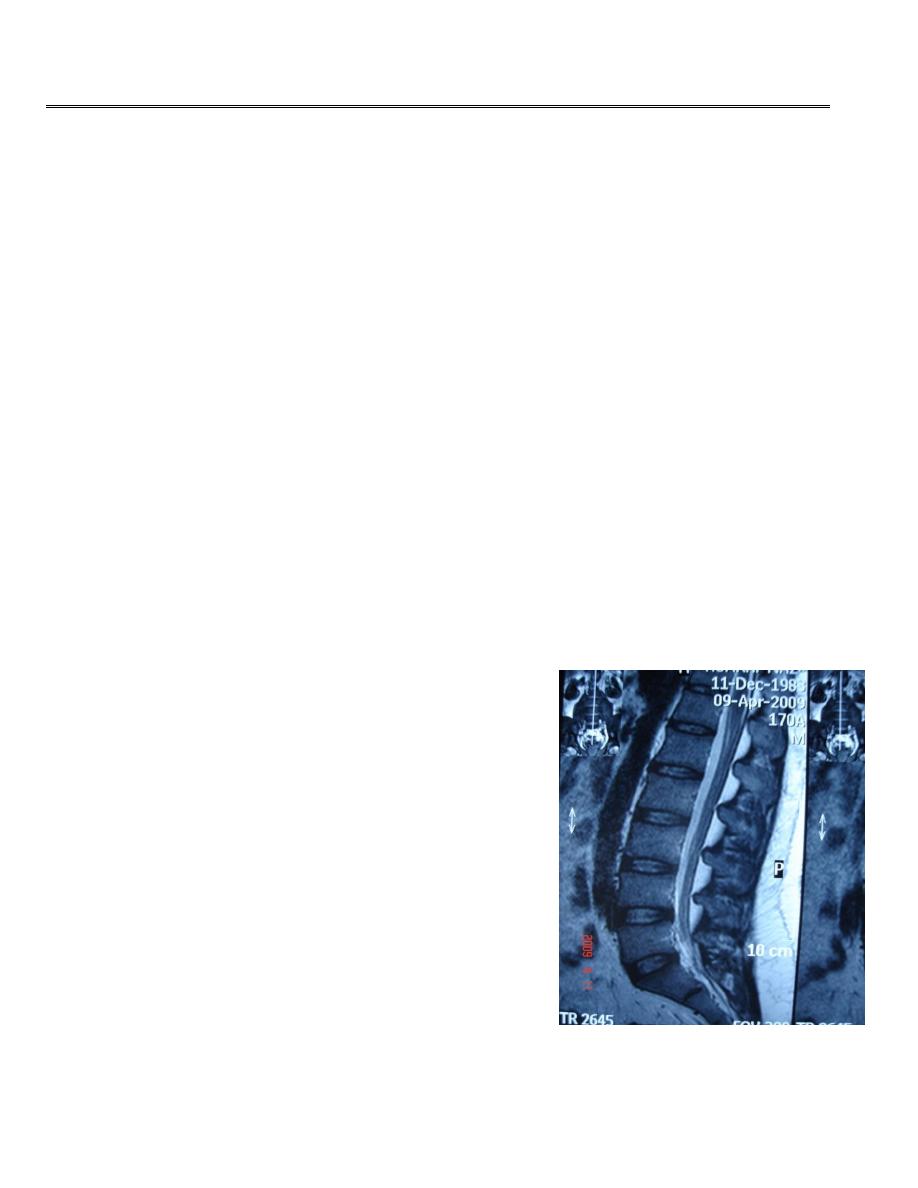
MRI OF LUMBER SPIN
T2 weighted image
Normal discs
Normal ligament
Normal thecal sac
NORMAL ANATOMY:
SPINAL CANAL
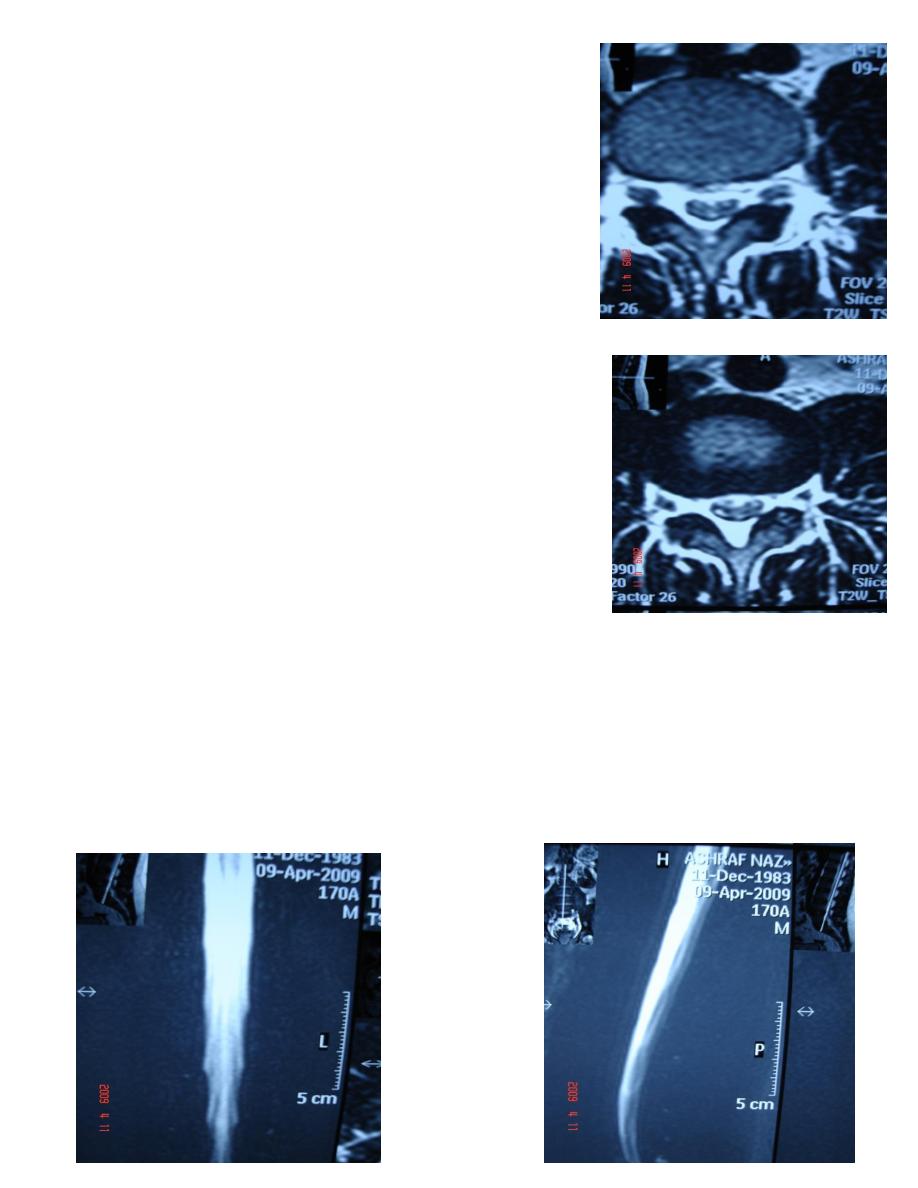
-The spinal canal is bounded anteriorly by vertebral bodies &
intervertebral discs , backed by the posterior longitudinal
ligament, poster laterally by pedicles & laminae lined by
ligamenta flava.
-The normal intervertebral foramens are oval or boot shaped
& symmetrical in the absence of scoliosis.
NORMAL DISC & INTERVERTEBRAL FORAMEN
Disc content:
Center: neuclus pulposus.
Annulus fibrosus
Vertebral body
Intervertebral foramen: contain dorsal root ganglion , spinal
nerve root & epidural fat.
NORMAL ANATOMY:
SPINAL CANAL
-If sagittal diameter in the cervical & lumber regions below 12mm ,&14 mm respectively ,
indicate potentially significant developmental narrowing.
The spinal cord descends from the medulla oblongata , commencing at about the level of
foramen magnum & terminates at the conus medullaris , which lies between the lower border
of 12th thoracic & the upper border of the third lumber vertebra.
MR
MYELOGRAM
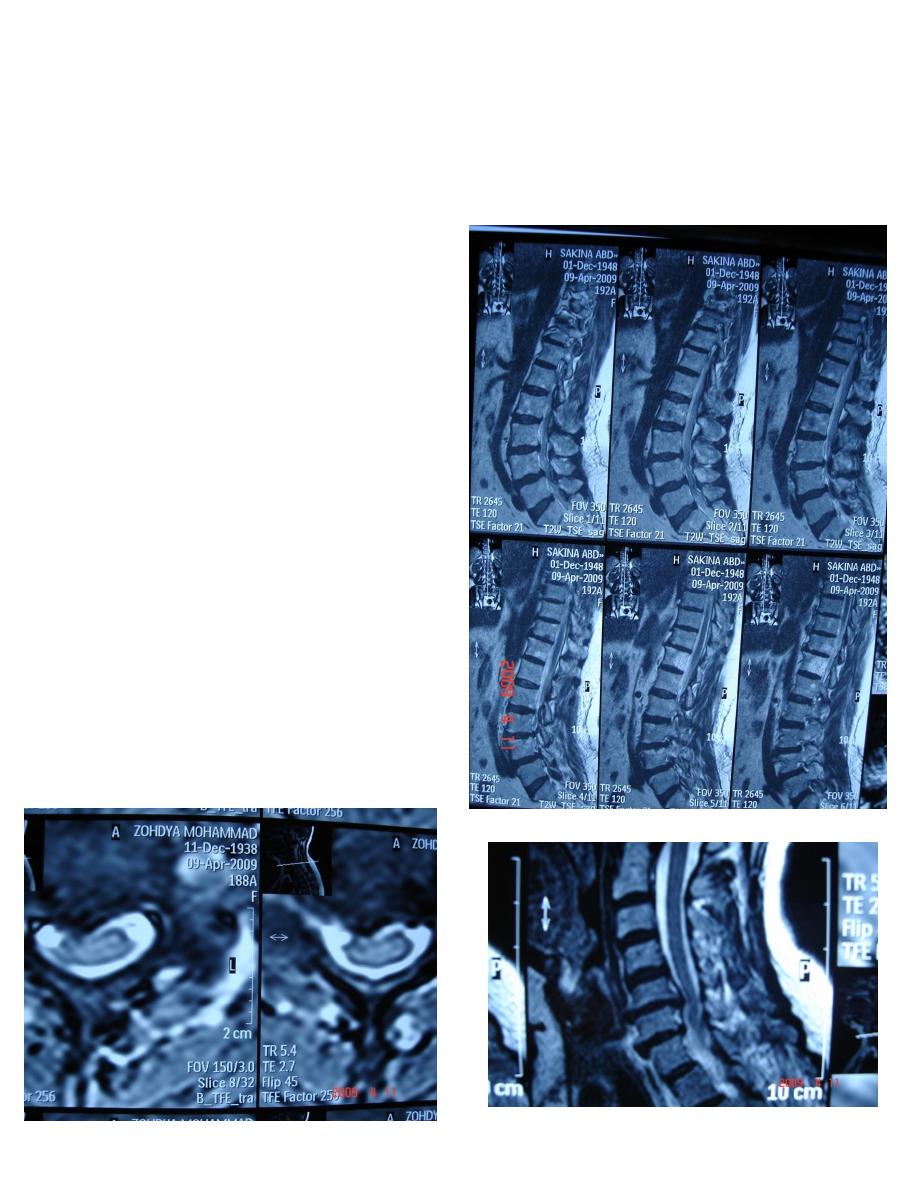
Spondylosis
:
This process involve intervertebral disc prolapse & degeneration & it is caused by wear &
tear , it involve intervertebral discs , vertebral bodies & facet joints , it is the commonest
cause of entrapment neuropathy & of neurological disability due to spinal cord disease.
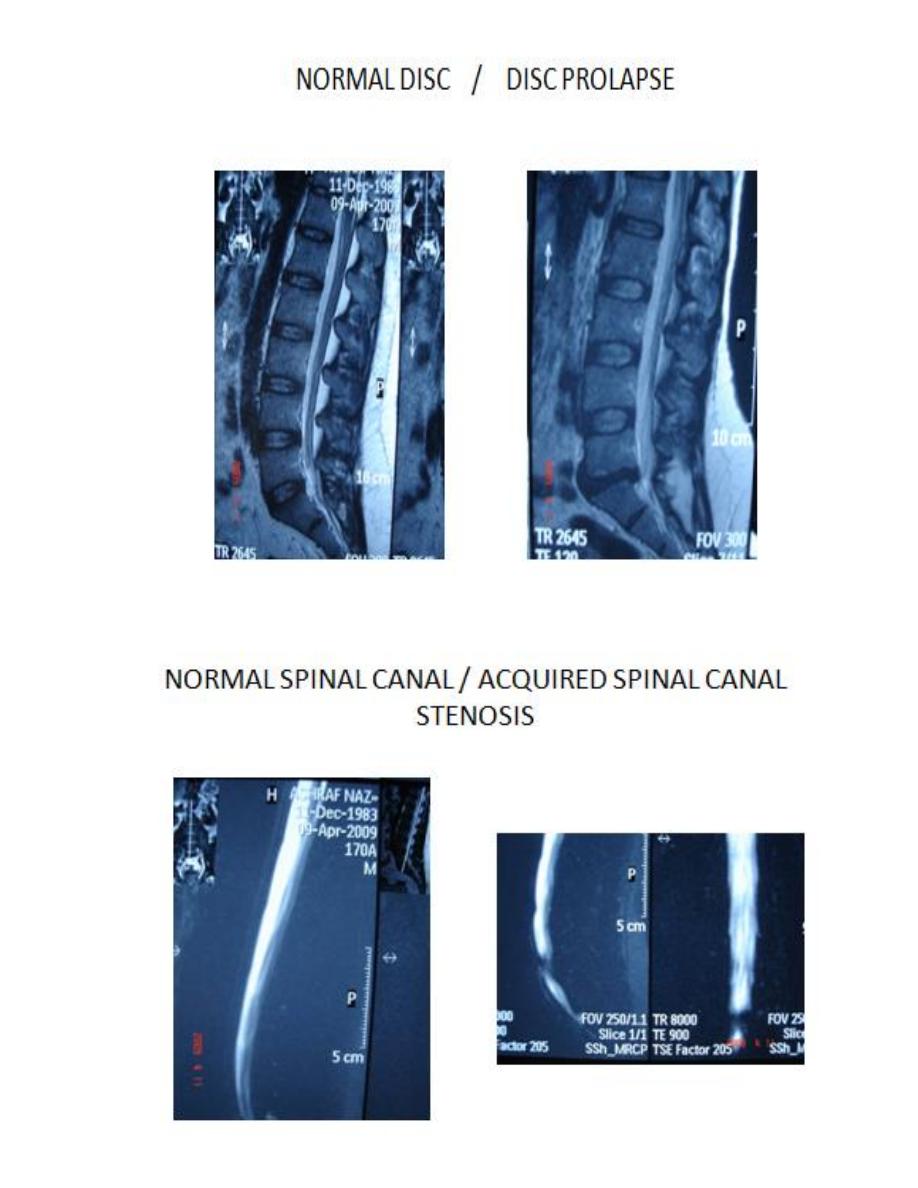
1-DISC PROLAPSE:
Extrusion of the softer material from within an
intervertebral disc into or through a posterior
or posterolateral radial tear in the annulus
fibrosus.
Disc prolapse takes the form of focal broad
based bulge in the margin of annulus or , a
focal mass extending upwards or downwards
in the anterior epidural space, Far lateral
protrusions or extruded fragments, Involve
the intervertebral foramens, not the spinal
canal & they are commonest in the lumber
spine.

2-DEGENERATIVE CHANGES:
When affect the disc leads to:
a-loss of normal bright signal of the nucleus on T2 weighted
image.
b- loss of the normal height of the disc.
When involve articular surface leads to: articular surface
irregularities & osteophyte formation.
When involve ligaments leads to calcification or ossification
which result in diffuse thickening or a focal mass which may
compress the neural tissue.
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Disc prolapse at c3-4, c4-5. c5-6, c6-7.
Posterior longitudinal ligament thickening , & ligamentum
flavum thickening.
SPINAL CORD COMPREESSION:
Spinal cord compression from disc prolapse & degeneration is damaging cord substance & is
seen in the form of focal signal changes in the cord substance
Axial section(Right picture), T2weighted image:
there is abnormal high signal intensity area within the cord substance ,indicate cord
degeneration
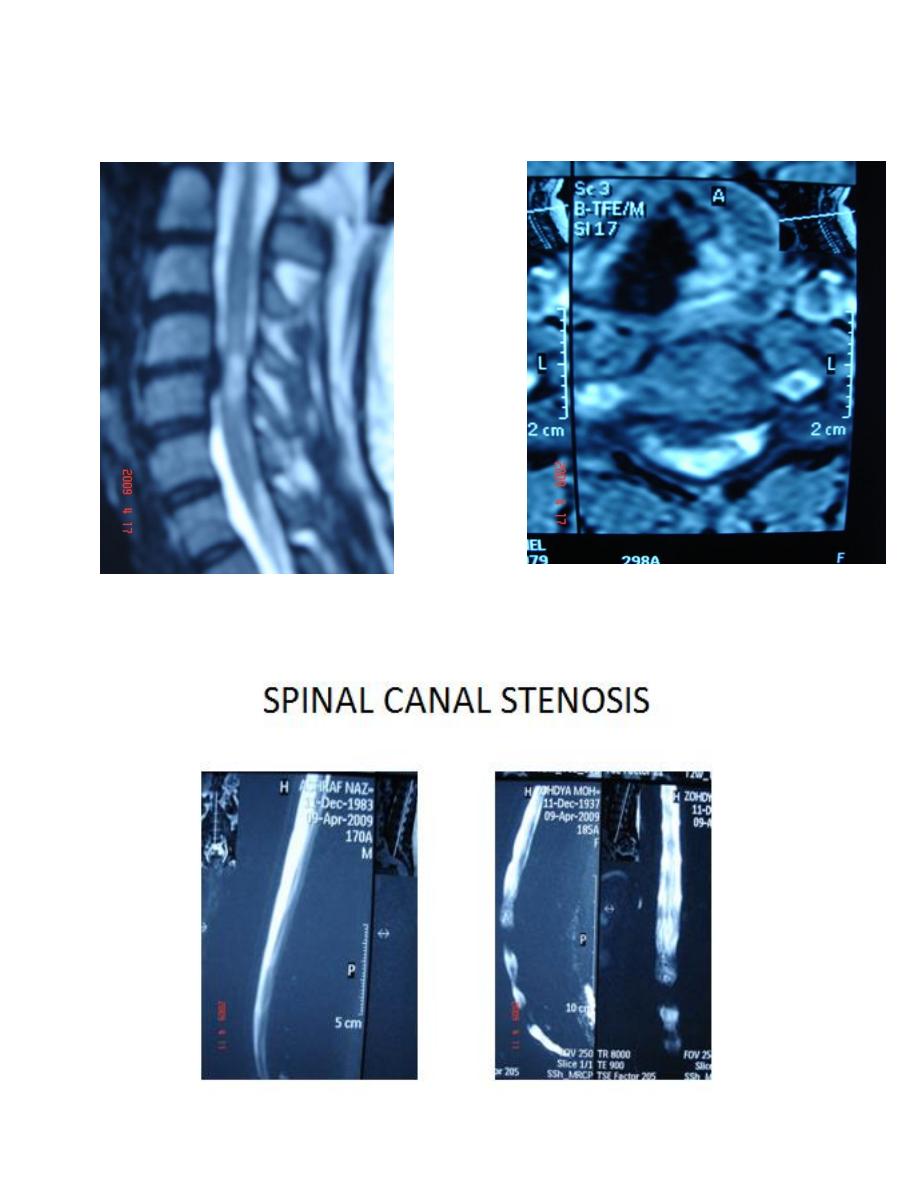
Posterior disc prolapse(Left picture ) at level c4-5 which obliterate anterior subarachnoid
space at this level , there is abnormal high signal intensity area within the cord substance
,indicate cord degeneration.
Significant spinal canal stenosis when?
1-The stenosis is enough to eliminate csf signal intensity on MRMYELOGRAPHY.
2-cauda equina entrapment.
