
1
Dermatology sessions
Description of any skin lesion:
Site of the lesion (part of the body)
hand, face, leg, scalp, etc.
Number of lesion
single, multiple, and write the exact number if you can.
Arrangement of the multiple lesions
discrete, coalesce, grouped, linear, circular.
Distribution of the lesions:
o On extensor surface: elbow, knee, sacral rejoin.
o On flexor surface: axilla, groin, sub-mammary, umbilicus.
o On distal site: on fingers called acral.
o Central site: like chickenpox.
o Sun exposed area: face, hand, neck, upper chest.
o Localized: unilateral or follow dermatome.
o Generalized: or called universal.
Type of lesion primary or secondary lesion.
Size of the lesion from mm to cm.
Color of the lesion silvery, erythematous, pink.
Shape of the lesion irregular, circular, flat, elevated.
Border of lesion like active border in some lesion.
Margin of the lesion well defined (psoriasis), ill defined (dermatitis).
Types of lesion:
Primary skin lesions:
Macule
A localized area of color or textural change in the skin.
Papule
A solid elevation of skin <5 mm in diameter.
Plaque
A palpable elevation of skin >2 cm diameter and <5 mm in height.
Vesicle
A clear, fluid-filled blister <5 mm in diameter.
Bulla
A fluid-filled blister >5 mm in diameter.
Pustule
A visible collection of pus in a blister.
Abscess
A localized collection of pus.
Wheal
A transitory, compressible papule or plaque of dermal edema, red or white,
indicating urticarial.
Angioedema a diffuse swelling of edema that extend to the subcutaneous tissue.
Nodule
A solid elevation of skin >5 mm in diameter.
Papilloma
A nipple-like projection from the surface of the skin.
Purpura
Extravasation of blood resulting in redness of skin or mucous membranes.
Ecchymosis
A macular red or purple haemorrhage, >2 mm in diameter, in skin or
mucous membrane.
2
Hematoma: a swelling form gross bleeding.
Burrow
A tunnel in epidermis caused by a parasite, e.g. Acarus in scabies.
Comedo
A plug of sebum and keratin wedged in a dilated pilosebaceous orifice on
the face.
Telangiectasia
Dilated dermal blood vessels resulting in a visible lesion.
Secondary skin lesions:
Scale
Accumulation of easily detached fragments of thickened keratin.
Crust
Dried exudate, e.g. serum, blood or pus, on the skin surface.
Ulcer
A circumscribed area of skin loss extending into the dermis.
Excoriation
A superficial abrasion, often linear, due to scratching.
Erosion
A superficial break in the epidermis, not extending into dermis, heals
without scarring.
Fissure
A linear split in epidermis, often just extending into dermis.
Sinus
a cavity or channel that permit the escape of pus or fluid.
Scar
Replacement of normal tissue by fibrous connective tissue at the site of an
injury.
Atrophy
Loss of epidermis, dermis or both, thin, translucent and wrinkled skin,
visible blood vessels.
Stria
Atrophic linear band in skin, white, pink or purple, from connective tissue
changes.
Other skin lesions:
Callus
Local hyperplasia of horny layer on palm or sole, due to pressure.
Cyst
A nodule consisting of an epithelial-lined cavity filled with fluid or semisolid
material.
Erythema
Redness of the skin due to vascular dilatation.
Freckle
A macular area showing increased pigment formation by melanocytes.
Lichenification
Chronic thickening of skin with increased skin markings, from rubbing
or scratching.
Milium
A small white cyst that contains keratin.
Petechia
A haemorrhagic punctate spot 1–2 mm in diameter.
See photos @ WWW.muhadharaty.com/lecture/3472
Hair loss:
Localized:
o Scarring Lichen planus, discoid lupus.
o Non scarring trachiotillamonia,
alopecia areata.
Diffuse:
o Scarring radiotherapy, burn, trauma.
o Non scarring cytotoxic drugs.
Causes:
Normal hair + abnormal skin Psoriasis,
seborrheic dermatitis.
Normal skin + abnormal hair (loss)
trachiotillomonia, alopecia areata, traction
alopecia.
Skin and hair are abnormal tenia capitis.
3
Photos form doctor:
Description
Photo
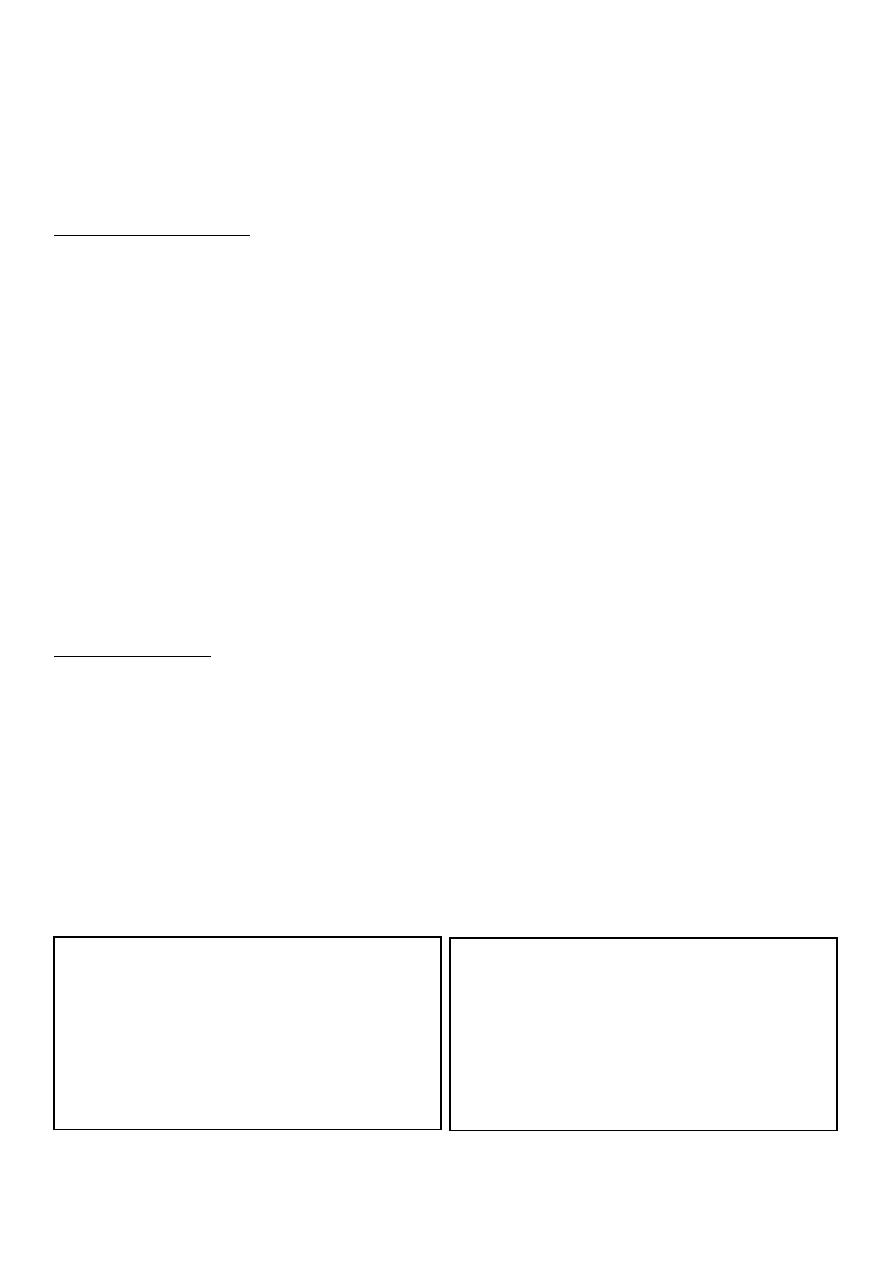
Psoriasis:
o Site: extensor part of elbow.
o Number: single.
o Type: primary (plaque) and secondary
(scale).
o Shape: oval and flat elevation.
o Size: few cm in diameter.
o Color: erythematous (red) plaques and
silvery and heavy scales.
o Margin: well defined.
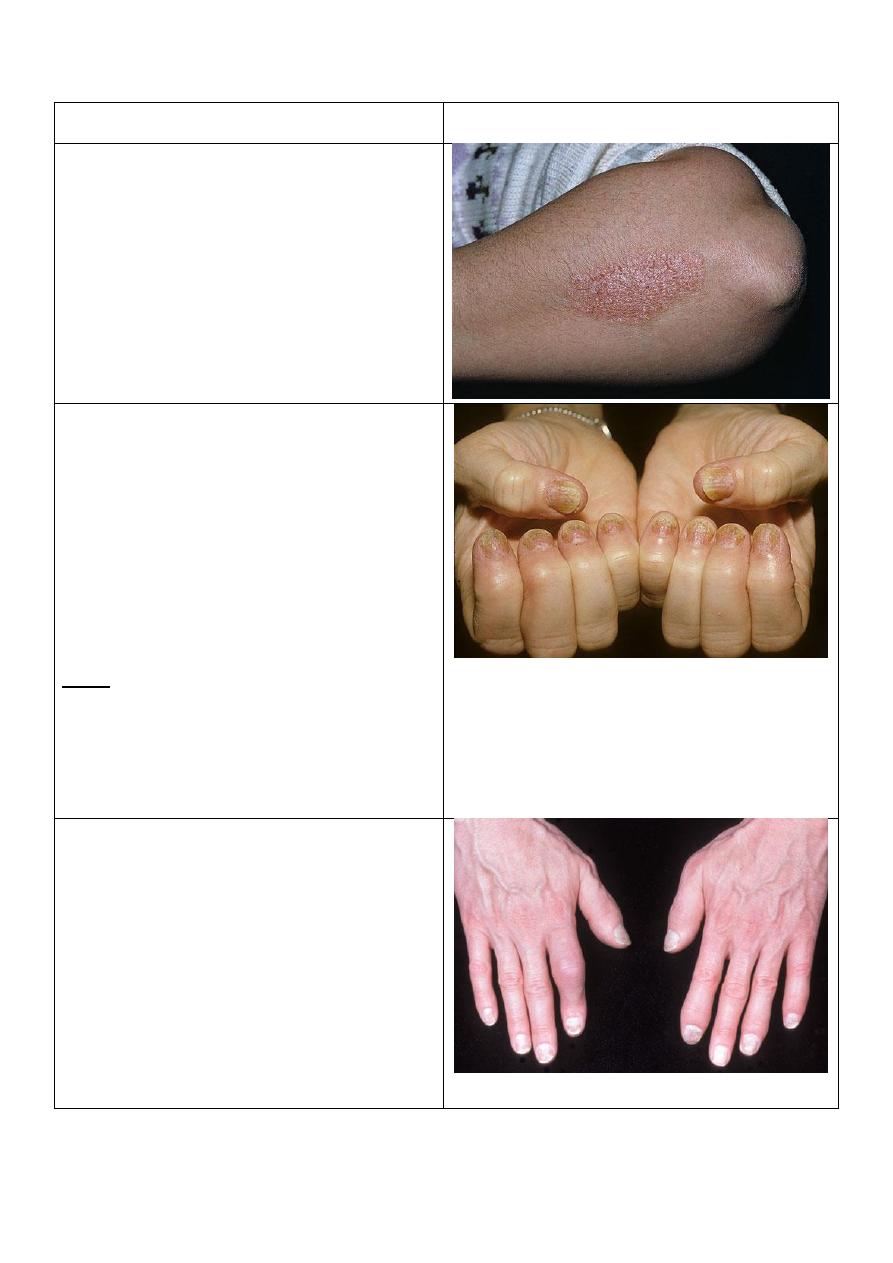
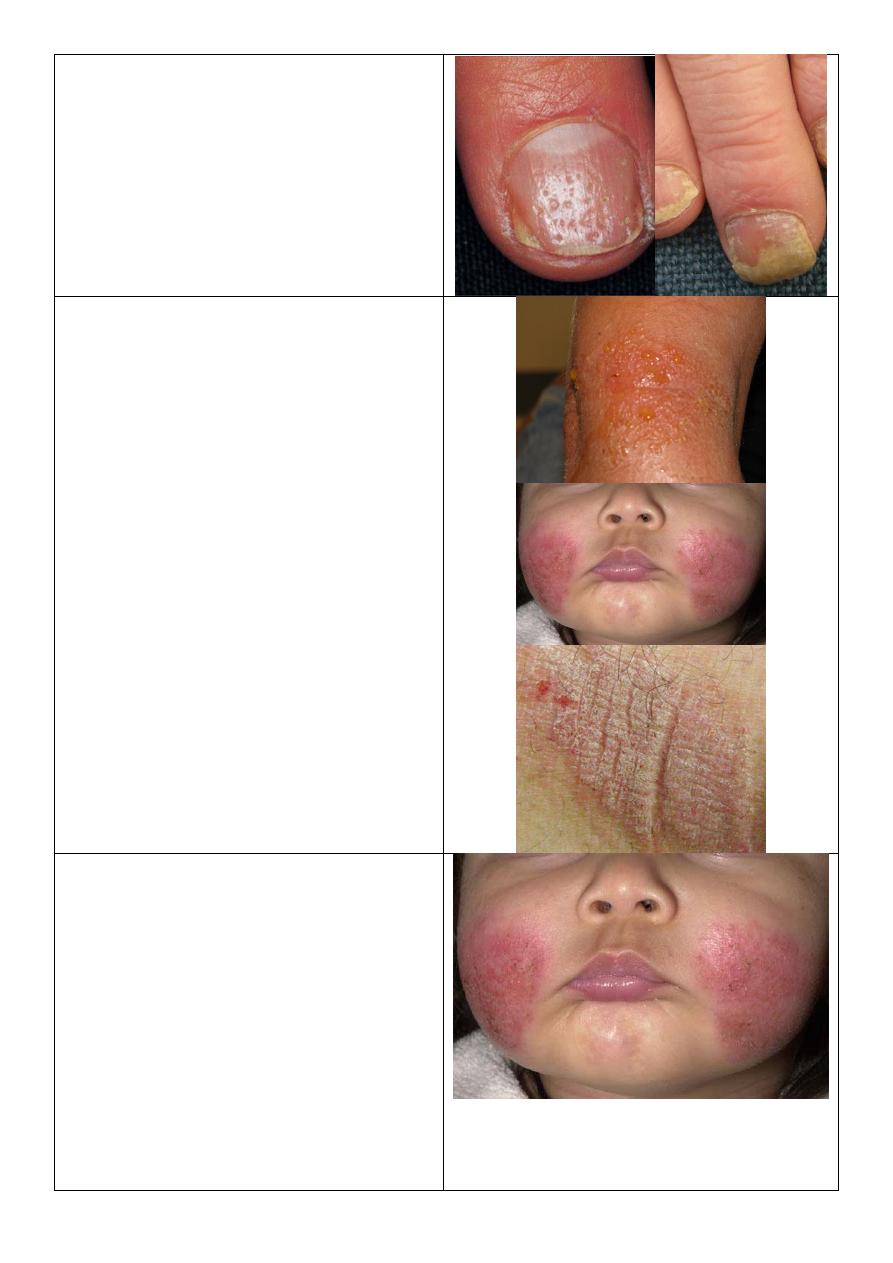
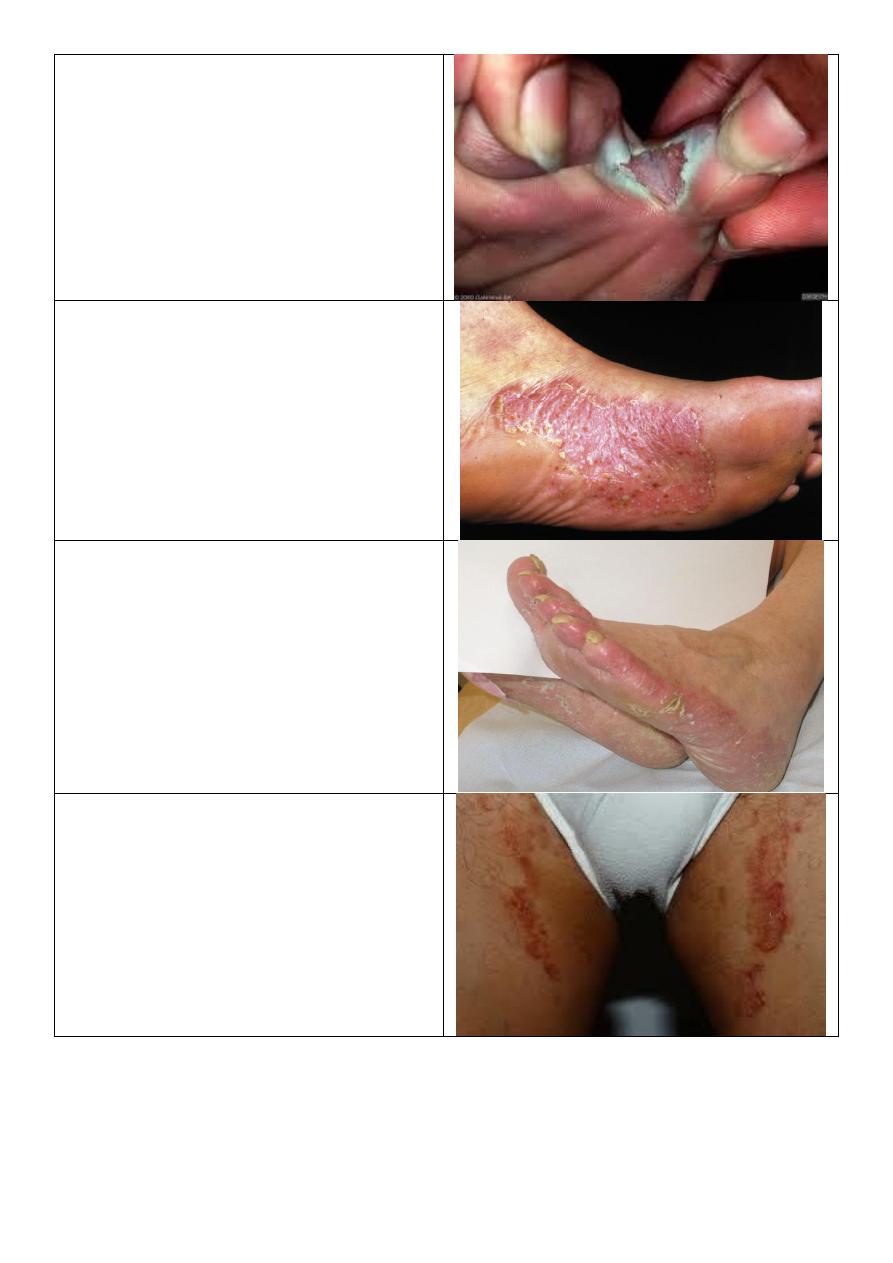
Nail changes in psoriasis:
o All nails are affected.
o Nail pitting.
o "End on" view Separation of nail
from nail bed called onycholysis,
thickening of nail, subangular
hyperkeratosis.
o "Above" view yellow color.
o "Lateral" view see the shape,
convexity, concavity of nail.
Note:
Nail changes in psoriasis occur before or
during or after the psoriasis, but it not
occur in all patients.
It may lead to psoriatic arthritis:
seronegative and DIPs affected.
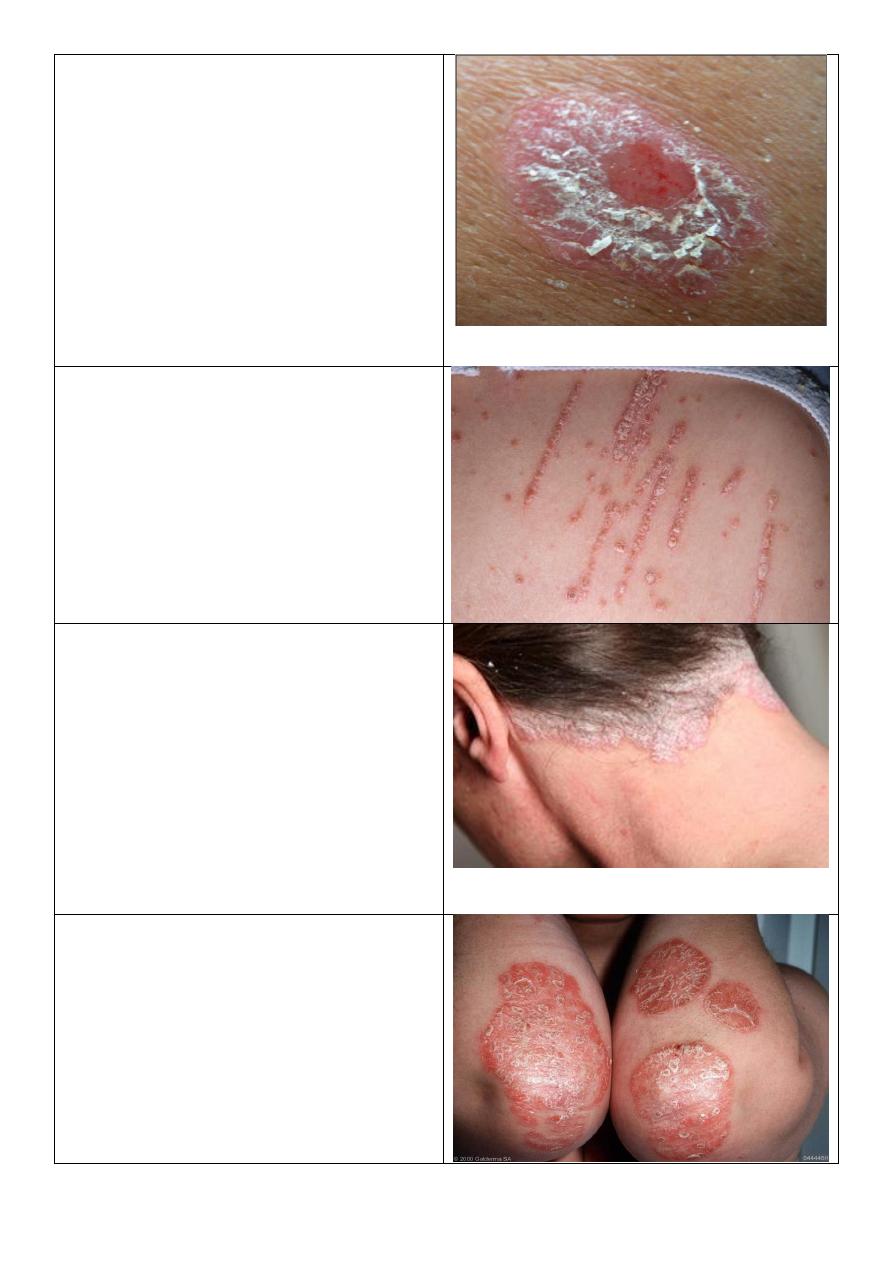
Psoriatic arthritis:
o The DIPs are affected.
o This is the typical picture.
o Sometimes the DIPs are not affected.
o Patterns of psoriatic arthritis:
1. Oligoarticular assymmetric arthritis.
2. Polyarticular symmetric arthritis (RA-like).
3. DIP joint predominant.
4. Destructive polyarthritis (arthiritis
mutilans).
5. Ankylosing spodylitis and sacroiliitis.
4
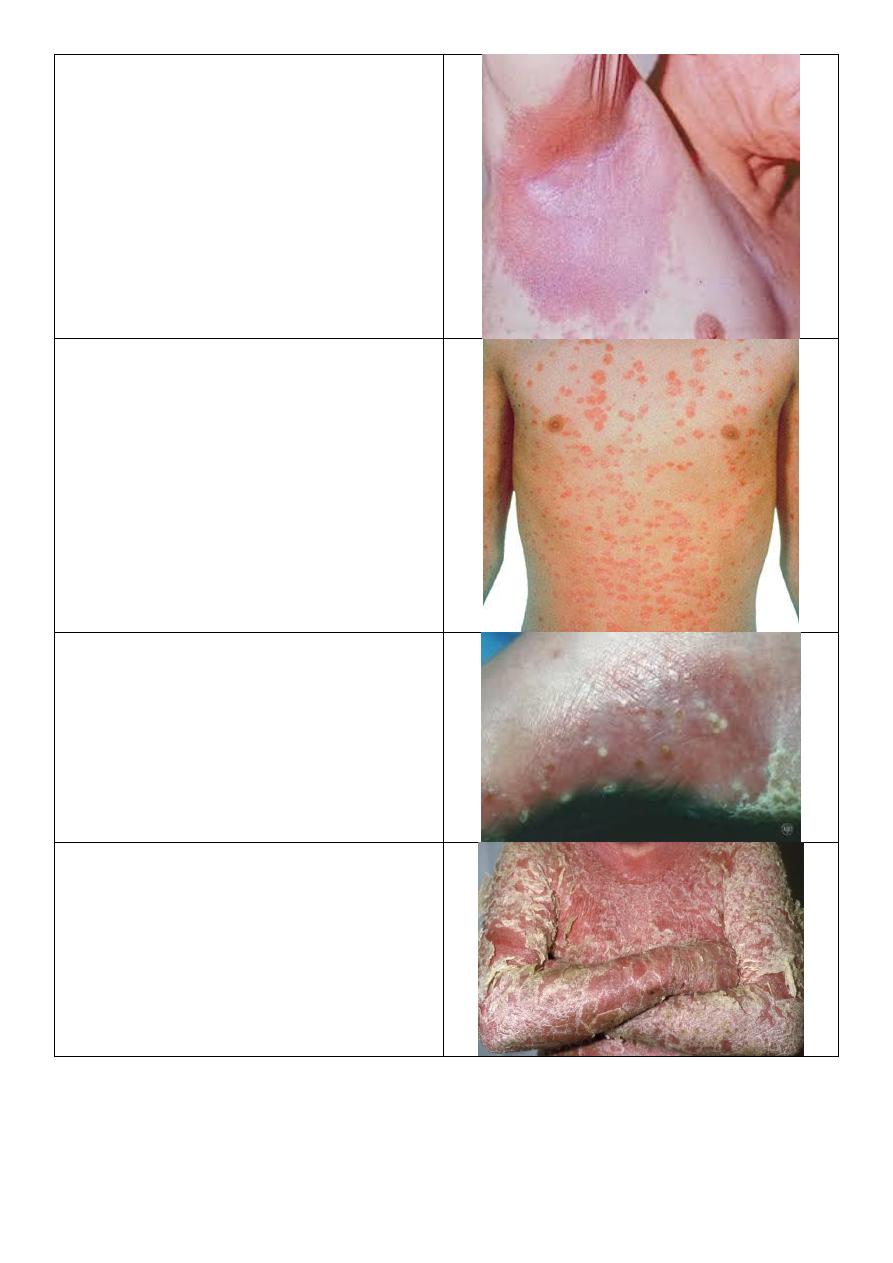
Psoriasis:
o Number: single.
o Type: primary lesion then the patient
scratch it lead to bleeding (Auspitz sign)
o Shape: oval.
o Size: few cm in diameter.
o Color: pink primary lesion, and white
scales.
o Margin: well defined.
o There are pin-point bleeding Auspitz
sign.
o This not occur in eczema.
Koebner phenomenon:
o Lines of scratching.
o Occur in psoriasis, warts, vitiligo.
o koebner phenomenon spread of a
disease in uninvolved skin by trauma.
Prosiasis:
o Site: scalp.
o Color: Silvery.
o Lesion: heavy scaly scalp.
o Occur in: psoriasis and seborrheic
dermatitis.
o Differences:
Seborrheic: yellowish greasy scales.
Psoriasis: powdery dry silvery scales.
Seborrheic: Stop at hair line.
Psoriasis: extend beyond hair line.
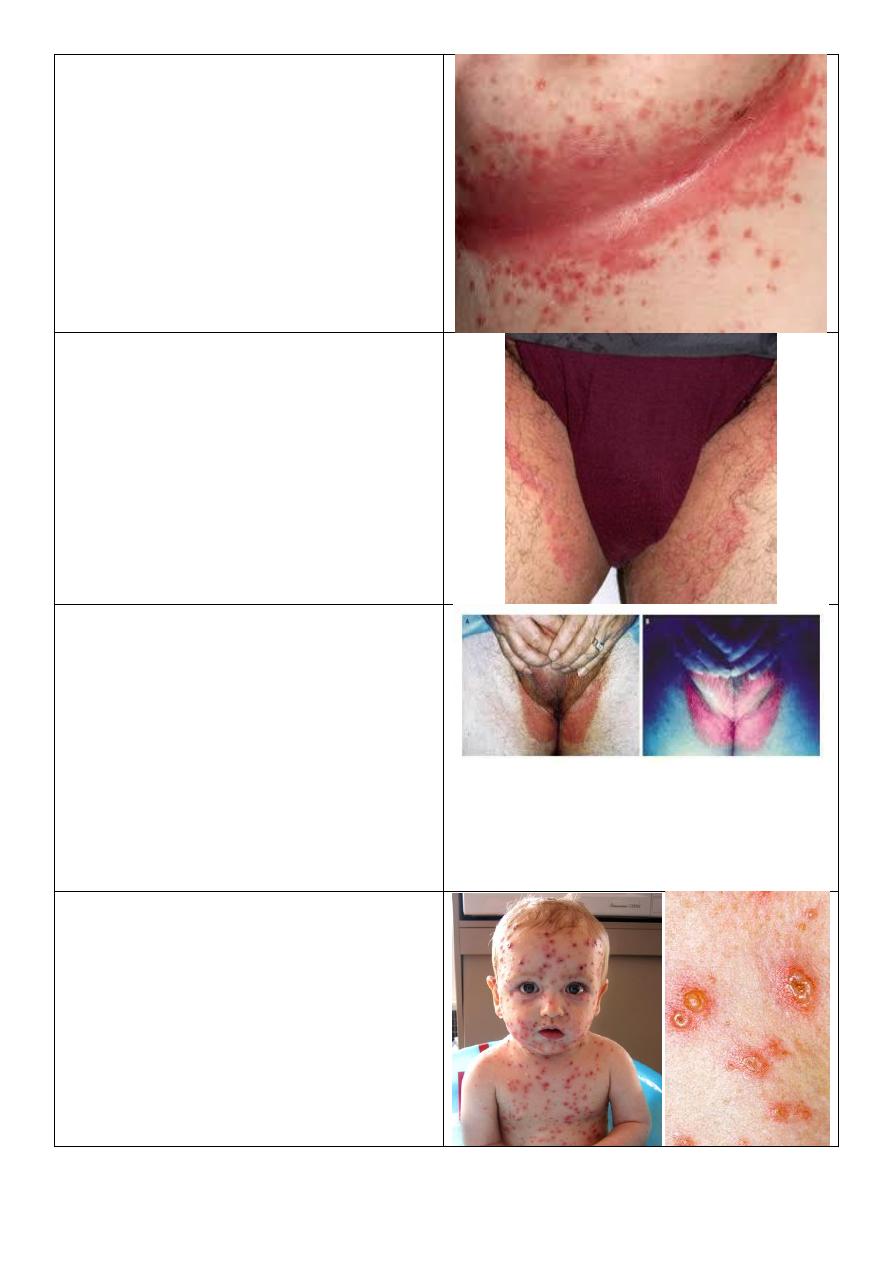
Chronic plaque psoriasis:
o Distribution: on extensor surface.
o Lesion: plaques.
o Covered by scales thick, white,
powdery.
o Color: erythematous.
o Margin: well defined.
o Scratching lead to Auspitz sign.
5
Flexor psoriasis:
o In axilla, groin, sub-mammary,
umbilicus.
o No scales because it is wet area.
Guttate psoriasis:
Tear drop lesions.
Occur in young children.
Pustular psoriasis:
Localized or generalized.
Erythrodermal psoriasis:
Red or erythematous exfoliation.
6
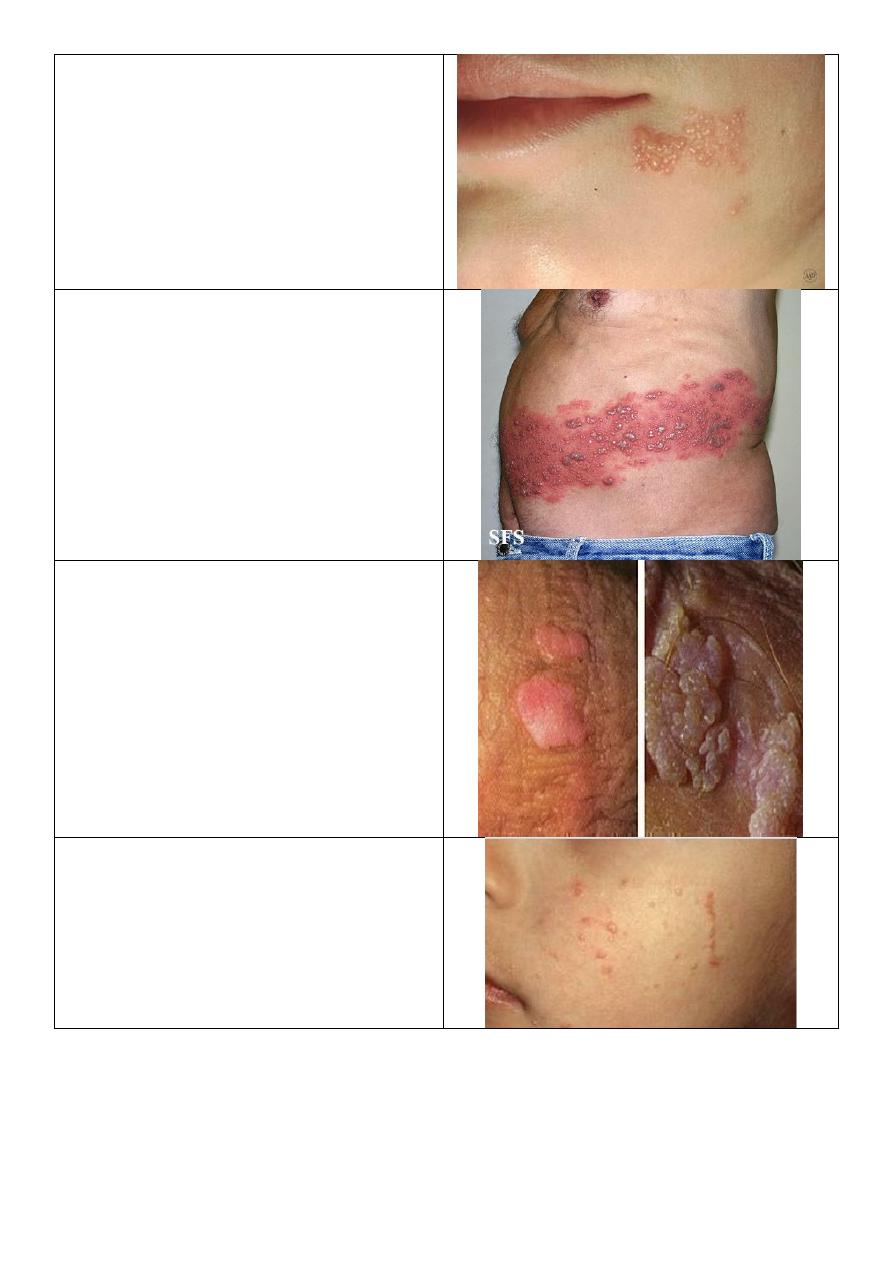
Psoriasis of nail:
o Pitting.
o Nail separation.
o Yellow discoloration.
Stages of eczema (dermatitis):
Acute stage:
o Ill defined.
o Small multiple vesicles.
o Oozing serious fluid.
Subacute stage:
o Erythematous plaque with ill-defined
border
Chronic stage:
o Ill defined.
o Lignification: thickening of skin +
exaggeration of skin marks.
Types of dermatitis Atopic dermatitis,
Seborrheic dermatitis, Stasis dermatitis, Contact
dermatitis.
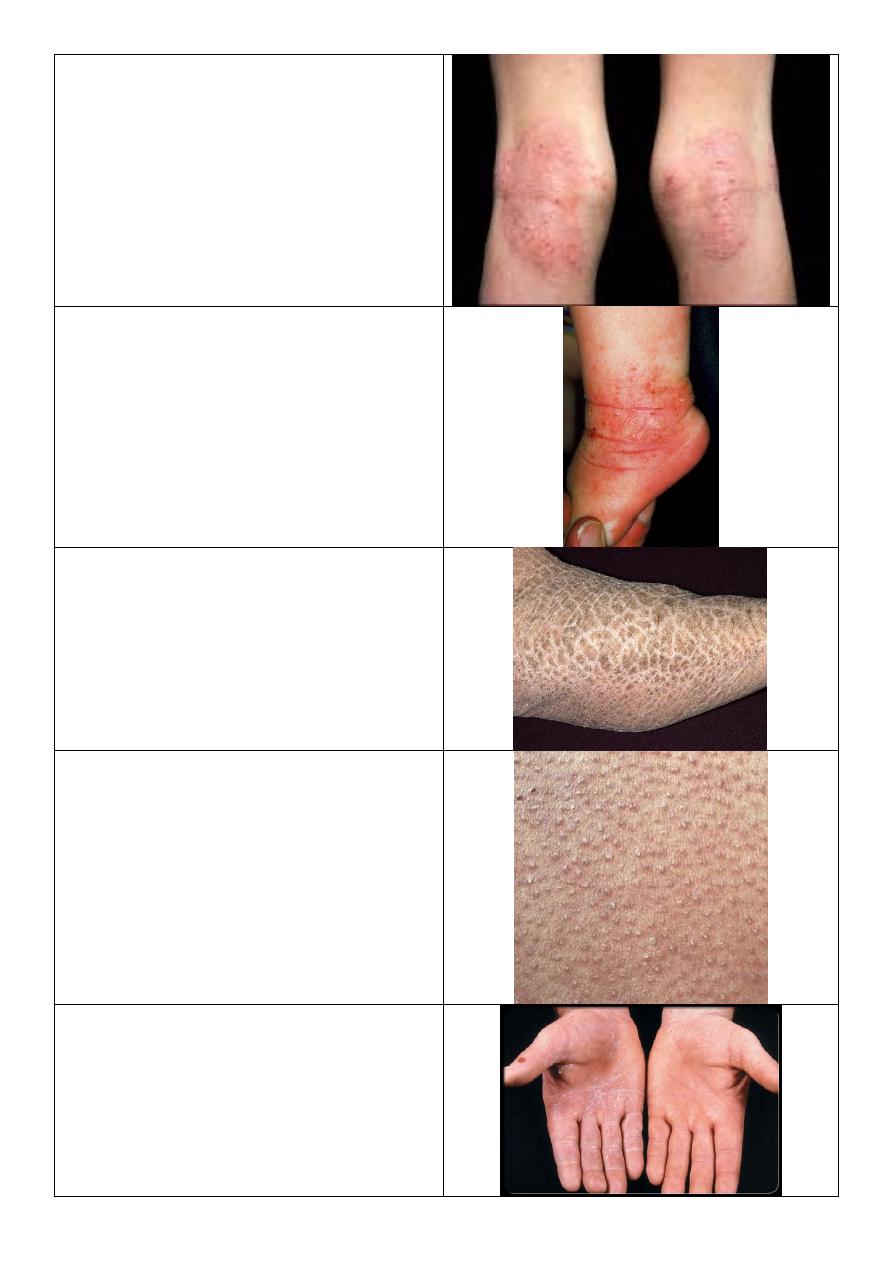
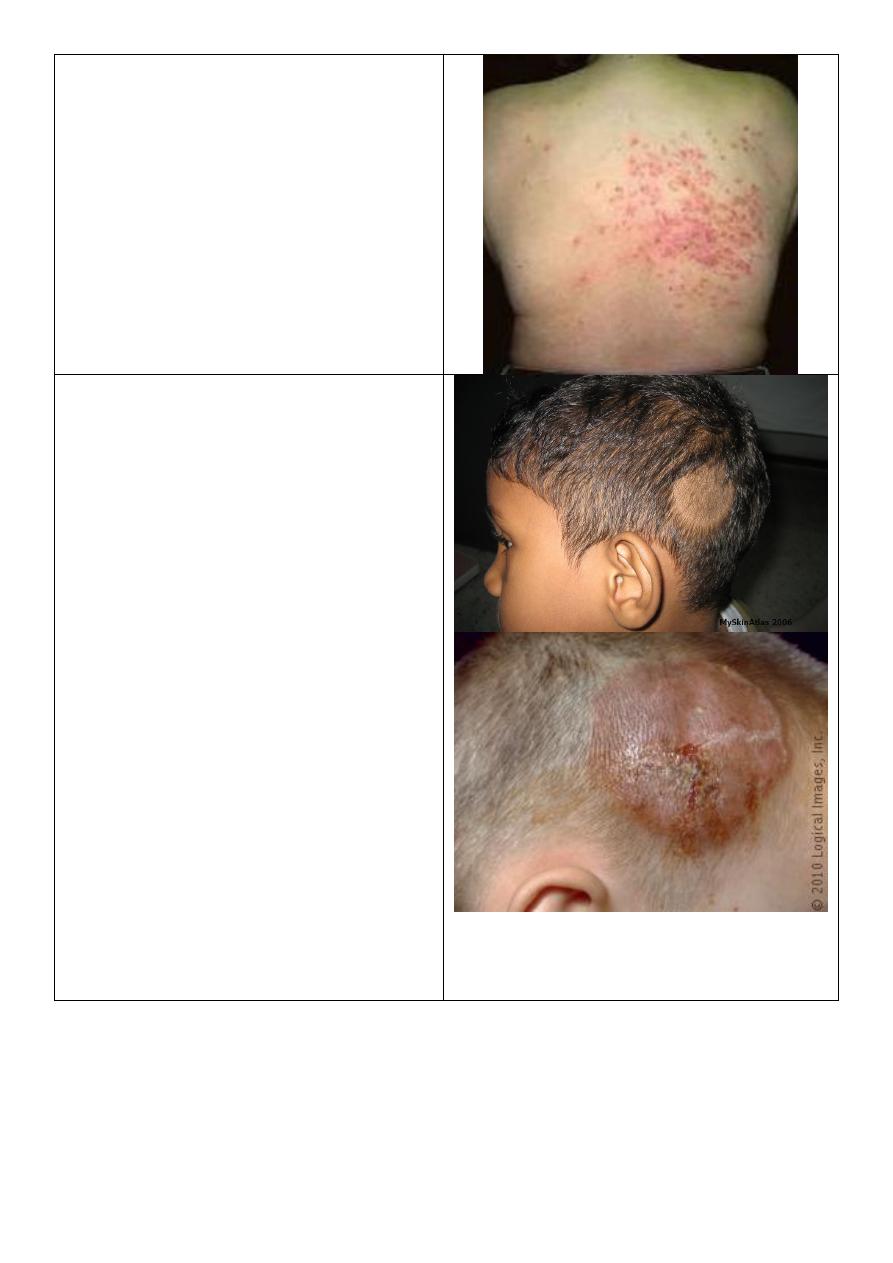
Atopic dermatitis:
o Major criteria of atopic dermatitis:
1- Severe itching.
2- Typical lesion + predilection
according to age.
3- Positive personal or family history of
other atopic diseases like asthma.
4- Chronic relapsing.
o Predilection:
Infant: in cheek.
Little older: cheek, elbow, knee.
Adult: generalized.
o Prognosis: 2/3 improve – 1/3 persist.
7
Atopic dermatitis:
o Severe itching.
o Childhood stage.
o In popliteal fossa and antecubital fossa.
o Lignification
Dermatitis:
o Severe itching.
o Infant age.
o
Occur in ankle, elbow, wrist.
Ichthyosis vulgaris:
Dry polygonal scales.
Keratosis pilaris:
o Keratosis = thickening.
o Pilaris = related to hair.
o Tiny thickening (keratosis) at hair
follicles.
o
Occur in shoulder, upper thigh, buttock.
Name the condition? Atopic patient.
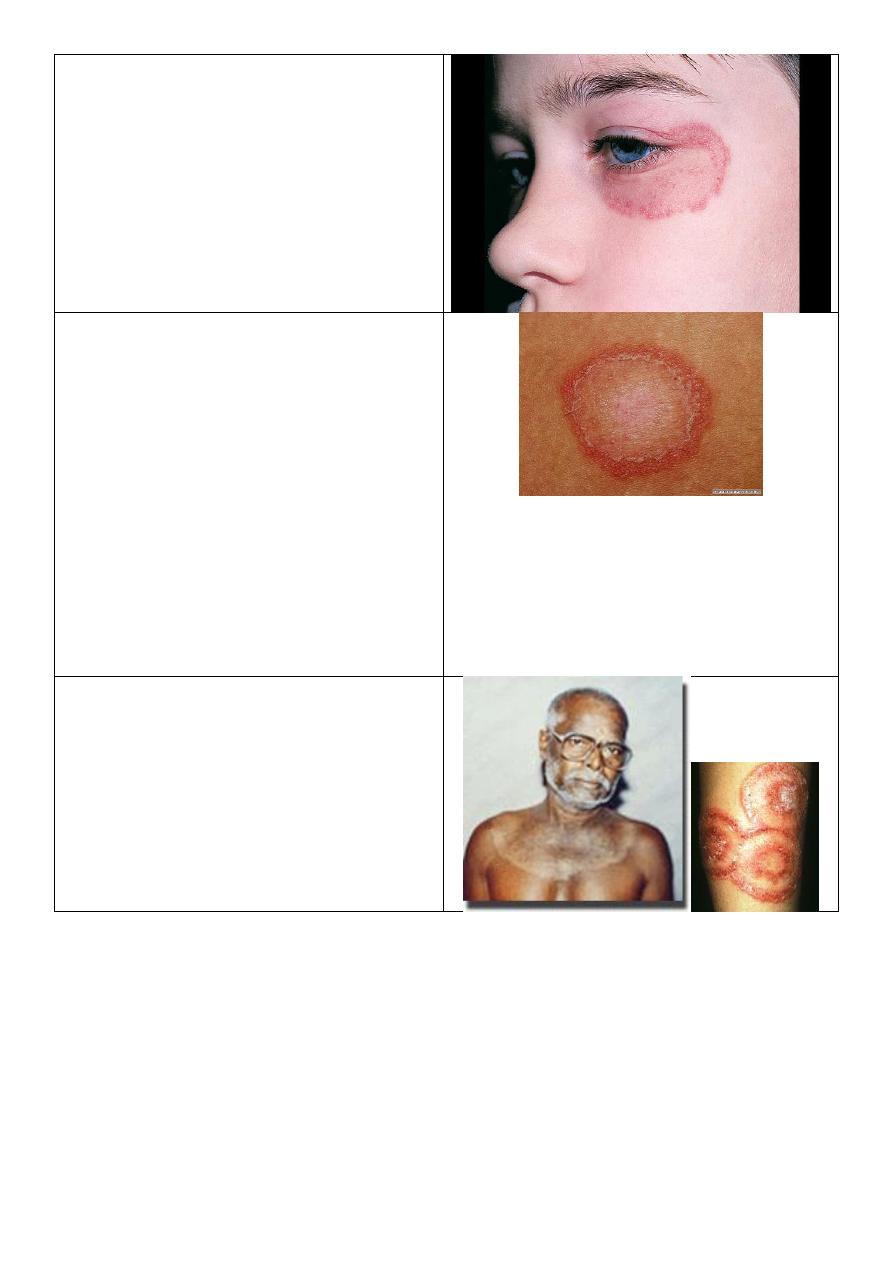
Tinea manuum:
o Unilateral (right hand).
o Scales concentrating in hand creases.
o Investigation: KOH.
o The cause is outside the body like fungal
infection,, because it is unilateral.
8
Tinea fasciae or corporis:
o Unilateral lesion (affecting the left eye).
o Erythematous plaque – well demarcated
o Active border with relatively central
healing.
o Due to localized problem from outside
like infection (fungal).
Active border in tenia:
o Round plaque.
o The border is more red and more scaly
and more elevated than the center.
o There is active border and relatively
healed center.
o The cause is dermatophyte it will eat
the keratin around it then eat the
surrounding keratin then extend and
eat more keratin so the lesion increase
in size.
o This is called tenia or ring worm.
o The tenia is named according to the site
of the lesion.
Tinea corporis:
o Has active border.
o Large size.
o Hand polycyclic lesion called
Tinea circinata
9
Tenia incognito:
o Due to steroid therapy (because it looks
like eczema).
o Unclear picture.
o The disease not treated by the steroids.
o Action of steroids anti-inflammatory,
vasoconstriction, anti-proliferative.
o Steroid facies
bright red, atrophy of
skin, appearance of hair, acne, very thin
skin.
Tenia capitis:
o School age child.
o There is localized area of hair loss.
o No complete devoid of hair and there is
scanty hair in the area.
o Broken hair.
o Early destructible hair.
o Lusterless hair.
o Scalp scaly, inflammatory.
Alopecia areata:
o Round patch.
o Completely devoid of hair.
o Normal skin of scalp.
o School age child and other ages.
Causes of hair loss:
o Generalized.
o Localized:
Tenia capitis.
Alopecia areata.
Male pattern.
Burn of hair.
Trichotellomania (psychological).
10
Athletes foot (tinea pedis):
o Erythematous, eroded.
o Exfoliation.
o Affect webspace.
o Mall odor due to superadded bacteria.
Tinea pedis:
o Vesico bullous.
o DDx: pustular psoriasis.
Tenia pedis:
o Scaly type.
o Affect whole sole then dorsum then
nails.
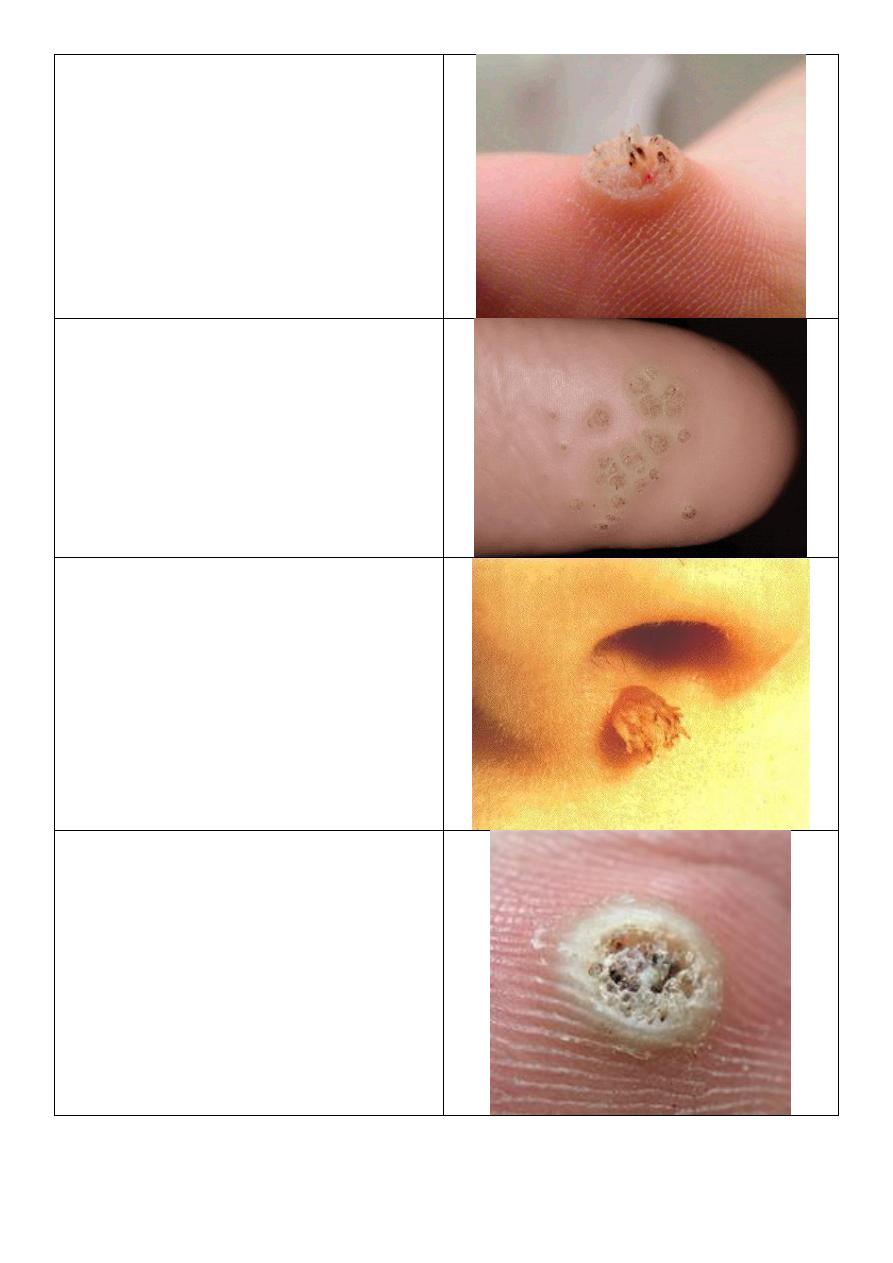
Tinea cruris:
o Old name: eczema marginatium.
o In upper inner thigh.
o Genitalia is free.
o Active border.
o Not symmetrical.
o Red brown color.
o Dry area.
11
Candidiasis:
o Folded area.
o Bright red.
o Macerated skin.
o Genitalia affected.
o Stellate lesion (lesions away from the
main lesion).
o Obese patient, Diabetic, Extreme age.
o Other endocrine diseases.
Tinea cruris:
o Dry.
o Red brown.
o Upper inner thigh.
o Active border.
o Genitalia free.
Erythrasma:
o It is bacterial infection.
o Brown color.
o Pink color under wood light.
DDx of lesion in thigh:
o Psoriasis.
o Eczema.
o Candidiasis.
o Erythrasma.
o Tenia cruris.
Chicken pox:
o Multiple and discrete.
o Pleomorphic (papule, vesicles, crust)
different stages at same time.
o Vesicles erythematous ground.
12
Herpes simplex:
o Multiple grouped vesicles.
o Erythematous base.
o At angle of mouth.
o History: only few days.
o Associated with tingling sensation.
Varicella zoster:
o One dermatome.
o Middle age or elderly.
o Pain could be post herpetic
neuralgia.
Warts
Plane warts:
o Strict to the surface.
13
Verruca vulgaris:
o Type of warts.
o Pale or skin color.
o Single papule.
o Well defined.
o Elevated.
o Rough surface.
Warts
Filiform wart:
o Finger like, filiform.
o Condylomata lata
affect genitalia
.
Wart:
o Painful in lateral site.
o Rough surface.
o With black dots.
o Interruption of skin markers.
o Multiple.
o Scratching
lead to bleeding.
o Affect sole of foot.
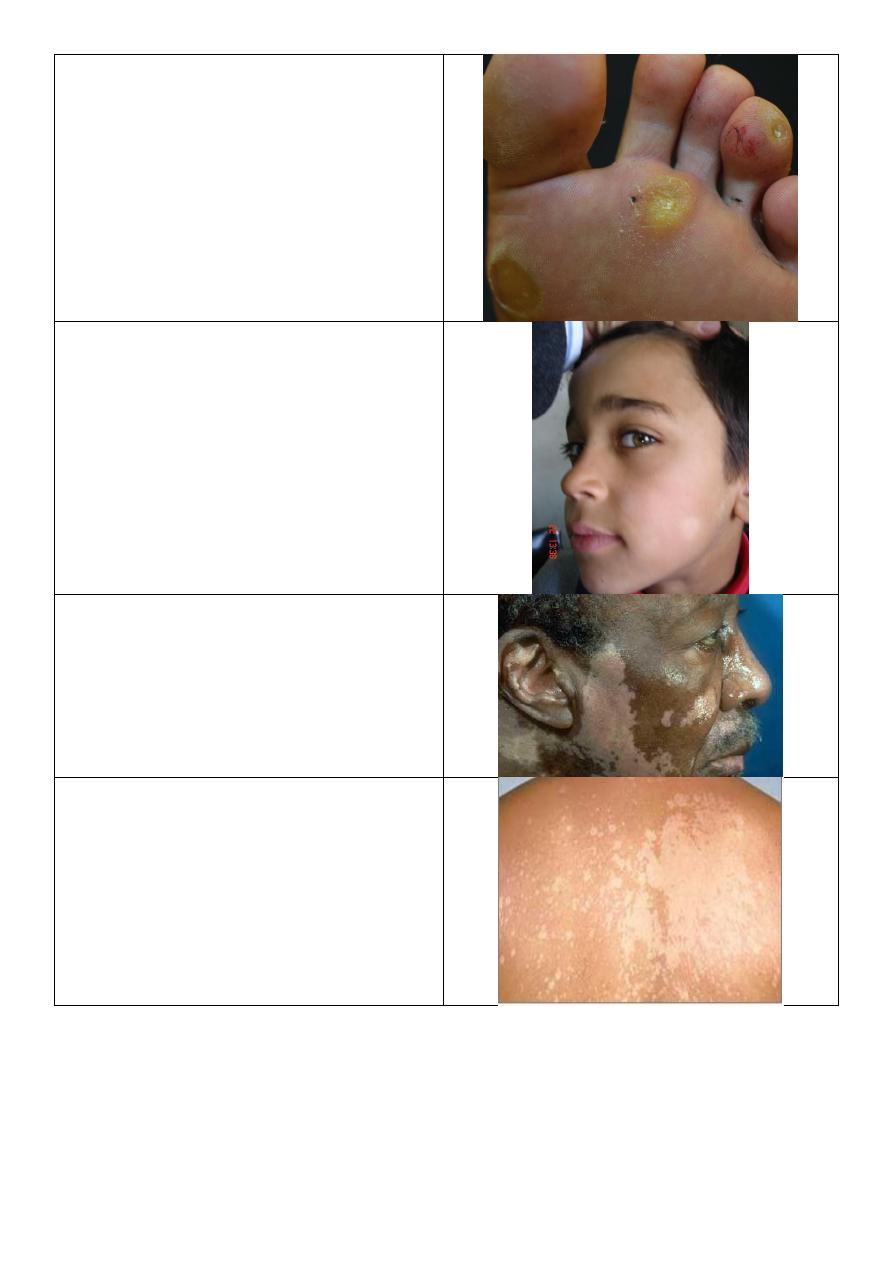
14
Corn:
o Painful in center.
o Apex in center.
o Smooth surface.
o Continuation of skin markers.
o Scratching lead to arrangement.
o Few.
o Over bone prominence.
o Affect sole of foot.
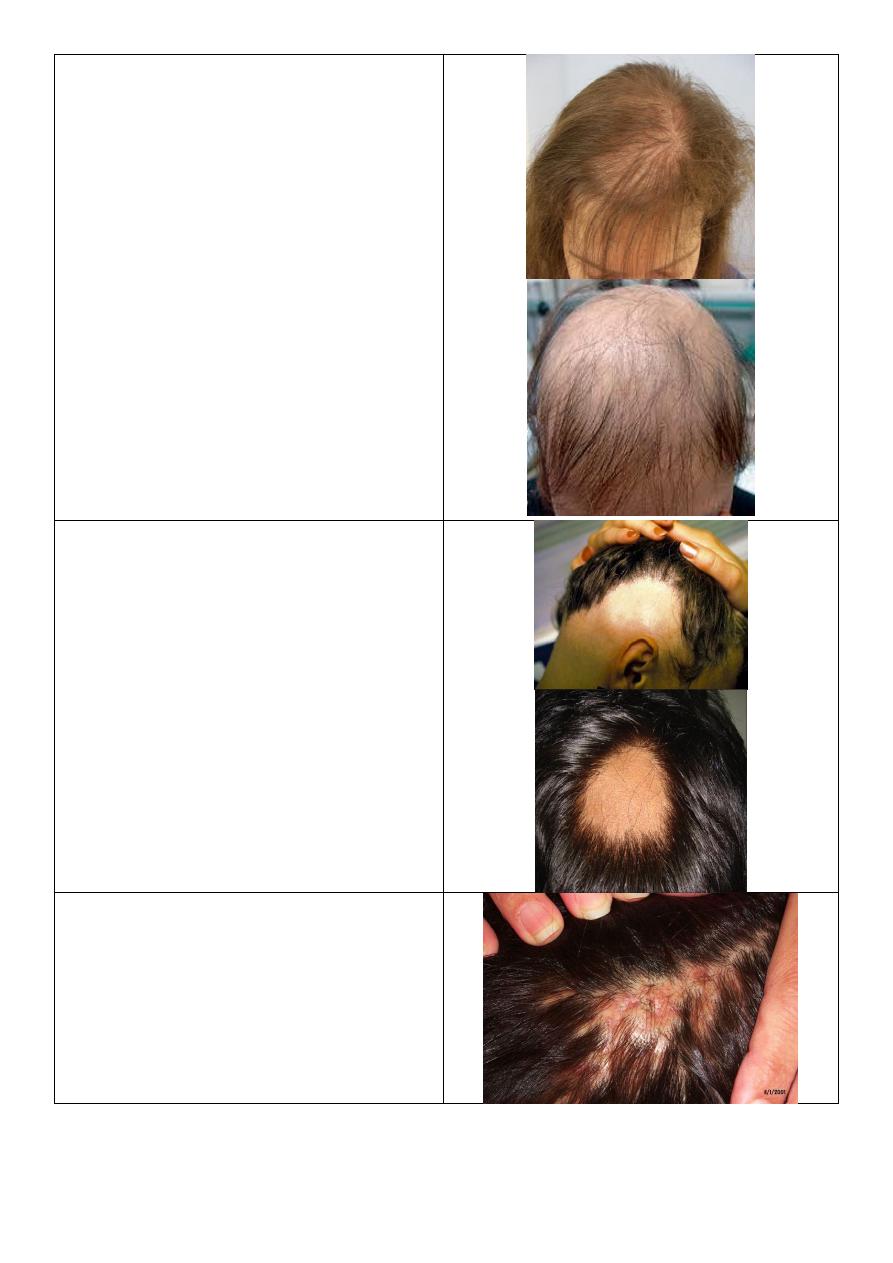
Pityriasis alba:
o Ill defined.
o Hypo pigmented.
o Scaly.
o Mainly in face then extremities.
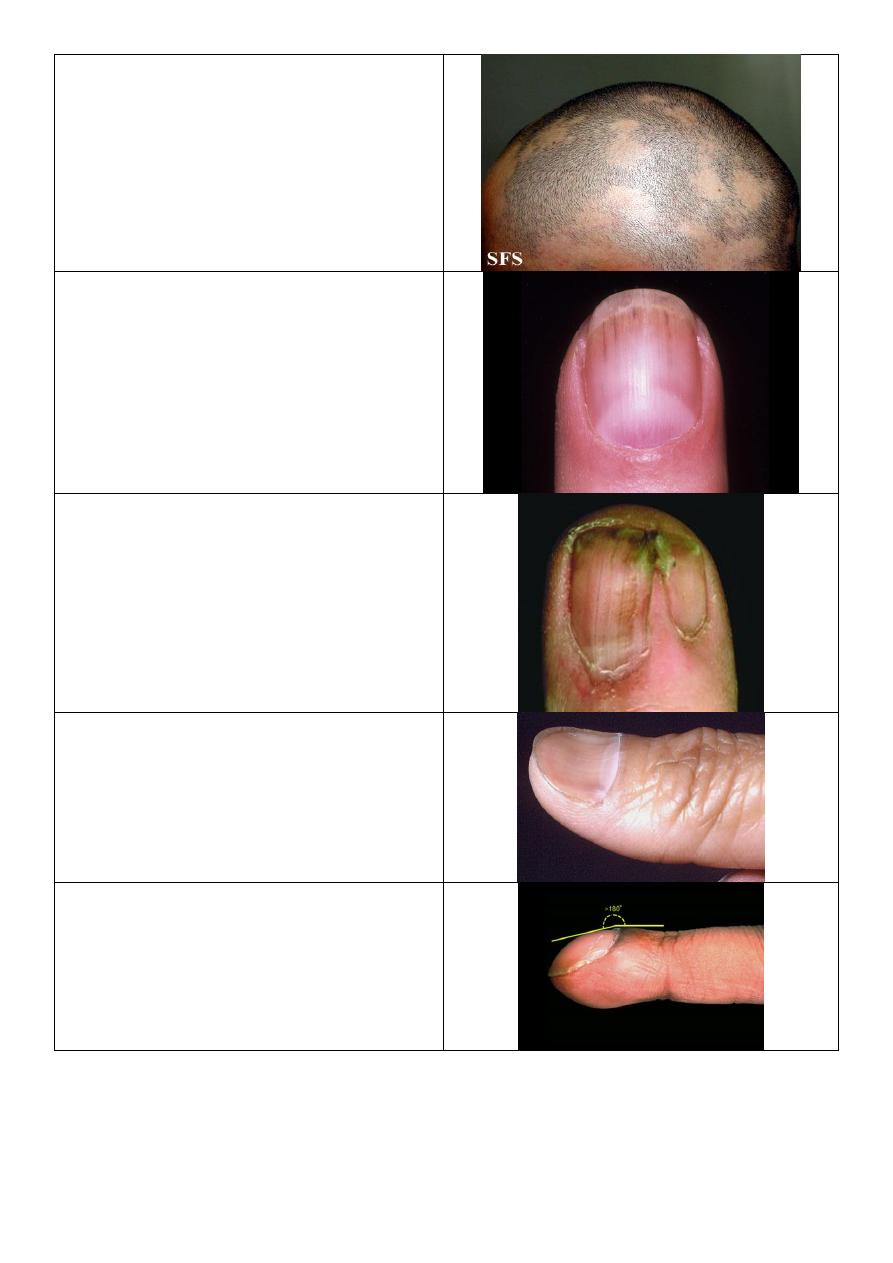
Vitiligo:
o Well defined.
o Hypo pigmented.
o Not scaly.
o Everywhere.
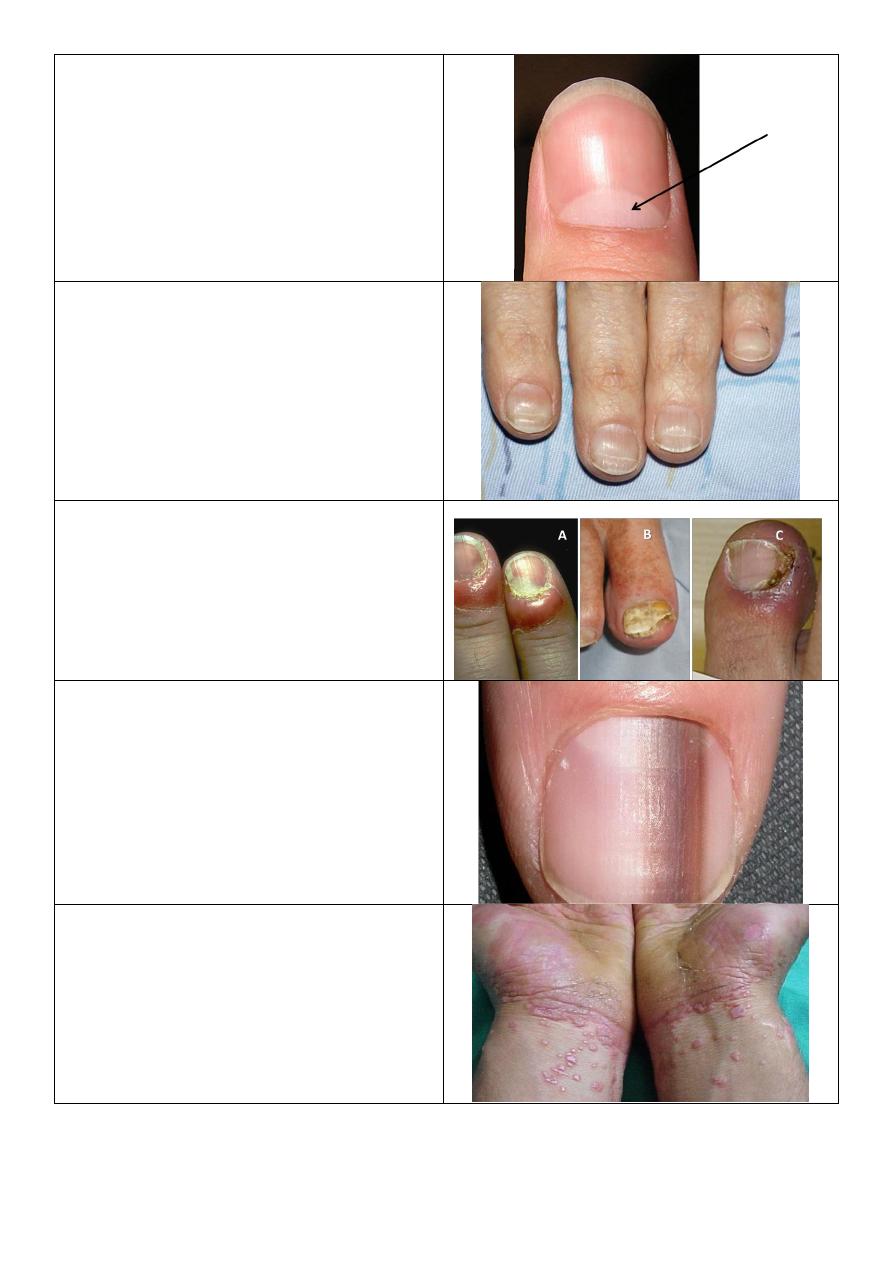
Tenia versicolor:
o Well defined.
o Hypo pigmented.
o Scaly.
o Mainly in the trunk and neck.
o Wood light and KOH exam.
15
Generalized hair loss:
Hair:
o Anagene (active growing) black pulp.
o Telogene (resting stage) white pulp
of hair.
Telogene effluvium: ---------------------->
o Sugery delived infecton.
o Chronic problem.
Anagene flovam: -------------------------->
o Cytotoxic drug.
o Transient problem.
Scalp hair:
o 3 years anagene.
o 3 weeks transient.
o 3 months telogene.
Localized hair loss:
Both:
o Alopecia areata.
o Round, complete hair lose.
o Normal scalp.
Upper:
o Bad prognosis because affect hair lines
and lead to generalized alopecia.
Lower:
o Better prognosis.
o Self-limited.
Cicatrical hair loss:
o Ill-defined bizarre shape of hair loss.
o Scalp: erythematous, crust, scar
formation.
16
Alopecia areata:
o Multiple.
o Bad prognosis.
Splinter hemorrhage:
o Bacterial endocarditis.
Pterygium of nail:
o Splitting of nail.
o Growth of proximal nail fold.
o It is lichen planus.
Koilonychia:
o Increased concavity.
o Occur due to IDA.
Clubbing of nail
17
Nail matrix:
o Make the nail grow forward not
upward.
Beau's line of nail:
o Groove of nails in same area.
o Benefit: calculate the time of onset of
the disease.
Infection of nail and nail fold:
o A: candidiasis: for months or years.
o B: fungal (onychomosis): distal part of
the nail, nail separate from nail bed,
destruction, lower infection of nail.
o C: bacterial: severe pain, red, hot.
Melanonychia
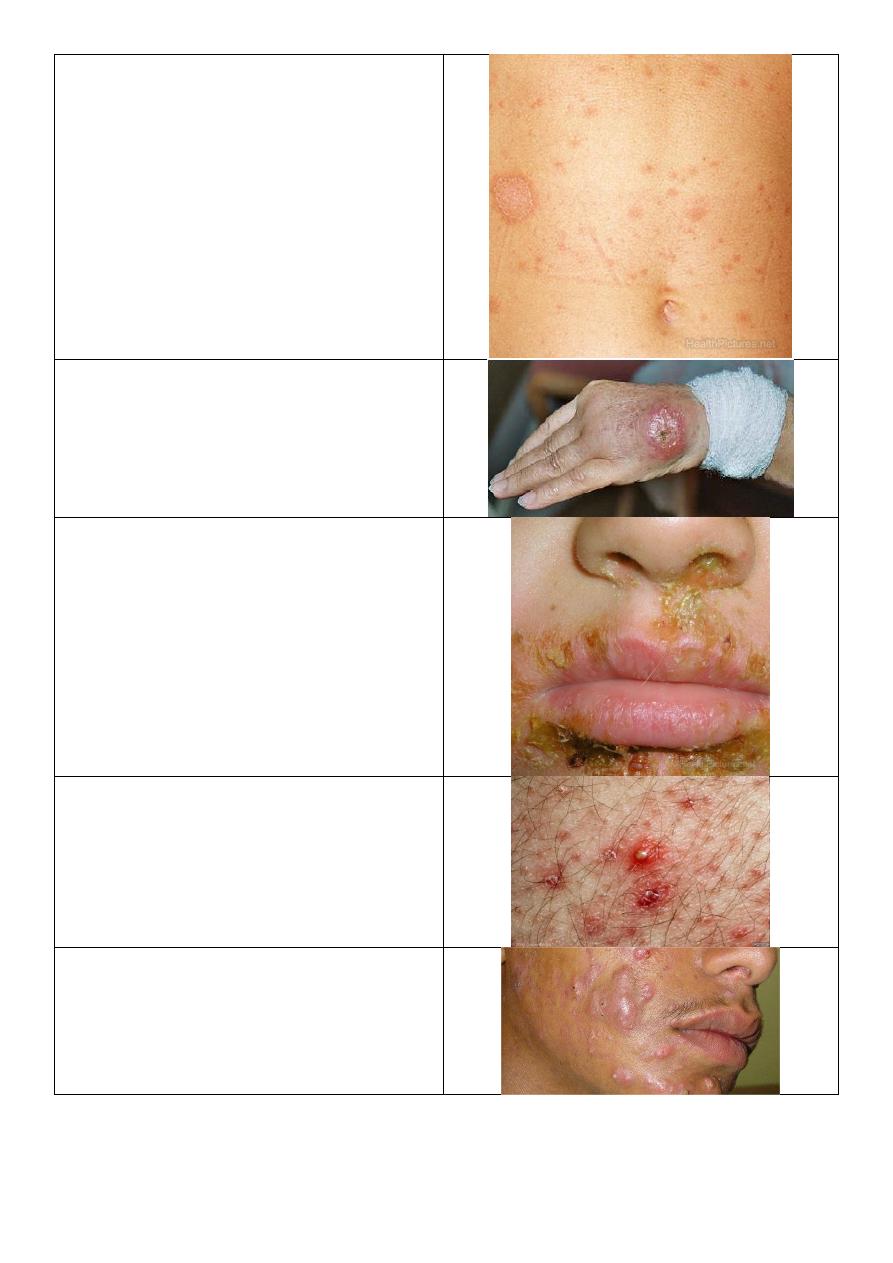
Lichen planus:
o Multiple, purple, plateform, pruritus,
papule.
o Shiny color, fine scales.
18
Pityriasis rosea:
o Eruption.
o Affect trunk and upper thigh and upper
arm.
o Oval shape.
o DDx: psoriasis.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis:
o Painless.
o Chronic.
o Large nodule.
Impetigo:
o Erythema.
o Golden yellow crust.
o Young age.
o Staphylococcus.
Folliculitis:
o Painful lesion.
o Affect hair follicles.
Cystic acne
19
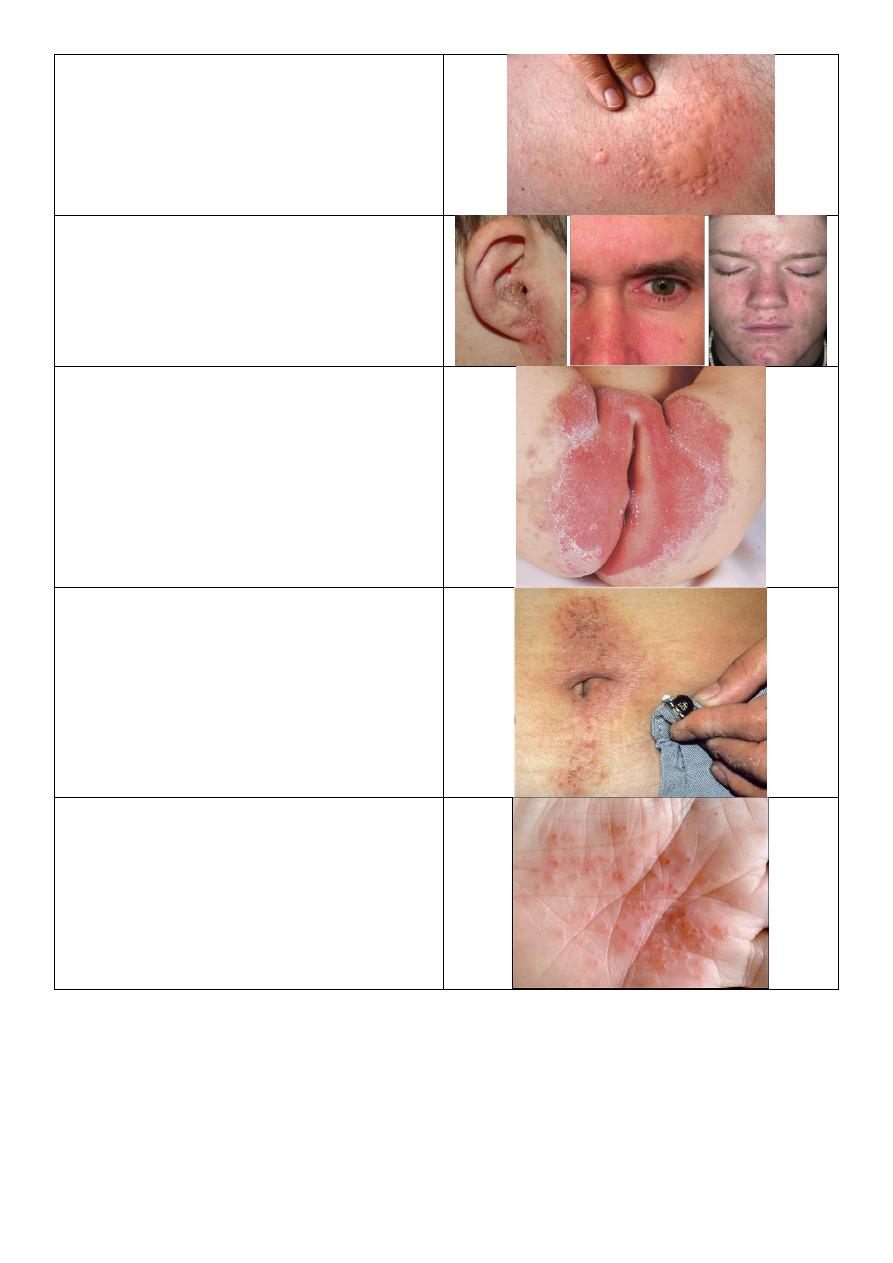
Urticaria
Seborrheic dermatitis:
o Area of predilection (center of body)
ear, glabella, napkin area, eye brows.
Napkin dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Secondary Syphilis:
o Deeply seated vesiculation in palm.
20
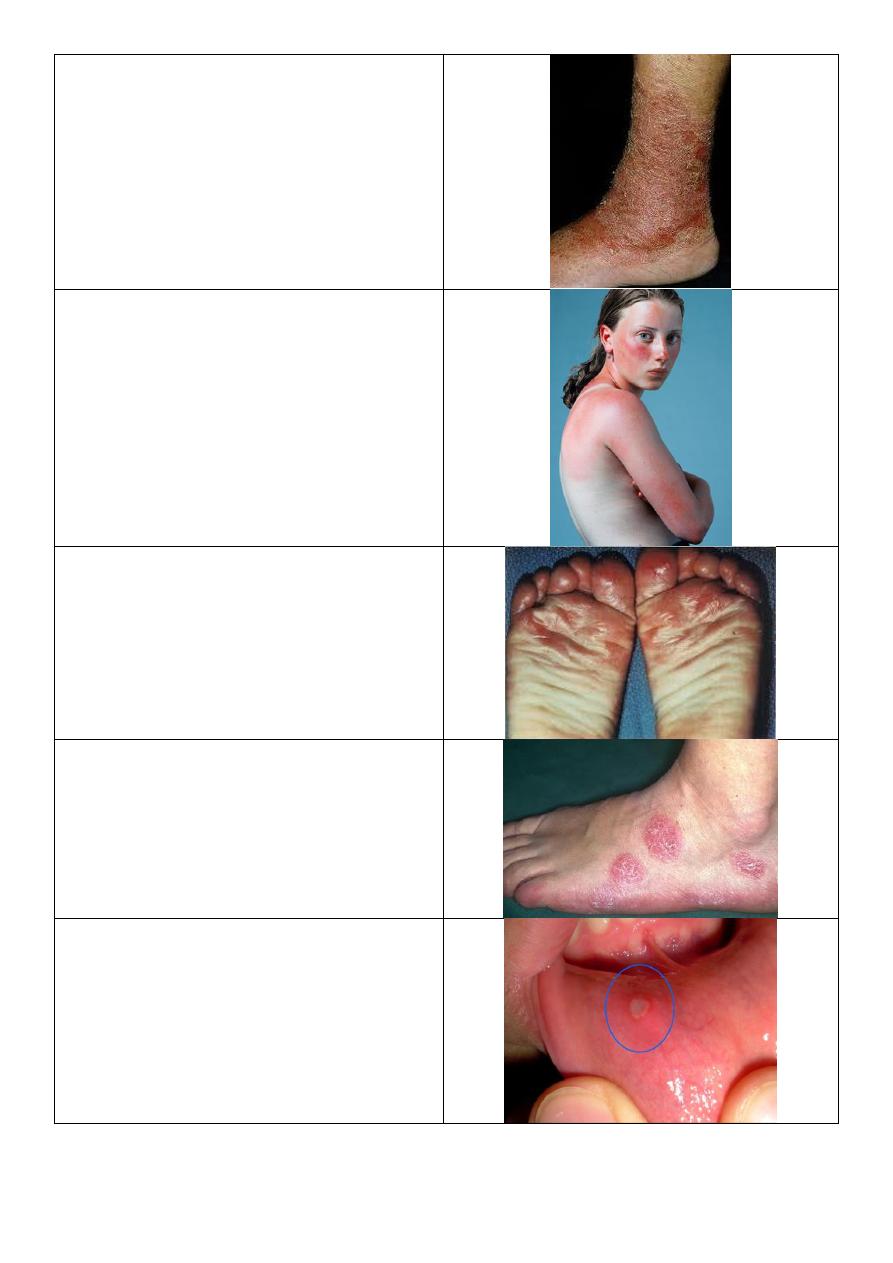
Stasis dermatitis
Photosensitivity:
o Some burn.
o Some areas affected, some not.
Juvenile planter dermatitis:
o Eczematous lesion in forefoot of baby.
Discoid lesion
Aphthous ulcer
21
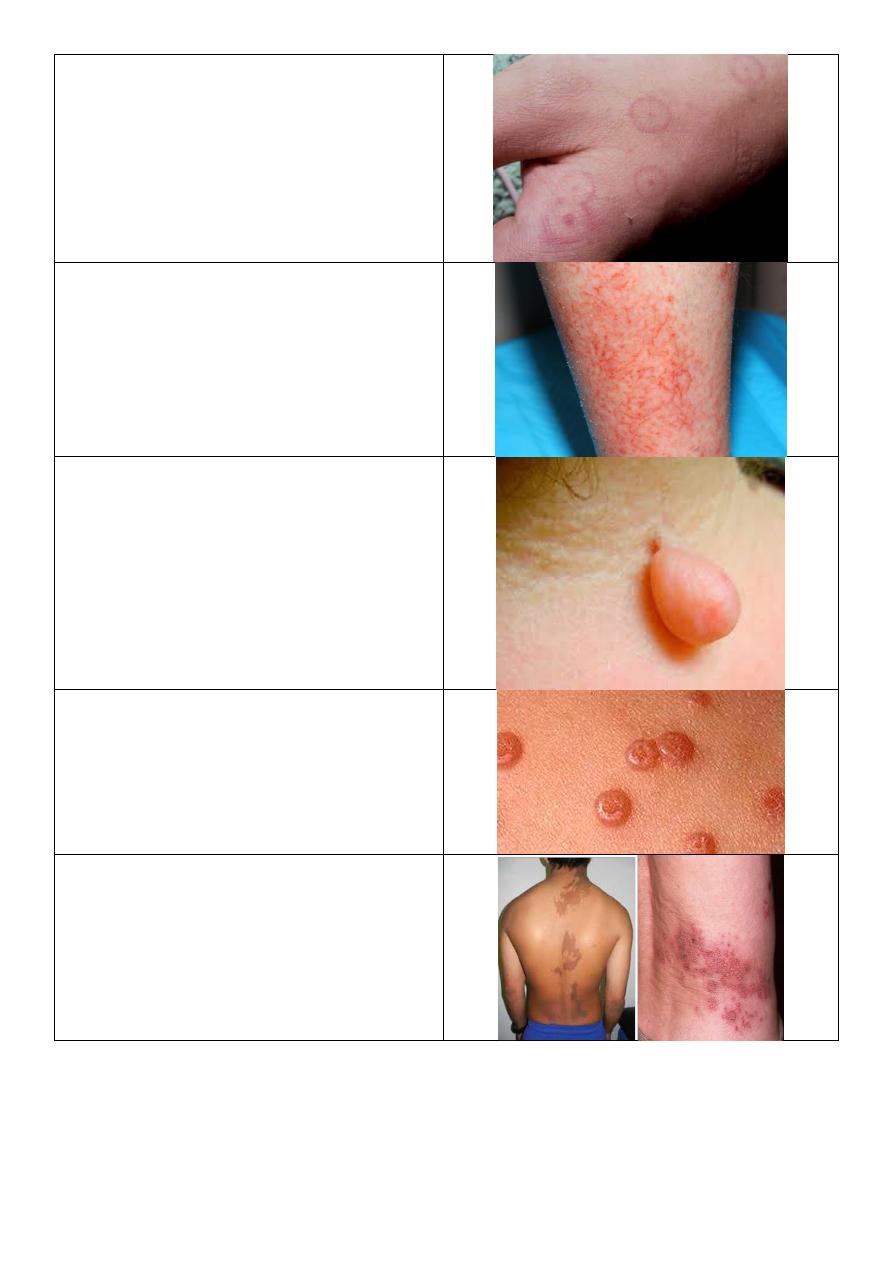
Erythema multiform
Dermatitis crculi
Pedunculated skin tag
Molluscum contagiosum
Unilateral dermatomal
