
AFTER MID
TOTAL LEC: 29
Gynecology
Dr. Shaimaa Kadhim
Lec 29 - Post menopausal bleeding
DR. Shaimaa- LEC 29

)
This lecture was edited by the students. The original lecture is present
on the main website (www.muhadharaty.com)
Introduction:
Refers to any vaginal bleeding in a menopausal woman (12
months or more of amenorrhea).
Age (50 - 55) years with a mean age of 51.5 years.
Post menopausal bleeding is ALWAYS ABNORMAL and should be
investigated.
Menstruation after 55 years is considered abnormal too.
Causes:
Factors Percentages
1) exogenous estrogens 30%
2) atrophic vaginitis & endometritis 30%
3) endometrial cancer 15%
4) endometrial or cervical polyp 10%
5) endometrial hyperplasia 5%
6) miscellaneous (cervical cancer, 10%
uterine sarcoma , urethral caruncle, trauma(.
1) EXOGENOUS ESTROGEN
- Hormone replacement therapy in post menopausal Hysterectomised
patients is estrogens only.
- Hormone replacement therapy in post menopausal Non
Hysterectomised patients is estrogen & progesterone to prevent
endometrial hyperplasia.
(the expected cyclical bleeding in a female taking sequential HRT is not
included within the definition of post menopausal bleeding, but Severe
continuous bleeding lasting more than 4 months after HRT use is
considered abnormal and should be investigated).
2) GENITAL TRACT ATROPHY
absence of estrogen leads to thin, dry epithelium with alkaline PH < 7,
hence the vagina shrinks in diameter, splits & tears easily.
Treatment: HRT
3) ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA
90
% presented with abnormal uterine bleeding.
Screening only for high risk population by:
1. Pap smear ( which can show endometrial cells with carcinomatous
changes)
2. Transvaginal ultrasound
4) URETHRAL CURUNCLE
Small fleshy outgrowth of the distal edge of the urethra that bleeds on
touch (the patient mistakes it as vaginal bleeding).
Treatment: excision or curettage
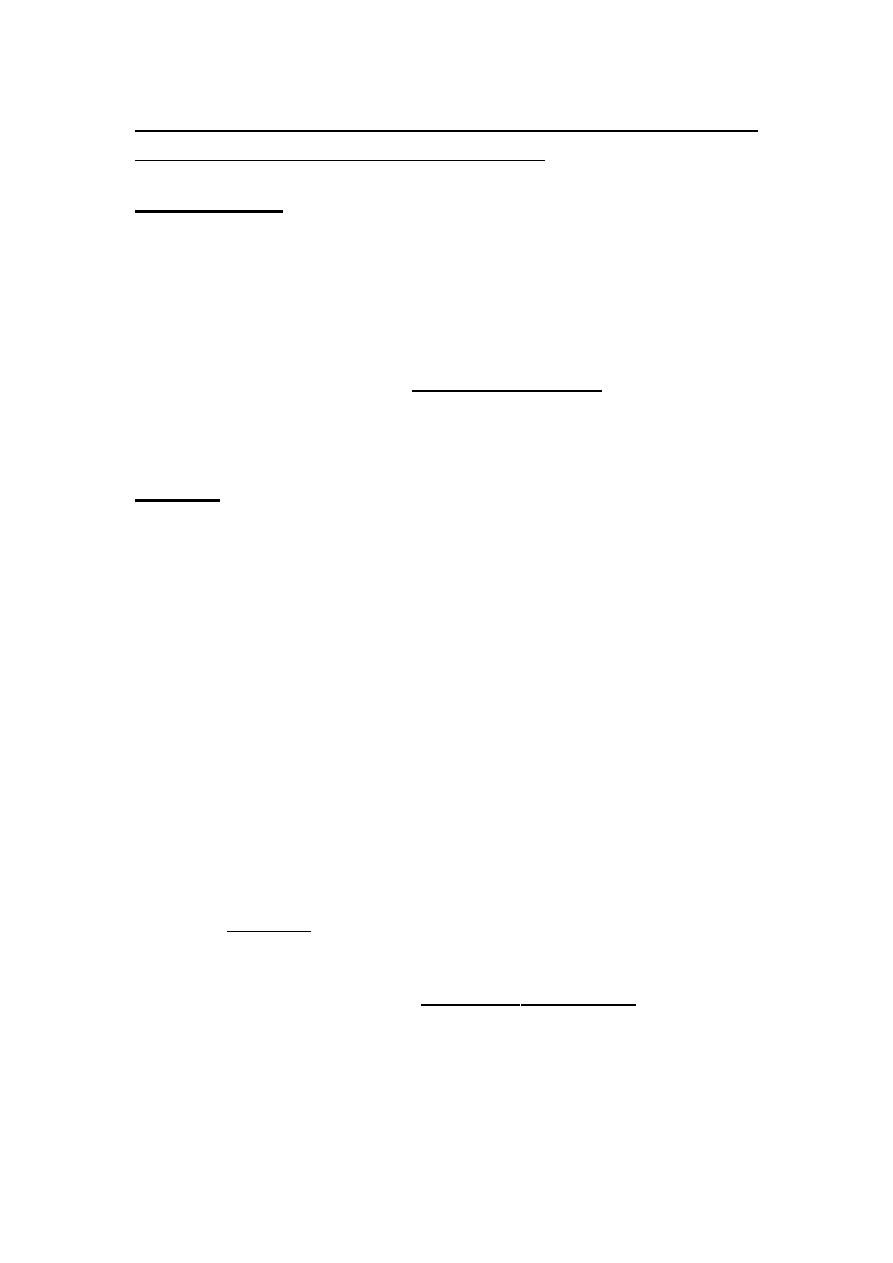
5) ENDOMETRIAL AND CERVICAL POLYP
most of them are benign. Incidence of malignancy is 1%.
i.e. Malignant tumors can present as
polypoid mass. (but polyps
themselves are benign. They could be multiple and are usually presented
as post coital bleeding).

Managment:
History
risk factors of endometrial cancer.
trauma (coitus).
family or personal history of malignancy.
drug history (Warfarin/ Aspirin / HRT)
Examination
General examination (look for Weight loss, emaciation, anemia,
goiter...etc)
Abdominal examination (palpate for the presence of a mass or an
enlarged uterus, ascitis may be present in case of malignancy)
Pelvic examination (there might be fullness of fornices. During
bimanual examination the uterus size can be assessed, so if
enlarged it can be detected)
Speculum examination & pap smear (look for ulcers or abnormal
blood vessels)
Transvaginal ultrasound
Suspicious findings:
1) endometrial thickness > 4 -5 mm.
2) irregular endometrial outline.
3) fluid in the endometrial Cavity.
4) mass.
If endometrial thickness < 4 - 5 mm, only reassure the patient .
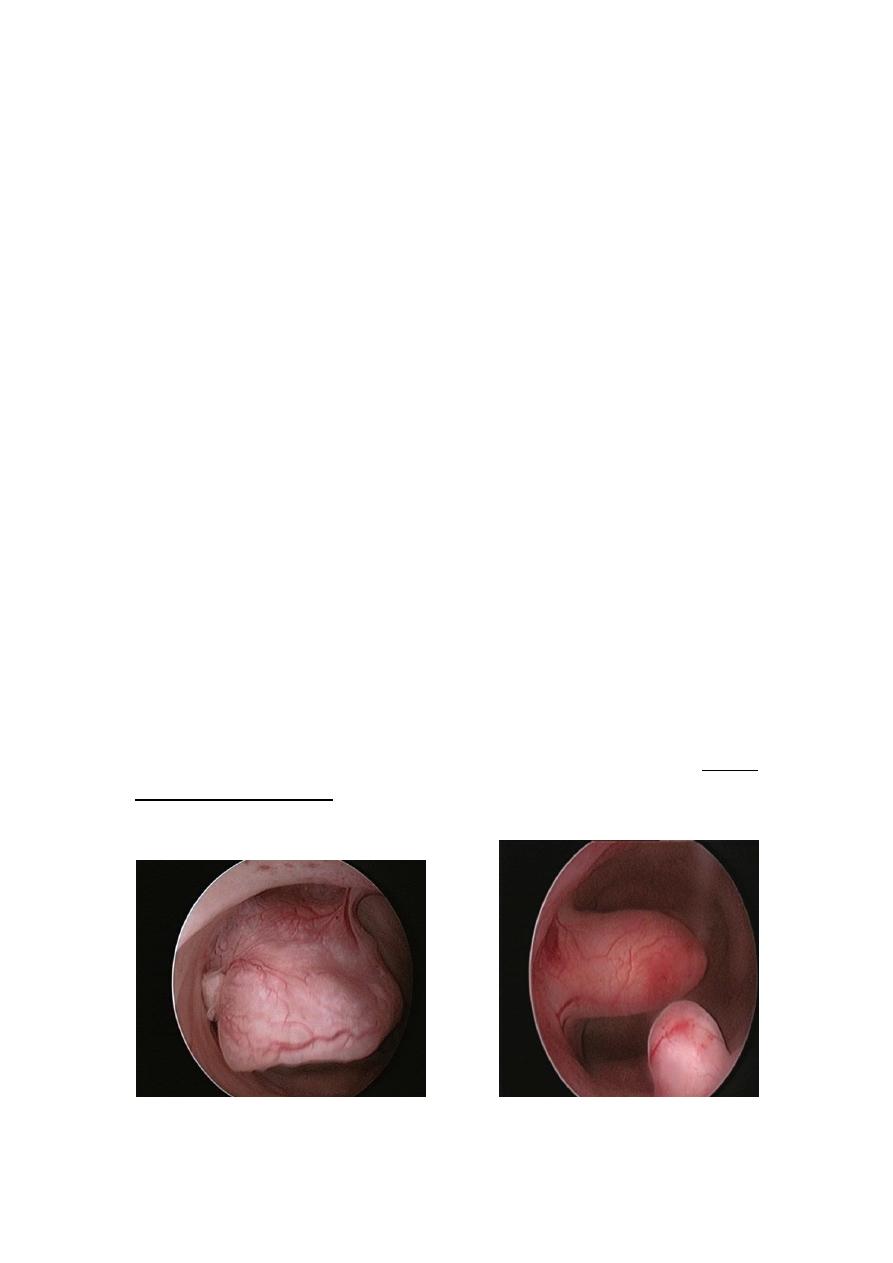
Outpatient endometrial sampling
a) aspiration biopsy (80 - 90% accurate)
o Novak curette: is a thin metallic
tube with a side opening at the
tip, suction with attached syringe
can be applied to remove tissue -
Blunt curettes: are used in case
there is risk of perforation while
the Sharp ones provide a better
sample.
o Pipelle: is a more flexible plastic
tube with a side opening at the
tip. A smaller tube inside the
Pipelle is withdrawn to create
suction.
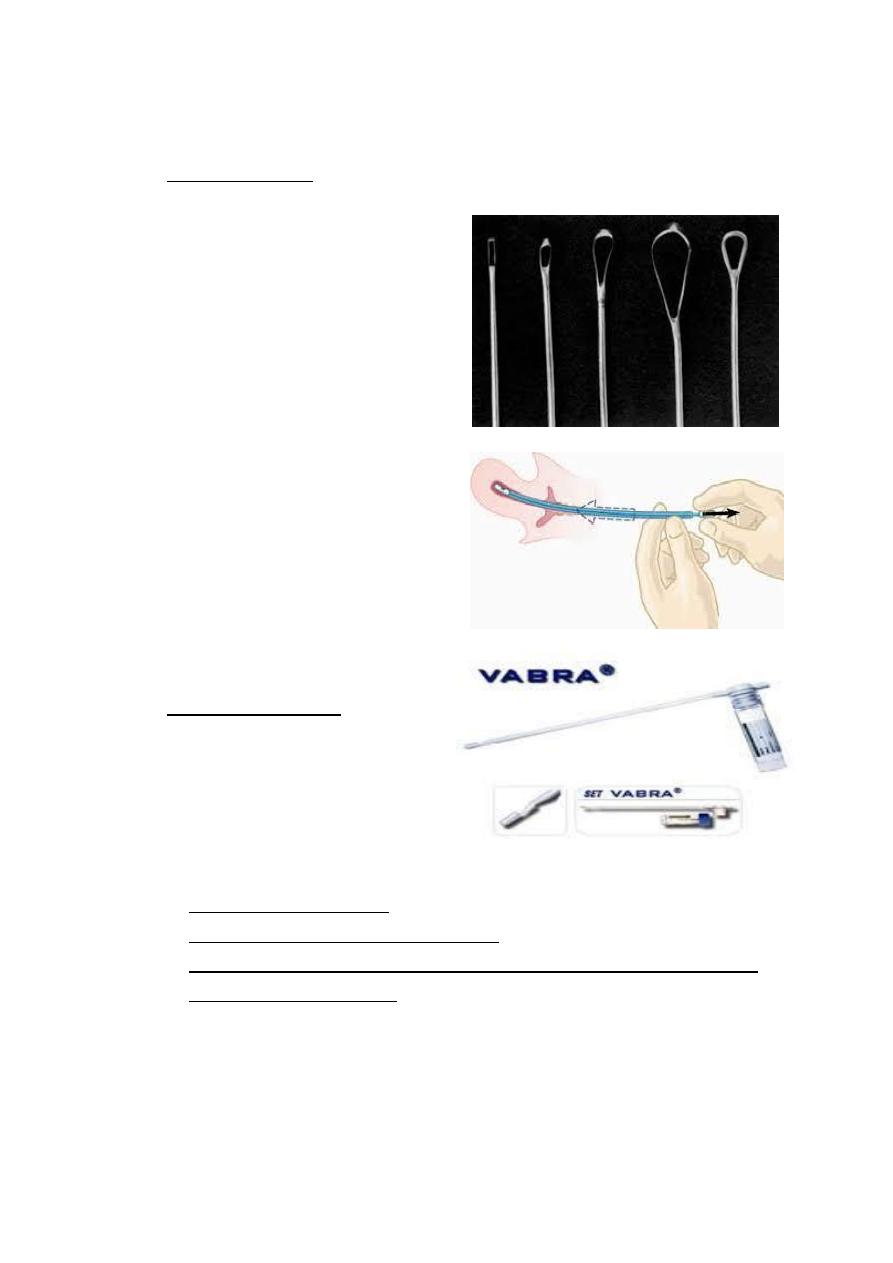
b) aspiration curettage
Ex: Vabra aspirator
Interpretation of results
o if it revealed carcinoma : definitive treatment of cancer.
o if it showed endometrial hyperplasia
: hysteroscopy & D&C
o if it was negative but the bleeding recurs or there is a strong
suspicion of malignancy : Hysteroscopy & D&C.

D&C under general anaesthesia is Indicated in:
i.
unsuccessful outpatient sampling.
ii.
inadequate sample for interpretation.
iii.
high suspicion of cancer with negative outpatient biopsy.
Hysteroscopy
Direct inspection of endometrial cavity.
Detect 95% of intrauterine abnormality.
Sensitive in identifying polyp or sub mucosal fibroid.
Can be used as outpatient procedure.
