Objectives;
1- Pathogenicity of E . Histolytica infection.2-Factors affecting amoebic infection.
2- Pathological anatomy of intestinal amoebiasis.3- Complications of intestinal amoebiasis.
4- Extra-intestinal amoebiasis.Pathogenicity
Factors affecting the severity of amoebic infection depends on:1.Host factors(immunity,intestinal flora,diet,nurishment)
2.Parasite factors(strain,size of inoculum).
3.Enviromental factors .
• Pathogenicity
• --The first step in the pathogenicity of E. histolytica
• infection includes colonization of the trophozoites on
• Intestinal mucosa which leads to adhesion of troph.
• On wall of intestine.
• .
• --The second step includes destruction and invasion of
• Intestinal wall and phagocytized of dead epithelial cells.
Factors affecting colonization of the trophozoites.
1.Infective dose: Number of active Trophozoite in contact with intestinal mucosa depend on number of viable mature cysts ingested by the host.2.Amount of food: Bulky food does not give opportunity for the parasite to be colonize.
.
3.Hypermotility of bowel (stasis) give less
chance for the parasite to become incontact with mucosa, this explains the high
rate of colonization in cecal area because of
reduced peristalsis.
After establishment of colonies on
intestinal mucosa, the trophozoite starts topenetrate intestinal wall.
Factors affecting destruction and invasion of intestinal wall
1.Motility of the parasite: more active parasite give more chance for penetration. Amoebae enter intestinal mucosa by their pseudopodial movements which cause displacement of the cells.
2.Bacteria: number of bacteria present in the intestine enhanced enterance of amoebae in the wall of intestine.
. 3- Injuries in the wall of intestine e.g. Salmonella or Shigella Infections
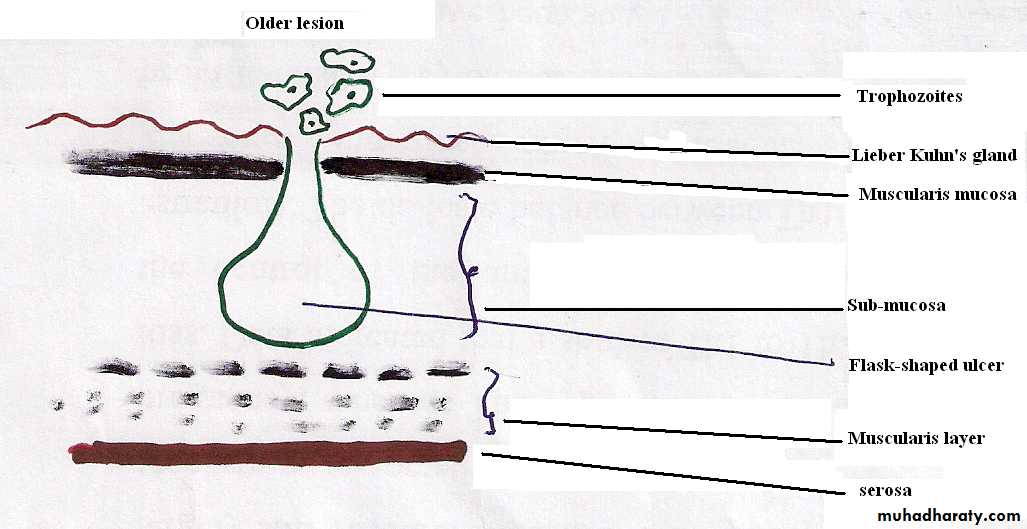
4.Enzymes: virulence strain of E. histolytica has the ability to secret enzymes e.g. cytolytic enzymes which cause lysis of epithelial cells.Pathological anatomy of intestinal amoebiasis:The trophozoites multiply and colonize in glandular crypts of large intestine and adher to intestinal mucosa which leads to the formation of early lesion.
.Early lesion: Nodular elevation with a tiny opening
Early lesion is a tiny area of necrosis on superficial mucosa with minute entry site and exhibiting a nodular elevation. These lesions seperated from one another by intact epithelium.
Flask Shape Ulcer
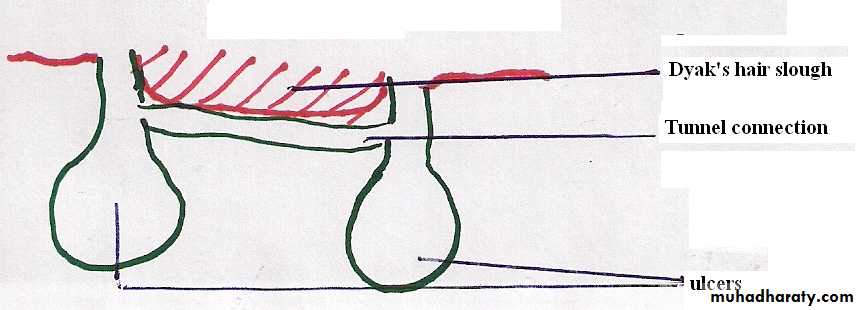
Sometime the dissolution of tissues may become so extensive resulting in a tunneled connection which occurs between two or more lesions, which lead to cutting off the blood supply to the overlying layers, the surface sloughs off and this sloughed area is called Dyak's hair slough.
A primary ulcer can cause rupturing of the bowel and can cause intestinal perforation and peritonitis.
Entamoeba histolytica Pathology
As a result of inflammatory process, fibrous thickening may result due to degenerative proliferation of connective tissues which make the surface of intestine irregular and this shape of intestine surface is called Sea Anemone ulcer. Sometimes invasion of serosa may result by further penetration which leads to perforation of large intestine.Complications of Intestinal Amoebiasis
1 - Appendicitis.
2 - Perforation.
3 - Peritonitis.
4-Haemorrhage.
5 - Amoeboma or amoebic granuloma: a tumor-like mass in the wall of intestine it is firm, nodular inflammatory thickening around an ulcer occuring mostly in cecum and may lead to intestinal obstruction. Amoeboma may be confused with neoplastic growth, tuberculosis or actinomycotic granulomas, but may be diagnosed by biopsy, serology and response to antiamoebic treatment.
6 - Extra-intestinal amoebiasis
Extra – intestinal amoebiasis
Extra – intestinal amoebiasis is secondary to intestinalinfection, this may occurs in patients with clinical
dysentery and in those with mild infections and only
trophozoites are found in infected tissues.
Usually trophozoites are disseminated by blood stream or
by direct extension from intestinal lesion or through
fistula. The liver is the most frequent involved, although
the amoebae may be carried to any organ of the body.
.
Amoebic liver abscess
usually result by direct extension from intestinal ulcer.or byhematogenous spread. The early liver abscess is small, oval
or rounded mass, usually solitary and occurs in right lobeof the liver. As the lesion increase in size, the center
liquefied and the wall thickened and the contents become
chocolate-brown in color resembling Ancovy SauceAmoebic liver abscess
The following three zones may be recognized grossly and under the microscope:. An inner necrotic center containing dead liver cells, dead amoebae mixed with bile, fat, and RBC.
. Median zone of connective tissue strands
. Outer zone of healthy liver cells invading by amoebae
Amoebic lung abscess
Pulmonary amoebiasis may usually result fromdirect extension of hepatic abscess through the
diaphragm to the lung and less frequently from
blood stream.It is usually occurs in right lung.
Amoebic brain abscess:
This infection rarely occurs and it is very difficult to diagnosed.Trophozoites can reach the brain through blood
stream and cause amoebic brain abscess and
amoebic meningoencephalitis.Cutaneous amoebiasis
Cutaneous amoebiasis is a rare reported complication ofamoebic infection ,it involve abdominal wall as aresult of
syrgical interference of colostomy or amoebic liver abscessaspirate or directly from fistulous tracts that arise from
intestinal ulcer or hepatic abscess.Also it involve anal andperianal areas by direct extention of rectal lesion .Genital
organs may involved mainly in homosexuals.
Summary
-Factors affecting pathogenicity of amoebic infection includes ; host,parasite and environmental factors.
-The first step in pathogenicity of E.histolytica infection
include colonization of trophozoites in glandular crypts oflarge intestine which lead to adhesion on intestinal
mucosa, followed by destruction and invasion of intestinal wall .-Flask-shaped ulcer is diagnostic for E. histolytica infection.
-Complications of E. histolytica infection includes ;appendicitis ,perforation,Peritonitis ,hemorrhage,amoeboma and extra-intestinal amoebiasis.
-Exta-intestinal infections occurs mainly in livereither directly from intestinal lesion or through blood circulation .
-Only trophozoites seen in tissue infections.Quiz