
Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
1
Bacteriology
Introduction to Microbiology
Learning Outcomes:
At the end of this lecture, the students should be able to:
1. Sate the general characteristics of microorganisms: Procaryotic / Eucaryotic
and viruses.
2. Describe the bacterial structure and composition in comparison with
eukaryotic cells (e.g., nucleoid and cytoplasm).
Microbiology:
Is the science that studies a great variety of living organisms that are too small for
us to see without of microscope- the microbes, or microorganisms, and that exist as
single cells or cell clusters; it also includes viruses, which are microscopic but not
cellular.
Microorganisms have a tremendous impact on all life and the physical and
chemical makeup of our planet. They are responsible for cycling the chemical
elements essential for life, including carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, hydrogen, and
oxygen; more photosynthesis is carried out by microorganisms than by green
plants.
Humans also have an intimate relationship with microorganisms; more than
90% of the cells in our bodies are microbes.
Important features of Microbes:
Microbes that cause human infectious diseases belong to five major groups of
organisms: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminthes, and viruses. These microbes have
many important characteristics features shown in Table 1-1, but the most
significant one is that bacteria, fungi, protozoa and helminthes are cellular whereas
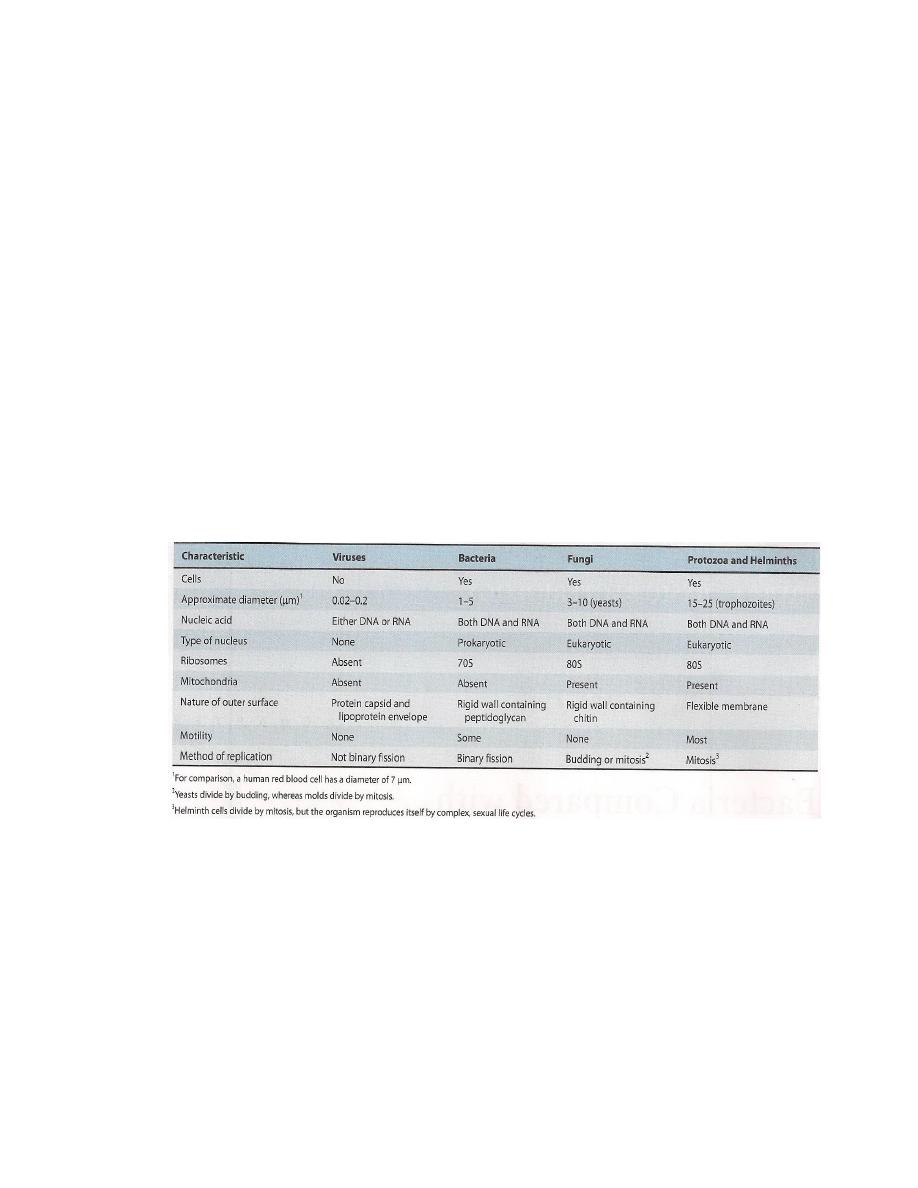
Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
2
viruses are not but can replicate only within cells. This difference is based on the
following criteria:
1- Structure: Cells have nucleus, while viruses are not cells and do not have
a nucleus.
2- Method of replication: Cells replicate either by binary fission (e.g.,
bacteria) or by mitosis (e.g., fungi). In contrast, viruses disassemble,
produce many copies of their nucleic acid and protein, and then reassemble
into multiple progeny viruses.
3- Nature of the nucleic acid: All cells contain both DNA and RNA, whereas
viruses contain either DNA or RNA, but not both.
Table 1-1 Comparison of Medically important Organisms
Discovery of Microorganisms & germ theory
-Antony van Leewenhock (1632-1723) who invented the first
microscope (50-300x), was first to accurately observe and describe
microorganisms.

Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
3
-
The French chemist and microbiologist Louis Pasteur, the English
surgeon Joseph Lister, and the German physician Robert Koch are
given much of the credit for development and acceptance of the germ
theory, the theory that certain diseases are caused by the invasion of the
body by microorganisms.
Cell structure
Historically, it was the microscope that first revealed the presence of bacteria, the
secrets of cell structure.
Today, it remains a powerful tool in cell biology.
Optical Methods
1- The light microscope: Several types of light microscopes are commonly used
in microbiology:
1) Bright-Field Microscope: These microscopes generally employ a 100-power
objective lens with a 10-power ocular lens, thus magnifying the specimen
1000 times.
2) Phase Contrast Microscope: The phase contrast microscope was developed to
improve contrast differences between cells and the surrounding medium,
making it possible to see living cells without staining them; with bright-field
microscopes, killed and stained preparations must be used.
3) Dark-Field Microscope: Is a light microscope in which the lighting system
has been modified to reach the specimen from the sides only.
4) Fluorescence Microscope: Is used to visualize specimens that fluoresce,
which is the ability to absorb short wavelengths of light (ultraviolet) and give
off light at a longer wavelength (visible).

Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
4
5) Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscope: Microscopes employ a
polarizer to produce polarized light. The polarized light beam passes through
a prism that generates two distinct beams; these beams pass through the
specimen and enter the objective lens where they are recombined into a
single beam. Because of slight differences in refractive index of the
substances each beam passed through, the combined beams are not totally in
phase but instead create an interference effect, which intensifies subtle
differences in cell structure.
2- The electron microscope: The superior resolution of the electron microscope
is due to the fact that electrons have a much shorter wavelength than the
photons of white light so it enlarges objects up to 0.01-0.2 Mm.
1) Transmission electron M. (TEM)
2) Scanning electron M. (SEM).
3- Confocal Scanning Laser Microscope: couples a laser light source to a light
microscope to get 3D image
4- Scanning Probe Microscopes: measure surface features by moving a sharp
probe over the object's surface.
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
Cells have evolved into two fundamentally different types, eukaryotic (Fungi and
Protozoa) and prokaryotic (e.g., Bacteria).
Eukaryotes and prokaryotes are organisms because they contain all of enzymes
required for the replication and possess the biologic equipment necessary for the
production of metabolic energy so they are distinguished form viruses which
depend upon host cells for their necessary functions.

Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
5
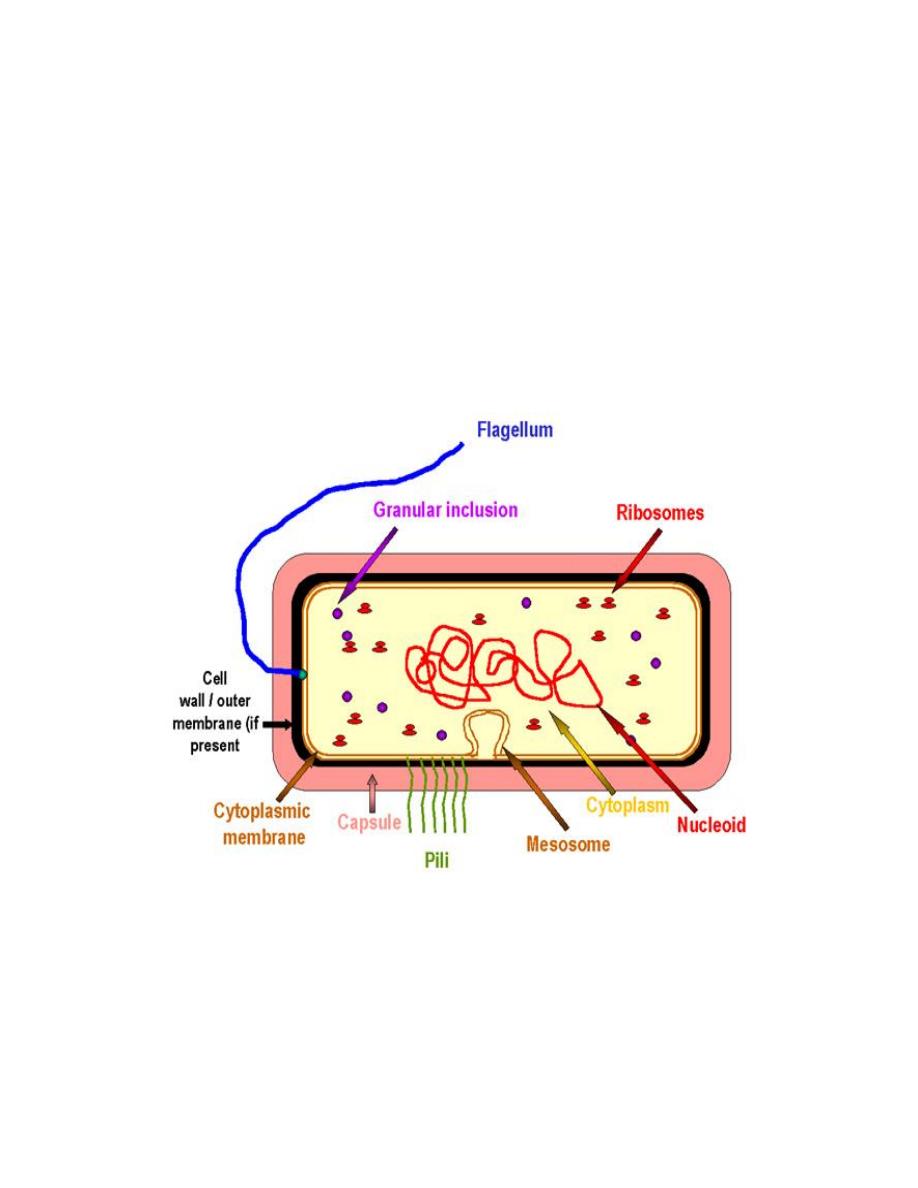
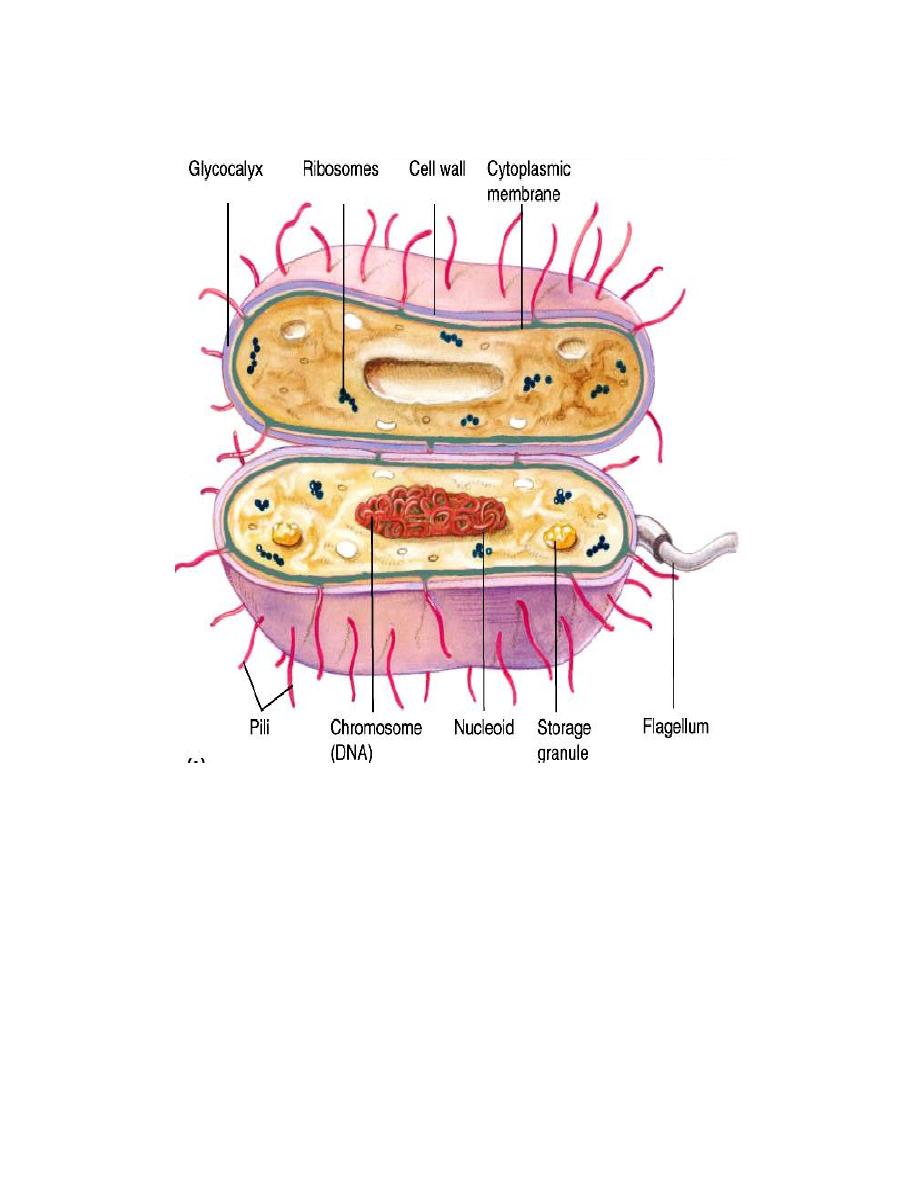
Bacterial cell structure
1- The Nucleoid
The prokaryotic cells have nucleoid filled with DNA fibrils, which
equivalent to the eukaryotic nucleus and can be seen in light microscope.
Prokaryotes generally possess only a single circular chromosome. Since
there is no nuclear membrane, the chromosome is bound to a specific site on
the cell membrane - the mesosome, this attachment plays a role in the
separation of the two sister chromosomes following replication. The number
of copies of these chromosomes in a cell depends on the growth conditions.
Bacterial nucleoid contains no nuclear membrane and no histones, there is
little resemblance to the eukaryotic nucleus. (Figures 1A, B, and 2).
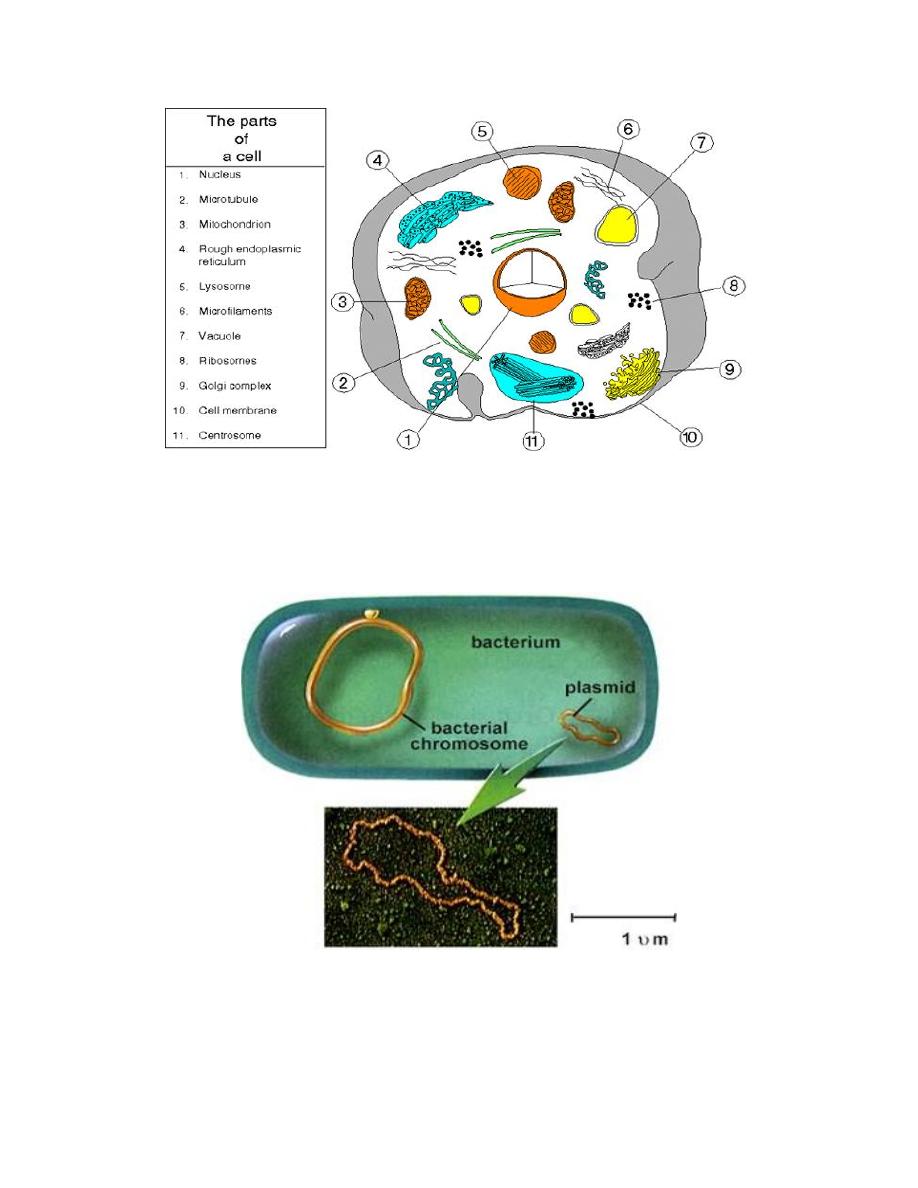
2. Cytoplasmic structure
The prokaryotic cell, in contrast to the eukaryotic cell, is not
compartmentalized. Nuclear membranes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi
body, phagosomes, lysosomes and mitochondria are not present, so the
electron transport enzymes are located in cell membrane instead of
mitochondria (Figures 1A, B, and 2).
The bacterial cytoplasm contains several different types of granules that
serve as storage areas for nutrients and stain with certain dyes. When the
source of nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus is limited or when the pH is low,
excess carbon in the medium is converted to starch and glycogen. These
granular are then used as carbon source when protein nucleic acid synthesis
is resume. For example, volutin granules is a reserve of high energy stored
and it stains red with methylene blue dye, so then it appears as a
metachromatic granules that are present in Corynebacterium diphtheria.
Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
6
Bacterial ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis as in eukaryotic cells,
but they differ from eukaryotic ribosomes in size and chemical composition.
The bacterial one is smaller than eukaryotic ribosome.
Bacterial Plasmids are extrachromosomal, double-stranded, circular DNA
molecules that are capable of replicating independently of the bacterial
chromosomes (Figure 3).
A
Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
7
Figure 1: The prototype bacterial cell
B
Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
8
Figure 2:
An animal cell
Figure 3: Bacterial Plasmid

Lec.1
Dr. Inas Khalifa Al-Sharquie
2012-2013
9
Summary
• Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa and viruses are the agents of human infectious
diseases
• There are two fundamentally two types of cells: Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes.
• Viruses are not cells and do not have a nucleus.
• Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles
• Eukaryotes may be multicellular with highly specialized cells
• Certain structures are unique to eukaryotes
Main References:
1. Jawetz, Melnick and Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology (Brooks,
Butel,Morse), 2010.
2. Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, 12th Edition, (2012).
