Candida Species
EpidemiologyMost common fungal pathogen
4th most common nosocomial infection
75% of women may become infected at least once in their lifetime
Common infection in patients with AIDS , cancer ( ex:-leukemia)
Most common fungus affecting immunecompromised
Mycology
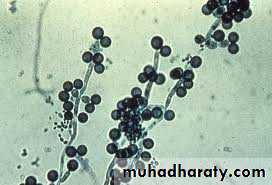
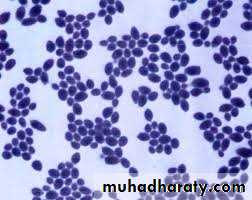
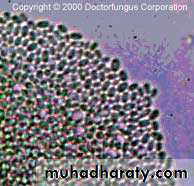
Yeast like fungusThere are 6 species that infect man
C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, C.kusei, & C. lusitaniae
The most common species is Candida albicans
Found in mouth , vagina and intestinal tract in small colonies suppressed by immune system and other flora
Candida albicans
Morphology
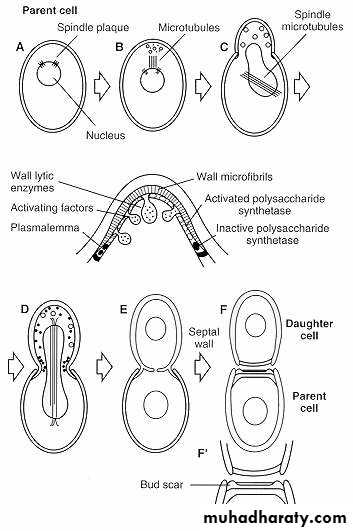
solitary, unicellularreproduction via budding
rounded shape
moist & mucous colonies
Pathogenesis
Surface molecules that permit adherence of the organism to other structures (eg, human cells, extracellular matrix, prosthetic devices)Acid proteases and phospholipases that involve penetration and damage of cell envelopes
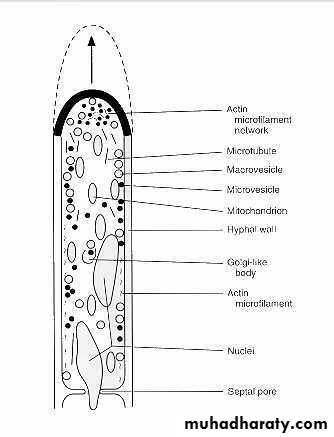
Ability to convert to a hyphal form (phenotypic switching)
Virulence assay of different C. albicans
strains using the skin equivalentFigure 1. skin equivalent before infection
Figure 2. Infection with pathogenic clinical isolate of C. albicans.
After 48 h the yeast penetrates the skin equivalent and destroysthe tissue
Figure 3. Infection with non-pathogenic C. albicans. This strain is not able to penetrate into the tissue and thus behaves as a virulent as shown in the mouse model of systemic infection
How Does It Cause Disease ?Effects on immune system
Disturb immune system
Stimulate the body to form autoantibodies
Induce endocrinopathies
IgA protease
Contain glycoproteins that stimulate mast cells to release histamine and prostaglandins
How Does It Cause Disease Effects of its growth
It assimilates all sugars except lactose.It depresses the activity of lactase.
Dietary carbohydrates are fungal growth promoters and associated with increased adherence of Candida species to mucosal epithelial cells.
Release of toxic fungal metabolites.
Risk Factors of Infection
Physiological:- Pregnancy, age (elderly & infants) ,Diet high in sweets, fruit juices, alcoholTrauma:- Infection, burn wounds.
Haematological:- Neutropenia, cellular immunodeficiency (leukemia, lymphoma, AIDS, aplastic (anemiaRisk Factors of Infection
Endocrinological:- Diabetes mellitus, Addison’s disease, hypoparathyroidismIatrogenic:- Chemotherapeutics, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, antibiotics catheters, surgery
Others:-Intravenous drugs, malnutrition, malabsorption, Chronic Stress
Diseases by C. albicans
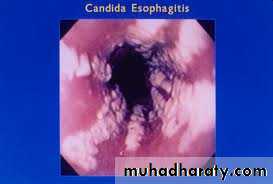
ThrushEsophagitis
Cutaneous candidiasis
Genital candidiasis
Deep candidiasis
Note:- Esophagitis and Deep Candidiasis occur only in immuncompromised patients
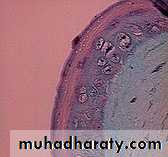
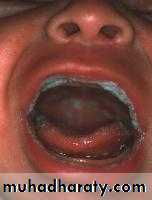
Thrush
Common in infants (Considered normal unless it lasts longer than a couple of weeks.)Diabetics are more likely to get oral thrush because the extra sugar in their saliva acts like food for Candida.
High antibiotics doses or prolonged use increases the risk of oral thrush. Antibiotics kill some of the healthy bacteria that help keep Candida from growing too much.
Poorly fitting dentures are increases the risk of thrush.
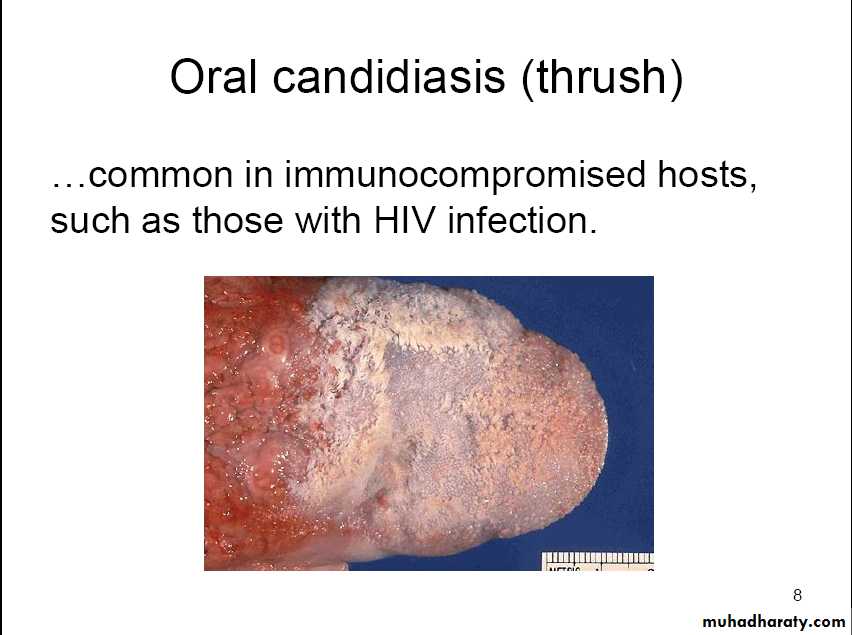
Common in immunocompromised hosts,such as those with HIV infection.
Oral thrush
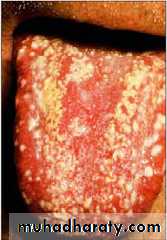
multiple white plaques on lips, gingivae, tongue, and palateThrush appears as whitish, velvety lesions in the mouth and on the tongue. Underneath the whitish material, there is red tissue that may bleed easily. The lesions can slowly increase in number and size.
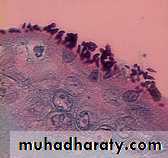
Oropharyngeal ThrushFeatures
Pseudo membranousOropharyngeal ThrushFeatures
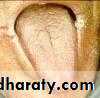
Atrophy of tongue
Oropharyngeal ThrushFeatures
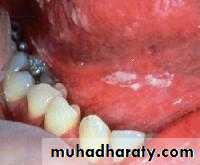
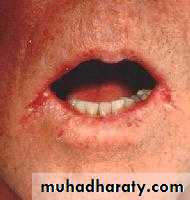
Angular chelitisCandida Esophagitis
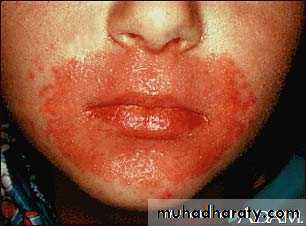
Cutaneous Candidiasis
This child has a large rash caused by Candidiasis, affecting the skin around the mouth. There are also other lesions that aren't connected to the large lesion, called "satellite lesions".
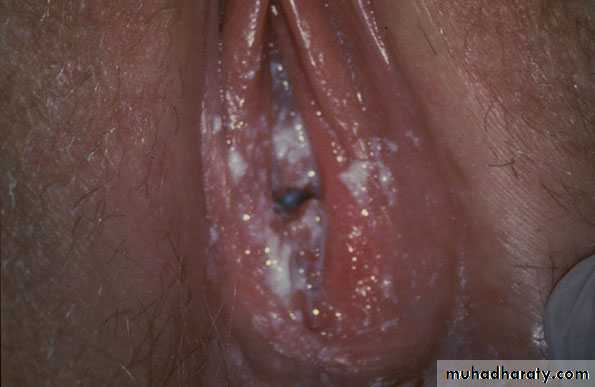
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VVC)
Vulvar component often dominant
Women are often misdiagnosed as having VVC when they really have
- Genital herpes - Contact dermatitis
- Lichen planus - Atrophic vaginitis
- Recurrent BV (Bacterial Vaginosis)
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Deep CandidiasisFour forms of invasive candidiasis
Catheter related candidemiaAcute disseminated candidiasis
Chronic disseminated candidiasis
Deep organ candidiasis
Candidemia
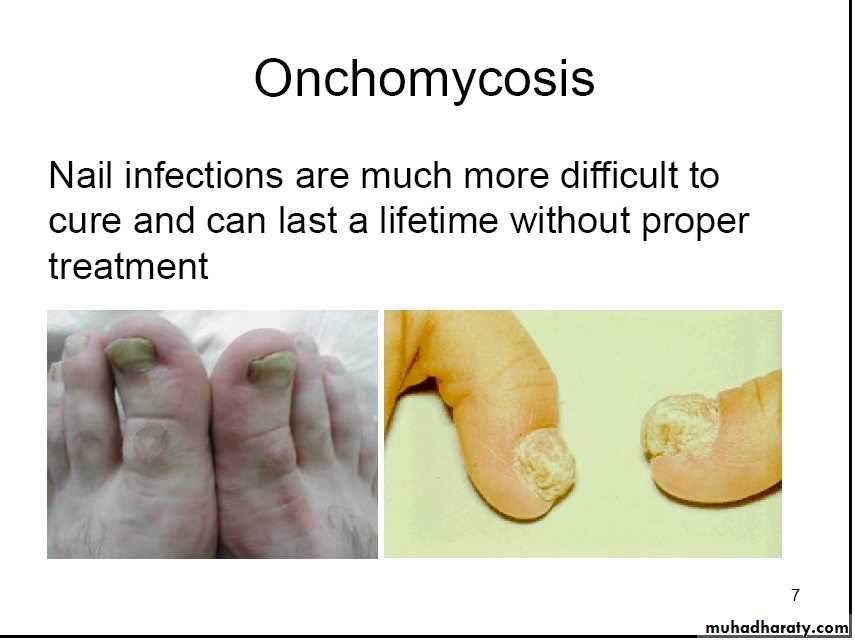
Onchomycosis
Nail infections are much more difficult tocure and can last a lifetime without proper
treatment
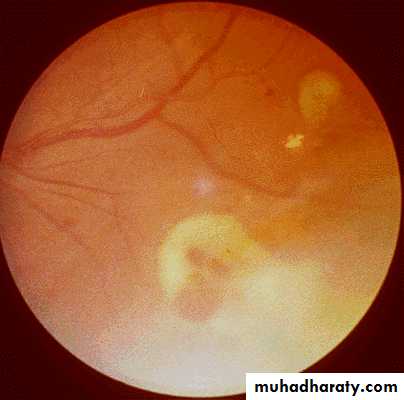
Candidemia
Hematogenous seeding
Spread to the eye Can cause blindnessLaboratory diagnosis
SpecimenScrapings of surfaces
Laboratory diagnosisSlide preparations
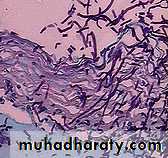
Visualization of pseudohyphae (mycelia) and/or budding yeast (conidia)KOH or saline
Laboratory diagnosisStaining
Lacto phenol blue
Gomoris methylamine sliver stains(GMS)
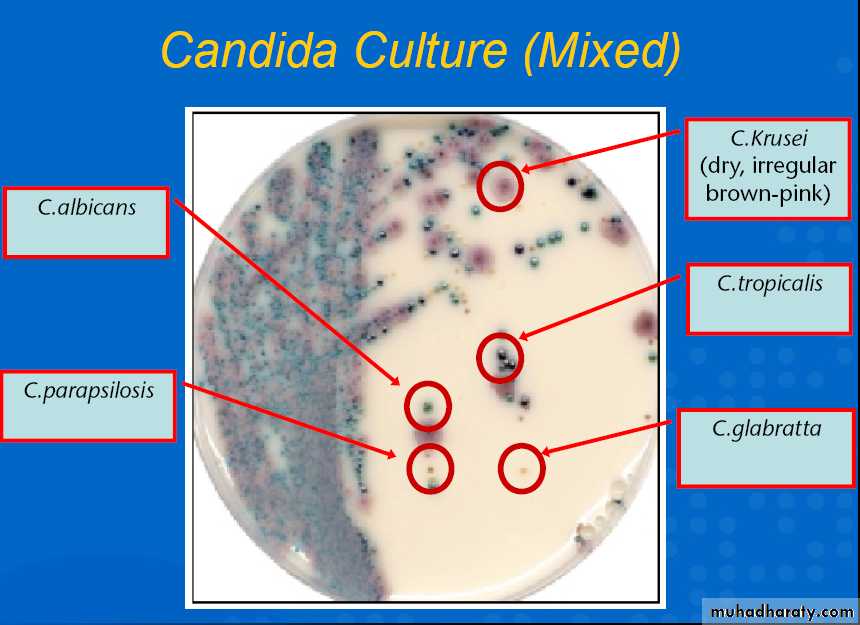
Laboratory diagnosis
CultureSabourauds glucose agar medium
Brain heart infusion.Laboratory diagnosis
SerologyCFT
Latex agglutinationELISA
Fluorescent Abs
Laboratory diagnosis
Other Diagnostic
MethodsSkin test
PCRCandida culture
Immunofluorescence
Treatment of Candida albicans
Dietary :-Eliminate all sugar:
–fruit juice
–white flour
–refined grains
Eat a higher protein, lower carbohydrate and high fiber diet.
Avoid fermented foods including alcohol.
Treatment of Candida albicansAntifungal drugs:-
Amphotericin B (Fungizone)
Clotrimazole (Mycelex)
Fluconazole (Diflucan)
Itraconazole (Sporanox)
Ketoconazole (Nizoral)
Nystatin (Mycostatin)