Obesity
is a state of excess adipose tissue mass.BMI ≥30 obesity
BMI ≥ 25 overweight
abdominal (android or apple-shaped) obesity
generalized (gynoid or 'pear-shaped)obesity
Obesity
Many complications of obesity, as insulin resistance, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, are linked more strongly to intraabdominal than to overall adiposity.Obesity
Prevalence30.5% American adult population had obesity
64% of U.S. adults were overweight4.7% of the population Extreme obesity
Obesity is more common in women and in the poor.
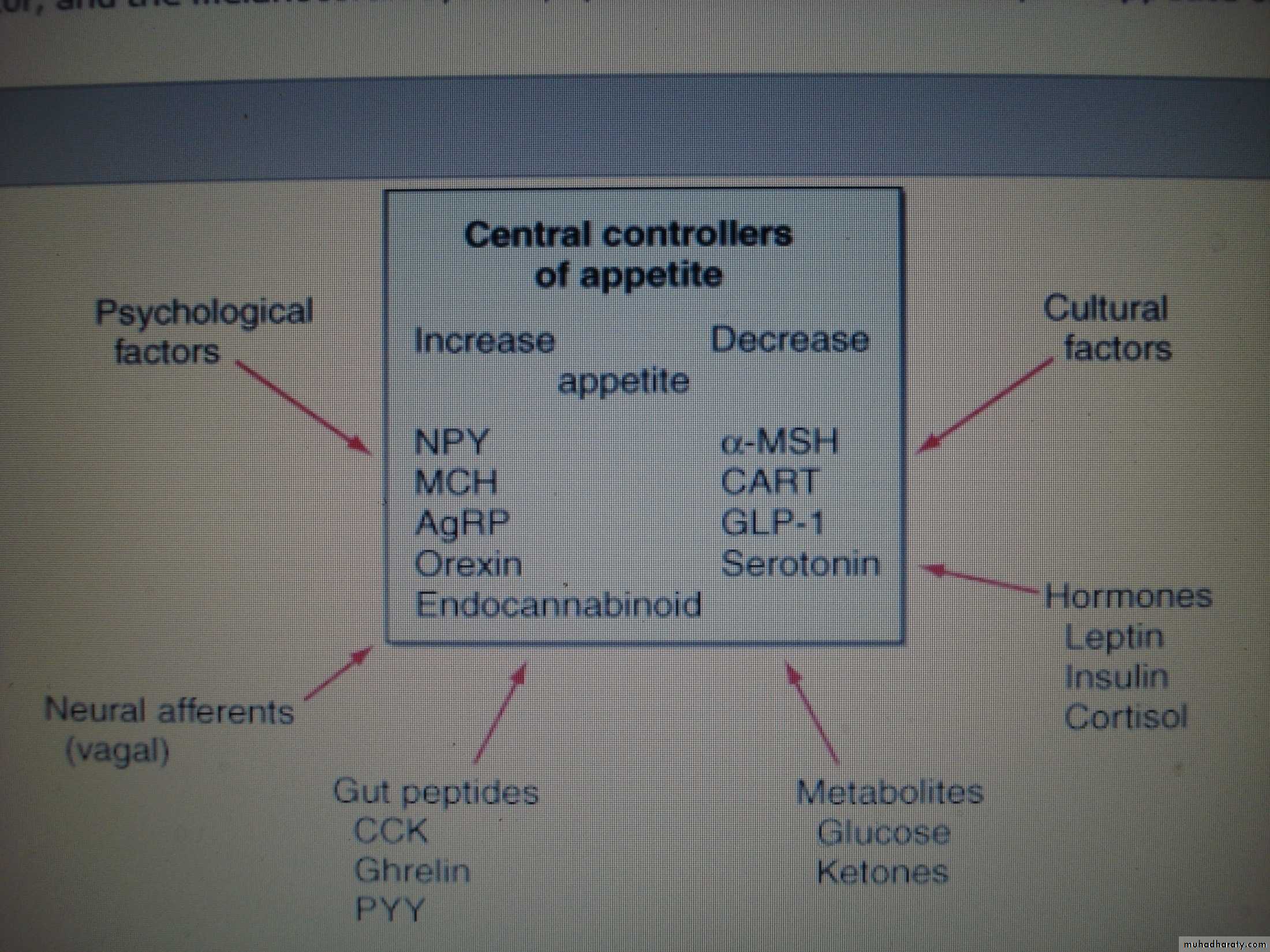
Factors control the appetite
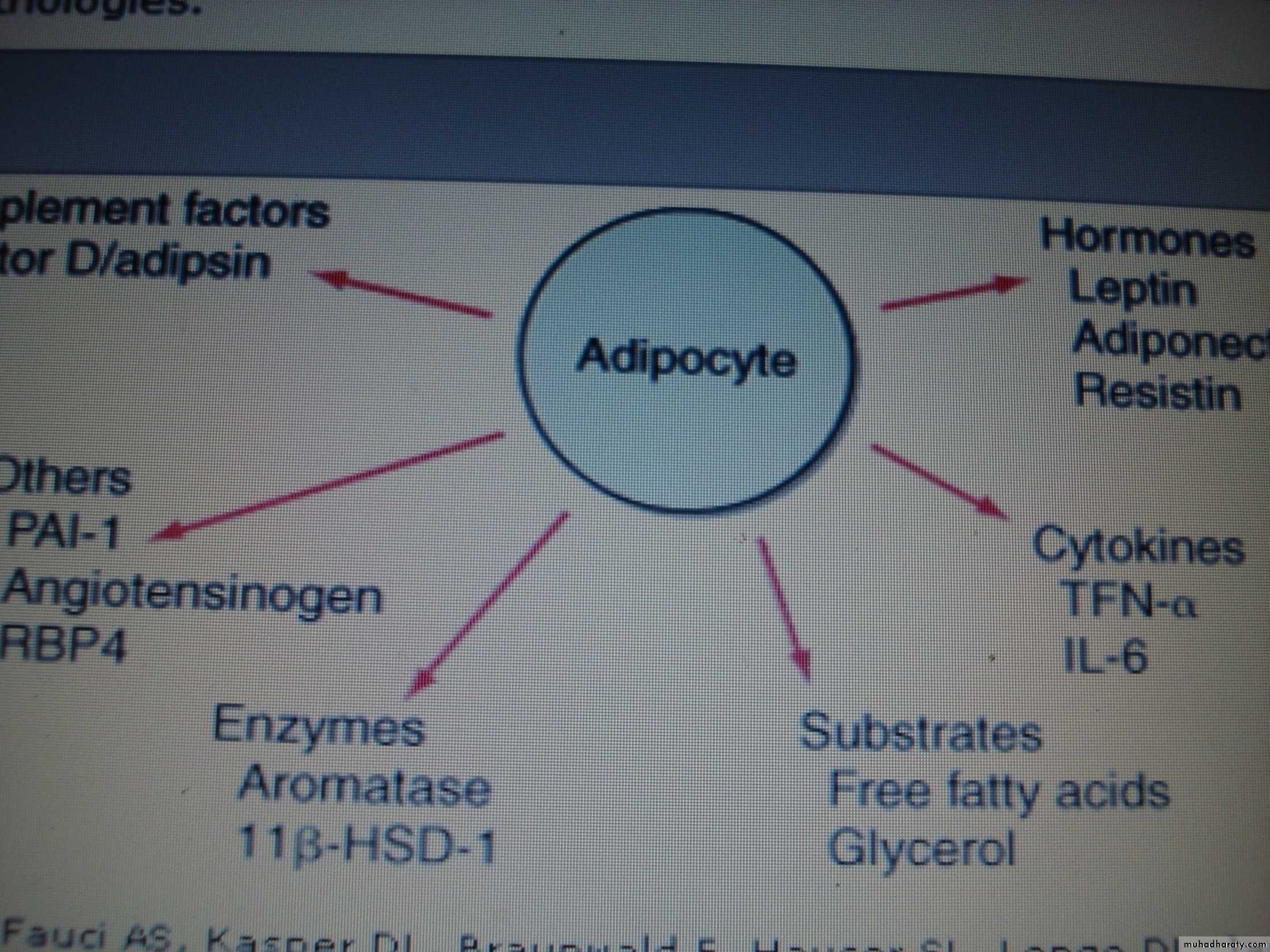
Factors released from the adiposity tissue
ObesityEtiology
The environmental factors
plays a key role in obesityEvidence
Famine protect against obesityRecent and rapid increase in the prevalence of obesity
Obesity
Factors increase prevalence
Increasing energy intake
↑ Portion sizes
↑ Snacking and loss of regular meals
↑ Energy-dense food (mainly fat)
↑ Affluence
Decreasing energy expenditure
↑ Car ownership
↓ Walking to school/work
↑ Automation; ↓ manual labour
↓ Sports in schools
↑ Time spent on video games and watching
Obesity
The genetic factorsgenes influence the susceptibility to obesity
Evidence:
Obesity is commonly seen in familiesidentical twins have very similar BMIs
Obesity is part of specific genetic syndromes (Laurence-moon biedl)
Obesity
Gene mutation detected
ob gene coding the peptide leptin.
High leptin levels decrease food intake
increase energy expenditure.
Db gene coding leptin receptor.(leptin resistant)
POMC coding proopiomelanocortin ( neuropeptides)Obesity
To date, there is no evidence to suggest that mutations in the leptin or leptin receptor genes play a prominent role in common forms of obesityObesity
Secondary causes (reversible)Endocrine factors
Hypothyroidism
Hypothalamic tumours or injury
Cushing's syndrome
Insulinoma
Drug treatments
Corticosteroids
Tricyclic antidepressants
Sulphonylureas
Sodium valproate
Oestrogen-containing contraceptive pill
β-blockers
Obesity
Complications
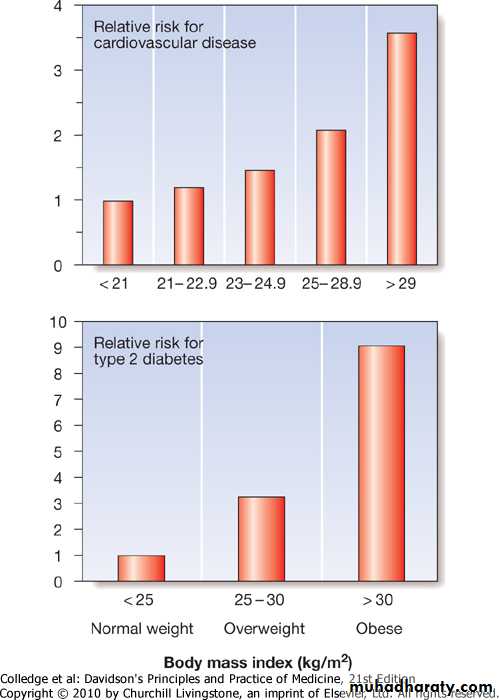
Obesity is associated with an increase in mortality, mostly due to cardiovascular causes
Mortality rates rise as obesity increases
Obesity related 300,000 deaths per year.
Life expectancy shortened by( 2–5 years) moderately obese
BMI > 45 may lose 13 years of life.
Obesity
• Complications• Metabolic complications:
Insulin resistance, diabetes type 2, hyperlipidemia
• Most obese individuals do not develop diabetes.
• 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus are obese
• Increase the risk coronary heart disease, Stroke
Obesity
Metabolic syndromeCentral obesity: waist circumference ≥ 94 cm (male)
≥ 80 cm (female)
AND any two of the following
< 50 mg/dL in females
systolic BP > 130 or diastolic BP >85 mm Hg
Raised fasting plasma (FPG): >100 mg/dL or previously diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Obesity
2. Cardiovascular Disease
coronary disease
stroke
congestive heart failure (CHF)
atherogenic lipid profile
increase (LDL) ,VLDL, and triglyceride.
decreased HDL
Hypertension
increased peripheral resistance, cardiac output
increased sympathetic nervous system tone
increased salt sensitivity, and insulin-mediated salt retention
Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 6 December 2011 05:10 PM)
© 2005 ElsevierObesity
3. Endocrine Disorders :In men :
plasma testosterone often reduced
estrogen levels increased
Gynecomastia may be seen.
In women:
menstrual abnormalities
increased androgen
increased conversion of androgen to estrogen.
oligomenorrhea
polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Obesity
4. Pulmonary Disease:Exertional dyspnoea Sleep apnoea Respiratory failure (Pickwickian syndrome)
caused by (restrictive ventilation)
reduced chest wall compliance
decreased functional residual capacity and expiratory reserve volume
Obesity
5. Gastrointestinal :
Gallstones: cholesterol gallstones
caused :
enhanced biliary secretion of cholesterol
supersaturation of bile
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease :
simple steatosis
steatohepatits
cirrhosis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease:
Obesity
6. Musculoskeletal : increased risk of osteoarthritis7.Skin :
Skin infection (submammary Candida)varicose vein
8. cancer: colorectal CA, uterine CA, breast CA
9. Psychological : depression, Social stigmatization