
Autoimmune Diseases
and
Allergy
1

Learning Objectives
Terms:
Inflammatory response
,
immunological
tolerance
Autoimmune disease(AID):
Predisposing factors
,Classification of HSD, C/P, Ix
Allergy:
Definition, R/F, C/P, IX, Mx
Summary & Quiz
2

Inflammatory Response:
is response of tissues to injury or infection
Types:
1.
Acute Inflammation
Is a rapid
Classical external signs: heat, redness, pain and
swelling
3
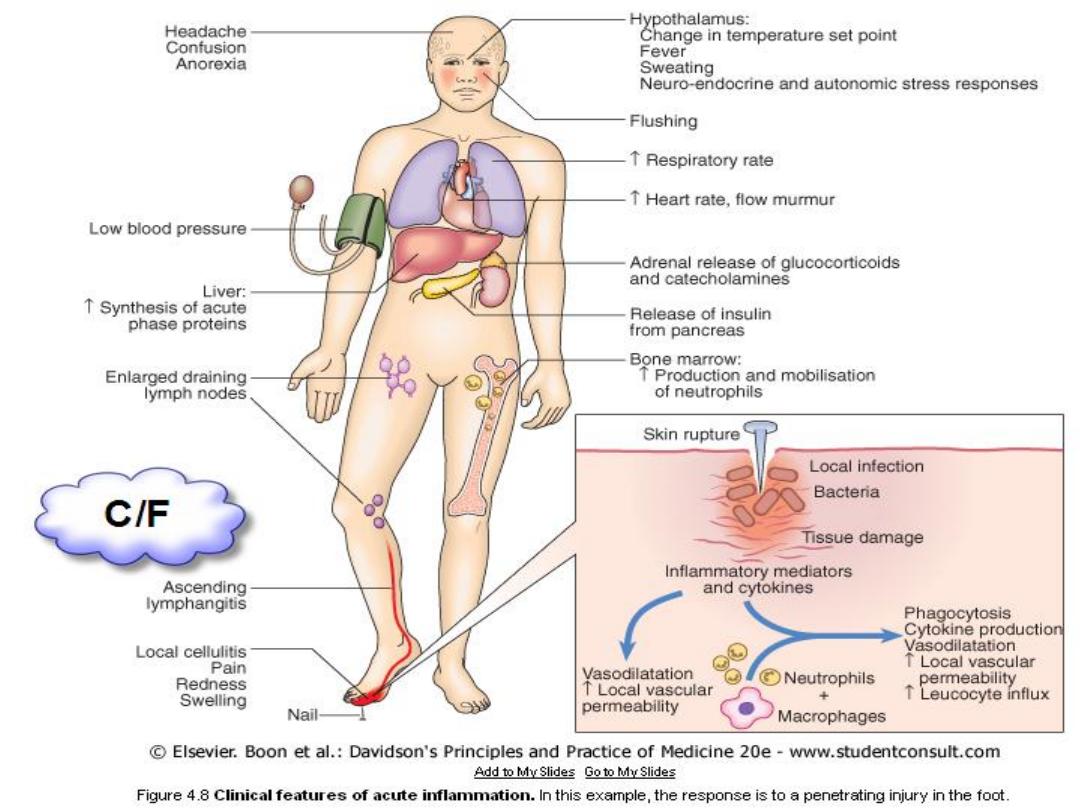
4

1)Acute phase proteins
:
Produced by the liver
Include: C-reactive protein (CRP)
Serum amyloid A
Fibrinogen
α
1
-
antitrypsin and α
1
-antichymotrypsin
Haptoglobin (antioxidant)
Transferrin, ferritin and lactoferrin (iron-
binding proteins )
5

2)Resolution of inflammation
repair of damaged local tissues
3) Sepsis and Septic shock
is C/M of overwhelming inflammation
Most frequently results from infection with
Gram-
negative bacteria.
Multi-organ failure, and often death
6

2)chronic Inflammation
local deposition of fibrous connective tissue
(
granuloma
)
characteristic of infections such as
tuberculosis
and leprosy
7
8

Immunological tolerance
immune system distinguishing self tissue from
foreign tissue.
Failure
of
tolerance
mechanisms-----------
autoimmune disease.
9

Auto-immune disease:
Immune response against self-targets
Major cause of chronic morbidity and disability
Affecting up to 1 in 30 adults.
10

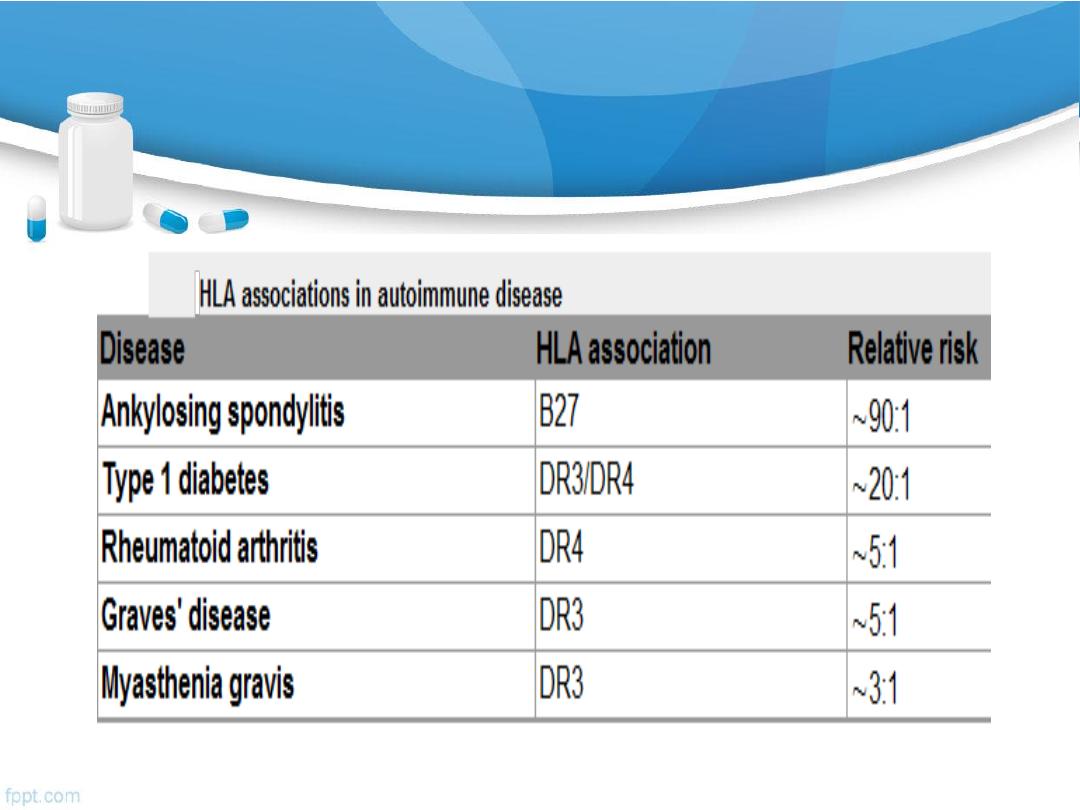
Factors predisposing to autoimmune disease
1.
Genetic :
HLA genes
2.
Environmental
:
infection- as acute rheumatic fever, reactive
arthritis
Drug: anaesthetic agent halothane
3.
Unclear
reasons: much more common in
women
than in men.
11
12
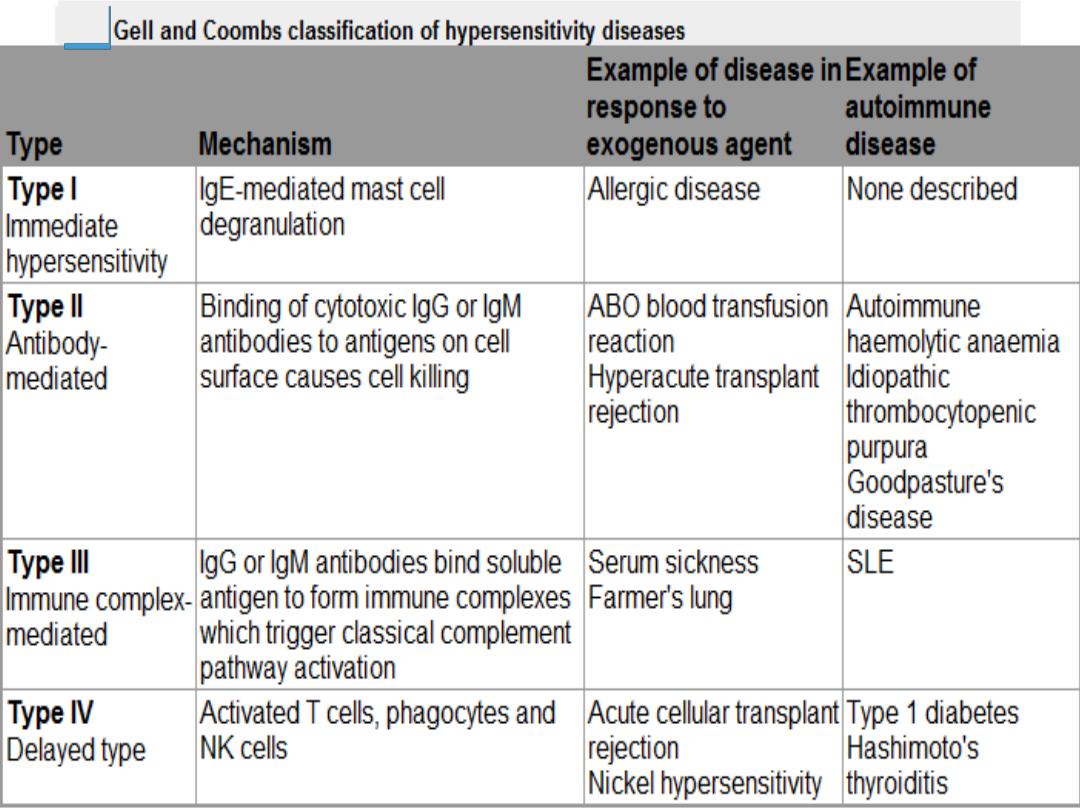
Classification Of Hypersensitivity Diseases
13

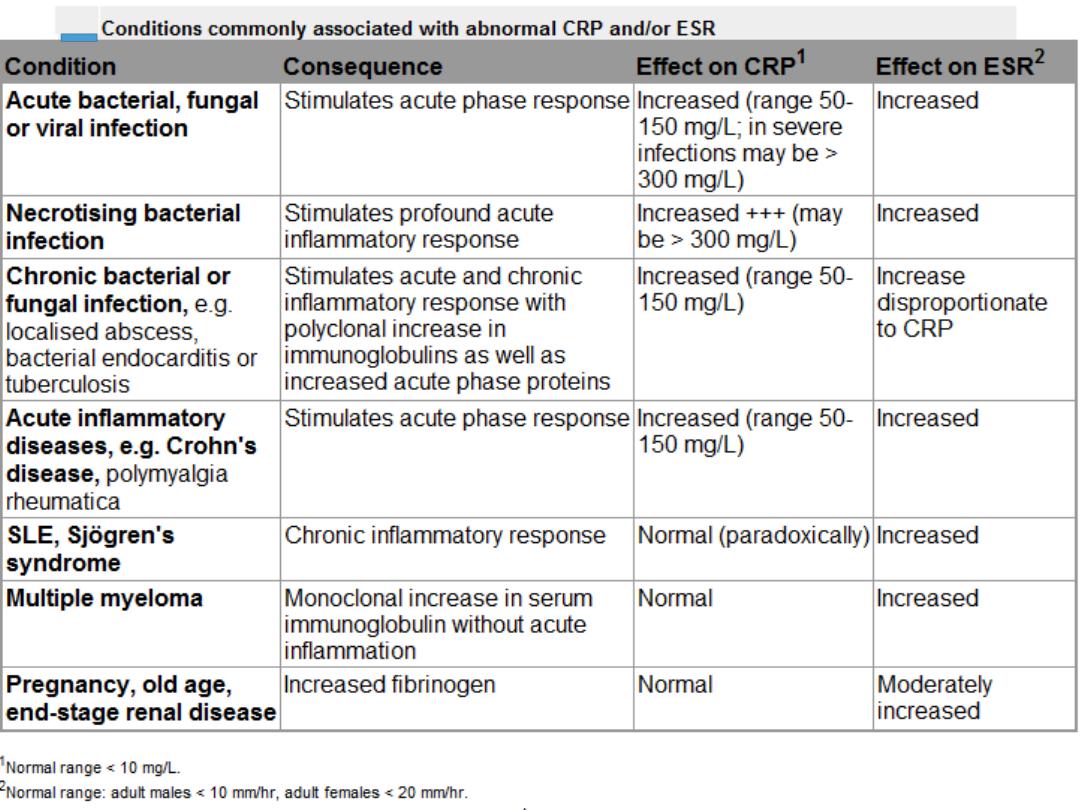
Investigations In Autoimmunity
1)AUTOANTIBODIES
1)Rheumatoid factor
2)Anti-CCP antibody
3)Antinuclear antibodies: (ANA)
4)Antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens
5)Anti-ds-DNA antibodies
6)Antiphospholipid antibodies
7)Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA
14

2) Cryoglobulins
3) Measures Of Complement Activation
15

Clinical presentation of Autoimmune Diseases
1)Organ-specific:
Immune response against
localized
antigens
:
e.g: Graves' disease, pernicious anemia, type 1
DM
2)Multisystem
Immune response against
widespread target
antigens
: e.g: Systemic sclerosis, SLE, MCTD
16
17
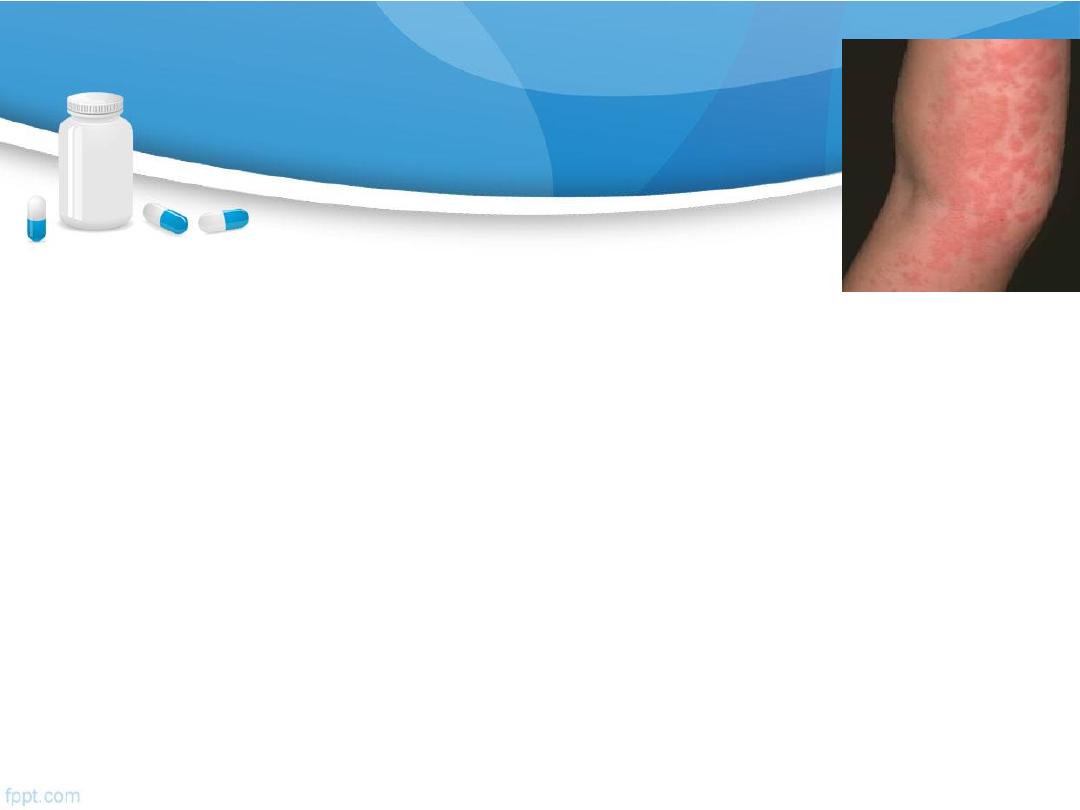

Allergy
is C/M of inappropriate IgE immune response to
harmless environmental substances .
Risk Factors
1.
Genetic:
A family history (the strongest factor).
2.
Environmental
factors :pollutants, cigarette
smoke, infection
3.
Unexplained
18
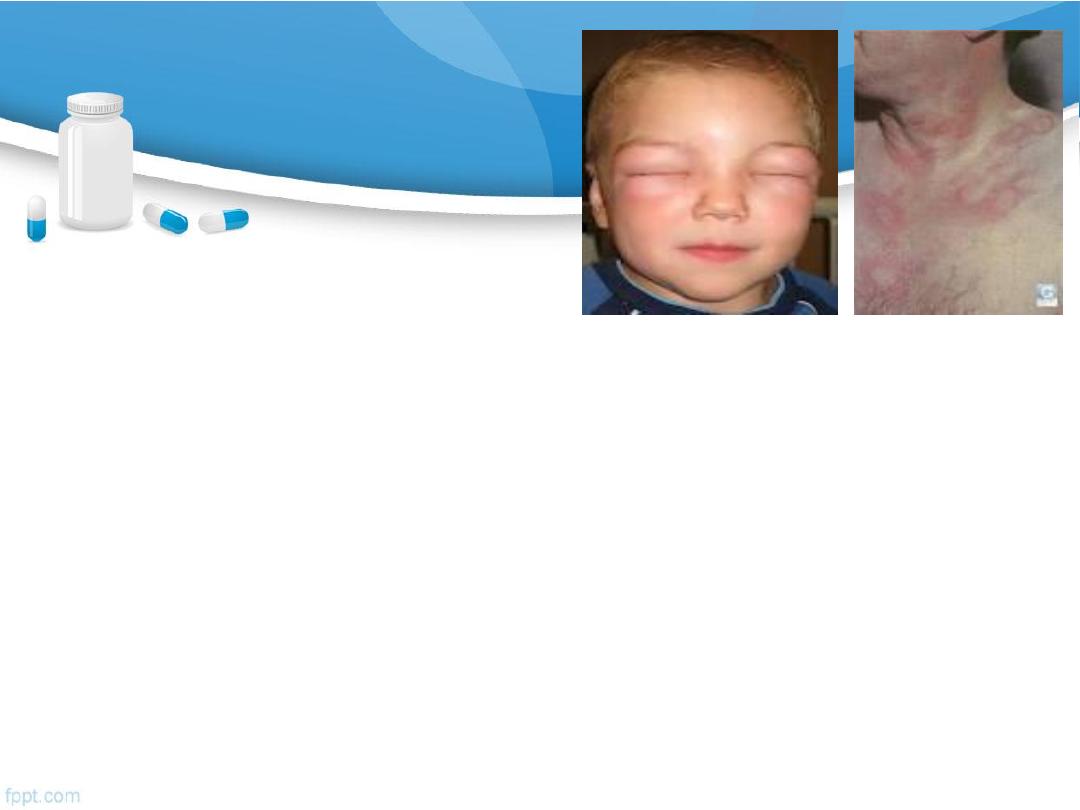
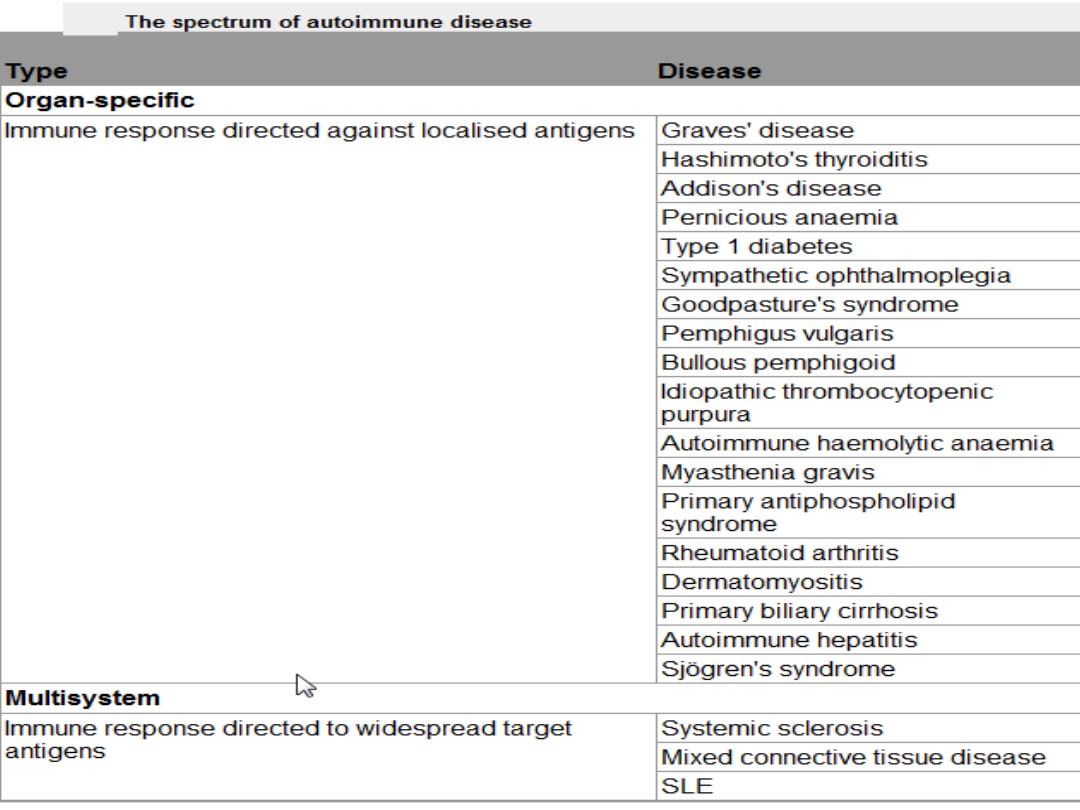
C/P of allergy
Symptoms (angioedema, urticaria, wheezing
….).
Other allergic symptoms
usually occurs within minutes of exposure to allergen
R/F
–HX of allergic disease.
-Hx of potential allergens in the home and
workplace
-DHx: Hx of complementary therapies
19
20

Investigations
1)Skin prick test:
is the
'gold standard'
of allergy testing
A droplet of diluted standardized allergen solution
is placed on the forearm, and the skin is
superficially punctured through the droplet with a
sterile lancet.
21

• After 15 minutes
, a positive response is
indicated by a
local weal and flare
response ≥ 2 mm
larger than the negative
control.
The results clearly seen.
22

Disadvantages : remote risk of a severe allergic
reaction, so resuscitation facilities should be
available.
Antihistamines inhibit the magnitude of the
response and should be discontinued for at least 2
days before testing.
23

2) Specific IgE test
An alternative to skin prick testing
very useful if skin testing is inappropriate
24

3)Supervised exposure to allergen (challenge test)
Placebo-controlled allergen challenges
usually performed in specialist centers
e.g. food challenge
May be useful in the investigation of
occupational asthma or food allergy.
25

4)Mast cell tryptase
useful in investigating a possible anaphylactic
event
5) Non-specific markers of atopic disease:
-
↑total serum IgE
- eosinophilia (up to 20%, = 1.5
× 10
9
/l )
26

Management
1.Education:
Avoidance of the allergen
2.Drugs:
-Antihistamines
-Corticosteroids,
-Sodium cromoglicate,
-Antigen-specific immunotherapy
-Omalizumab(a monoclonal antibody against IgE)
-Preloaded self-injectable adrenaline (epinephrine)
27

Summary
28
• IR: tissue response to injury or infection, acute &
chronic.
• IT: immune system distinguishing self tissue from
foreign tissue
• AD: Immune response against self-targets,
predisposed
by
genetic,
environmental,&
unkown. Screened by certain Ab.
• HSD: 4types.

29
Allergy
:↑↑IgE response to painless env. Stimuli. ,
gentic-env-unkn, has spcial Cf & Rx
