CSF and Peripheral Nervous System
L5Dr. Thana Al-Khishali
:Learning Objectives
In this session, we are going to discuss:The CSF elaboration, circulation and absorption
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, and related gangliaThe peripheral nervous system; nerve fibers, ganglia ,regeneration after injury, and nerve endings
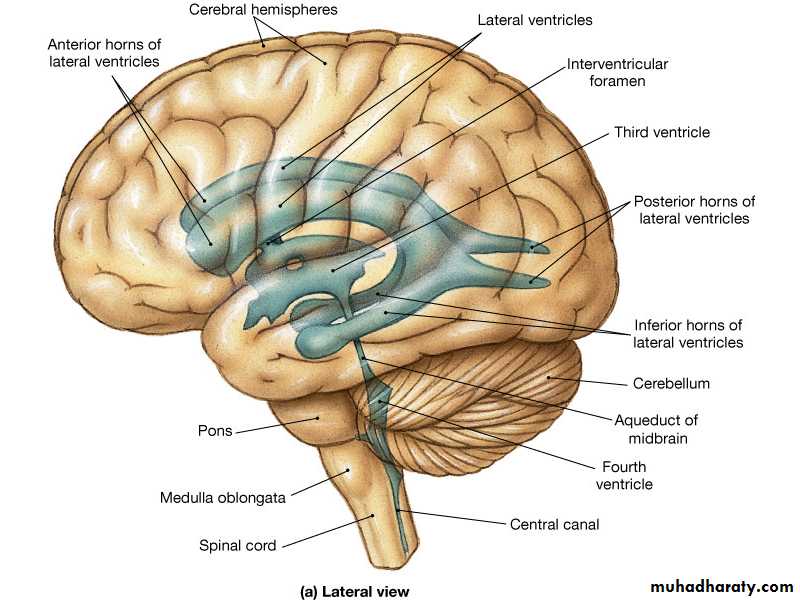
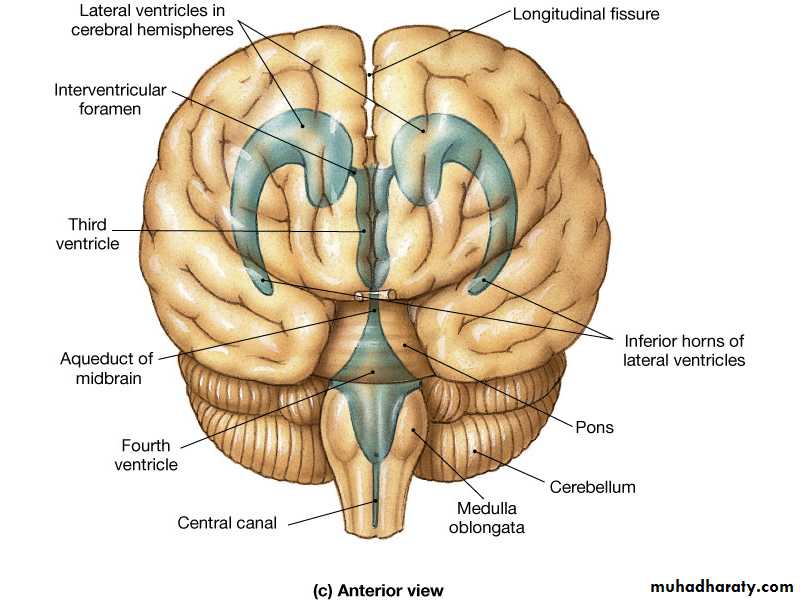
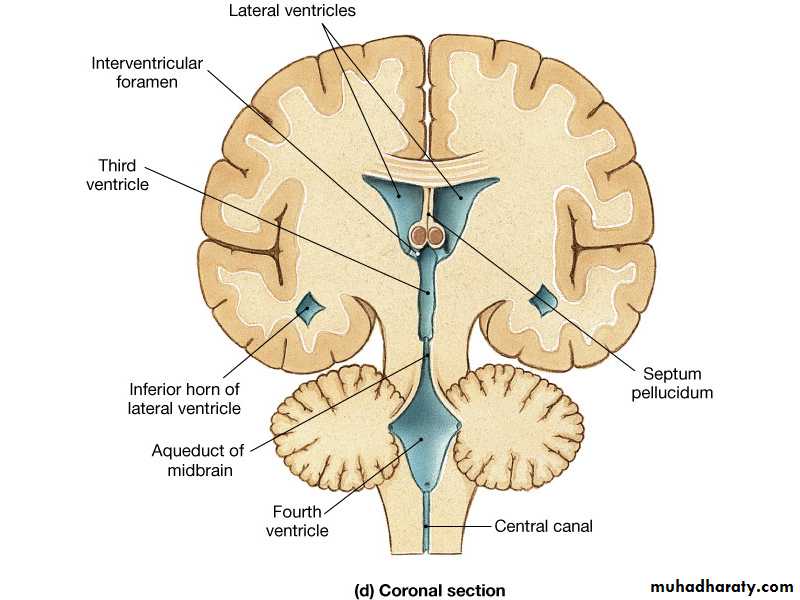
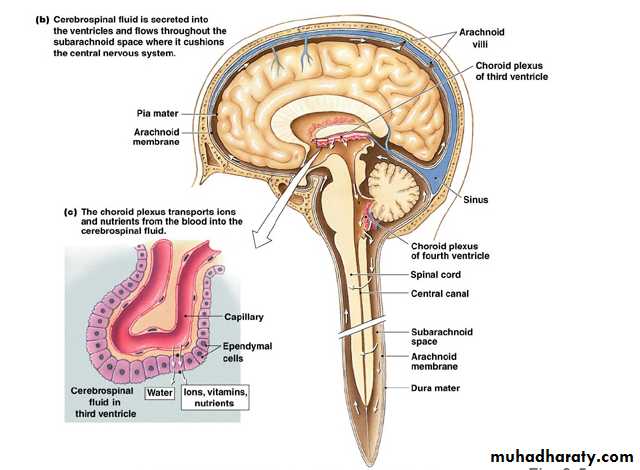
Cerebrospinal Fluid
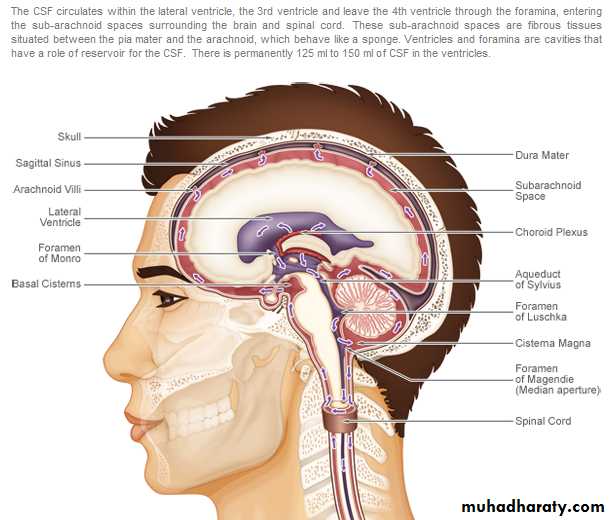
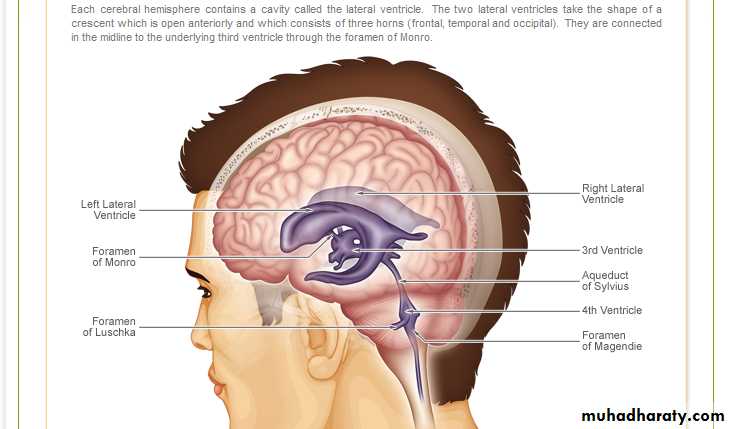
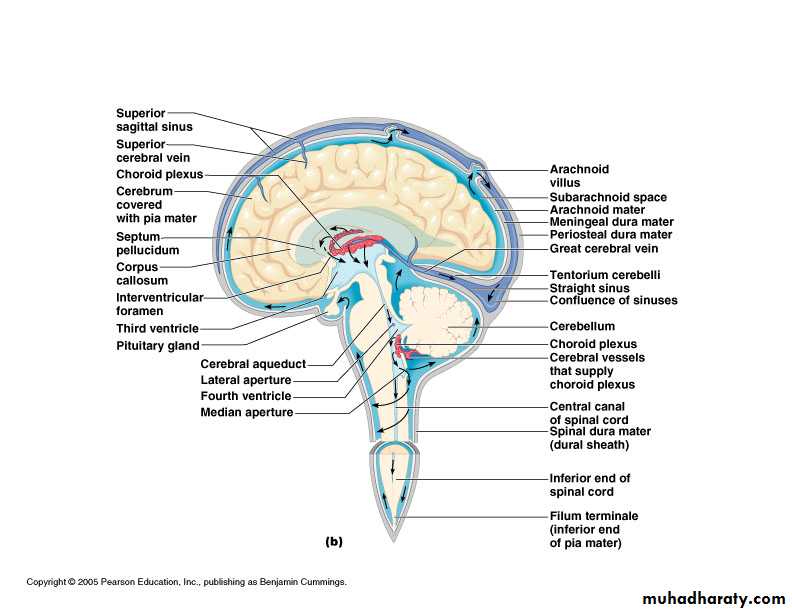
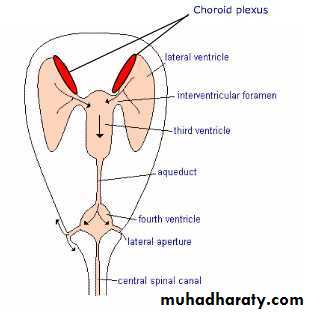
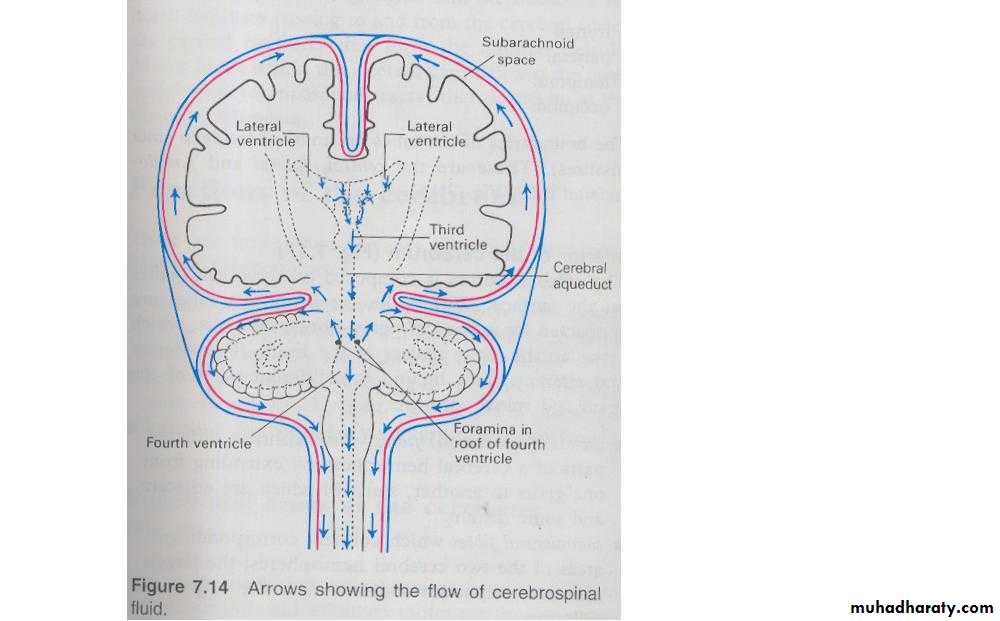
FormationSecreted by choroid plexuses into each ventricle
Choroid plexus are areas where the lining wall of the ventricle is very thin and has a profusion of capillaries
Drainage
From the roof of the 4th ventricle CSF flows through foramina into the subarachnoid space and completely surrounds the brain and spinal cordWhen CSF pressure is higher than venous pressure CSF passes into the blood and when the venous pressure is higher the arachnoid villi collapse, preventing the passage of blood constituents into the CSF
The CSF passes back into blood through tiny diverticula of arachnoid mater called arachnoid villi (arachnoid granulations), which project into the venous sinuses
Some reabsorption of CSF by cells in the walls of the ventricles occurs
12
Constituents of the CSF versus the Blood Plasma
• CSF Plasma• Na+ 148 142
• K+ 2.9 4.0
• HCO3- 22 27
• Cl- 125 100
• Glucose 4.4 5.0
• Urea 5.0 5.0
• PCO2 6.6 5.3
• pH 7.3 7.4
• Protein 30 7000
Force of circulation
Movement of the CSF is by pulsating blood vessels, respiration and changes of postureCSF is secreted continuously at a rate of about 0.5ml per minute i.e. 720 ml per day
Total CSF in the brain 120 ml
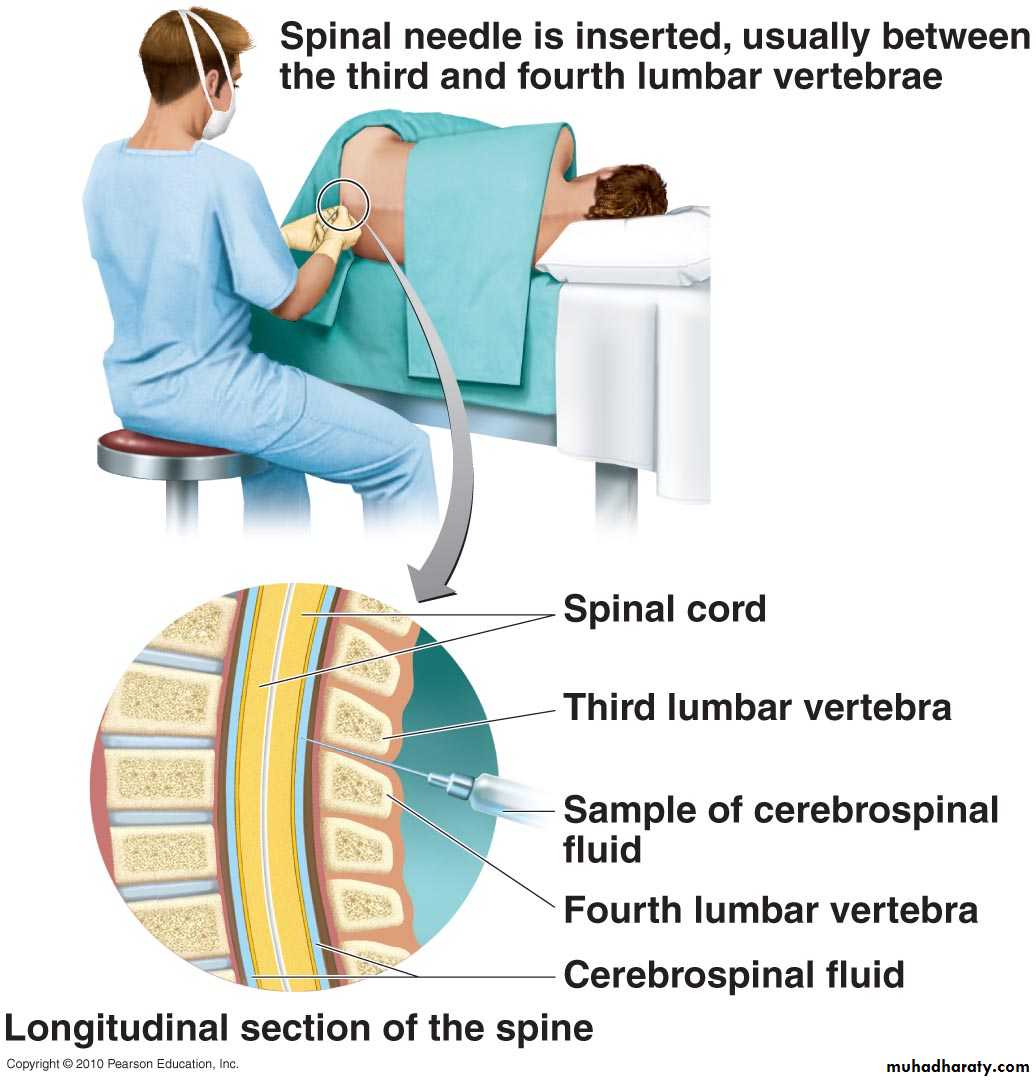
CSF pressure can be measured by attaching a vertical tube to the lumbar puncture needle – 10 cm water
14
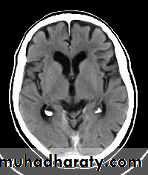
Normal Ventricles
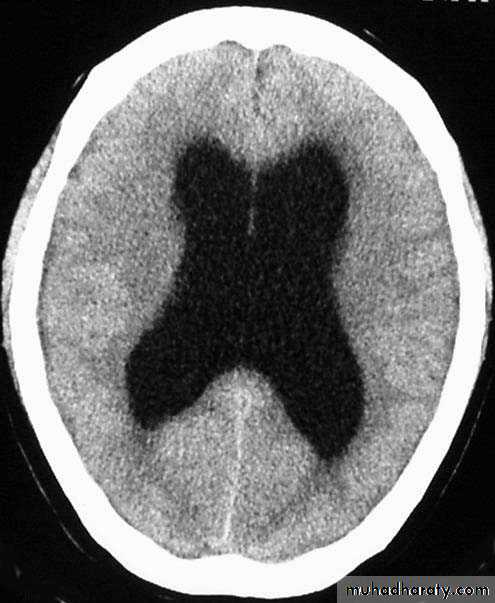
Hydrocephalus
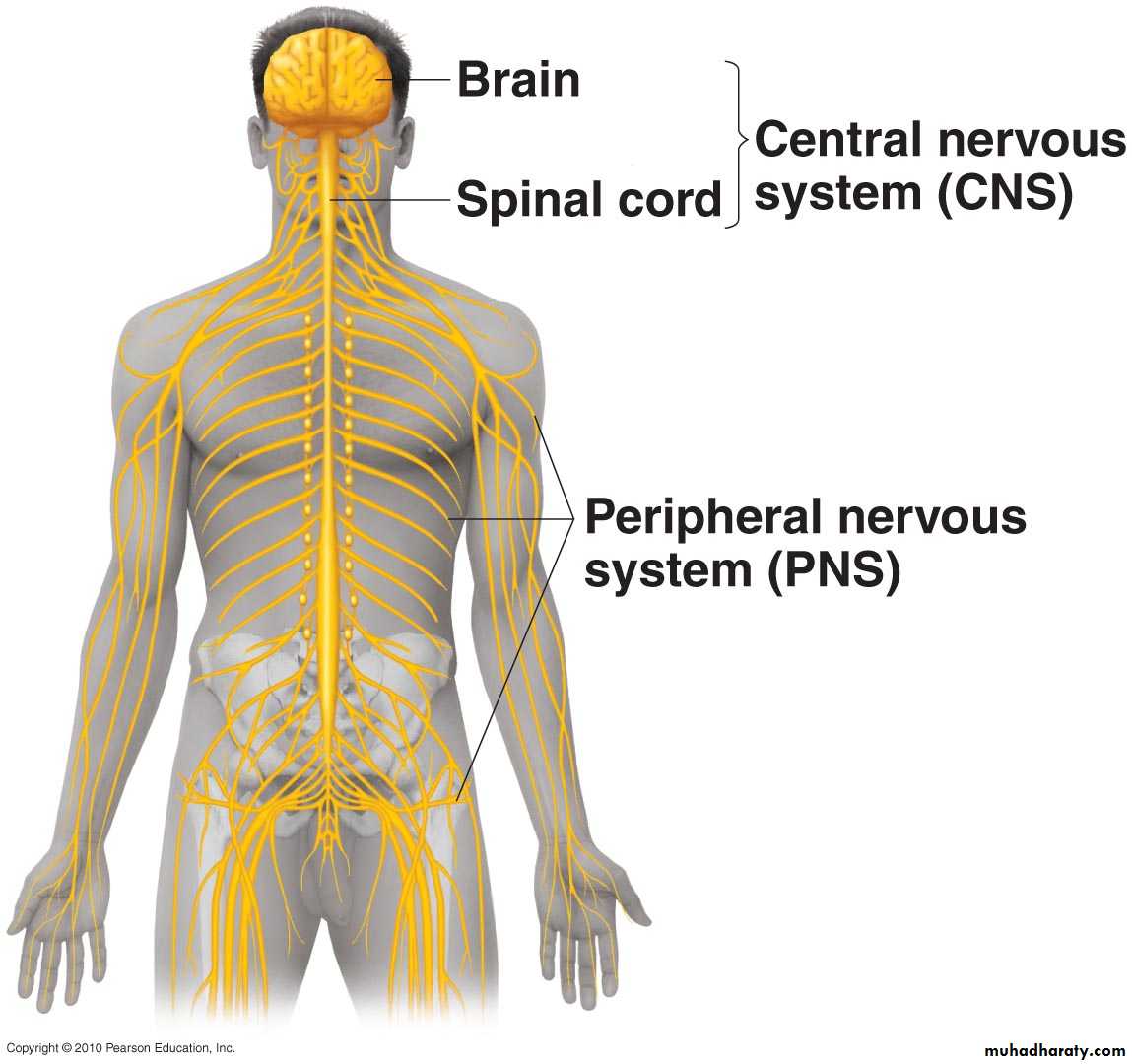
Peripheral Nervous System
NervesGanglia
Cranial, spinalAutonomic
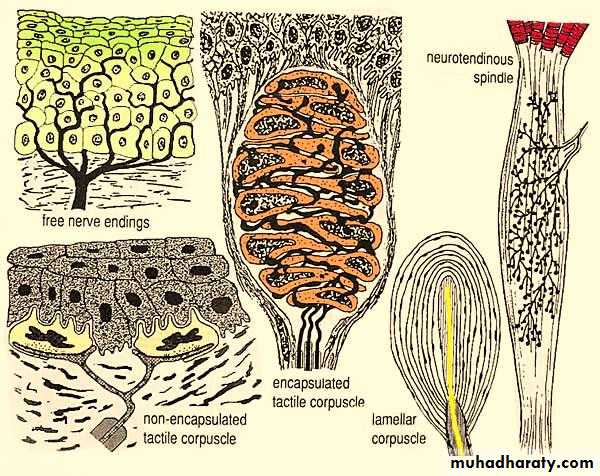
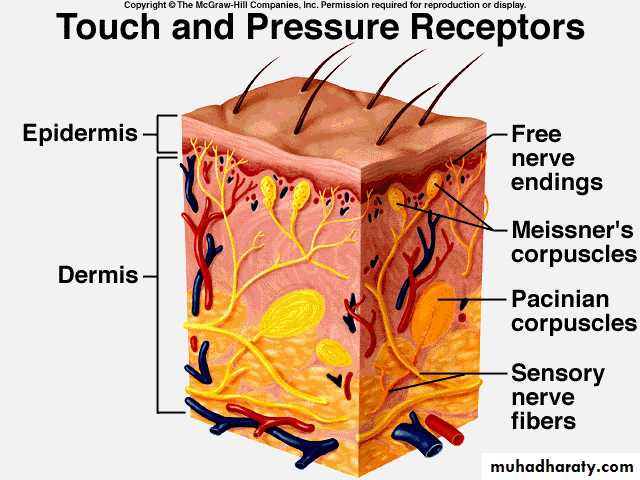
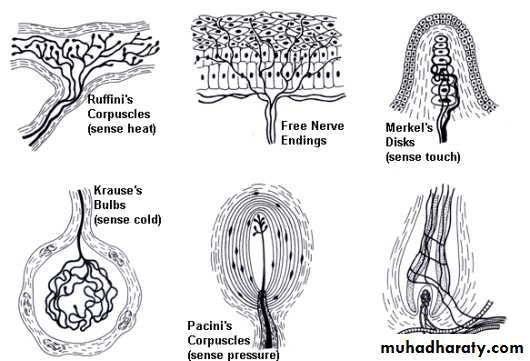
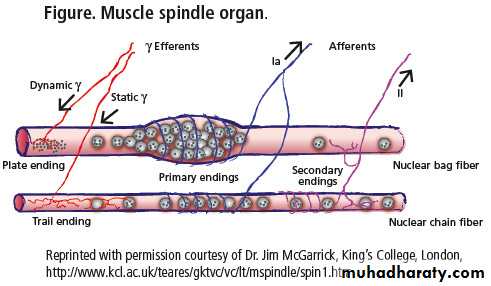
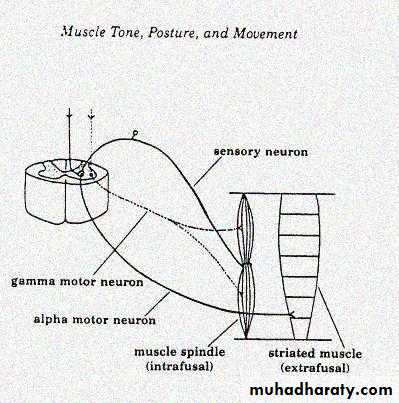
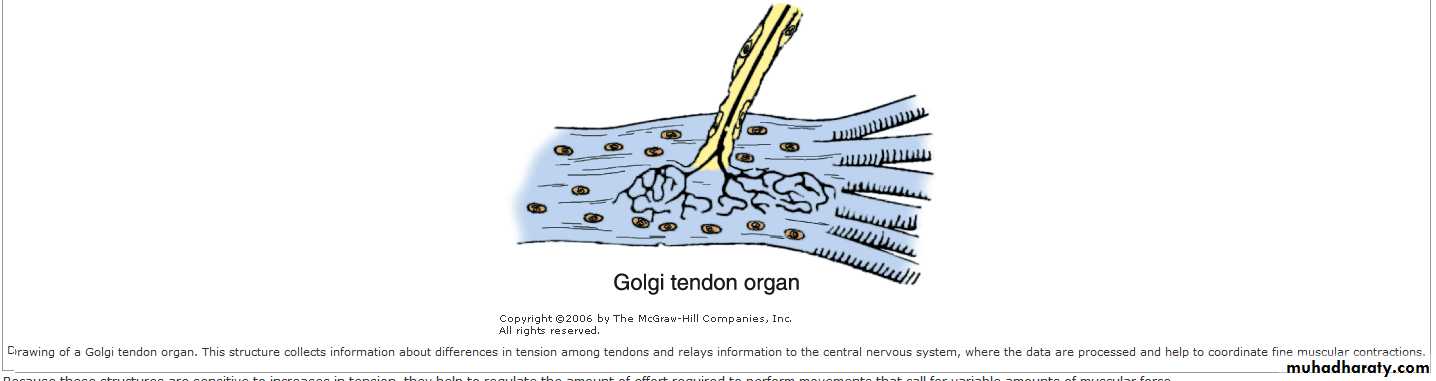
Nerve endings
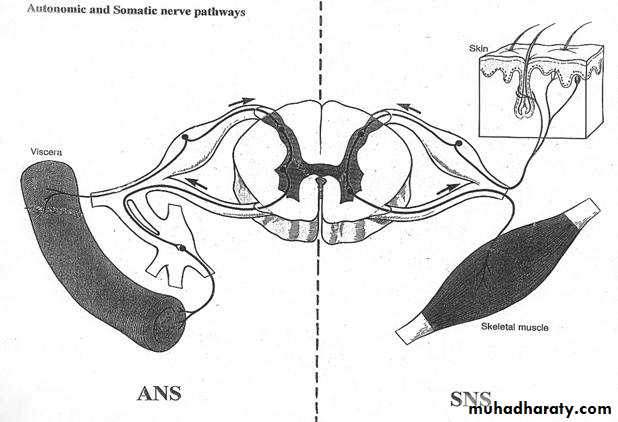
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
Autonomic Nervous System
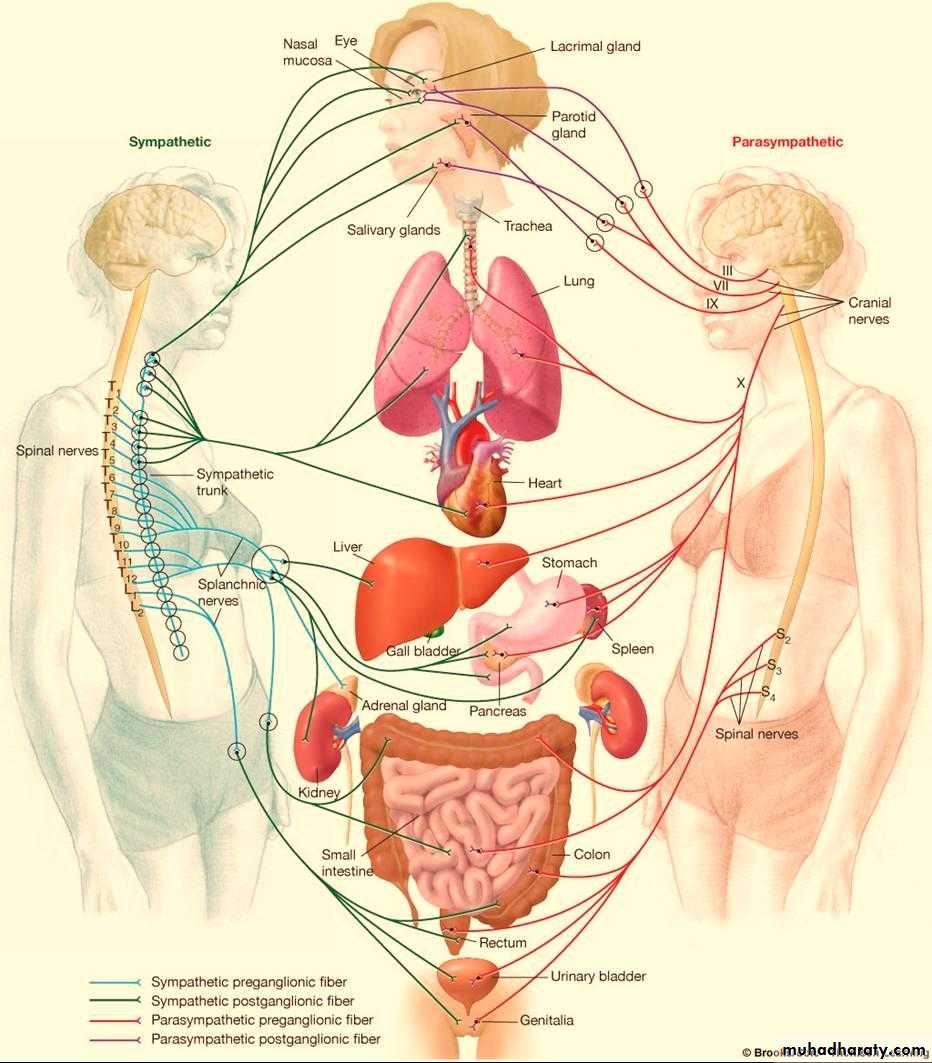
Concerned with visceral functions (homeostasis)Two major divisions
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
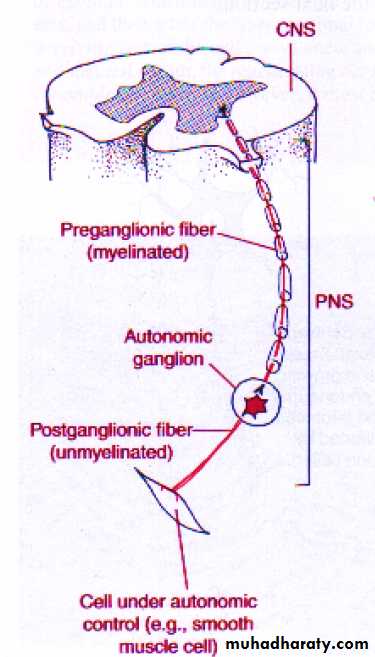
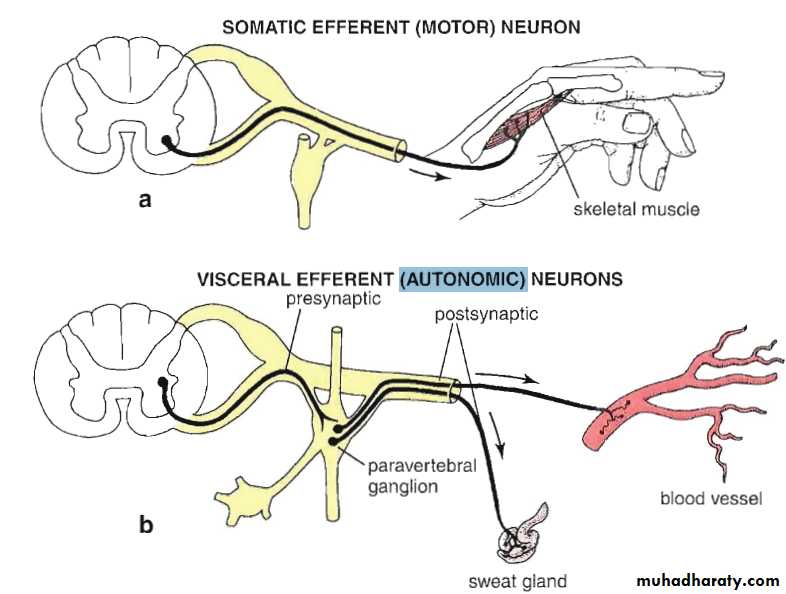
Preganglionic and postganglionic neurons
Autonomic Efferent Pathway
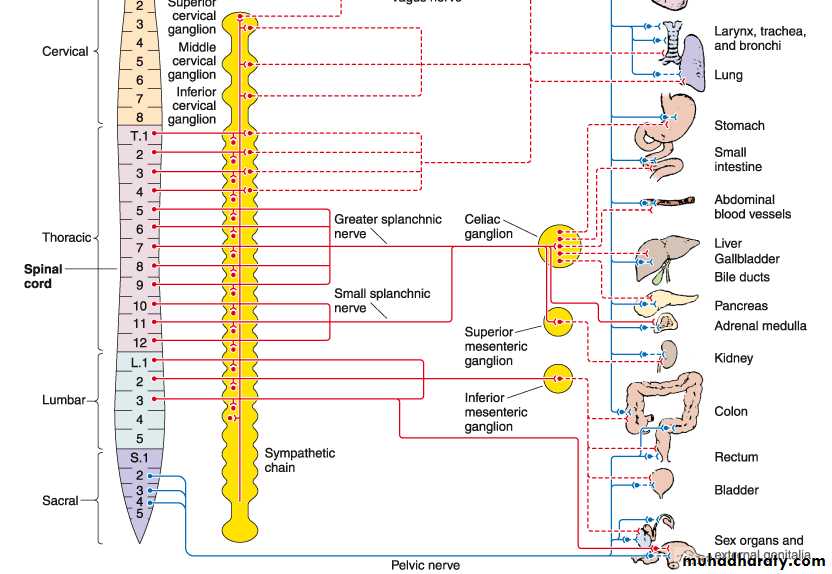
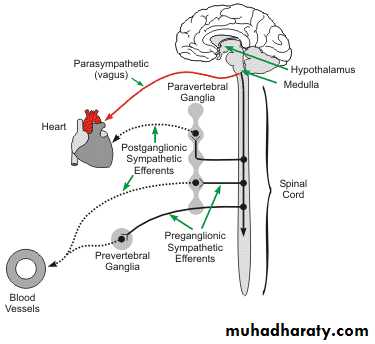
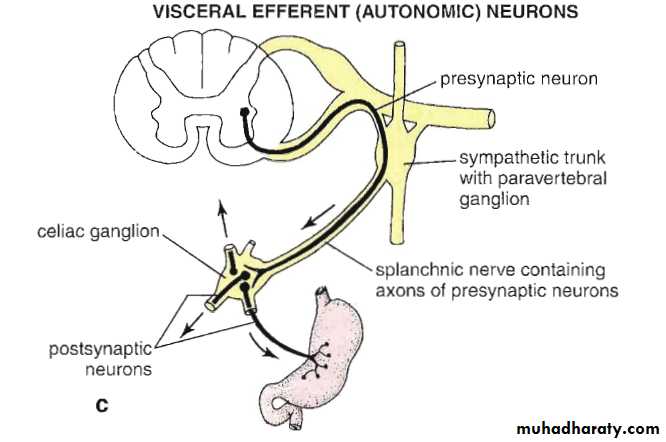
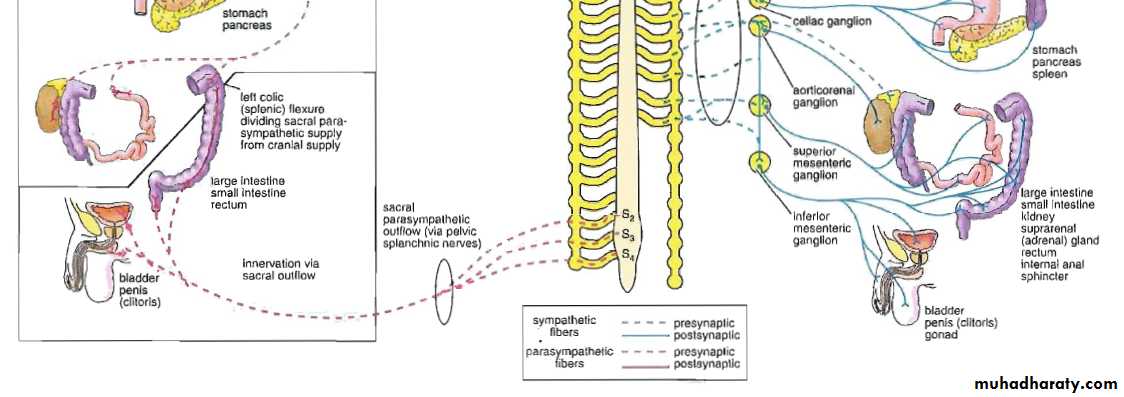
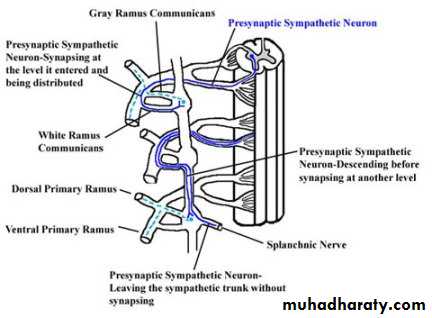
Sympathetic System
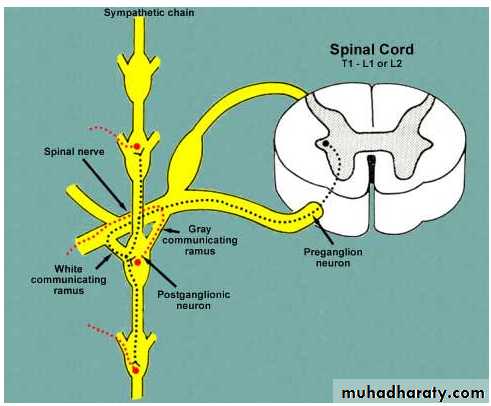
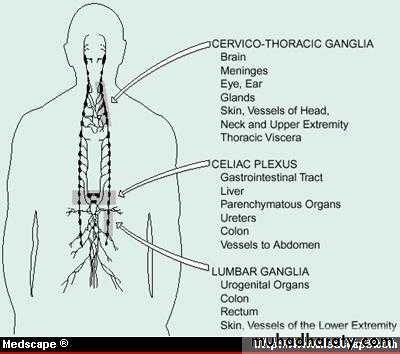
Sympathetic SystemNuclei in thoracolumbar region
Paravertebral ganglia
Chemical mediator noradrenalin (adrenergic)Adrenal medulla is the only organ receives preganglionic fibers
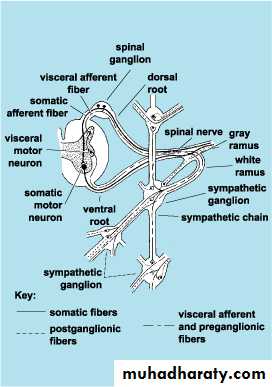
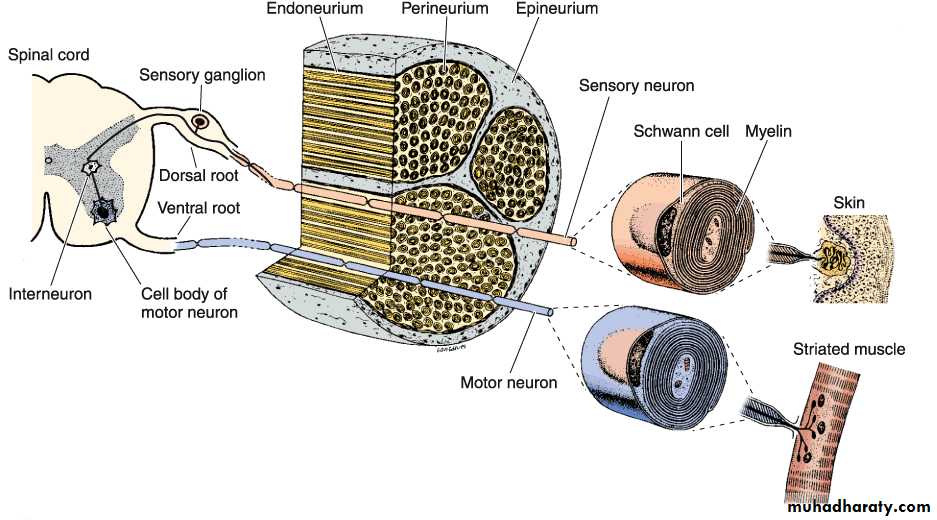
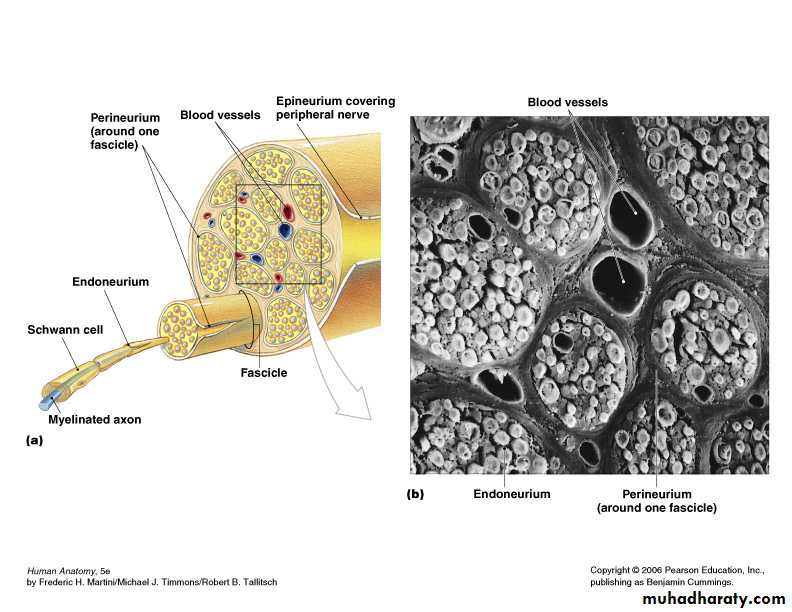
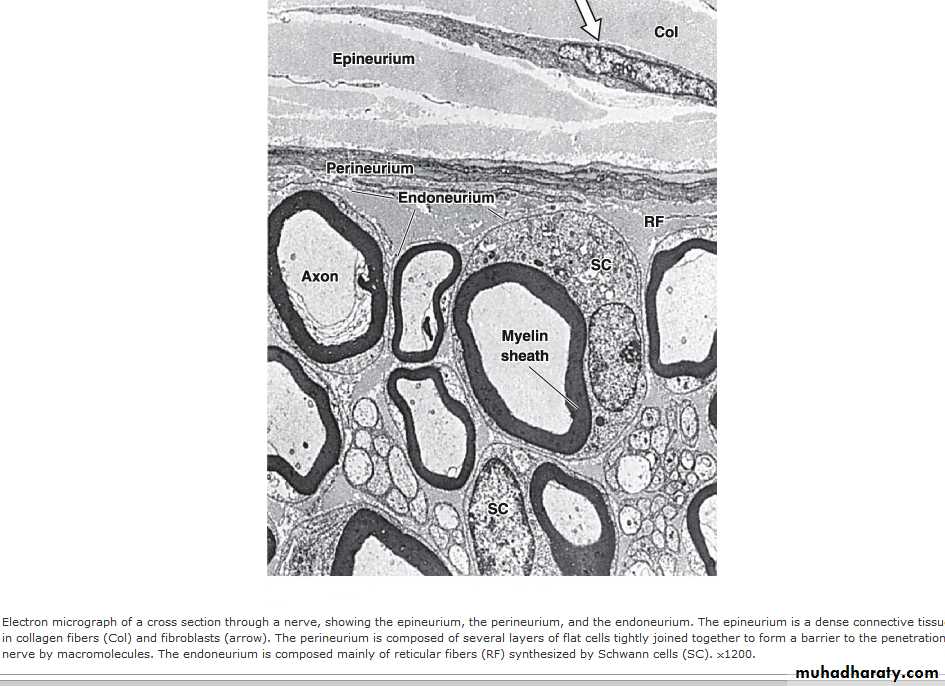
Scheme showing structure of a typical spinal nerve.
• Somatic efferent.• Somatic afferent.
3,4,5.Sympathic efferent. 6,7.Sympathetic afferent.
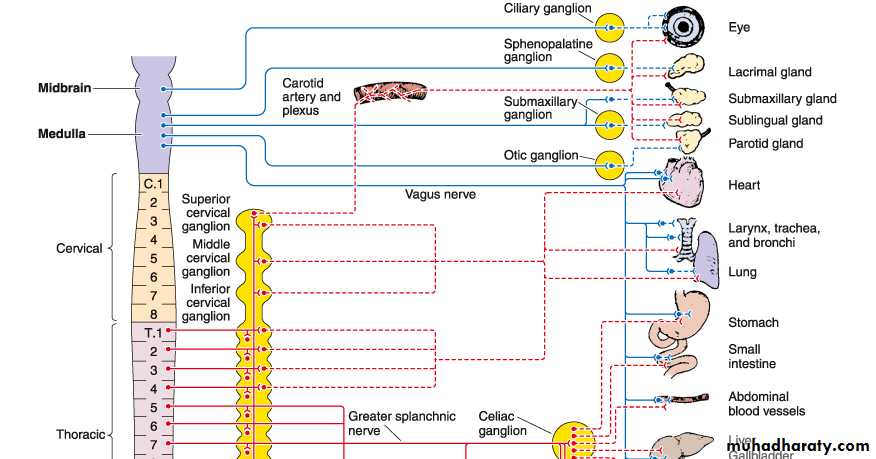
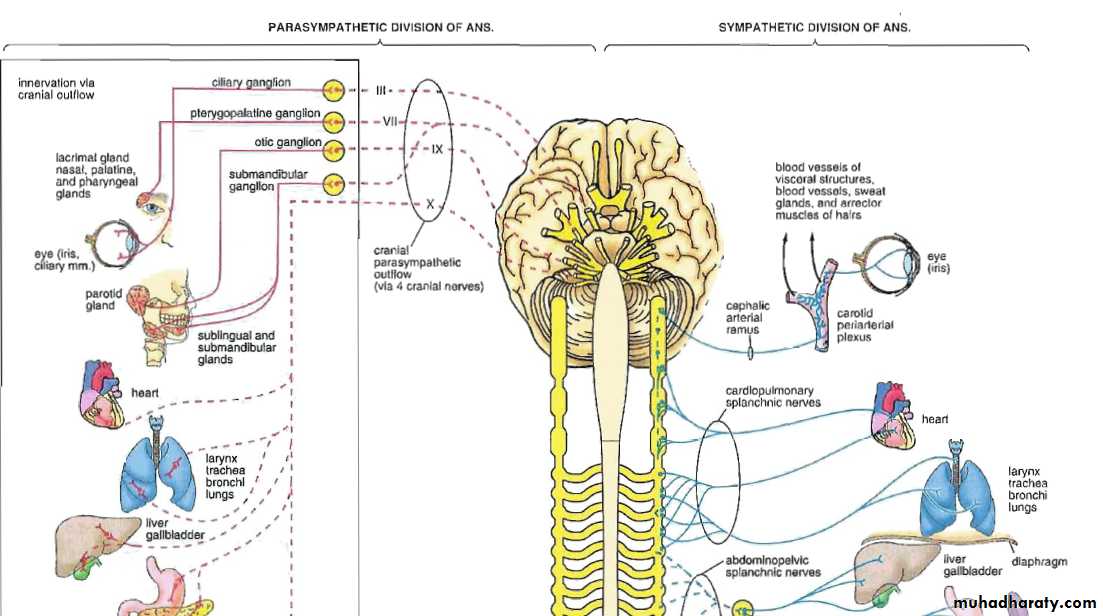
Parasympathetic System
• Nuclei in medulla, midbrain, and sacral portion of the spinal cord• The cranial portion leave through III,VII,IX,and X cranial nerves
• Ganglia located near or within the effector organ
Peripheral Nervous System
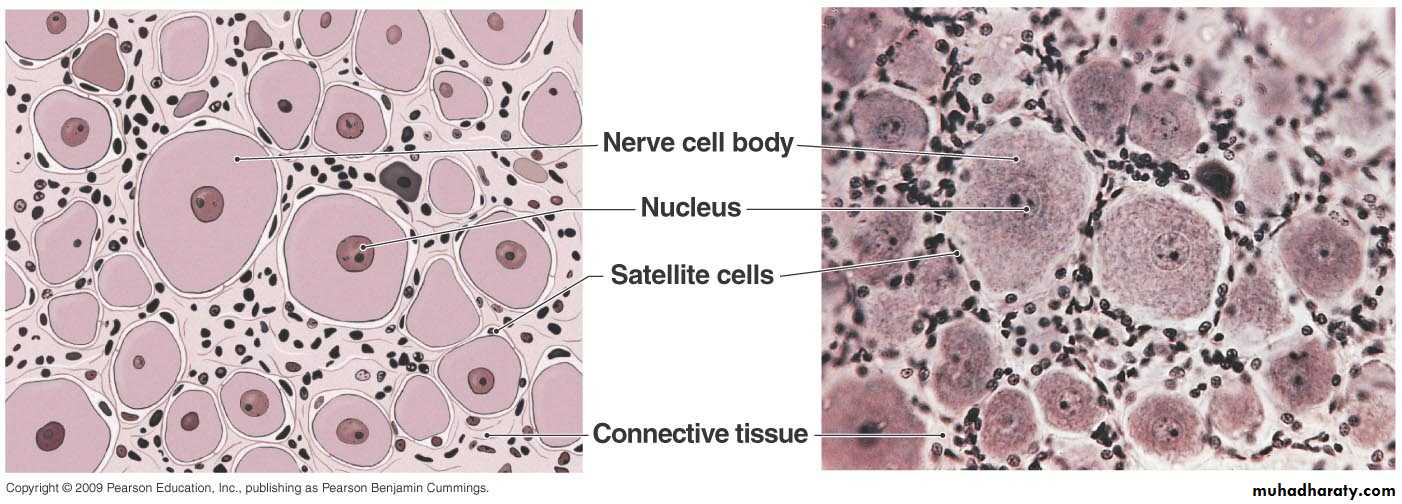
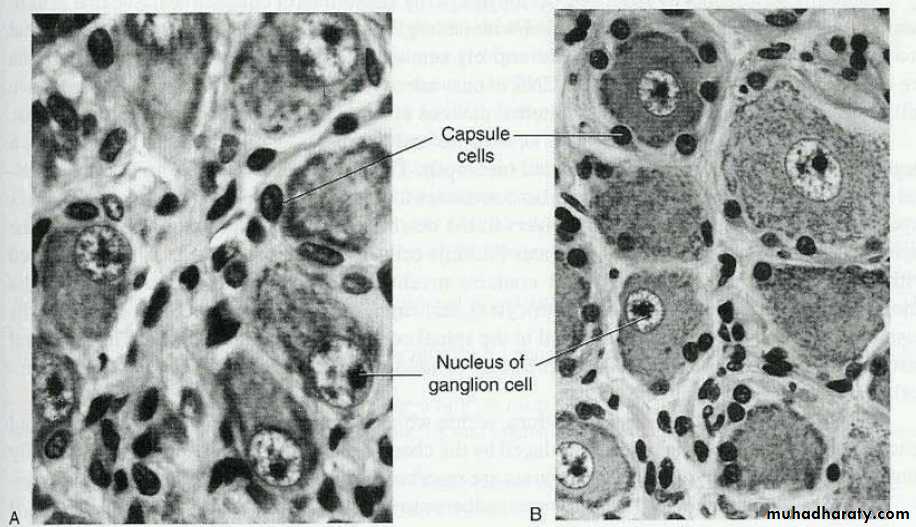
Spinal GangliaLarge cell body (Pseudounipolar)
Intense basophilia with fine Nissl granules
Centrally located large nucleus with prominent nucleolus (owl’s eye)
Lipofuscin pigment
Satellite (capsule) cells
Connective tissue capsule
Cerebrospinal fluid
• Circulates in the subdural space
• Elaborated in the venous sinuses• Related to ependymal cells
• Both 1&2
• Both 2&3
Satellite cells surround neuron cell bodies in the peripheral ganglia
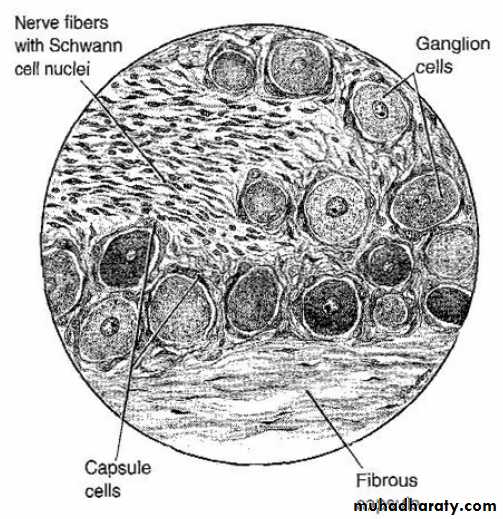
Autonomic GangliaMultipolar neurons
Discontinuous satellite cells
Eccentric nucleus
Fine Nissl granules
Capsule not prominent
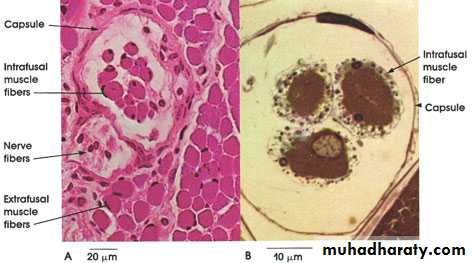
Spinal ganglion, Notice The ganglion cells, continuous satellite (capsule)cells, central nucleus, fibrous capsule, and nerve fibers
Autonomic ganglion cells, Notice the eccentric nucleus and discontinuous satellite (capsule) cells
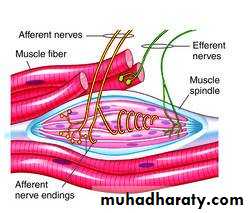
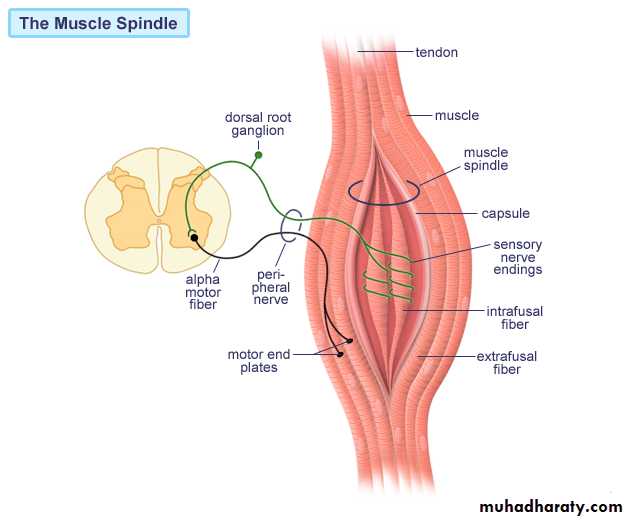
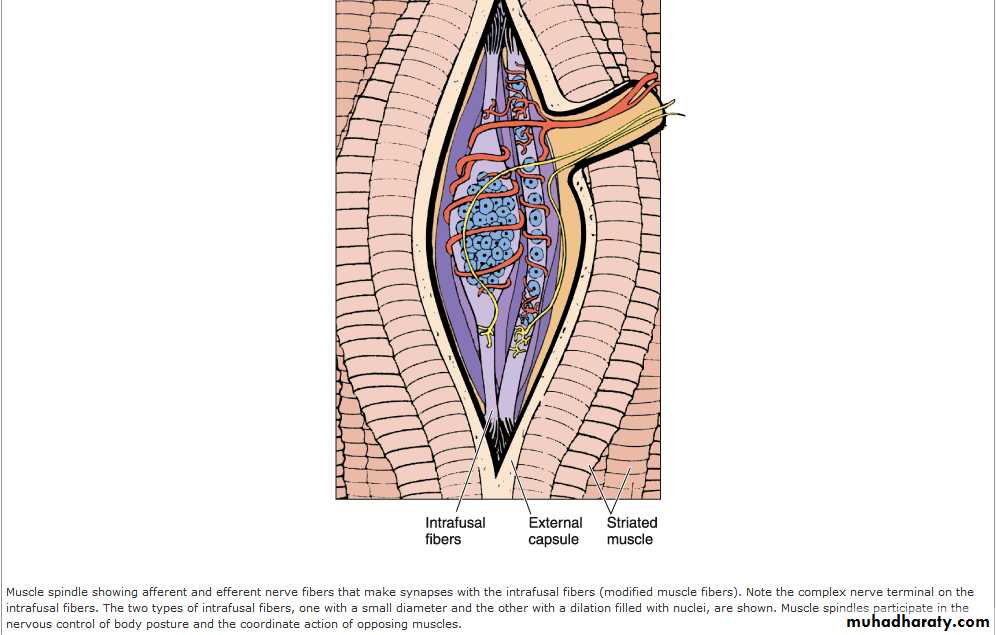
Schematic representation of a nerve and a reflex arc. In this example, the sensory stimulus starts in the skin and passes to the spinal cord via the dorsal root ganglion. The sensory stimulus is transmitted to an interneuron that activates a motor neuron that innervates skeletal muscle. Examples of the operation of this reflex are withdrawal of the finger from a hot surface and the knee-jerk reflex