Lecture 1
NERVOUS SYSTEMDr. Thana Al-Khishali
NERVOUS SYSTEM
AnatomyPhysiology
Histology
Neurons
Glial cells
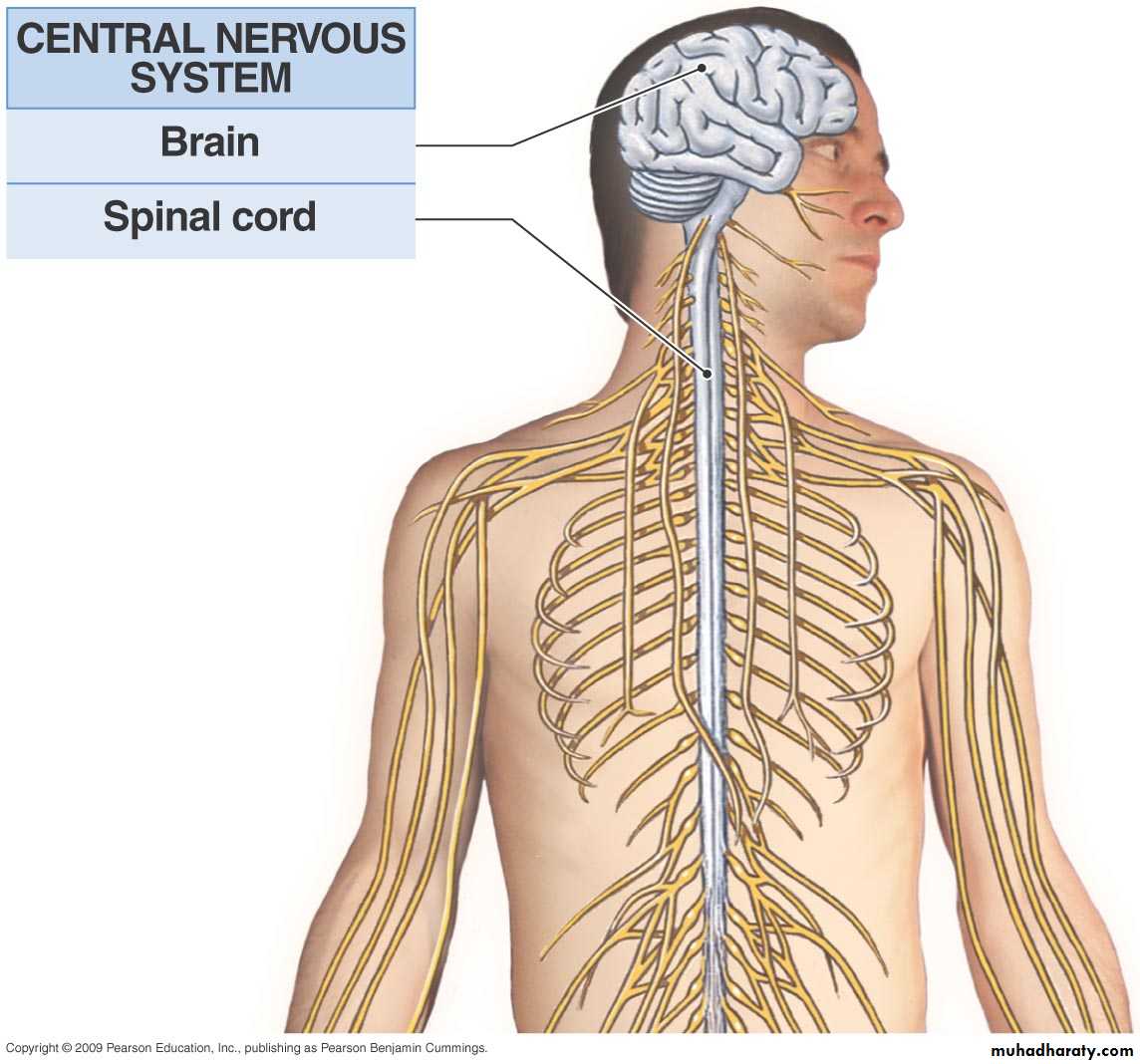
Central Nervous System
CSF, BBB, Meninges
Peripheral Nervous System
NF, Ganglia
Neural Plasticity and Regeneration
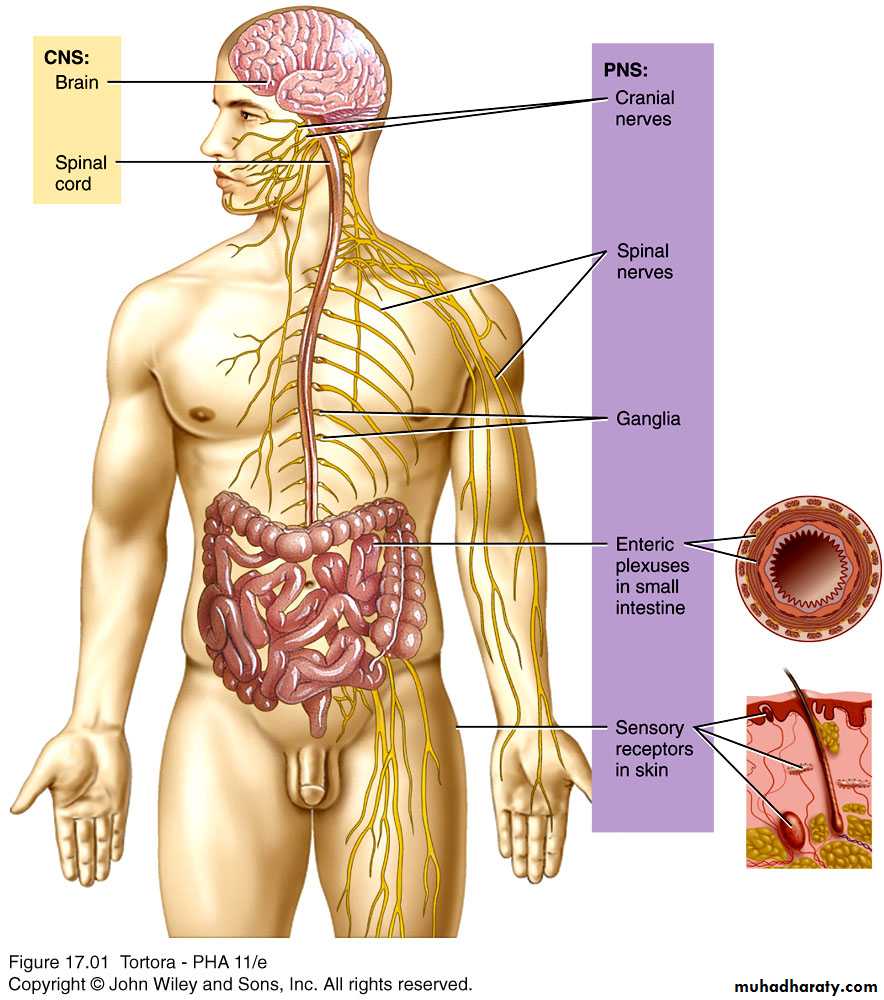
Nervous System
Divided Anatomically intoCentral Peripheral
CNS PNS
Brain and Spinal Cord Nerves (motor and sensory)
Ganglia
Nerve Endings
Both CNS and PNS consist of :
Nerve cells (Neuron) and Glial cells
Components of the Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
The Nervous System
Nervous Tissue as an integrated communications network :
CREATESANALYZES
IDENTIFIESINTEGRATES
The informationOrganization of the Nervous System
Central nervous systemBrain & spinal cord.
Integrative & control centers.
Peripheral nervous system
Cranial & spinal nerves.
Communicates between CNS and rest of body.
Sensory (afferent division)
Impulse from receptor to CNS.
Motor (efferent) division
Impulse from CNS to effector.
Autonomic nervous
System
-to visceral organs.
Somatic nervous
System
-to muscles
Sympathetic Division
“Excites”
Parasympathetic Division
“Retards”
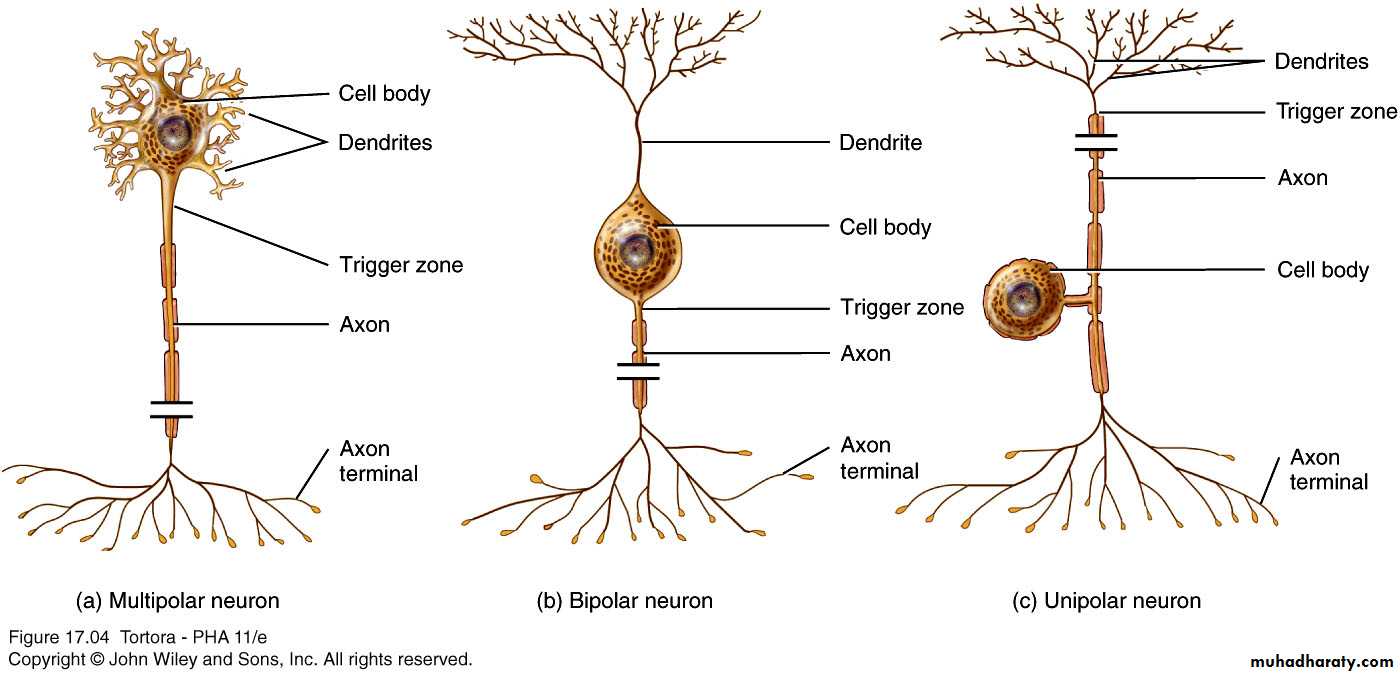
The Neuron
Multipolar,Bipolar , and
Unipolar (pseudounipolar)
THE NEURON
• Motor• Sensory
• Internuncial
Classification of Neurons
based on direction of impulse
Afferent (sensory) neurons – conduct impulses towards the CNS
Efferent (motor) neurons – conduct impulses away from the CNS
Internuncial (association) Neurons –carry impulses between neurons within the CNS (may be either sensory or motor)
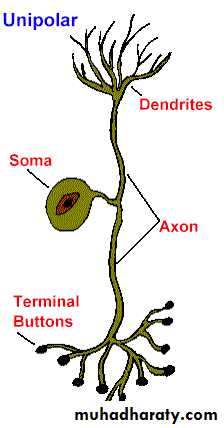
Structural Classification of Neurons
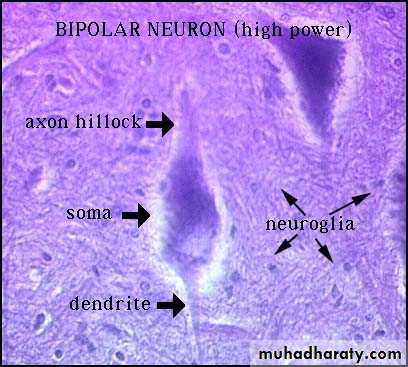
Unipolar NeuronBipolar Neuron
Multipolar Neuron
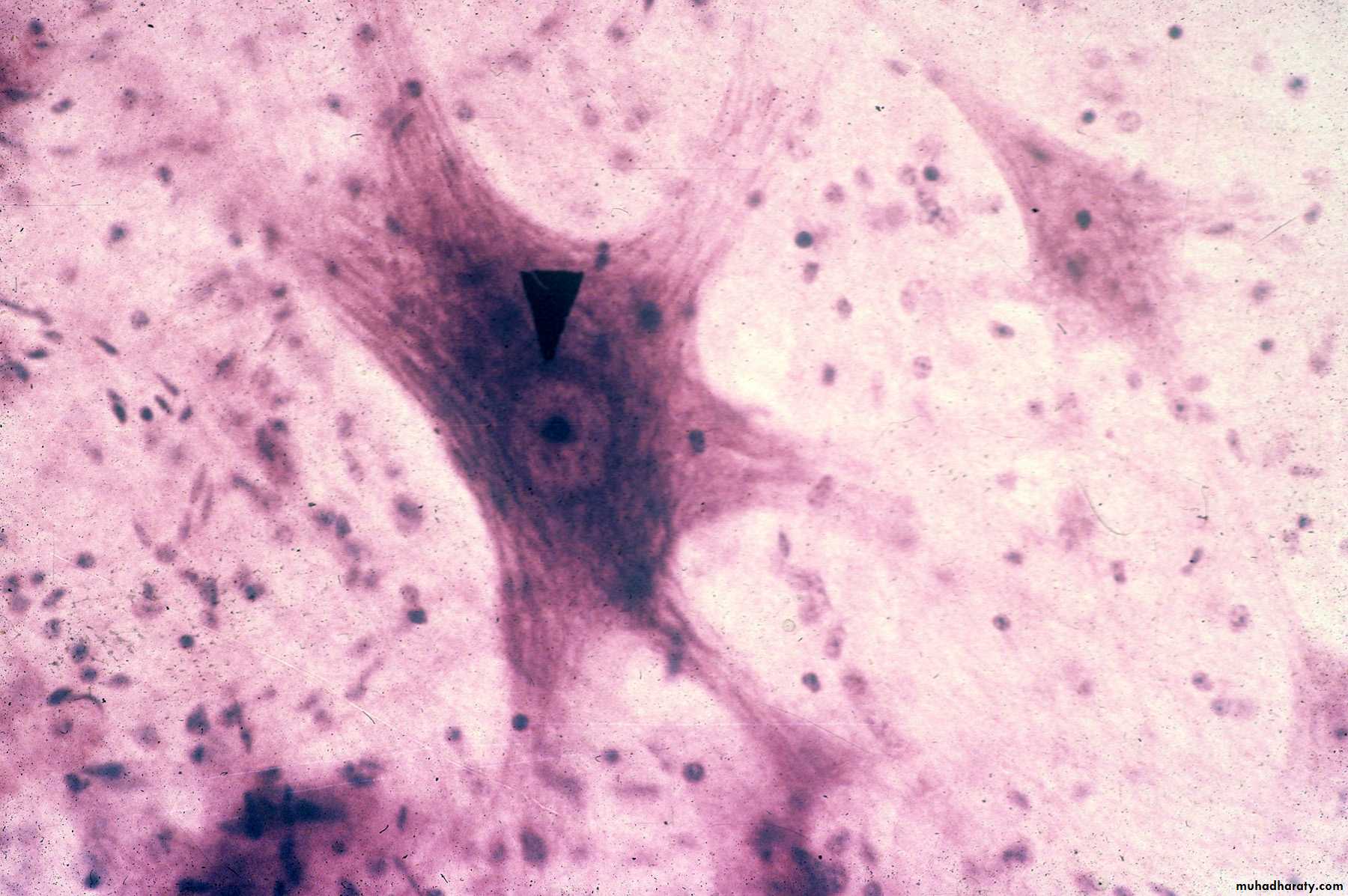
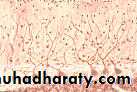
Pyramidal Cells (slide #29)
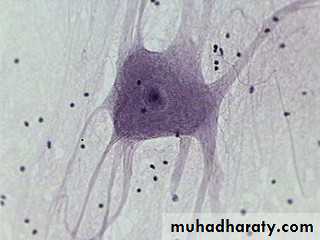
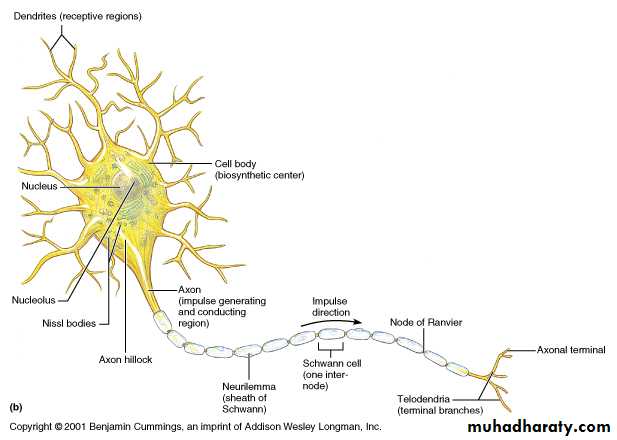
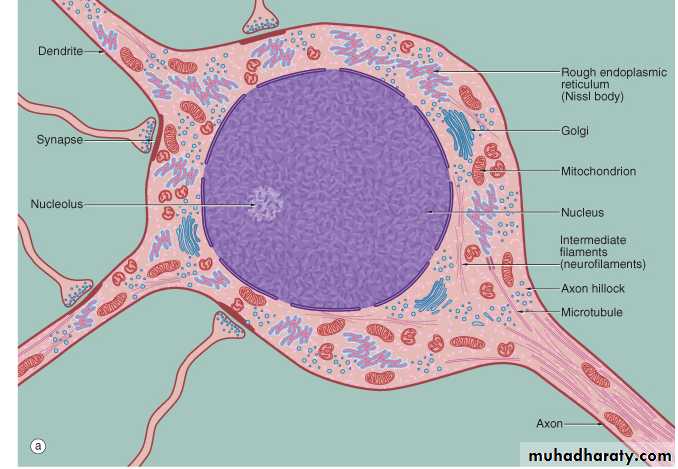
Neuron Structure – Cell Body (= Soma)
Neuron Structure – Cell Body (= Soma)
contains the usual cellular organellessynthesis & metabolism occurs primarily in the soma
the outer cell membrane contains the receptors for incoming information (stimuli)
most cell bodies are located within the CNS
clusters of neuron cell bodies in the CNS are called nuclei
clusters of neuron cell bodies in the PNS are called ganglia
Histology of Nervous Tissue
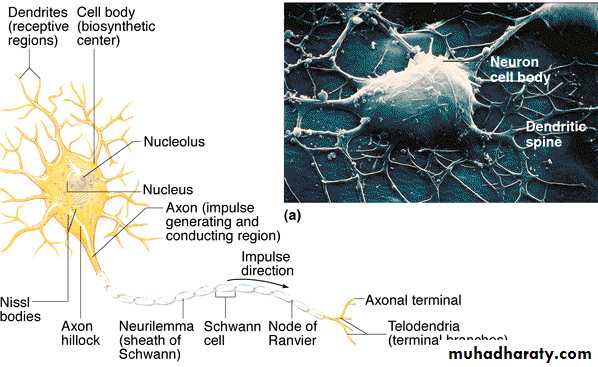
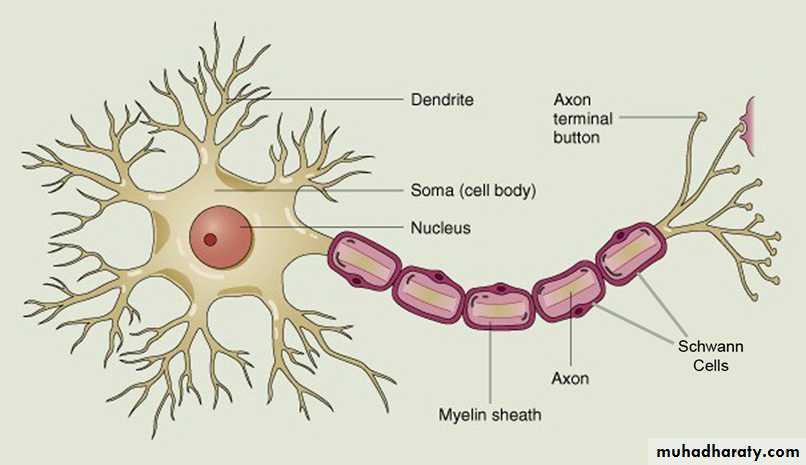
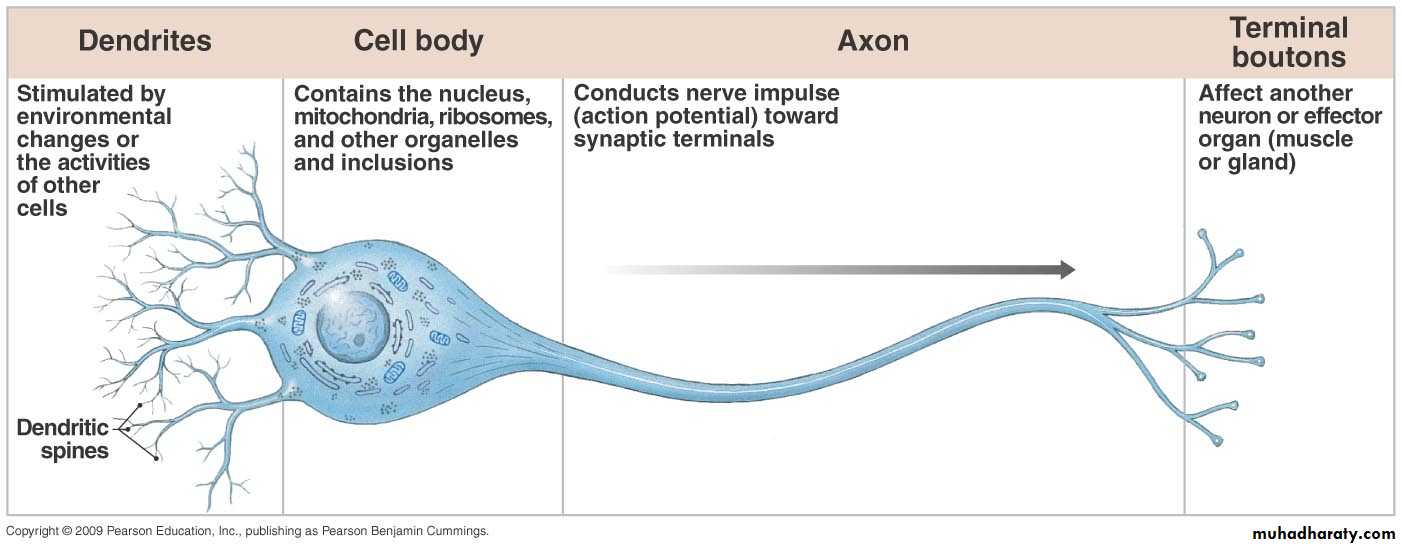
Parts of a NeuronSchematic diagram of a neuron
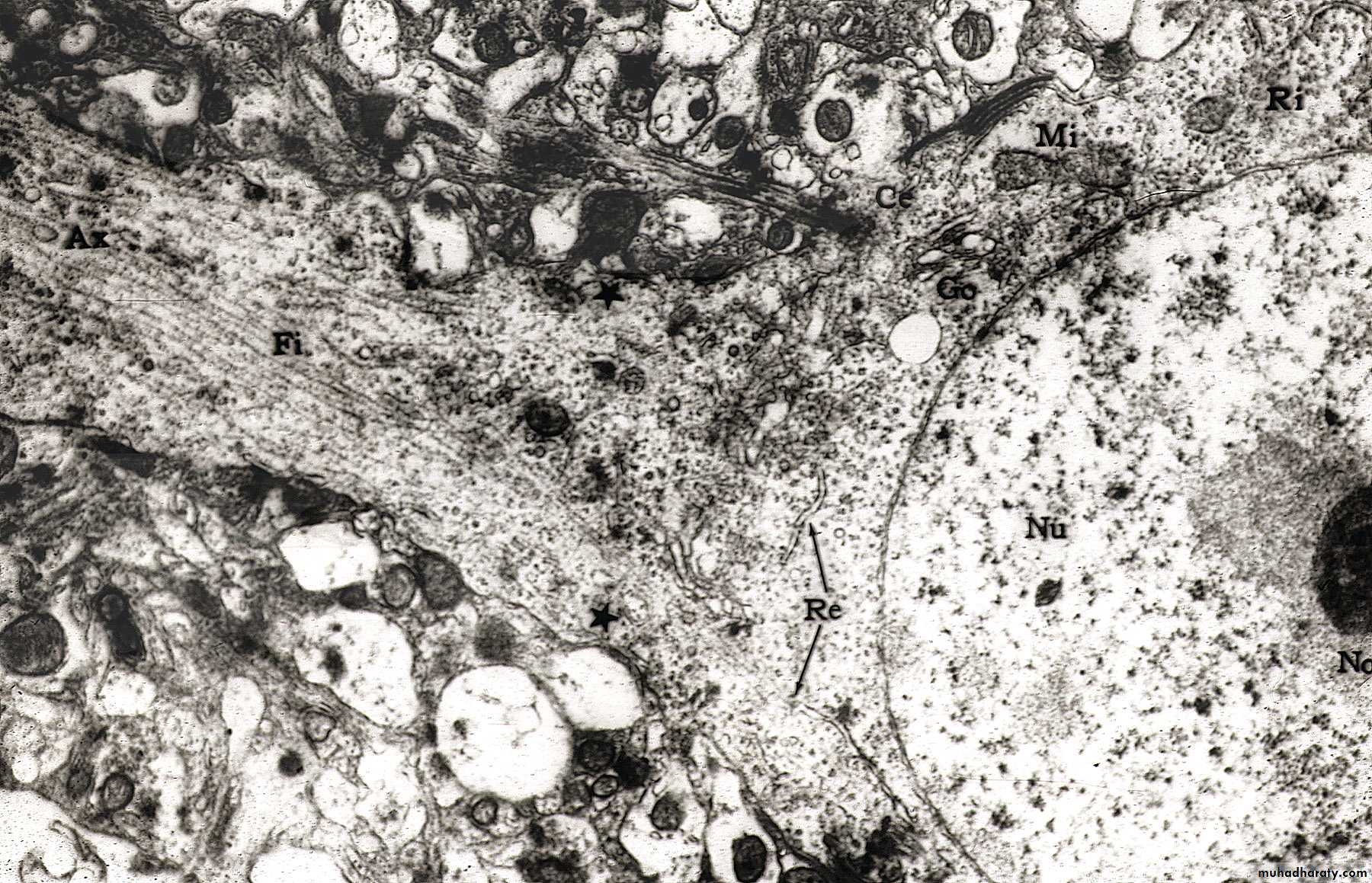
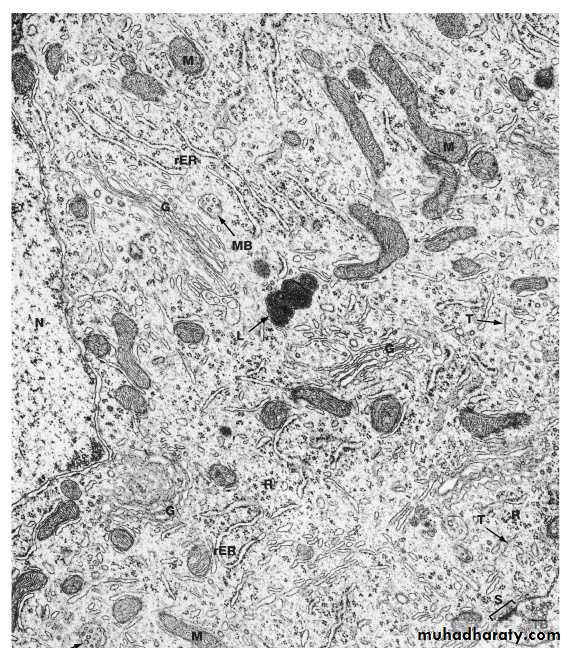
TEM of Nerve Cell Body and Axon
Nu = nucleus
Ax = Axon
Fi = neurofilaments; Re = RER; Go = golgi; Mi = MitochondriaNerve Cell Body with dark staining Nissl
Mitochondria M
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum rERNucleus N
Golgi Apparatus G
Microtubules T
Synapse
Terminal bouton TB
Ultrastructure of The Neuron (Electron Microscope) EM
Lysosome L
A Review of the Neuron Structure
Relationship of the 4 parts of a neuron (dendrites, cell body, axon, and synaptic terminals);- the functional activities of each part
- the normal direction of action potential conduction
Pyramidal Cells, 2
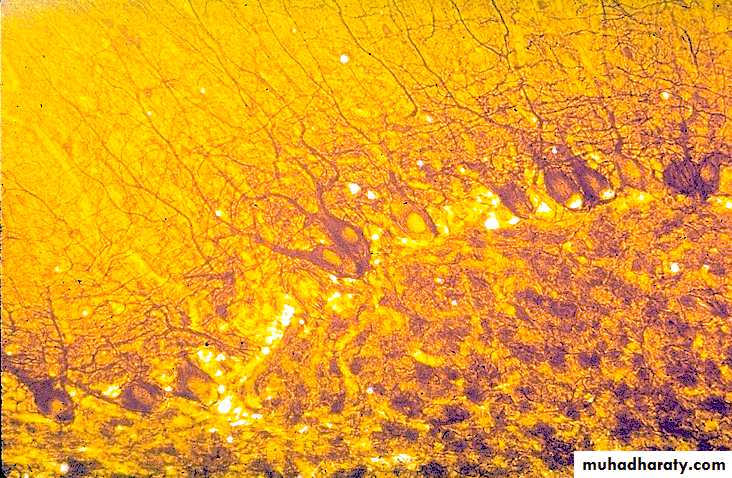
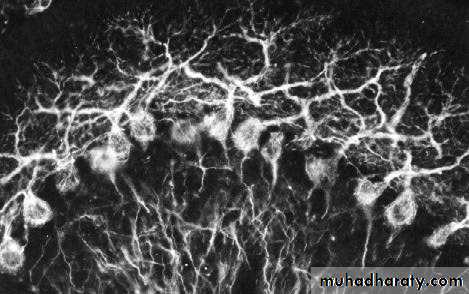
Purkinje Cells, 2
Purkinje Cells, 3
Purkinje Cells, 4
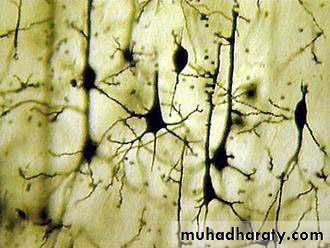
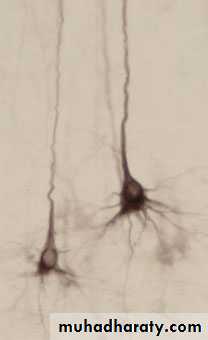
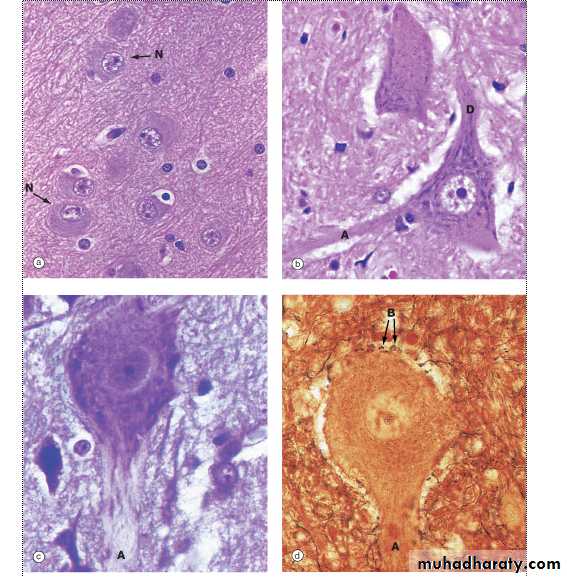
cytoskeleton stainNeurons with different staining methods
Axon ADendrite D
Neuron N
Terminal bouton B