Plasma LIPOPROTEINS METABOLISM & DISORDERS Basil OM Saleh
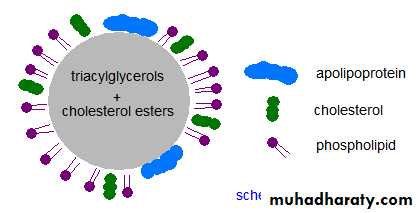
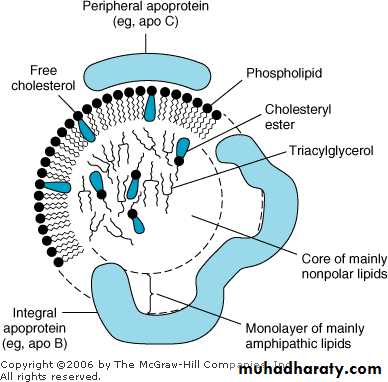
Lipoproteins LPs are spherical structures composed from lipids and proteins and function in supporting the transport of lipids in circulation. In these structures the water insoluble lipids (TG and esterified cholesterol) are oriented to the core of the spherical LP, while the water soluble lipids(PL, Free chol. ) are directed to the surface of LP.However, these structures in their later form still relatively insoluble in systemic circulation and need for addition of specific proteins, called apolipoproteins(apoLPs) to confer them sufficient water solubilitiy and so transporting in blood.
Apolipoproteins
• Structural determinants of lipoproteins• Enzyme cofactors
• Ligands for binding to lipoprotein receptors
• The apoLPs; apo AI,AII, Apo B48, apo B100, apo CI, apo CII, apo CIII, apo E 2, apo E3, apo E4
Anatomy of a Lipoprotein
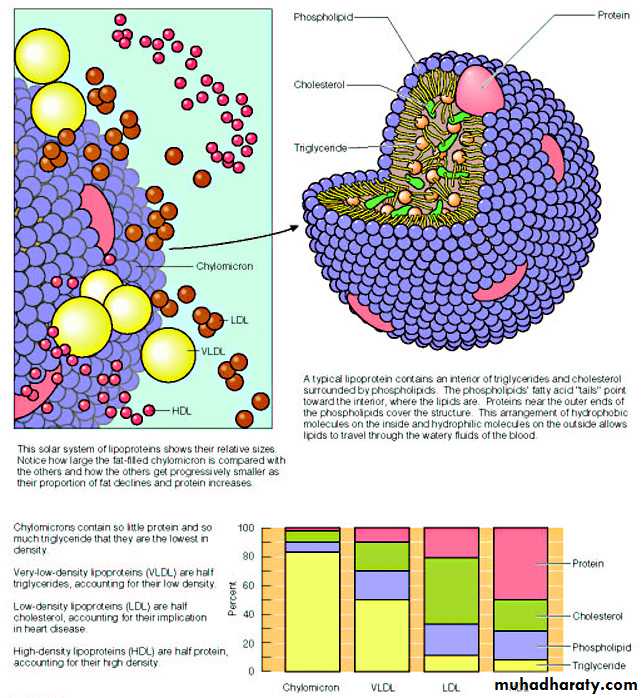
Fig. 25-1There are five major LPs in blood of human body,along with additional sixth one LP(a) that is related to LPs structurally but not functionally
1.Chylomicron2.Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)3.Intermediate Density Lipoprotein(IDL)4.Low Density Lipoprotein(LDL)5.High Density Lipoprotein(HDL)
CHYLOMICRON
Density (g/ml)Diameter (nm)
1000
8060
40
20
10
5
1.20
1.10
1.06
1.02
1.006
0.95
VLDL
IDL
CHYLOMICRON
REMNANTS
LDL
HDL2
HDL3
Chylomicrons
Synthesized in small intestineTransport dietary lipids
98% lipid, large sized, lowest density
Apo B-48
Receptor binding
Apo C-II
Lipoprotein lipase activator
Apo E
Remnant receptor binding
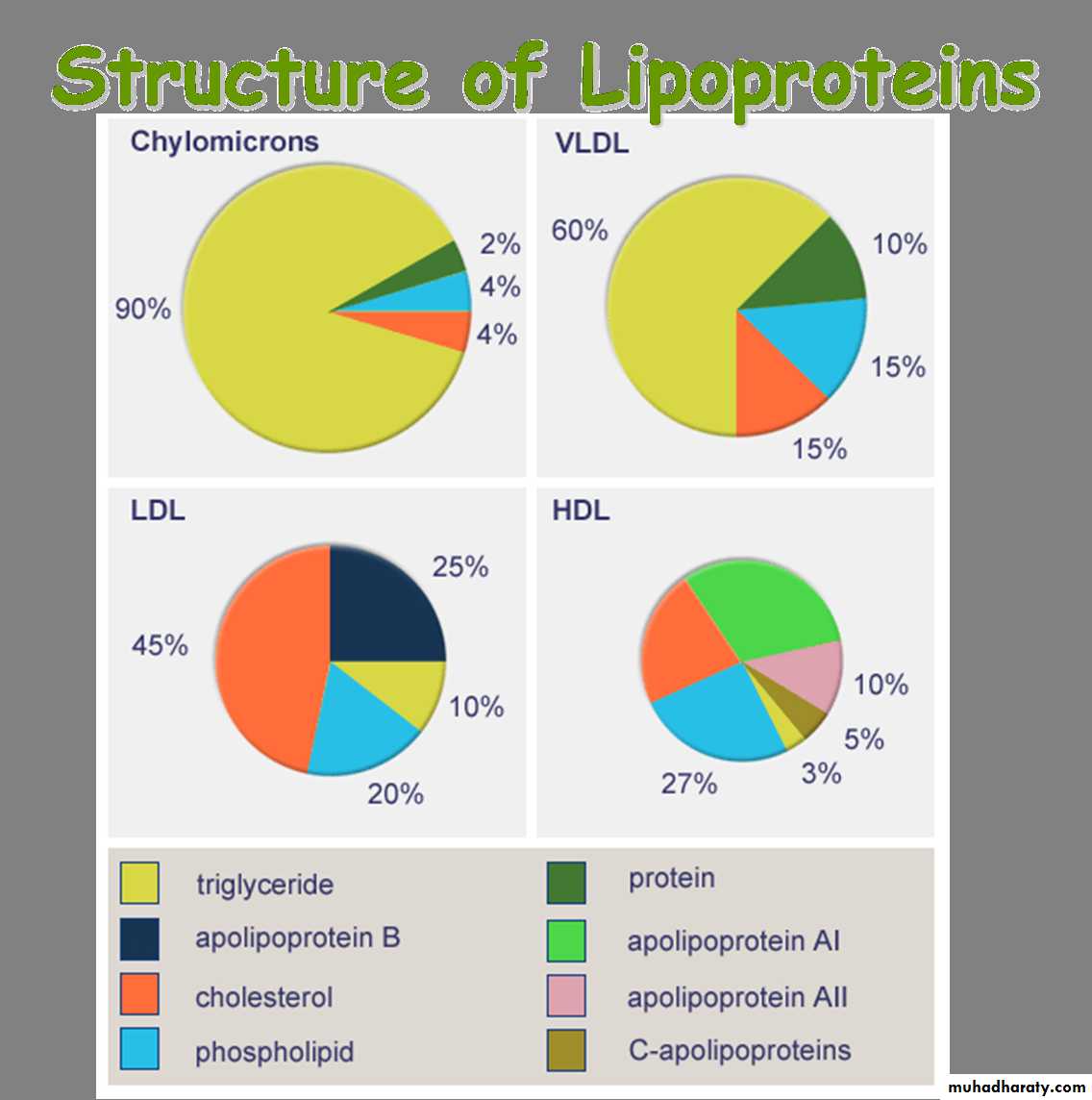
Plasma LipoproteinsClasses & Functions
TRIGLYCERIDE-RICH LIPOPROTEINS
CHYLOMICRONVLDL
TRIGLYCERIDE
CHOLESTEROLESTERS
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
FREECHOLESTEROL
PROTEINS
30-80 NM80-1000 NM
90-95%
2-4%2-6%
~1%
1-2%
50-65%
8-14%
12-16%
4-7%
5-10%
CHOLESTEROL-RICH LIPOPROTEINS
LDL
HDL
TRIGLYCERIDE
CHOLESTEROL
ESTERS (CE)PHOSPHOLIPIDS
FREECHOLESTEROL
PROTEINS
5-6%~7%
10-20%
35-45%
25%
22-26%
6-15%
~5%
22-26%
~45%
20-25 nm
8-13 nm
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE Tg
CE Tg
CE Tg
B
CE Tg
CE TgCE Tg
B
B
Tg Tg Tg
Tg Tg Tg
Tg
Tg
Tg
Tg
CE CE
CE CE
CE
B
Tg Tg Tg
Tg Tg Tg
Tg
Tg
Tg
Tg
CE CE
CE CE
CE
B
Tg Tg Tg
Tg Tg Tg
Tg
Tg
Tg
Tg
CE CE
CE CE
CE
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
CE
CE
CE
B
Tg
VLDL IDL LDL
Plasma LipoproteinsClasses & Functions
Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)Synthesized in liver
Transport endogenous triglycerides
90% lipid, 10% protein
Apo B-100
Receptor binding
Apo C-II
LPL activator
Apo E
Remnant receptor binding
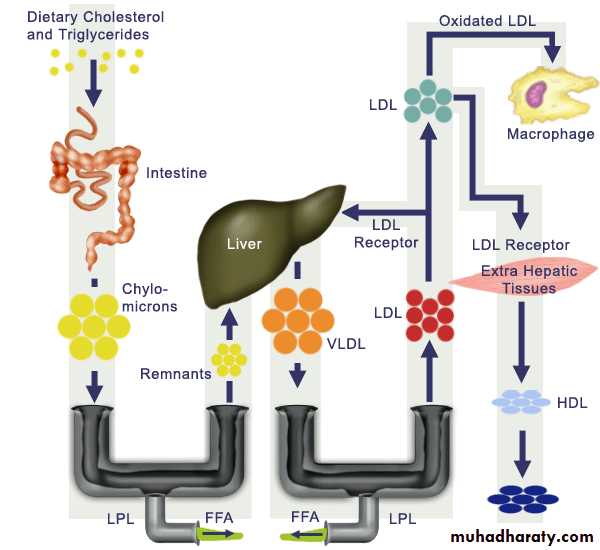
Dietary Lipoproteins
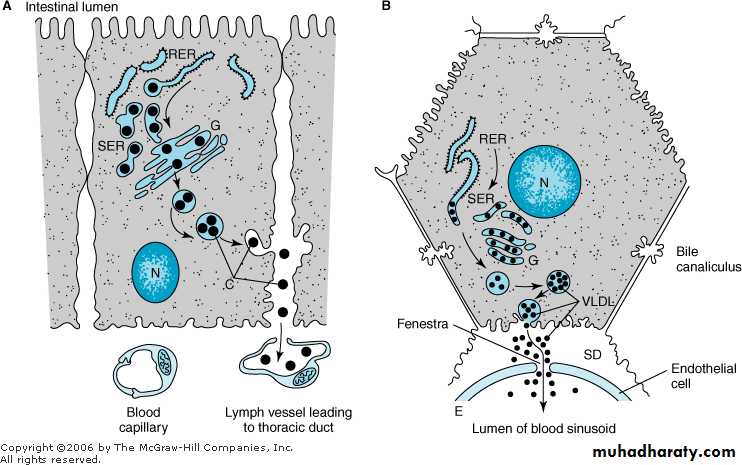
The formation and secretion of (A) chylomicrons by an intestinal cell and (B) very low density lipoproteins by a hepatic cell. (RER, rough endoplasmic reticulum; SER, smooth endoplasmic reticulum; G, Golgi apparatus; N, nucleus; C, chylomicrons; VLDL, very low density lipoproteins; E, endothelium; SD, space of Disse, containing blood plasma.) Apolipoprotein B, synthesized in the RER, is incorporated into lipoproteins in the SER, the main site of synthesis of triacylglycerol. After addition of carbohydrate residues in G, they are released from the cell by reverse pinocytosis. Chylomicrons pass into the lymphatic system. VLDL are secreted into the space of Disse and then into the hepatic sinusoids through fenestrae in the endothelial lining.