
LIPID
Aim : Introduction and
Definition

Lipid are compounds that are
soluble in organic solvents, such as
ether and relatively insoluble in
water or aqeous media e.g.human
body fluid; blood,…. .The principal
unit of different forms of lipid is
fatty acid with general formula
RCOOH; R
is alphatic carbon chain

structure:
CH3(CH2)nCH2; n
is the
number of carbon. In nature, fatty
acid may be:
1.Saturated;
CH3CH2…….,
the
common one in human body is
Palmitic acid(C16)

2.Monounsaturated
CH3CH2CH=CH……(
one double
bond), and 3.Polyunsaturated(2 or
more double bonds). The EFAs are
those fatty acids that are required
in human body but cannot be
synthesized in it, so must be
supplied in the diet to support the
growth and include:

Linoleic acid C18, 2 double bonds
Linolenic acid C18, 3 double bonds
Arachidonic acid C20, 4 double
bonds. These EFAs are important
components of phospholipids of
cell membrane and mitochondrial
membrane and their deficiencies
result in defect in growth and
development.

Even the incidence of EFAs
deficiencies is rare, it can lead to
scaly dermatitis, visual and
neurologic defects. The absolute
EFAs are the linoleic acid, the
precursor of arachidonic acid that
is a substrate for Prostaglandins
synthesis and the Linolenic acid,
the precursor for other ω-3 fatty
acids

formula important for growth and
development and used
antihypertriglyceridemic drug.
Fatty acids also may be:
Short : C2-C4
Medium: C6-C10
Long: C12 and more.

The saturated fatty acids are
naturally found in Zigzag form,
while the unsaturated ones are in
kink form. The degree of
unsaturation(number of double
bonds) and
the carbon chain length are
important in determining of

melting point of fatty acids and so
of biological membrane fluidity
(permeability to lipid soluble
substances).
The important structures of lipid
materials are:
1. Triglycerides; Simple lipid
2. Phospholipids; Complex lipid
3. Sphingolipids and Glycolipids;
Complex lipid.

4.Cholesterol(Cyclolipid)
5. Lipoproteins, Male and Female Sex
Hs, Adrenal Cortical Hs(cortisol and
aldosterone), Vitamin D, and other.
Definitions:Triglyceride; TG. It is fatty
acid ester of glycerol.
(Triacylglycerol):
CH2OCOR1
glycerol CHOCOR2fatty
CH2OCOR3acids

R1,R2,R3 are different fatty
acids.TG is considered as nonpolar
structure and so not implied in CM
formation.
Glycerol+R1=Monoglycerol
Glycerol+R1+R2+Diacylglycrol
Glycerol+|R1+R2+R3=Triacylglycer-
ol

TG represents(its function) the
principal storage form of energy in
adipose
tissues
that
needed
physiologically in prolonged fasting
and starvation and pathologically,
for
example
in
uncontrolled
diabetes mellitus. It is also the
preferred form of nutrient that is
used by muscle in producing of
chemical
energy
ATP
under
normaons.
Physiolog. and pathologic
conditions. TG forms about 95 %
of dietary fat.
Phospholipids;PL(
Phosphoglycerolipids):
CH2OCOR1
CHOCOR2
CH2O
PO3-b
b: is Nitrogen base

Base
PL
Choline Lecithin
Ethanol amine Cephalin
Serine Phosphatidylserine
Inositol Phosphatidyl inositol
triphosphate
And Cardiolipin phospholipid;
Diphosphatidyl glycerol.

PLs are considered amphipathic
compounds because of their
formation from polar(PO4 and
nitrogen base) and nonpolar(fatty
acids) structures.

Lecithin PL is:
1.the predominant type of PL in
CM
2.the source of choline component
of the neurotransmitter, the
Acetylcholine
3.the principal lipid component of
Lung surfactant(90 % lipid and 10
% protein), its
deficiency in preterm infants is

is associated with inadequate
production or secretion of
surfactant causes Respiratory
Distress Syndrome(RDS), the
significant cause of death.
Lecithin is made and secreted by
pneumocytes to act as surfactant,
decrease the surface tension of
fluid lining the alveoli so reducing
the pressure needed to reinflate

alveoli, thereby preventing alveolar
collapse(atelectasis)
4. involved in emulsification of fat
diet in small Intestine along with
Bile salt. Cardiolipin PL is the
principal type of PL that involved in
inner mitochondrial
membrane structure(important for
maintenance of certain respiratory
complexes).

Anti-cardiolipin ACL is used in
investigation of abortion or dead
infant delivery, because this PL
cardiolipin is recognized by
antibodies that raised against
Treponema Pallidum the bacterium
that causes Syphilis. Phosphatidyl
inositol triphosphate in CM act as
a second messenger(internal
messanger) for protein hormones
action

action. Platelet activating factor
PAF and Plasmalogensare
compounds that belong to PL
structure but differ in containing
ether linkage ROR instead of ester
linkage ROCOR at C1 of PL. PAF is
synthesized and released by a
variety of cell types, binds to

surface receptors with triggering
potent thrombotic and acute
inflammatory processes. It causes
platelets to aggregate and
degranulate, and neutrophiles and
macrophages to produce
superoxide radicals, the killing
substance of infected bacterium.
Sphingolipids(Phosphoshingolipids
: Sphingomyelin):
These are also PL but differ from
phosphoglycerolipids(previous
types) in their structure: They are
composed of Sphingosine alcohol
instead of Glycerol. Sphingosine is
C18 monoalcoholamine:

CH3(CH2)12CH=CHCHOHCHNH2CH2OH
Sphingosine+fatty acid=Ceramide
Ceramide+Nitrogen base=
sphingolipid. Of the most
significant type of these PL in
humans is sphingomyelin in which
the base is choline. It is an
important component

of myelin sheath of nerve fibers,
insulates and protects neuronal
fibers of the central nervous
system(preventing the short
circulation of nerve electrical pulse
transmission).

Glycolipids:
These are another type of lipid.
Their structures are relatively
similar to sphingolipid;
Ceramide+ carbohydrate moity(or
moities)=Glycolipids. Of which :
the simple forms are
glucosylsphingolipid and
galactosylsphingolipid(only one
unit of

CHO).The complex forms are
Globoside and Ganglioside(2-9
units of CHO).They are found in
outer leaflet of plasma membrane
and contribute to cell surface
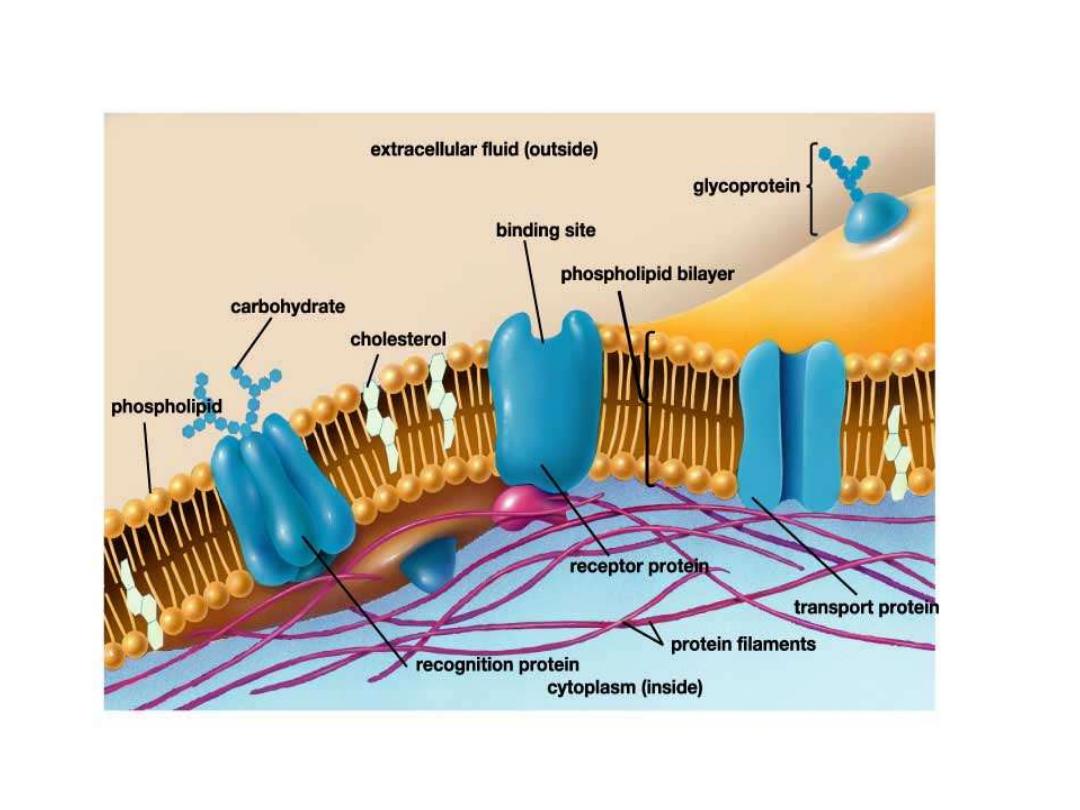

In summary
1.Lipids are water insoluble
substances(insoluble in systemic
circulation). 2. TG is the major
dietary lipid and functions as
stored metabolic energy, the major
component that act as source of
energy is fatty acids, particulary
the saturated one.

3.EFAs; are polyunsaturated fatty
acids; particulary Linoleic acid and
Linolenic acid which are precursors
of ω-
drug(antihypertriglyceridemia).
EFAs are essential for growth and
development.4. Phospholipids are
amphipathic and so involved in CM
and mitochondrial membrane

Structure. The most important one
is lecithin. RDS, ACL and APL.
Sphingomyelin is also PL, but
contains sphingomyelin instead of
glycerol alcohol. It is an important
CM component of CNS and myelin
sheath.
