
Structure and Types
Objective:
Illustration the nature structure
Basil O M Saleh
Immunoglobulins (Igs)
of Immunoglobulins, Types, AND Functions
Immunoglobulins:Structure and Function
• Definition: Glycoprotein molecules that are
immunogen and which function as antibodies
Immune serum
Ag adsorbed serum
α
1
α
2
β
γ
+
-
albumin
globulins
Mobility
A
m
o
unt
o
f
pr
o
tei
n
produced by plasma cells (Specific Immune system )in response to an

General Functions of
Immunoglobulins
• Effector functions
– Fixation of complement
– Binding to various cells
(Usually require Ag binding)
• Ag binding
– Can result in protection
– Valence

Basic Immunoglobulin Structure
• Immunoglobulins - heterogeneous
• Myeloma proteins - homogeneous
immunoglobulins
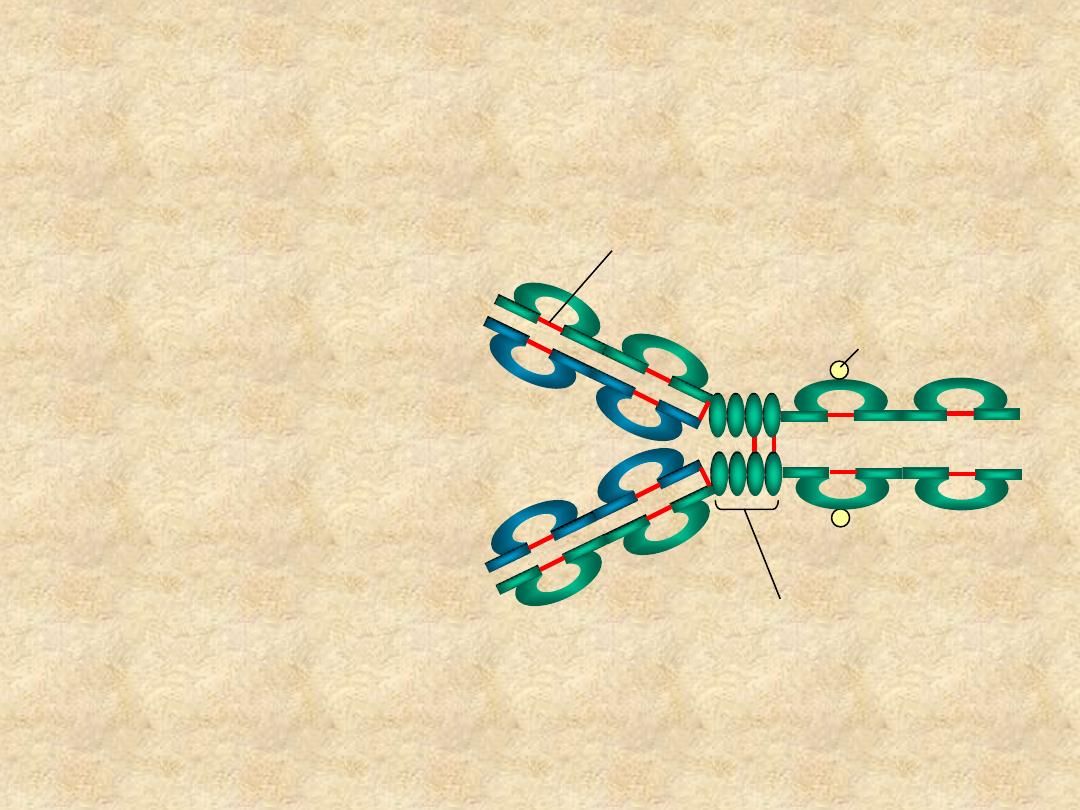
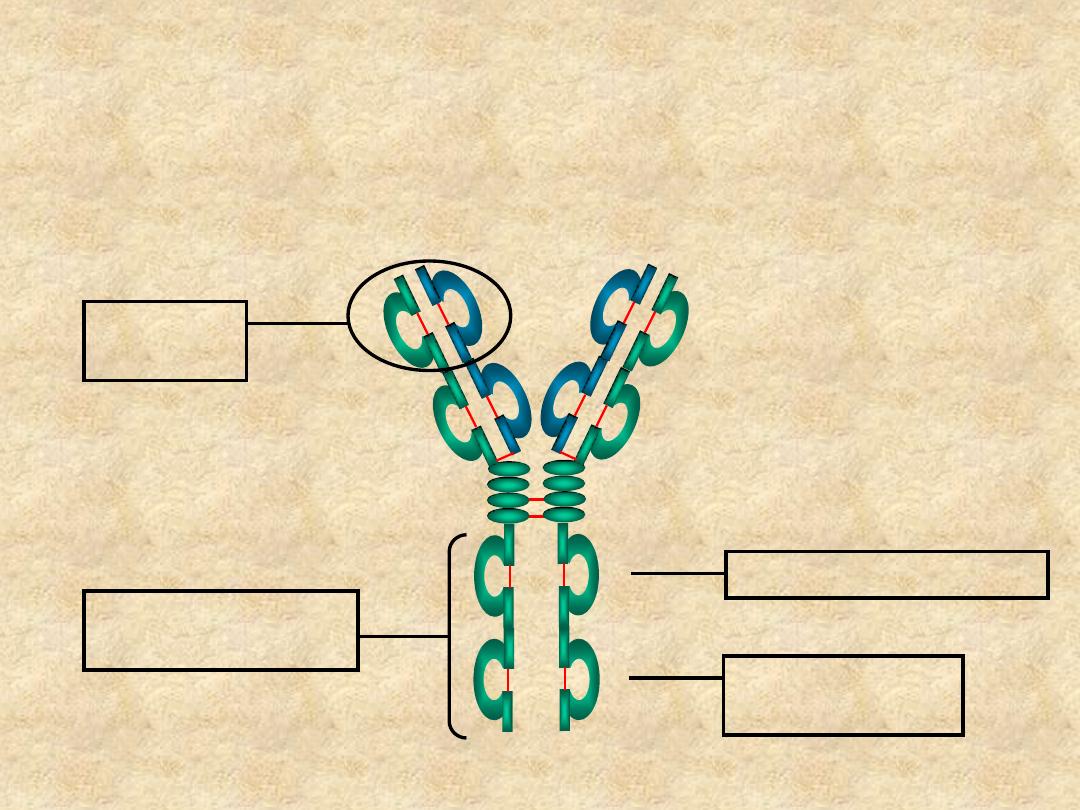
Immunoglobulin Structure
• Heavy & Light
Chains
• Disulfide bonds
– Inter-chain
– Intra-chain
C
H1
V
L
C
L
V
H
C
H2
C
H3
Hinge Region
Carbohydrate
Disulfide bond
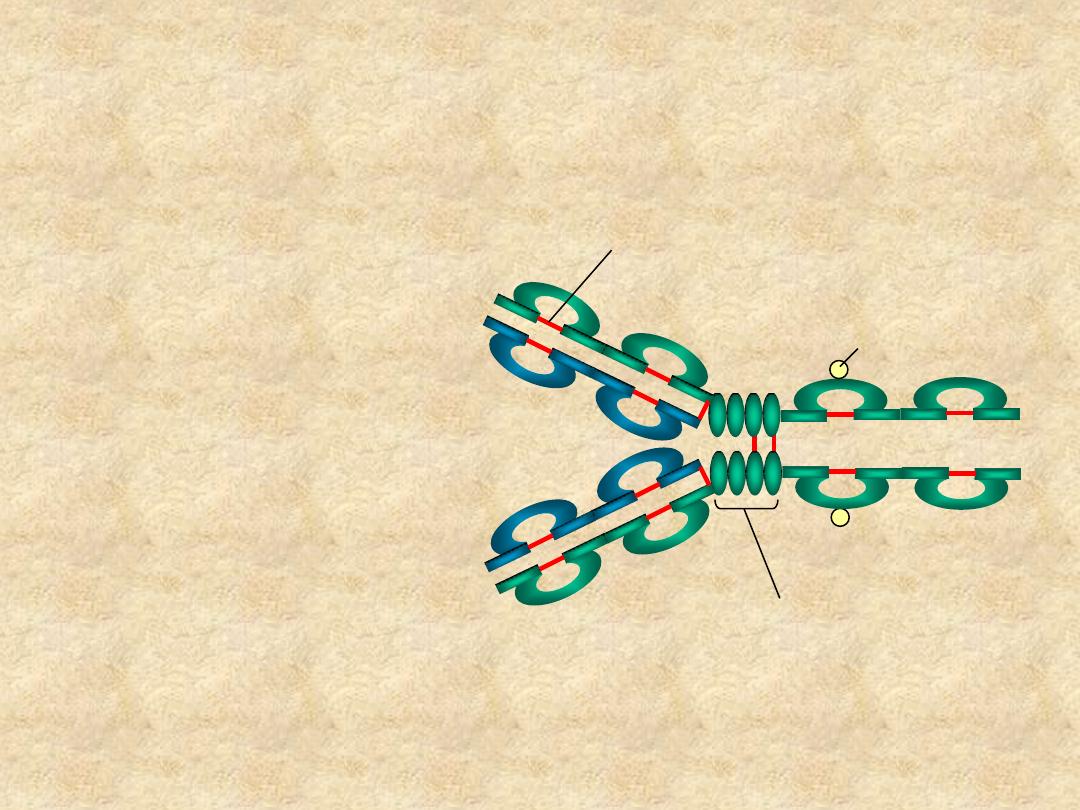
Immunoglobulin Structure
•
– V
L
& C
L
– V
H
& C
H
• Hinge Region
C
H1
V
L
C
L
V
H
C
H2
C
H3
Hinge Region
Carbohydrate
Disulfide bond
Variable (V) &
Constant (c) Regions
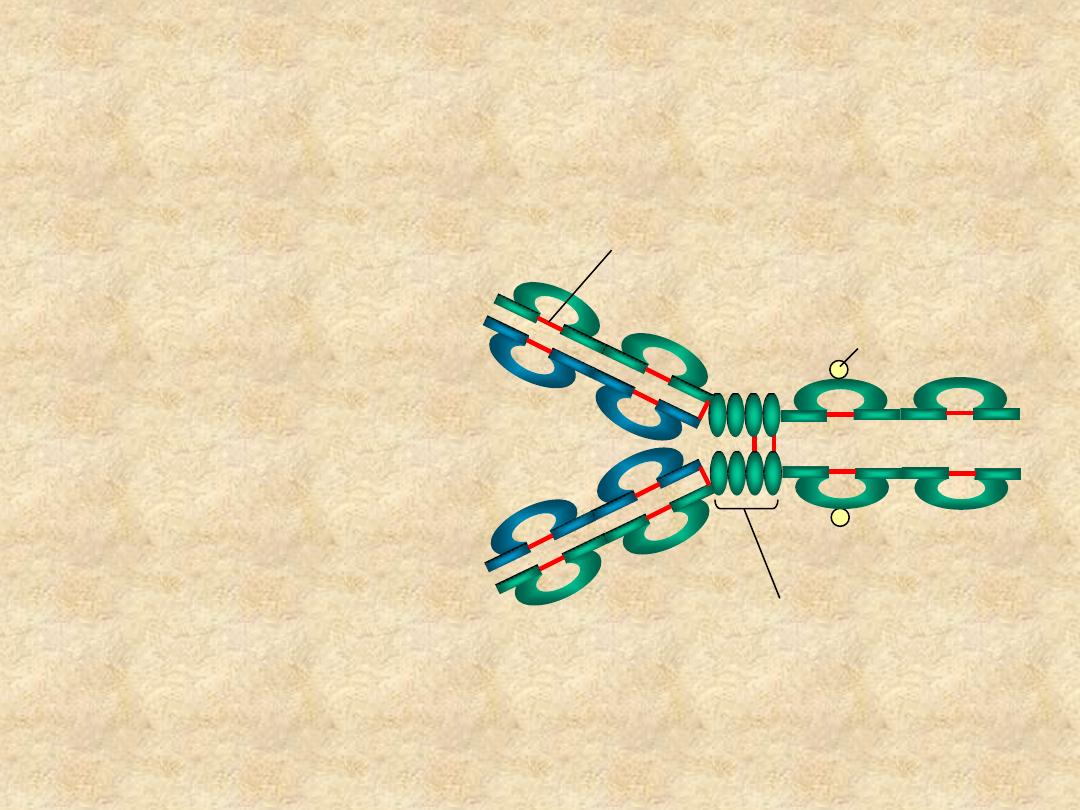
Immunoglobulin Structure
• Domains
– V
L
& C
L
– V
H
& C
H1
- C
H3
(or C
H4
)
• Oligosaccharides
C
H1
V
L
C
L
V
H
C
H2
C
H3
Hinge Region
Carbohydrate
Disulfide bond

IgG molecule
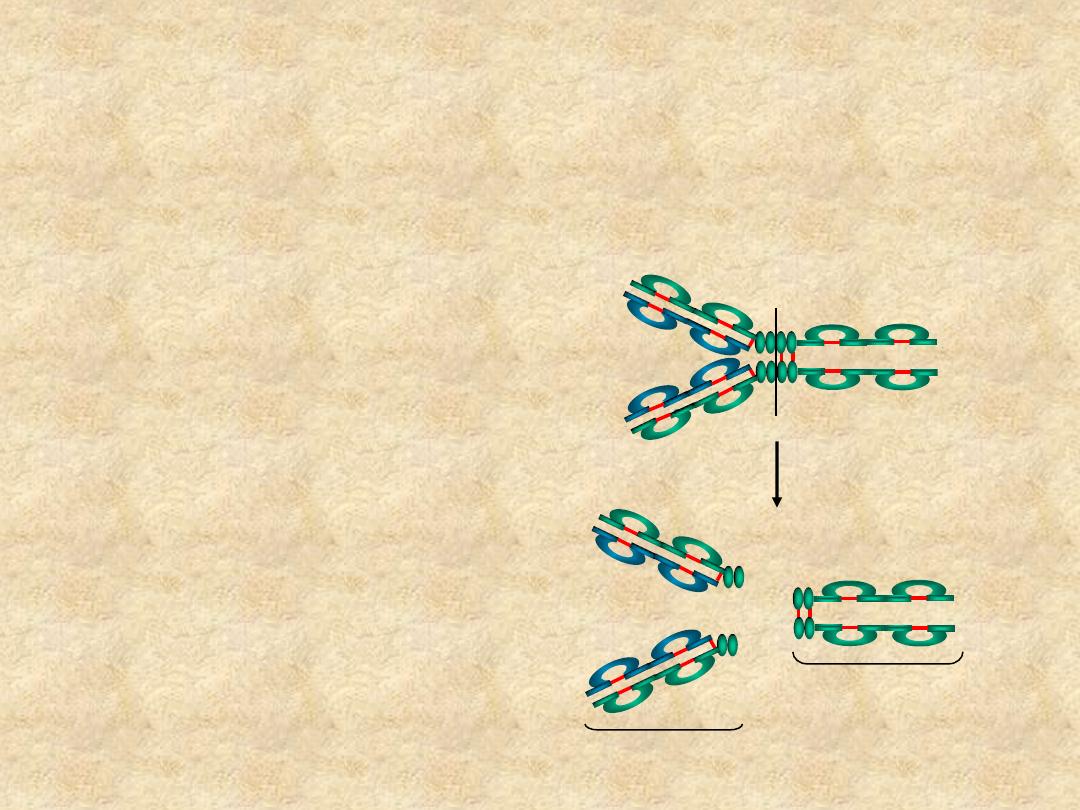
Immunoglobulin Fragments:
Structure/Function Relationships
• Fab
– Ag binding
– Valence = 1
– Specificity
determined by V
H
and V
L
Papain
Fc
Fab
• Fc
– Effector functions
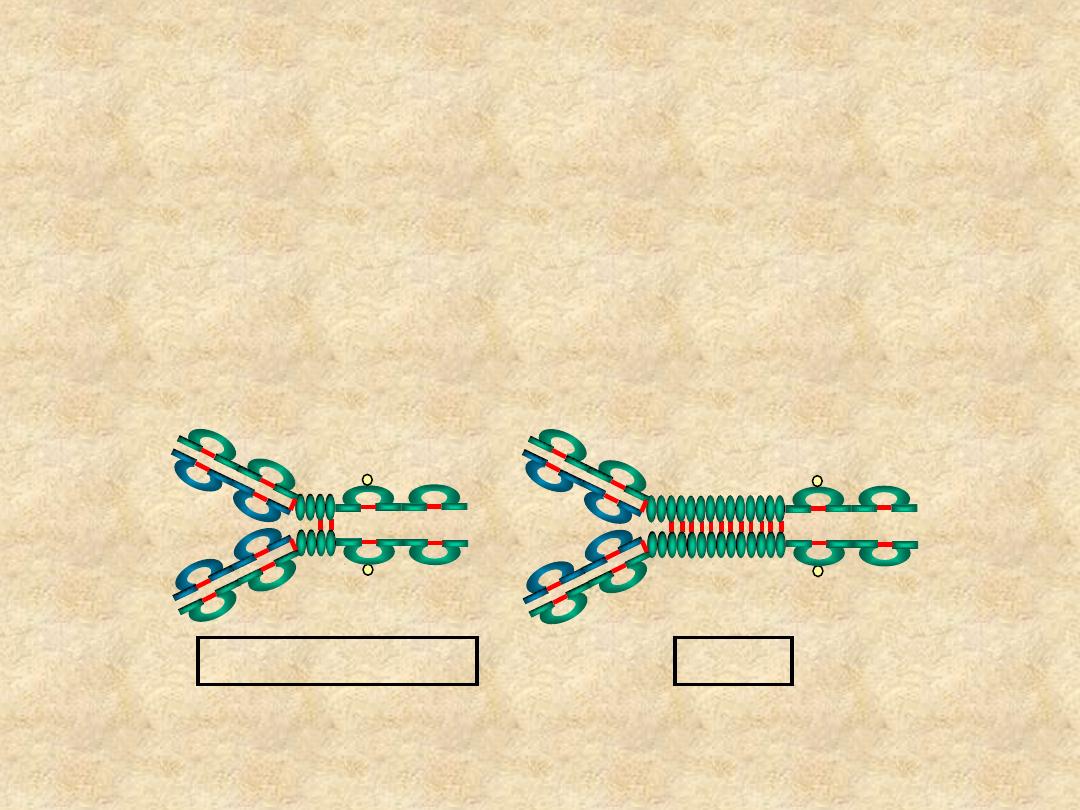
Immunoglobulin Fragments:
Structure/Function Relationships
Ag Binding
Complement Binding Site
Placental Transfer
Binding to Fc
Receptors
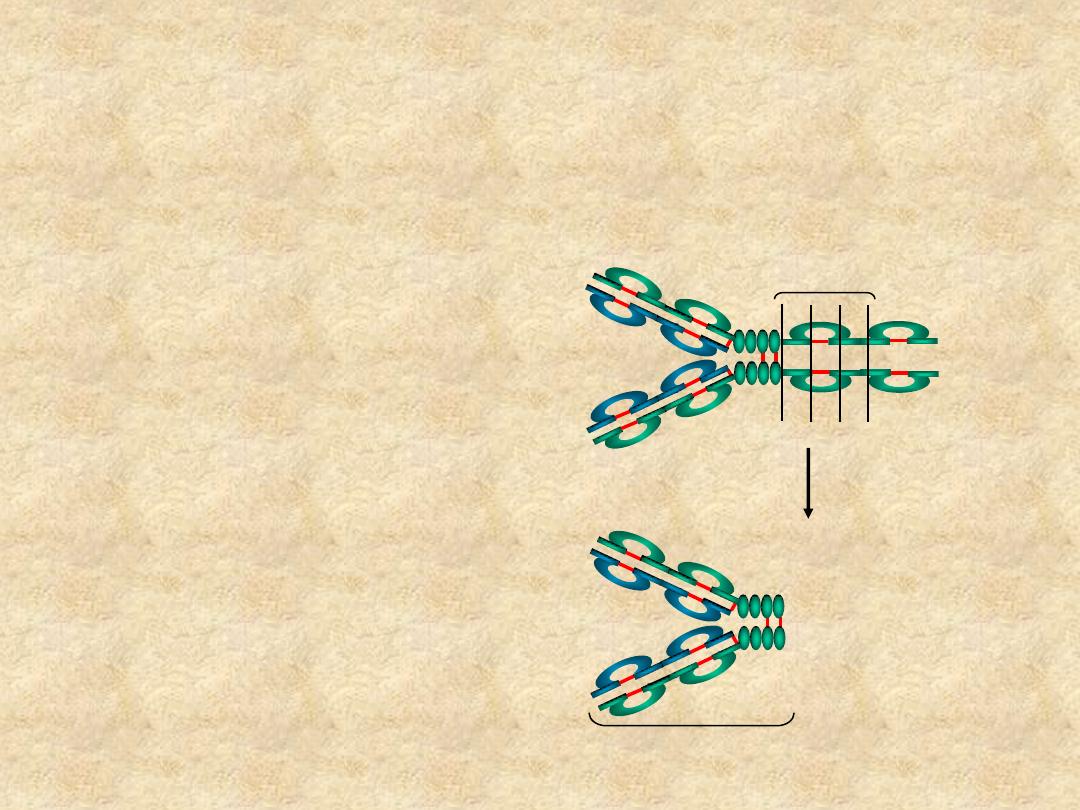
Immunoglobulin Fragments:
Structure/Function Relationships
• Fab
– Ag binding
• Fc
– Effector functions
• F(ab’)
2
Pepsin
Fc
Peptides
F(ab’)
2

Human Immunoglobulin Classes
• IgG - Gamma (γ) heavy chains
• IgM - Mu (µ) heavy chains
• IgA - Alpha (α) heavy chains
• IgD - Delta (δ) heavy chains
• IgE - Epsilon (ε) heavy chains

Human Immunoglobulin
Light Chain Types
• Kappa (κ)
• Lambda (λ)
IgG
• Structure
– Monomer (7S)
IgG1, IgG2 and IgG4
IgG3
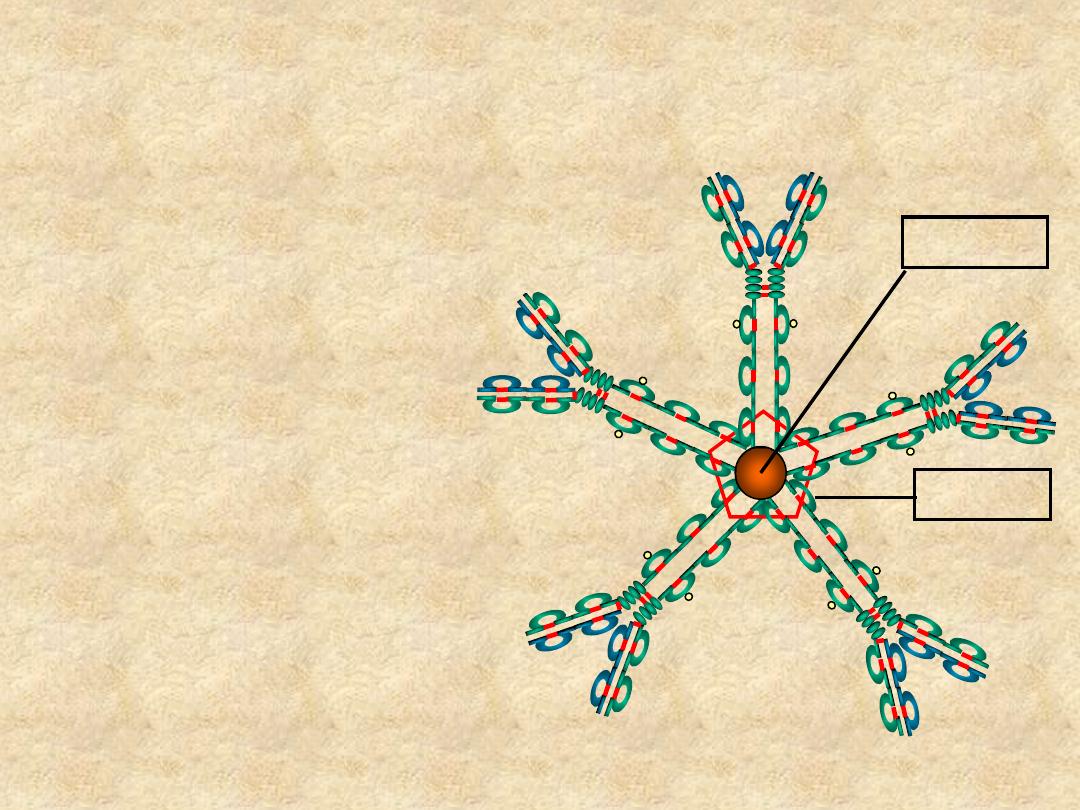
IgM
• Structure
– Pentamer (19S)
– Extra domain (C
H4
)
– J chain
Cµ4
J Chain
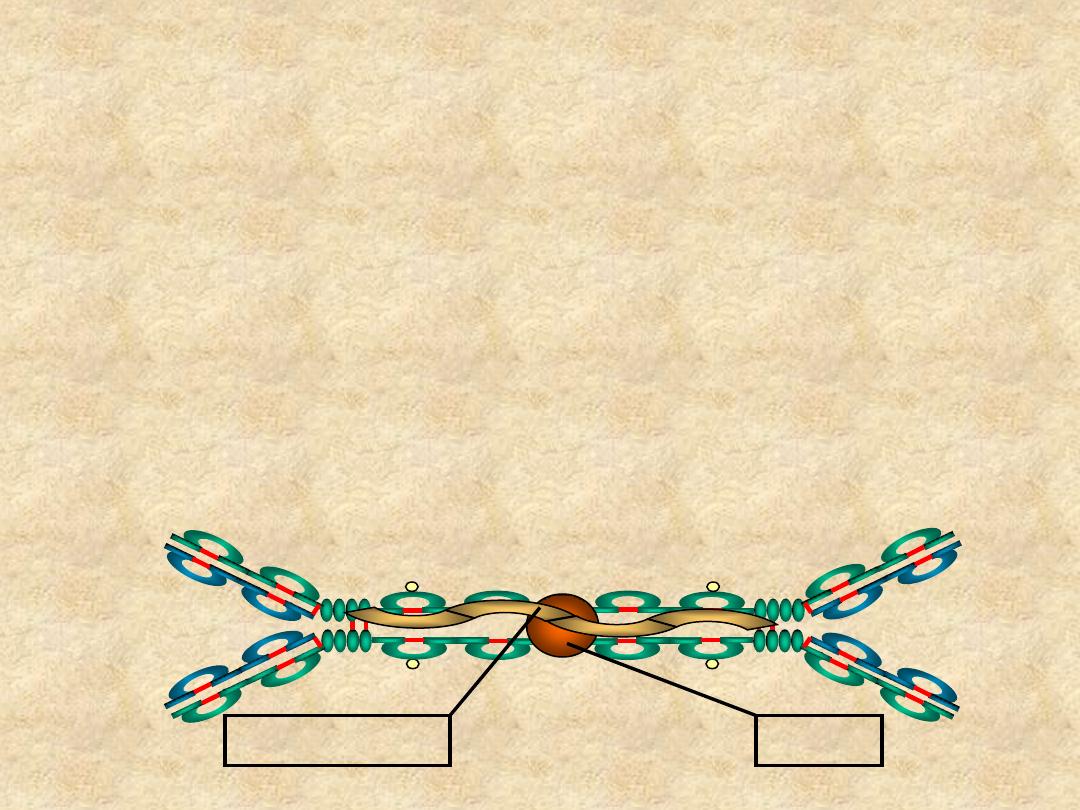
IgA
• Structure
– Serum - monomer
– Secretions (sIgA)
• Dimer (11S)
• J chain
• Secretory component
J Chain
Secretory Piece
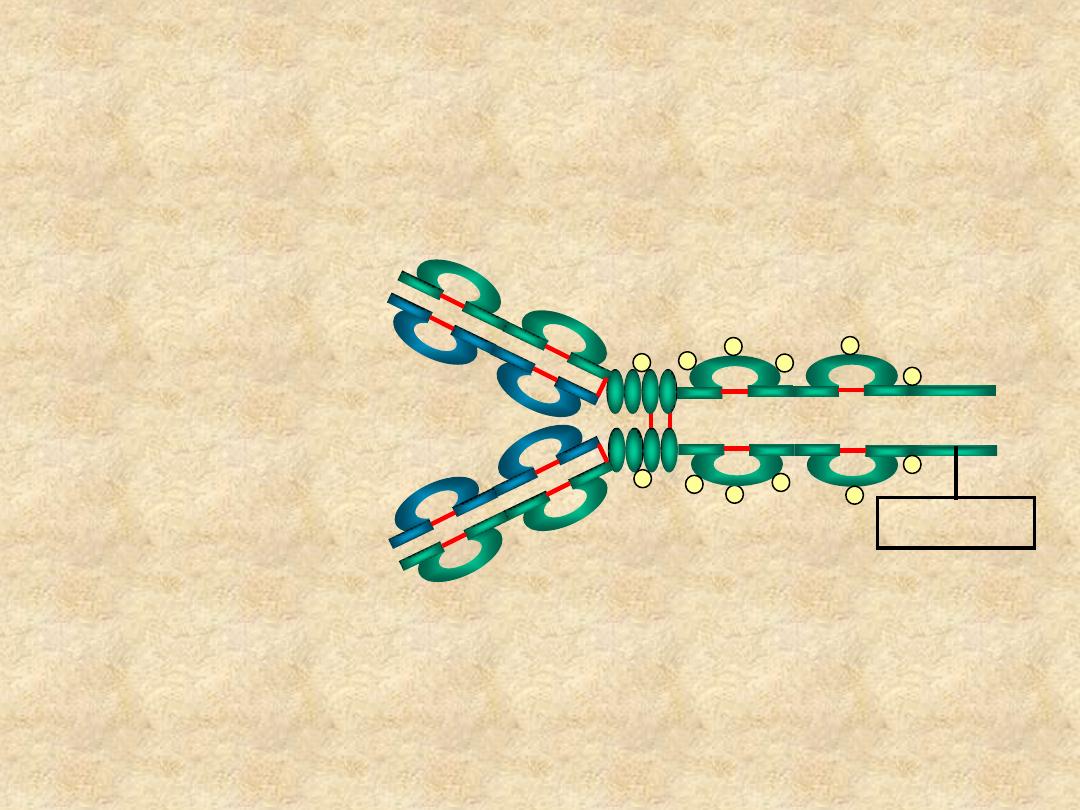
IgD
• Structure
– Monomer
– Tail piece
Tail Piece

IgD
• Structure
• Properties
– 4th highest serum Ig
– B cell surface Ig
– Does not bind complement
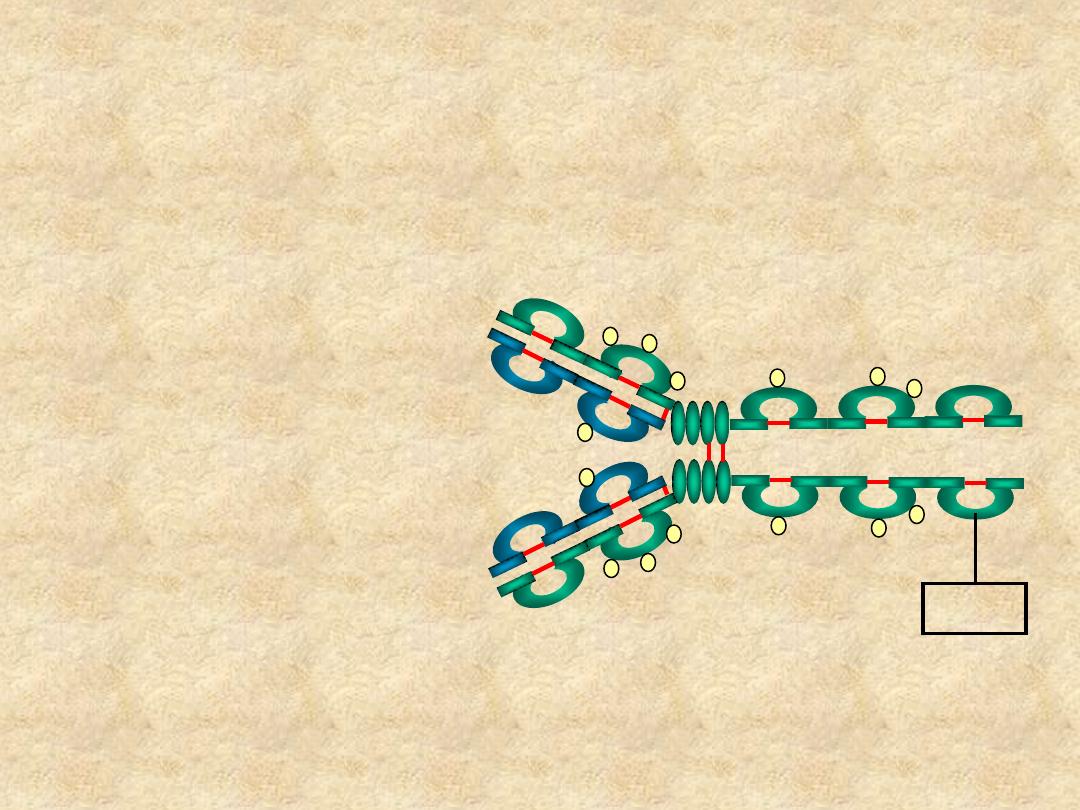
IgE
• Structure
– Monomer
– Extra domain (C
H4
)
Cε4

In Summary
The Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein(CHO+Protein) in structure
and of different types IgG, M,A,D and E. All Igs are of two chain; heavy and light chain
The light chain is of two types; Kappa and lymbda, the heavy chain are five types;
of Heavy Chain(not Light Chain) defines the type of Immunoglobulin
The light chains and heavy chains are linked by sulfide bonds (S-S).
The MW of Igs is defined by the number of their amino acids and so by their
poly peptide; the IgM has five poly peptides[PPs; (pentamer)], IgA has two PPs (dimer),
while other are monomer (one PP). The CHO is imprtant for protection of Igs from digestion
All Igs are synthesized by plasma cells of immune system and invloved in defence mechanism.
The IgG is the immunoglobulin that pass the plecenta ?? tofetus and protect his or her during pregnancy.
gamma (IgG), alpha (IgA), delta (IgD), muo (IgM), and epsilon (IgE). The type of
