
Immunoglobulins:
Structure and Types
Objective:
Illustration the nature structure
of Igs and their types
Basil O M Saleh
Immunoglobulins:Structure and Function
• Definition: Glycoprotein molecules that are
produced by plasma cells in response to an
immunogen and which function as antibodies
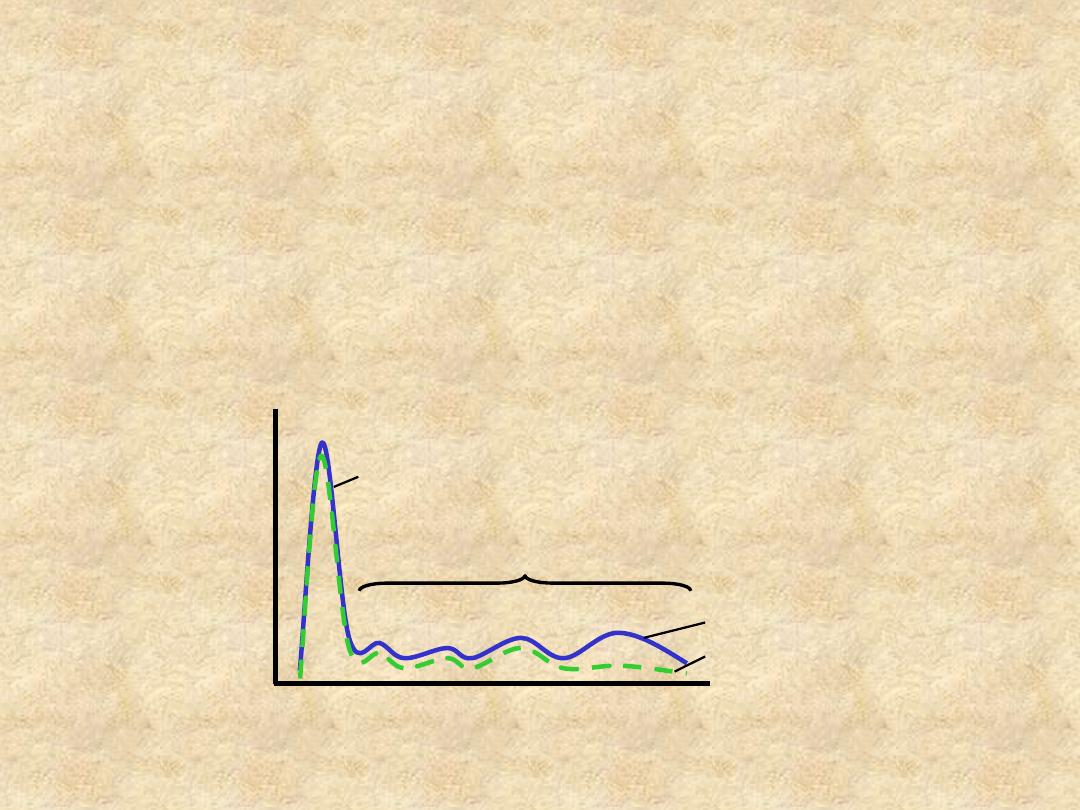
Immune serum
Ag adsorbed serum
α
1
α
2
β
γ
+
-
albumin
globulins
Mobility
A
m
o
unt
o
f
pr
o
tei
n

General Functions of
Immunoglobulins
• Effector functions
– Fixation of complement
– Binding to various cells
(Usually require Ag binding)
• Ag binding
– Can result in protection
– Valence

Basic Immunoglobulin Structure
• Immunoglobulins - heterogeneous
• Myeloma proteins - homogeneous
immunoglobulins
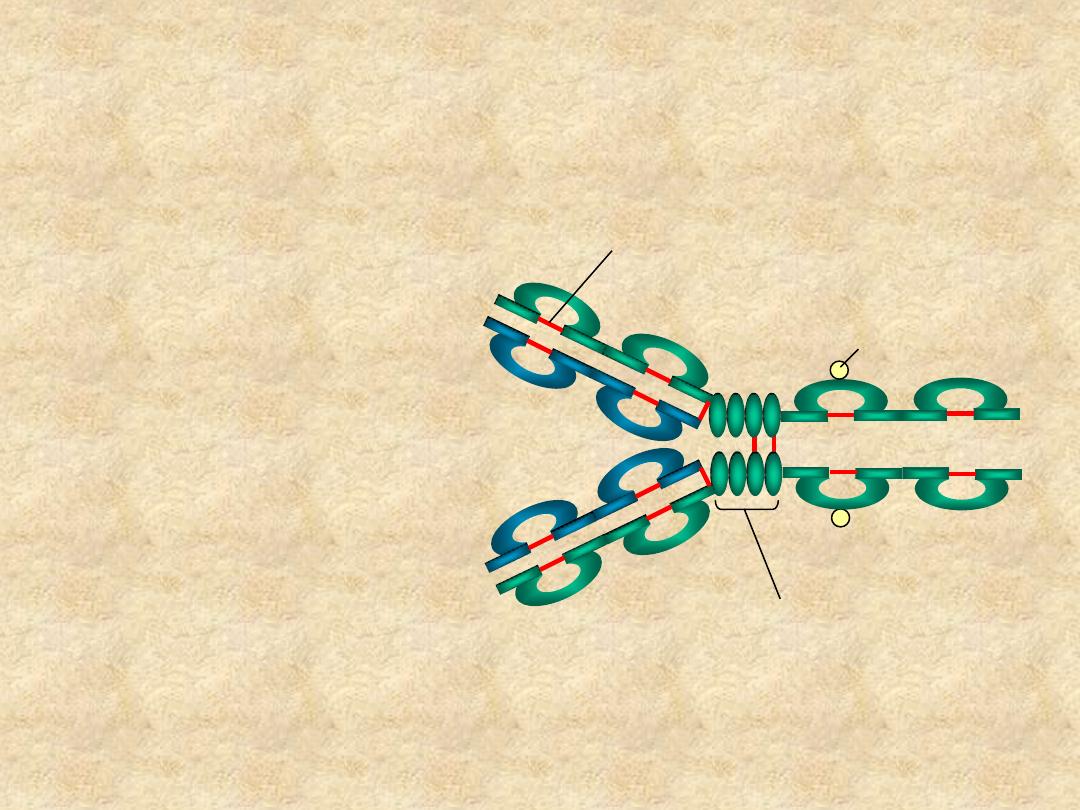
Immunoglobulin Structure
• Heavy & Light
Chains
• Disulfide bonds
– Inter-chain
– Intra-chain
C
H1
V
L
C
L
V
H
C
H2
C
H3
Hinge Region
Carbohydrate
Disulfide bond
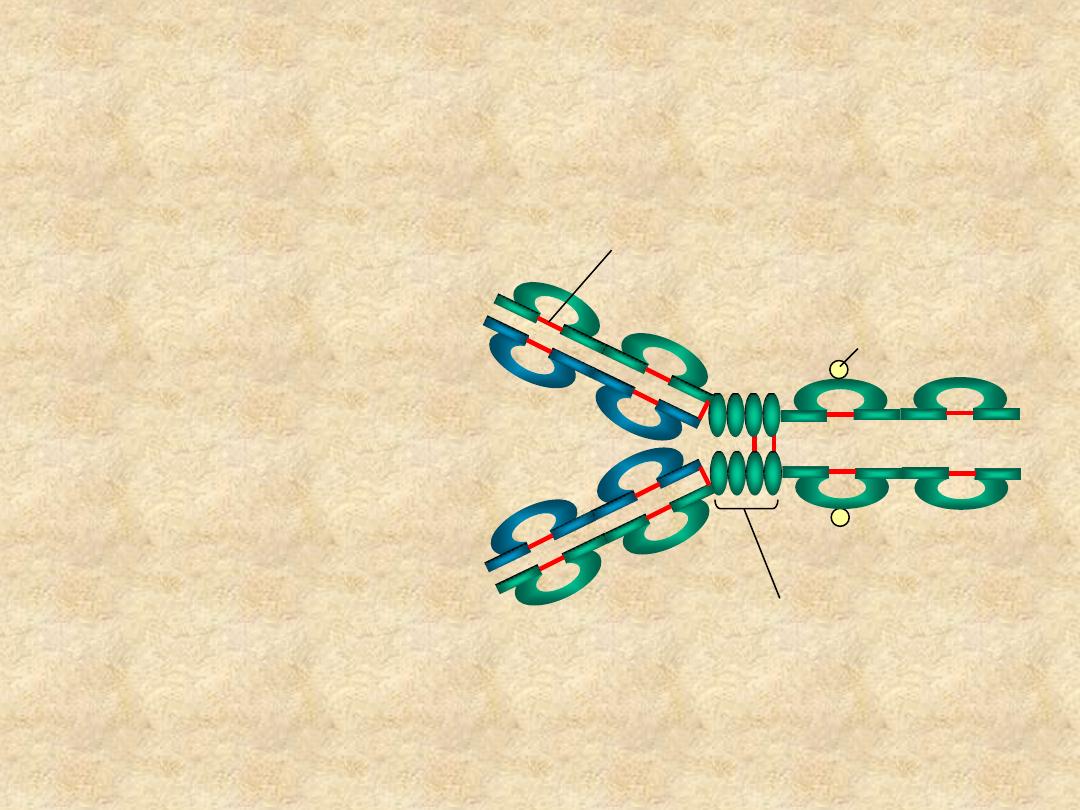
Immunoglobulin Structure
• Variable &
Constant Regions
– V
L
& C
L
– V
H
& C
H
• Hinge Region
C
H1
V
L
C
L
V
H
C
H2
C
H3
Hinge Region
Carbohydrate
Disulfide bond
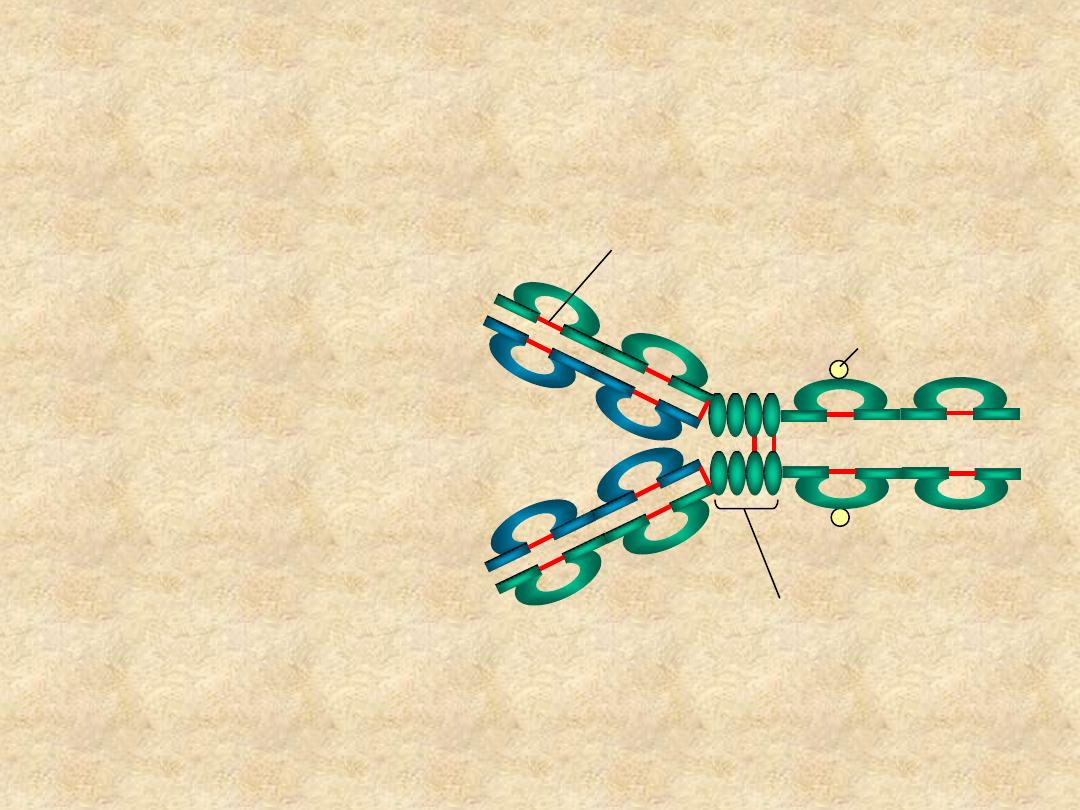
Immunoglobulin Structure
• Domains
– V
L
& C
L
– V
H
& C
H1
- C
H3
(or C
H4
)
• Oligosaccharides
C
H1
V
L
C
L
V
H
C
H2
C
H3
Hinge Region
Carbohydrate
Disulfide bond

IgG molecule
Immunoglobulin Fragments:
Structure/Function Relationships
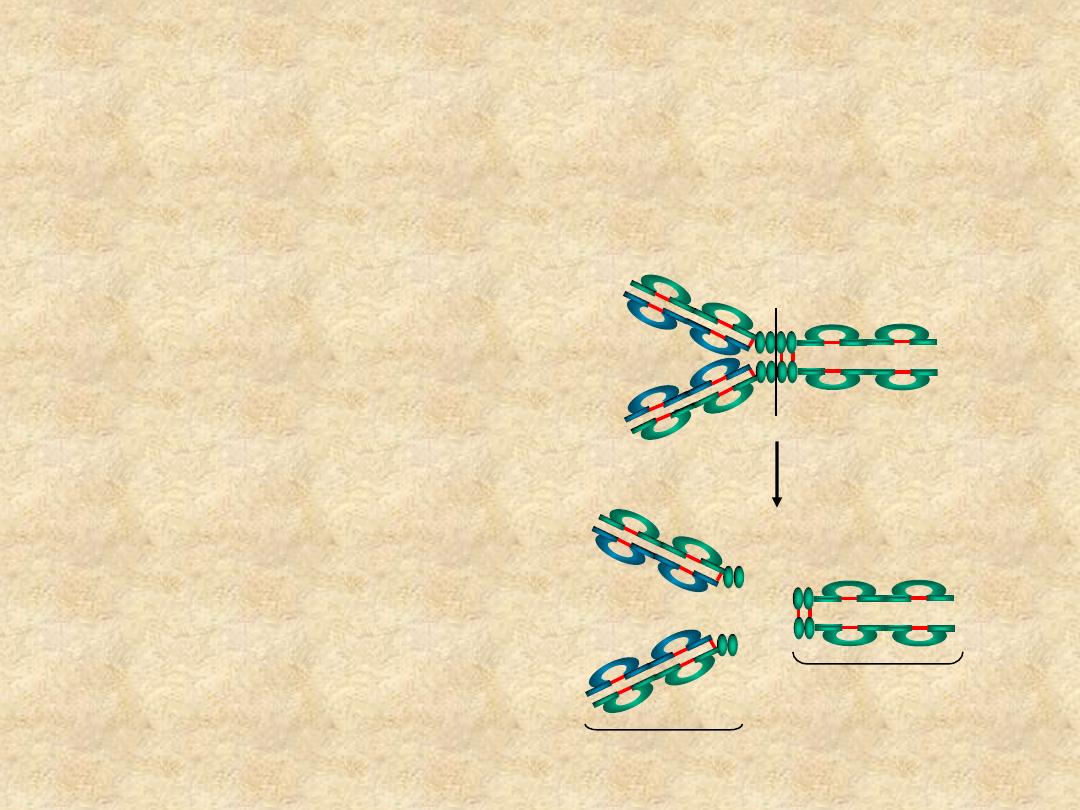
• Fab
– Ag binding
– Valence = 1
– Specificity
determined by V
H
and V
L
Papain
Fc
Fab
• Fc
– Effector functions
Immunoglobulin Fragments:
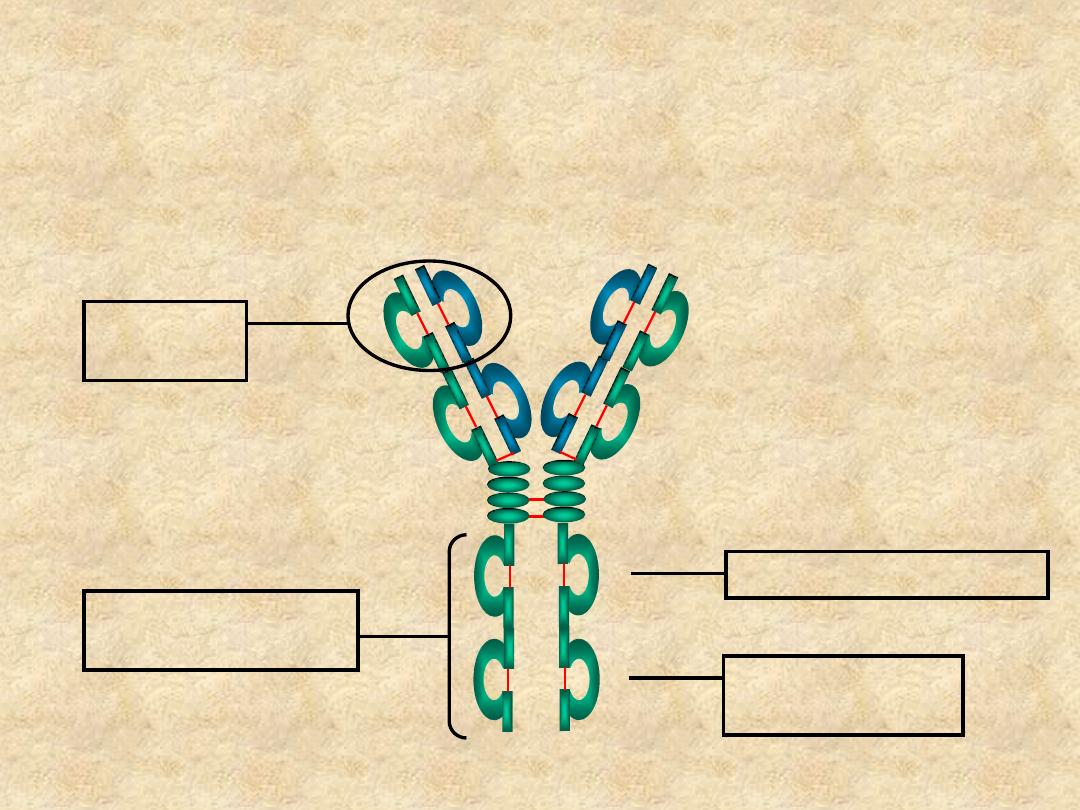
Structure/Function Relationships
Ag Binding
Complement Binding Site
Placental Transfer
Binding to Fc
Receptors
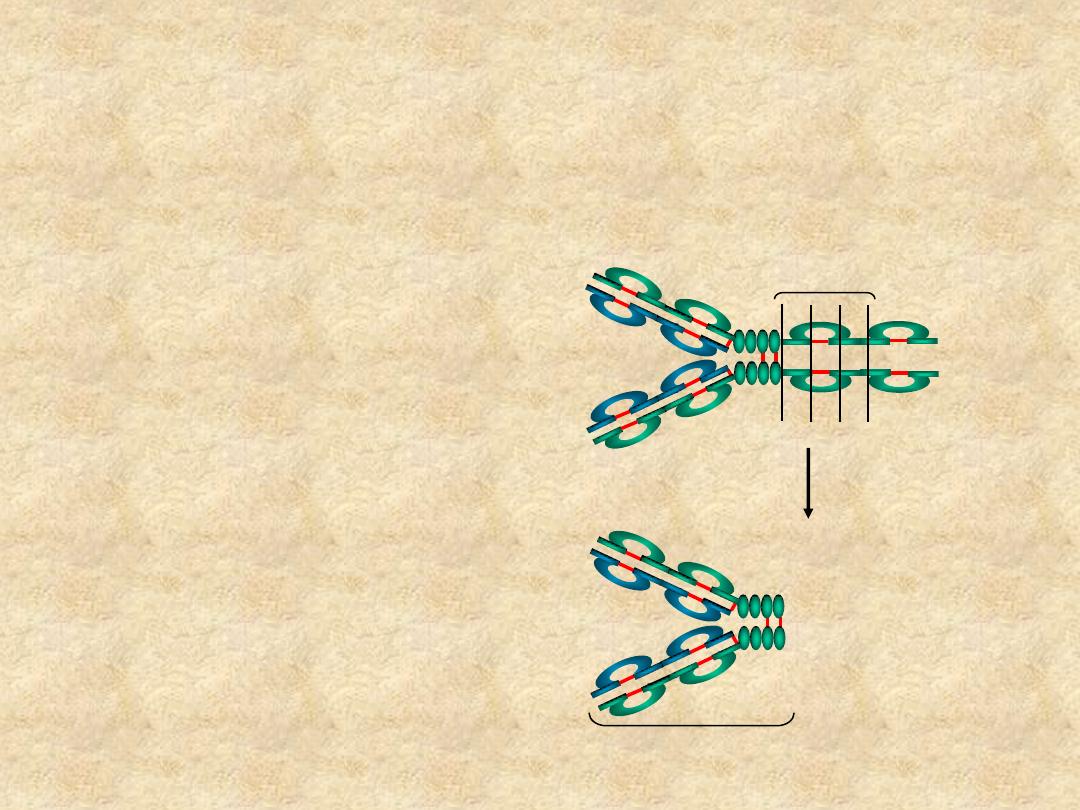
Immunoglobulin Fragments:
Structure/Function Relationships
• Fab
– Ag binding
• Fc
– Effector functions
• F(ab’)
2
Pepsin
Fc
Peptides
F(ab’)
2

Human Immunoglobulin Classes
• IgG - Gamma (γ) heavy chains
• IgM - Mu (µ) heavy chains
• IgA - Alpha (α) heavy chains
• IgD - Delta (δ) heavy chains
• IgE - Epsilon (ε) heavy chains

Human Immunoglobulin
Light Chain Types
• Kappa (κ)
• Lambda (λ)
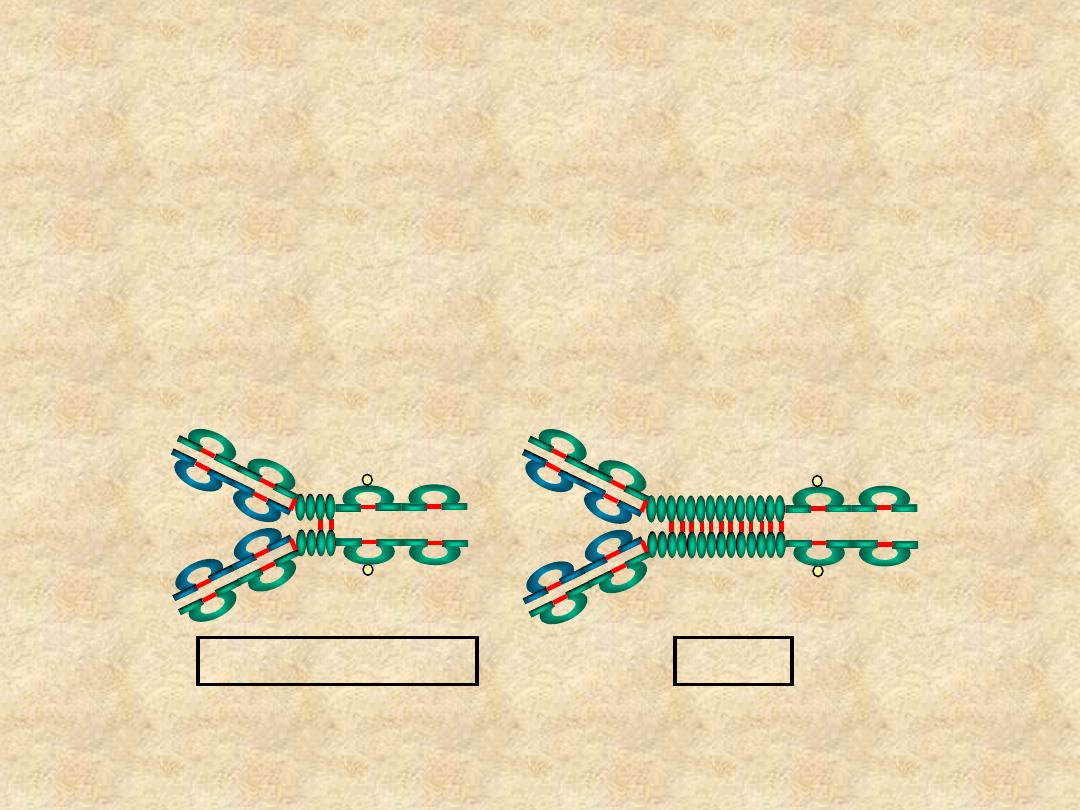
IgG
• Structure
– Monomer (7S)
IgG1, IgG2 and IgG4
IgG3
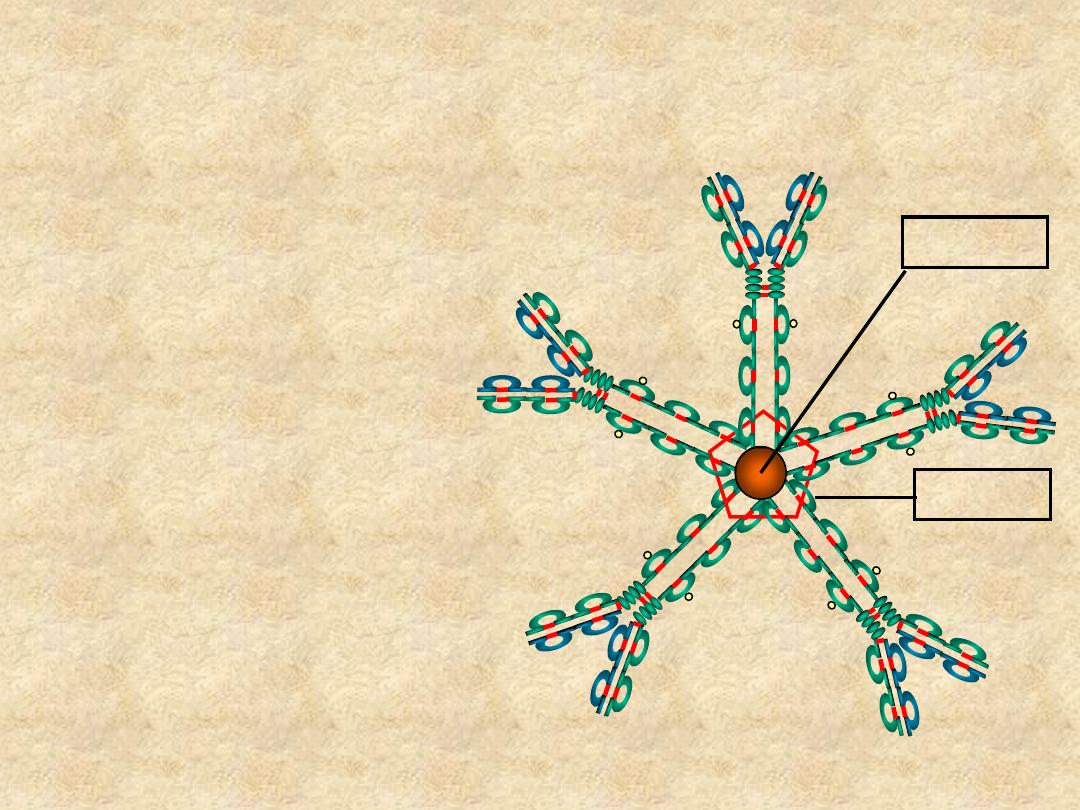
IgM
• Structure
– Pentamer (19S)
– Extra domain (C
H4
)
– J chain
Cµ4
J Chain
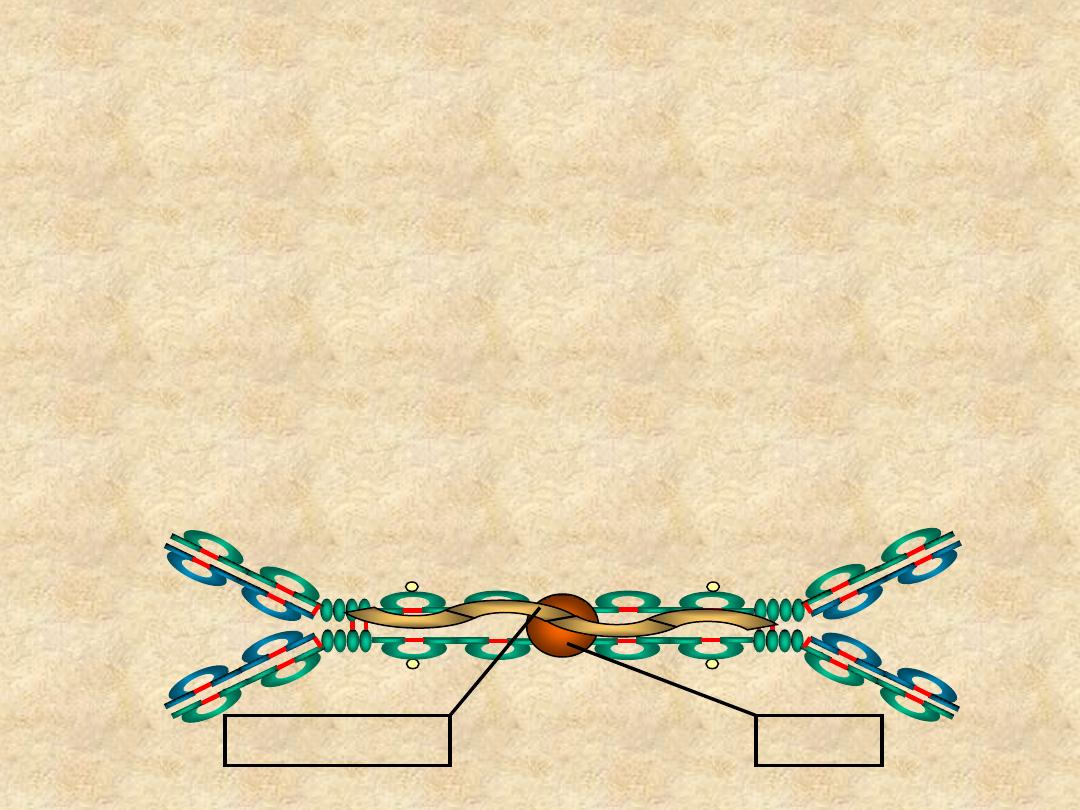
IgA
• Structure
– Serum - monomer
– Secretions (sIgA)
• Dimer (11S)
• J chain
• Secretory component
J Chain
Secretory Piece
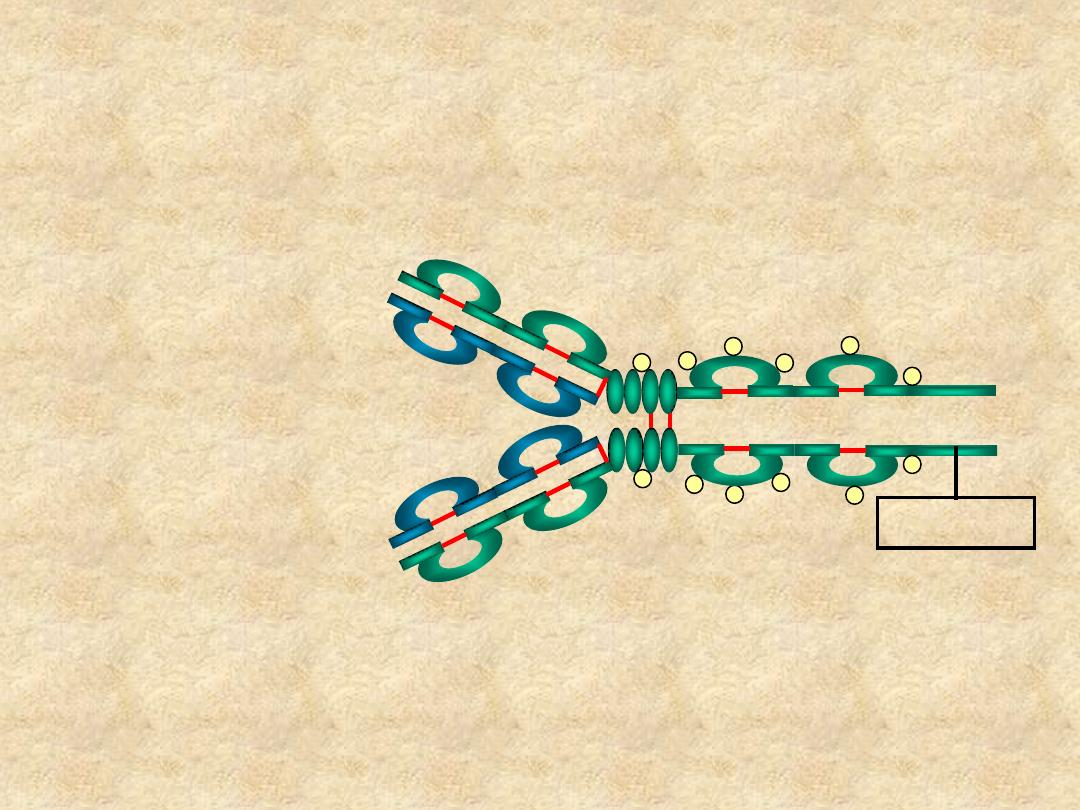
IgD
• Structure
– Monomer
– Tail piece
Tail Piece

IgD
• Structure
• Properties
– 4th highest serum Ig
– B cell surface Ig
– Does not bind complement
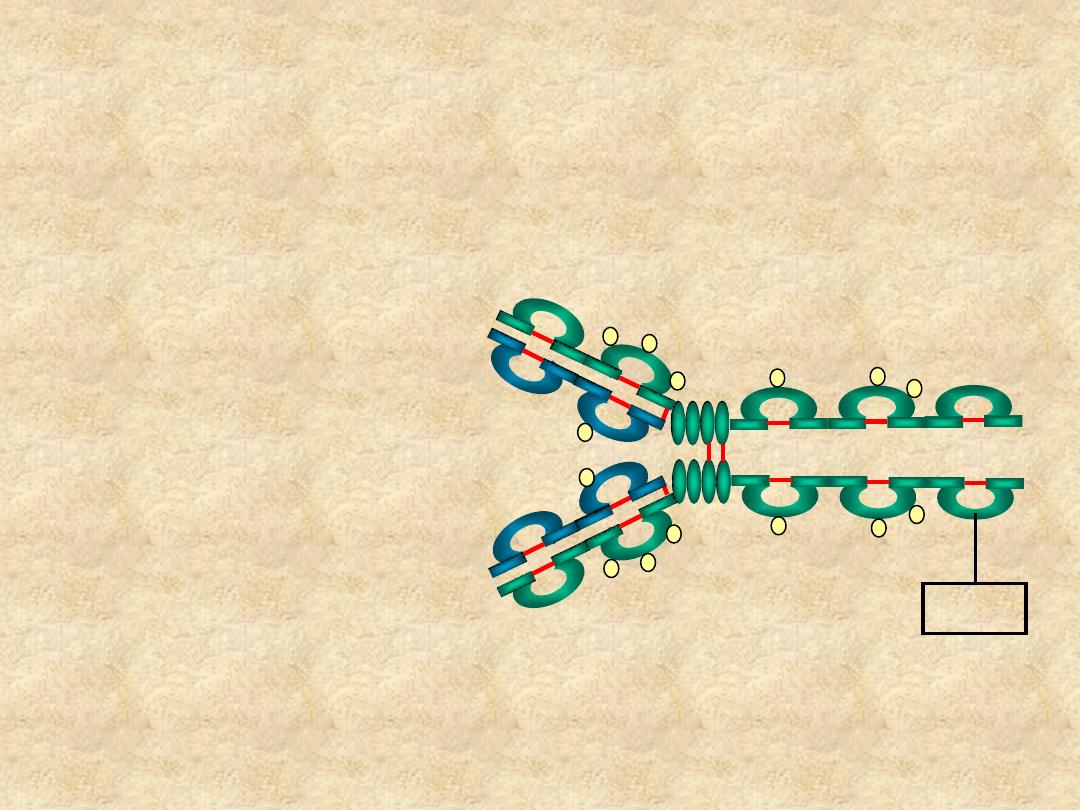
IgE
• Structure
– Monomer
– Extra domain (C
H4
)
Cε4
