
Fatty Acid Metabolism
1. Fatty acid synthesis
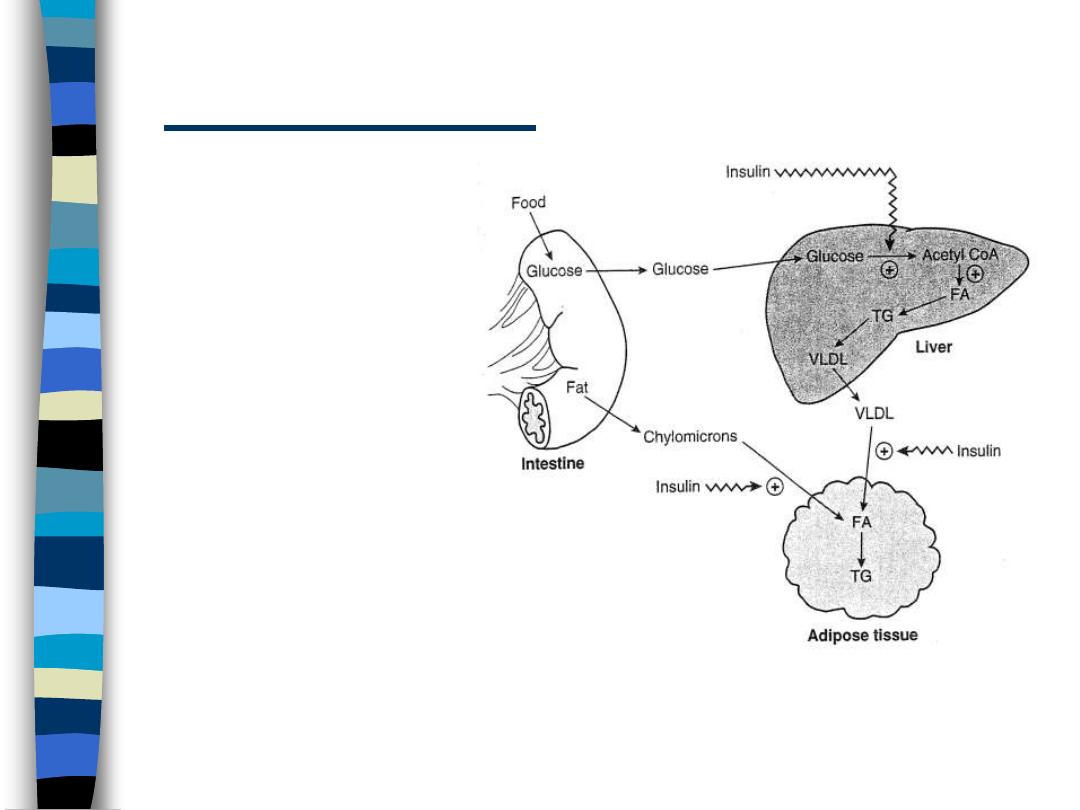
Insulin Effects
figure 1
Liver
– increased fatty acid
synthesis
• glycolysis, PDH, FA
synthesis
– increased TG
synthesis and
transport as VLDL
Adipose
– increased VLDL
metabolism
• lipoprotein lipase
– increased storage of
lipid
• glycolysis
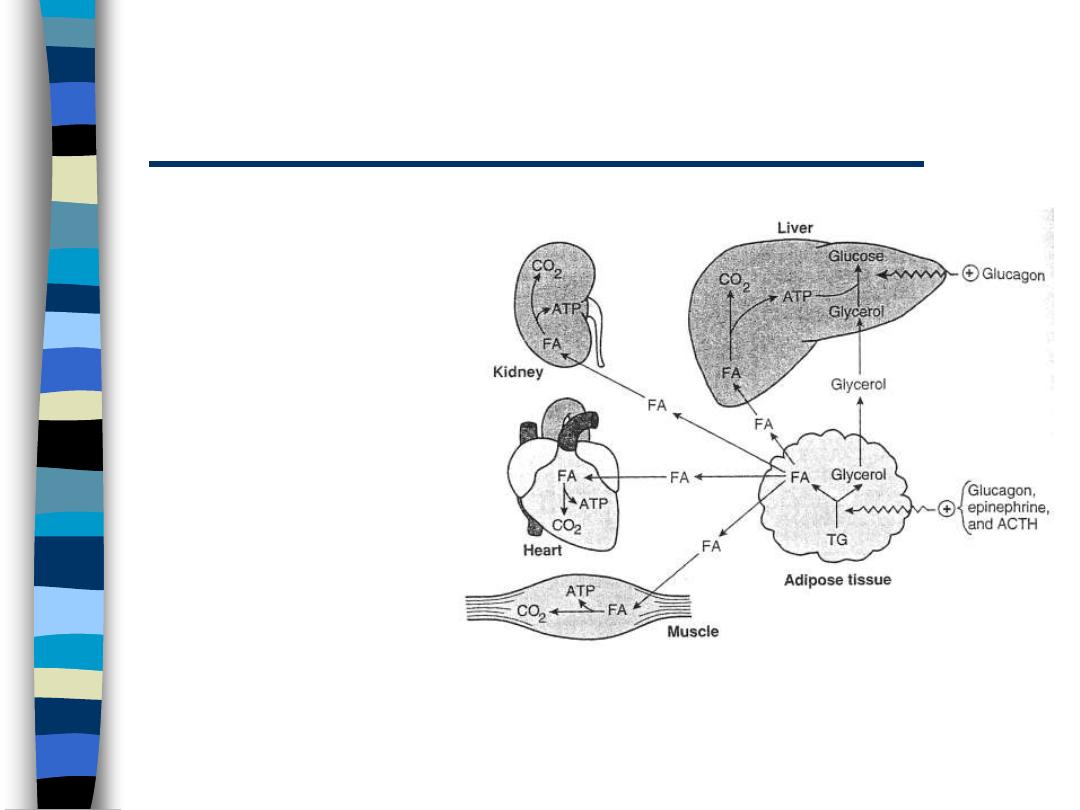
Overview of Fatty Acid Metabolism:
Glucagon/Epinephrine Effects
figure 2
Adipose
– increased TG
mobilization
• hormone-
sensitive
lipase
Increased FA
oxidation
– all tissues
except CNS
and RBC
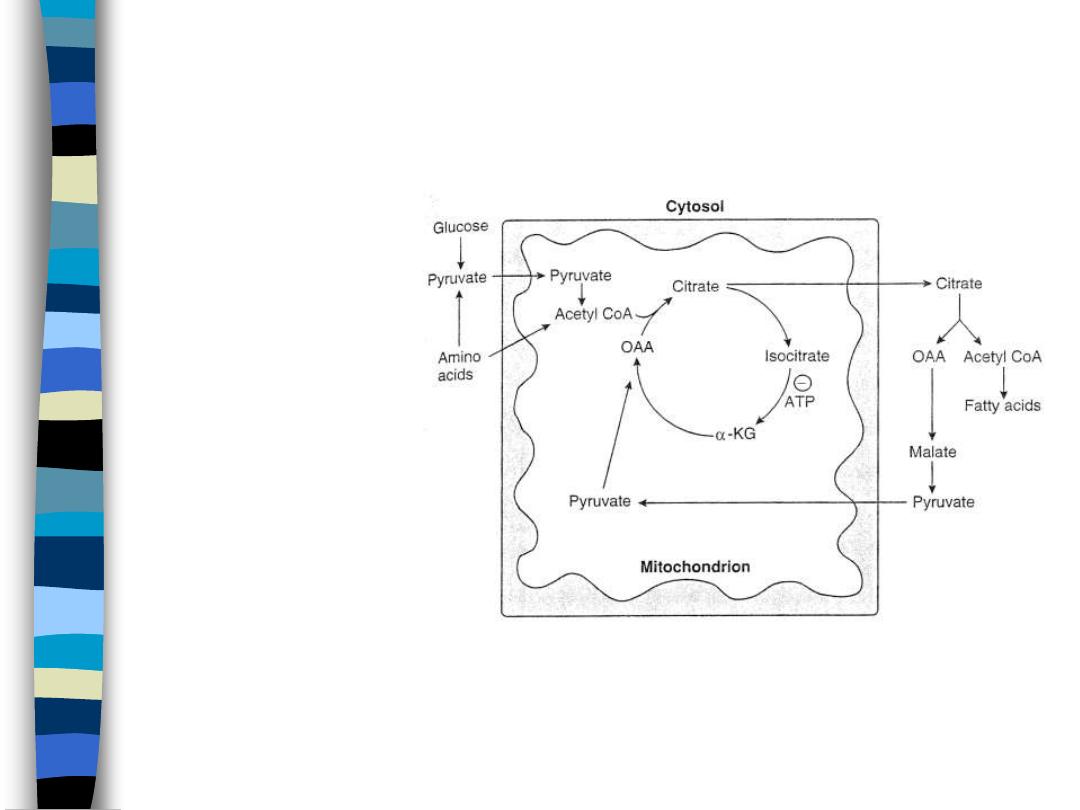
Fatty Acid Synthesis
figure 3
Glycolysis
– cytoplasmic
PDH
– mitochondrial
FA synthesis
– cytoplasmic
– Citrate Shuttle
• moves AcCoA to
cytoplasm
• produces 50%
NADPH via malic
enzyme
• Pyruvate
malate cycle

Fatty Acid Synthesis Pathway
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase
‘first reaction’ of fatty acid synthesis
AcCoA + ATP + CO
2
malonyl-CoA + ADP + Pi
malonyl-CoA serves as activated
donor of acetyl groups in FA
synthesis
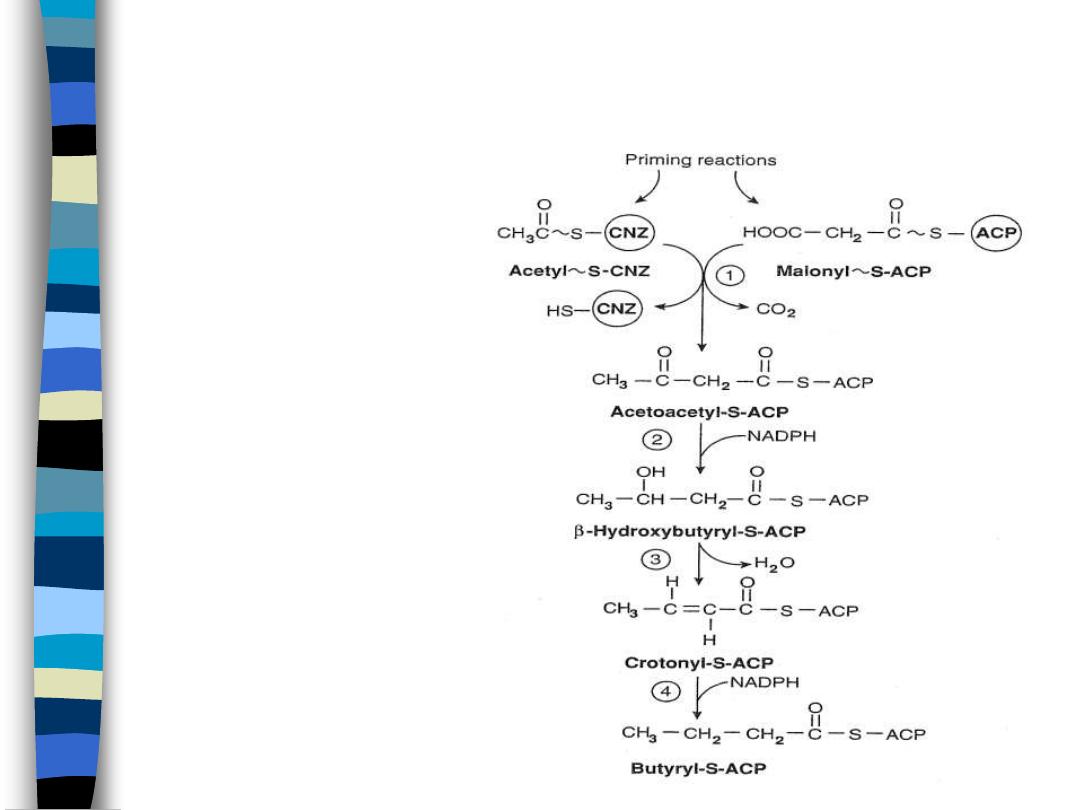
Fatty Acid Synthesis Pathway
FA Synthase Complex
figure 4
Priming reactions
– transacetylases
(1) condensation
(2) reduction
(3) dehydration
(4) reduction
Regulation of FA synthesis:
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase
Allosteric regulation
stimulated by citrate
– feed forward activation
inhibited by palmitoyl CoA
– hi B-oxidation (fasted state)
– or esterification to TG limiting
Inducible enzyme
– Induced by insulin
– Repressed by glucagon
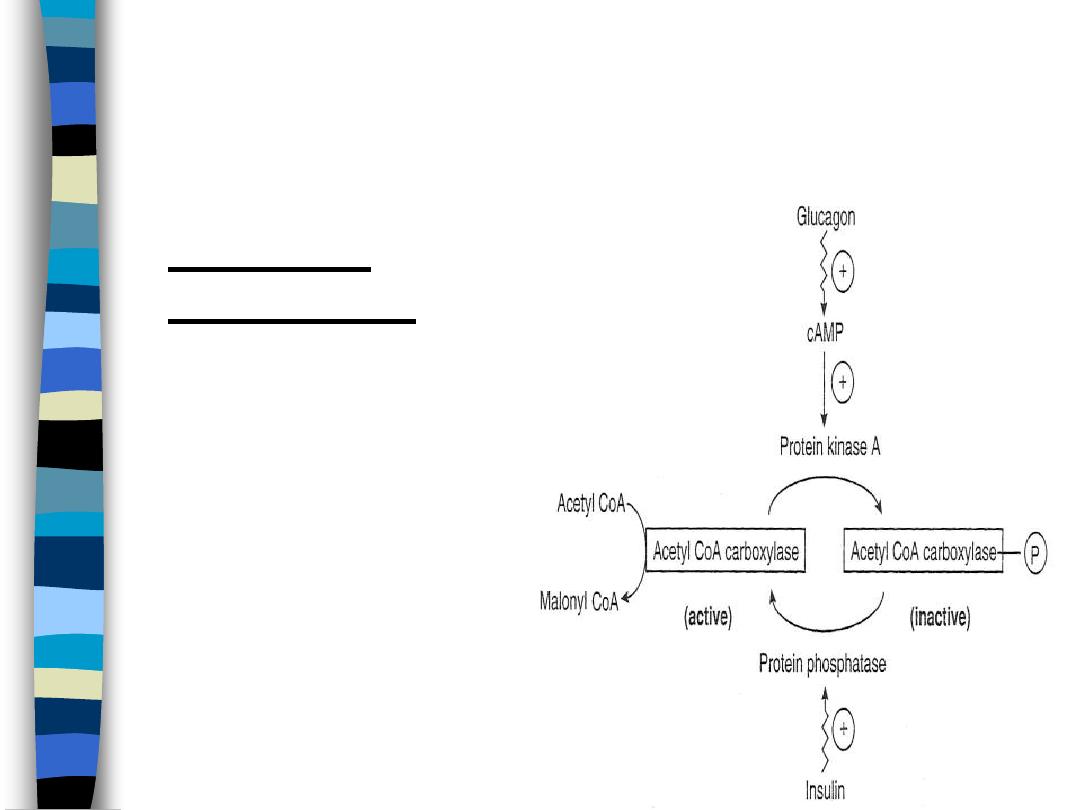
Regulation of FA synthesis:
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase
figure 5
Covalent
Regulation
Activation (fed state)
– insulin induces
protein phosphatase
– activates ACC
Inactivation (starved
state)
– glucagon increases
cAMP
– activates protein
kinase A
– inactivates ACC
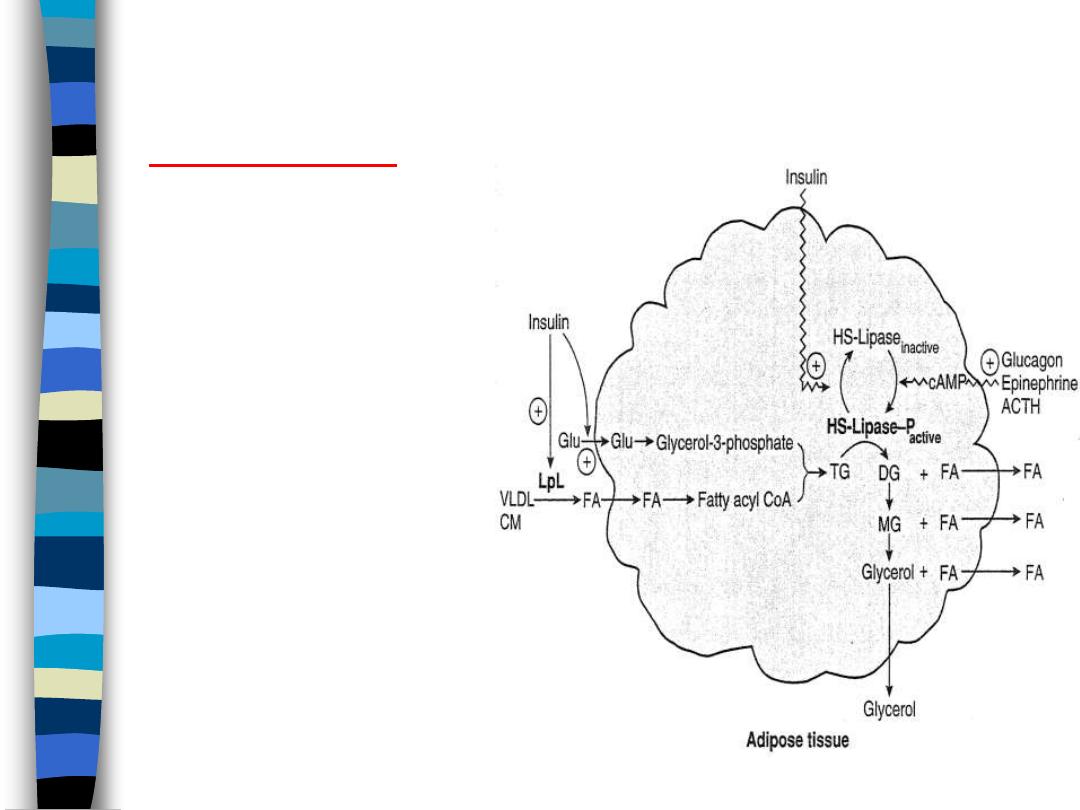
Lipid Metabolism in Fat Cells:
Fed State
figure 6
Insulin
stimulates LPL
– increased uptake of FA
from chylomicrons and
VLDL
stimulates glycolysis
– increased glycerol
phosphate synthesis
– increases esterification
induces HSL-
phosphatase
– inactivates HSL
net effect: TG storage
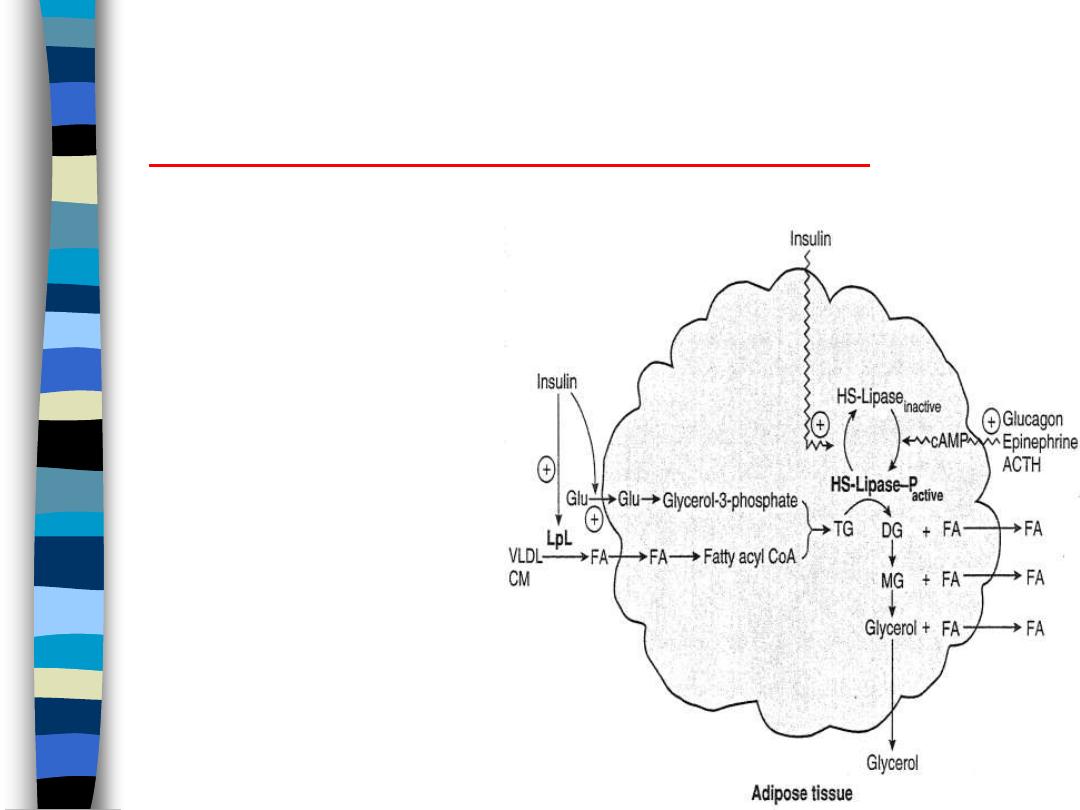
Lipid Metabolism in Fat Cells:
Starved or Exercising State
figure 7
Glucagon,
epinephrine
activates adenylate
cyclase
– increases cAMP
– activates protein
kinase A
– activates HSL
net effect: TG
mobilization and
increased FFA
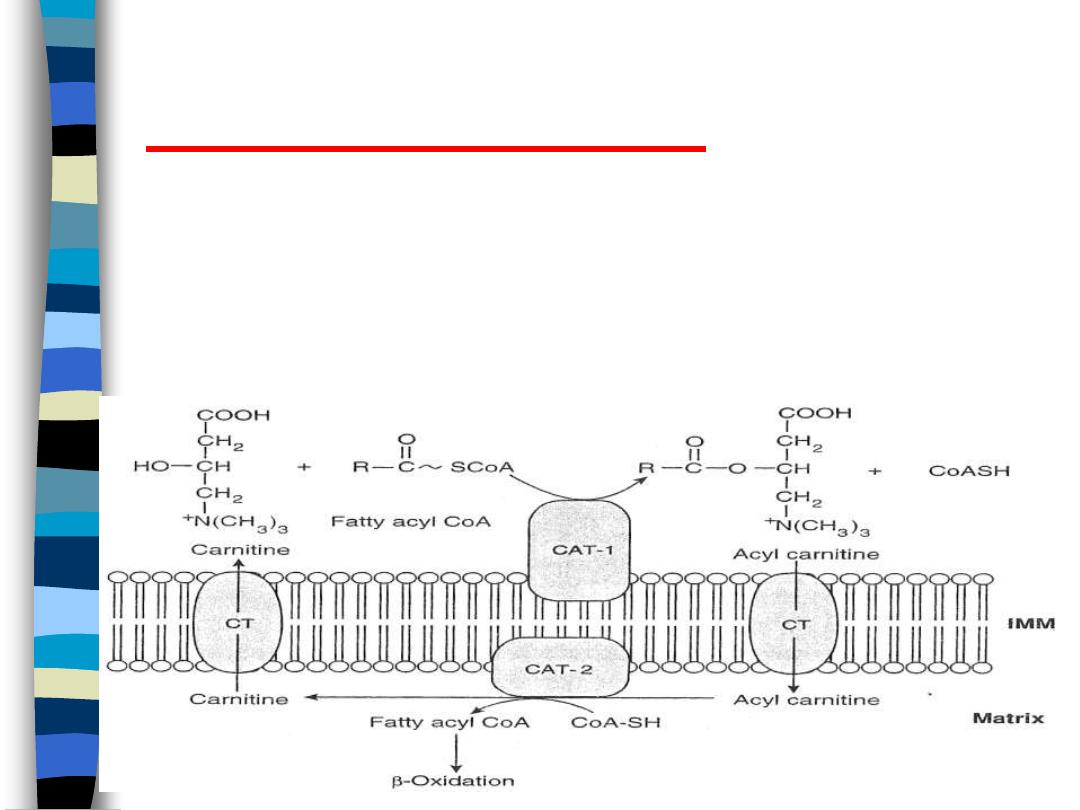
Oxidation of Fatty Acids
The Carnitine Shuttle
figure 8
B-oxidation in mitochondria
IMM impermeable to FA-CoA
transport of FA across IMM requires the
carnitine shuttle
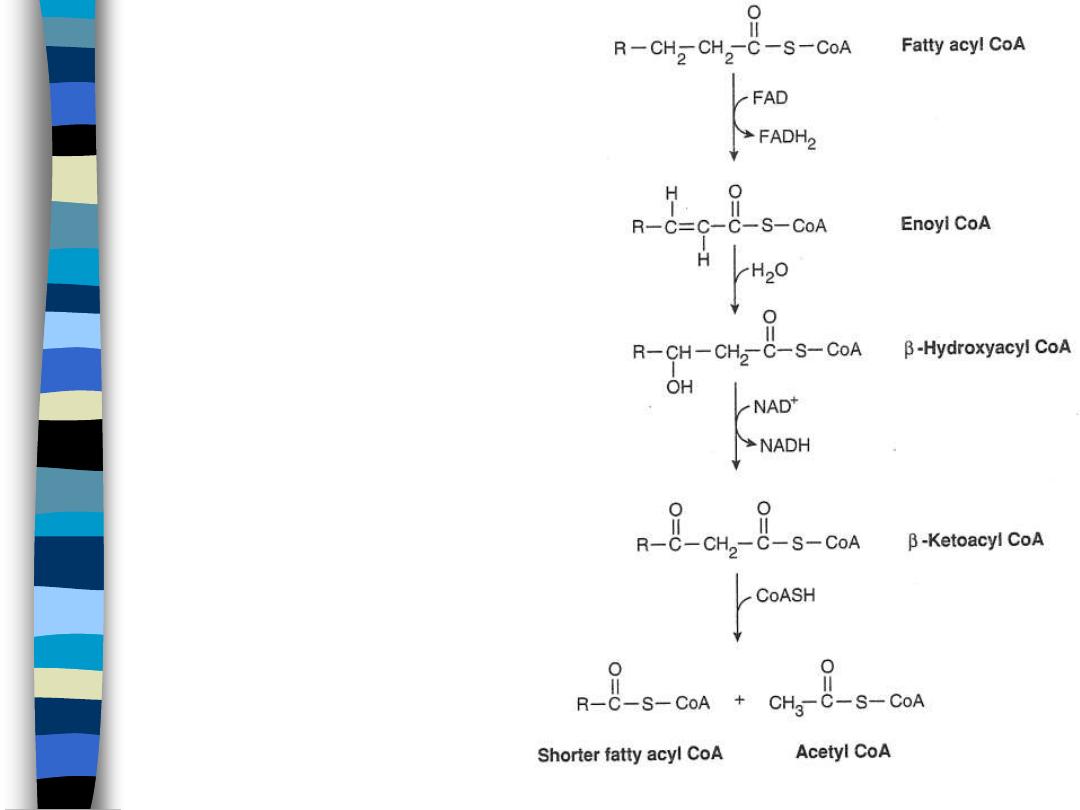
B-Oxidation
figure 9
FAD-dependent
dehydrogenation
hydration
NAD-dependent
dehydrogenation
cleavage
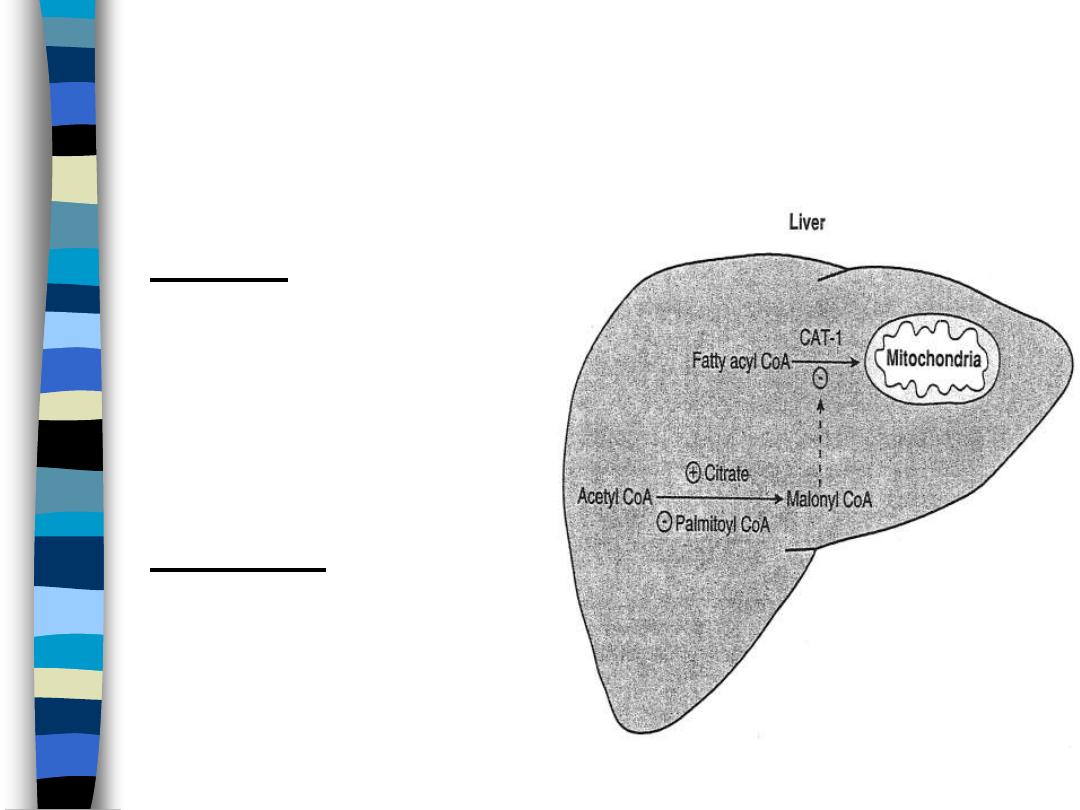
Coordinate Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation
and Fatty Acid Synthesis by Allosteric Effectors
figure 10
Feeding
– CAT-1 allosterically
inhibited by malonyl-
CoA
– ACC allosterically
activated by citrate
– net effect: FA synthesis
Starvation
– ACC inhibited by FA-
CoA
– no malonyl-CoA to
inhibit CAT-1
– net effect: FA oxidation
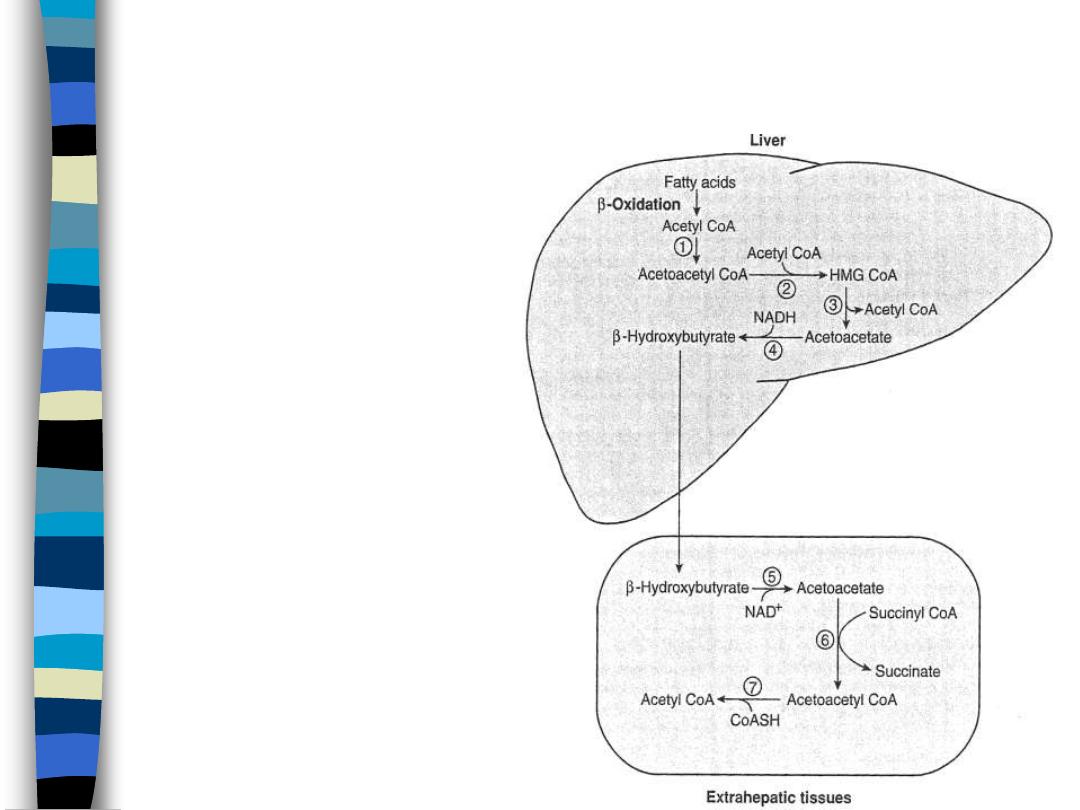
Hepatic Ketone Body Synthesis
figure11
Occurs during
starvation or
prolonged exercise
– result of elevated FFA
• high HSL activity
– High FFA exceeds
liver energy needs
– KB are partially
oxidized FA
• 7 kcal/g
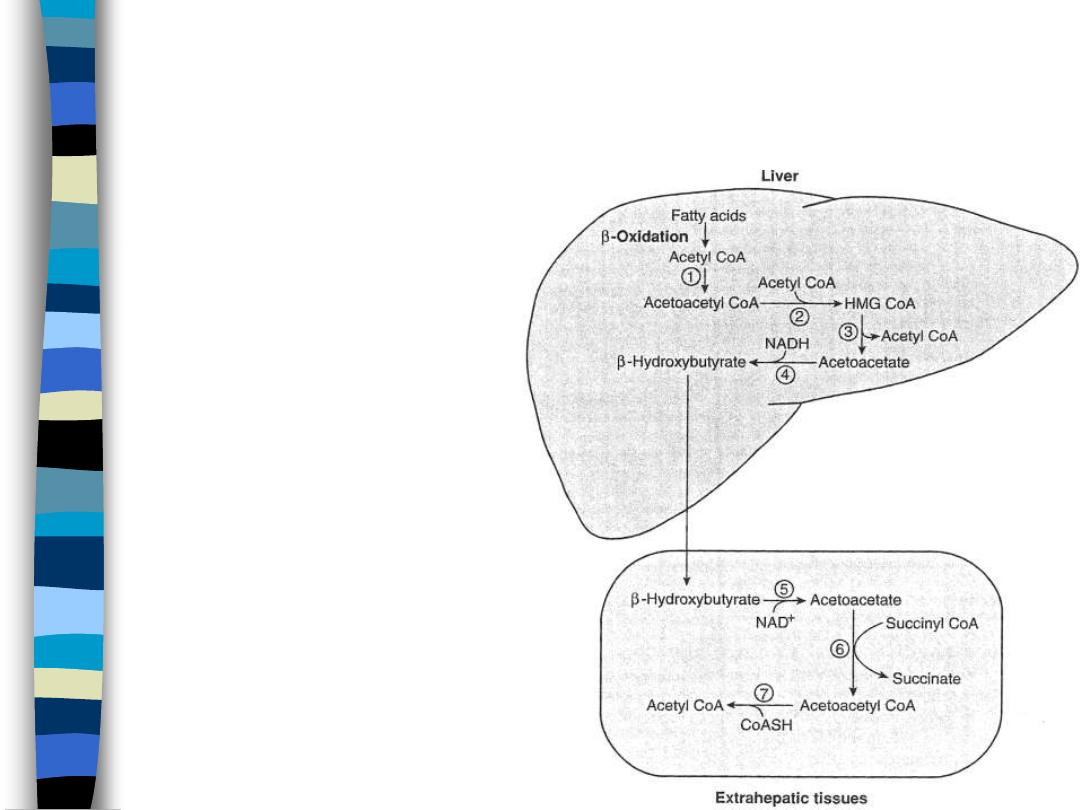
Utilization of Ketone Bodies by
Extrahepatic Tissues
figure 12
When [KB] = 1-3mM, then
KB oxidation takes place
– 3 days starvation
[KB]=3mM
– 3 weeks starvation
[KB]=7mM
– brain succ-CoA-AcAc-
CoA transferase induced
when [KB]=2-3mM
• Allows
the brain to
utilize KB as energy
source
• Markedly reduces
– glucose needs
– protein catabolism
for
gluconeogenesis

Clinical significances of
impairment of β-oxidation:
1. acquired and genetic
deficiency of carnitine substance.
2.genetic deficiency of one or
more of enzymes of pathway.
Hypoglycemia, muscle weakness
, cardiomyopathway, coma and
death

Ketosis: Increased production of
ketone bodies(K.Bs) with
ketonemia and ketonuria. This
may occurs in physiologic
conditions; prolonged fasting and
starvation, and in pathological
condition; uncontrolled D M.
