PELVIS
Learning objec ves
1- Be able to describe the main features of pelvic bones,
walls, & peritoneum
2- Be able to differen ate between male & female ar culated
pelvic girdles
3- Be able to describe main measurements of female pelvis
4- Be able to describe the main features of the perineum & its
contents
5- Be able to describe the main features of the various pelvic
organs & their rela onships.
Recommended further reading textbook
1. ANATOMY, REGIONAL AND APPLIED
By: R. J. LAST
4/29/2012
1
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Pelvic Inlet (pelvic brim):
*
Formed by the pubic crest, Pec neal line, arcuate line of Ilium,
ala & promontory of Sacrum
*
In female is round or oval. In male is heart-shaped
*
It is an oblique plane (60 degrees with horizontal plane)
Pelvic cavity:
*
Bounded by the ar culated Hip bones (Os Innominatum ),
the Sacrum, Sacro-tuberous & sacro-spinous ligaments
*
Short curved canal with a post. Wall 3X as long as ant. Wall
Pelvic outlet:
*
Diamond-shaped
*
Extends from lower bordre of symphsis pubis to coccyx
*
Bounded lat. By ischio-pubic rami & sacro-tuberous ligaments
4/29/2012
2
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Horizontal plane
: passes thru. Upper border of symphysis
pubis, spine of ischium, p of coccyx, head and apex of
greater trochanter of femur.
Pos on of Pelvis:
In erect person, it is lted. The ant. Sup. Iliac spine & the
upper margin of symphysis pubis lie in same
ver cal plane
The subpubic angle is nearly a
right angle
in the female
and about
60 degrees
in the male.
4/29/2012
3
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
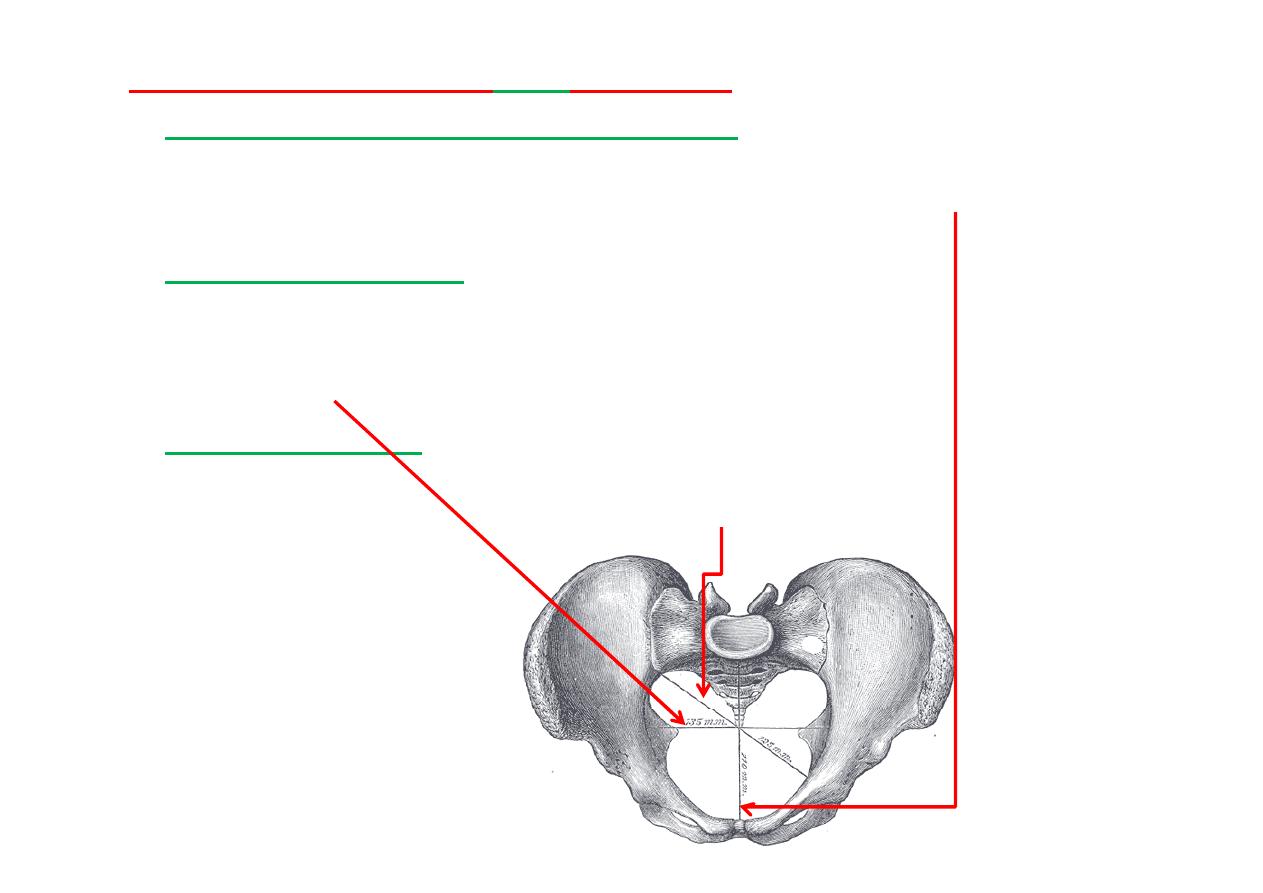
Superior aperture or
inlet
(Female)
The
anteroposterior or conjugate diameter
extends from the
sacrovertebral angle (promontory) to the upper part of symphysis
pubis; its average measurement is about
110 mm (11cm)
.
The
transverse diameter
extends across the greatest width of the
superior aperture, from the middle of the
brim
on one side to the
same point on the opposite; its average measurement is about
135
mm (13.5cm)
.
The
oblique diameter
extends from the iliopec neal eminence of one
side to the sacroiliac ar cula on of the opposite side; its average
measurement is about
125 mm(12.5cm).
4/29/2012
4
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
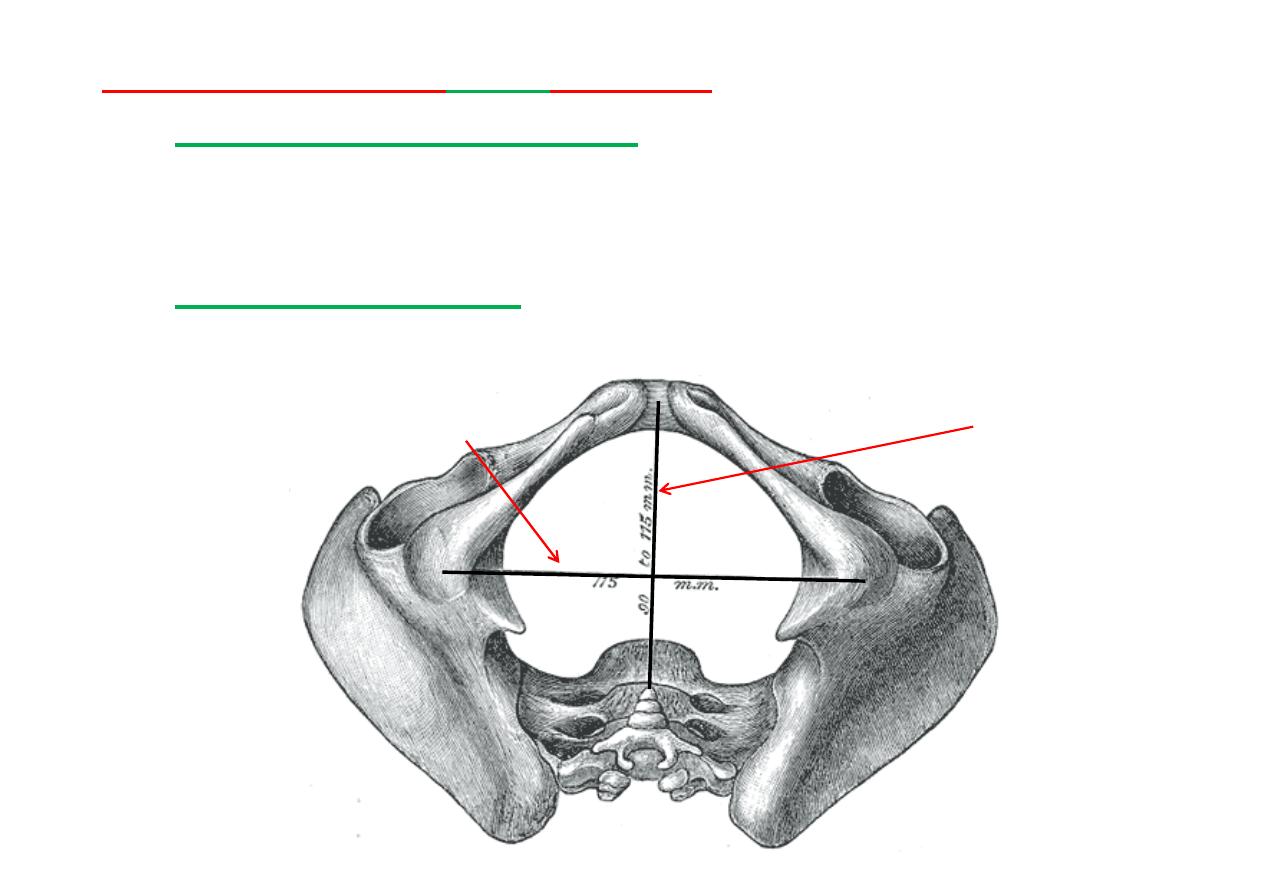
inferior aperture or
outlet
(Female)
The
antero-posterior diameter,
extends from the p of the
coccyx to the lower part of the pubic symphysis, is about
115 mm (11.5-13cm)
.
The
transverse diameter
, measured between the posterior
parts of the ischial tuberosi es, is about
115 mm (11.5-
12cm)
.
Antero-posterior Diameter (13 cm)
Transverse Diameter (12 cm)
4/29/2012
5
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
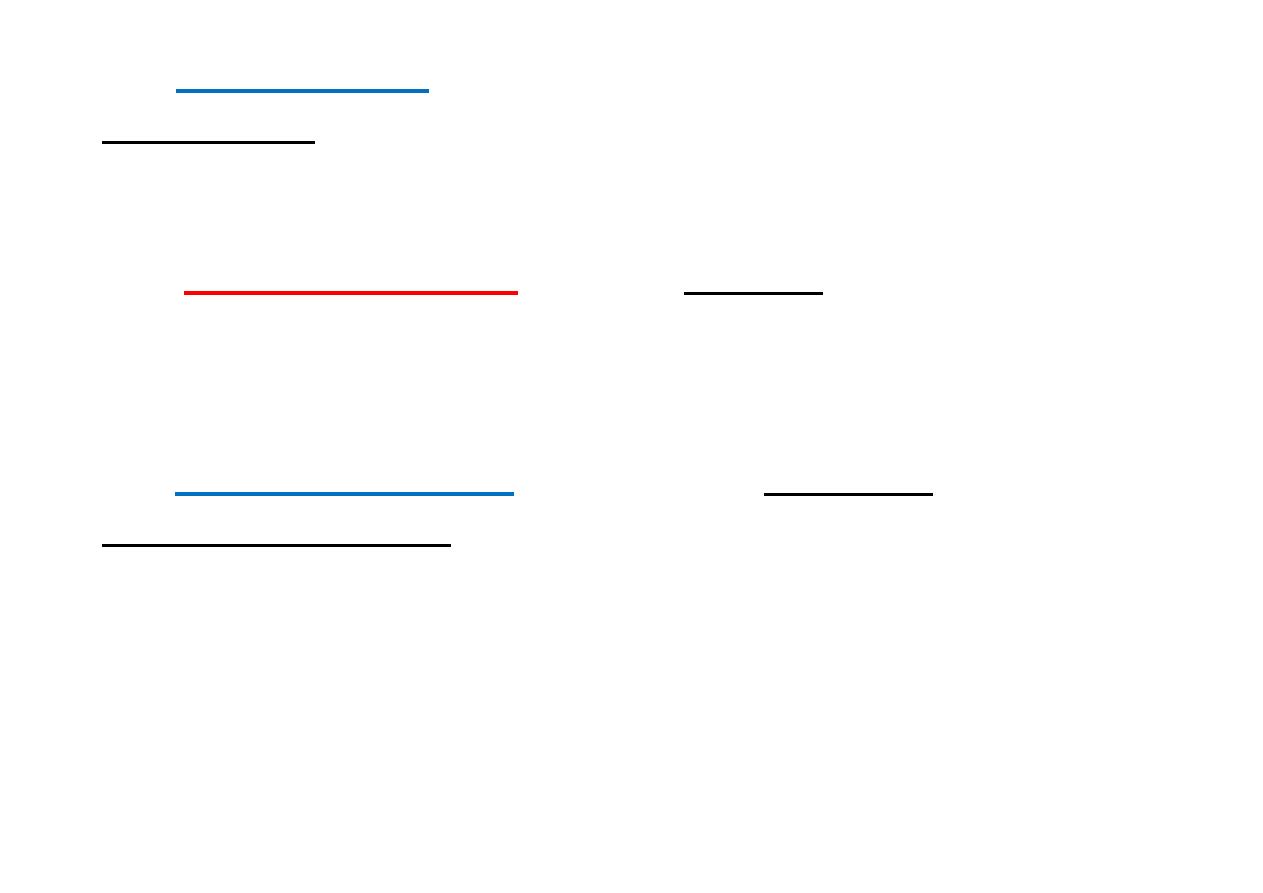
The
true conjugate
(T) can be measured only on
radiographic films because it extends from the sacral
promontory to the top of the symphysis pubis. Its
normal measurement is
11
cm
or more.
The
obstetric conjugate
(O)is the shortest of the
three. It extends from the sacral promontory to the
thickest part of the pubic bone and measures
10
cm
or more.
The
diagonal conjugate
(D)is the most easily and
commonly assessed because it extends from the lower
border of the symphysis pubis to the sacral
promontory. It normally measures
11
.
5
cm
or more.
The inlet is said to be contracted when any of these
diameters is smaller than normal.
4/29/2012
6
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
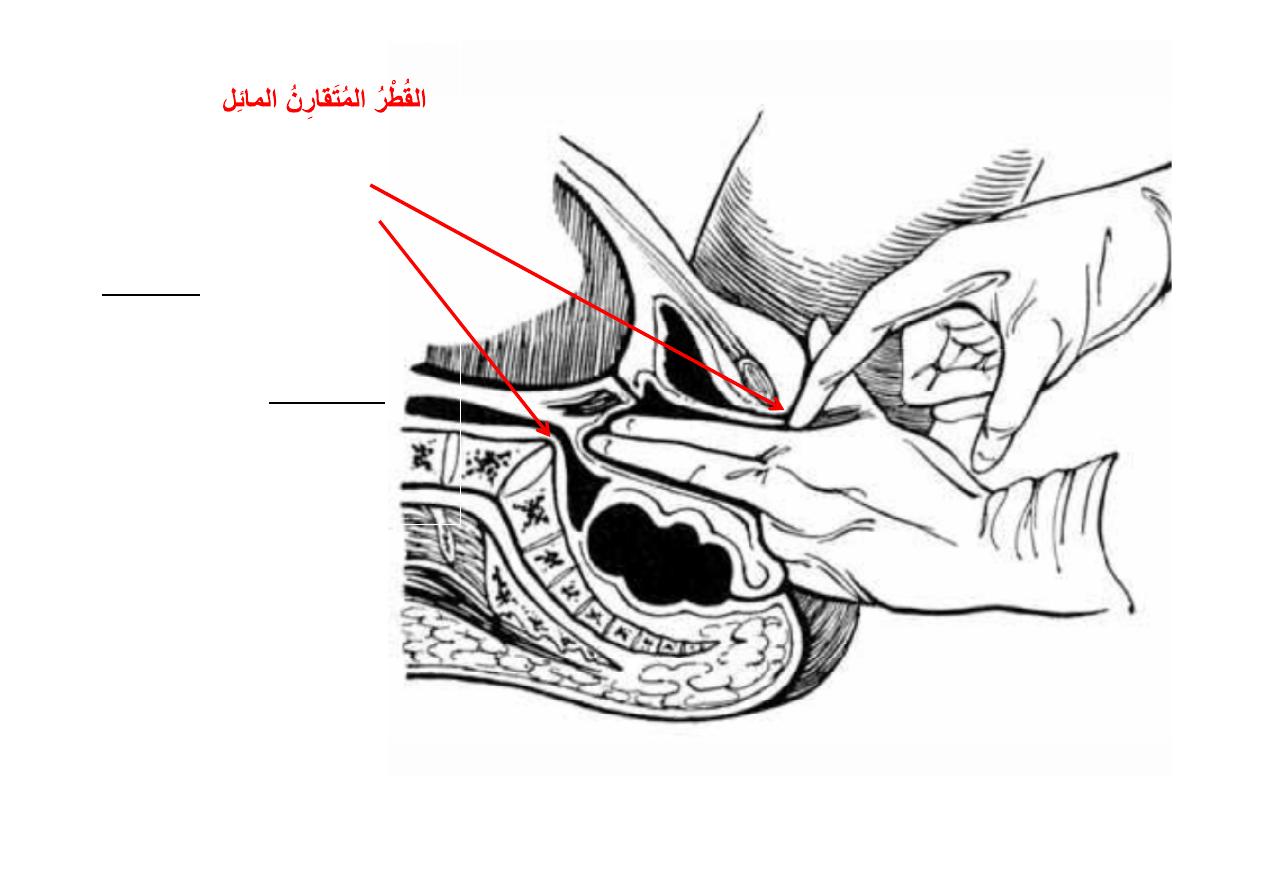
Measurement of the
diagonal
conjugate diameter
by the middle finger.
The indicated length on the index finger gives the
true conjugate
,
because the index is about 1.5 cm shorter than the middle finger.
The
diagonal
conjugate
diameter(
)
,
between the lower margin
of the
pubic symphysis
and
the
sacral promontory
is
measured per vaginam.
Inability to palpate the
sacral promontory suggests
that the conjugate diameter
of the inlet is adequate for
parturi on, whereas
palpa on indicates a
contracted pelvis
.
4/29/2012
7
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
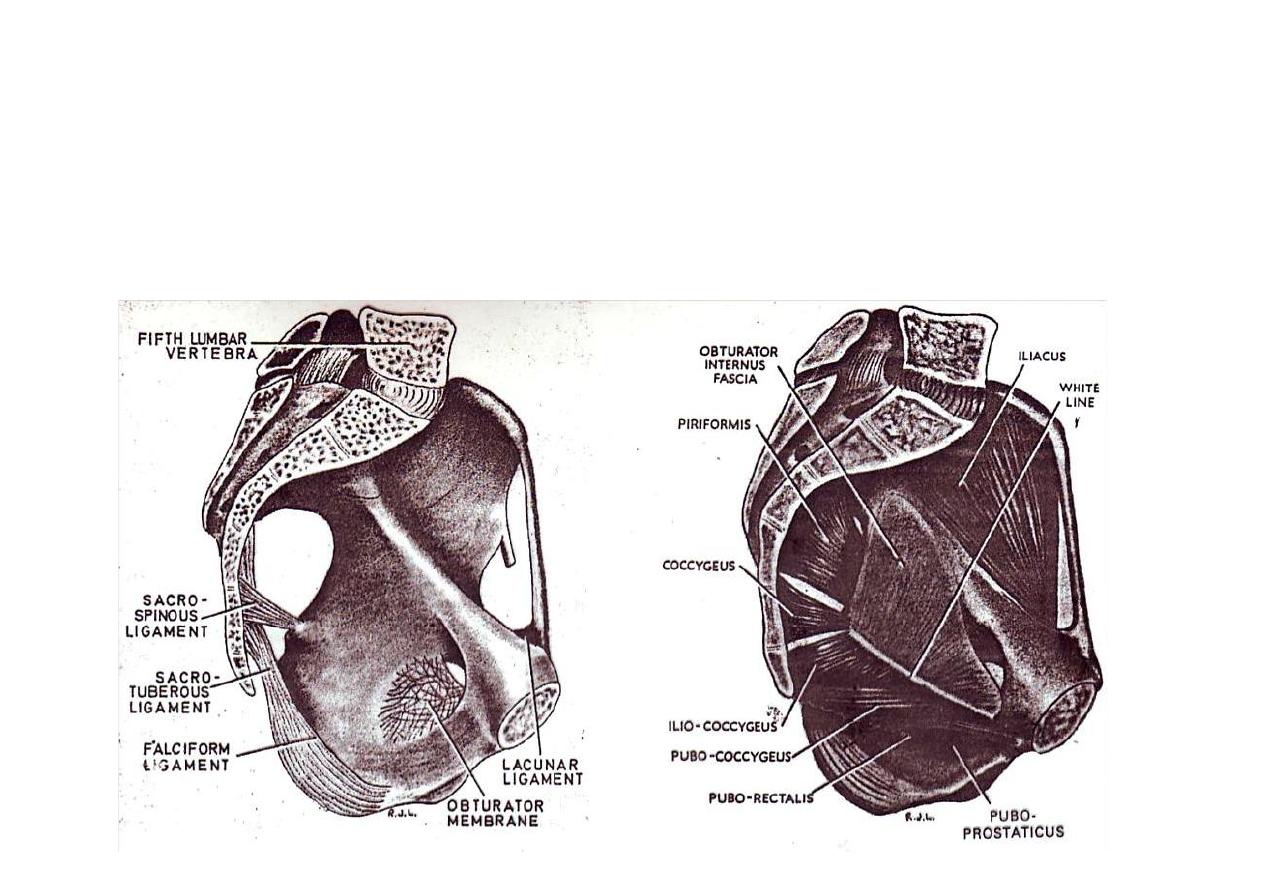
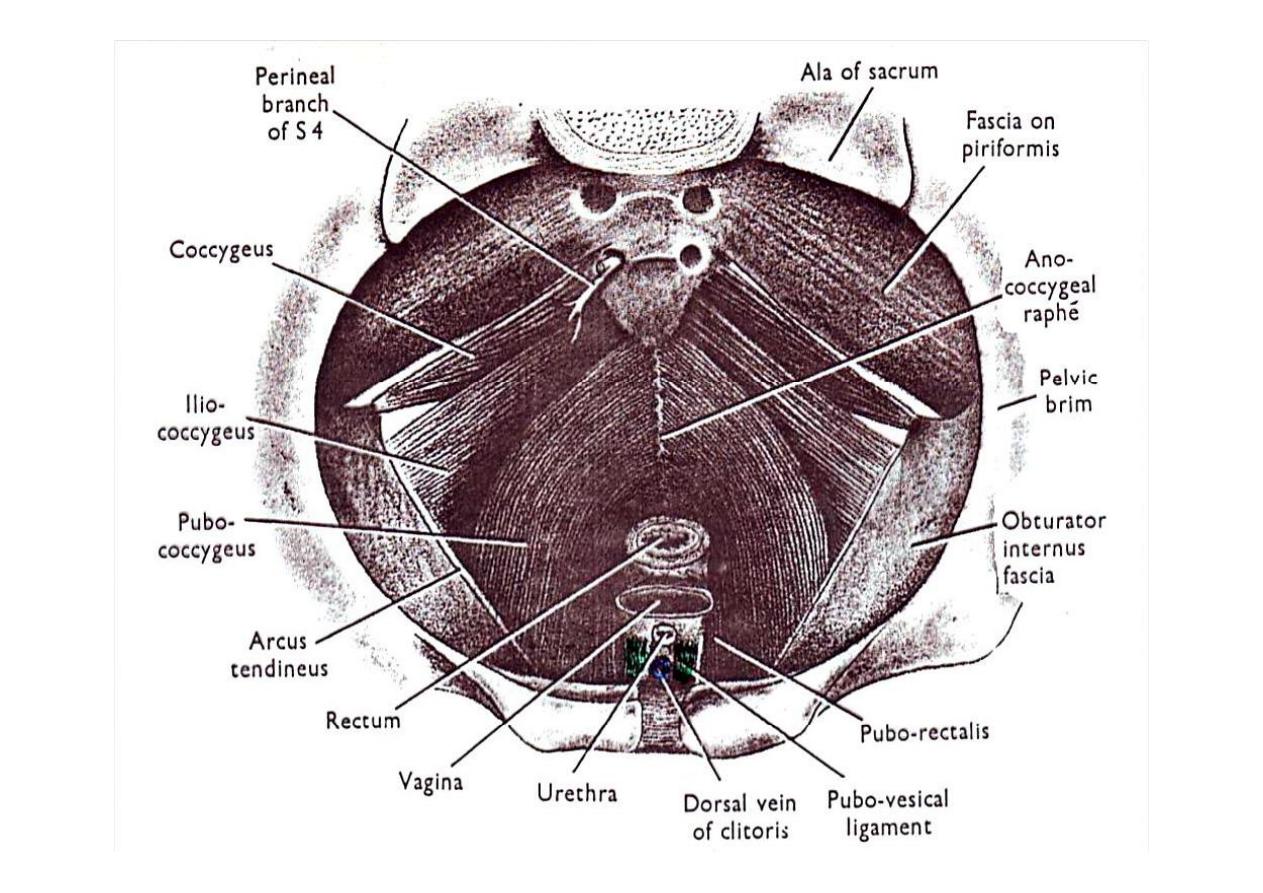
The pelvis is composed of:
1-
Pelvic brim:
( promontory of sacrum & ilio-pec neal line)
2-
Pelvic floor (pelvic diaphragm):
(levator ani & coccygeus)
3-
Pelvic walls:
(sacrum, os innominatum, piriformis &
obturator internus muscles)
4/29/2012
8
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
4/29/2012
9
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
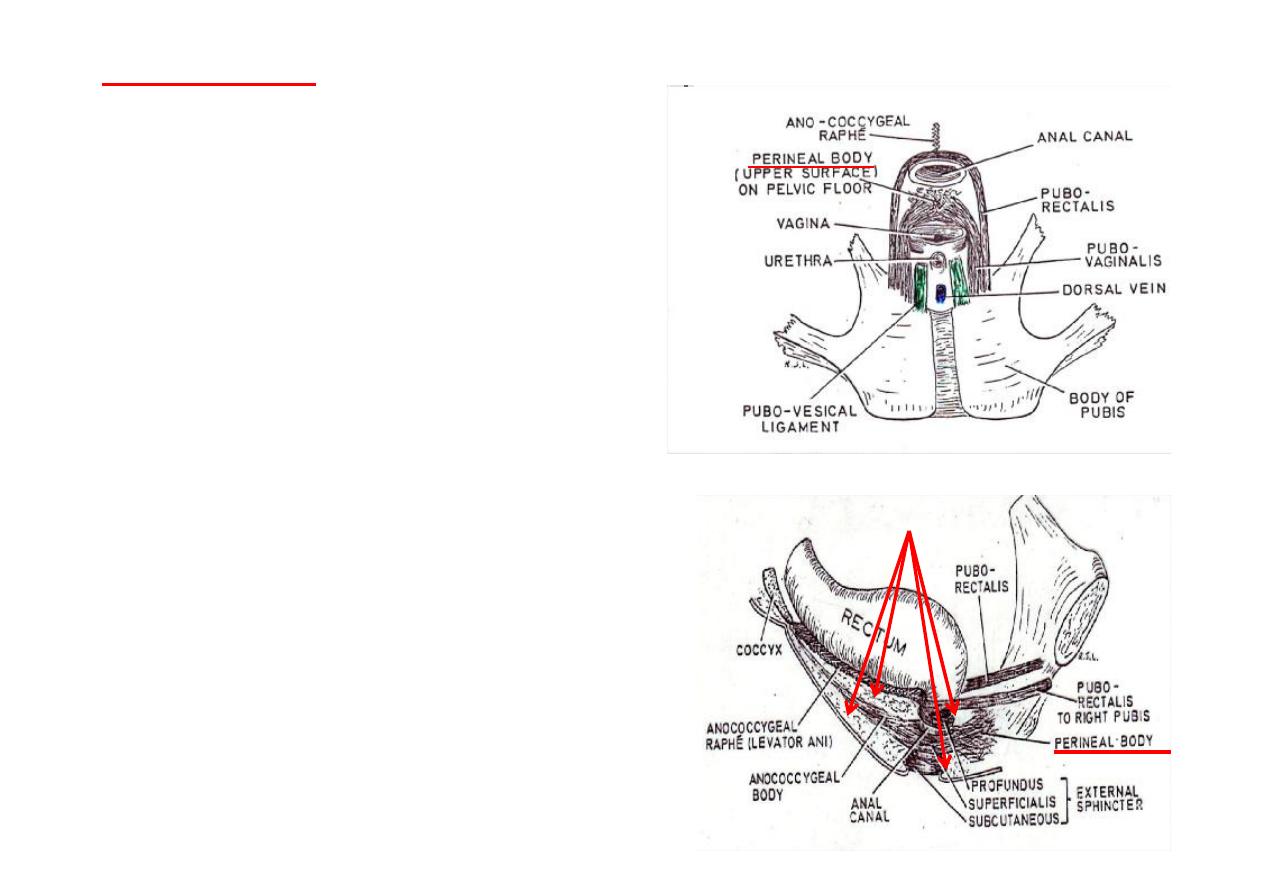
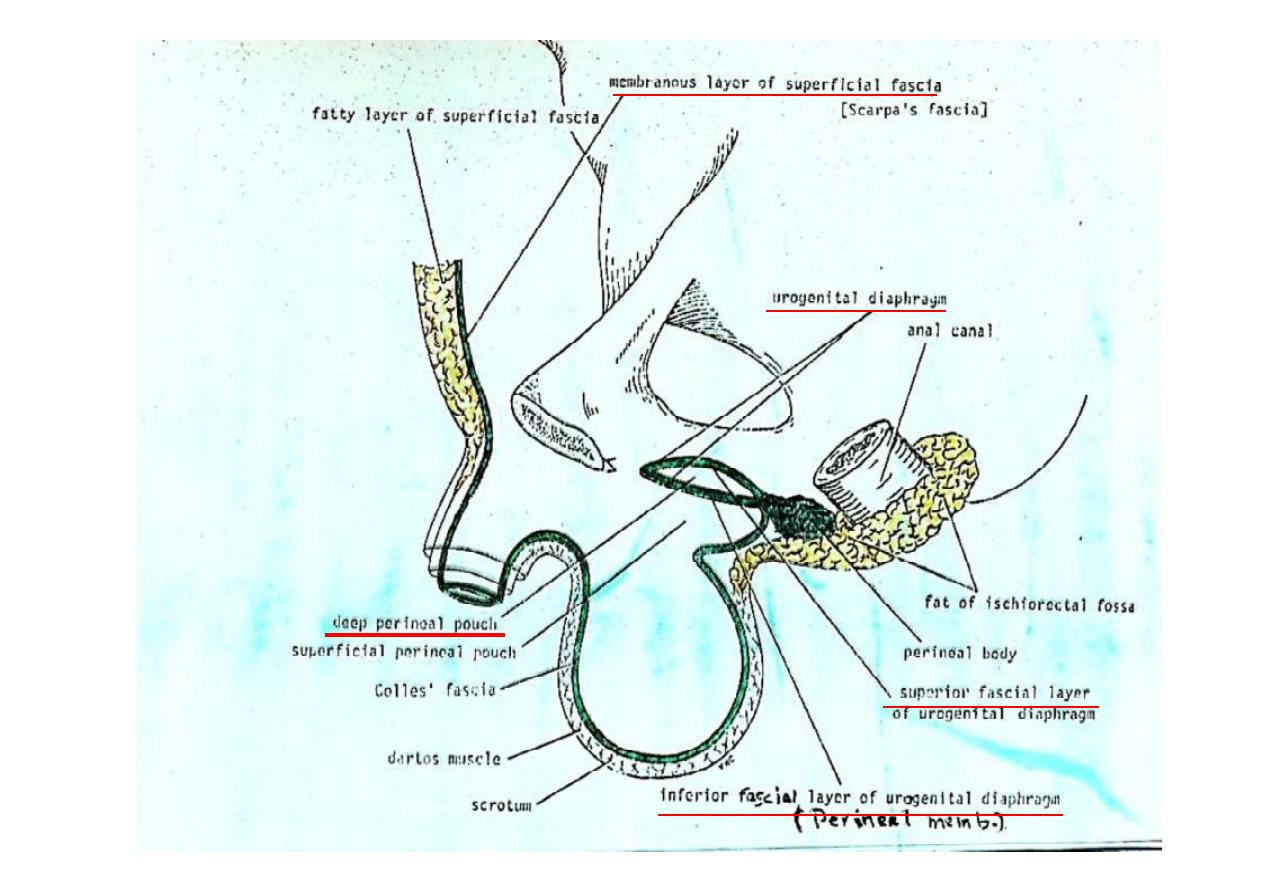
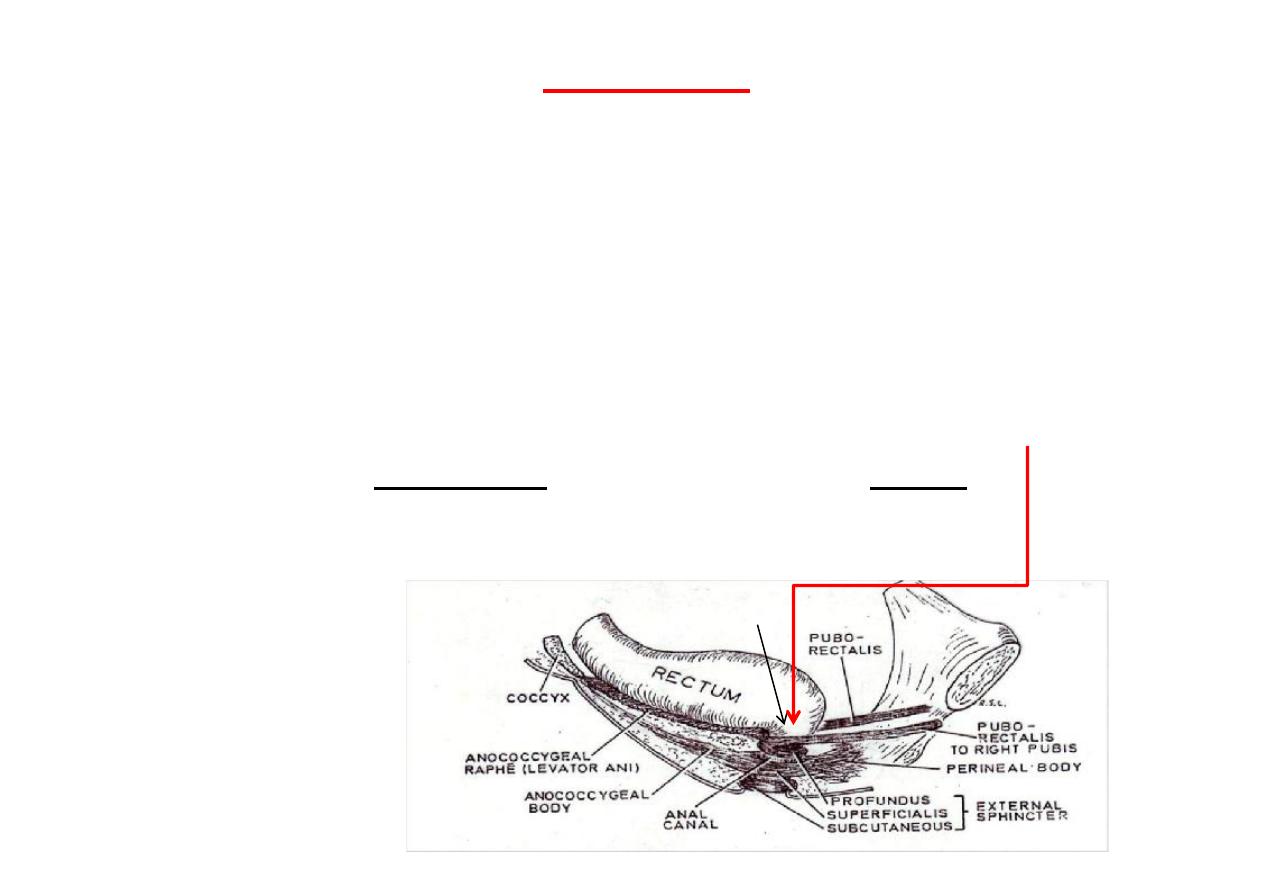
Perineal body
(Central Perineal Tendon)
(Perineum)
*
Lies infront of anal canal
*
Fibro-muscular mass of ssue
*
Fixed to & forming part of the pelvic
floor
*
Composed of:
1. Interdigita ng fibers of
pubo-
prosta cus (pubo-vaginalis)
(mainly )
2.
Transverse perinei
muscles
3.
Bulbo-spongiosus
muscle
4.
Superficialis
part of external anal
sphincter
*
Extends from level of pelvic floor to
skin of perineum
(closes the space between the ant.
Parts of le & right ischio-rectal fossae
*
Very important in support of pelvic
viscera
Ischio-rectal fossae
4/29/2012
10
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
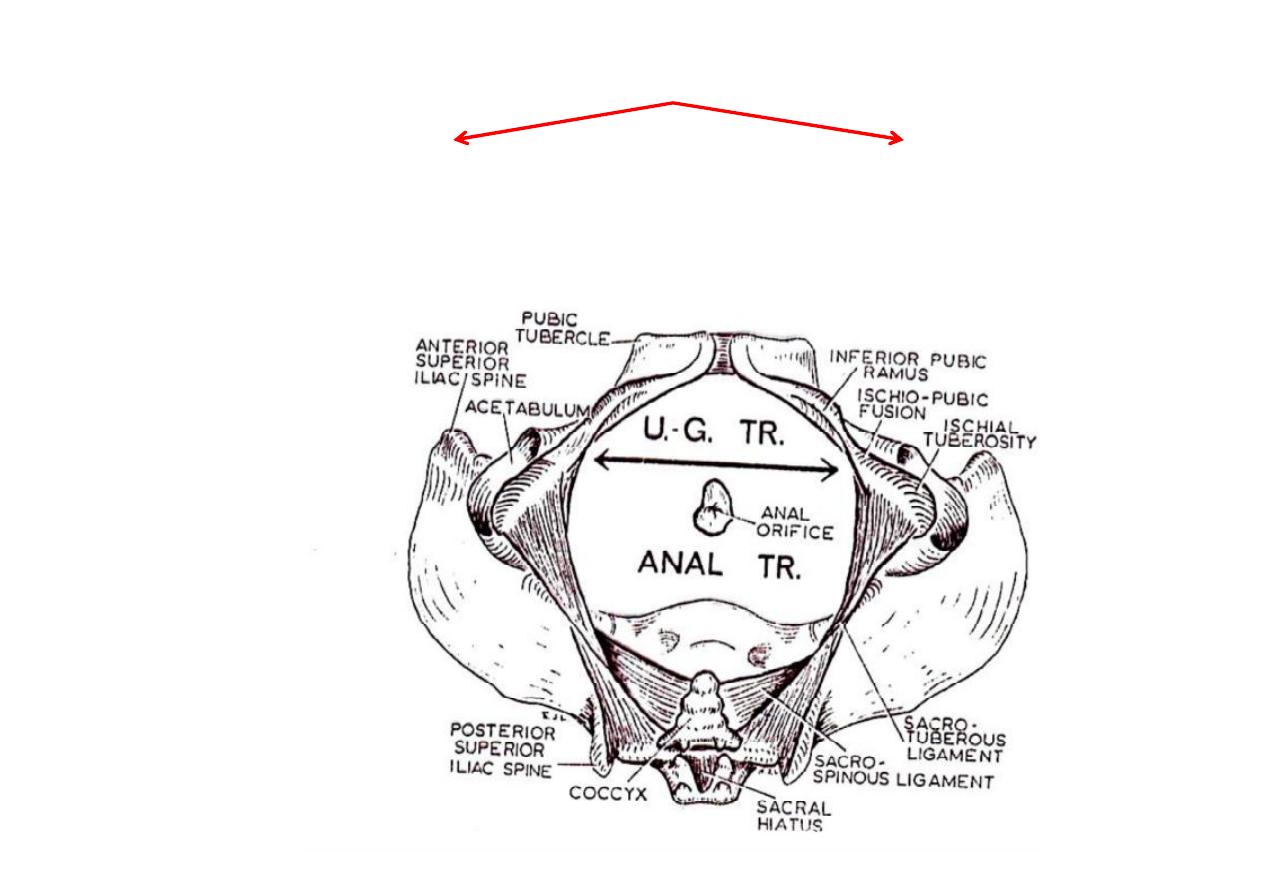
The Perineum
Anal Triangle
(Large & posterior)
Urogenital Triangle
(small & anterior)
4/29/2012
11
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Anal Triangle
*
Composed of:
1-
Anal canal
2-
Ischio-rectal fossae & contents
*
Sides formed by Sacro-tuberous ligaments
*
Base formed by the line joining ant. Parts of ischial tuberosi es
Anal Canal
*About 3 cm long muscular tube
*Its muscle fibers are all arranged in a circular fashion
*Consis ng of an internal (smooth) and an external (striated)
sphincters
*The junc on of rectum and anal canal is at the pelvic floor
*From this junc on the anal canal passes downwards and
backwards to the skin of perineum
4/29/2012
12
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

The anal canal has a point of demarca on between
visceral and
soma c
por ons called the
pec nate (dentate) line
, which is a
serrated line following the anal valves and crossing the bases of
the anal columns.
*
The
epithelium
is
columnar
or cuboidal above
the pec nate line and
stra fied squamous
below it.
*
The
Arterial supply
Above
the pec nate line from the superior (of Inf. mesentric art.) &
middle rectal arteries (of Int. iliac art.)
Below
line from inf. Rectal artery ( of Int. pudendal artery)
*
The
Venous drainage
Above
the pec nate line goes into 1. The
portal venous system
mainly via the superior rectal veins. 2. To the
caval venous system
(systemic)
via middle rectal veins
Below
the line, it goes into the
caval venous system
via the inferior
rectal veins or Saphenous vein.
(N.B. site of hemorrhoids-at junc on between systemic & portal
systems---
Internal hemorrhoids
occur above
the pec nate line, and
external hemorrhoids
occur below it
4/29/2012
13
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
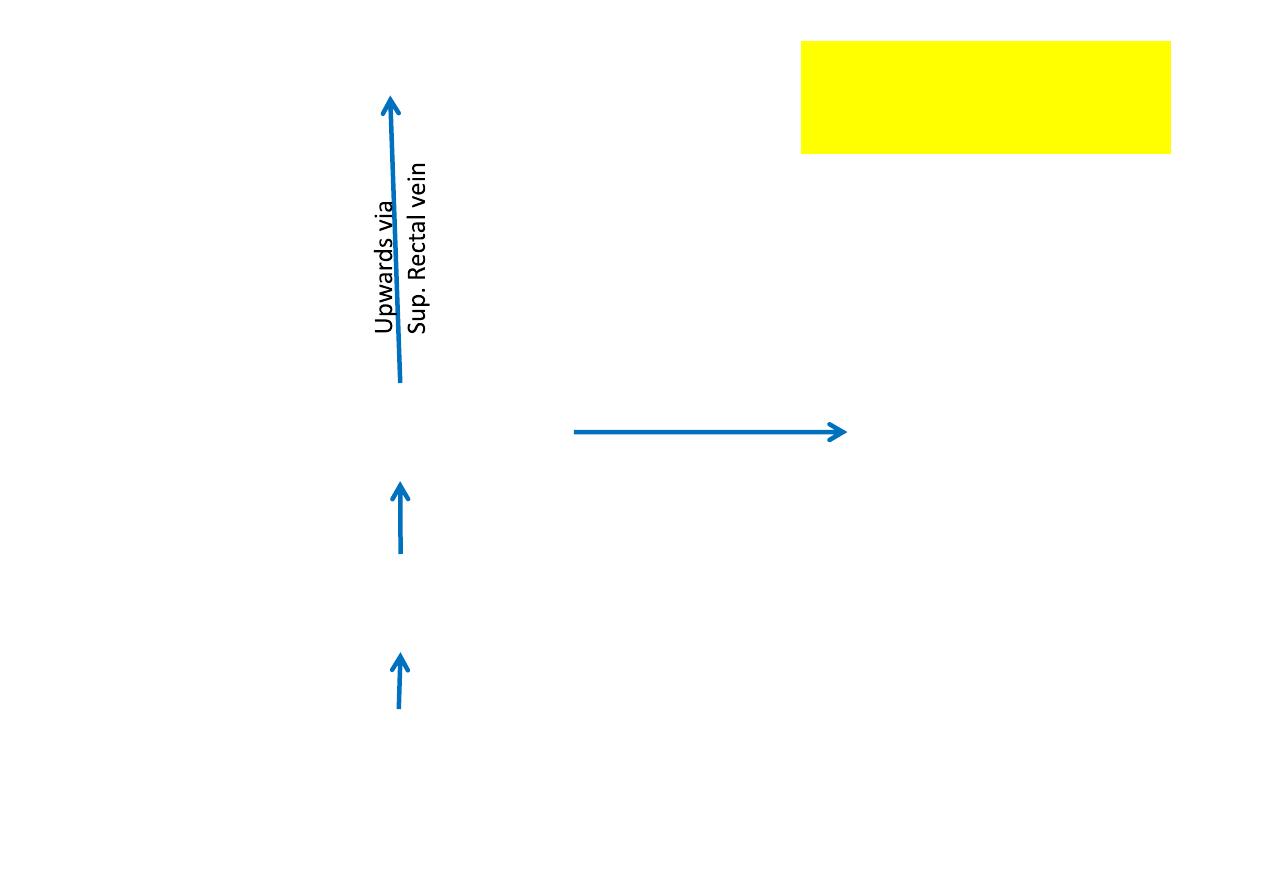
Thru.
Muscle wall of ampulla
External rectal plexus
(Surrounding Ampula)
Submucous plexus of veins
(in Ampulla & anal canal)
Internal iliac vein
(Caval system)
Across via
middle rectal vein
Portal system
Venous drainage
above pec nate line
4/29/2012
14
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
*
The
lympha c vessels:
( follow arteries) above the line: from
lymph follicles in mucous membrane drain upwards to join
those of rectum which drain across wall of rectum into lymph
nodes along the 1. Median sacral art. 2. Middle rectal art. 3. Inf.
Mesenteric art.
below it: into the superficial inguinal nodes.
*
The
sensory innerva on
above the line: is through fibers from
the
pelvic plexus (inf. Hypogastric plexus)
and thus is of the
visceral type (rela vely insensi ve to touch but sensi ve to
pressure).
below it: is by soma c nerve fibers of the
pudendal nerve
(Inf.
rectal nerves, which are very sensi ve).
PN. The sympathe c innerva on of the rectum & upper anal
canal contracts the circular muscles & internal sphincter, while
the parasympathe c (pelvic splanchnic) empty the rectum.
-The lower 1/3 of anal canal & ext. sphincter under voluntary
control (Inf rectal nerve & perineal branch of S4)
4/29/2012
15
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Anal columns
- (6-10 in No.)
- In upper 2/3 of mucouss membrane
- Longitudinal ridges in mucous membrane produced by ver cal blood
channels
- Each column contains a terminal radical of the superior rectal art. & vein
- Three of these anal columns ( their veins , being largest at 4, 7, 11) are
prone to become varicose as the three primary hemorrhoids
- Vary in prominence according to amount of blood it contains (anal valves
remain constant irrespec ve of blood it contains)
- United to each other inferiorly by cross channels of anastomosing veins
which raise small mucosal folds known as the
anal valves
(near
muco-cutaneous junc on). These cross channels form a venous ring
called the Annulus hemorrhoidalis .
- Anal valves form a series of small pockets (
Anal sinuses
) each at the
Inf. End of a groove between two columns
4/29/2012
16
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Ischio-rectal fossa
*
Wedge shaped space
*
Fills lateral Part of anal triangle & extends forwards into
urogenital triangle
*
Filled with so fat which forms dead spaces into which the
anal canal can expand during defeca on
**
Lateral Wall : Formed by Obturator internis fascia,
Falciform margins of sacro-tuberous ligament & Ischial
tuberosity
**
Medially: The 2 fossae are separated by the anal canal,
perineal body, & ano-coccygeal body
**
Roof : By levator ani muscle
Contents:
1- Loose fa y ssue. 2- Internal pudendal vessels &
Pudendal nerves (in Pudendal canal). 3- Inf. Rectal vessels &
nerves. 4- Scrotal vessels & nerves. 5-Perineal branch of S4
4/29/2012
17
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Urogenital Diaphragm
*Musclo-fascial
*Triangular double layer of fascia (Sup. & Inf. layers)
* Inf. Layer is the
perineal membrane
*Situated in ant. Perineum (filling in the gap of pubic arch)
*
Ant.
: The two layers fuse, leaving a small gap beneath
symphsis pubis
Post.
: The two layers fuse with 1. each other
2. membranous layer of
superficial fascia
3. perineal body
Lat.
: The layers are a ached to pubic arch
Formed by
1. Sphincter Urethrae muscle
2. Deep transverse prineal muscles
* The closed space between layers is called the
deep perineal
pouch
4/29/2012
18
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Uro-genital triangle
Perineal membrane (Triangular ligament)(male)
* Sta onary sheet of connec ve ssue
*Form the basis upon which the penis (root) & penile musculature
(body) are a ached.
* Below it lies the scrotum
* Above it lies the membranous urethra & sphincter urethra muscle.
*Pierced by urethra, nerves & vessels
* A ached to ischio-pubic rami --- from sub-pubic angle back to level
of ant. Part of ischial tuberosity (along a ridge on med. Srface of pubic
rami)
* Antero-posterior extent = 3.5 cm
* Fascia of Colles a ached to its post. margin
4/29/2012
19
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Central perineal tendon
4/29/2012
20
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Perineal body
Inferior fascial layer
Of urogenital diaphragm
(perineal membrane)
4/29/2012
21
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

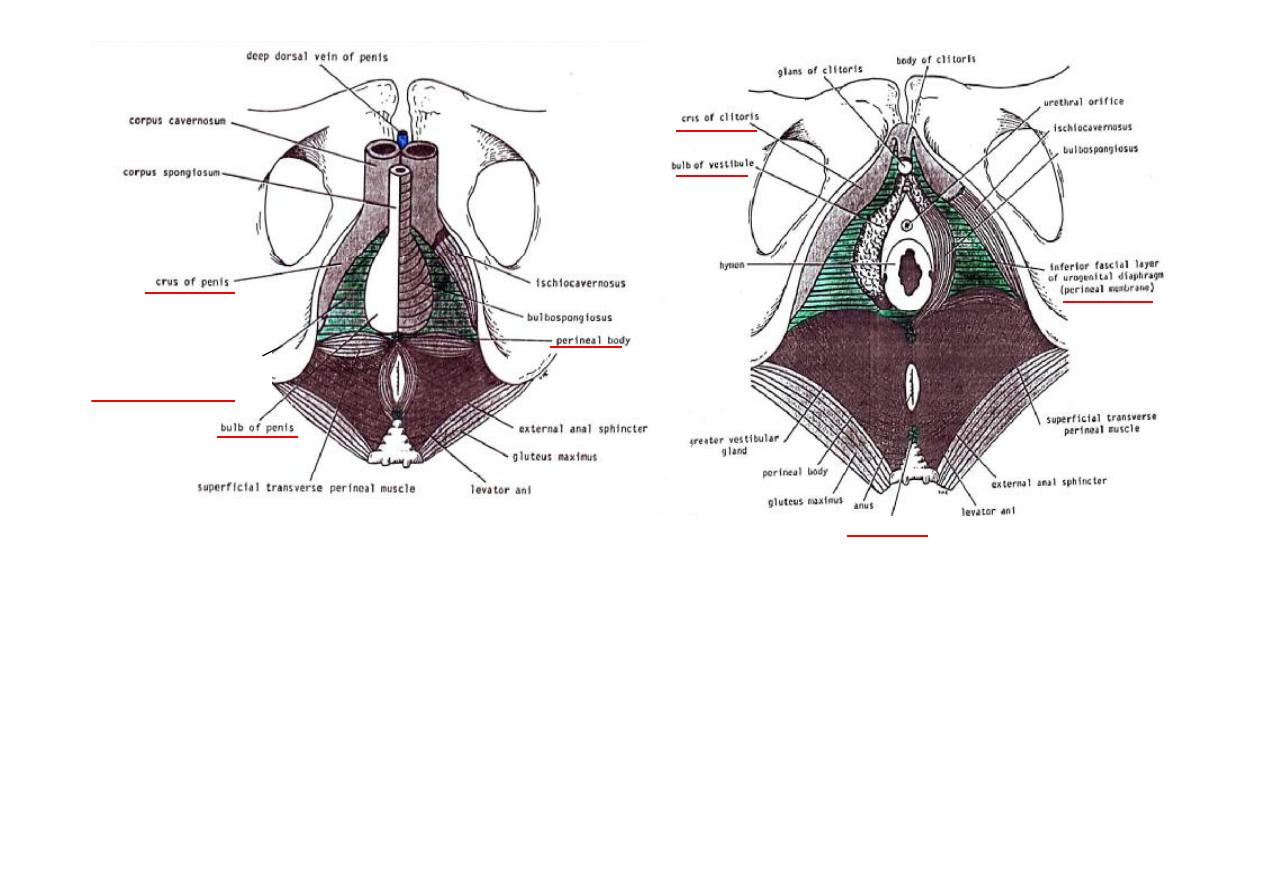
Superficial perineal pouch
Space between perineal membrane & fascia of Colles
Contents in the male
1.Testes & sperma c cords
2.Penis & muscles of corpora
3.Scrotal & penile nerves & vessels
4.Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Contents in the female
1.Root of Clitoris (crura)
2.Bulb of Ves bule
3.Greater ves bular glands
4.Labial & clitoral nerves & vessels
4.Superficial transverse perineal muscles
5.Terminal parts of Vagina & Urethra
4/29/2012
22
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Deep Perineal Pouch
Space between the two facial layers of Urogenital diaphragm
Contents in the male
1.Membranous urethra
2.Sphincter urethrae muscle
3.Bulbo-urethral glands of Cowper
4.Internal Pudendal vessels & branches
5.Dorsal nerves of penis
6.Deep transverse perineal muscles
Contents in the female
1.Part of Urethra
2.Part of Vagina
3.Sphincter Urethra muscle
4.Internal Pudendal vessels & branches
5.Dorsal nerve of Clitoris
6.Deep transverse perineal muscles
4/29/2012
23
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

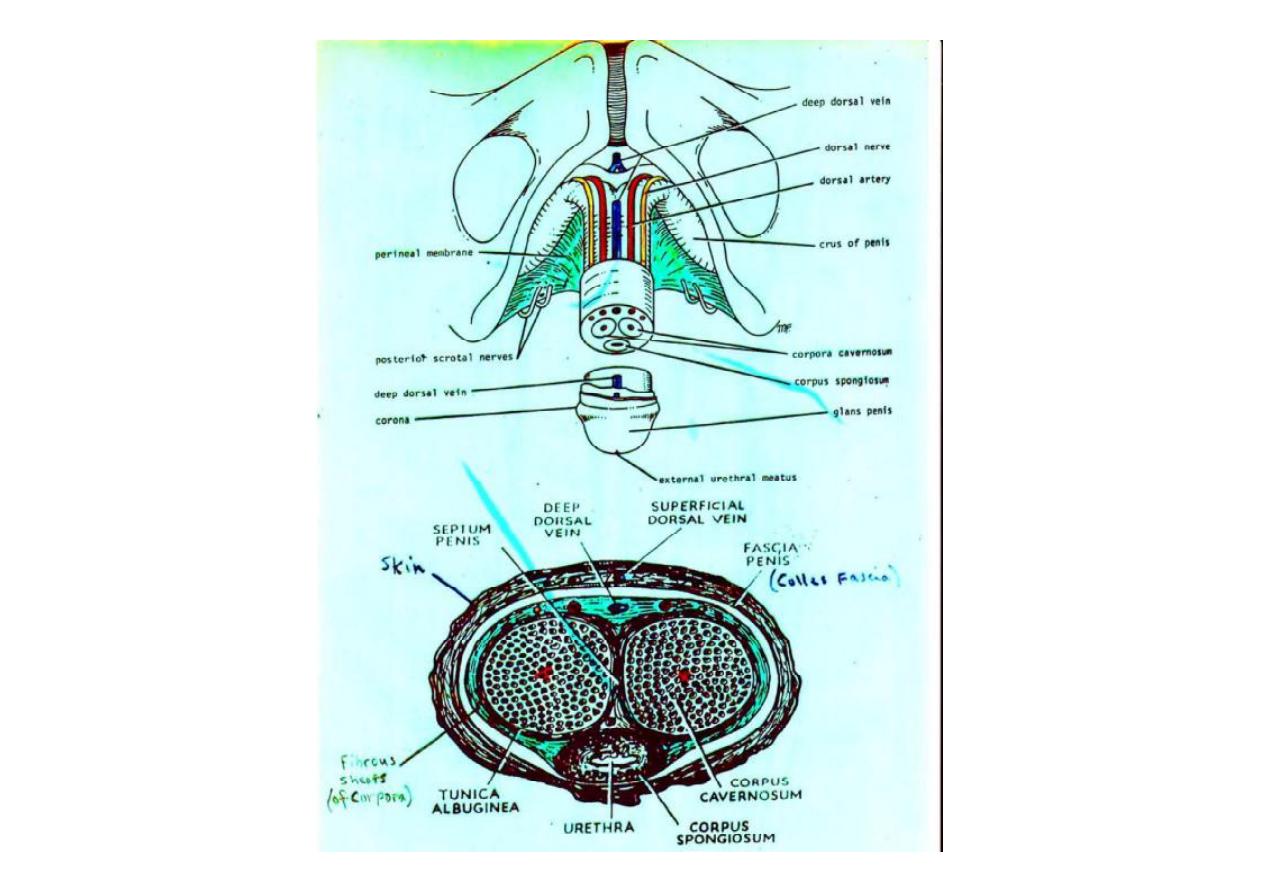
Internal Pudendal Artery
-Passes forwards along the ischio-pubic ramus above perineal
membrane
- Braches perforates the ant. Angle of perineal membrane as:
1-Artery to the bulb
(two)
-Supply corpus spongiosum & glanis penis
2-Deep artery of the penis
(two)
-Supply corpus cavernosum only
-Enter the crus by Helicine arteries
3-Dorsal artery of the penis
(two)
-Supply skin, fascia, glans penis & anastomose with
terminal branches of artery to the bulb.
4/29/2012
24
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
4/29/2012
25
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Deep dorsal vein of penis (one)
-Drains most of blood from corpora
-Runs proximally in midline & pierce the suspensory ligament
and enter pelvis between the two pubo-prosta c ligaments
-Joins the prosta c plexus
Dorsal nerves of penis (two
)
-Con nua on of pudendal nerve & run on perineal membrane
-Pierces ant. Angle of perineal membrane on lat. Side of deep
dorsal artery of penis
-Supply : 1.Skin of penis. 2. Glans penis. 3. Corpus cavernosum
Perineal Nerve (two)
-Passes into superficial pouch
-Supply : 1.Penile muscles. 2.Urethra 3. Scrotal skin
4.Gives a branch to deep pouch which is motor to sphincter
urethra & 5. Ant. Fibers of levator ani muscle.
6.Sensory to membranous urethra
4/29/2012
26
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Cutaneous nerve supply of urogenital triangle
*
Ant. 1/3 scrotum (labium majus): ilio-inguinal N. (L1)
Lat.(Labium majus): Post. Cut. N. of thigh
(Perineal branch - S2)
*
Post. 2/3 scrotum
Med. (Labium minus): Perineal N. (S3)
(Scrotal or labial branches)
*
Skin of penis, glans, (clitoris): Dorsal N. of penis
L1(dorsal aspect of penile root), S2,3 (rest)
*
Mucous membrane of penile urethra (labia minora): Perineal N. (S3)
*
Penile musculature: Perineal N.
4/29/2012
27
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
The Rectum
* About 13 cm long
* Con nuous with Sigmoid colon & have similar structure,
(only difference is peritoneal a achment, where there is mesocolone
it is called sigmoid)
* Ends where
its
muscle coats are replaced by the anal sphincters
* Starts at the hollow of sacrum at level of S3 vertebra, then curves
forwards over the coccyx & ano-coccygeal raphe to pass thru. Pelvic
floor into the anal canal at ano-rectal junc on. The ano-rectal junc on
lies
3
cm above skin of anus, and
5
cm from p of coccyx
* The mucouss membrane together with the circular layer of muscle
form 3 permanent folds called the transverse folds of the rectum
(Rectal valves)
Ano-rectal junc on
4/29/2012
28
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Rela ons of rectum
Posteriorly: (both sexes)
In contact with sacrum & coccyx, Piriformis,
coccygeus, Levator ani, Sacral plexus, Sympathe c trunk
Anteriorly:
In male:
Upper 2/3: which is covered by peritoneum, & is related to sigmoid
colon & coils of ileum that occupy the recto-vesicle pouch
Lower 1/3 : is devoid of peritoneum, & is related to
1. post. Surface of bladder.
2.termina on of vas deferens.
3. seminal vesicles.
4.prostate
In female:
Upper 2/3: which is covered by peritoneum, is related to
sigmoid colon & coils of ileum that occupy the recto-vesicle pouch
Lower 1/3: is devoid of peritoneum, is related to
1. post. Surface of vagina
4/29/2012
29
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Stability of rectum
1. Fascia of Waldeyer (around sup. Rectal vessels)
2.Lat. Ligament of rectum (around middle rectal vessels)
3.Pelvic peritoneum (upper 1/3 ant. & lat.,
middle 1/3 ant. Only, lower 1/3 devoid of peritoneum)
4. Pelvic floor
4/29/2012
30
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Urinary bladder
-- Form & size are the same in both sexes
-- Trigone is fixed
-- The full bladder is
ovoid
(pyramidal when empty)in both sexes
-- Having a Fundus (apex & sup. Surface), base (Trigone, Post. Surface)
& two inferolateral surfaces
-- Average capacity = 700 800 ml. ( mictur on starts at
200 -400 ml.)
APEX
BASE
NECK
4/29/2012
31
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
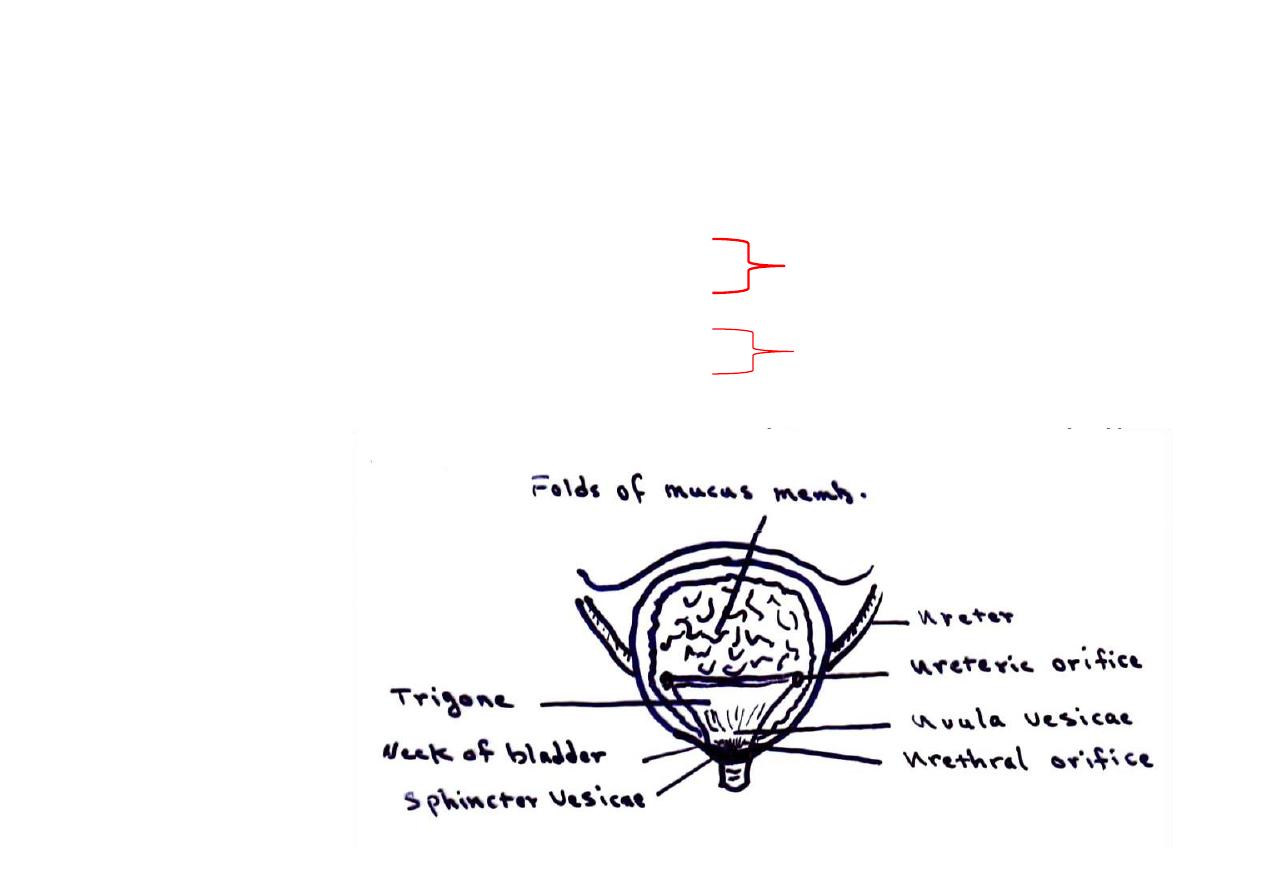
Trigone
- Triangular area lying between the internal urethral orifices & the
orifices of the ureters
- Rela vely indistensible & immobile
-Held in pos on by: 1.Lat. Lig. Of bladder
2. Fixed to prostate
1. Cervix uteri
2.Ant. Vaginal fornix
-Smooth walled & mucous membrane is firmly adherent to underlying
muscle
In female
In male
4/29/2012
32
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
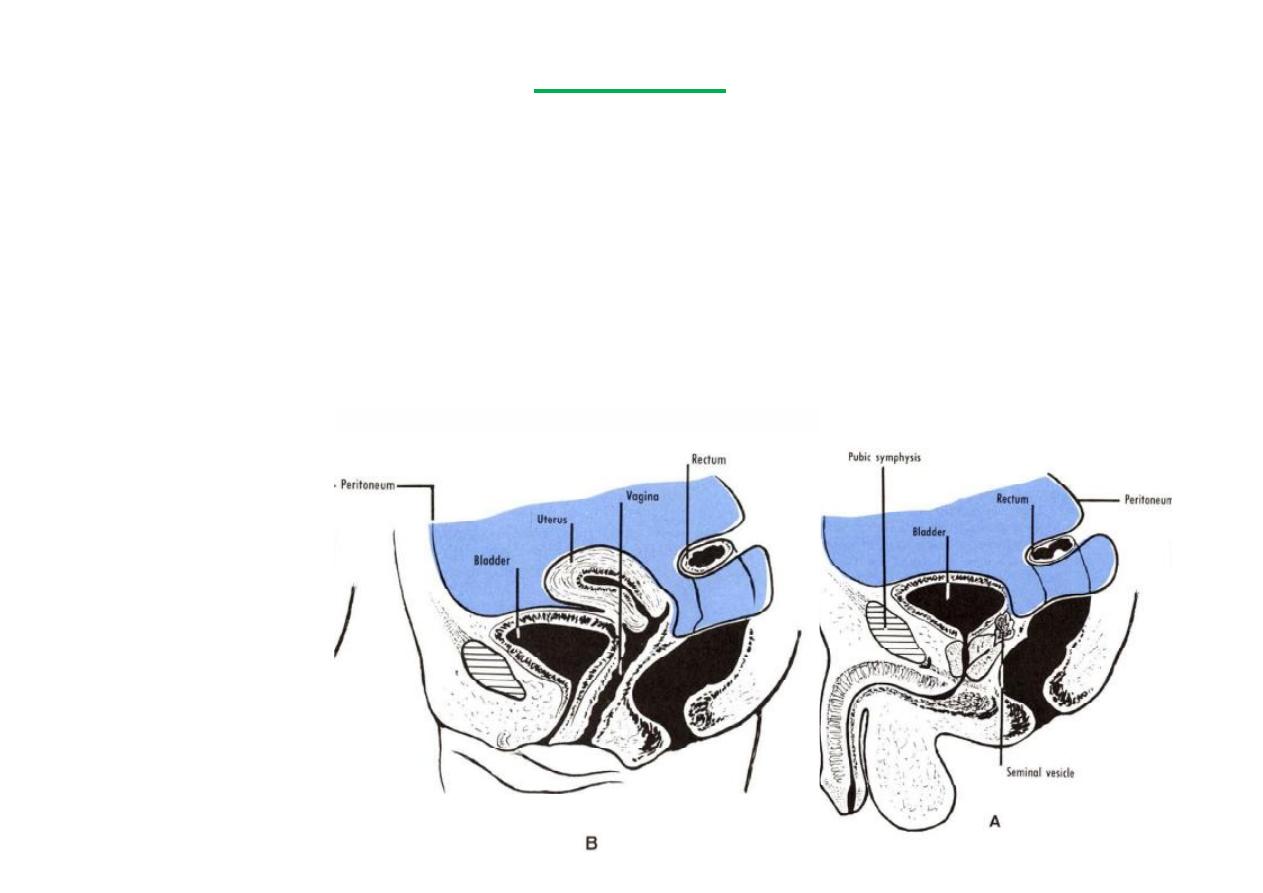
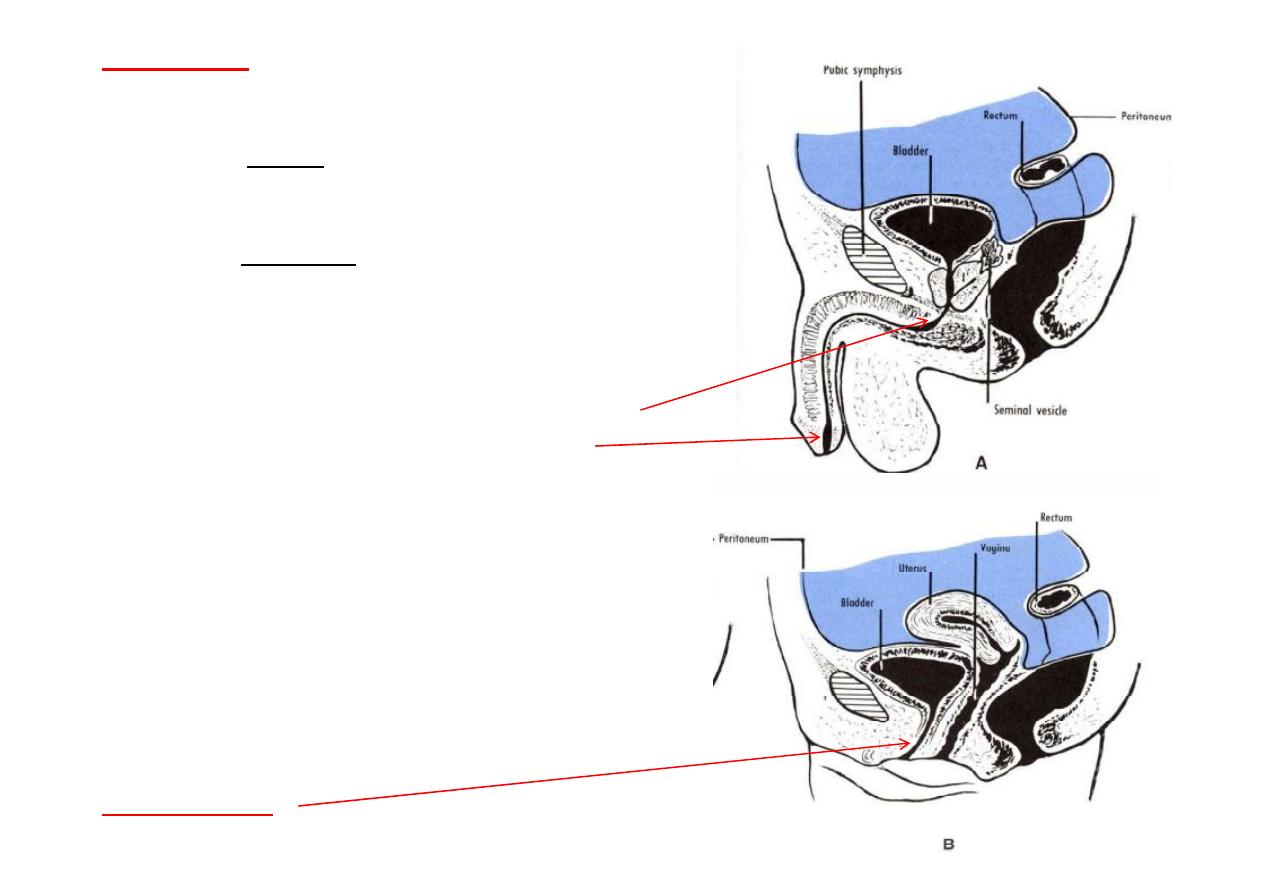
Posterior surface in male
A- Upper part: Covered by pritoneum (ant. Wall of rectovesical pouch)
B- Lower part: Separated from rectum by vas deferen a, Seminal vesicles
& rectovesical fascia of Denonvelliers
Posterior surface in female
-Firmly a ached to cervix uteri & ant. Vaginal fornix
Inferiolateral surface (
2
) (both sexes)
- Infront: Retropubic pad of fat & pubic bones
- Posteriorly: Obturator internis (above) & Levator ani (below)
Above(both
sexes):
Pelvic peritoneum,
sigmoid colon &
coils of ileum
RELATIONS
4/29/2012
33
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Blood supply
* Arteries
1. Sup. Vesicle
2. Inf. Vesicle
3. Inf. Epigastric (few twigs)
* Veins
-From vesicle plexus at base of bladder
# In male: it communicates with prosta c plexus & middle rectal veins
which in turn drain across pelvic floor into internal iliac veins
# In female: it communicates with uterine plexus at base of broad
ligament
Which in turn drains across pelvic floor into internal iliac veins
*Lymph
- Follow arteries to nodes on side wall of pelvis alongside
1. Internal iliac art.
2. External iliac art. (from funds along pubic art.)
4/29/2012
34
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
*Nerves
- From both sympathe c (hypogastric plexus L1,2) &
parasympathe c (pelvic splanchnic nerves S,2,3,4 via inf.
Hypogastric plexus)
-
Sympathe c
is: 1. Inhibitory to detrusor muscle
2. S mulatory (motor) to internal vesicle sphincter
* Reach inf. Hypogastric plexus via the hypogastric nerves (
Lumbar splanchnics or presacral nerves, these are divided in
presacral neurectomy)
-
Parasympathe c
is: 1. S mulatory (motor) to detrusor muscle
2. Inhibitory to internal vesicle sphincter
* Afferent fibers of normal disten on & pain : -majority pass in
pelvic splanchnic nerves (parasympathe c) --some pass with
sympathe c via hypogastric plexus to L1,2 segments of spinal cord
4/29/2012
35
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Hypogastric plexuses
-Visceral branches from all lumbar sympathe c ganglia (
paravertebral
)
join loosely & pass down in front of common iliac vessels, these are
the hypogasric nerves. They contain a mixture of pre (parasympathe c)
& postganglionic (sympathe c) fibers. They are joined by similar fibers
from the Aor c plexus (
prevertebral
).
-They unite in front of body of the 5
th
. Lumbar vertebra to make the
small
Sup. Hypogastric plexus
, which divide into right & le
Inf.
Hypogastric plexuses
. They supply pelvic viscera only.
4/29/2012
36
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Male urethra
20 cm long, S-shaped tube, 3 parts
1
-prosta c urethra
*
3 cm long , Widest & most dilatble,
*
Upper post. Part contains the urtheral crest
2
-Membranous urethra
*
1 cm long, Narrowest, more ridged, 3 cm behind
symphysis pubis, surrounded by sphincter urethra
muscle, pierce perineal membrane
3
- Spongy urethra
16 cm long, slit like lumen (narrowest at ext. ureth.
Orifice, dilated post. in bulb (intra-bulbar fossa),
dilated ant. at glance penis (navicular fossa)
*Blood suplly
: Inf. Vesical (prosta c part), branches
int. pudendal (rest)
-
Veins:
Prosta c plexus, int. pudendal vein
*
Nerves
: mucous membrane by pudendal nerve
*
Lymph
: From prosta c & membranous parts to
int. iliac nodes
From spongy part to superficial ing. Nodes
-Mucous memb. Very vascular (prosta c--
transi onal, membranous & spongy-- stra fied
columnar, (at navicular fossa it is squamous)
Female urthera
*
3.5 cm long , surrounded by sphincter urethra
4/29/2012
37
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
UTERUS
*
Hollow pear shaped
*
8X5X3 Cm (nulliparous)
*Possesses
Fundus, Body &
Cervix
-Fundus:
Part above entrance of
tubes
-Body:
Receives Uterine Tubes at
cornua. Cavity is triangular in
coronal sec on
- Cervix:
(neck of uterus) = 2.5
cm.
-
Cervical canal is spindle in shape
-
Cervix opens & protrudes into
Vault of Vagina
-
Vaginal fornix (deep sulcus
surrounding the protruding
cervix)
4/29/2012
38
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Rela ons
-Covered by peritoneum
-Ant. Down to level of internal os
(from internal os down to ant. Vaginal fornix is firmly
a ached to base of bladder by fibrous ssue)
-Post. Down to level of post. Vaginal fornix
4/29/2012
39
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
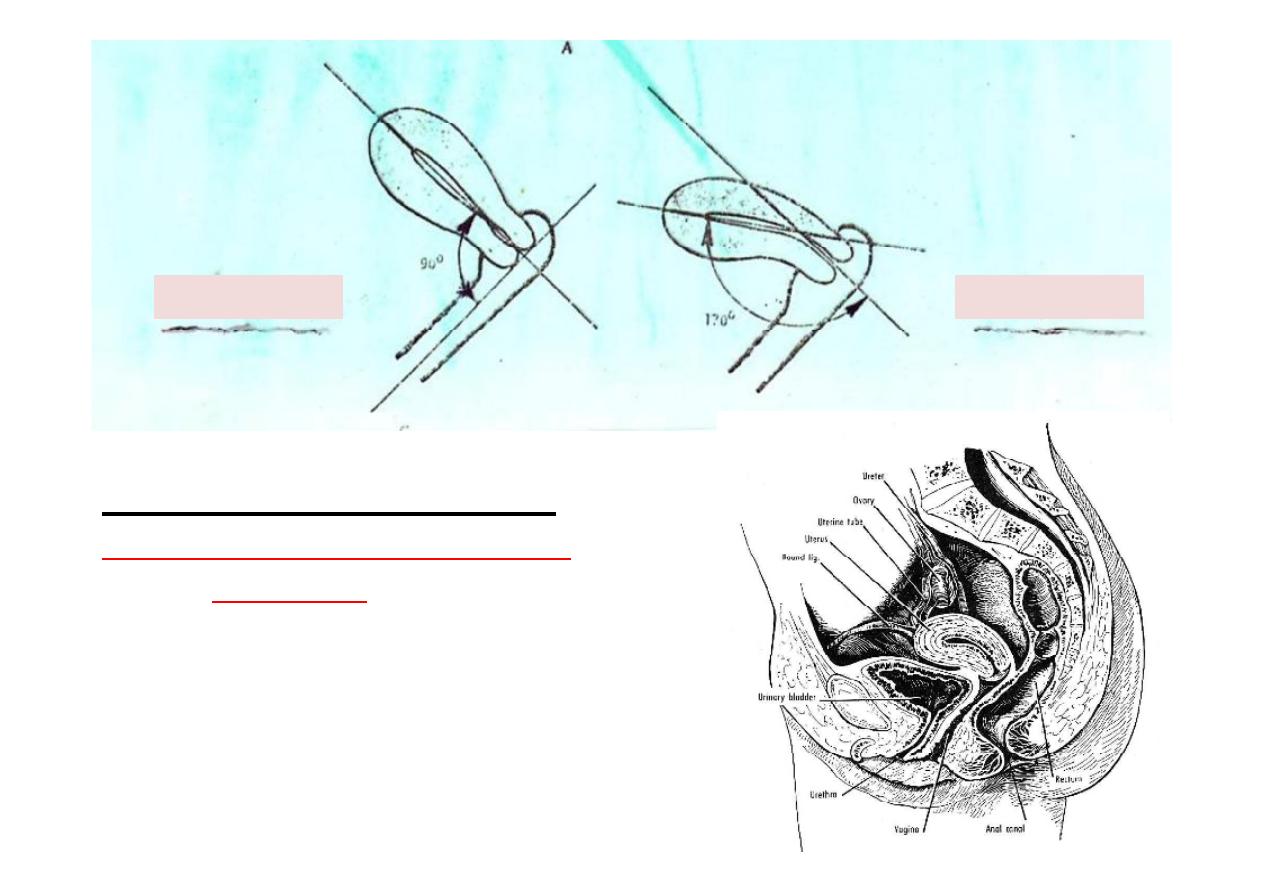
Normal posi on of Uterus
Anteversion & slight Anteflexion
(almost
horizontal
)
(Maintained in this posi on by:
1-Support from pelvic floor.
2-Presence of ligts (eg.Round & Utro-sacral)
90
170
Anteversion
Anteflexion
4/29/2012
40
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Ligaments of Uterus
*
Round ligaments.
(lie in ant. leaf of broad lig.,
below uterine tubes--- holds funds forwards in
anteversion) )
*
Utero-sacral ligaments.
(from cervix to lower
sacrum---keep cervix braced backwards, so maintain
anteversion)
*
lateral cervical ligament
(of Mackenrodt),
cardinal
ligament
.
(thick connec ve ssue around
uterine
vessels---
It a aches the
cervix
to the lateral pelvic wall
at the
ischial spine
,
give lat. stability to cervix)
*
Pubo-cervical ligaments.
P
or on of the tendinous
arch of the pelvic fascia.
(from cervix to body of pubis)
*
Broad ligaments.
peritoneum
that connects the sides of
the
uterus
to the walls and floor of the
pelvis
.
4/29/2012
41
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Supports of the Uterus
The uterus is a mo le organ which undergoes extensive changes in size and shape
during the reproduc ve period of life. It is supported and prevented from Sagging
(
down by a number of factors which are chiefly muscular and fibromuscular.
Classifica on:
I PRIMARY SUPPORTERS
A. Muscular (or ac ve)
*
Pelvic diaphragm (floor)
*
Perineal body
*
Urogenital diaphragm
B. Fibro-Muscular & mechanical
*
Uterine axis
*
Pubocervical ligament
*
Lat. Cervical lig.
*
Uterosacral ligament
*
Round ligament of uterus
II SECONDARY SUPPORTERS
are formed by peritoneal ligaments.
*
Broad ligament
*
Uterovesical fold of peritoneum
*
Rectouterine fold of peritoneum.
4/29/2012
42
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Blood supply of uterus
Arteries
*
Uterine artery
: - of internal iliac artery, pass over pelvic floor in base
of broad lig., above ureter, reach level of supra-vaginal part of cervix
where it gives a branch to cervix & upper vagina.
- It then turns upwards, between leaves of broad lig. To run alongside
of uterus as far as entrance of tube, where it anastomoses, end on,
with tubal branch of Ovarian artery.
-During its course it gives off branches which penetrate walls of uterus.
Veins
* Pass below artery at lower edge of broad lig. Where they form the
Uterine plexus
of veins across pelvic floor.
-This plexus communicates with vesicle & rectal plexuses & drain into
internal iliac vein.
4/29/2012
43
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Lympha cs
*Pass along arteries into internal iliac group of nodes which drains
upwards into common iliac nodes.
- Some pass along round lig. To superficial inguinal nodes. Others with
ovarian artery to Para-aor c nodes at origin of artery.
Nerves
* Branches from inf. Hypogastric plexus
-Sympathe c:- Efferent preganglionic sympathe c fibers are from
T12,L1 segments of spinal cord.
- Parasympathe c:- Efferent preganglionic parasympathe c fibers are
from S2,3,4 (pelvic splanchnics) segments of spinal cord.
- Sympathe c ac vity produce uterine contrac on & vasoconstric on
- Parasympathe c ac vity produce uterine inhibi on & vasodilata on
- The results of the ac vi es of these two systems are complicated by
the hormonal control of uterine func ons)
- Pain from cervix via pelvic splanchnic nerves, while pain from funds
(labour pain)via hypogastric nerves to T12,L1 segments.
4/29/2012
44
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
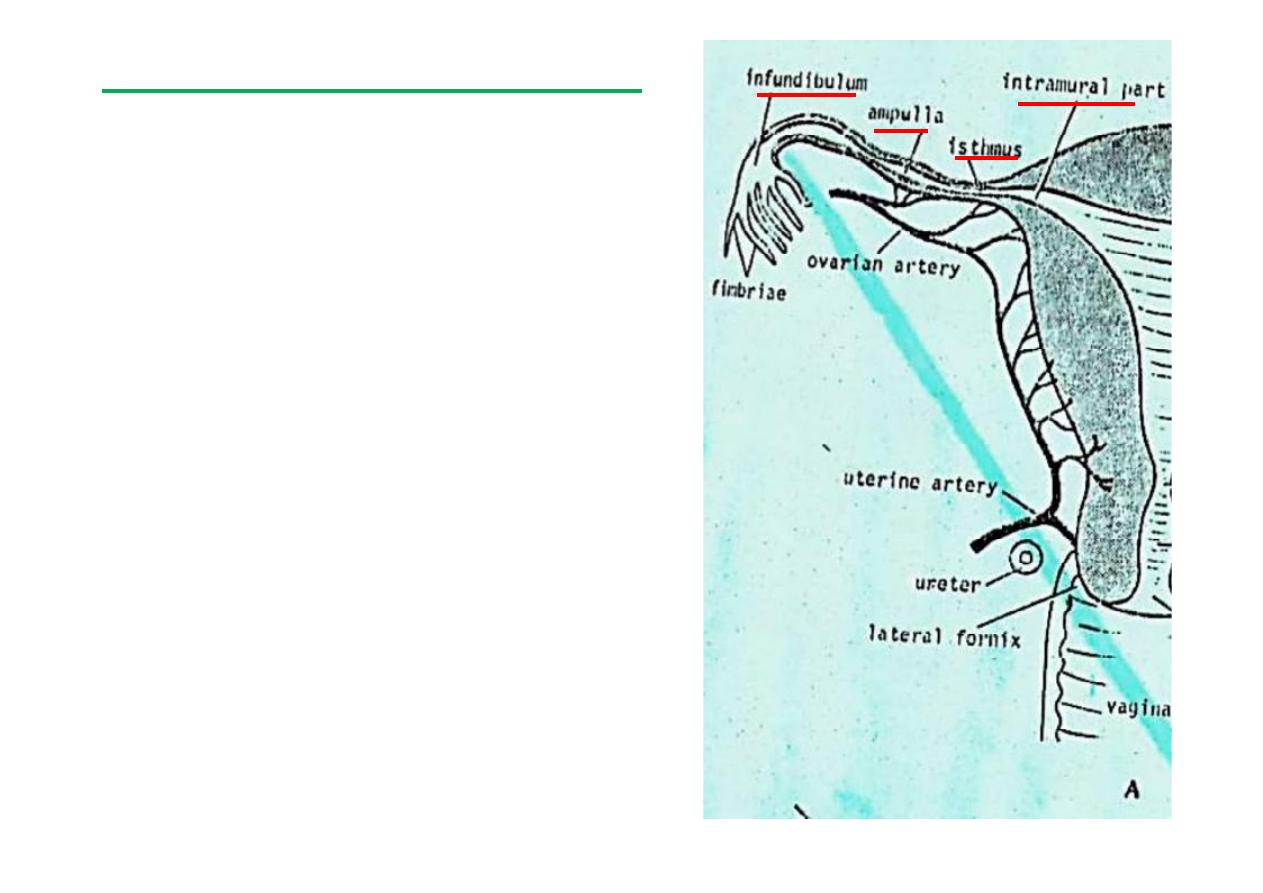
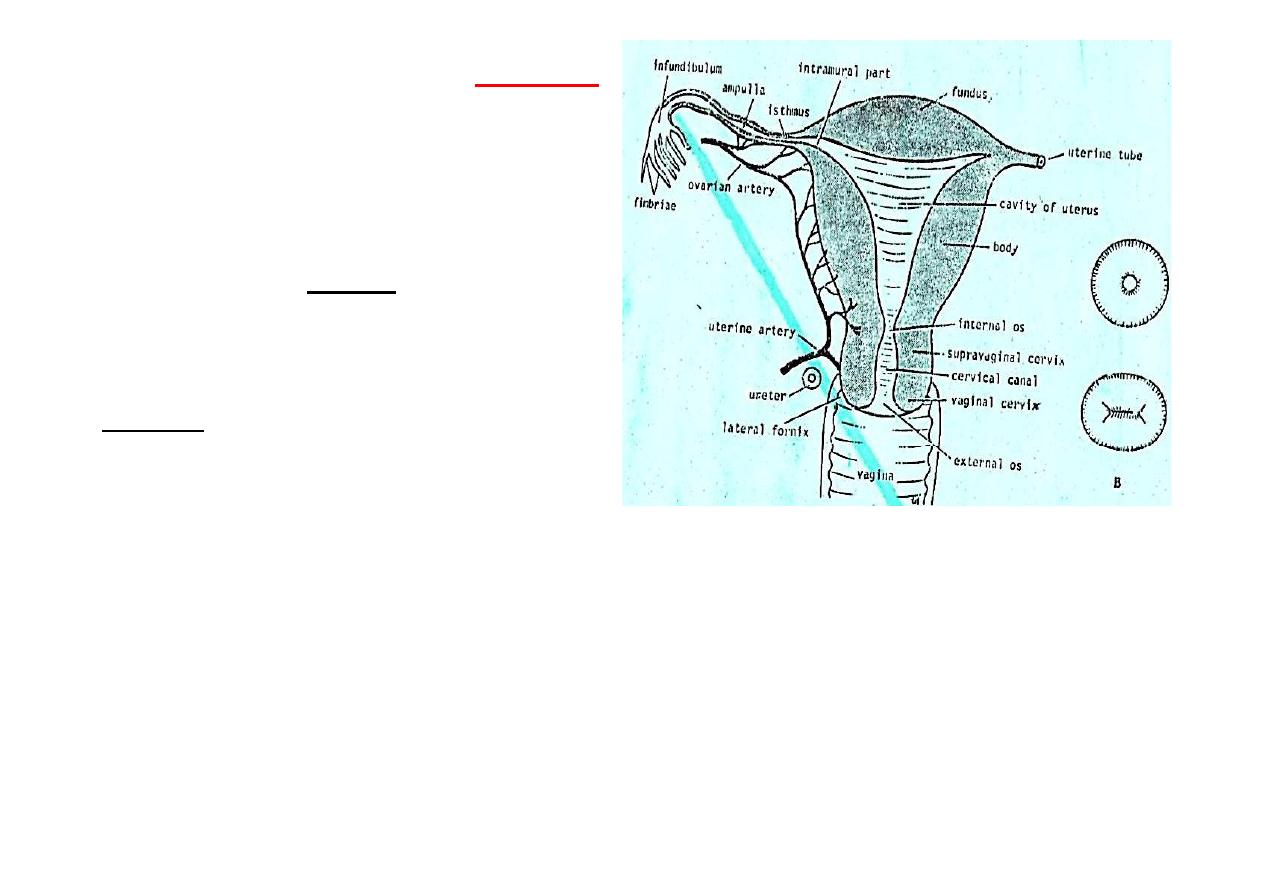
Uterine tubes (Fallopian tubes)
*
10 cm long
*
Lies in upper boarder of broad lig.
*
Connects peritoneal cavity with
that of uterus.
*
Four parts (
Infundibulum,
Ampulla, Isthmus, Intramural part
).
*
Nerves: Inf. Hypogastric plexus
(Sympathe c & parasympathe c)
*
Blood: Ovarian & Uterine arts. &
veins.
*
Lymph: Corresponds to arts. (ie:
internal iliac & aor c nodes).
4/29/2012
45
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Ovary
*
Almond-shaped, 2X4 cm.
*
Have med. & lat. Surfaces & tubal & uterine ends.
*
A ached to back of broad lig. By Mesovarium (double folds of
peritoneum through which ovarian vessels enter its hilus & a ached to
its equator).
*
Long axis is ver cal in posi on
*
Lies in angle between internal iliac & external iliac vessels on obturator
*
Suspensory lig. of ovary (Infundibulopelvic Lig.): That part of broad lig.
Between a achment of mesovarium & lat. Wall of pelvis (ie. beyond
ovary & infundibulum of uterine tube to lat. Wall of pelvis). (uterine
tubes lie in med. 2/3 of free upper border of broad lig., the remaining
1/3 is the suspensory lig.).
-Contains the ovarian blood vessels, nerves and lympha cs
*
Round lig. of ovary: Remains of upper part of Gubernaculum, extends
from upper end of lat. Wall of uterus to med. margin of ovary (mass of
smooth muscle & fibrous ssue lying between two layers of broad lig. &
is con nuous with round ligament of uterus.
4/29/2012
46
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Rela ons of ovary
*
Lies against lat. Wall of pelvis, in ovarian fossa on obturator
nerve bounded by:
1-above:
ext. iliac Vs.
2-behind:
int.iliac Vs. & ureter
3-infront:
obliterated umbilical art.
*Blood supply
: ovarian (at L1) & uterine arts.
Veins drainage
: (by a pampiniform plexus)
Lt. ovary Lt. renal vein,
Rt. Ovary Inf. Vena cava .
*
Lymph
: Follow Ovarian arts. To pre & para-aor c nodes at L1
*
Nerves
: From Aor c plexus (accompany ovarian arteries.)
(Sympathe c from T10 segments of spinal cord)
4/29/2012
47
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Prostate Gland
*
Size & shape of a chestnut.
*
Apex below between bladder & pelvic floor.
*
Perforated by urethra (most substance lie behind & lat. To
urethra).
*
Between Alveoli there is fibromusclar stroma which is in
direct con nuity with muscle of bladder.
*
Perforated by ejaculatory ducts which open separately
into prosta c urethra, on urethral crest.
*
Its own ducts (30-40) open separately all around prosta c
urethra.
4/29/2012
48
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

*
Surface covered by thin condensa on of
fibrous ssue and smooth muscle =
Capsule
.
*
The capsule is completely covered by thick
membrane of condensed areolar ssue of
pelvic fascia =
Prosta c fascia
.
*
This fascia is separated from the capsule by a
narrow space which contains the
prosta c
plexus of veins
.
Rela ons:
Sup.: neck of bladder & seminal vesicles
Inf.: Sphincter urethra
Antro-lat.: Levator ani
Post.: Rectum
4/29/2012
49
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

*
The prostate Possesses a base (sup.) & an apex (inf.) & ant.,
post. & 2 inferiolat. Surfaces.
*
Traversed by
urethra
& in post. Upper ½ by
ejaculatory ducts
which divide gland into a median & 2 lat. Lobes .
Median lobe
: between urethra & ejaculatory ducts.
Lateral lobes
: below & lat. To median lobe & are con nuous
ant. But separated post. By a midline groove.
4/29/2012
50
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji

Prosta c fluid
*
Thin milky fluid
*
Slightly acidic (Ph=6.5) P.N.: Semen Ph =7.5
*
About 30% of Semen volume.
*
Contributes to mo lity & viability of sperms.
*
Contains acid phosphatase ,citric acid, several
proteoly c enzymes ( pepsinogen, amylase,
hyaluronidase & prostate specific an gen)
Prostate-specific an gen (
PSA
) helps to keep the
semen in its liquid form. It is an enzyme in the form of
a glycoprotein produced primarily by cells lining the
acini and ducts of the prostate gland.
4/29/2012
51
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
Seminal vesicle
-Pair of thin-walled elongated and lobulated sacs, each consis ng of a
blind tube folded on itself
-Length unfolded = 10-15 cm
folded = 5 cm
-Applied to base of bladder above prostate
-Covered post. By fascia of Denonvilliers
-Each joins the lower end of ampulla of ducts deferens to form the
Ejaculatory duct
-Produce seminal fluid & contain no spermatozoa
-Its secre on impart mo lity to Spermatozoa, slightly alkaline & contains
fructose & a coagula ng enzyme called vesiculase
-
Arteries
from branches of inf. Vesicle & middle rectal arteries
-
Nerves
from hypogastric plexus & Hypogastric nerves (motor---
sympathe c from L1 Ganglion)
-Contracts during ejacula on & secre on forms bulk of ejaculated fluid
(60% of semen volume)
52
4/29/2012
Prof. Dr. F. AL-Khafaji
