hormonal control of calcium
PARATHYROID GLANDVery small (less than 5 mm).
Called parathyroid glands because of their position on posterior margins outer surface of thyroid gland.Development: Like thyroid gland, develop from early pharynx .
PARATHYROID GLANDFunction:
PARATHYROID HORMONE (PTH) – raises the level of calcium in the blood, decreases levels of blood phosphate. Partially antagonistic to calcitonin of thyroid gland.Kidney
G.I.Tract
Bone
Target Organs
PARATHYROID HORMONE
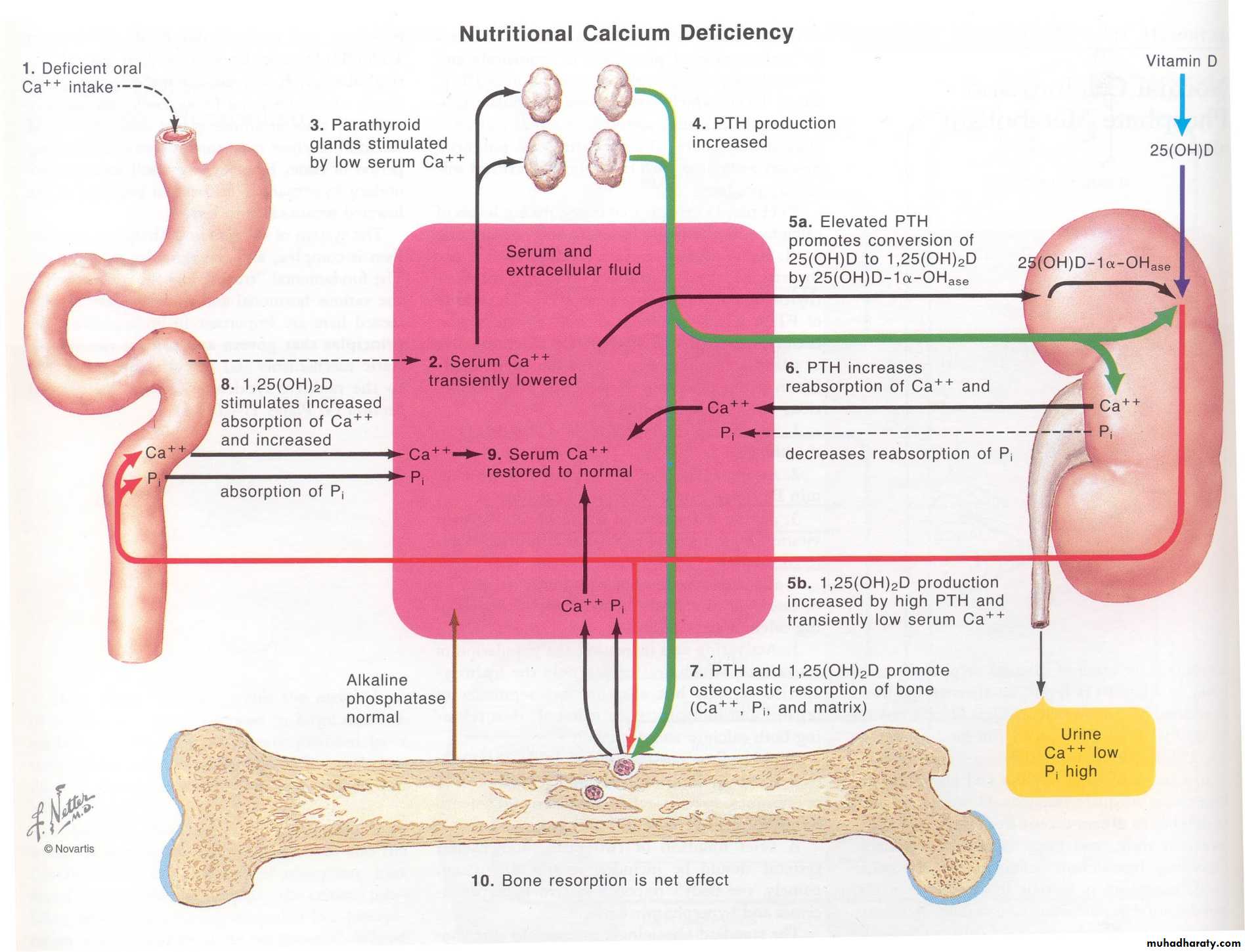
Secreation stimulated by fall in serum Ca.mobilize calcium from bone
Increases renal reabsorption of cadecreases renal clearance of calcium
increase calcium absorption - intestineCalcium homeostasis
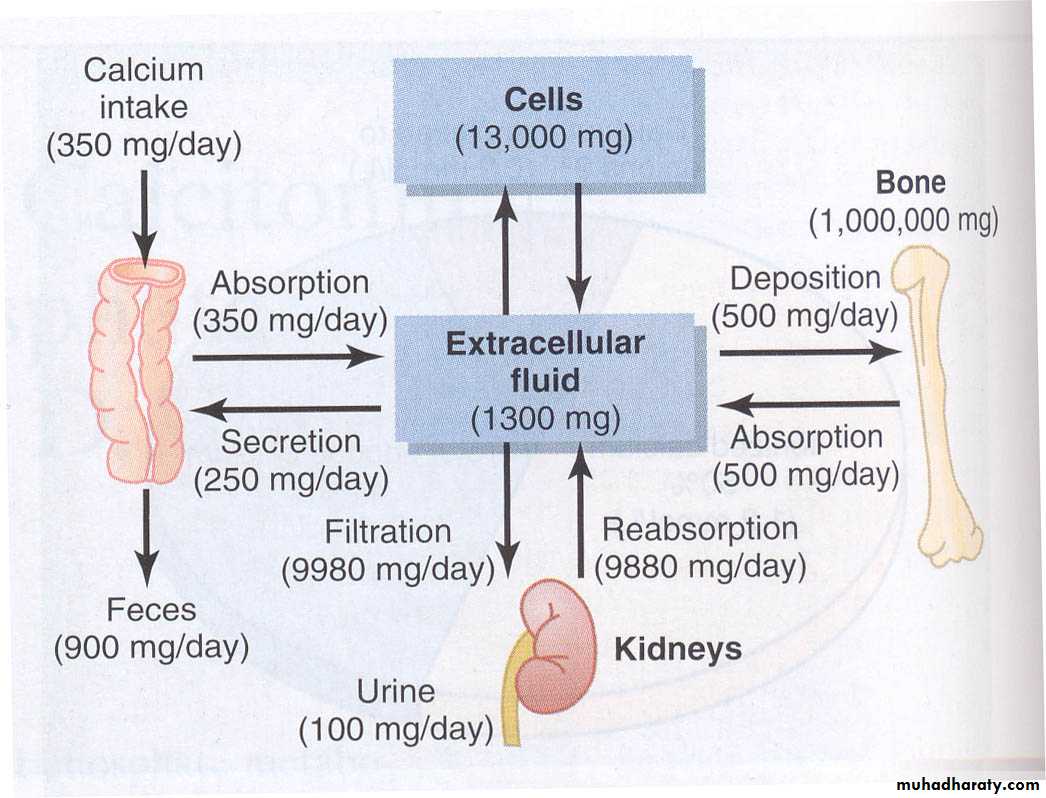
Plasma Calcium Regulation
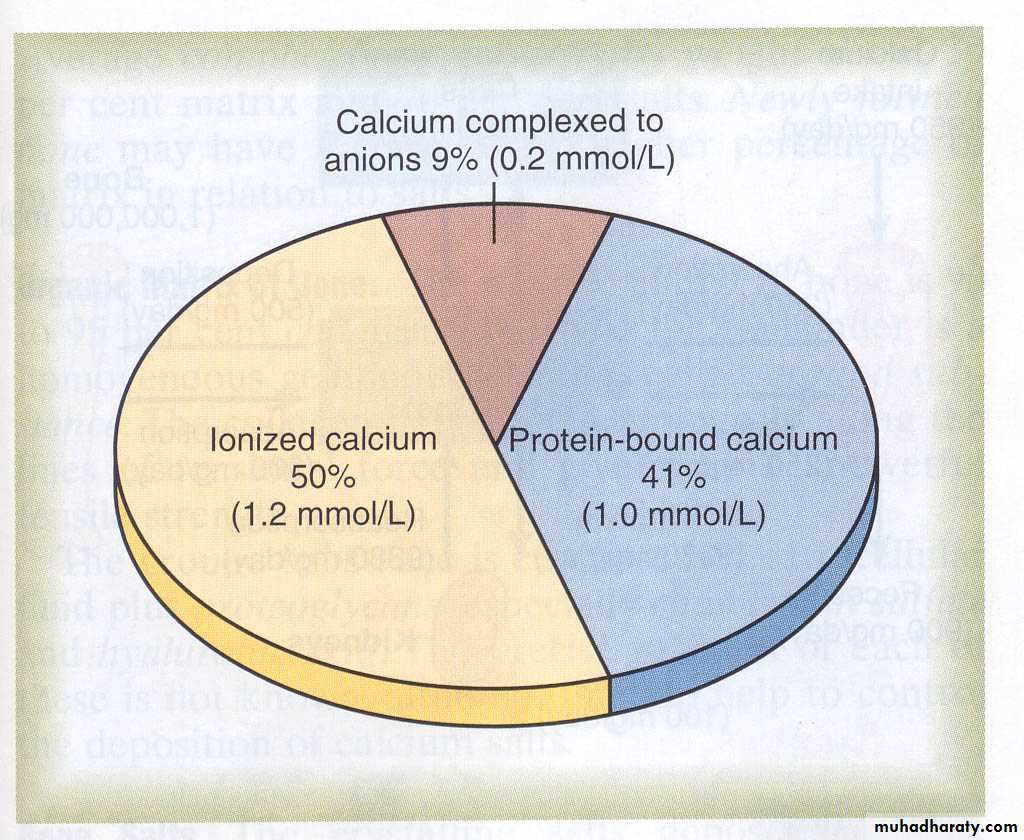
Plasma calcium totals 2.4 mM (9.4 mg/dl)
Free calcium is 1.2 mM
Free calcium is tightly regulated (5%)
Too low = neuronal hyper-excitabilityToo high = neuronal depression
Control points for calcium
Absorption – Via intestines
Excretion – Via urine
Temporary storage – Via bones
Plasma Calcium Regulation
Active Control of Calcium
Vitamin D3Diet and sun
Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid gland
Calcitonin
Thyroid gland
Skeletal loading
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts
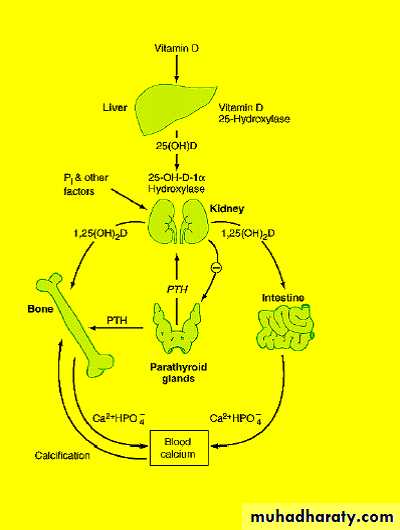
Vitamin D3 and Calcium Control
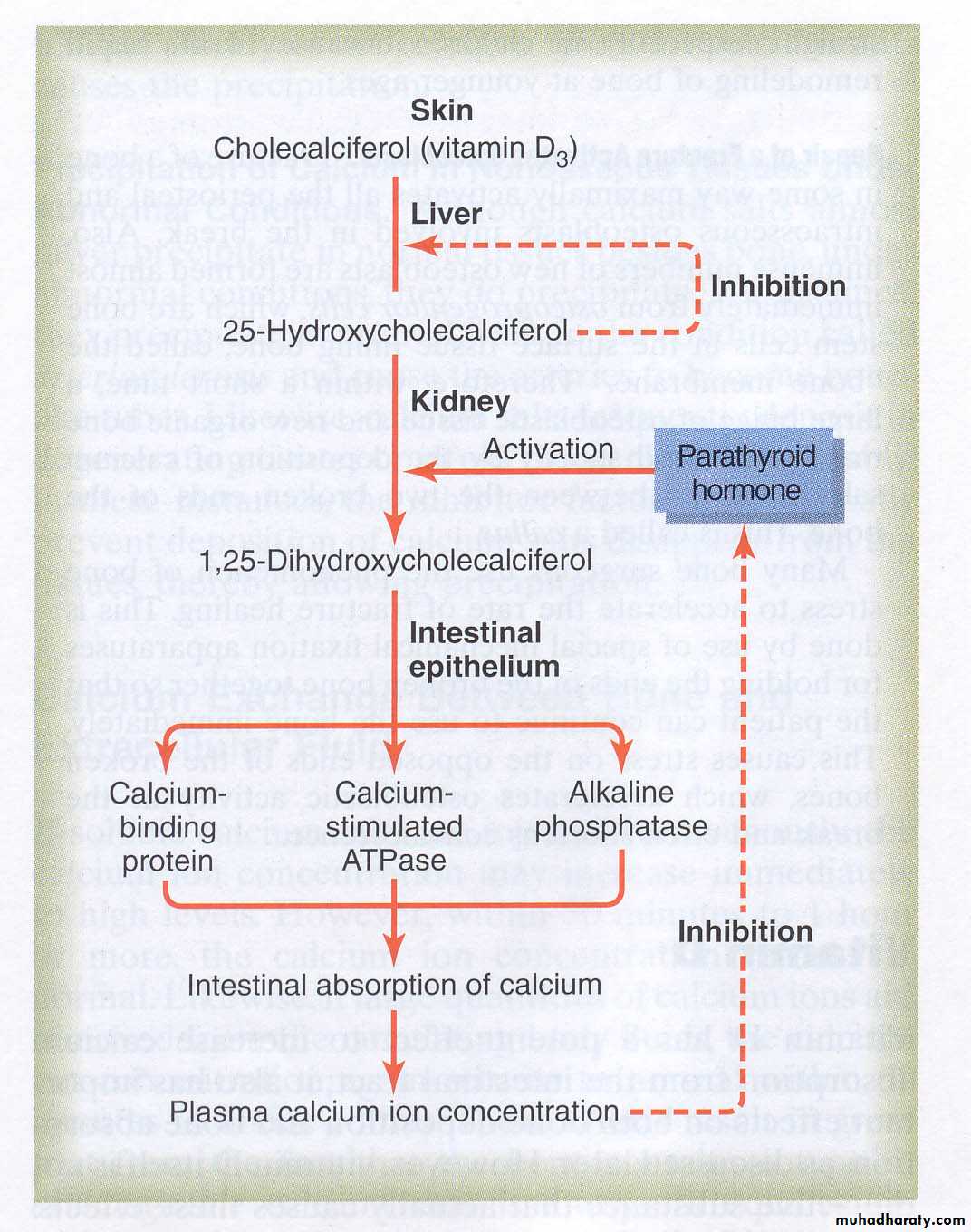
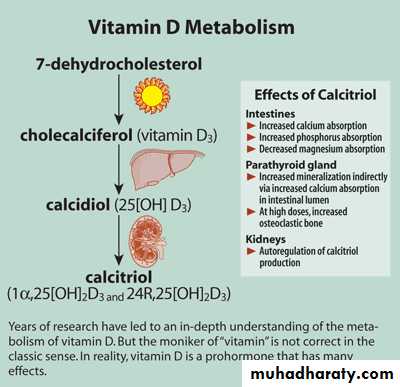
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)
Converted to precursor in liver
Initially stored
Converted to 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
Feedback control limits concentration
Converted to active form in kidney
1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
Under the feedback control of parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Effects of Active Form of Vit D3
Promotes intestinal absorption of calciumCauses synthesis of calcium-binding protein and related facilitated transport
Takes a couple of days to fully develop response
Has slight effect to increase calcium re-absorption in kidneys
Works with PTH to cause calcium absorption from bone
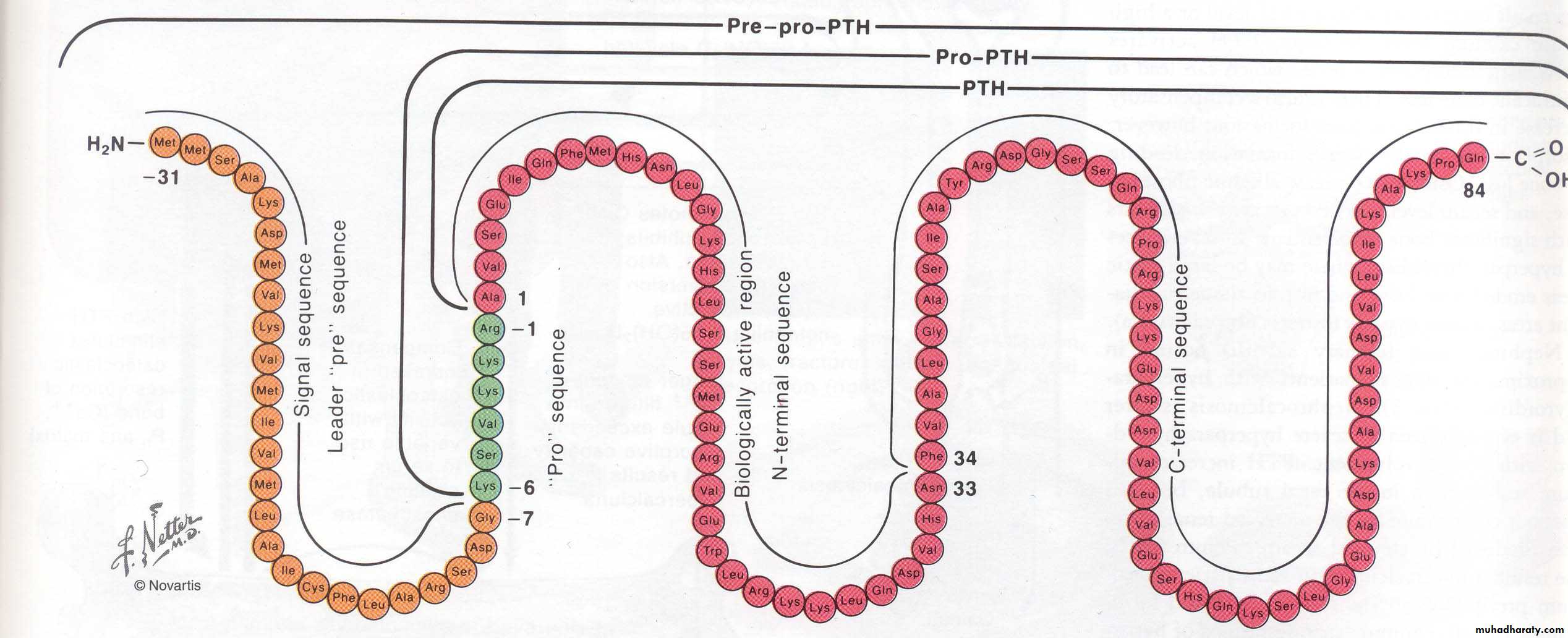
Parathyroid Hormone
Secreted by parathyroid glands
Rapid response to reduced calcium (minutes)
Polypeptide
84 amino acid residues
9,500 daltons M.W.
Peptide fragments can be active for periods measured in hours
Operates in tissues via cAMP second messenger
Parathyroid Hormone
Increases calcium absorption from boneExisting osteocytes stimulated (minutes to hours) to transport calcium – calcium pumps
Existing osteoclasts activated and new osteoclasts formed (days to weeks) to digest bone and release calcium
Stimulated indirectly by osteoblasts
Effects of PTH
Decreases excretion of calcium by kidneys
Important to prevent bone deterioration
Increases calcium absorption
Effect manifested via Vitamin D3
Produces most active form of D3 in the kidney (1,25-dihydroxy-cholecalciferol)
Other Effects of PTH
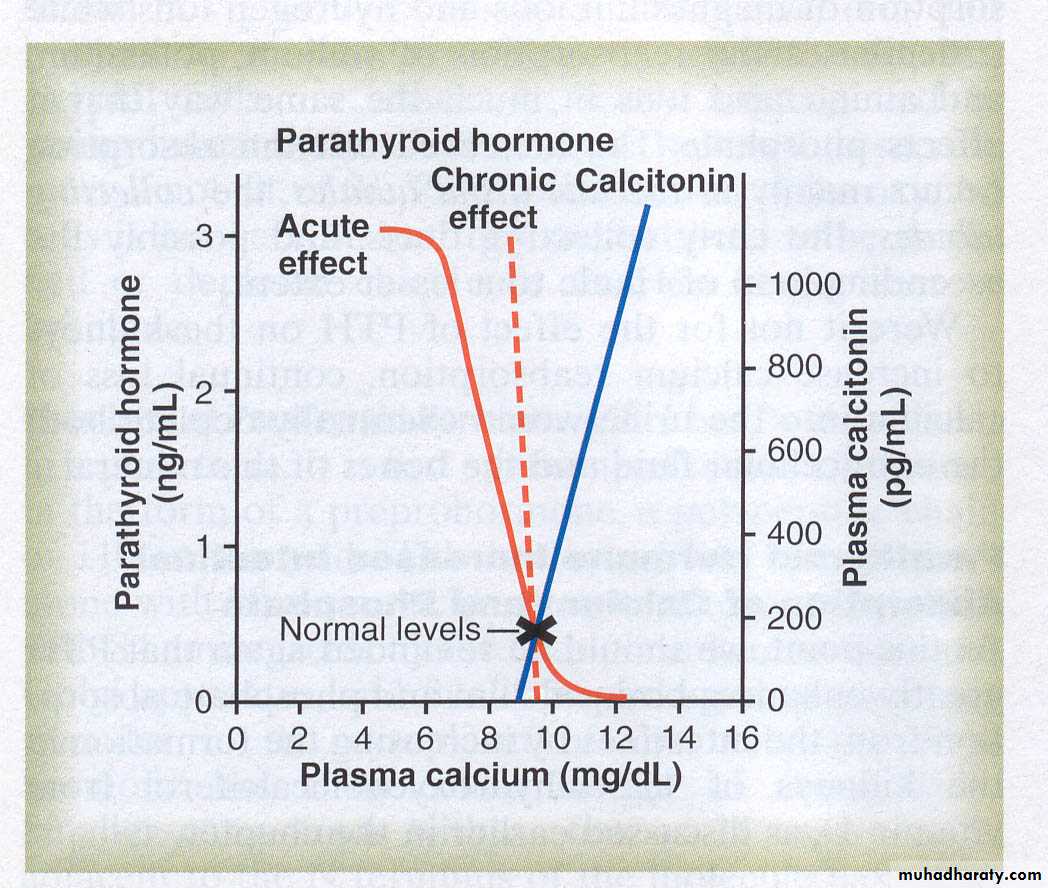
Calcitonin
Secreted by the thyroid glandEffects are much less than those of PTH
Attenuates absorptive ability of osteoclasts
Inhibits formation of new osteoclastsOsteoclast decrease causes osteoblast decrease
Effect to decrease calcium is transitory
Causes reduced bone turnover
Has weak effect in kidney and intestines
Effects of Calcitonin
Non-Hormonal Control of Plasma Calcium
Changes in calcium intake can be rapidly accommodatedBuffer capacity of amorphous calcium in bone
Calcium is sequestered in intracellular spaces
Can help restore plasma calcium in tens of minutes
Dysfunction of parathyroid Gland
1. Too little parathyroid hormone – hypoparahypothyroidismcauses low serum calcium and high phosphate
2. Too much parathyroid hormone– hyperparahyperthyroidism
causes high calcium and low phosphatePARATHYROID HORMONE
Secreation stimulated by fall in serum Ca.mobilize calcium from bone
Increases renal reabsorption of ca
decreases renal clearance of calcium
increase calcium absorption - intestineCalcium homeostasis
Vitamin D
Fat soluble ‘vitamin’Synthesised in skin
Food sources include fish oils
Vitamin D
The active hormone is 1,25(OH)2D3It increases absorption of calcium from gut.
It increases reabsorption of ca from kidney.
.
Calcium profile
To diagnose a metabolic bone diseasecalcium
Phosphate
Alkaline phosphatase
Parathyroid hormone
Vitamin D
Urinary calcium and phospherus