Myopathies
ObjectivesTo recognize existence of muscle diseases
To differentiate them from other disorders.
To know about various causes of myopathy.To know of basic investigations of myopathy.
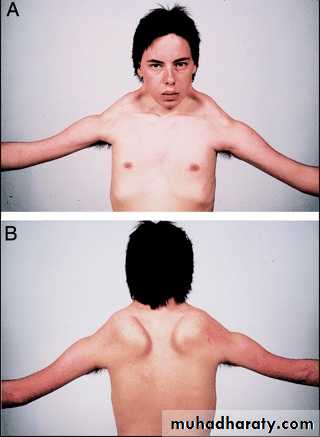
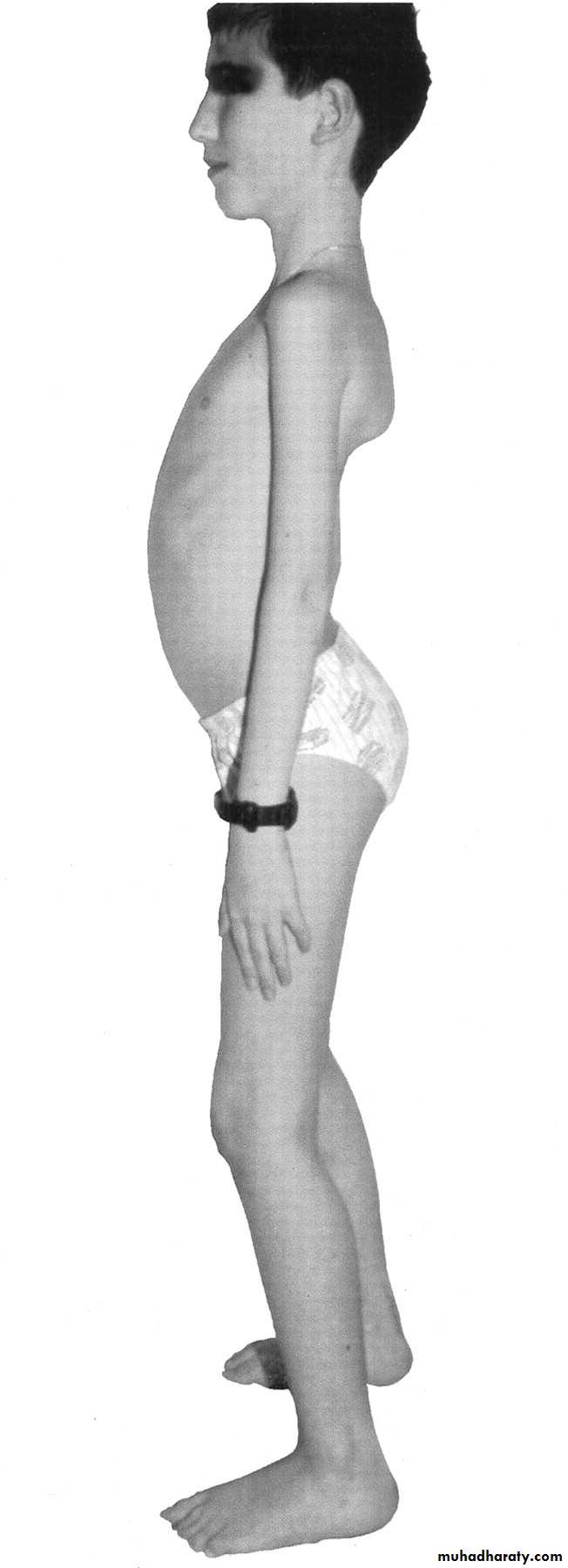
CLINCIAL PICTUREProximal, large muscles.
Steadily progressive , s.t. episodic
Symmetric
Preserved tone and tendon reflexes
No sensory\autonomic abnormality
Cardiac failure
Cardiac conduction abnormalities
Respiratory problems (sleep apnea)
Differential Diagnosis
Lower motor neuron disorders
Neuropathy (reflexes, distal, Sensory, autonomic)
Neuromuscular (bizarre, asymmetric, variable)
Anterior horn cell (reflexes)
Outline of investigations
Creatinine phosphokinase (CK)EMG-NCS
Muscke Biopsy (histo-biochemistry)
ECG
CXR
Underlying cause:
Genetic\metabolic screen and counseling
Inflammatory/Endocrine/Electrolytes etc..
Causes
HereditaryDystrophies
Congenital
Inherited metabolic
Channelopathies
Duchenne Muscular dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophies
Fascio-Scapulo-Humoral Dystrophy
Periodic Paralysis:
Hypokalemic :Na, Ca channel
After heavy carbohydrate meals, salt
Treament:
Low sugar\salt diet, rich K diet
Acetazolamide
Hyperkalemic :
Na channelAfter K rich meals
Treatment: low K diet