
Dr Fatma Galal
Teacher at civil law department
Dr.fatmagalal.law@gmail.com

1- Be on time

2- Keep mobile silent

3- No side talking

Revision
Our goal this term is to …..
Study the basics of law : those basics are distributed
between three theories:
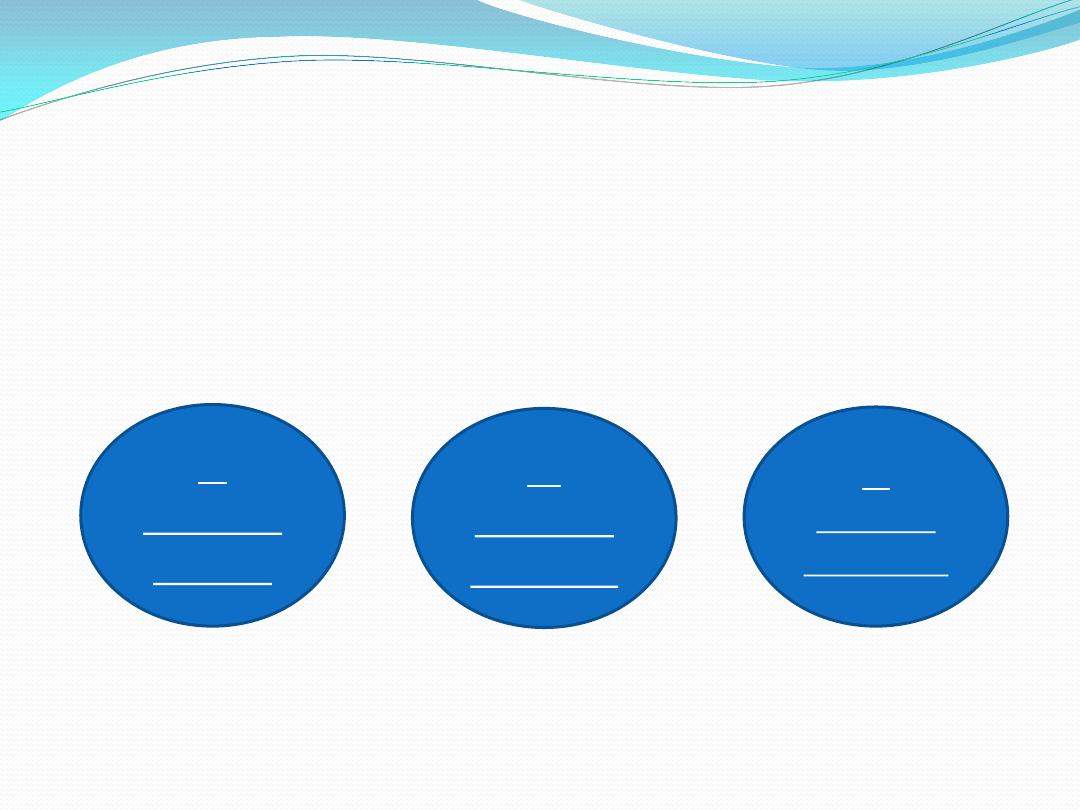
1-
Theory
of law
2-
Theory
of right
3-
Theory
contract

Book 1: introduction to law
This book includes both the theory of law and the
theory of rights….how to use what is called
the law
to
regulate who should have
the right
???

Part 1: the law.
Chapter one: Nature of law
Definition and characteristics of law:
law is a body of
general and abstract
rules which regulates
the
social
conduct of people and enforced by a
sanction
.

Chapter two: law, morality and religion
Law:
enacted by the legislature, controls external
behavior, sanctioned by the state.
Religion : ordered by God, controls external behavior
and internal thoughts , sanctioned by God.
Morals: rules of what is good and what is bad in the
society, sanctioned by the social disrespect.

Chapter 3: classification of law
Law is classified into
public
and
private law
according to
the nature of the person involved in the relation organized
by law.
Nature of persons: -
public persons
: such as state,
governorates, public authorities and universities.
- private persons:
either natural persons ( individuals) or
juristic persons ( private corporations and association.)
Note: public persons can act as private persons.

-
public law :
regulates the relations among public
persons or between public persons acting as
representative of the state and private persons.
-
private persons:
regulating relations among
private persons or between public persons and private
persons when public persons are acting as private
persons not as representative of state.
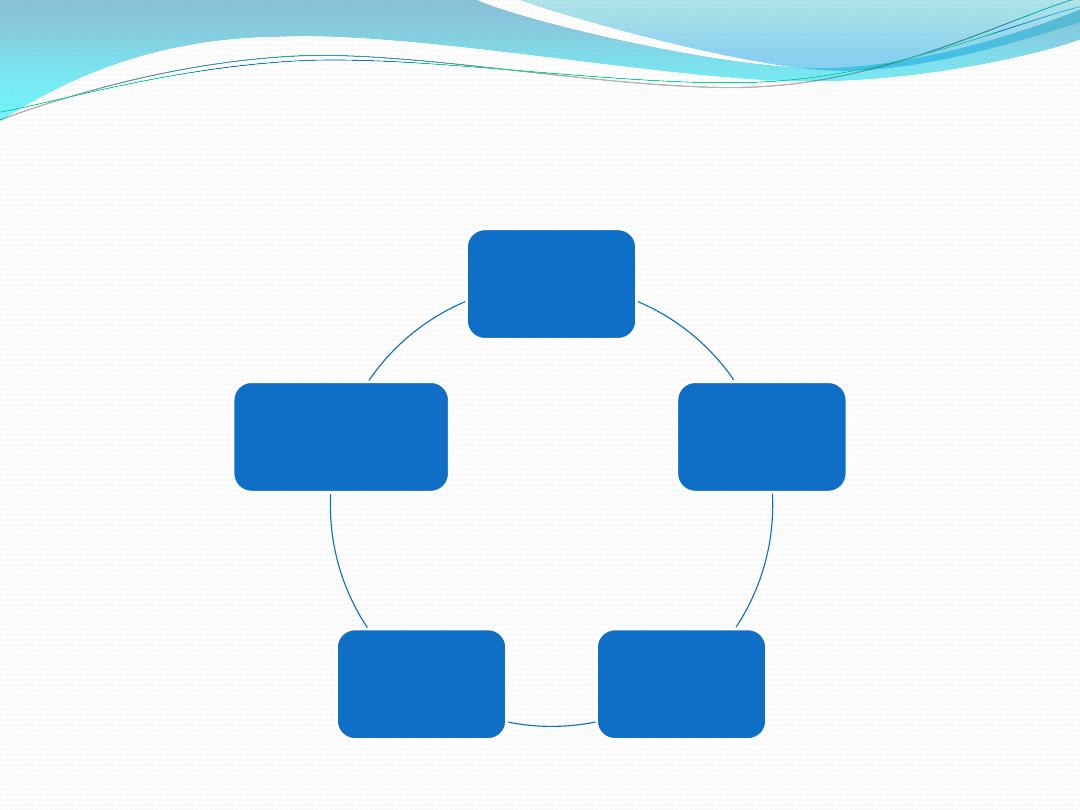

Section: subdivisions of public law
Constitution
al law
Taxation
law
Criminal
law
Public
internationa
l law
Administrative
law

1- constitutional law
It defines the
form of the state
( monarchy or republic)
and
organs of the state
( usually three: legislative,
executive and judicial ) and guarantees of
individuals
rights
( liberty of opinion and religion.. That is why it’s
the highest law any contradictory law is invalid)

2- administrative law
Deals with
executive authority
its public employees
and subordinate organs such as ministries and local
administrations , it also deals with organization and
functions of
administrative courts
.

3- tax law:
Imposition and collection of
taxes
( land , income
taxes… as part of the revenue )

4- criminal law
deals with
crimes
( ex: killing and stealing) and their
punishment
( fine, detention, hard labor and death)
Attached to it
law of criminal procedures
: define
authorities charged with the investigation and
prosecution of accused persons and procedures for
arresting them and bringing then before court

5- public international law
Regulates
relation between state
, it comes from
treaties, international custom and international courts
decisions.
It is divided into 3 categories: - rules of peace (
territory, treaties, diplomatic agents).
- rules of war ( declaration of war, legitimate
methods of war, duties of belligerent towards prisoners
and wounded people)
- neutrality: rights and duties of neutral states which
in peace with both belligerent state
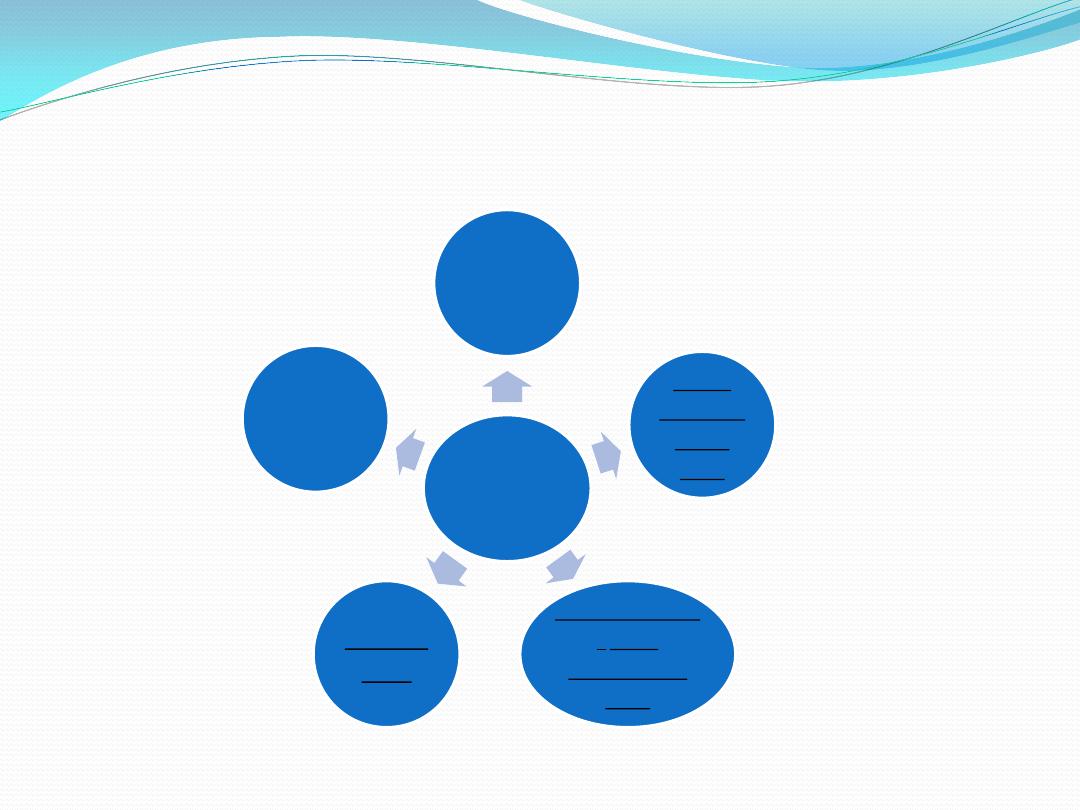
Section 2 : subdivisions of private
law
Branches
of private
law
Civil
law
Civil
proced
ures
law
Commercia
l
and
maritime
law
Labor
law
Private
interna
tional

1- civil law
Governs
relations between all ordinary individuals
.
Divided into 2 categories:
- the law of persons: or family law governs matters
related to capacity, marriage, divorce , rights and
duties of parents towards their children , alimony.
-
law of property
: deals with ownership, contracts
such as sale , lease and insurance.

Civil and commercial law of
procedures
It is a private law Though it regulate a public authority
( judicial).
Deals with
procedures of actions
which enforce
individuals rights and methods of
execution of
judgment.

3- commercial and maritime law
Deals with
trade in general
,
regulates relation
between merchants
such as partnership, companies,
bankruptcy.
It is not general such as civil law.
Maritime law relates to
trade on sea
, ownership of
ships , maritime insurance.

4- Private international law
If there is a case which involved a
foreign element
such as an Englishman bought a piece of land in
France from Egyptian what is the
applicable law
and
what is the
court that has the jurisdiction of the case
…
that is the private international law tell us

5- labour law:
It
regulates the relation between workers
and
employers which based on contract of work. it
regulated rights and duties of each of them.
Rules of labor law
are imperative
so they can not be
violated by agreements to the contrary.
Because they aim at protecting weak workers by
defining minimum age of worker, maximum no of
work hours, minimum rate for salaries and confirm the
right of workers syndicates.
