
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
1
Nephrology
Introduction to
nephrology
Total : 1
lec :1

د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
2
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
3
Introduction To Nephrology
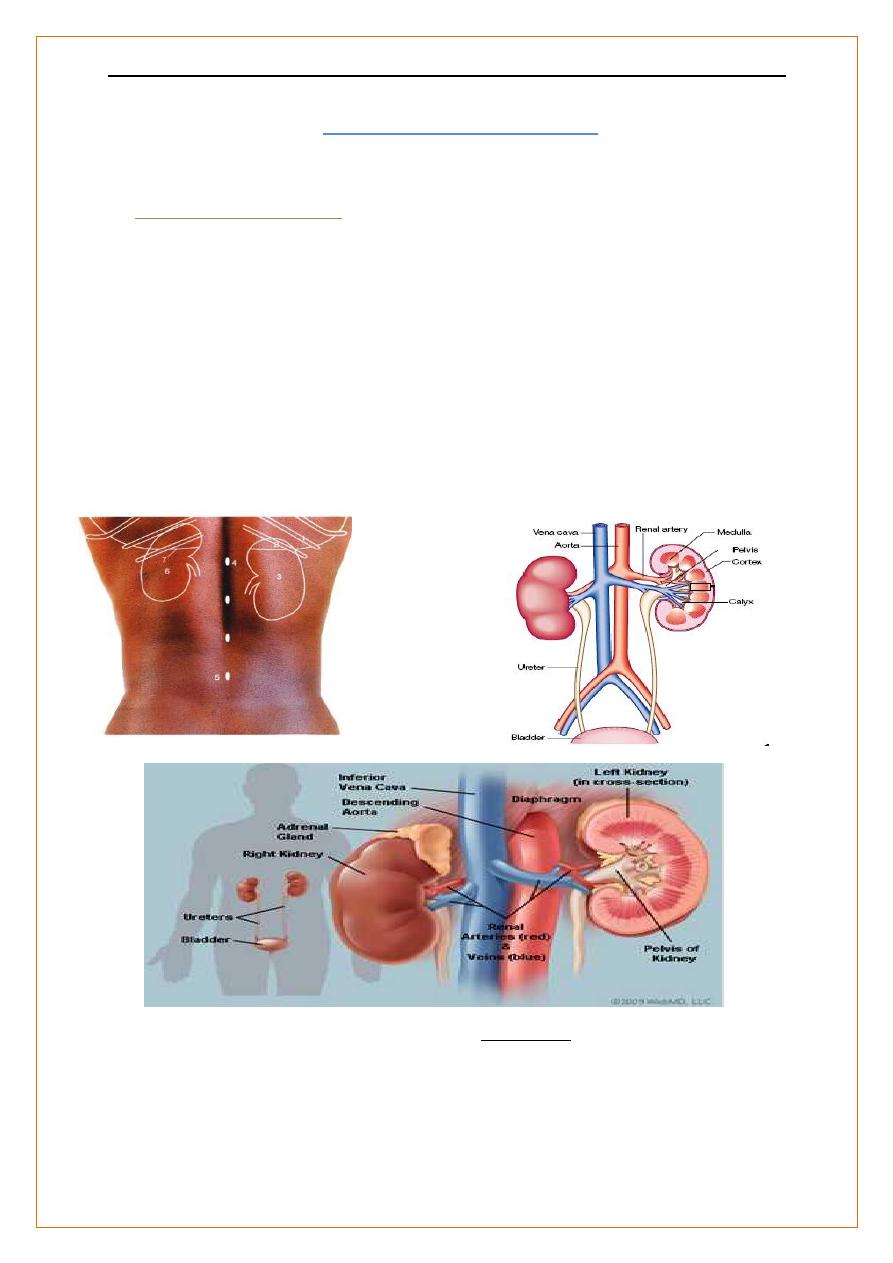
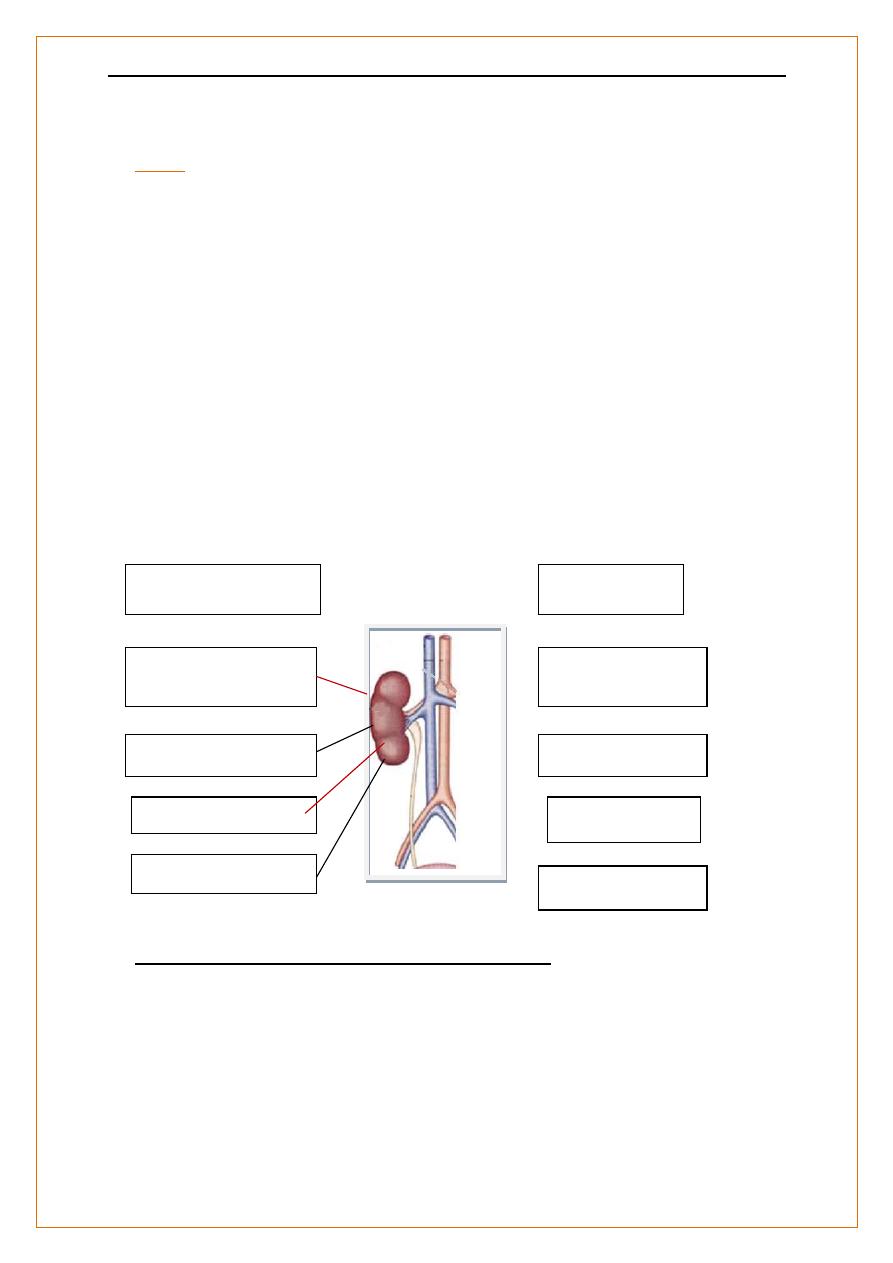
Anatomy of the kidneys
:-
Kidneys are two bean shaped organs ,retroperitoneal , on either side of the aorta and
inferior vena cava.
Two kidneys , about 2 million glomerular capillary tuft .
Each kidney is about 150 g ,
11–14 cm in length ( =3 lumbar vertebral bodies),
The Rt kidney is usually a few cm lower ( the liver lies above it).
Rise and descend several centimeters with respiration.
Each kidney contains 1 million functional units, ‘nephrons’.;-
The Glomerulus
(where filtration of plasma occurs),
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
4
The tubules
Proximal convoluted, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule (where selective re
absorption of fluid & solutes),
Collecting ducts
of multiple nephrons drain into the renal pelvis and ureters
150 L daily filtrate
99% is reabsorbed in the tubules.
After birth, new nephrons can not be developed ,a lost nephron can not be replaced
Renal blood flow
The blood supply ; 20–25% of cardiac output.
Aorta Renal artery interlobar arteries
interlobular arteries
afferent arterioles glomerulus efferent arterioles
In the cortex peritubular capillaries
In the juxtamedullary region vasa recta
Back to the heart through the interlobular intralobar renal veins
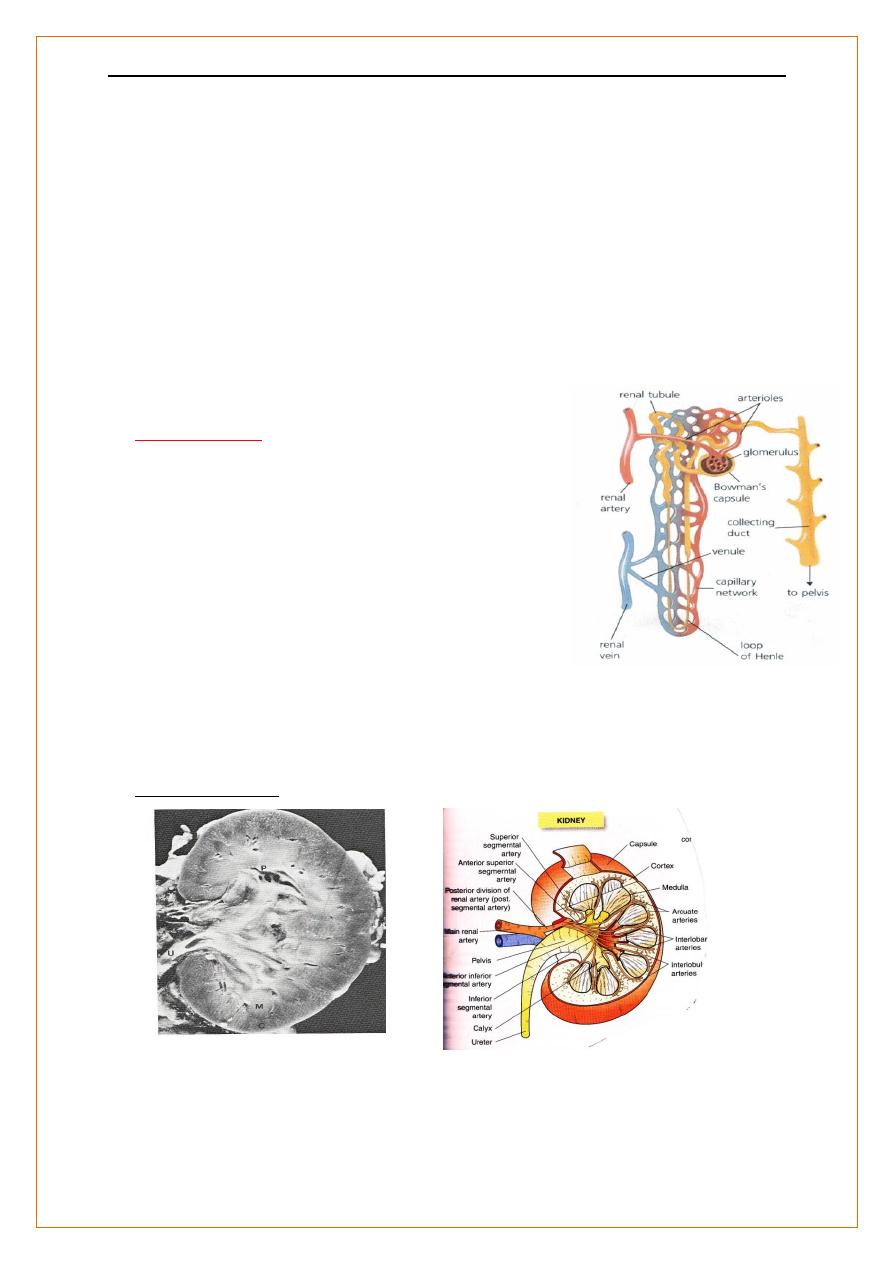
Kidney structure
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
5
Anatomy of the kidneys :-
Glomeruli
Glomerular basement membrane(GBM), produced by fusion of the BM of
epithelial and endothelial cells . Filtration occurs across GBM
-The glomerular capillary endothelial cells contain fenestrae (pores) which allow access
of circulating molecules to the underlying GBM.
- On the outer side of the GBM, glomerular epithelial cells (podocytes) put out multiple
long foot processes which interdigitate with those of adjacent epithelial cells
maintaining the filtration barrier,
Podocytes are involved in the regulation of filtration
Mesangial cells
,
lie in the central region of the glomerulus. have contractility function
with macrophage-like properties.
Electron micrograph of the filtration barrier. (GBM = glomerular basement membrane)

د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
6
Anatomy of the kidneys :-
Tubules and interstitium
Tubular cells are polarised, with a brush border (proximal tubular cells) and specialised
functions at both basal and apical surfaces. carry a specific complement of transporter,
channel and receptor molecules.
Fibroblast-like cells
in the cortex produce erythropoietin in response to hypoxia.
Collecting system and lower urinary tract
Allow free passage of urine to the bladder, and to store urine in the bladder for
controlled voiding (i.e. to maintain urinary continence).
Processes Occurring Along the Nephron
Site Absorption Secretion
PCT Na+, HCO3– Organic acids
glucose, amino acids,
phosphates, vitamins
Thick Ascending Na+, K+, Cl–
Limb of Loop of Henle
DCT Na+, Cl– H+, K+
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
7
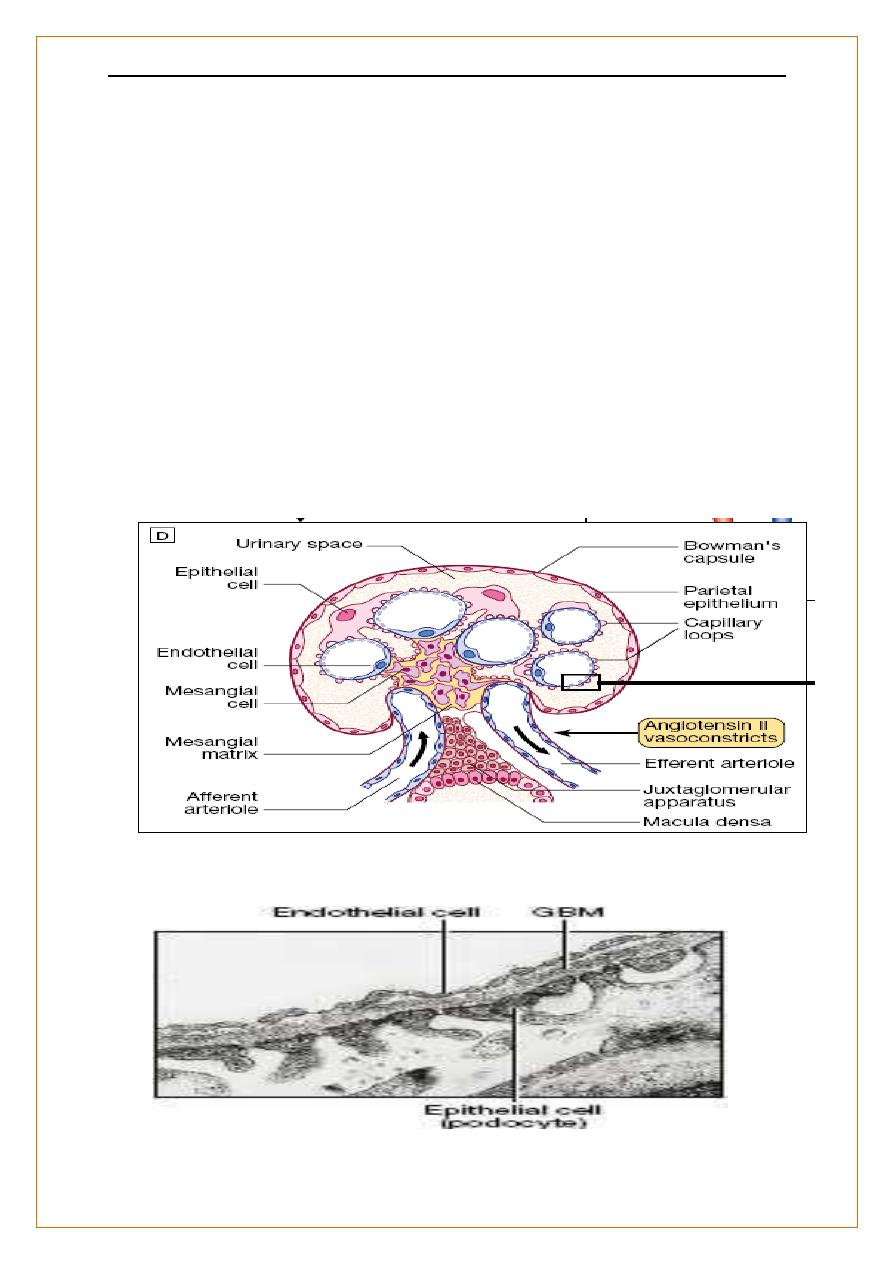
Anatomy of the kidneys
:-
Juxtaglomerular (J-G) apparatus
adjacent to glomerulus where afferent arteriole enters
consists of myoepithelial cells - modified granulated smooth muscle cells in the media
of the afferent
arteriole that contain renin
macula densa - specialized region of the distal tubule which controls renin release
↓GFR Renin
Angiotensin
Blood Pressure
JGA
Renin Angiotensin Axis

د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
8
Functions of the kidneys
:-
Regulating the volume and composition of body fluids
large volumes of an ultrafiltrate of plasma (120 mL/min, 170 L/day) glomerulus,
selectively reabsorbing components of this ultrafiltrate at points along the nephron.
controlled by many hormonal and haemodynamic signals.
Excretion of many metabolic breakdown products
;-
Ammonia, urea and creatinine from protein,
Uric acid from nucleic acids .
Drugs and toxins.
Not reabsorbed from the filtrate, or are actively secreted into it.
Functions of the kidneys
:-
ENDOCRINE FUNCTION
OF THE KIDNEY
Erythropoietin
hormone produced by kidneys (& liver) in response to hypoxia
stimulates erythrocyte production and maturation produced by fibroblast-like cells
(peritubular) in cortical interstitium
responds in 1.5 to 2 hours
in renal disease anemia results from decreased renal capacity for
Epo production and release, as well as decreased red blood cell life
span (toxic hemolysis
Vitamin D acivation
,
25-hydroxycholecalciferol to the active form, 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol vitamin D is
converted to the 25-hydroxy-vitamin D form in the liver. the kidney converts 25-hydroxy-
vitamin D to 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D
in renal disease this capacity becomes impaired and contributes to the tendency
towards hypocalcemia and subsequent secondary hyperparathyroidism (since 1,25-
dihydroxy-Vitamin D is necessary for intestinal calcium absorption)
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
9
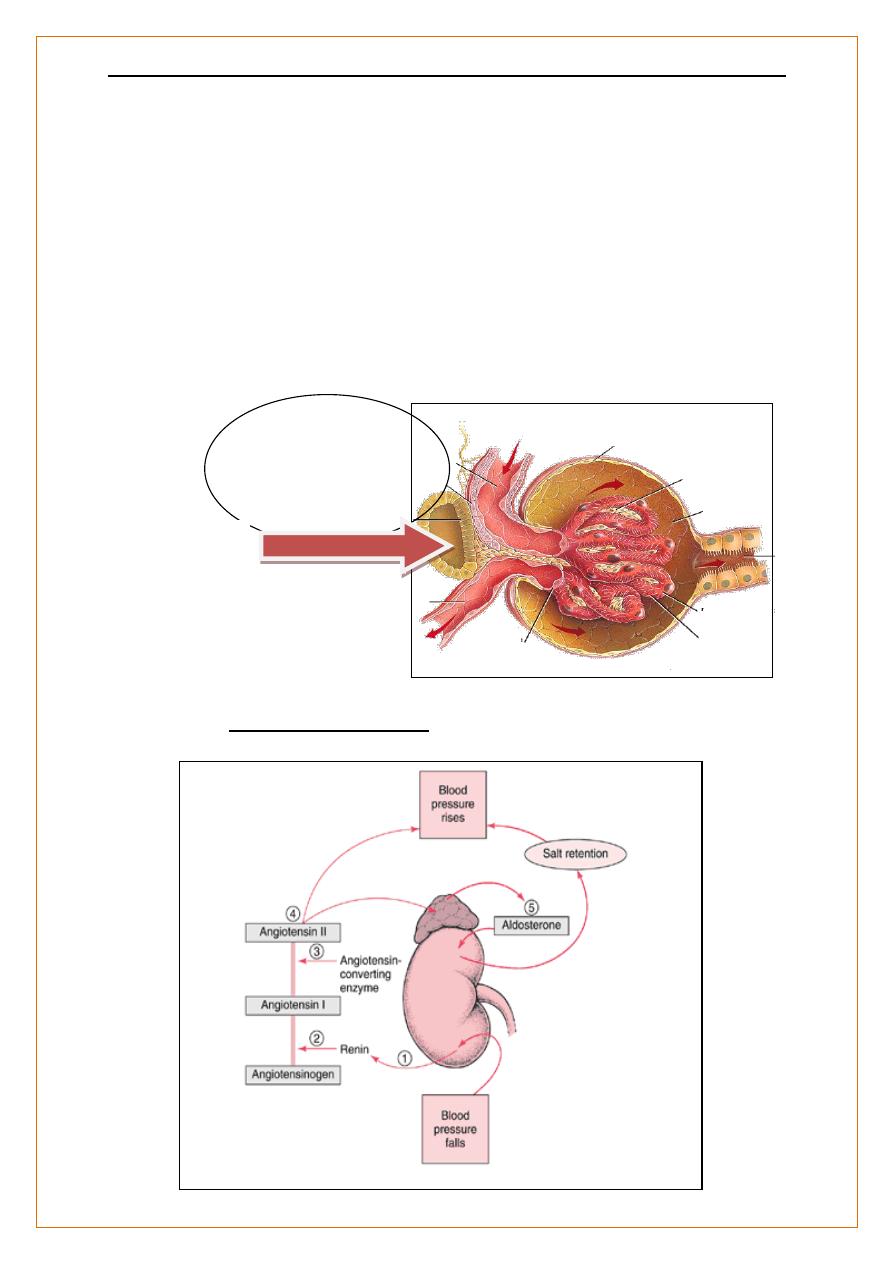
Functions of the kidneys;-
Renin
:-
secreted from the juxtaglomerular apparatus in response to;-
reduced afferent arteriolar pressure,
stimulation of sympathetic nerves
changes in Na
+
content of fluid in the DCT at macula densa.
Renin generates angiotensin II , which causes
aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex,
- constricts the efferent arteriole of the glomerulus and thereby increases glomerular
filtration pressure
induces systemic vasoconstriction.
Investigation of renal and urinary tract diseases
Serum levels of endogenous compounds excreted by the kidney
Blood urea
:-
it increases - with high protein intake + GIT haemorrhage
catabolic states,
Normal RF
Renal failure
Regulatory &Exretory
functions
Erythropietein
Vit D Activation
Renin
HrT ,fluid overload ,
,Acidosis, Uremia
Anemia
HrT
Hypo Ca++
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
11
it reduced - liver failure (low production from protein)
anorexia or malnutrition (low protein intake).
tubular reabsorption of urea is increased when concentrated urine is produced,
elevating blood levels..
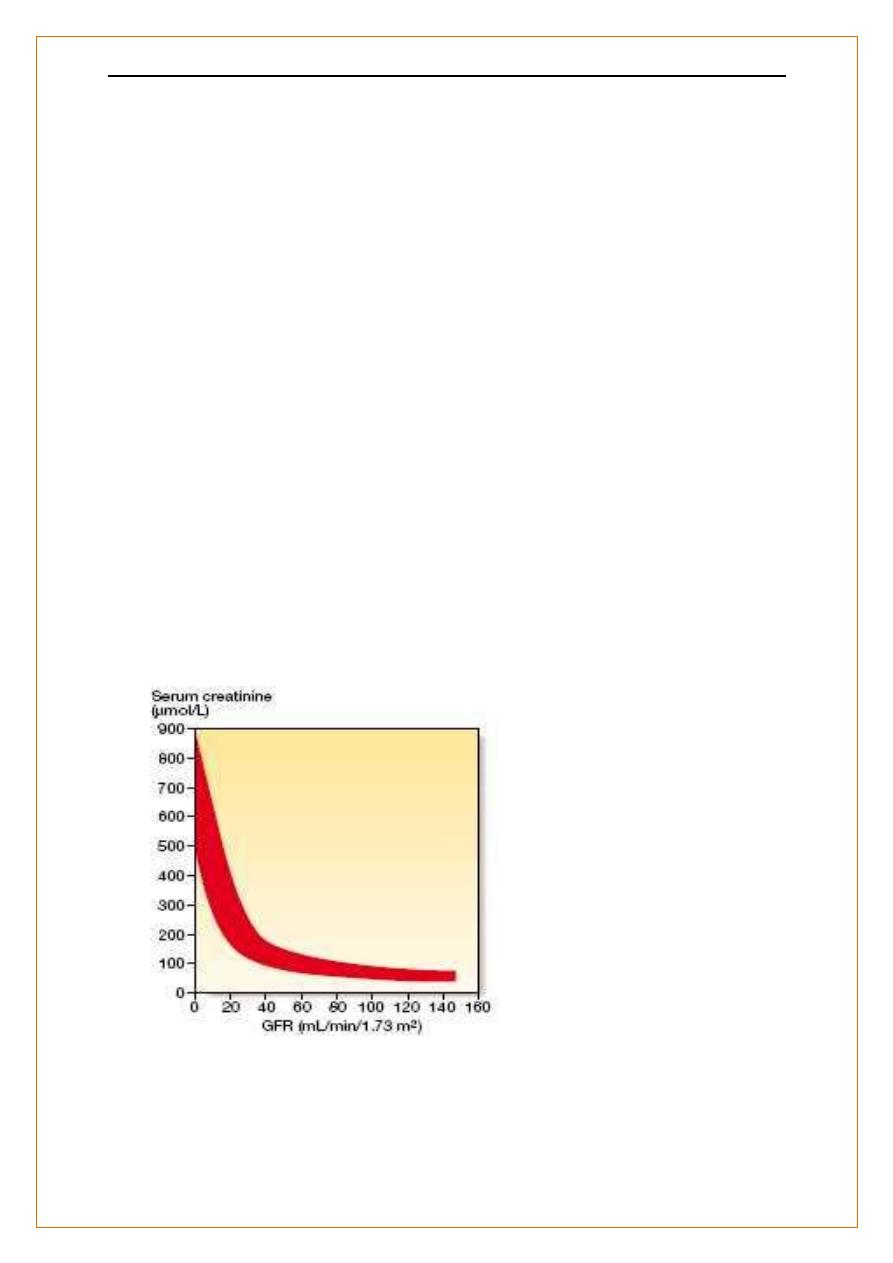
Serum creatinine
Reflects GFR more reliably than urea,
it is produced from muscle at a constant rate
almost completely filtered at the glomerulus.
While in patients with low muscle mass (e.g. the elderly) serum creatinine may not be
above normal until GFR is reduced by > 50%.
Serum creatinine and GFR
The inverse reciprocal relationship
a GFR as low as 30–40 mL/min without serum creatinine rising

د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
11
Investigtion of renal and urinary tract diseases
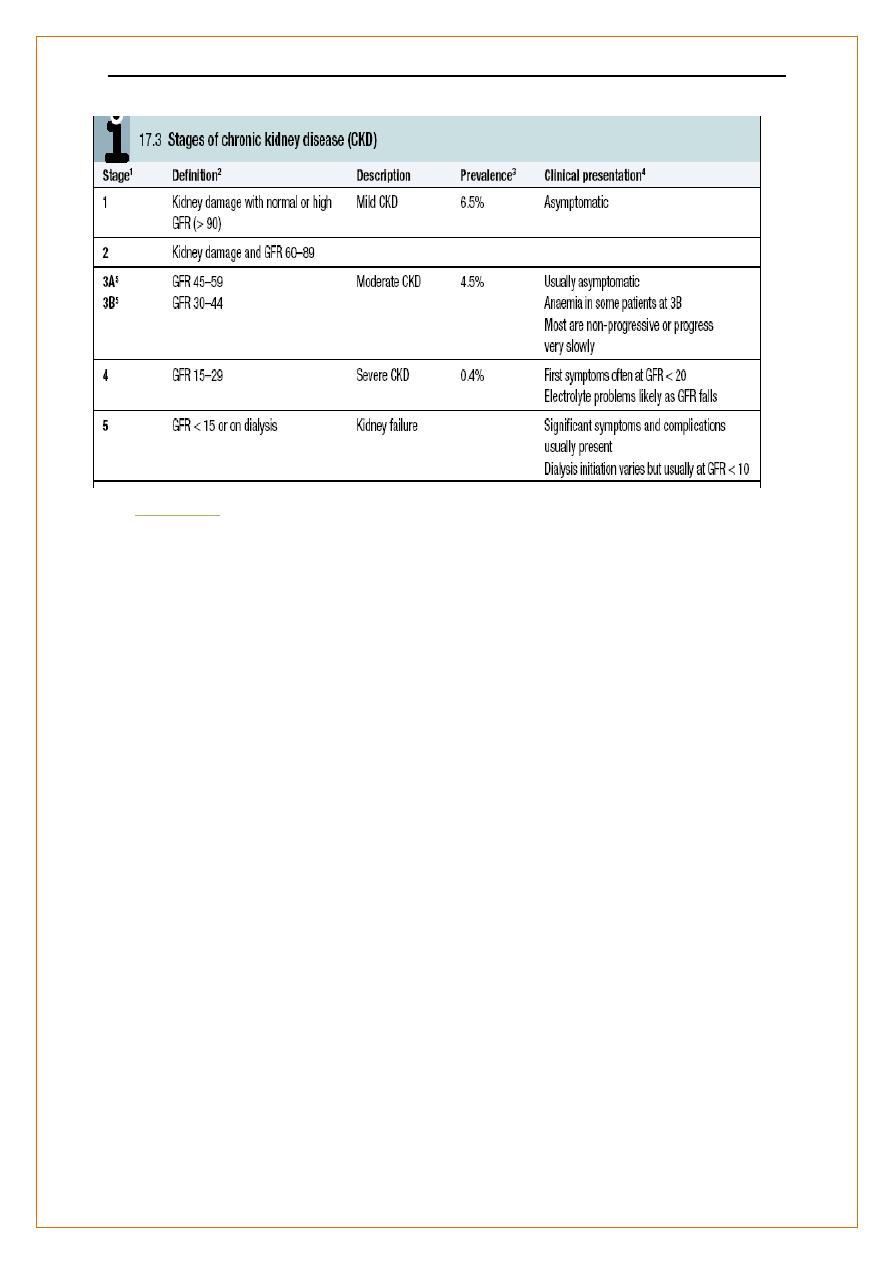
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
GFR is the rate at which fluid passes into nephrons after filtration
measures renal excretory function.
proportionate to body size ( 120 ± 25 mL/min/1.73 m2 )
Direct measurement of GFR
•
1. Direct measurement using labelled EDTA or Inulin
by injecting and measuring the clearance of compounds that are completely filtered and
not reabsorbed by the nephron (inulin, radiolabelled EDTA) is inconvenient and is
usually reserved for special circumstances (e.g. for potential live kidney donors).
2
. Creatinine clearance(CrCl)
A more accurate measurement of GFR
Serum level is related to 24-hour urinary creatinine excretion,
But 24-hour urine collections are difficult and often inaccurate.
Minor tubular secretion of creatinine causes exaggerate
- GFR affected by drugs (e.g. trimethoprim, cimetidine)
Needs 24-hr urine collection (inconvenient and often unreliable)
CrCl (mL/min) = UV / P / 1440 =
Urine creatinine concentration (μmol/L) × Volume (ml)
__________________________________________________
Plasma creatinine concentration (μmol/L) × time (min

د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
12
Estimating GFR with equations
Cockcroft and Gault (C&G) equation
;-
-accurate at normal to moderately impaired RF
-Estimates CrCl, not GFR ,Requires patient weight
CrCl (C&G) =
(140–age in yrs) × lean body wt (kg) × (1.22 males or 1.04 females)
_________________________________________________________ serum
creatinine (μmol/L)
CrCl (C&G) =
(140–age in yrs) × lean body wt (kg)
___________________________________ ( x 0.85 for females)
72 X serum creatinine (mg/dl)
Estimating GFR with equations
The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) study equation The MDRD equation
Performs better than C&G at reduced GFR
Requires knowledge of age and sex only
Can be reported automatically by laboratories
eGFR = 186* × (creatinine in μmol/L/88.4)− 1.154 × (age in yrs) −0.203× (0.742 if female)
× (1.21 if black)
د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
13
Urinalysis
detect abnormal constituents that indicate a pathological state.
General characteristics of urine
:
1. Volume: normally 1.5– 2 L / Day.
2. Color: urochrome (amber yellow).
3. Transparency: Clear transparent.
4. Odor: faint aromatic odor (volatile organic acid)
5. PH : slightly acidic 5.5 – 6.5.
Physiological and normal constituents of urine
:
Normally 99 % water and 1% solids. Solids are:
organic substances: urea, uric acid, creatine, creatinine,
amino acids, lactic acid , vitamins, pigments, enzymes……
inorganic substances: NH4, SO4, Ca+2, Cl-, PO4, Co3,
Na+, K+, Mg+2, NO3, Fe, F, silicate…………….

د
.
محمد حنون
Nephrology
lec1
14
Urinalysis
The following parameters are normally not present in urine:
Glucose: (glucosurea),
Protein: (proteinurea or albuminurea)
Blood: (hematurea or hemoglobinurea)
Bile salts: in patients with Jaundice.
Ketone bodies or Acetone: could appear in urine in late stages of diabetes mellitus
Urinalysis
Dipsticks
screen for blood and protein semi-quantitatively
Urine microscopy
;-red cells of glomerular origin and red cell casts, indicative of
intrinsic renal disease.
screen for white blood cells and bacteria.
Crystals
(e.g. of calcium oxalate, cysteine or urate)
seen in renal calculus disease, although calcium oxalate and urate crystals are also
sometimes found in normal urine that has been left to stand.
Urine pH
can provide diagnostic information of of RTA persistently
low specific gravity
may be found in diabetes insipidus).
Timed (usually 24-hour) urine collections
are now used less often to measure GFR or
protein excretion but are still required to measure excretion rates of sodium and of
solutes that can form renal calculi such as calcium, oxalate and urate .
Urinalysis
Fractional excretion of sodium
(= urinary Na/plasma Na × plasma creatinine/urine
creatinine) is reduced in volume depletion when the
tubules are avidly conserving sodium, and increased
in the tubular damage associated with acute tubular necrosis
