
Medicine
Dr. Akram
Neurology
“
Coma
”
Dr. Zuhair
LECTURE 13
Coma Dr. Zuhair
2
Coma
Objectives
• To roughly understand the anatomical basis of Consciousness
• To know the common causes of coma
• To know the basic management of patients with coma.
Definition
• Consciousness?
• A state of awareness of self and environment and responsiveness to
external stimulation and inner need. - Adams –
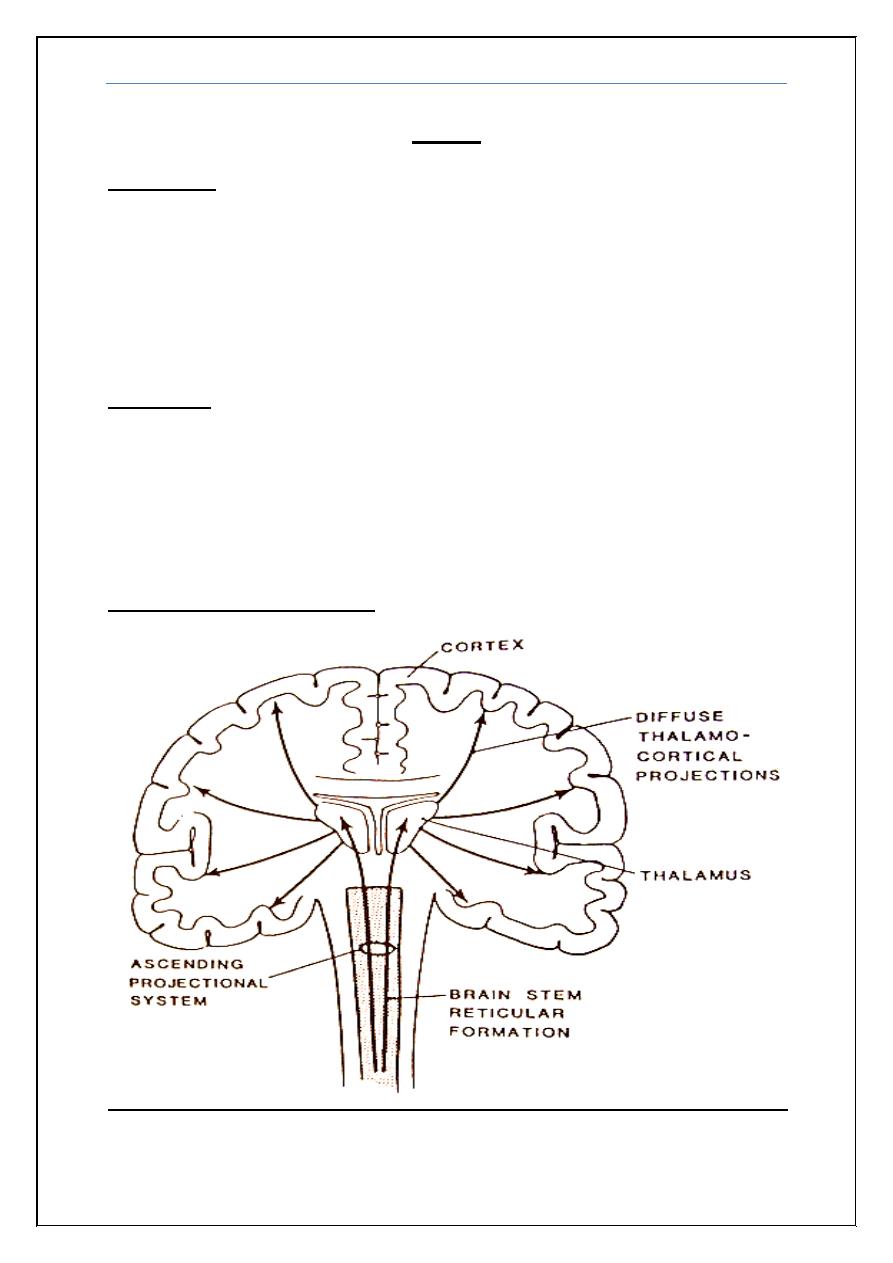
Anatomy of consciousness
Coma Dr. Zuhair
3
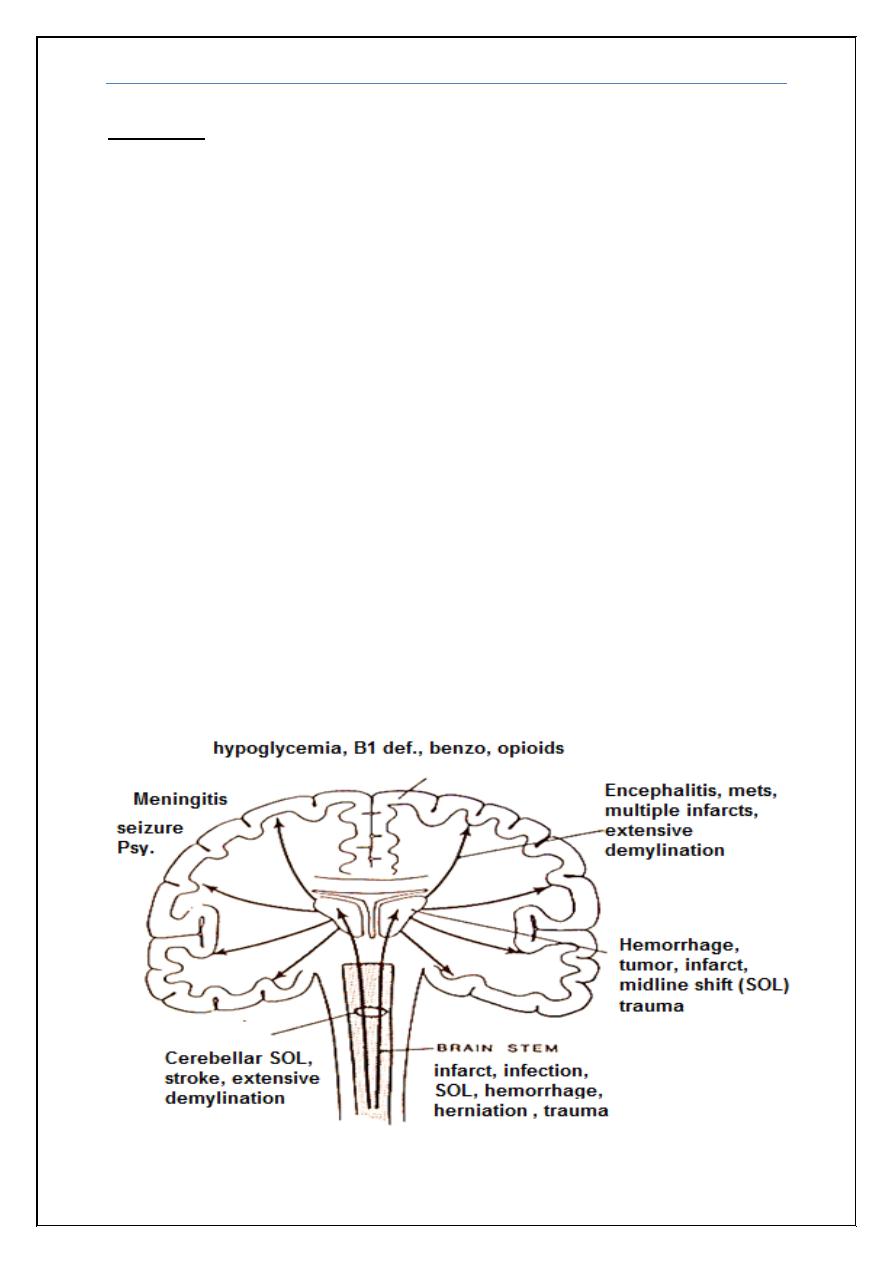
Aetiology
Metabolic
Extrinsic:
Alcohol
Substance abuse
Drugs
Heavy metals and poisons
Intrinsic:
Fluid (Shock) and electrolytes
Nutritional
Endocrine
Organ failure
Structural
Supratentorial
Traumatic
Vascular
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
Degenerative
Infratentorial
Traumatic
Vascular
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
Degenerative
Coma Dr. Zuhair
4
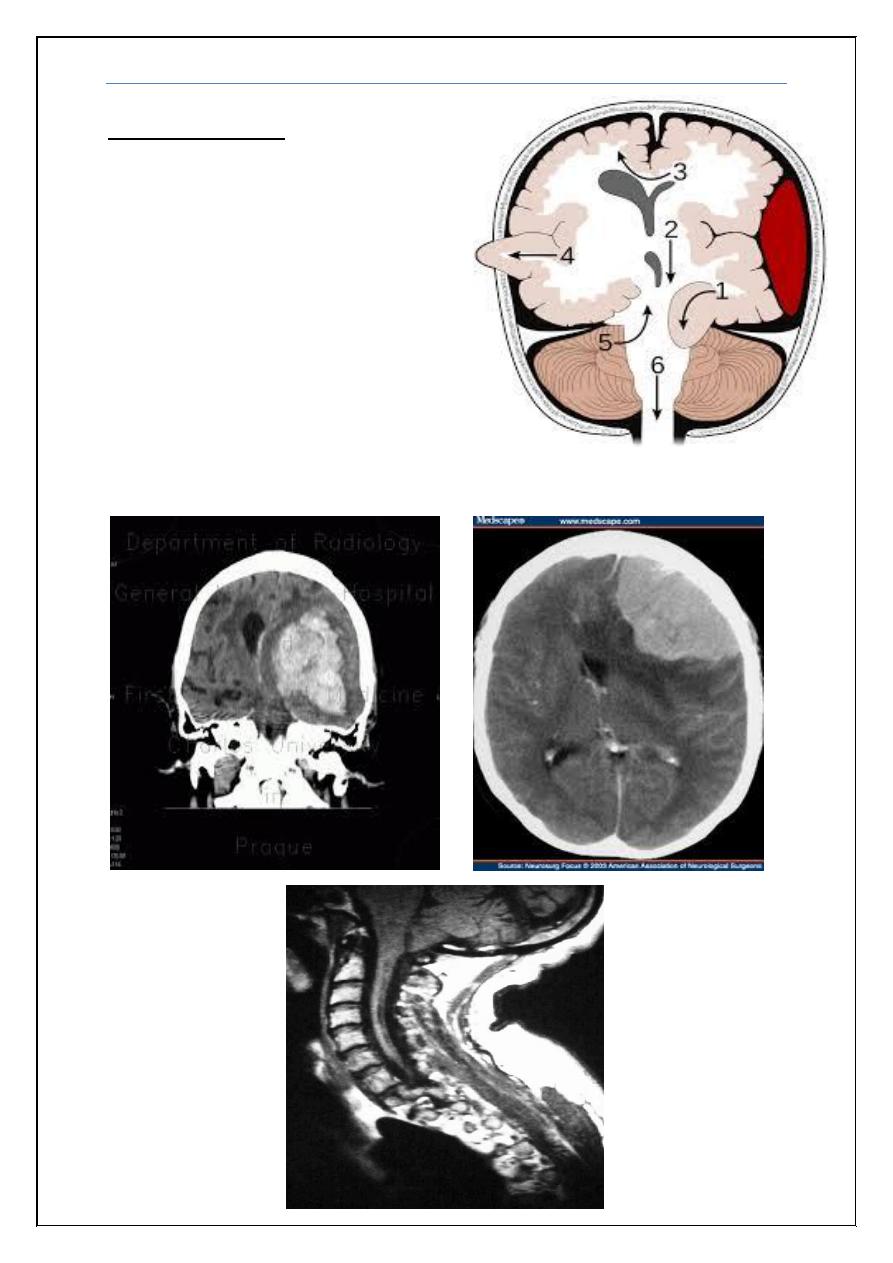
Brain Herniation
Supratentorial herniation
1. Uncal (transtentorial)
2. Central
3. Cingulate (subfalcine)
4. Transcalvarial
Infratentorial herniation
1. Upward (upward cerebellar or
upward transtentorial)
2. Tonsillar (downward cerebellar)

Coma Dr. Zuhair
5
Workup
How bad it is?
Is it Coma?
Is it metabolic or Structural?
Supra or Infratentorial?
ABC
History [Hypoglycemia, B1 def., Narcotic, Benzodiazipine]
immediate correction
Physical examination
Medical exam.
Neurological exam.
Neuroexam
Goals:
Functional assessment!
Is there structural brain damage?
Supra x Infra tentorial?
Differential diagnosis of Coma
Consciousness:
Responses to painful stimuli?
R/O:
locked in state,
Vegetative state,
Minimally conscious state
Glasgow-Coma scale
Ocular:
Hutchison's pupil -uncal herniation
Miotic sluggishly reacting to light – pontine
Midsized or Mydriatic fixed to light – Midbrain
Coma Dr. Zuhair
6
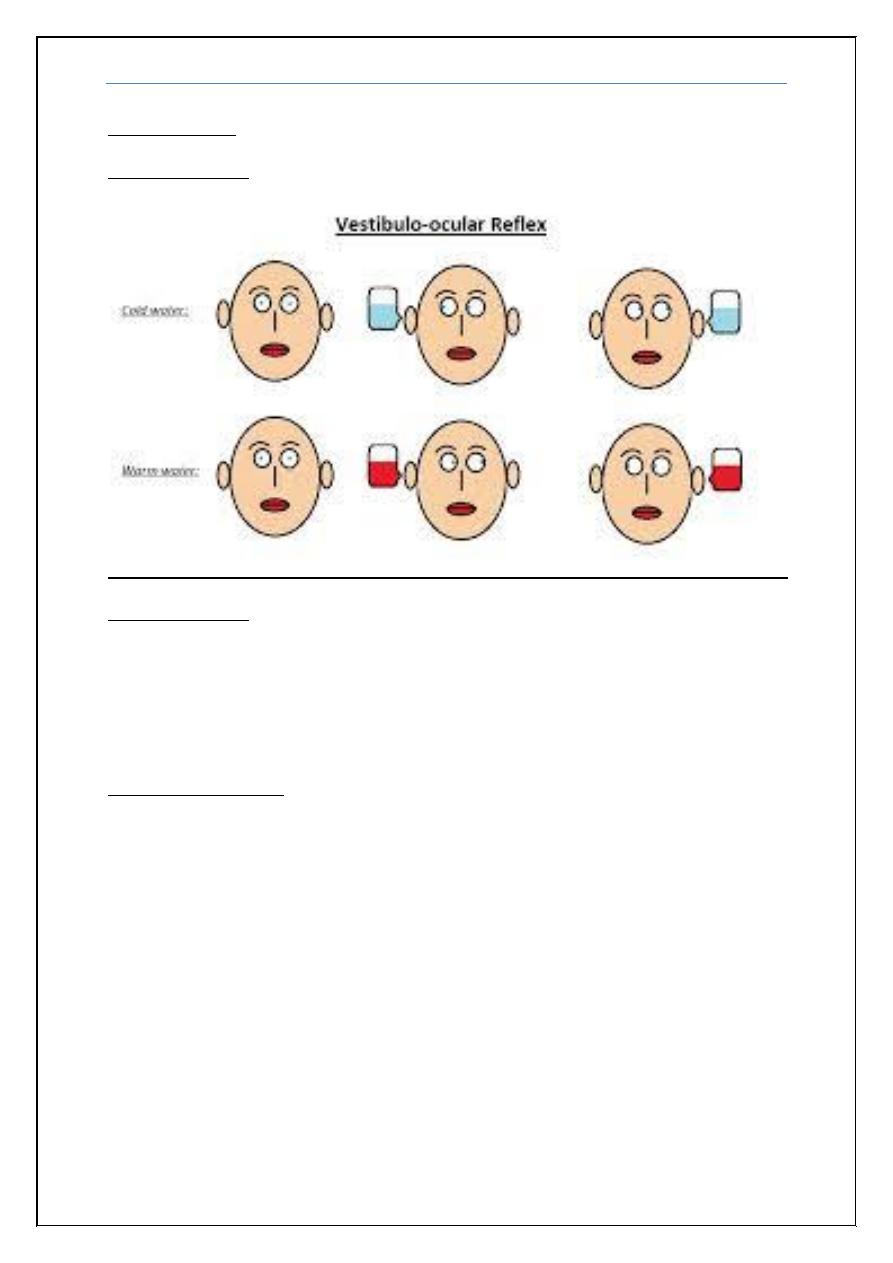
Oculo-cephalic
Vestibulo-ocular
Rest of Cranials:
Fundoscopy
V: blink
VII: cheeks and Eyes: Eyelid release test
Gag
Respiratory patterns:
Poorly localizing
Cheyne-Stokes : Supra-tentorial /metabolic
Central neurogenic hyperventilation: Midbrain/pons
Apneustic (short-cycle Cheyne-Stokes): pons/medulla
Ataxic (Biot): medulla
Intermittent: medulla
Coma Dr. Zuhair
7
Motor system
Signs of hemiplegia
Wrist-dropping test
Arm-dropping test
Legs-dropping test
Driven postures: Decorticate, Decerebrate.
Meningeal Irritation Signs
Neck stiffness
Kernig’s sign
Brudzniski
Further assessment
Investigations
Blood
Bed side
Imaging
Toxicology
Management
Specific: Treat the cause
Non specific: ABC, Feeding, Positioning, physiotherapy, monitoring,
nursing care, etc…
