Principles of Health Administration
Sound administration is essential for the success of any public health program whether on the national, intermediate or the local levelDefinition of Sound Administration
We can define sound administration as:“ The process of achieving defined goals at a defined time through the guidance, leadership, and control of the efforts of a group of individuals and the efficient utilization of non-human resources bearing in mind adequacy, speed, and economy to the utmost possible level.”
Another definition:
“Administration is the art and science of guidance, leadership, and control of the efforts of a group of individuals towards some common goal.”Management
Management is the operational part of administration.It is defined as:
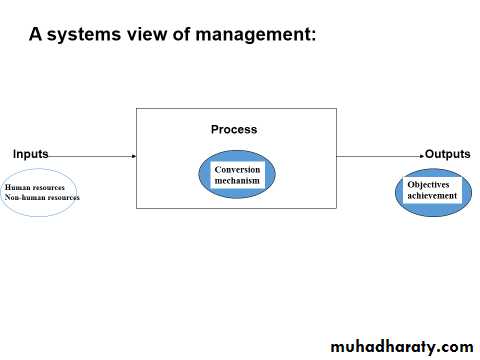
“ It is a set of interactive processes through which the utilization of resources results in the accomplishment of organization objectives.”
It is a “conversion mechanism”.
It is through “management” that the objectives of the health care organization are achieved by gathering and positioning of resources.
There are several elements for administration. In practice all these elements are interrelated to one another.
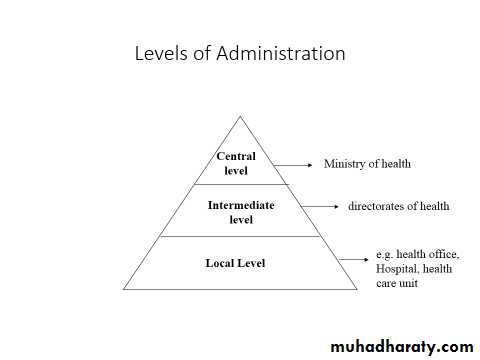
There are also 3 levels of administration.
Elements of Administration:
PlanningOrganization
Staffing
Directing
Coordinating
Reporting
Budgeting
Supervising
Evaluation
Every program must have an overall (general) goal which confirms with that of the nation’s policy, and various objectives to be achieved according to a definite plan.
Goals versus Objectives
A GOAL: it is a long range of specified states of
accomplishment towards which planning programs are directed.
Goals are not constrained by time or existing resources.
AN OBJECTIVE: is a measurable state of accomplishment aimed towards the goal. The objective should include a description of “what” outcome is desired, “when” it is expected, and “where” it will take place.
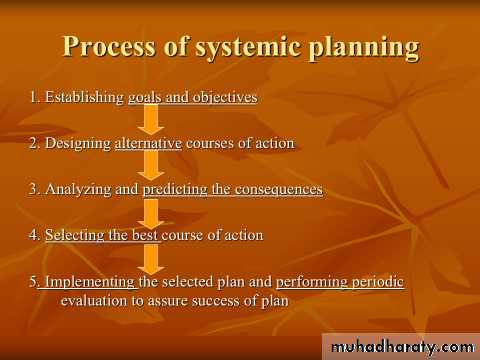
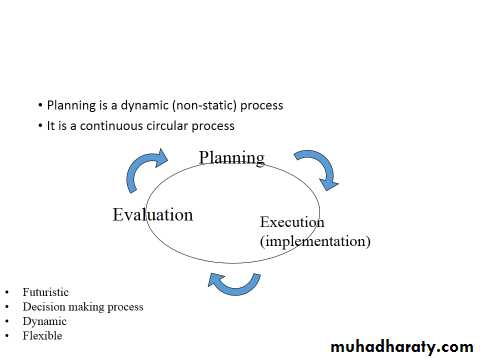
Planning is considered the most important element of the administrative process.
The higher the level of administration, the more the involvement and time devoting to planning. A good plan is the basis of any successful program. Sufficient time should be given to the process of planning.
More than one plan should be available to choose from to meet the existing obstacles.
Definition of Planning
“Planning is a projected or predetermined course of action designed to achieve a specific goal or objective.”Planning determines What? When? Where? How? Why? And by whom? Things will be done.
It involves “decision making for future events”.
Principles of planning
Being an intellectual activity it needs knowledge, experience, foresight, reasoning and the mastering of special skills and techniques.Examples of different techniques of planning are:
-PPBS: Planning/Programming/Budgeting system
-PERT: Performance/Evaluation/Review technique
-CPM: Critical Path Method
Participative planning is sharing the program planning with other people, staff and agencies concerned with the program.
Participative planning have advantages and disadvantages.
Planning of a program is based on:
Needs and demands of the publicAvailable resources
Attitude of the public
Establishing priorities are essential in planning
(What are these priorities???)
Constraints (intervening factors) to a plan may be social, economical or political, and they may be related to either:
External environment (community)
Internal environment (the organization)
Organization
Definitions:
“ Organization is any collection of persons, materials, procedures, ideas or facts arranged and ordered that the combination of parts makes a meaningful whole that works towards achieving organizational objectives.”
“The process of organization implies to the arrangement of human and non-human resources in an orderly fashion to make a meaningful whole that accomplishes organizational objectives.”
The organizational process is classified into:
Structural organization
Functional organization
Principles of organization:
Departmentation
Acquisition of human and non-human resources
Specialization and division of labor
Coordination
Authority and responsibility
Centralization and de-centralization
Unity of command
Line and staff
Staffing:
It is the process of “personnelizing” the organization, by hiring the right type and adequate number of workers to each unit for the time required for the program, through the following steps:Identifying the type and number of personnel
Recruitment
Selection and appointment
Orientation
Job analysis
Job description
Job specification
Budgeting:
Financial administration consists of a series activities were funds are made available for certain people in the organization under procedures that will ensure their efficient use.
The main activities are:
Budgeting
Accounting
Auditing
Purchasing
Definitions:
Budgeting:
It is the allocation of financial resources in support for programs or projects for a special period of time. A budget is defined as “a balanced estimate of expenditures and receipts for a given period of time”.
Accounting:
“It is recording assembly and summarization of financial effects of executive action. a harmonious relationship between budget and account is important to current comparisons, between goals set in and accomplished.”
Auditing:
“It is the investigation and report on the fidelity and legality of all financial transactions”.Purchasing:
“It is the acquisition of the property and materials needed in administration”.Supervision
Supervision refers to the day-to-day relationship between an executive and his immediate subordinates.Supervision aims at satisfying both:
Work
Workers
Motivation is defined as: “an externally induced behavior which occurs in order to bring about or maintain fulfillment”.
The following conditions if present build high levels of motivation:
AchievementRecognition
Advancement
Working conditions
Responsibility
Organizational policy
Technical supervision
Interpersonal relations
Salary and compansations
Job security
Styles of leader authority:
Autocratic
Consultative
Participative
Democratic
Free rein
Factors affecting style of supervision:
Type of workSubordinates characteristics
Personal characteristic of manager
Condition present
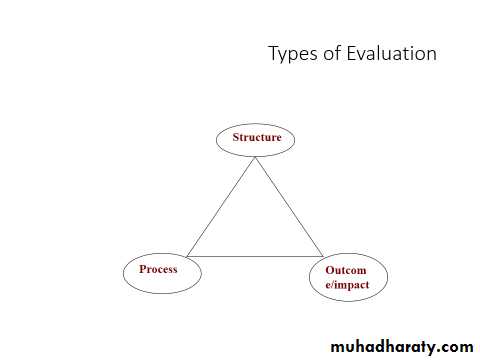
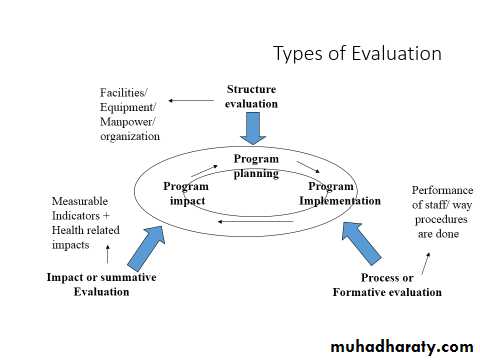
Evaluation
Definition:“systemic collection of information about the activities, characteristics and outcomes of programs, personnel, and products for use by specific people to reduce uncertainties, improve effectiveness and make decision with regard to what those programs, personnel or products are doing and affecting.”
Elements of Evaluation
RelevanceAdequacy
Accessibility
Acceptability
Effectiveness
Efficiency
Impact
Steps of Evaluation
(1) Describe the program in terms of objectives expected. Objectives can be either outcome or process objectives.Outcome objectives: “a statement of the amount of change expected for a given health problem for a specified population within a given time frame
Process objectives: “a statement of the amount of change expected in the performance and utilization of interventions that impact on the outcome.”
(2) specify the evaluation design.
Define the purpose of evaluation
Define the methodology of evaluation (census/ client records/ interviews/ surveys/ expenditures reports).
Define who will be making use of the data
(audience/ policy makers).
(3) gather credible evidence (information):
Types of data include:
Demographic description
Indicators of health status (morbidity, mortality, disability)
Qualitative indicators ( community values, public and private policies)
Utilization indicators
Expenditures
(4) Analysis and justification of results
What does the findings mean?
How do they compare to the objectives?
What is the degree of success of the program?
What recommendations are indicated for program improvement?
(5) Taking action
Evaluation findings has to be used and shared for the purpose of improvement of the effectiveness of the program. “evaluations that are not or inadequately used are simply not worth of doing”.(6) Re-evaluation
Evaluation is an ongoing process.