4th stage
surgeryLec-
د.محمد فوزي
21/2/2016
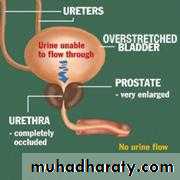
Retention of UrineAcute or Chronic
Acute Retention
Causes of Acute Retention: most frequent are
Male: Female1-BOO 1-Retroverted gravid uterus
2-Urethral stricture 2-Multiple Sclerosis
3-postoperative
4-Acute urethritis or prostatitis
5-phimosis
Both
1-Blood clot in the bladder 6-smooth muscle dysfunction with aging
2-Urethral calculus 7-faecal impaction
3-Rupture of urethra 8-Anal pain (hemorrhoidectomy )
4-Neurogenic (SCI) 9- Some drugs
5-fecal impaction 10-Spinal anesthesia
Clinical Features of Acute Retention of urine
No urine is passed for several hoursThe bladder may be visible & is tender to palpation & dull to percussion.
Rarely cauda equina lesion due to prolapsed lumber disc is a cause ( check reflexes in lower limbs & perineal sensation).
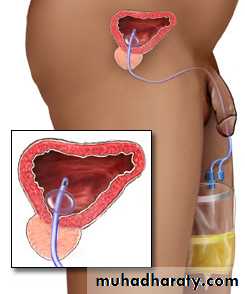
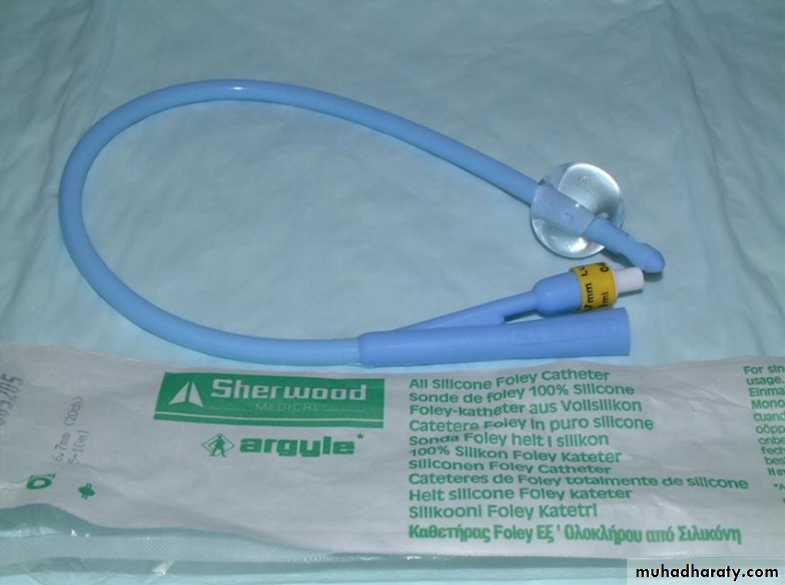
Treatment
In most patients the correct treatment is to pass a fine urethral catheter & to arrange further urological management
Occasionally post-op. Retention treated conservatively.
Chronic Retention of Urine
Chronic Vs. Acute1-Painful.
2-No risk of upper tract dilation.
3-No increase in serum creatinin
1-Painful.2-No risk of upper tract dilation.
3-No increase in serum creatinin1-The distention of the bladder is almost painless
2-Risk of upper. Tract dilation becauseof high intravesical tension due to large Residual urine.
3-Those with serum creatinin level >200 mic.mol/l are at risk of developing a post obstructive diuresis & haematuria following catheterisation so careful monitoring + replacement of inappropriate urine loss+slow decompress
1-The distention of the bladder is almost painless
2-Risk of upper. Tract dilation becauseof high intravesical tension due to large Residual urine.
3-Those with serum creatinin level >200 mic.mol/l are at risk of developing a post obstructive diuresis & haematuria following catheterisation so careful monitoring + replacement of inappropriate urine loss+slow decompress
Retention with overflow
The patient has no control of his or her urinesmall amount of urine passing involunterily from time to time from a distended bladder
it may follow neglected acute or chronic retention
treatment principle similar to acute retention
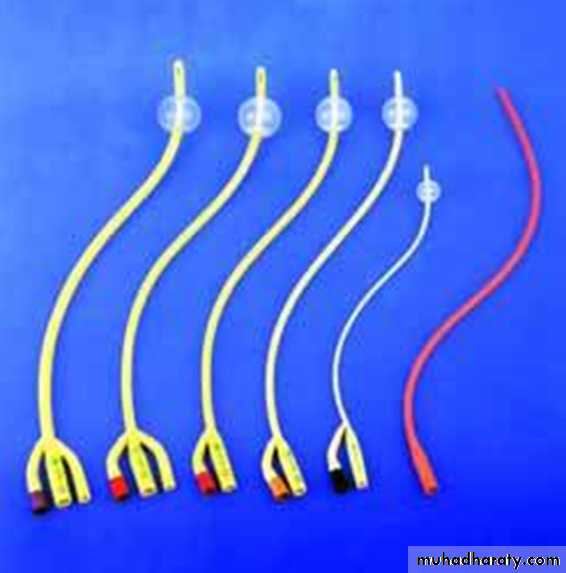
Catheters
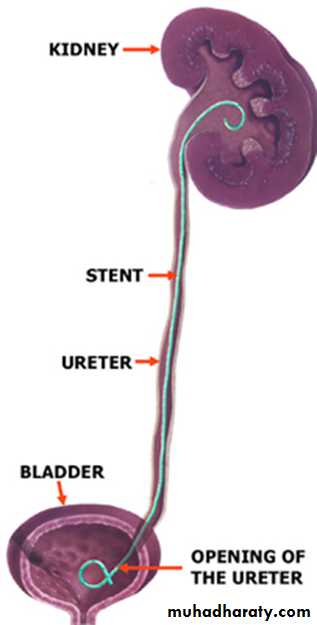
Ureteric stent JJ
IndicationTo bypass ureteric obstruction
After ureteric surgery
End to end anastomosis
pyeloplasty for PUJ obstruction
reimplantation of ureter
3 .After uteteroscopic manipulation
4. With ESWL in a single kidney
BLADDER INFECTIONS
Uncomplicated Cystitis.
Clinical Presentation: dysuria, frequency or urgency, and suprapubic pain .Hematuria or foul-smelling urine may develop.
Because acute cystitis, by definition, is a superficial infection of bladder mucosa, fever, chills, and other signs of dissemination are not present.
Diagnosis:
a urinalysis that is positive for pyuria, bacteriuria, or hematuria, or a combination should provide sufficient documentation of UTI and a urine culture may be omitted .A urine culture should be obtained for patients i
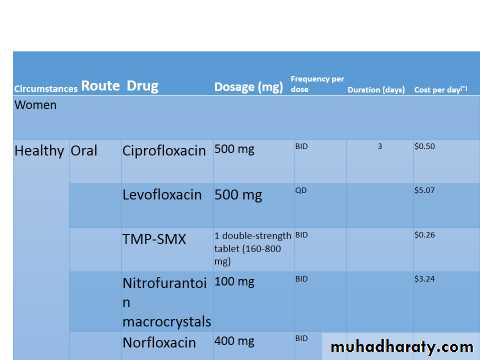
Treatment:
Interstitial cystitis (IC)
Interstitial cystitis (IC) or painful bladder syndrome (PBS), defined as “the complaint of suprapubic pain related to bladder filling, accompanied by other symptoms such as increased daytime and night-time frequency, in the absence of proven urinary infection or other obvious pathology”Female to male ratio = 5:1
Median age at onset is 40 years .
PBS/IC can be considered one of the chronic visceral pain syndromes, affecting the urogenital and rectal area, These include vulvodynia, orchialgia, penile pain, perineal pain, and rectal pain.
IC is a diagnosis of exclusion , laboratory tests include urine dipstick ,urine culture in all patients.
urine cytology done in risk group only
Urodynamic study .
Kcl PARSON TEST.
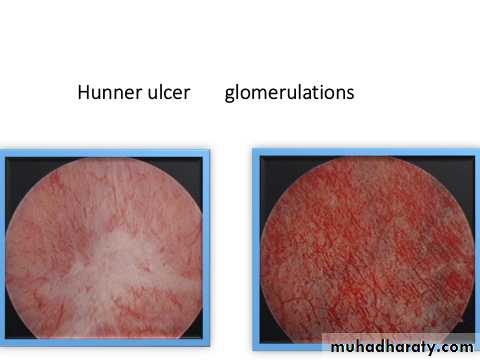
Cystoscopy under general or spinal anesthesia.