Fifth stage
pediatricLec-1
د.اثل
3/3/2016
Normal DevelopmentDevelopment :
Is an increase in function of processes related to body and mind. The individual level of functioning is determined by both genetics and environmental factors.
There are 4 areas for developmental assessment:
Gross motor.
Fine motor and vision
Speech, language & hearing
Social, emotional, behavior
Speech: production of intelligible sounds.
Language: underlying mental action of speech.
NEWBORN PERIOD
Primitive neonatal reflexes are unique in the newborn period, a consequence of the continued development of the CNS after birth.
Any asymmetry, increase, or decrease in tone elicited by passive movement may indicate a significant CNS abnormality and requires further evaluation.
Similarly a delay in the expected disappearance of the reflexes may warrant an evaluation of the CNS.
The most important reflexes to assess during the newborn period are as follows:
The Moro reflex is elicited by allowing the infant's head gently to move back suddenly (from a few inches off the crib mattress). This results in abduction and upward movement of the arms followed by adduction and flexion. The Moro reflex disappears by 4 to 6 months.
The rooting reflex is elicited by touching the corner of the infant's mouth, resulting in the lowering of the lower lip on the same side with tongue movement toward the stimulus. The face may turn to the stimulus. The rooting reflex disappears at 4 to 6 months.
The sucking reflex occurs with almost any object placed in the newborn's mouth. The infant responds with vigorous sucking. The sucking reflex is replaced later by voluntary sucking only.
The glabelar reflex occur when pressing the forehead of a baby with a finger elicits the closing of the eyes.
The palmar grasp reflex occurs when placing an object, such as a finger, onto the infant's palm. The infant responds by flexing fingers. The palmar grasp usually disappears by 3 to 4 months.
The plantar grasp reflex: when you rub your finger against the sole of your baby’s foot, the response is that his little toes begin to curl around your finger. The plantar grasp usually disappears by 6 to 8 months.
The asymmetric tonic neck reflex is elicited by placing the infant supine and turning the head to the side. This placement results in ipsilateral extension of the arm and the leg into a "fencing" position. The contralateral side flexes as well. This reflex disappears by 2 to 3 months of age.
Trunk incurvation reflex: stroke back along one side of the vertebral column will cause the infant to move hips toward the stimulated side.
Placing: the infant withdraws his foot when it touches a flat surface.
Stepping: hold him up and let his feet touch the ground, observe that he displays stepping movements alternately.
Emerging Patterns of Behavior During the 1st Year of Life:
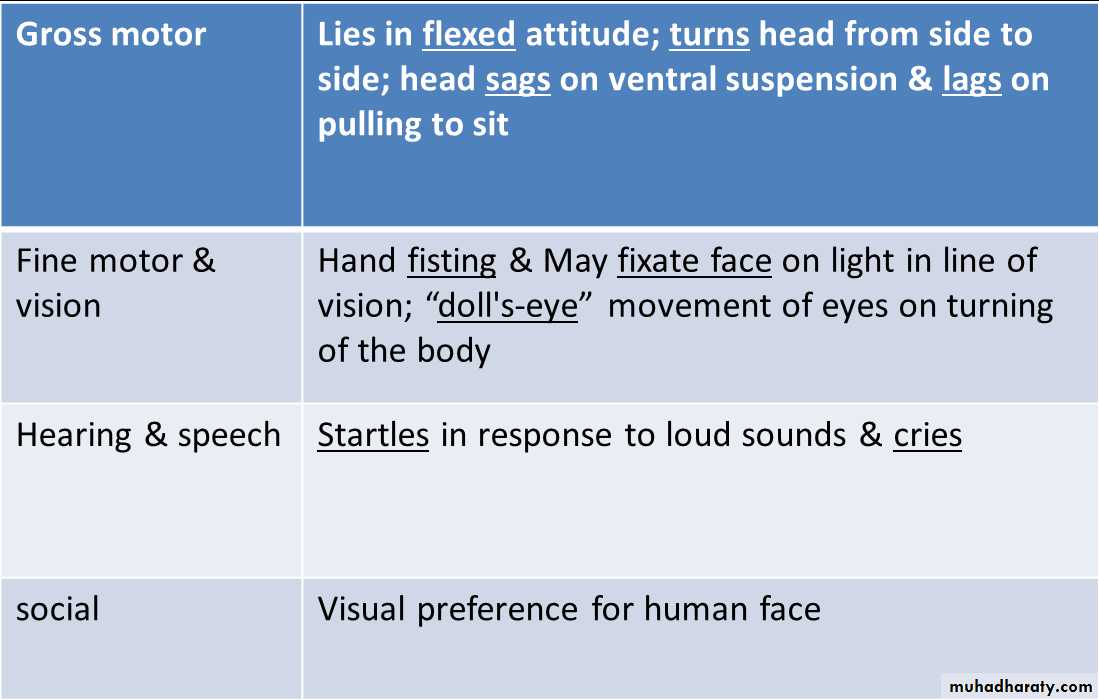
Neonate (1st 4 wk)
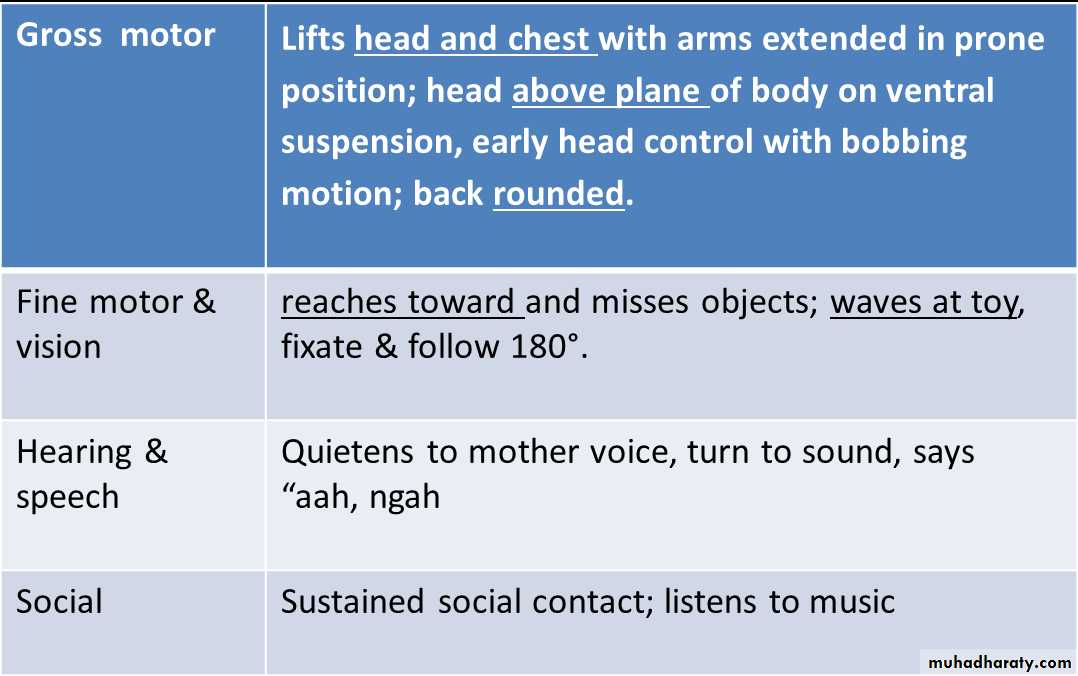
At 1-2 month
At 3 month
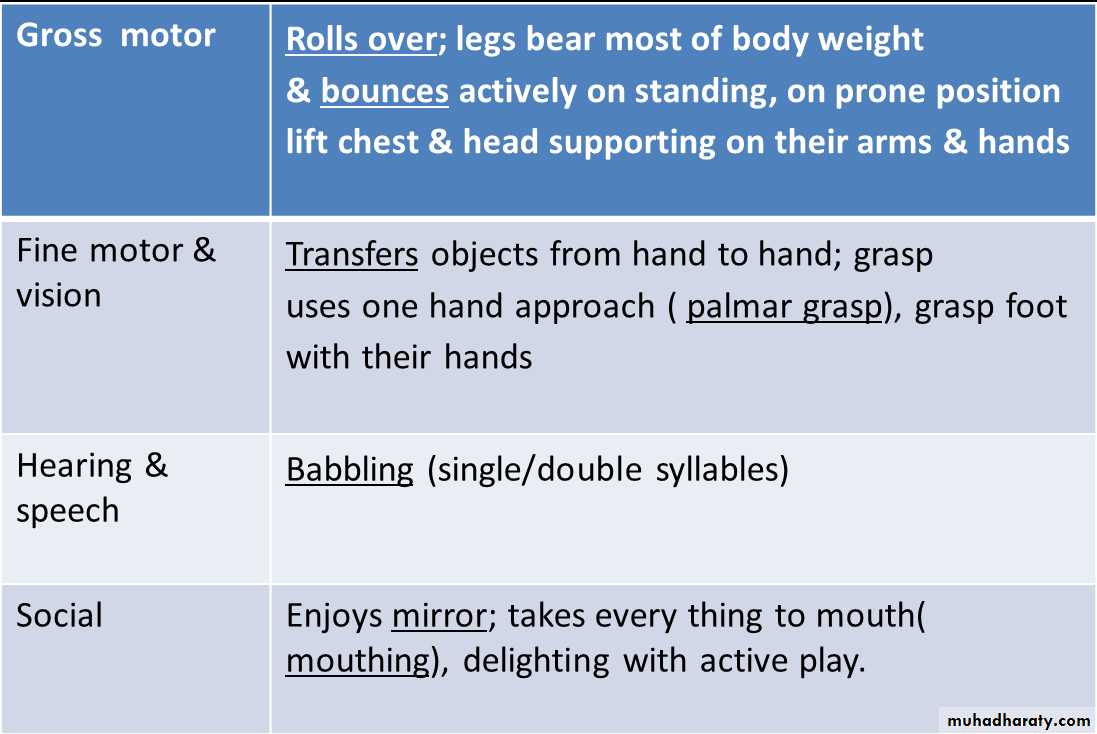
At 4 month
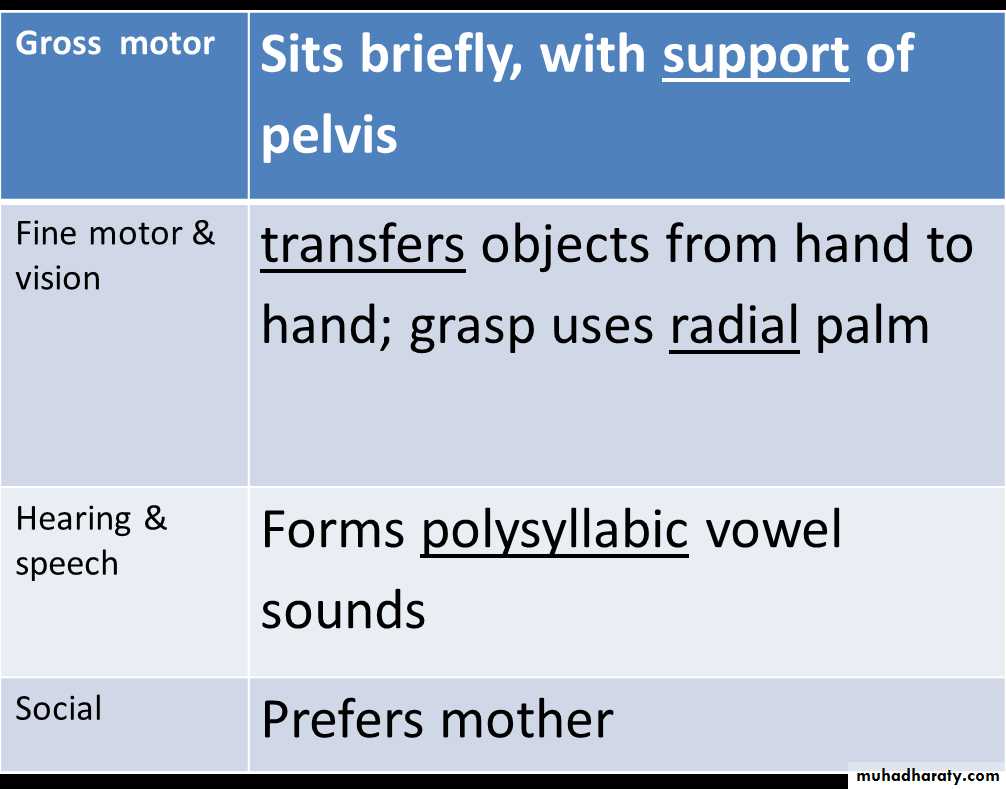
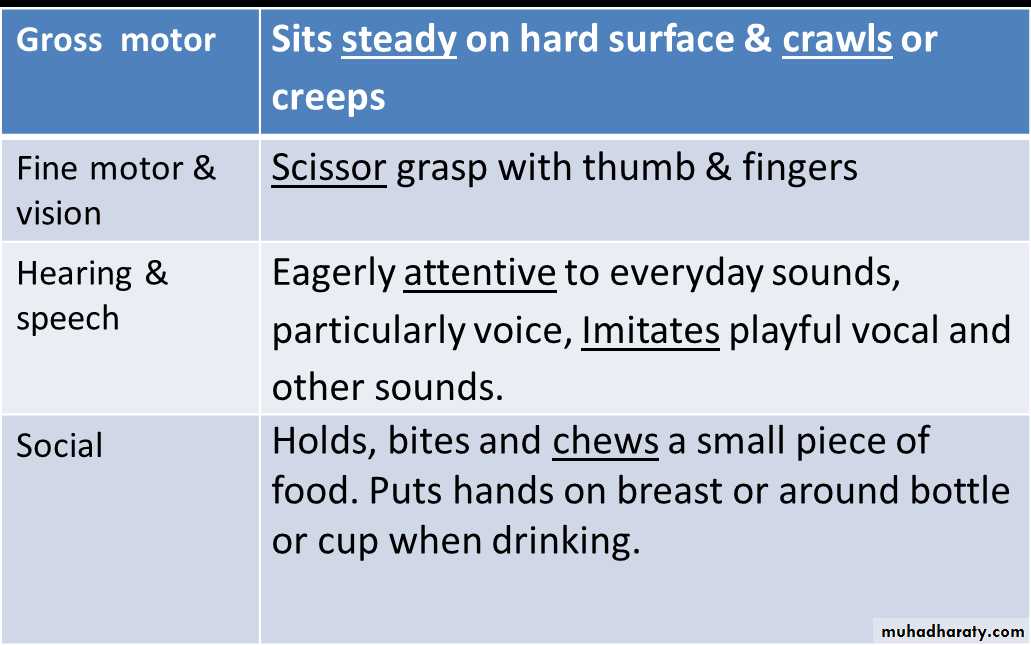
At 6 month
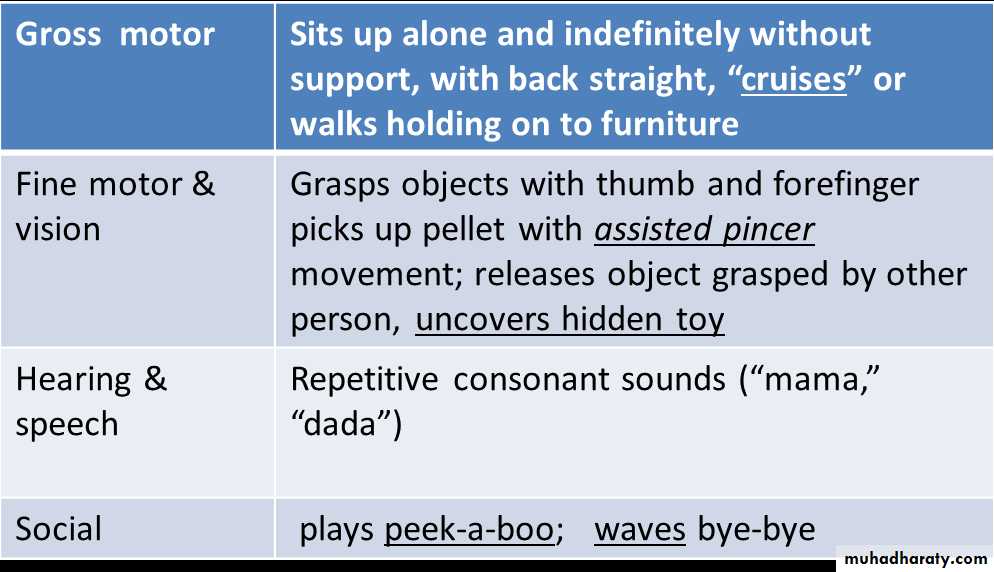
At 7 month
At 8 month