Psoriasis
• Meaning• Greek psora to itch
• Arabic
30% nail psoriaisis
5% psoriatic arthritis
Objectives
• Discuss definition and epidemiology of psoriasis• Explain causes and aggravating factors of psoriasis
• Describe clinical signs of psoriasis
• List topical and systemic treatment options including side effects
Psoriasis
• Psoriasis is a genetic, immunologically-mediated systemic disease primarily affecting skin and joints• It is a chronic, incurable, debilitating disease that profoundly affects the quality of life of patients and their families.
How common is Psoriasis?
• 2% of population
• Racial variation
• Affects men and women equally
• Two age groups of onset
• Late teens to early 20s,
Aetiology
• Genetic,environmental and immunological• Family history (30%)
• 70% concordance MZ twins
• 20 % DZ twins
• HLA - CW6
Aetiology 2- Environmental factors
• triggering factors :external factors may provoke psoriatic lesion• a-Physical trauma (Koebner s phenomenon1872)
• b-infections strep tonsillitis
• viral HIV
• c-climate and sun lights
• d- stress
• e – drugs
• antimalarial B-bloker lithium
• withdrawal of systemic steroid
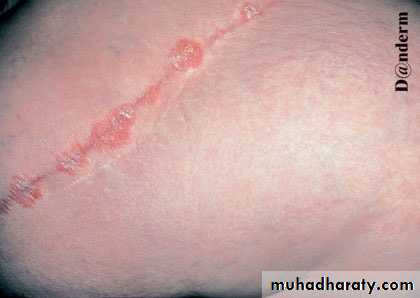
• Koebner’s phenomenon
• Production of the same lesion after trauma
• Lichen planus ,vitiligo viral warts behchet disease
• 25% of patients
• poor prognosis
• Reverse k phenomenon
Aetiology 3-immunological factors
• Evidence• cyclosporin immunosupressor
• Bone marrow transplant of psoriatic donor
• activatedT lymphocyte increase no in dermis producing interluekin 12 and 17
• And tumor necrosis fator TNF
Pathogphysiology
• rapid turn over of cell proliferation of the basal cell layer
• excessive but controlled 3days
• two fold increase in proliferative cell population
• Immune system
• Increase activation of T cells
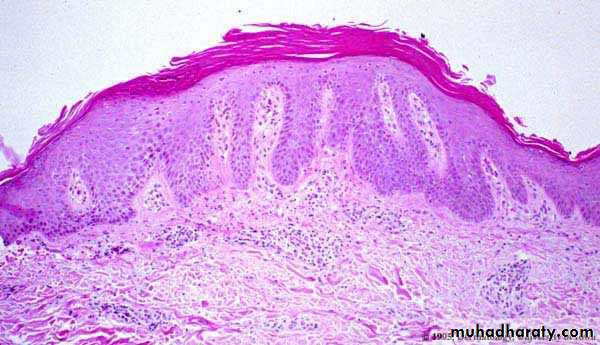
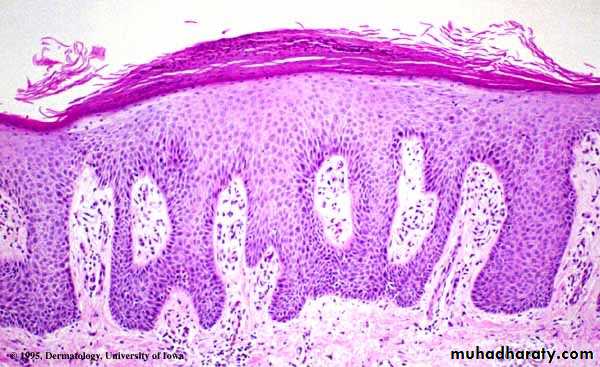
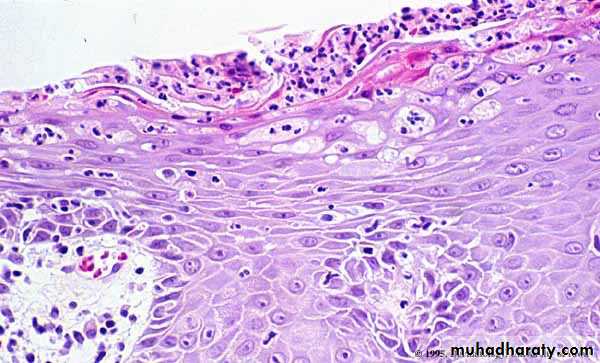
Histopathology
Histopathology
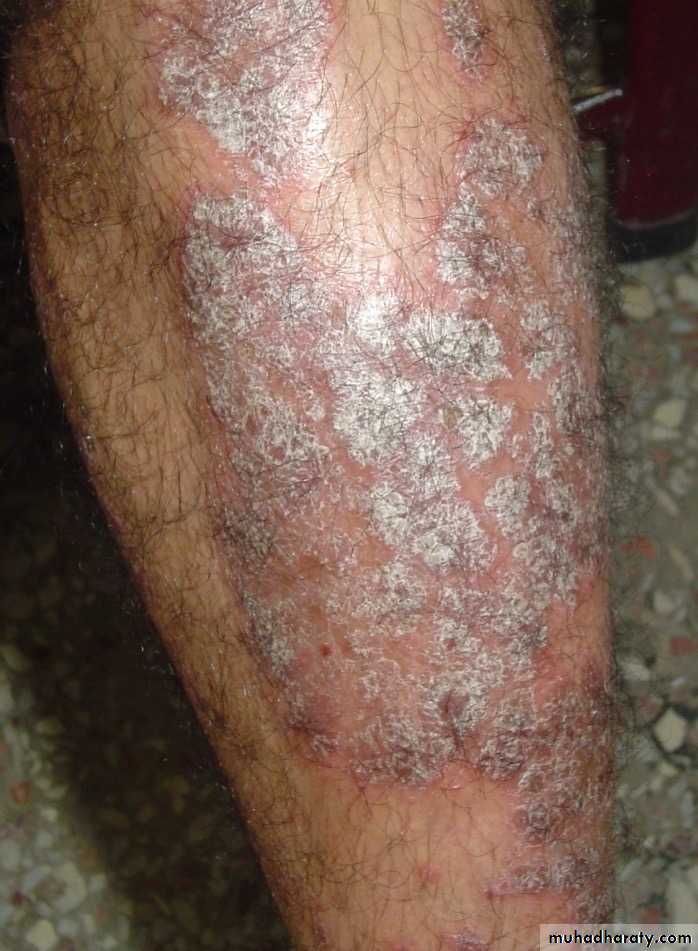
Histopathology• Auspitz sign
• silvery scale• Membrane like layer
• Pin point bleeding
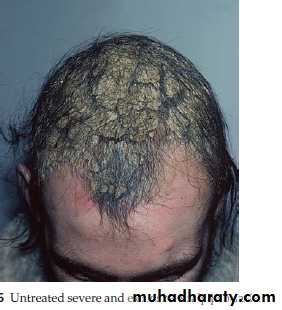
Types of Psoriasis
• Chronic plaque psoriasis (90%)
• Palmoplantar psoriasis
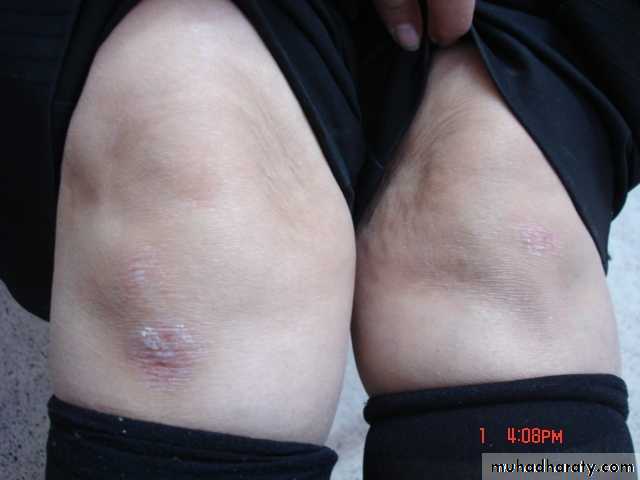
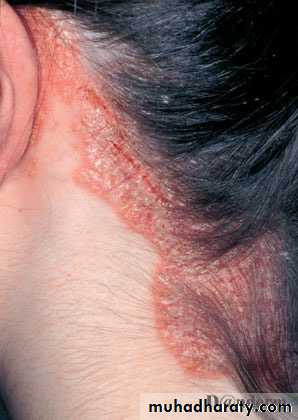
• Flexural psoriasis
• Guttate psoriasis
• Erythrodermic psoriasis
• Pustular psoriasis
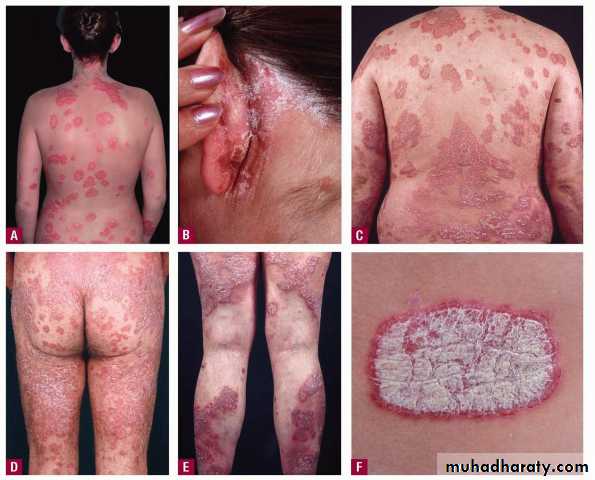
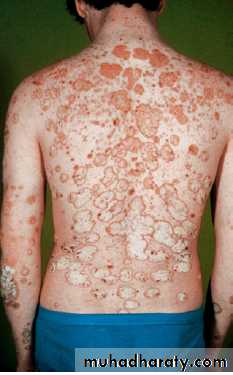
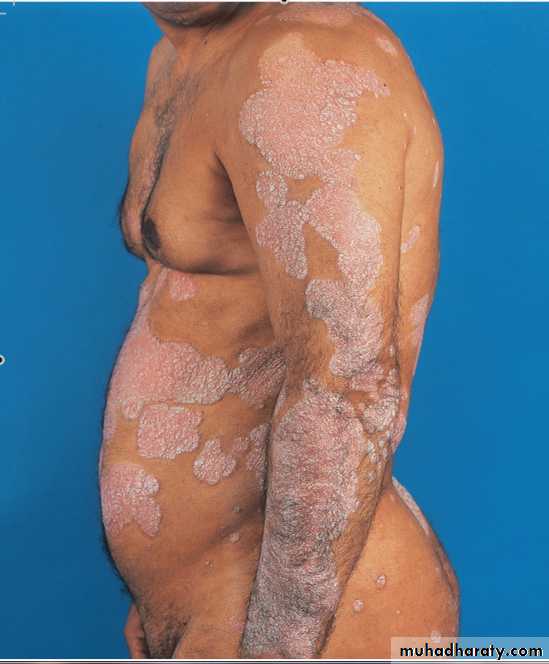
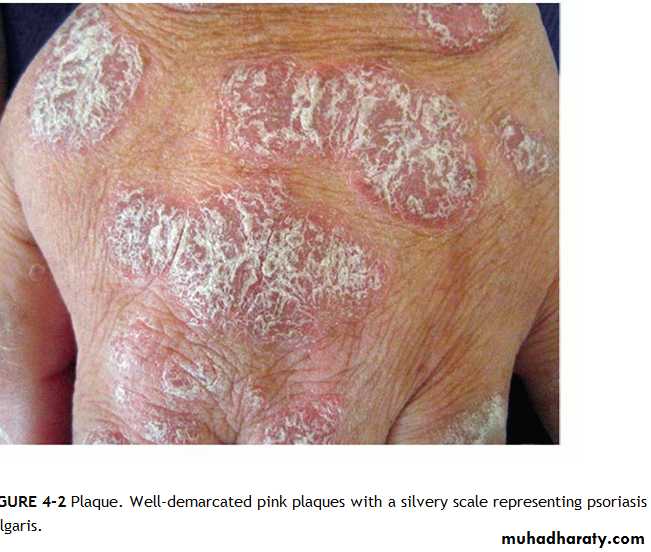
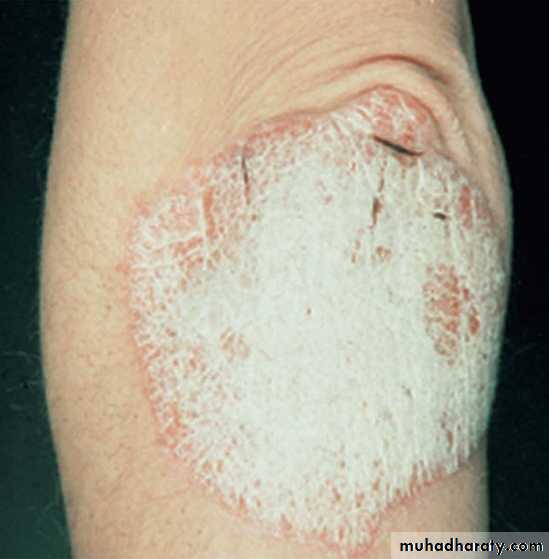
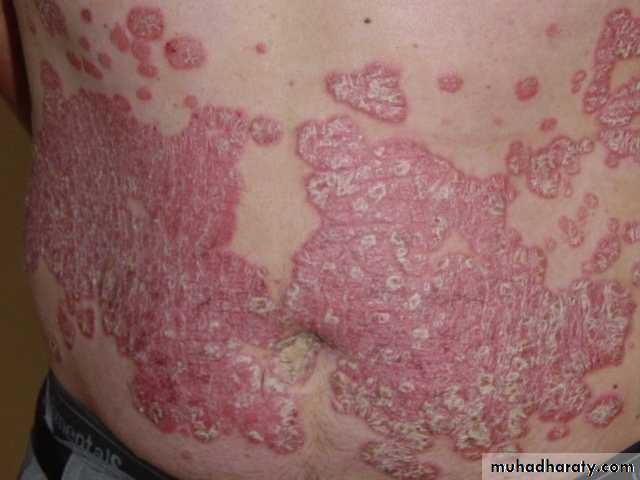
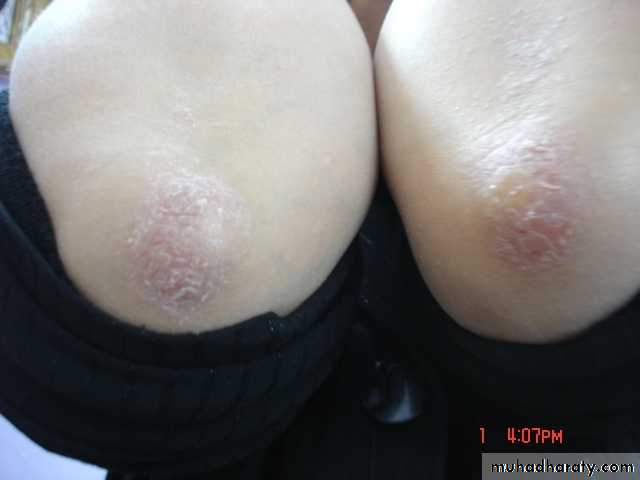
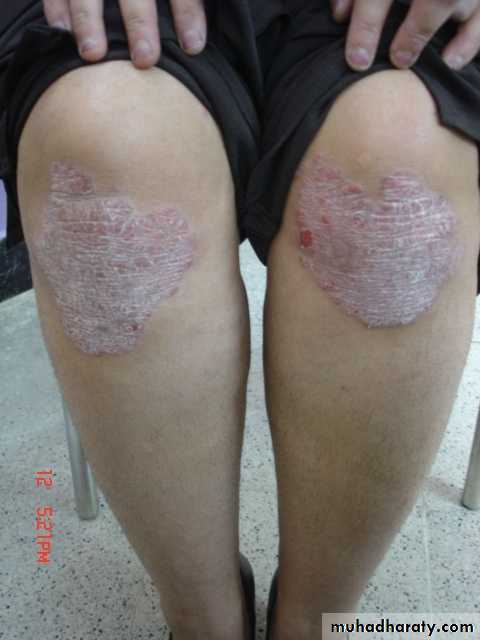
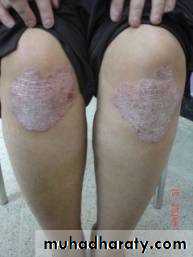
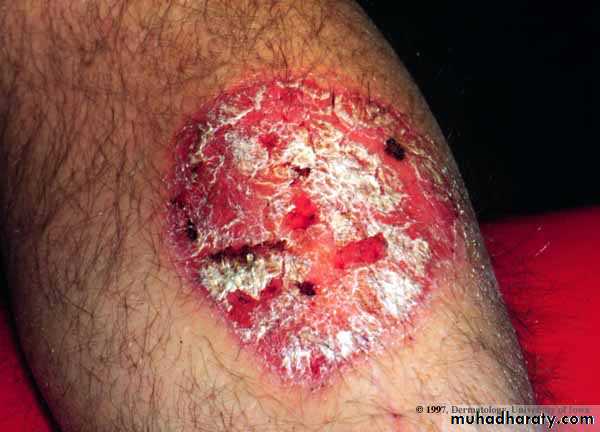
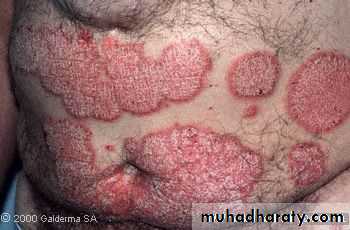
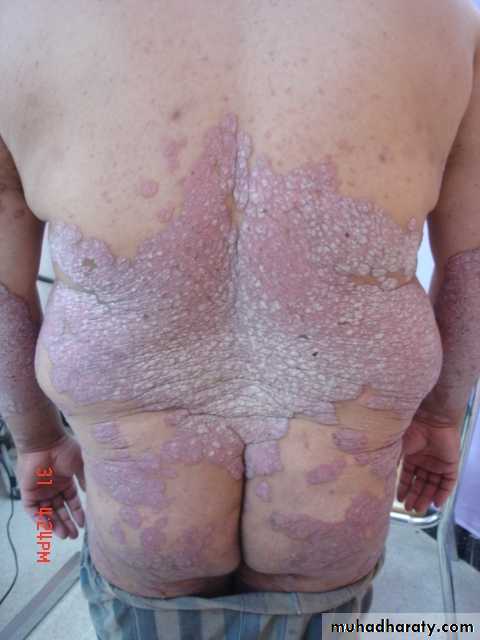
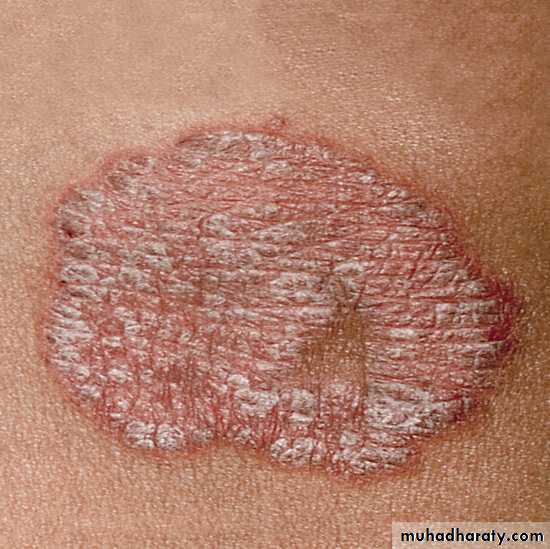
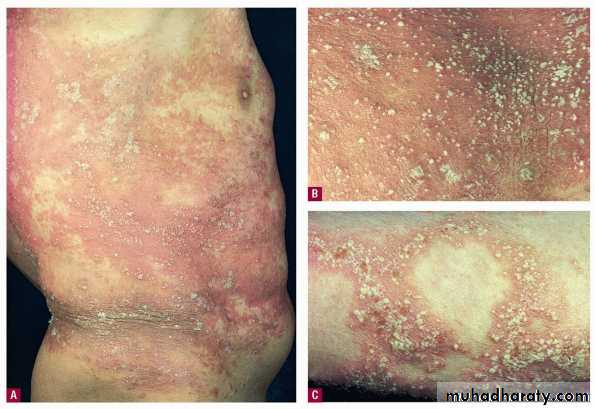
Chronic plaque psoriasis
Salmon pink patchesWell demarcated
Silvery scales
Symmetrical
Extensor surfacesClinical types 1-psoriasis vulgaris or chronic plaque psoriasis commonest .any age young ,extensor
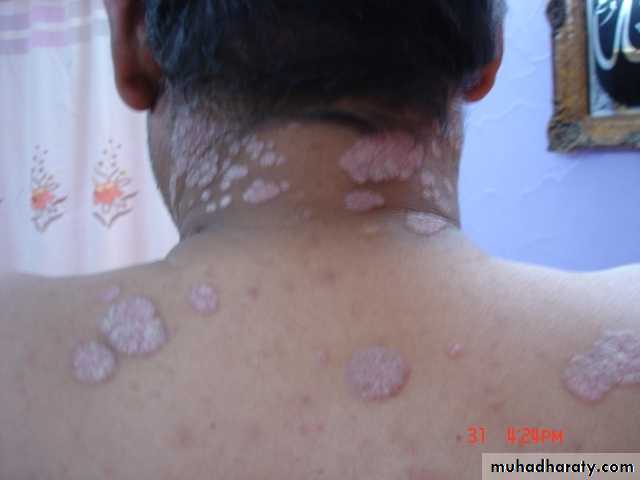
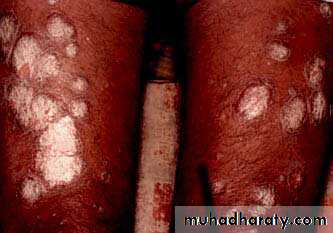
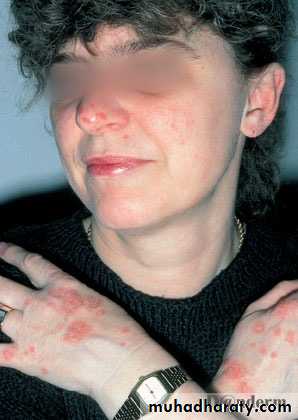
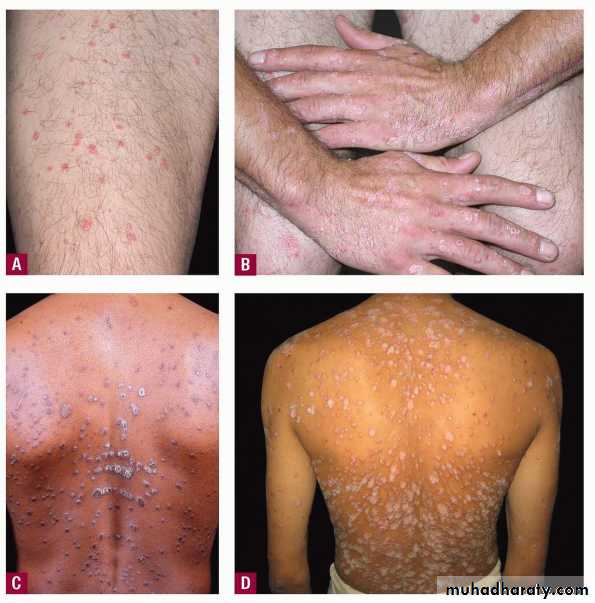
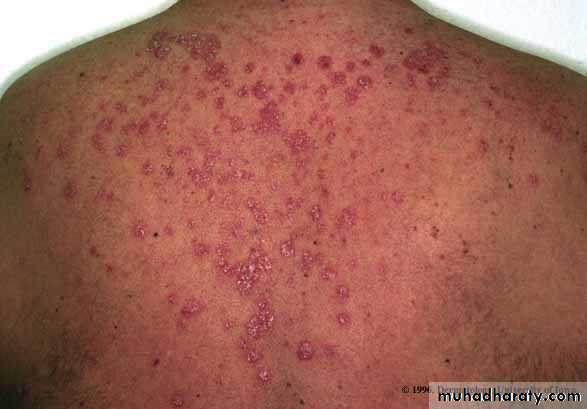
Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasisMore common in children / adolescents
Acute streptococcal infection
Rain drop-like lesionsSelf-resolving (months)
May precede chronic psoriasisClinical types
• 2- Guttate ps children strept small papule red scaly• treatment treat infection
Pustular psoriasis localized- Palmoplantar
Commoner in femalesAdults
Assoc with smoking? Distinct from ordinary psoriasis
SymmetricalPustular psoriasis - Generalised
RareAcute generalised pustular psoriasis (von Zumbusch)
Can occur with ordinary psoriasis
Precipitated by steroid withdrawal
Sheets of pustules, background erythemaMay be systemically unwell
Clinical types 3-Pustular psoriasisb-generalized trunk extremities nail palm sole toxic fever leucocytosis loss of appetite etretinate ,dapson
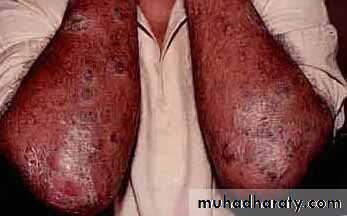
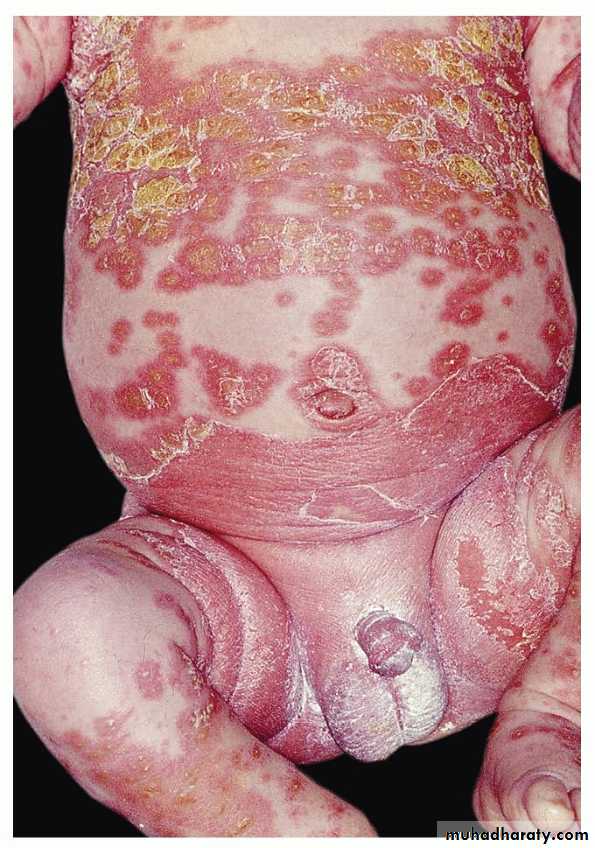
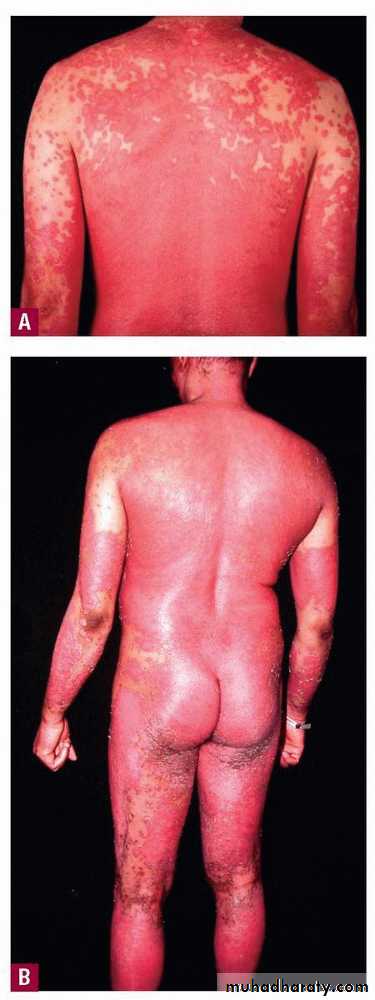
ErErythrodermic psoriasis
ythrodermic psoriasisErythroderma – more than 90% body surface area
Uncommon
Most likely preceding history of psoriasis
May not have other features psoriasisMay be systemically ill
Clinical types
• 4- Erythrodermic or Exfoliative psoriasis• whole body face
• other causes of erythroderma eczema drugs malignancies ichthyosis
• metabolic changes :Hypoprotienemia , Iron deficiency anemia ,vitamins deficiency hypothermia hyperkinetic condition may lead to heart failure ,electrolyte disturbance
Erythrodermic or Exfoliative psoriasis
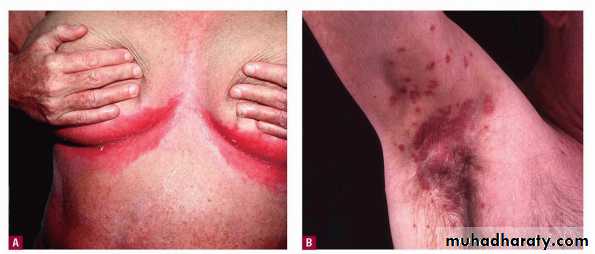
flexural pso axilla groin diffuse erythematous oozy affecting the vault differentiate from tinea active border clear vault +ve scraping
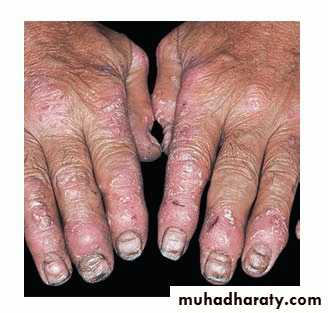
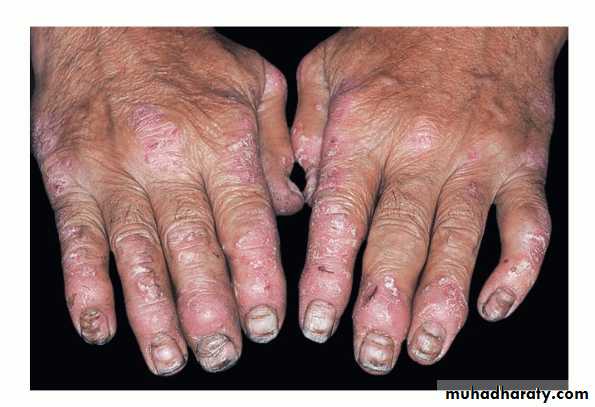
Psoriatic arthritis
• ½ have HLA B-27• sero –ve RF ANF
• with or without skin lesions
• a- poly arthitis rheumatoid like
• b-Mono arthritis like pyogenic arthritis
• c-Axial skeleton ankyloing spondylitis like
• d Arthritis mutilans complete destruction of small joints of hand
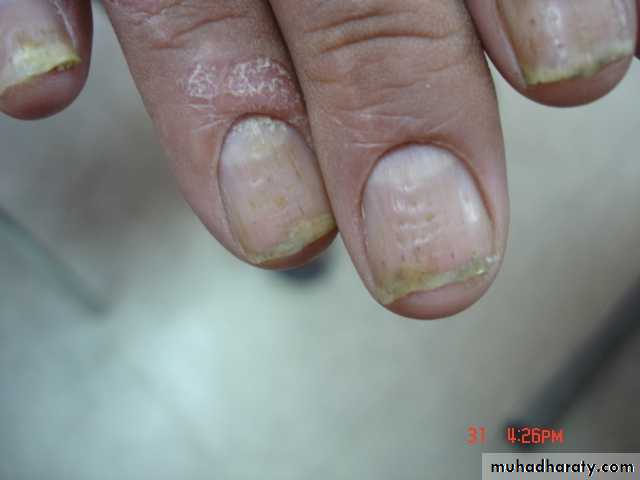
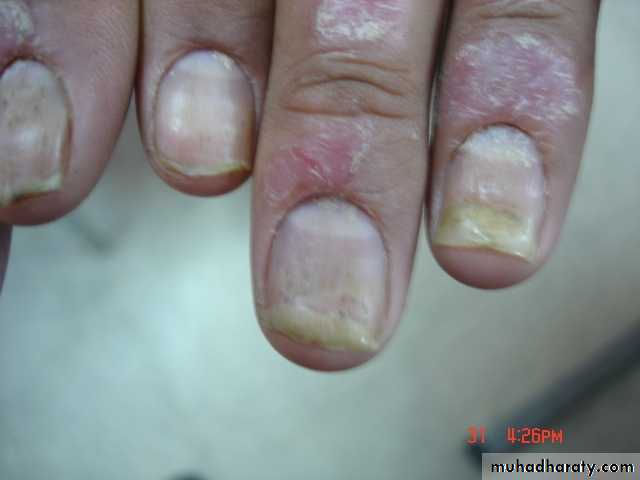
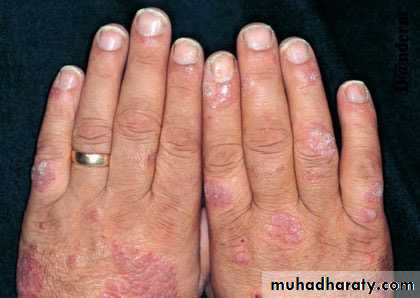
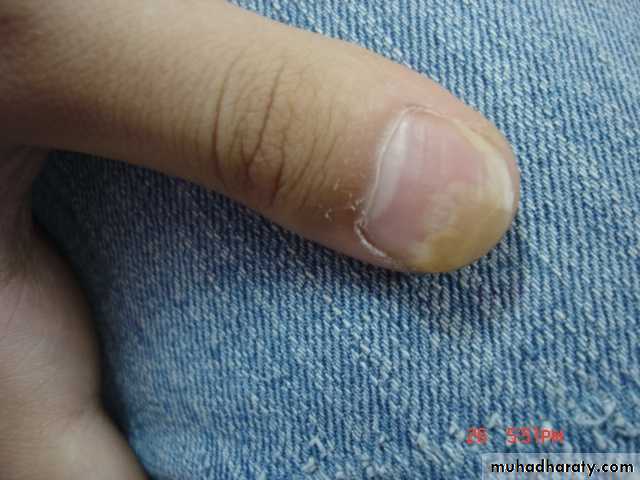
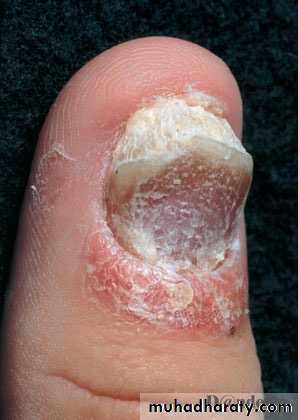
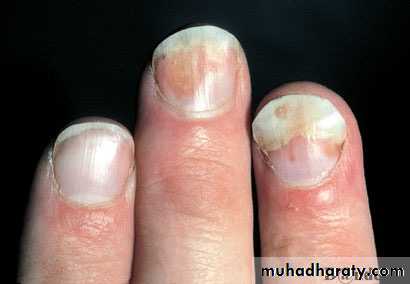
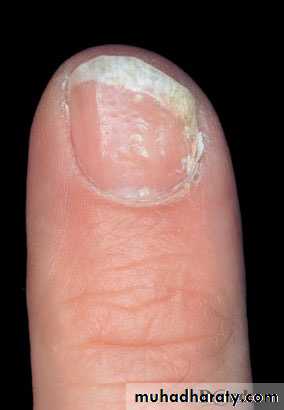
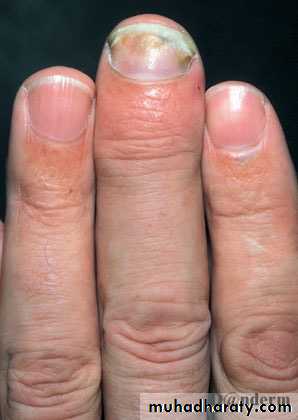
psoriasis - Nails
Nail pitting
Onycholysis
Subungal hyperkeratosis
• Prognosis
• Bad early onset +ve family history ,generalized, koebner +ve
• Good guttate reverse koebner
Management Psoriasis
• Education• Topical treatment
• Phototherapy
• Systemic treatment
1st line: Topical treatment
• Emollients e.g. E45• Vitamin D3 analogues (e.g.Calcipotriol)
• Topical corticosteroids
• Keratolytics e.g. 5% Salicylic acid
• Coal tar
• Dithranol (Short contact, dithrocream)
• Emollients
• Reduces scale and dryness• Thick preparations can give folliculitis
•
• Vitamin D analogues
• Calcipotriol
• Irritation / hypercalcaemia
• Topical steroids
• Skin atrophy
• Coal tar
• Messy, folliculitis, irritation
• Dithranol
• Irritation, stains skin
First-line topical treatment – Chronic plaque psoriasis
2nd Line: Phototherapy
• UVB
• (narrowband UVB)
• UVA plus tablets (8 methoxypsoralen)
• = PUVA
• Side effects - Erythema / pruritis
• Nausea (PUVA)
• L/T – Skin cancer
• Admit, supportive treatment with careful monitoring of BP, temperature and urine output
Emollients and mild topical steroids
Consider systemic treatmentManagement of erythrodermic psoriasis and
generalised pustular psoriasis3rd Line: Systemic treatments
• Mode of Action• Methotrexate
• Folic acid antagonist
• Selective inhibition of rapidly dividing cells
• Ciclosporin
• Suppression of T lymphocytes
• Blocks production of lymphokines
• Acitretin
• Vitamin A derivative
• Suppresses DNA synthesis and cell differentiation
• Side effects
• Methotrexate
• Teratogenicity, nausea and GI upset
• Liver fibrosis, marrow suppression
• LFT and CBP
• Ciclosporin
• Hypertrichosis, gym hypertrophy, tingling peripheries, carcinogenesis
• Hypertension, nephrotoxicity
• Blood pressure, blood urea serum creatinin
• Acitretin
• Teratogenic, dry skin and lips
• Hyperlipidaemia, hepatotoxicity
• Fasting lipids, LFTs
Biological therapy
Target t lymphocyteTarget TNF
Question 1
• What is the prevalence of psoriasis in the western world?• 8%
• 15%
• 2%
Question 2
• What % of patients with psoriasis have a positive family history?
• 10%
• 30%
• 70%
Question 7
How could you treat Psoriasis on the face?a. Mild steroid
b. Vitamin D analoguesc. Coal tar
d. Dithranol
Question 3
• What is the most common type of psoriasis?• Chronic plaque psoriasis
• Palmoplantar psoriasis
• Flexural psoriasis
• Guttate psoriasis
• Pustular psoriasis