INFANT FEEDING
DR. MOHAMMAD F. IBRAHEEMDEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS
(1)
Objective
The basic goals of feeding .Physiology of lactation.
What is the Colostrum?
Advantages , Contraindications and problems associated
with breast feeding.Problems affect successful breast feeding.
The Factors that conductive to successful breast-feeding
•The dramatic growth of infants during the first year of life and continued growth, even thought at lower rates, from one yr. of age through adolescence impose unique nutritional needs.
•Because the rapid rates of growth are accompanied by marked developmental changes in organ function and composition, failure to provide sufficient nutrients during this time is likely to have adverse effects on development as well as growth.
Infant feeding Proper nutrition is crucial in promoting the normal growth & development of children. The basic goals are: (1) satisfying growth. (2) Avoidance of deficiency status.
Breast feeding
Formation , ejection & secretion of milk is affected by different hormones in the body :- Thyroid hormones, insulin ,adrenal steroids & pancreatic enzymes.Suckling will affect the hypothalamus through the auditory , visual & emotional stimuli .
Physiology of lactation:
Lactation consists of two distinct phases:First Humeral phase:
The secretion of milk by the alveolar cells into the alveoli & this begins in the last 3 months of pregnancy & continue after that. Here Prolactin secretion is increased and affects the milk secretion and further more the suckling mechanism will increase the prolactin by 10 folds.
Second Neurohumeral phase:
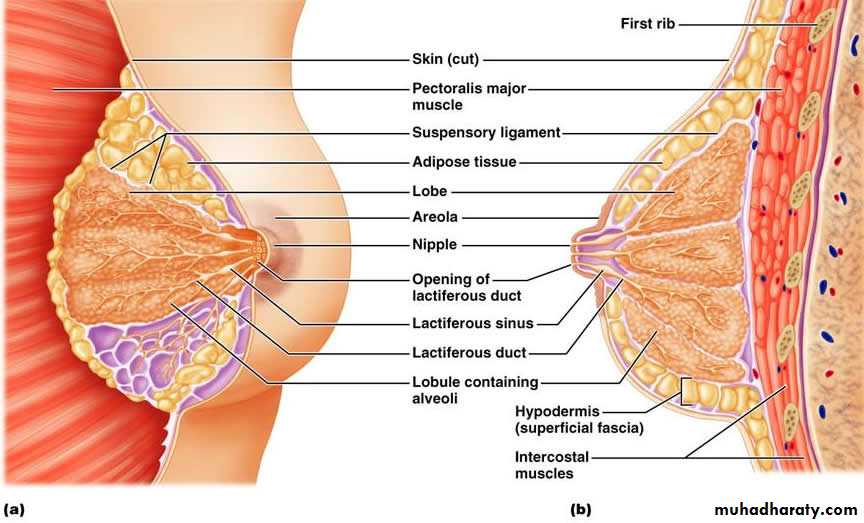
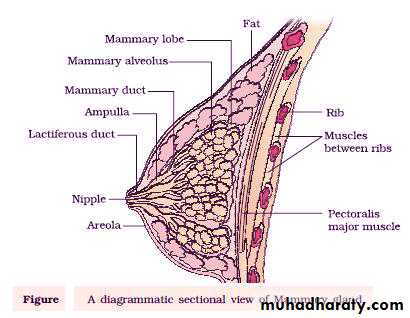
It is the process of milk ejection whereby the alveolar milk is ejected from the alveoli into the lactiferous ducts andthen to the
lactiferous sinuses
so that it will be
readily
available to the
infant
( the let down
reflex)
and it is due to the contraction of the myoepithelium that envelops the alveoli. This is caused by combination of neuorogenic & hormonal mechanism involving the Oxytocin hormone
and to lesser extent
Vasopressin.
The release of Oxytocin is stimulated not only by suckling mechanism but also by condition reflex when the hungry infants starts to cry.!!!
The milk ejection reflex is inhibited by : Pain from cracked nipple, anxiety, physical exertion, previous breast surgery and smoking.
The AAP recommends
exclusive breast-feeding for a minimum of 4 mo and preferably for 6 mo.It is preferable to empty the 1st breast
before offering the 2nd in order toallow complete emptying and therefore
better milk production.
follow-up appointment is recommended
within 24-48 hr after hospital discharge.Colostrum:
(1)The earliest milk to be secreted, the daily volume is only 10-40 ml/day and it is sufficient to the newborn baby.(2) ) It is lemon color, thick, sticky, alkaline, with high sp. Gravity (1.040-1.060).
(3) It is very rich in proteins
,vit. A, and Nacl.
(4) but less amounts of
fat , CHO (as lactose) ,and
potassium.
(5) contains high concentrations of leukocytes, which can destroy disease-causing bacteria and viruses.
(6) It has unique immunological factors such as : IgA ,IgG ,IgM , lysosomes and lactoferrin.
(7) It has a mild laxative effect, encouraging the passing of the baby's first stool, which is called meconium.
Problems associated with breast feeding
1-Nipple PainNipple pain is one of the most common complaints of breastfeeding mothers in the immediate postpartum period. Poor infant positioning and improper latch are the most common reasons. If the problem persists and the
infant refuses to feed, consideration needs
to be given to nipple candidiasis.
2-Engorgement
the breasts are firm, overfilled, and painful
the cause may be incomplete removal of
milk.
Frequent breastfeeding or, in some cases,
with a combination of hot compresses and
manual milk expression before breast
Feeding.
• 3-Mastitis
• 2-3% of lactating , (u) unilateral,• C/F: localized warmth, tenderness, edema, and
• erythema after the 2nd post-delivery week.
• m.o: Staph. aureus, E.coli,
• group A strept ,H. influenzae,
• Klebsiella pneumoniae, andBacteroides spp.
• Diagnosis is confirmed by physical examination.
• Oral antibiotics and analgesics,
• while promoting breast-feeding or emptying of the affected breast
• 4-Milk Leakage
• common event
• milk is involuntarily lost from the breast either
• in response to breast-feeding on the opposite
• side or as a reflex in response to other stimuli,
• such as an infant’s cry. Milk leakage usually
• resolves spontaneously as lactation proceeds.
• 5-Inadequate Milk Intake
• may be due to:-• 1- insufficient milk production or
• 2- failure of established breast-feeding,
• but also fetal cause that prevent proper
• breast stimulation.
• breast-fed neonates must feed a minimum of 8 times per day.
• 6- Jaundice
• Breast-feeding jaundice is a common
• reason for hospital readmission of
• healthy breast-fed infants.
• Breast milk jaundice causes
• persistently high serum indirect
• bilirubin in a thriving healthy baby.
*Exclusive breast feeding --------nothing added to the breast milk.
*Almost exclusive B .F.----------addition of water & juice (>4m)*Partial breast feeding ------------only 20-80% of breast feeding.
*Token breast feeding ------------ <20 % of BF
Lactating woman supplies 800-850 ml/day of milk which is equal to energy loss of 600 kcal The diet of a lactating woman should be rich in minerals, protein and vitamins.
Advantages of Breast Feeding:
1- Breast milk is the natural food for full-term infants and is the appropriate milk for the 1st year of life.2- Easier , safer, cheaper and readily available.
3- It is fresh and free of
contaminating bacteria.
4-Breast-feeding is associated with fewer feeding difficulties incident to allergy and/or intolerance to bovine milk; These include diarrhea, intestinal bleeding, occult melena, “spitting up,” colic, and atopic eczema.
5-Breast-fed infants also appear to have a lower
frequency of certain allergic and chronic diseases in later life than formula-fed infants.6-Emotionaly satisfactory for the
mother and it gives feeling ofsecurity to the baby.
7-Antimicrobial property as :
(a) antibodies ( Ig against bacteria & viruses ) and relatively high conc. of secretory IgA.
(b) phagocytic cells (granulocyte: macrophage ,lymphocytes, 90% of which are T- lymphocytes).
(c) enzymes (lysozyme ,lacto-peroxidase ).
(d) proteins ( lactoferrin ,the iron –bindingwhey protein which inhibit the growth of E.coli ).
(e) resistant factors against staphylococci and bile salt- stimulated lipase kills Giardia lamblia and E.histolytica.
(f) the lower pH of the stool of breast-fed infants is thought to contribute to the favorable intestinal flora of infants fed human milk compared with formula (more bifidobacteria and lactobacilli; fewer Escherichia coli).
(g) complements .
(i) Interferon-producing cells.Contraindications of breast feeding:
Most of them are temporary.In mother:
1-Severe systemic diseases as acute heart failure, thyrotoxicosis, neoplasia &receiving cytotoxic therapy.
2-HIV, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1, rubella virus, and herpes simplex virus have also been demonstrated in breast milk.
3-Acute infections as Active TB (this may be managed by treating the mother with anti TB treatment and giving the baby INH resistant BCG ).
4-Septicemia, malaria, acute typhoid & local bilateral breast abscesses.
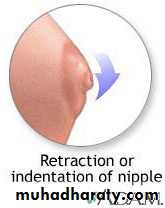
5- Insanity & uncontrolled epilepsy.6-Severely inverted nipples not responding to local treatment.
In the baby:1-Inborn error of metabolism ( like Galactosemia ,Primary disaccharidase deficiency & phenylketonuria) .
2-Severe physical abnormalities as bilateral cleft palate & cleft lip.
3-Weak and premature infants.
4-Cerebral anoxia.
5-Severe dyspnea as RDS& HF.
•Milk from the mother whose diet is sufficient and properly balanced will supply all the necessary nutrients except fluoride and
vitamin D.
•The vitamin D intake
should be 400 IU/day,
starting in the first few
Days of life for all
breast-fed infants.(AAP
2008)
•The iron content of human milk is low, but most normal term infants have sufficient iron stores for the 1st 4–6 mo of life. Human milk iron is well absorbed. Nonetheless, by 4–6 mo of age, the breast-fed infant's diet should be supplemented with iron-fortified complementary foods and/or a ferrous iron preparation.
•The vitamin K content of human milk also is low and may contribute to hemorrhagic disease of the newborn. Parenteral administration of 1 mg of vitamin K at birth is recommended for all infants, and this is especially important for those who will be breast-fed.
PROBLEMS AFFECT SUCCESFUL BREAST FEEDING
1-Retracted nipplesusually benefit from daily manual
breast-pump suction during the latter
weeks of pregnancy.
2- Truly inverted nipples
may be helped by the use of milkcups, starting as early as the 3rd
month of pregnancy.
3-Weight gain
If the mother's diet is adequate, she need not gain or lose weight while breast-feeding. Nursing will help the uterus return to its normal size sooner and also may help the mother return to her pre-pregnancy weight sooner.4- Breast size
Many women must be reassured that breast tone will be preserved by the use of a properly fitted brassiere to support the breasts, especially before delivery and during the nursing period. Breast-feeding has no long-term adverse cosmetic effects on the breast appearance.Q- Is it necessary to stop breast feeding in pregnant mother?
A-Pregnancy does not necessitate immediate cessation of nursing, but the combined demands of supplying milk to the infant and supplying nutrients to the developing fetus are formidable, necessitating special attention to maternal nutrition.
Q- What are the Factors that conducive to successful breast-feeding?
1-good nutritional health.
2- proper balance of rest and exercise.3- freedom from worry.
4- early and sufficient treatment of any intercurrent disease.
5- and adequate nutrition.
Summary• Proper nutrition is crucial in promoting the normal growth & development.
• Colostrum is the earliest milk to be secreted It is lemon color, thick, sticky, rich in proteins but less amounts of fat & CHO .
• Advantages of Breast Feeding could be summarized as:- Easier , safer, fewer feeding difficulties ,emotional satisfaction and antimicrobial property.
• Assessing and managing the problems that affect successful breast feeding