Caries Management by Risk Assessment
Dr . Huda YasirCaries is a bacterial infection caused by specific bacteria.
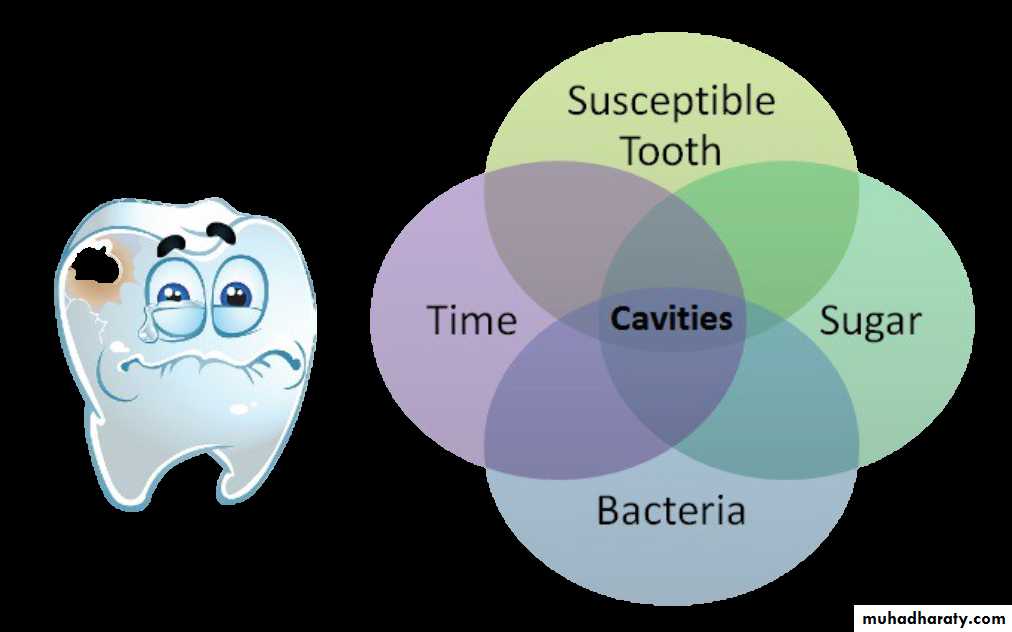
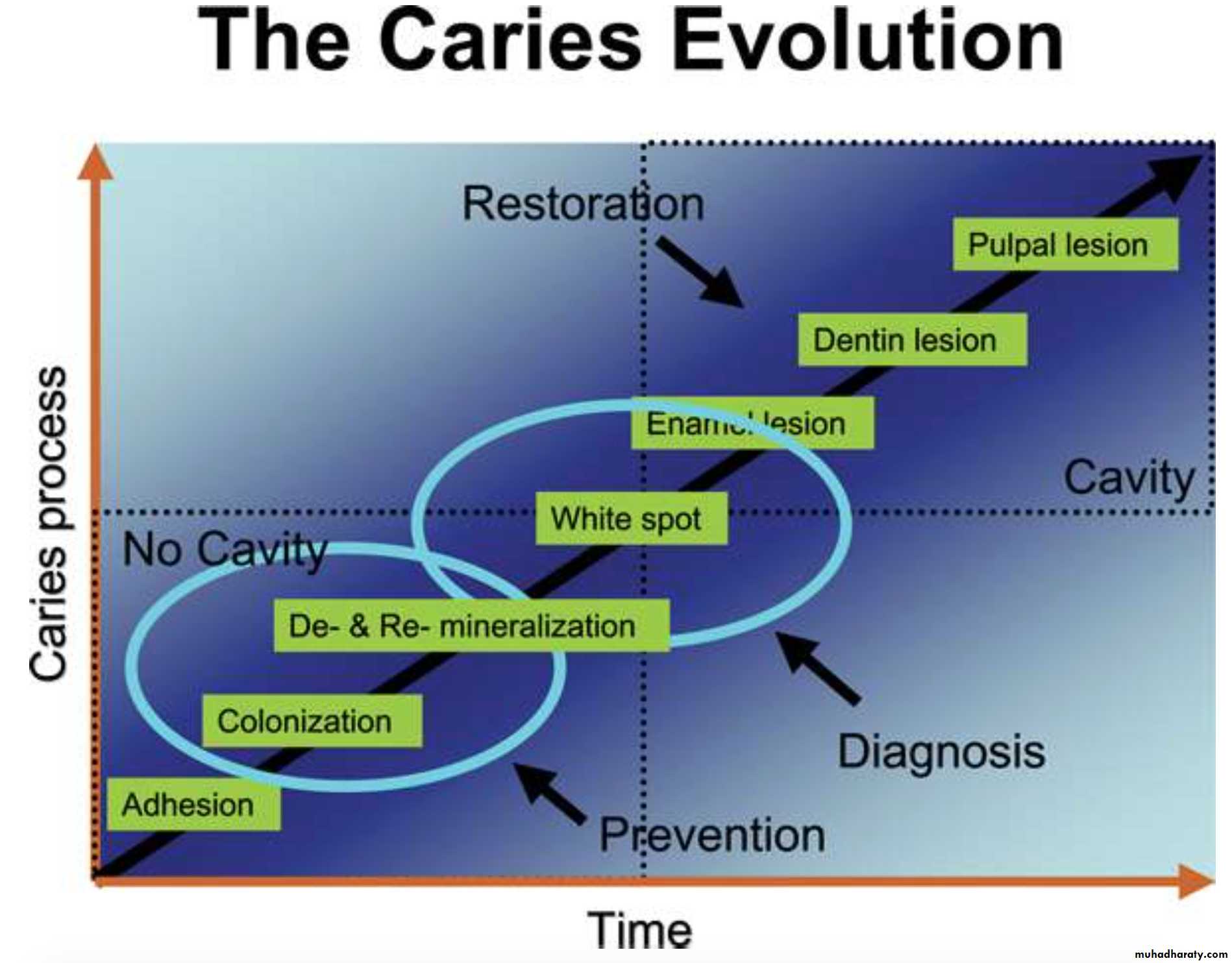
Caries is a reversible multi-factorial process.In other words, caries is an infectious disease with cavitation being the last step of the process
Caries
CariesWhat do you need to create tooth decay?
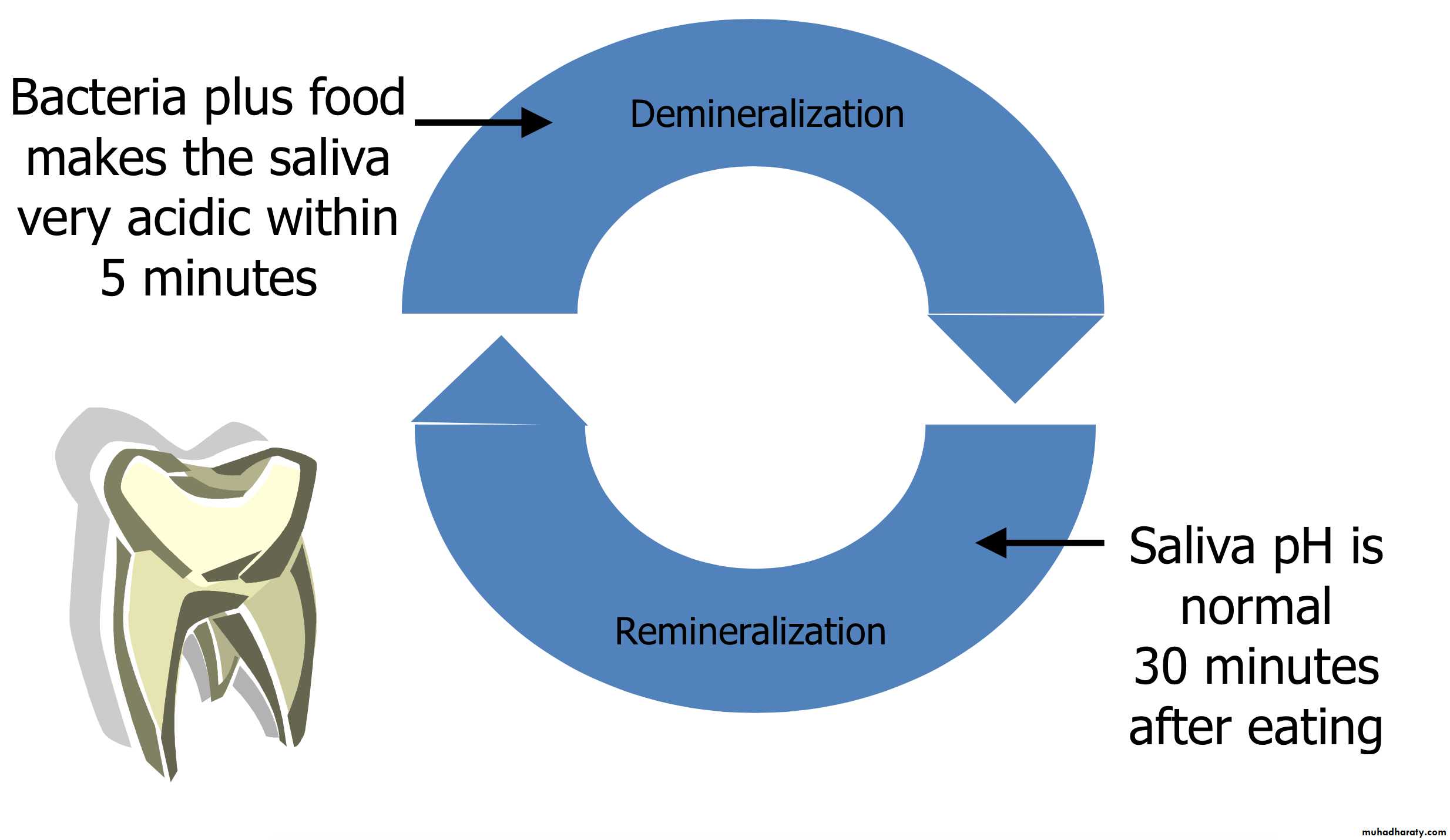
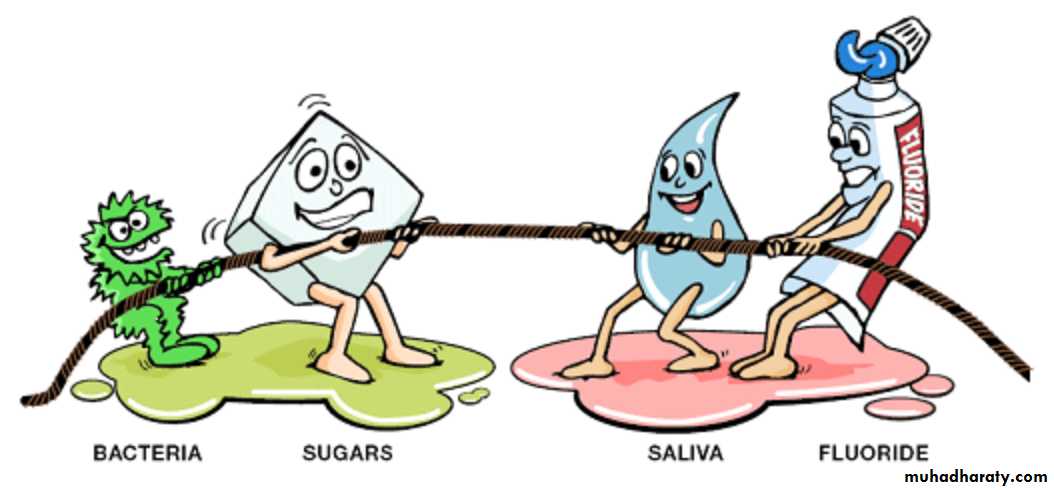
If fluoride is present in the water between the crystals it inhibits mineral lossDemineralization
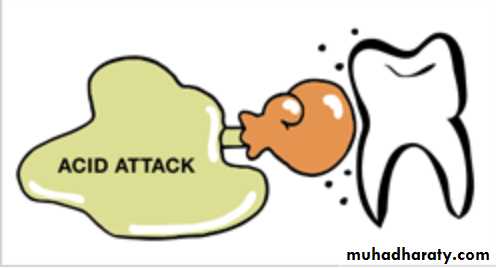
Dental Mineral Acid soluble Calcium phosphateOrganic Acid
Demineralization Calcium & Phosphate into solution
Fluoride speeds up remineralization creating a less soluble mineral
RemineralizationCalcium in tooth + Water (from saliva)
Phosphate In tooth
Water (from Saliva)
Remineralization
•Builds on existing crystal remnants•New mineral less soluble
Cyclic Process of Decay
PROGRESSION OF CARIES
CAMBRA= Caries Management By Risk Assessment
Caries risk assessment is the first step in Caries ManagementFor more than two decades, medical science has recommended that physicians identify and treat patients based on their risk status, rather than treating all patients as if they were the same.
CAMBRA
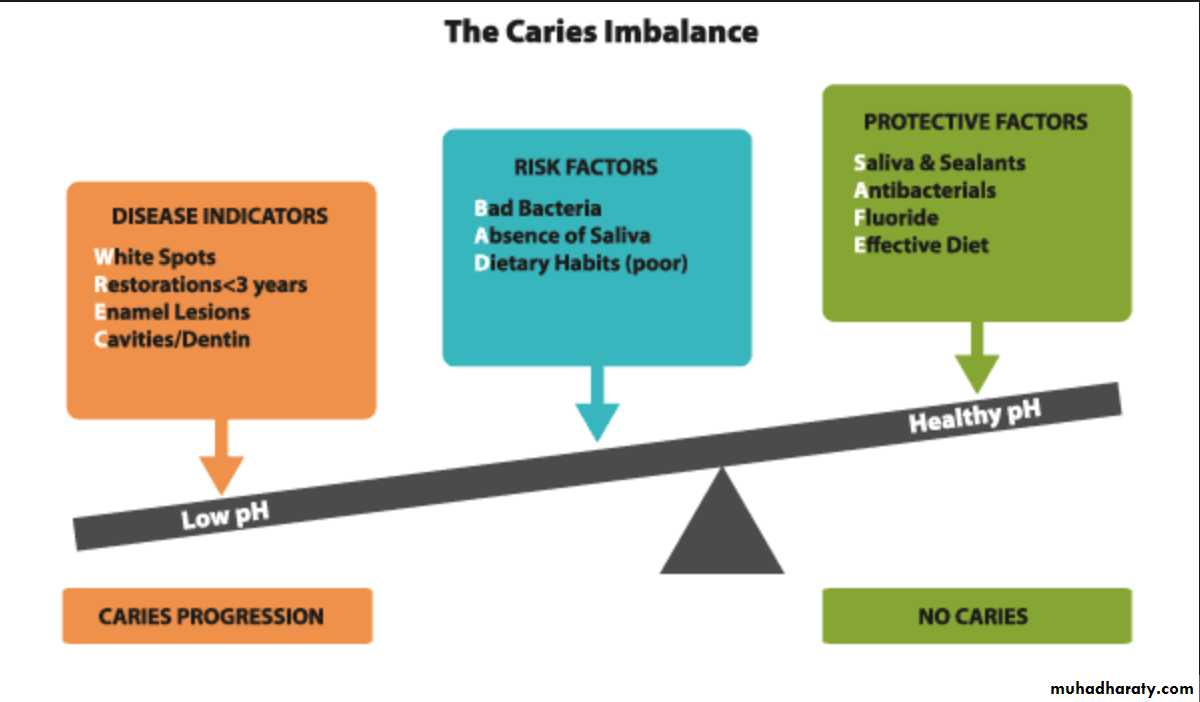
• Disease indicators• Caries risk factors
• Caries Protective factors
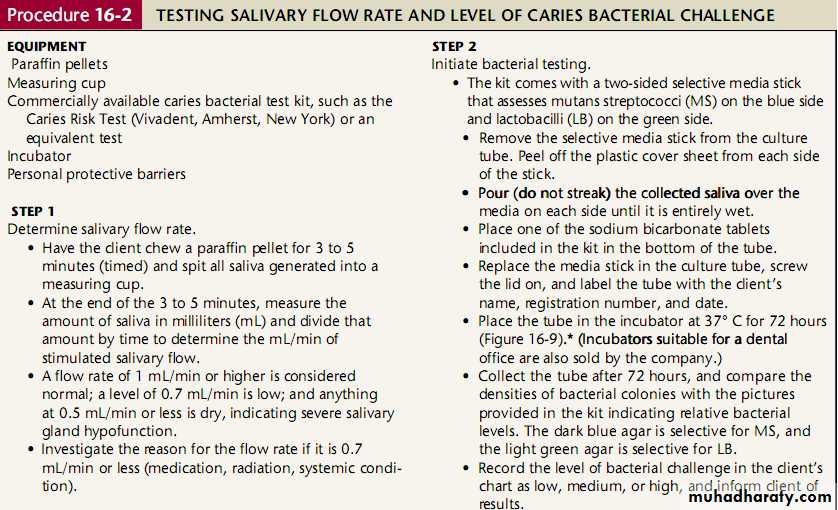
• Tests: Bacterial test ,Salivary flow rate
• Caries management
Caries risk assessment
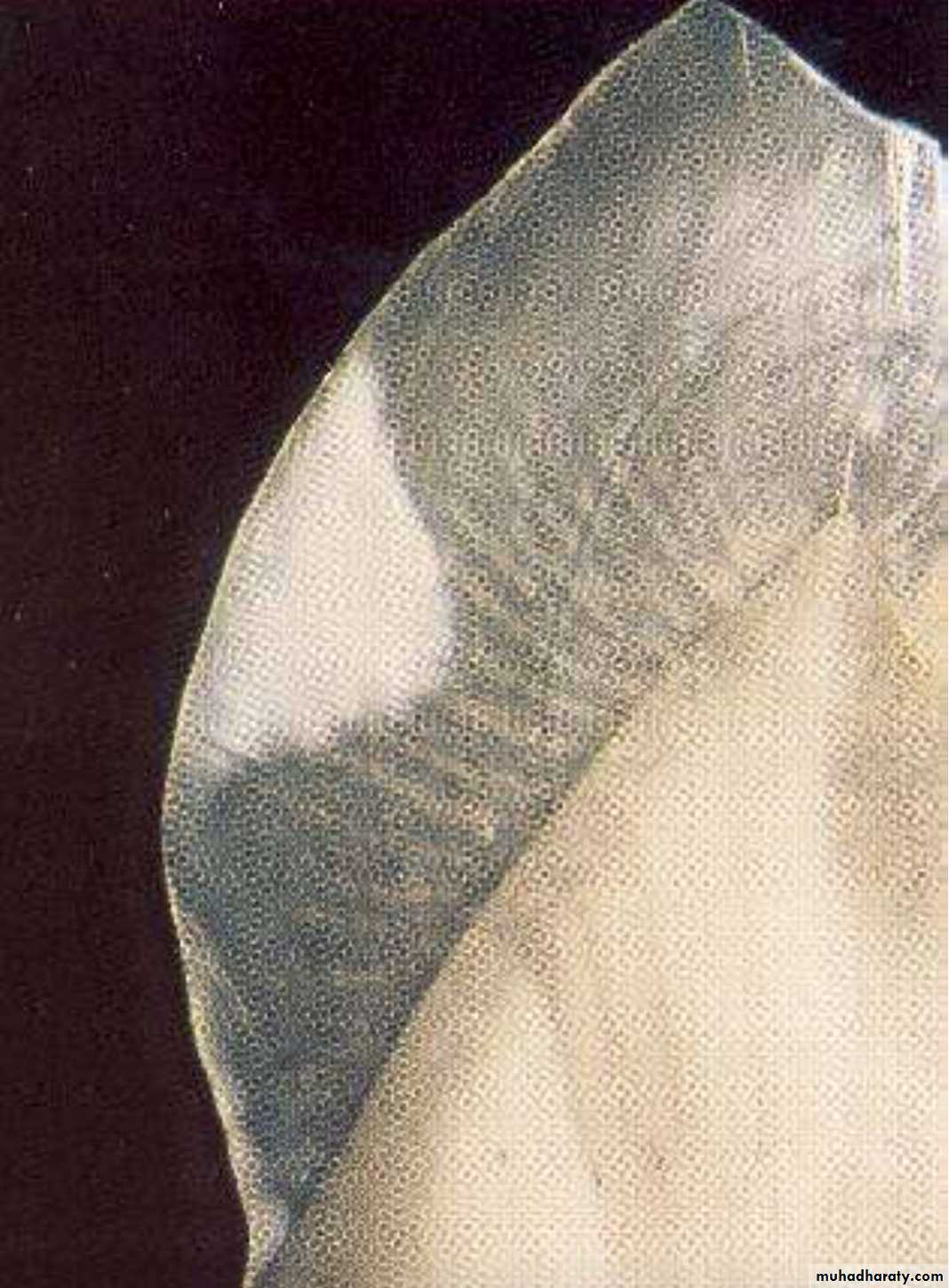
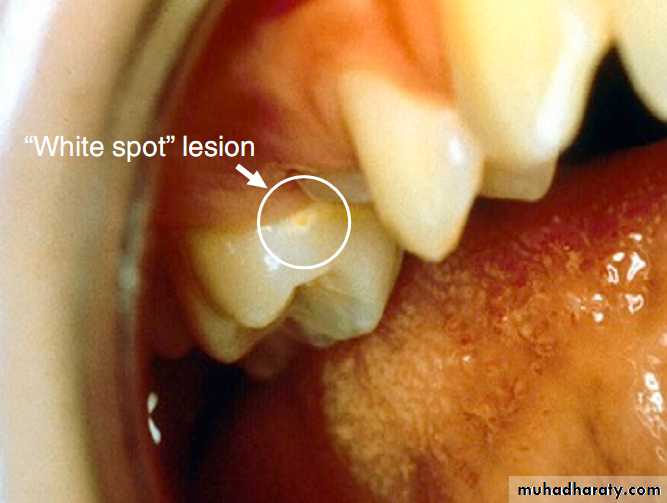
White spots
Restorations <3 years
Enamel lesions
Cavities present (Dentin)
These tell us nothing about the cause of the disease – they only indicate the presence of the disease
• Disease indicators
The white spot lesion is a signal to intervene to avoid the development of a frank carious lesion.
• Disease indicators
• Caries risk factors• Caries Protective factors
• Tests: Bacterial test ,Salivary flow rate
• Caries management
Caries risk assessment
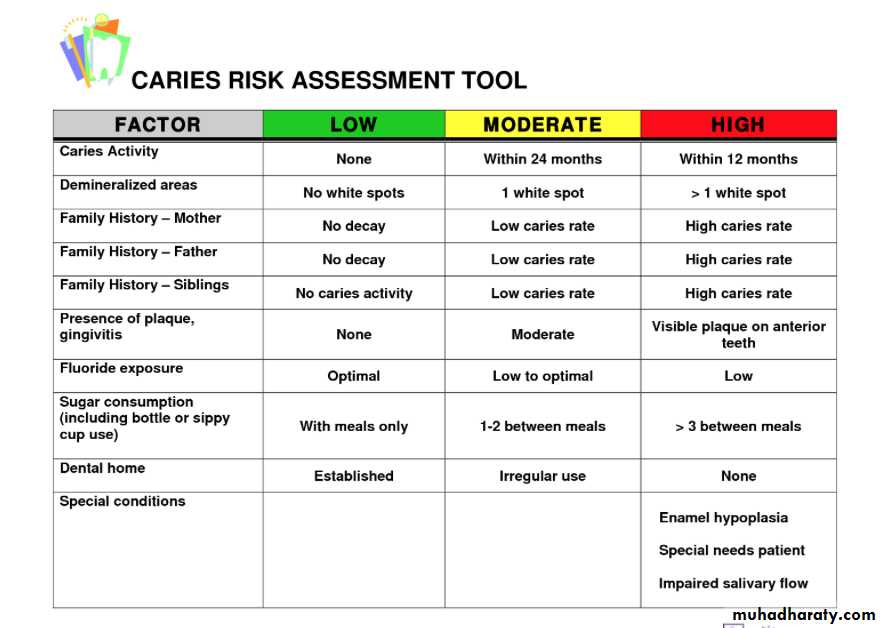
These nine pathologic risk factors are as follows:
Medium or high mutans streptococci and lactobacilli counts
Visible heavy plaque biofilm on teeth
Frequent (>3 times daily) snacking between meals
Deep pits and fissures
Recreational drug use
Inadequate salivary flow by observation or measurement
Saliva-reducing factors (medication, radiation, systemic condition)
Exposed roots
Orthodontic appliances
• Caries Risk Factors
• Disease indicators
• Caries risk factors• Caries Protective factors
• Tests: Bacterial test ,Salivary flow rate
• Caries management
Caries risk assessment
Lives, works, attends school in a fluoridated community
Uses fluoride toothpaste at least once dailyUses fluoride toothpaste at least two times daily (implies an additional benefit over and above once a day or less).
Uses fluoride mouth rinse (0.05% NaF) daily
Uses 5000 ppm fluoride tooth paste daily
Had fluoride varnish applied in the last 6 months
Had an office fluoride topical application in the last 6 months
• Caries Protective factors
CAMBRA is just “removing weight” from one side and “adding weight” to the other
• Disease indicators• Caries risk factors
• Caries Protective factors
• Tests: Bacterial test ,Salivary flow rate
• Caries management
Caries risk assessment
Bacterial ATP test .
• Disease indicators
• Caries risk factors• Caries Protective factors
• Tests: Bacterial test ,Salivary flow rate
• Caries management
Caries risk assessment
Caries management is aimed at restoring and maintaining a balance between protective factors and pathologic factors
• Caries management
Suppressing bacteria that cause the infection
Remineralizing early non cavitated carious lesions by enhancing salivary flow, using fluorides, and possibly using calcium and phosphate paste products, especially if the client is at extreme caries risk e.g., low salivary flowCaries management involves the following:
Protecting tooth surfaces by using sealants and fluorides
Decreasing the frequency of sugar intake
Surgically removing carious lesions that are beyond hope of remineralization and restoring the teeth with minimally invasive techniques and materials
Caries management…cont
Decreasing pathologic factors involves strategies such asClient education
Oral hygiene instruction
Reduction of the intake of fermentable carbohydrates
Addition of the use of chlorhexidine rinse and/or xylitol gum.
Caries management
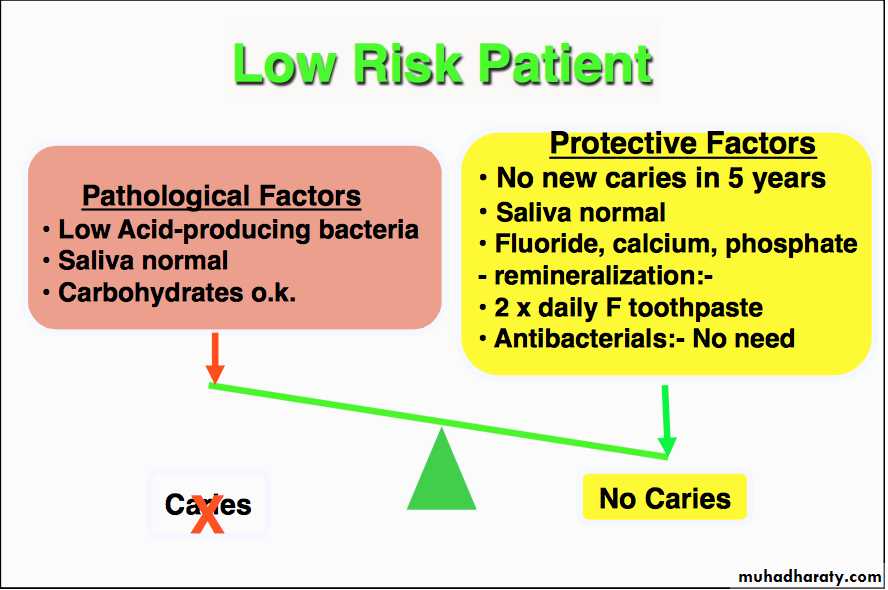
35 yrs old female
No new caries lesion in the last 5 yrs.No signs of salivary dysfunction, no medications with salivary side effects
Assume low cariogenic bacterial level or confirm with bacterial tester showing low level.
Not a frequent snacker
Eg1:What is the caries risk of this individual?
LOW RISK PATIENT
CamBra Clinical guidelines for Patients age 6 Years and olderRisk Level*
Frequency of
Radiographs
Frequency of
Caries Recall
Examinations
Saliva Test (Saliva
Flow and Bacterial
Culture)
Antibacterials,
Chlorhexidine,
Xylitol
Fluoride
pH
Control
Calcium
Phosphate Topical
Supplements
Sealants
(Resin-Based
or Glassionomer
Low risk
Bitewing radio-
graphs every
24-36months
Every 6-12
Months to
reevaluate
Caries risk
Maybe done as a
Baseline reference for new patients
Per saliva test if
done
OTC fluoride-containing
Tooth paste twice daily, after breakfast and at bedtime
Optional NaF varnish if
excessive root exposure
or sensitivity
Not
required
Not required
Optional for excessive root exposure
Or sensitivity
Optional or
As per ICDAS
Sealant pro-
tocol
Moderate
risk
Bitewing
radiographs
every18-24
months
Every4-6
Months to
reevaluate
Caries risk
Maybe done as a
Baseline reference for new patients or
If there is suspicion
Of high bacterial
challenge and to
Assess efficacy and
Patient cooperation
Per saliva test if
done
Xylitol(6-10
g/day) gum or
Candies ; two tabs
Of gum or two
Candies four to
five times daily
OTC fluoride-containing
tooth paste twice daily plus0.05% NaF rinse daily
Initially, one or two
applications of NaF varnish; one application at
4-to6-month recal
Not required
Not required
Optional for
excessive root exposure or sensitivity
As per
ICDAS
sealant
protocol
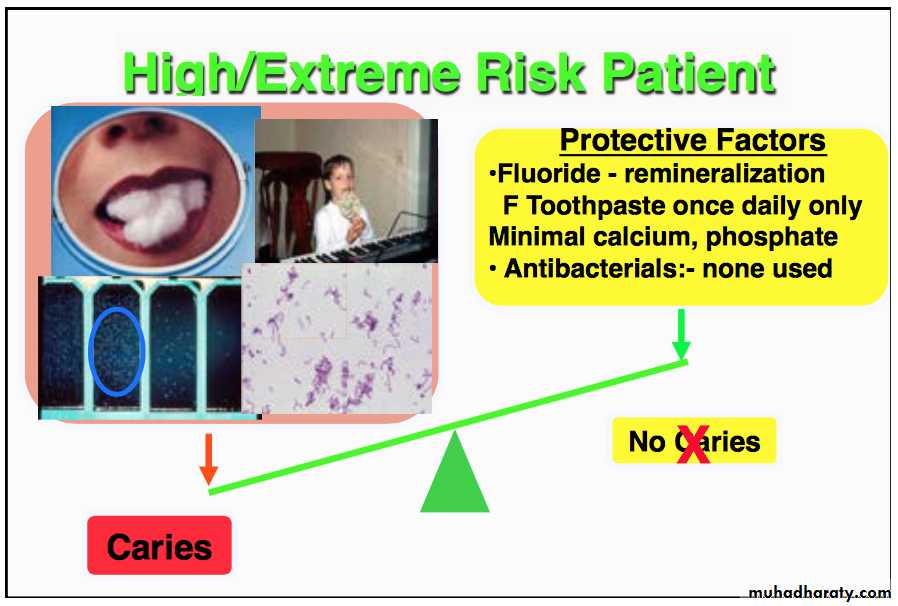
50 yrs old male
Several radiographic lesions in to dentin
Symptoms of salivary disfunction (dry mouth), taking anti-anxiety medications and major analgesic daily for two years
Risk assessment signals (high) by bacterial test
Admits to be a frequent snacker
Eg2: What is the caries risk of this individual?
HIGH RISK PATIENT
Risk Level*Frequency of
Radiographs
Frequency of
Caries Recall
Examinations
Saliva Test (Saliva
Flow and Bacterial
Culture)
Antibacterials,
Chlorhexidine,
Xylitol
Fluoride
pH Control
Calcium
Phosphate Topical
Supplements
Sealants
(Resin-Based
or Glass
Ionomer
High risk
Bitewing
radiographs
every 6-18
months or until
no cavitated
lesions are
evident
Every3-4
months to
reevaluate
caries risk and apply fluoride
varnish
Saliva flow test and bacterial culture
-recall
appointment to assess efficacy and patient cooperation
Chlorhexidine
gluconate 0.12%
10-mL rinse for
1 minute daily
for 1 week each
Month Xylitol (6-10g/day) gum or candies; two tabs of gum or two candies four to five times daily
1.1%NaF tooth paste
twice daily instead of
regular fluoride tooth-paste
Optional0.2%NaF rinse daily(one bottle)
thenOTC0.05%NaF rinse two times daily
Initially , one to three applications at 3-to4-month recall
Not required
Optional:Apply
calcium/phosphate paste several times daily
Asper
ICDAS
sealant
protocol
Extreme
risk§(high
risk plus
dry mouth
or special
needs)
Bitewing radio-
graphs every
6months or
until no cavi-
tated lesions
are evident
Every
3 months to
reevaluate
caries risk and
apply fluoride
varnish
Saliva flow test and
bacterial culture
initial recall appointment to assess
efficacy and patient
cooperation
Chlorhexidine
0.12%(preferably
chlorhexidine in
water base rinse)
10-mLrinsefor
1minutedaily
for1weekeach
month
Xylitol(6-10
g/day) gum or
candies ;two tabs
of gum or two
candies four to
five times daily
1.1% NaF tooth paste
twice daily instead of regular fluoride tooth-paste
OTC0.05%NaFrinsewhenmouthfeelsdryandaftersnacking,breakfast,andlunch
Initially1-3 applications
of NaF varnish;one application at 3-month
recall
Acid-neutralizing rinses
as needed if
mouth feels
dry;after
snacking , at
bed time, and
after breakfast
Baking soda
gum as
needed
Required : Apply
calcium/phosphate
paste twice daily
AsperIC-
DASsealant
protocol