What is the diagnosis?
Complications ?
Answers
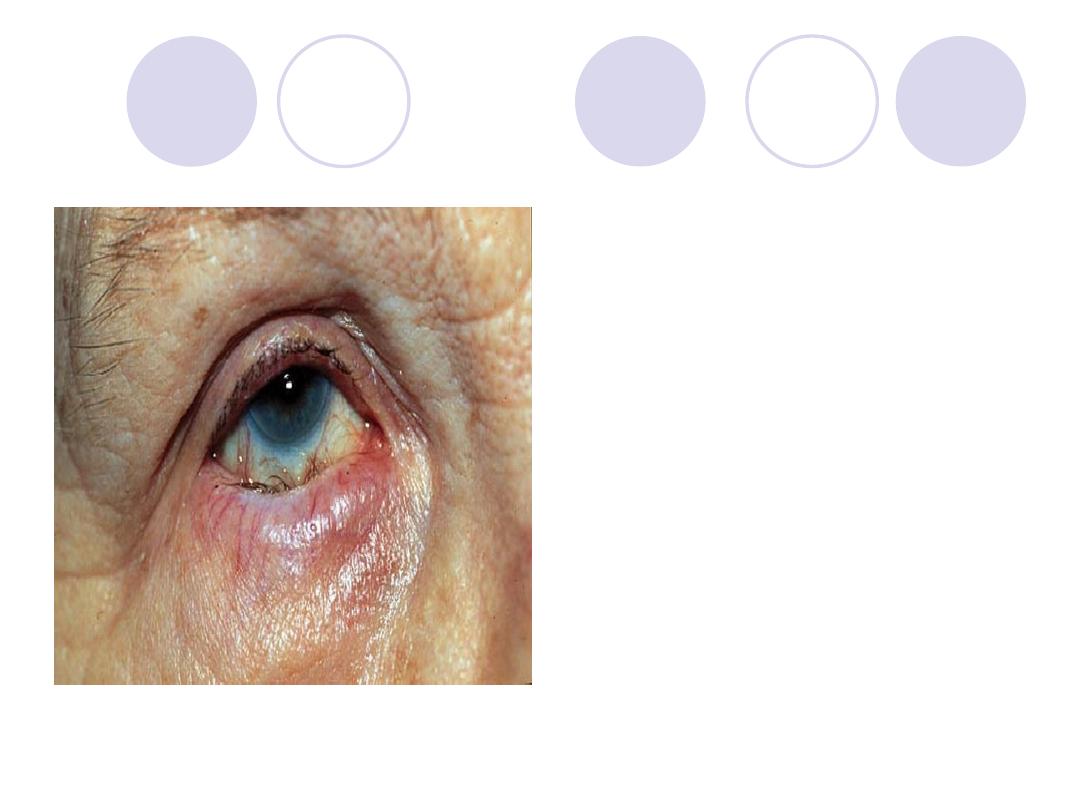
Diagnosis :
Entropion of lower lid
with trichiasis
Complications:
Chronic
conjunctivitis,
conjunctival scar, corneal
ulcer & corneal opacity
What is the diagnosis?
Treatment ?
Answers
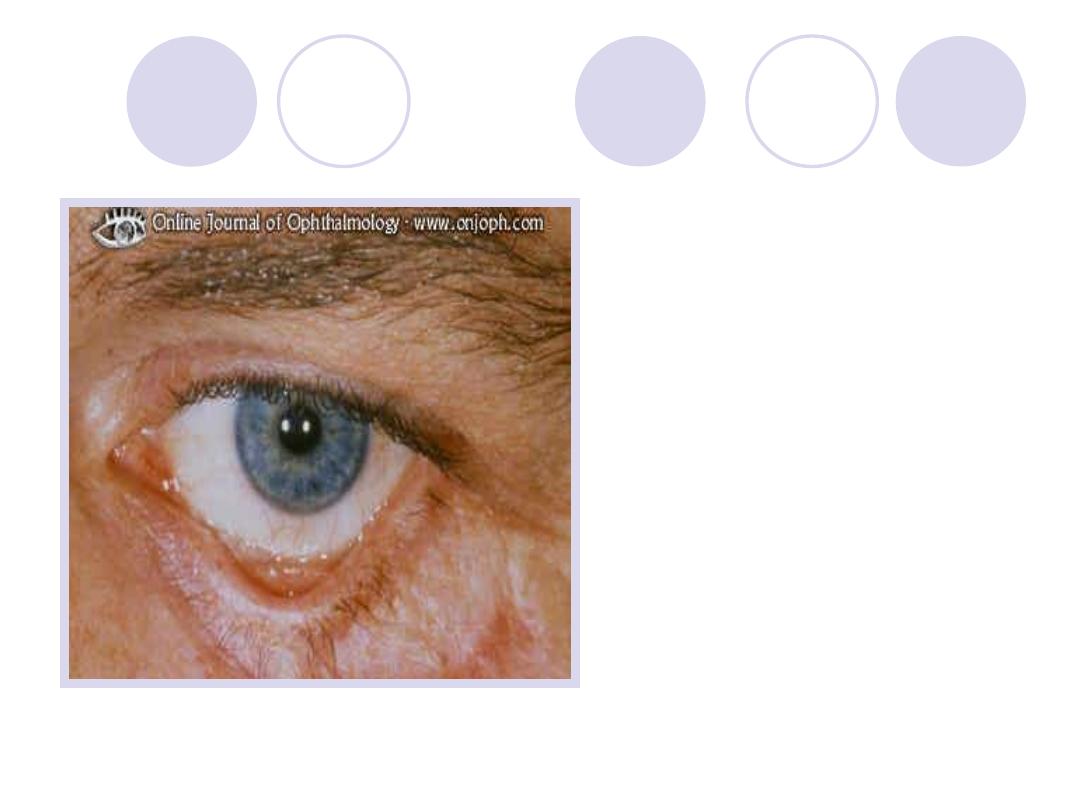
Diagnosis :
Cicatricial ectropion
Treatment :
V to Y plasty or Z plasty
- What is the diagnosis?
- Surgical operation in the
lid ?
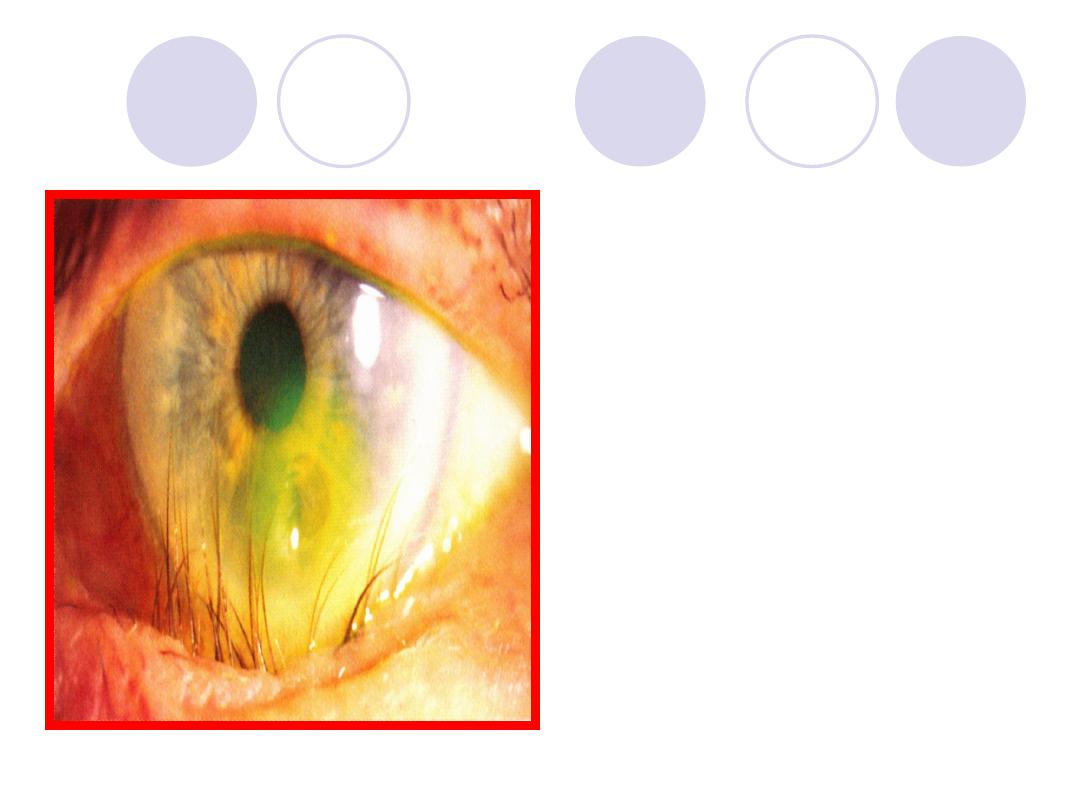
Answers
Entropion in lower lid,
trichiasis & corneal ulcer
Surgical operation:
Lateral canthotomy, lateral
canthoplasty
Diagnosis
treatment
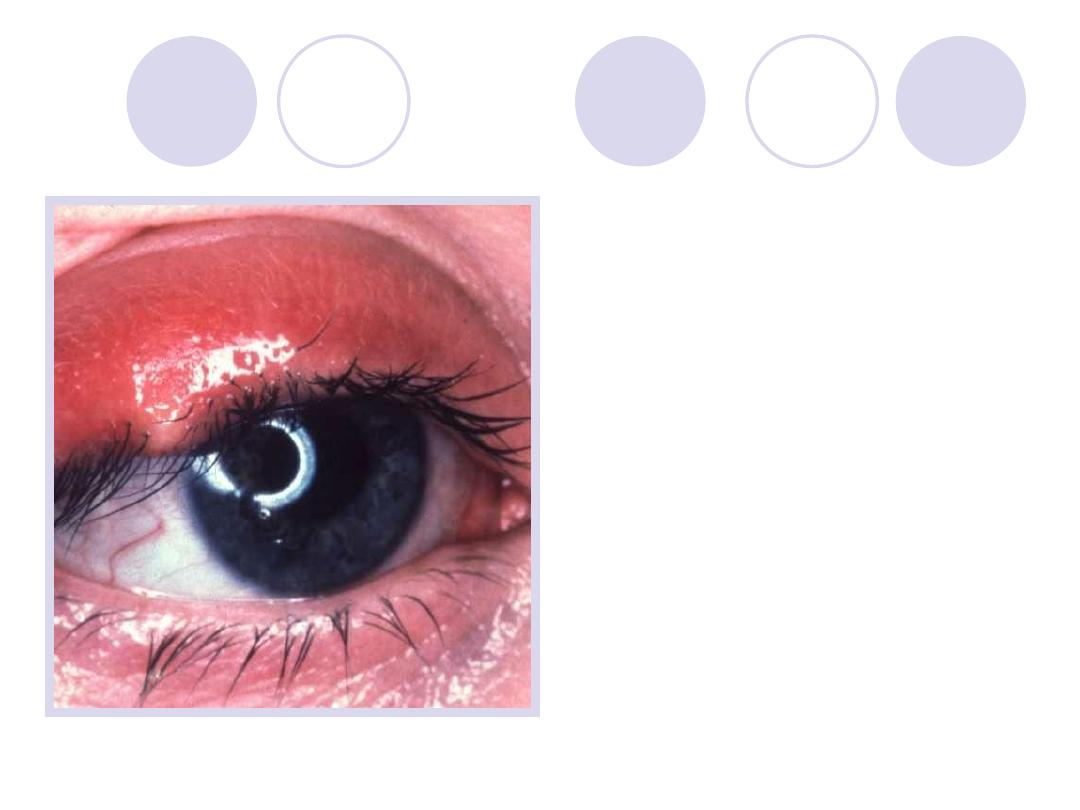
Answers :
-Stye
ttt of P.F. “ staph. Aureus”
-local antibiotics & eye
drops
-Hot fomentation
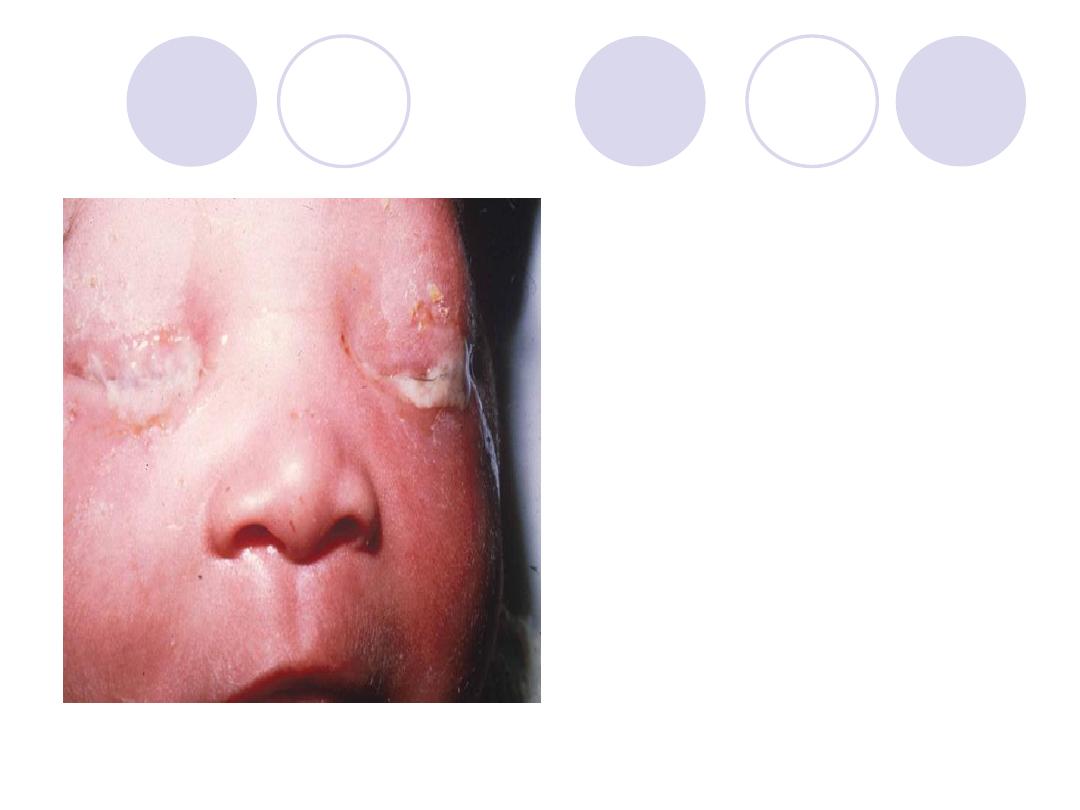
Diagnosis
Complications
treatment
Answers:
-Diagnosis:
Ophthalmia
neonatorum
-Complications:
Corneal ulceration , iridocyclitis
-ttt:
-Prophylactic ttt.
-Curative ttt: lotions, topical and
systemic antibiotics and
atropine ointment in case of
corneal involvement.
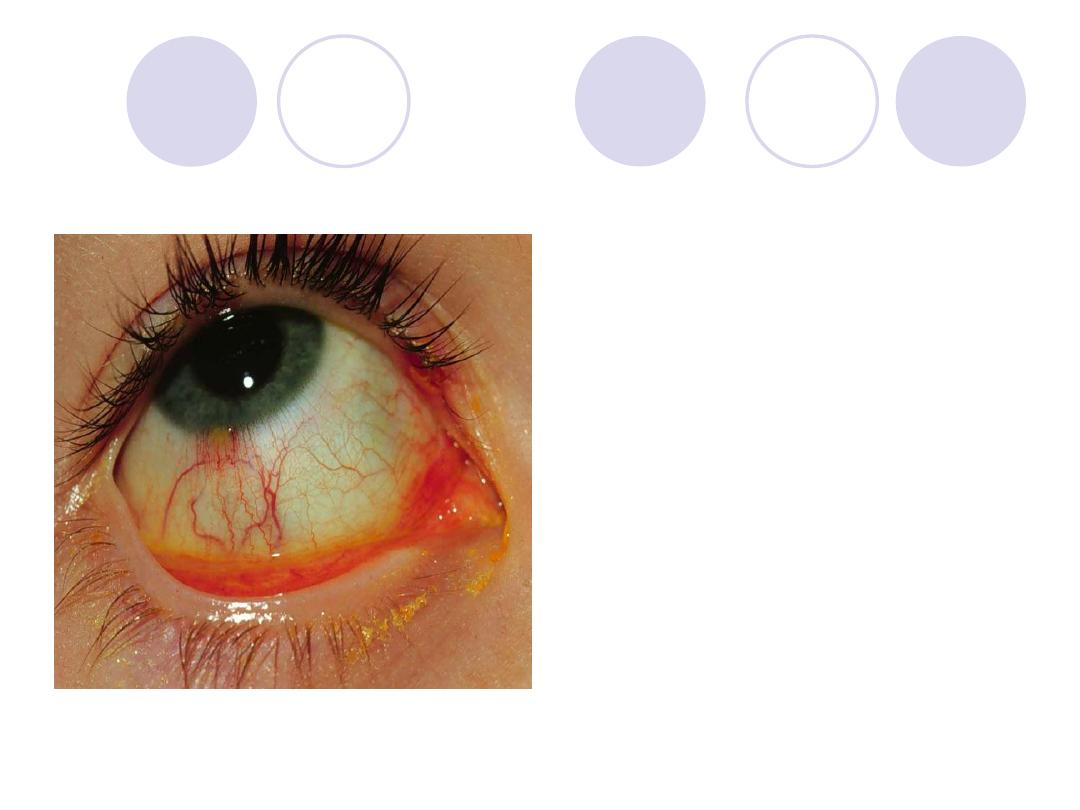
Diagnosis
etiology
Answer:
Phlyctenular conjunctivitis
(limbal phlycten)
Etiology :
Hypersensitivity reaction to
endogenous antigens e.g.
bacterial antigens as T.B &
chlamydia.
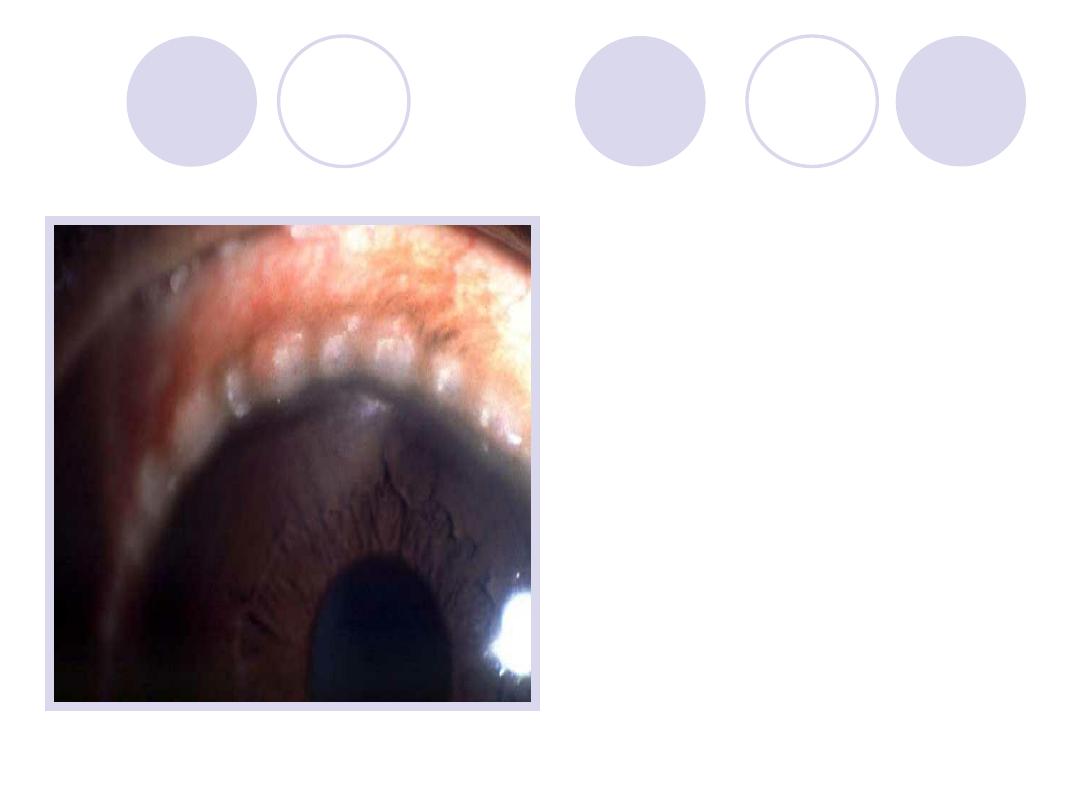
Diagnosis
treatment
Answers:
-Bulbar spring catarrhal
ttt :topical steroids, mast cell
stabilizers,
anti histaminic
Dark glasses & cold
compresses.
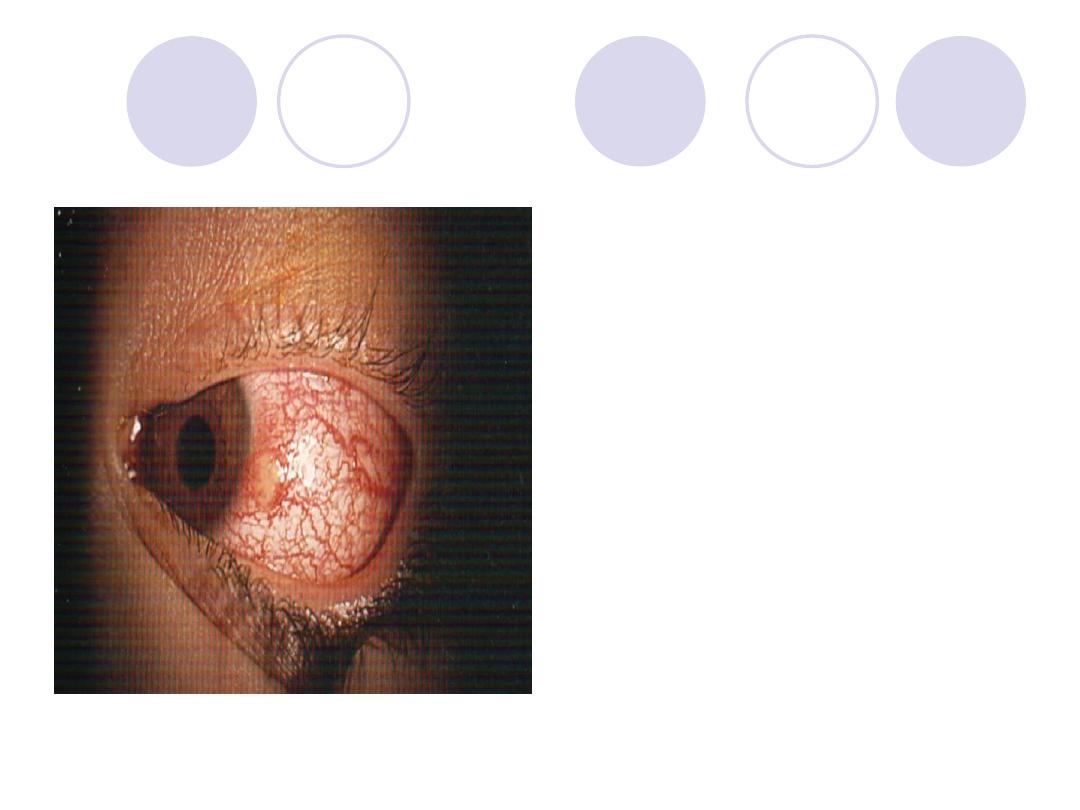
Diagnosis
2 causes
Answers:
-phlycten
-Causes:
Hyper sensitivity to an
endogenous antigen e.g.
tuberculo-protein, Intestinal
parasites, staphylococcal
blepharoconjunctivitis.
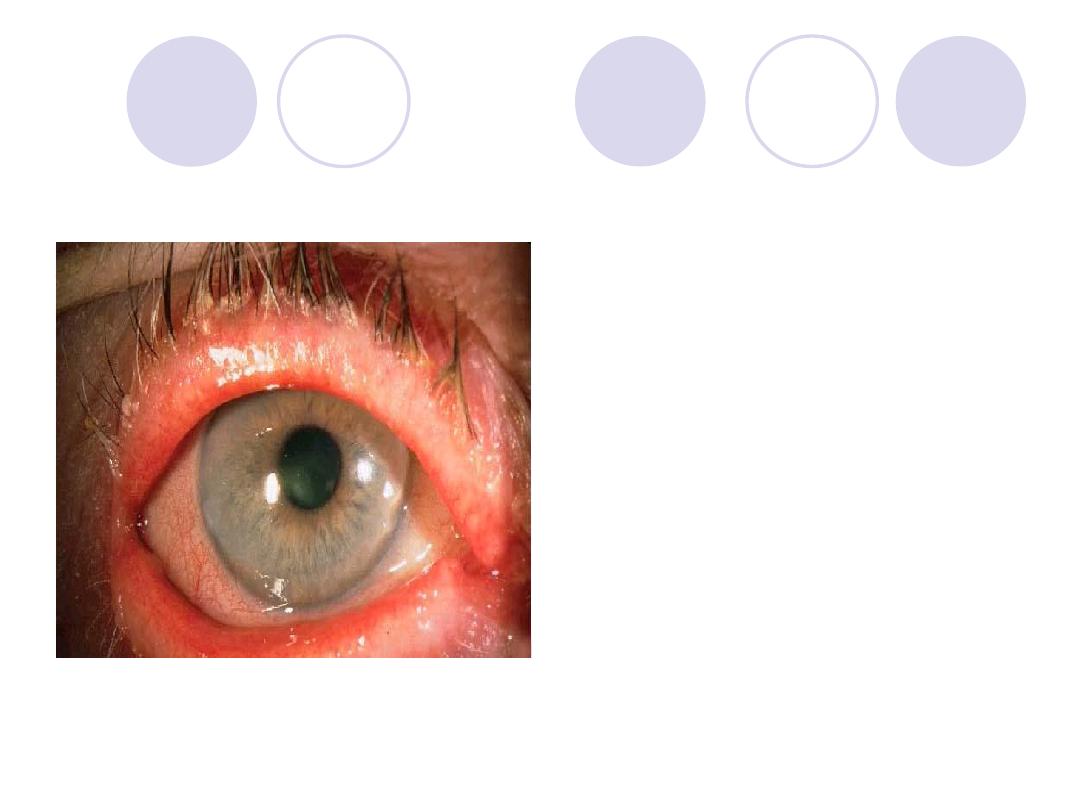
Comment on
lashes
complications
Answers:
-Ulcerative blepharitis
-Complications:
Chronic conjunctivitis,
Madarosis,
trichiasis, ptylosis, epiphora,
Ectropion, corneal ulcer.

What is this sign called?
pathogenesis
Answers:
Sign:
Marcus
–Gunn
phenomenon
Pathogenesis:
Faulty Innervation
“motor fibers from 5
th
nerve reach levator
instead of the 3
rd
nerve”
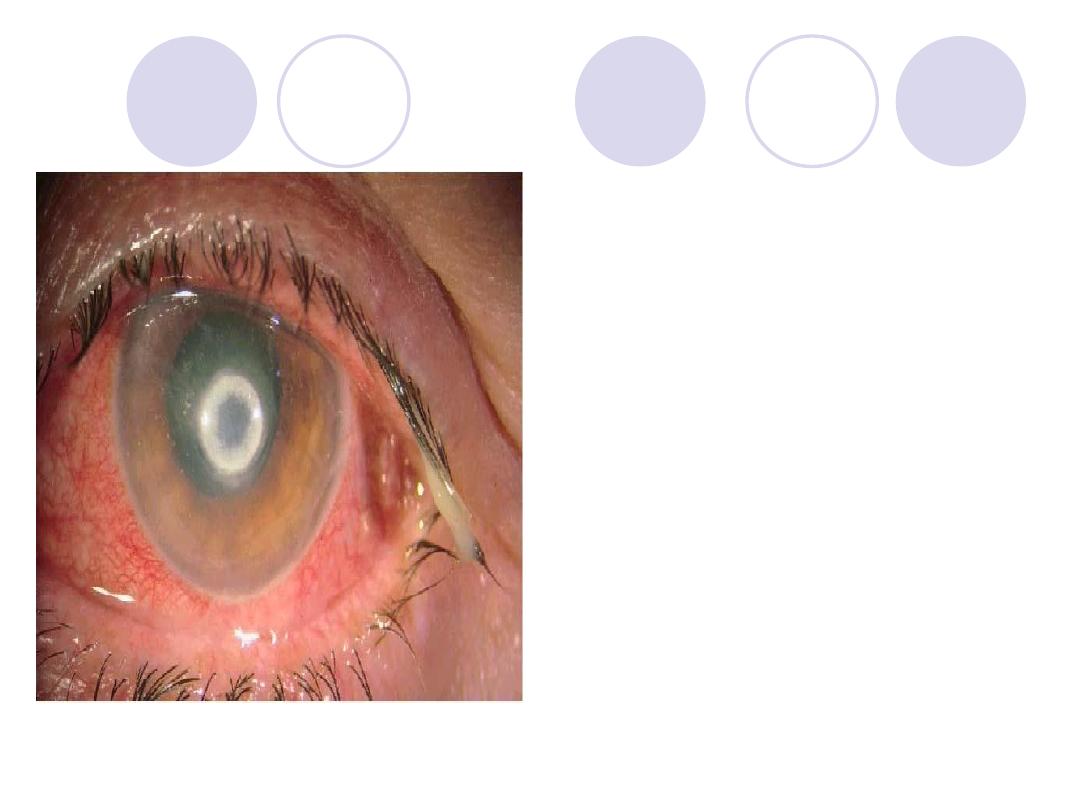
Diagnosis
treatment
Answers:
Diagnosis:
mucopurulent conjunctivitis
Ttt:
-Eye lotions
-Antibiotics ointments e.g.
tobramycin at night
-Antibiotic eye drops
-Hot foments
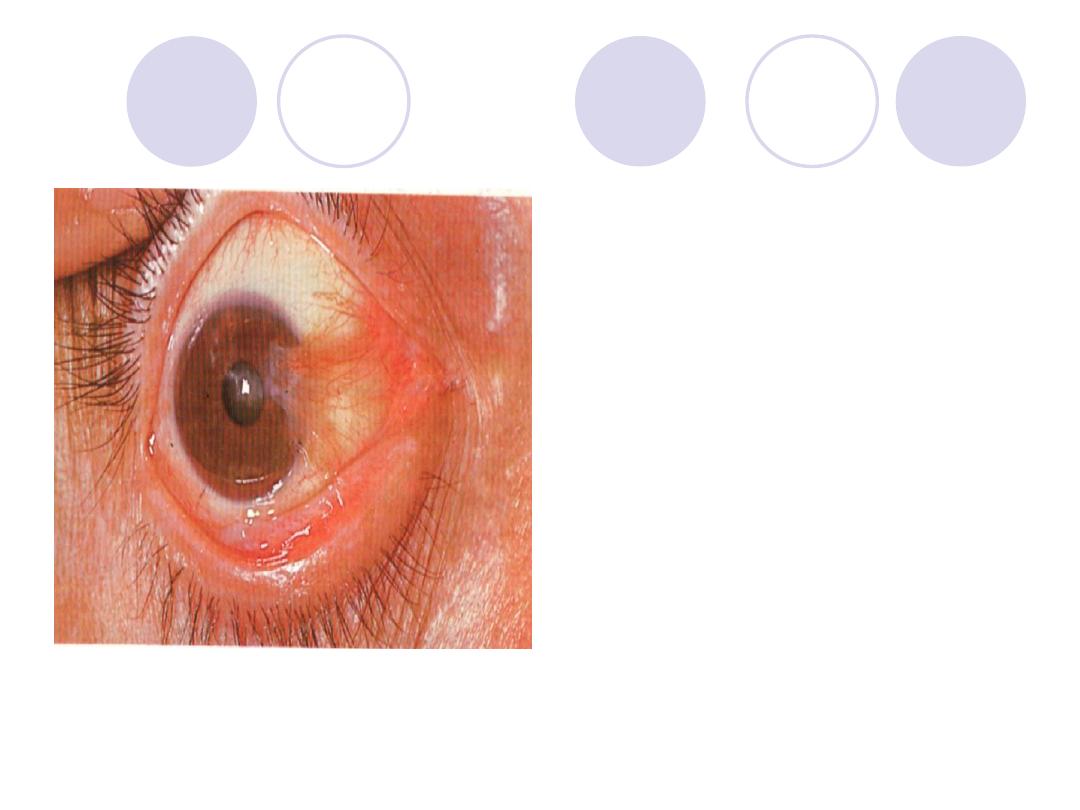
Comment on conjunctiva &
cornea
What are the indications of
surgical treatment ?
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Ptyregium
Comment :
Conjunctiva > conj. Epith.
hyperplasia
Cornea >covered by apex of
Ptyregium.
Indications of surgical ttt:
- If encroaches the pupillary area
- Progressive type
- Cosmetically annoying the patient
- Recurrent cases
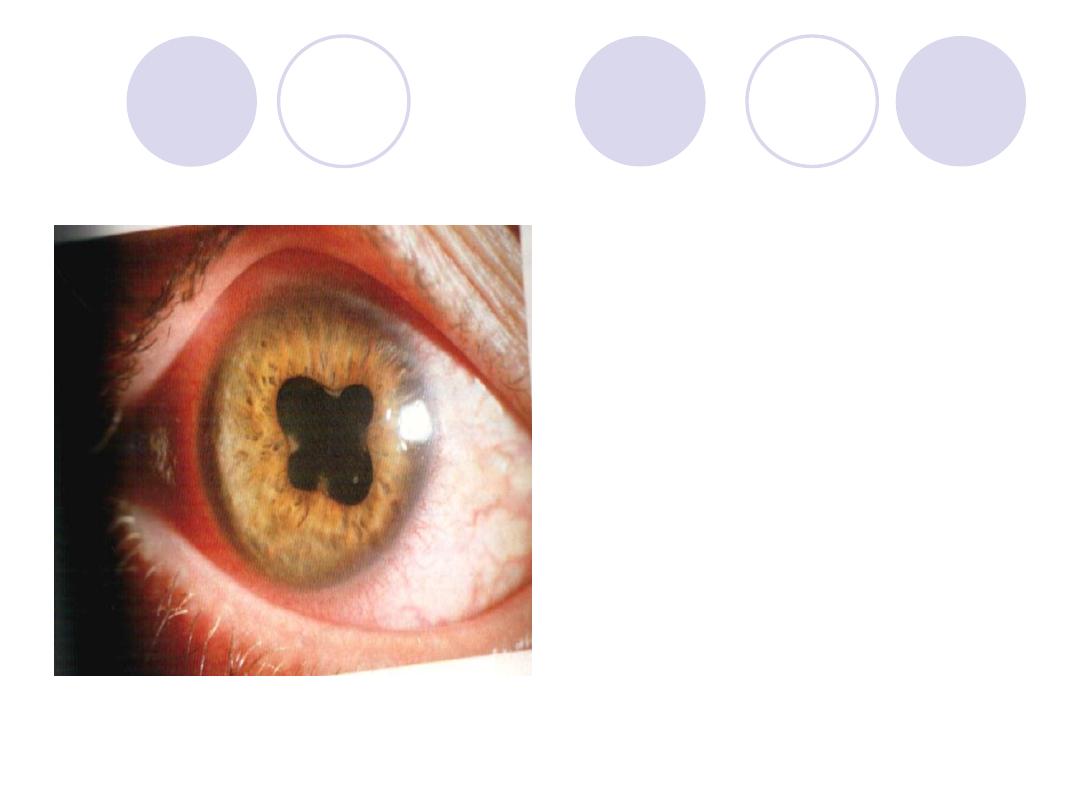
Cause of this appearance
2 eye drops
Answers:
Cause:
post. Synechiae
2 eye drops:
Atropine sulfate
corticosteroids
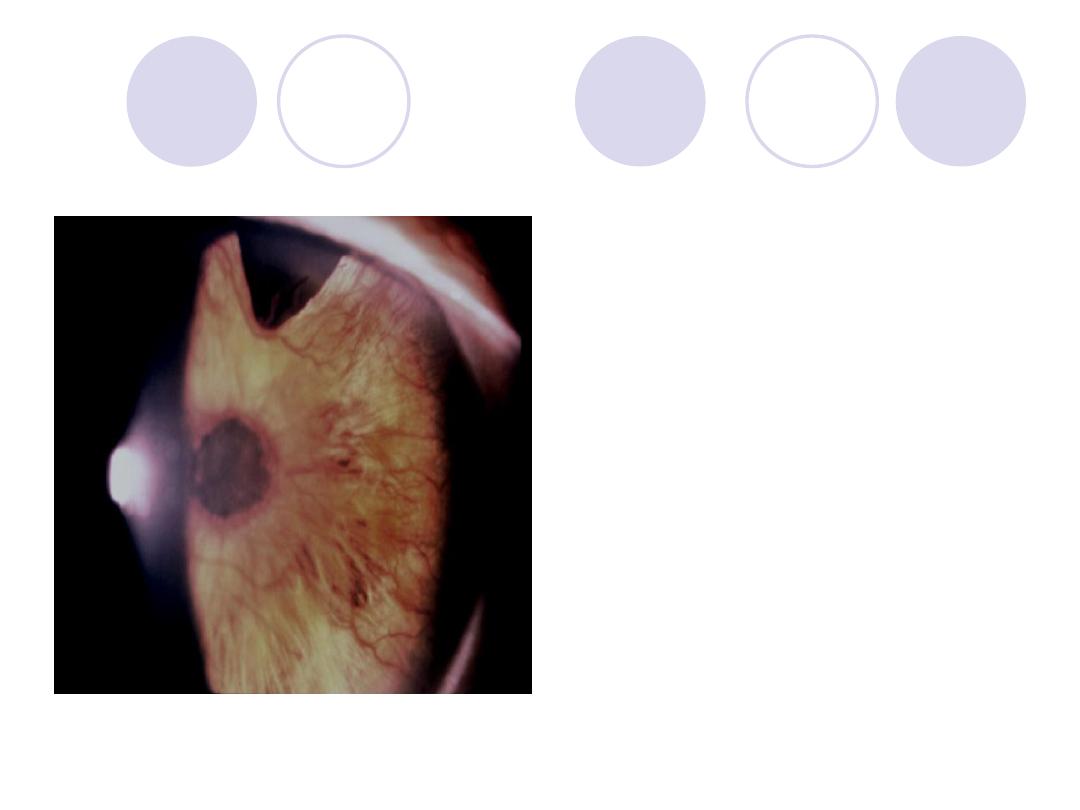
Diagnosis
Name 2 causes
Answer
Diagnosis :
rubeosis iridis
–
Peripheral iridectomy
Causes :
Diabetic Retinopathy and
CRVO
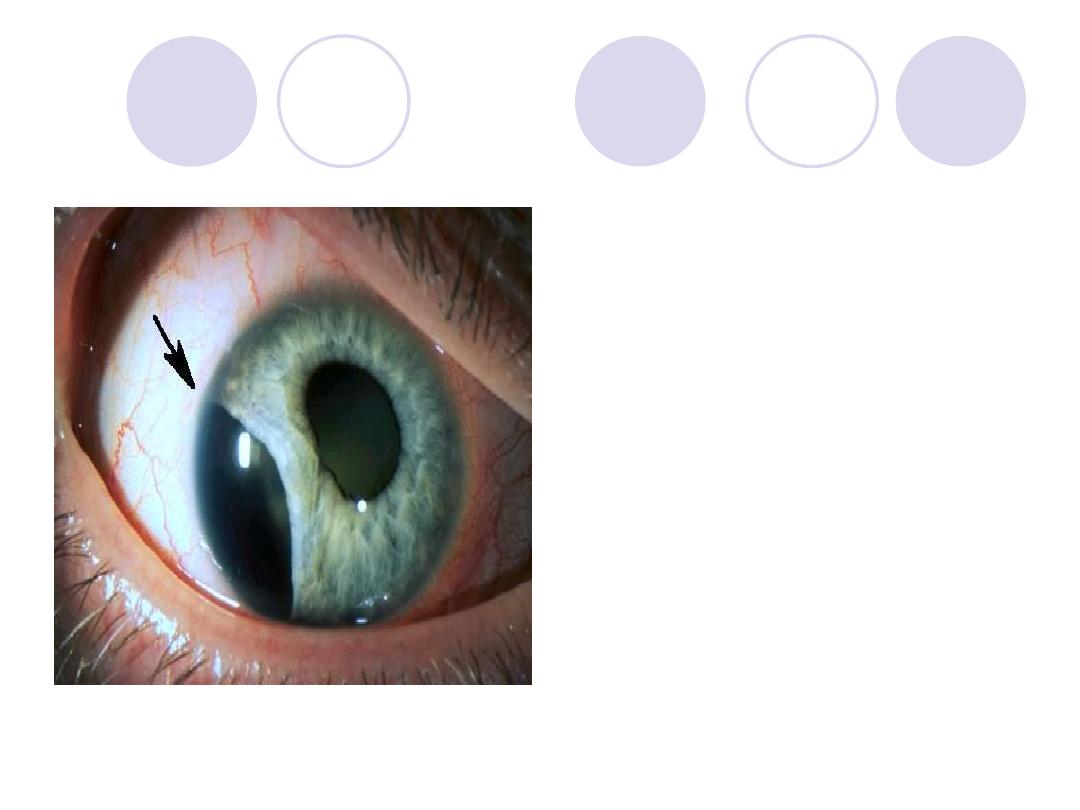
Diagnosis
What is the visual
complaint?
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Irido-dialysis
Visual complaint :
Uniocular diplopia

Diagnosis
Factors affecting prognosis
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Lt. congenital ptosis
Factors affecting
prognosis:
-
Amount of ptosis
-
Extent of levator function
-
If 3
rd
nerve palsy >> correct
squint first
-
If 5
th
nerve palsy >>
postpone the op. till 5
th
n.
regenerates .
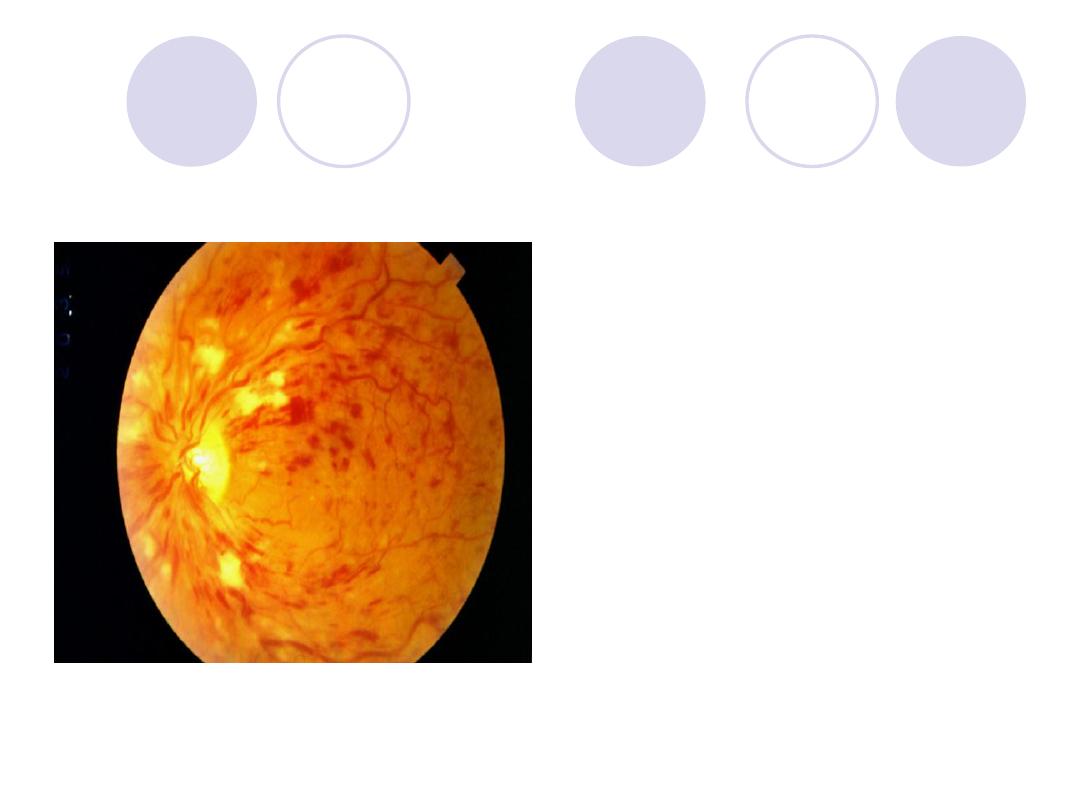
A 68y patient complaining of
sudden
diminution
of vision
.
What is the Diagnosis?
mention two systemic
predisposing condition
Answers:
Diagnosis:
CRVO
2 Systemic P.F.:
Systemic hypertension &
Diabetes mellitus
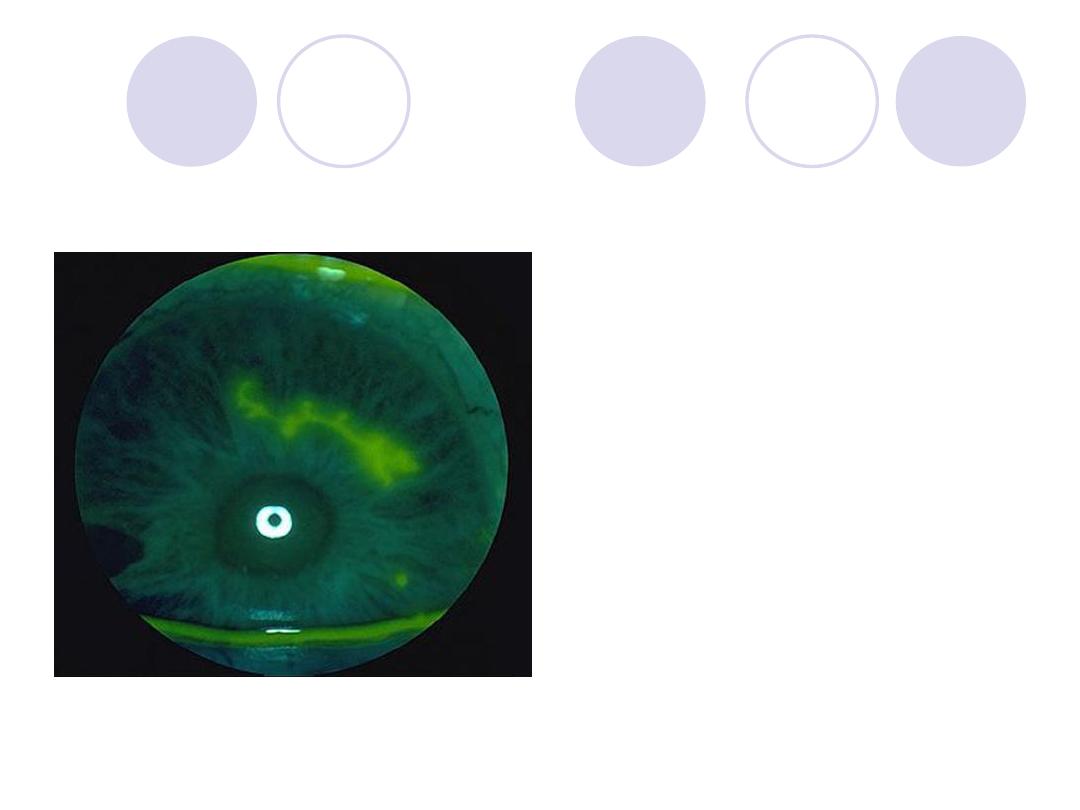
Diagnosis
Antiviral drugs for ttt
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Herpetic corneal ulcer
“Dendritic ulcer”
Antiviral drugs:
Acyclovir , vidarabine ,
T3F & IDU
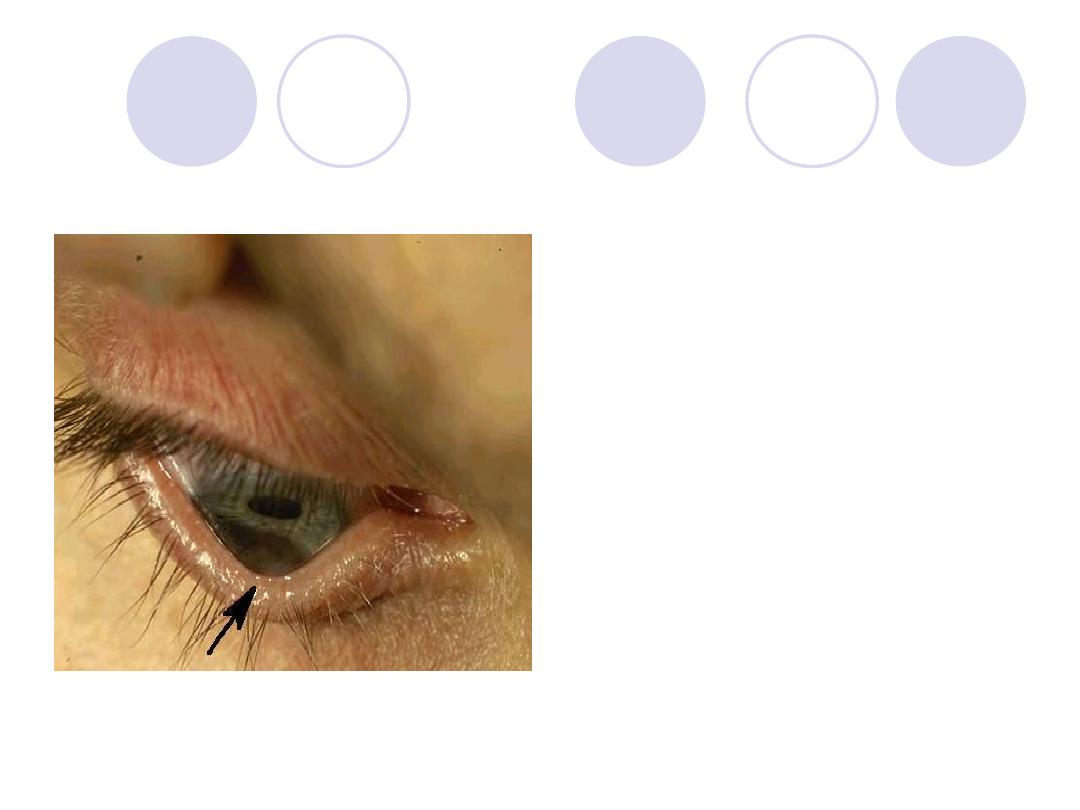
Diagnosis
What is the suspected
refraction of this patient?
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Keratoconus “ Munson`s
sign”
Suspected refraction:
axial myopia & Astigmatism.
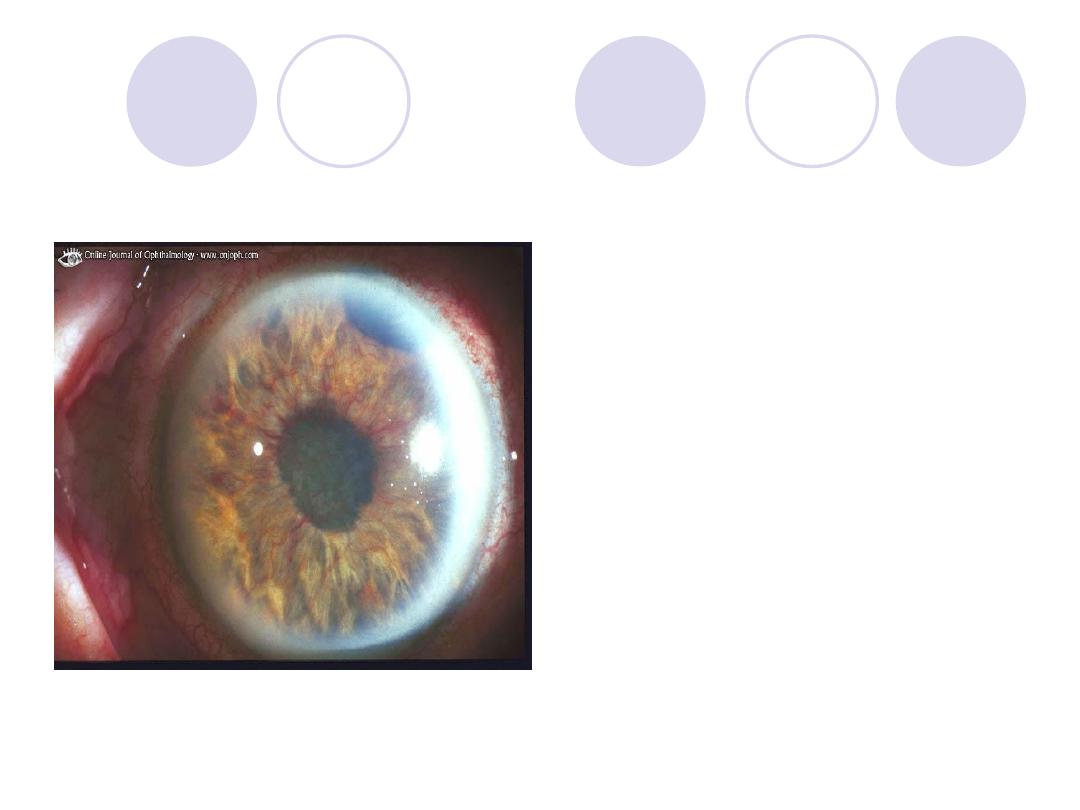
Diagnosis
2 posterior segment
diseases cause it
Answer
Diagnosis:
rubeosis iridis
Causes:
Diabetic
Retinopathy and CRVO
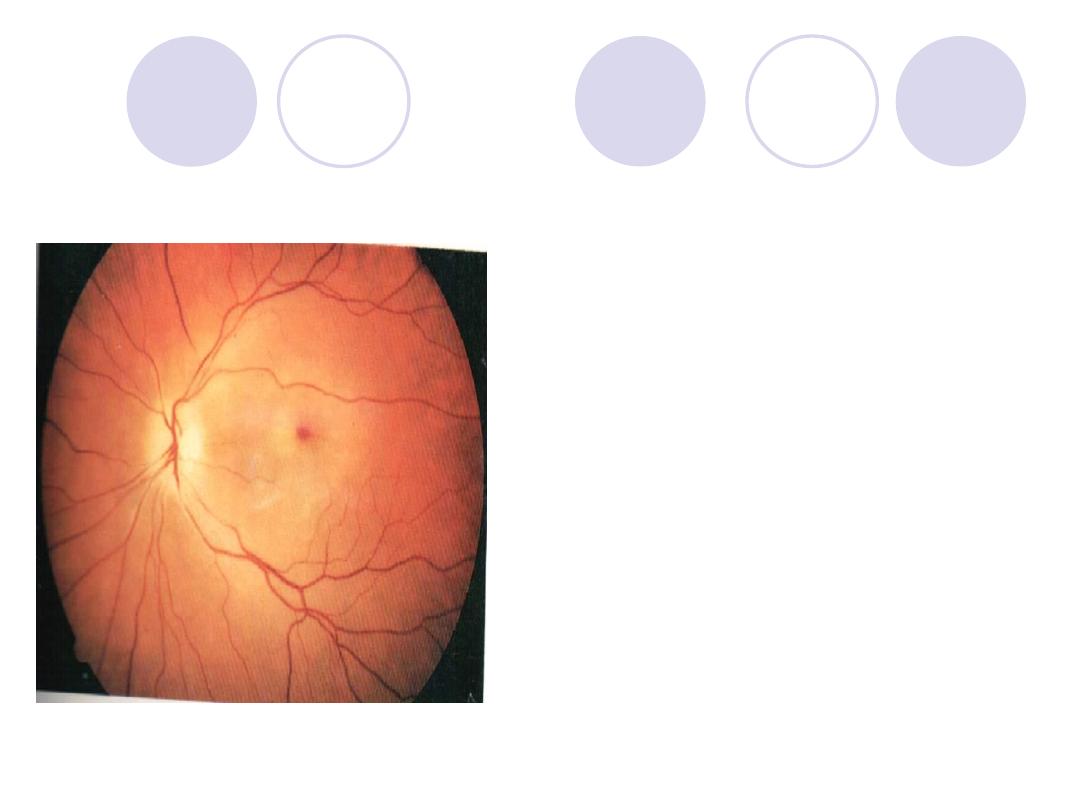
Diagnosis
Deferential diagnosis
Answers:
Diagnosis :
CRAO
D.D.:
“For cherry red
spot”
-
Commotio retinae
-
Quinine poisoning
-
Macular hole surr. By
RD
-
Amauratic family idiocy
Diagnosis
Expected field of vision
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Glaucomatous cupping of
optic nerve
-
Expected field of vision:
-
Tubular field.
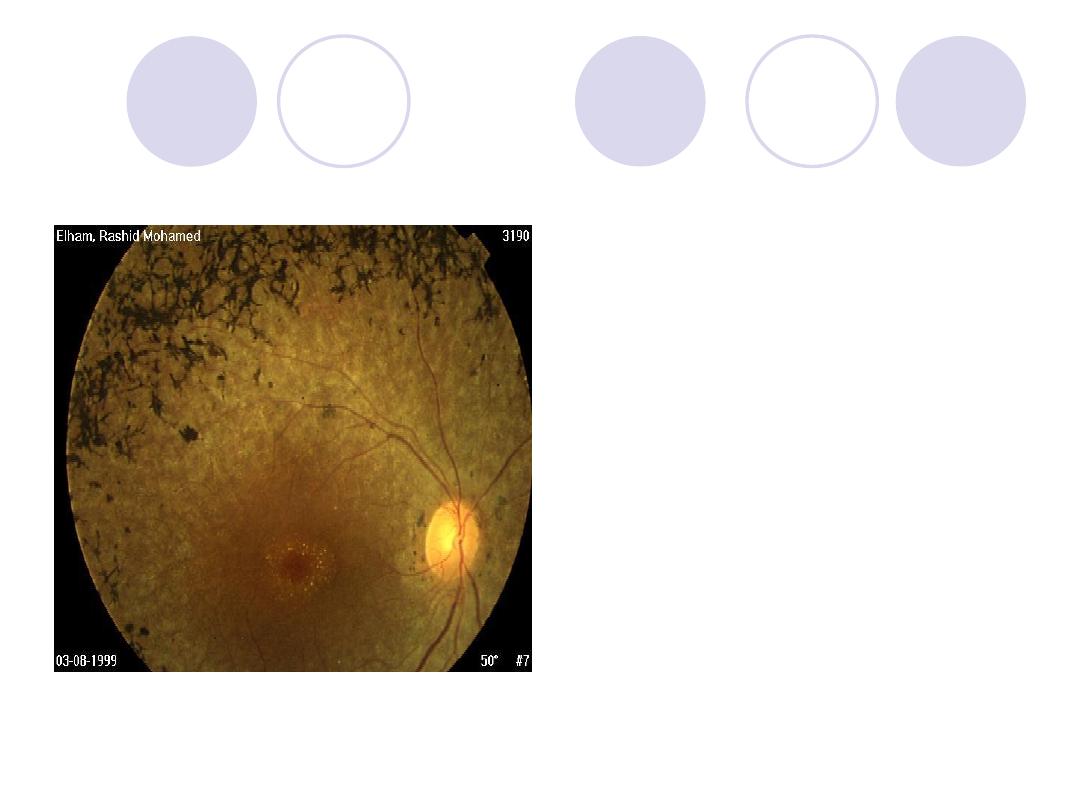
Diagnosis
2 syndromes associated with it
mention effect on optic nerve
Answers:
Retinitis Pigmentosa
2 Syndromes :
Bardet - biedl syndrome
Refsum’s disease
Effect on optic n.:
Waxy disc pallor due to
consecutive optic atrophy
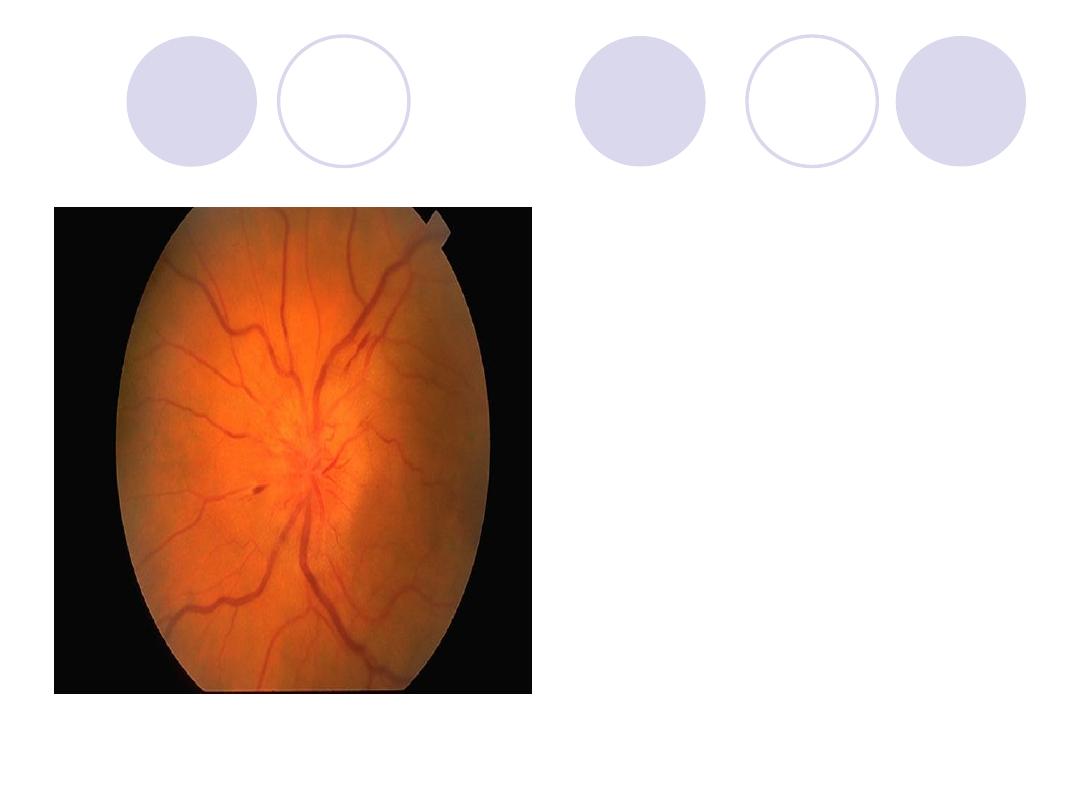
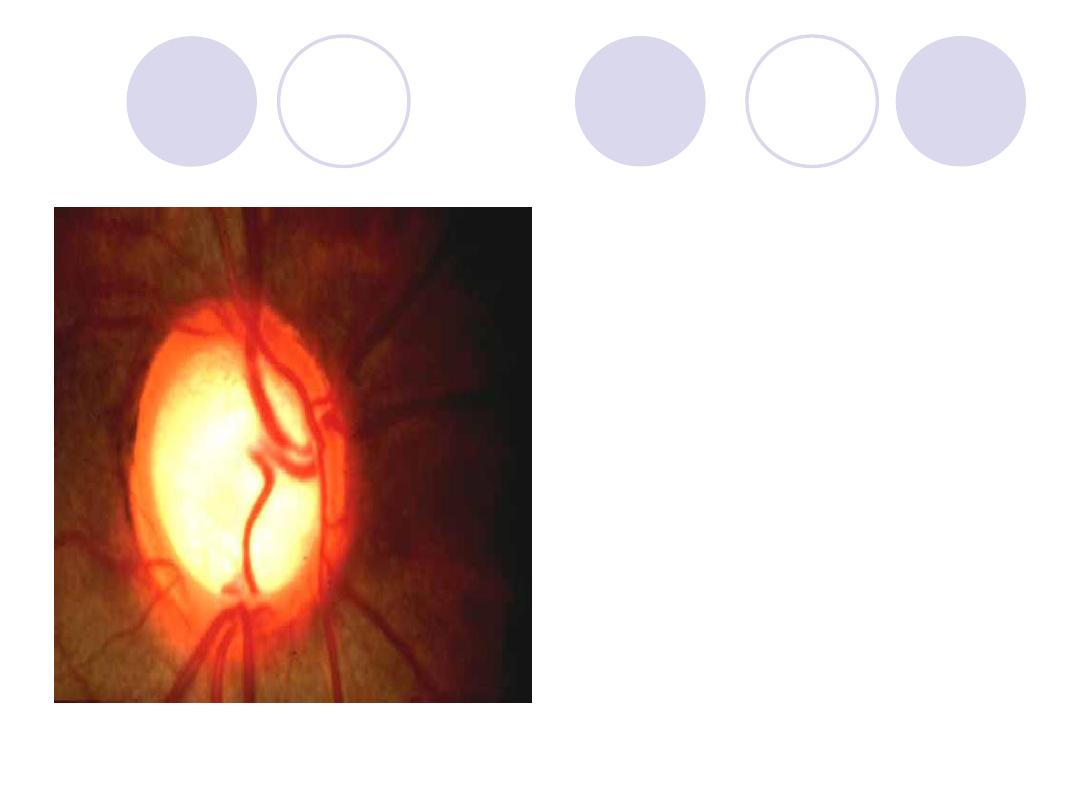
The optic disk of this
patient show…….
Name a cause for this
condition
Answers
Comment :
Papilleodema
Cause:
Elevated intracranial
tension.
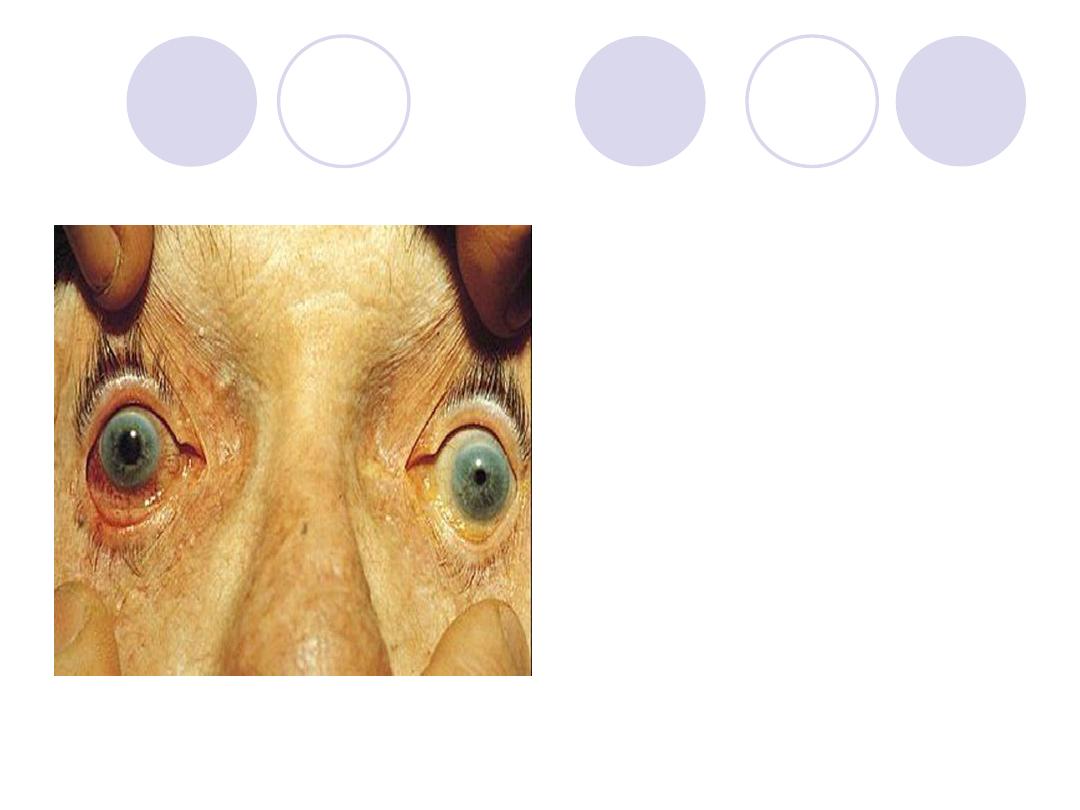
A 57y patient with sudden painful
drop of vision IOP is stony
hard
Name 2 medication for emergency
treatment of this case
Answer
Diagnosis:
Acute congestive
glaucoma
2 Medications for emergency :
hyper-osmotic agent, topical
miotics, topical steroids
Ttt: ttt essentially surgical
recent….surgical iridectomy
late….their is PAS ,an external
fistulizing operation
.
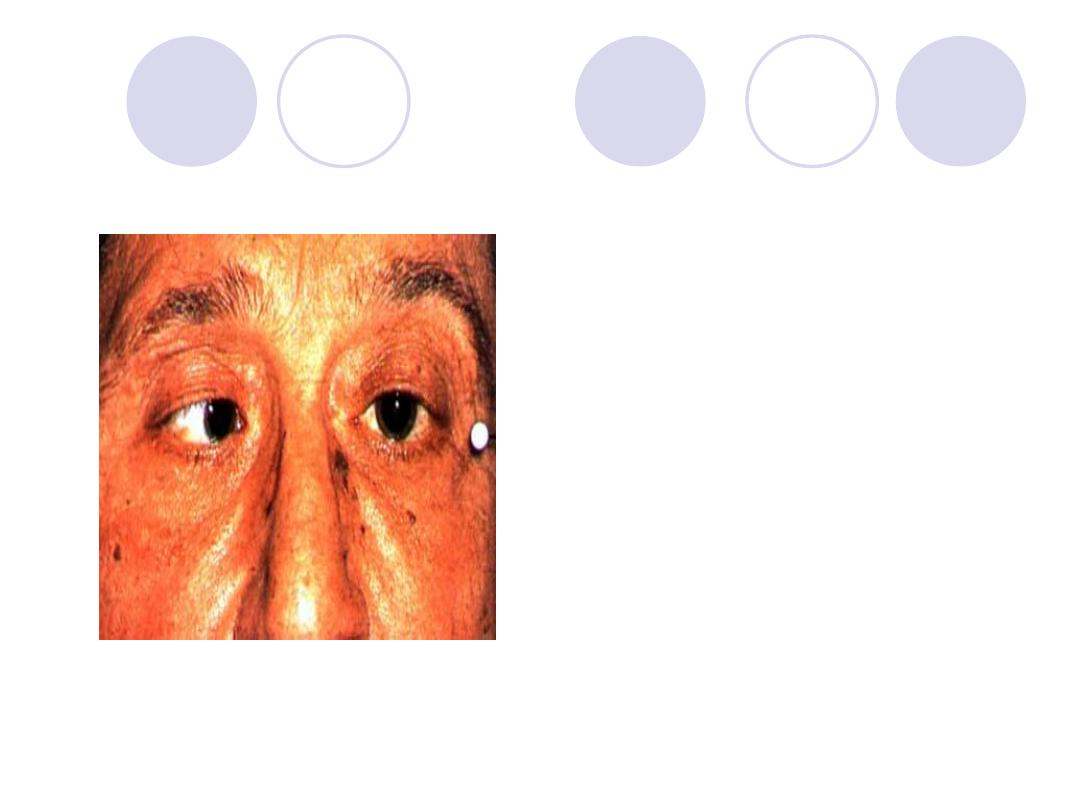
Nerve& muscle affected ?
Direction of gaze which diagnose
this case ?
The main complaint of the patient
Answer
Nerve& muscle
affected:
Rt Abducent
nerve-RT. Lateral rectus
Direction of gaze:
To
the right
Main complaint:
Binocular Diplopia
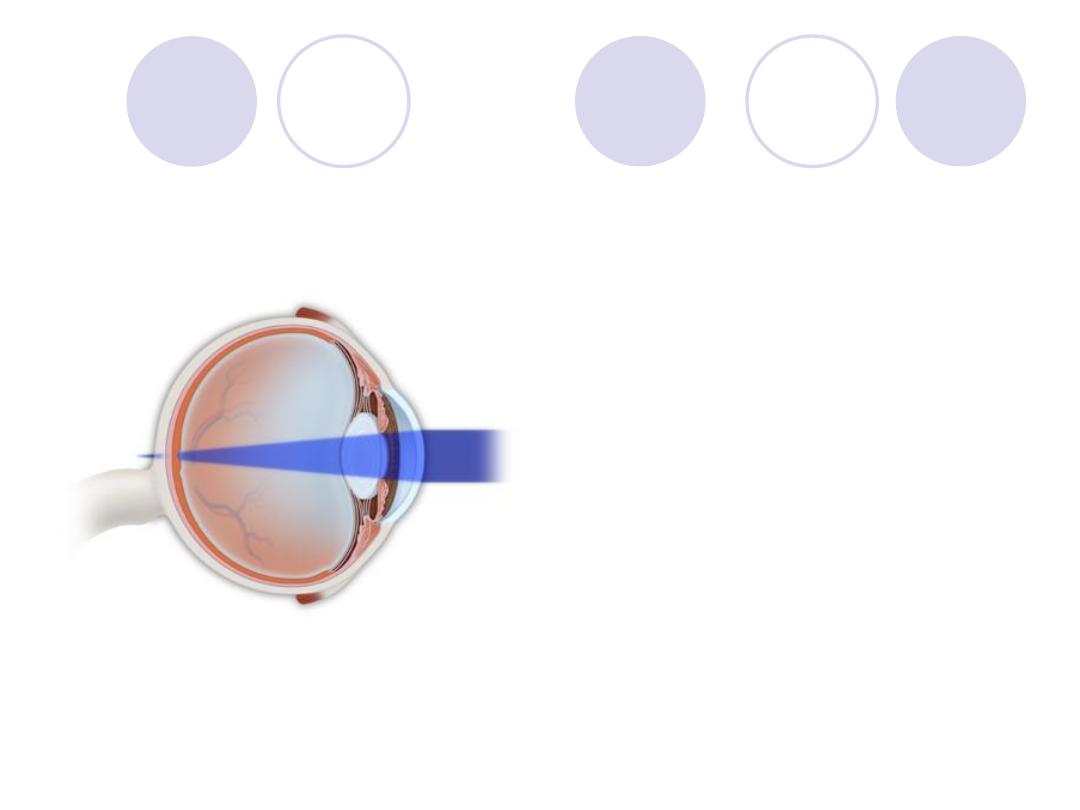
Diagnosis
Component of it
Answers:
Diagnosis:
hypermetropia
Components
:
Total , Latent , Manifest
hyperopia

Type of squint & its angle
Confirmatory test
Answers:
Type of squint :
exotropia
angle:
30
Confirmatory test:
Cover test
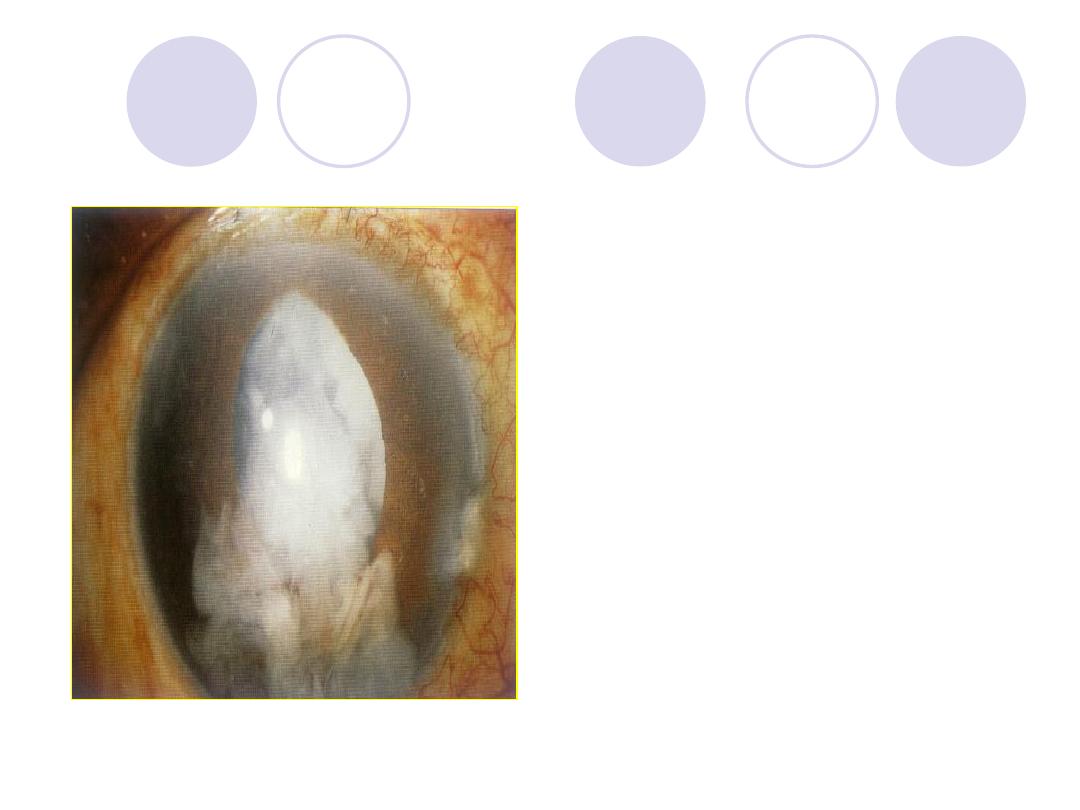
Diagnosis
treatment
Answers:
Diagnosis:
After cataract
TTT:
- No interference if vision
is not affected
- If thick : surgical
intervention
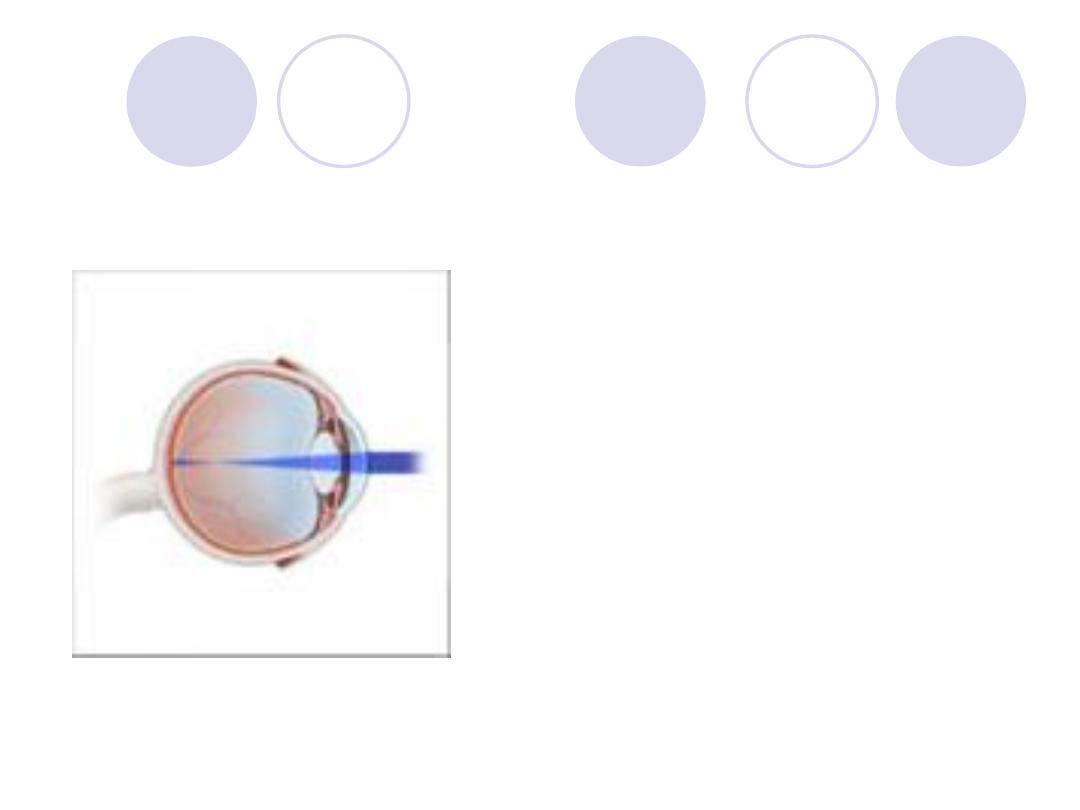
Diagnosis
treatment
Answers:
Diagnosis:
myopia
TTT:
- eye glasses with
concave minus lenses
- contact lenses
- refractive surgery if
indicated
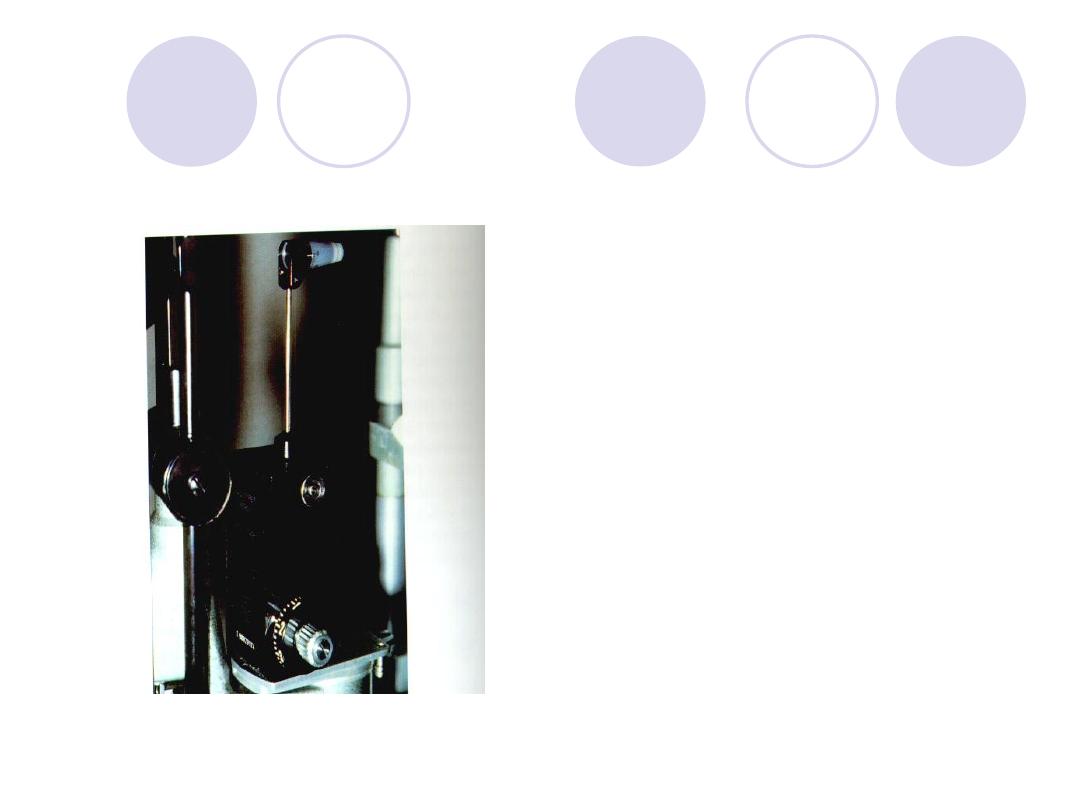
What s this inustrument
called
Used for……..
Answers:
Instrument:
Applanation tonometry
(gold mann)
usage:
IOP measurement
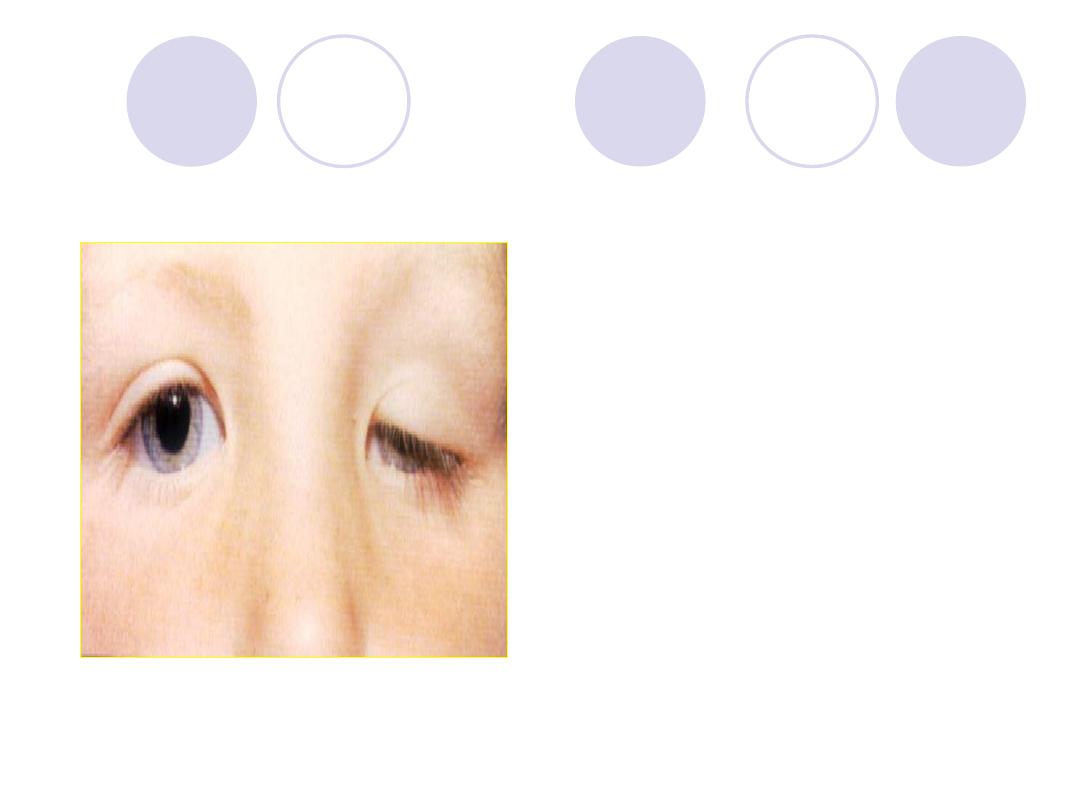
What is the upper lid abnormality?
What are the complications?
Answers:
Comment :
Left upper lid ptosis
Complications:
Amblyopia & Squint
scoliosis and ocular
torticollis.
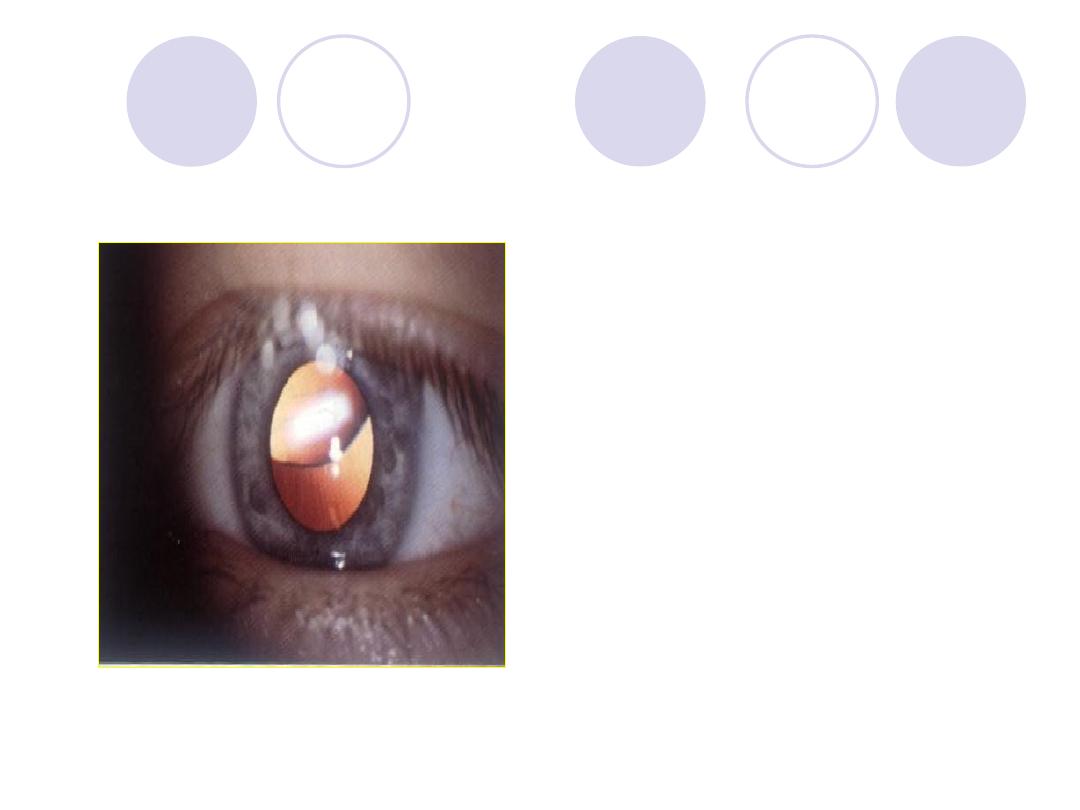
Comment on lens
This is an association
of………..syndrome
Answer
Comment :
lens subluxation
Syndrome:
Marfan’s syndrome
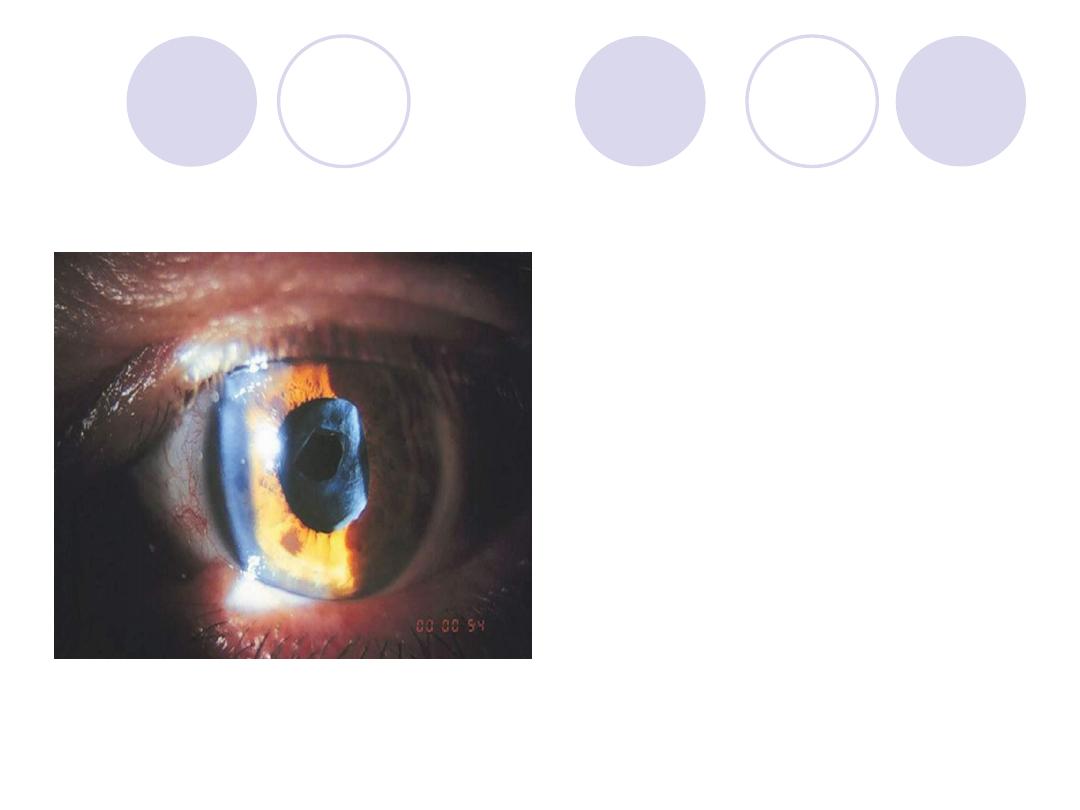
A 68y old woman with cataract
extraction . Complaining of
drop of vision which was
managed
What was the cause of drop of
vision?
What was the management?
Answer
Cause:
posterior capsular
opacification (after
cataract)
Management:
YAG laser capsulotomy
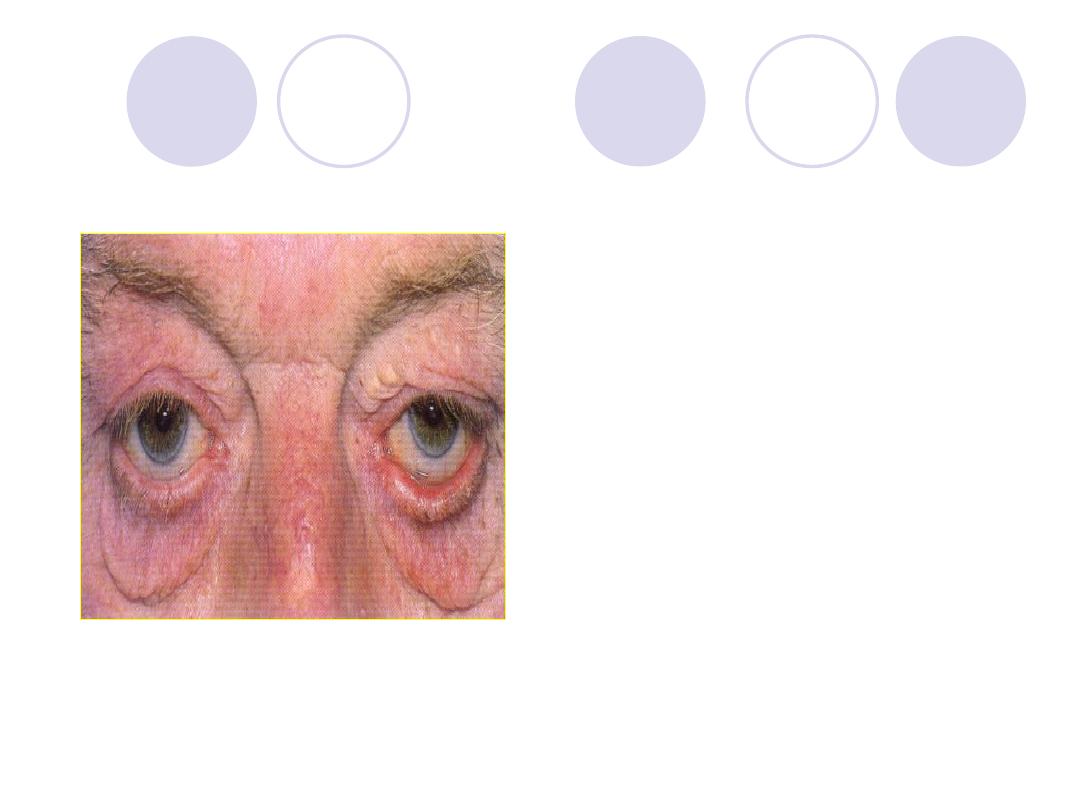
Comment on the lower lid
Name 2 possible
complications of this
conditions
Answers:
Comment:
Senile ectropion
2 possible complications:
xerosis
corneal ulcer
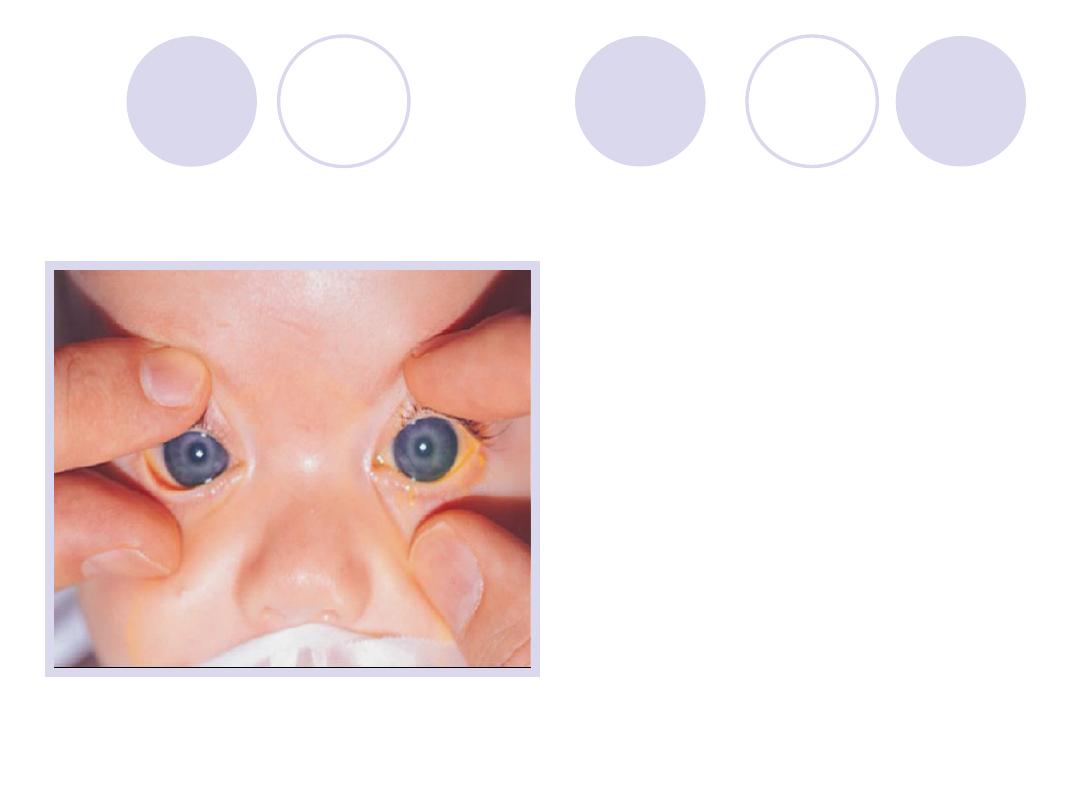
Diagnosis
Name 2 surgical
procedures for ttt of this
condition
Answers:
Diagnosis :
Buphthalmos
2 Surgical procedures:
-goniotomy
-trabeculotomy

What are these field
defect called?
Name the cause
Answer
Field defect:
Bitemporal hemianopia
Cause:
Optic chiasma lesions
(nasal fibers damage)
e.g. Pituitary gland tumor
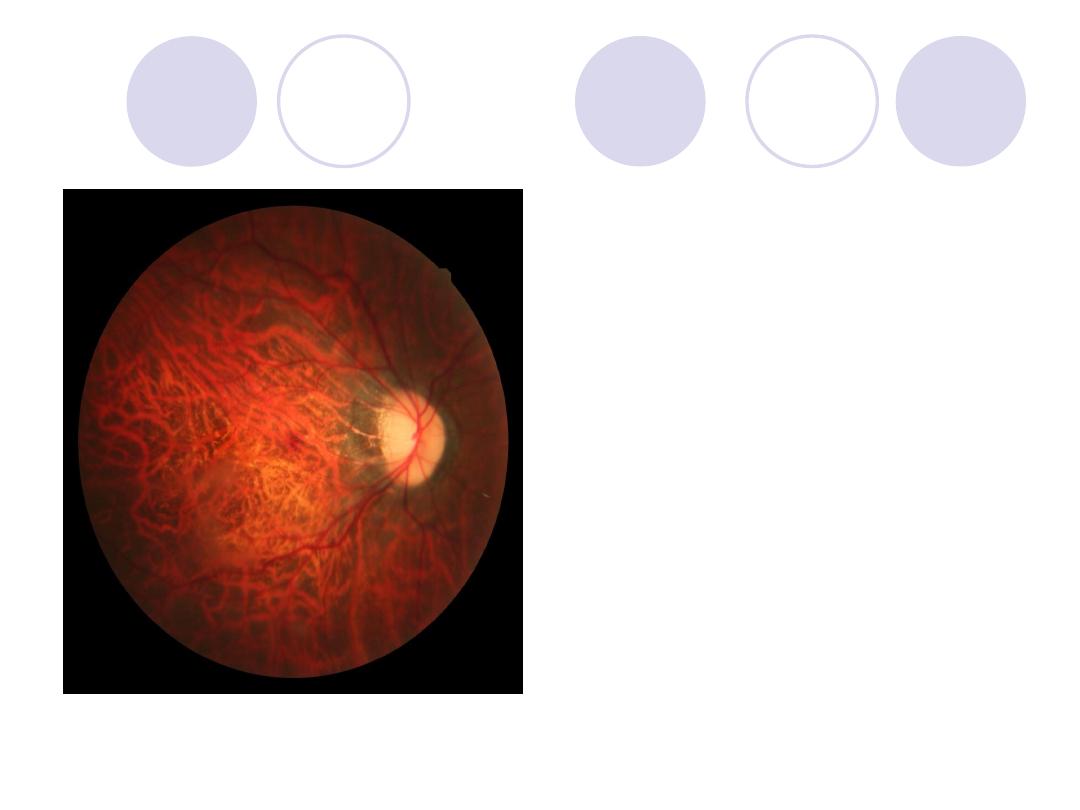
What's the error of
refraction in this patient ?
What're the complications
of this case ?
Answer
Error of refraction :
High myopia
Complications:
Chorio-retinal degenerations
retinal tears
retinal detachment
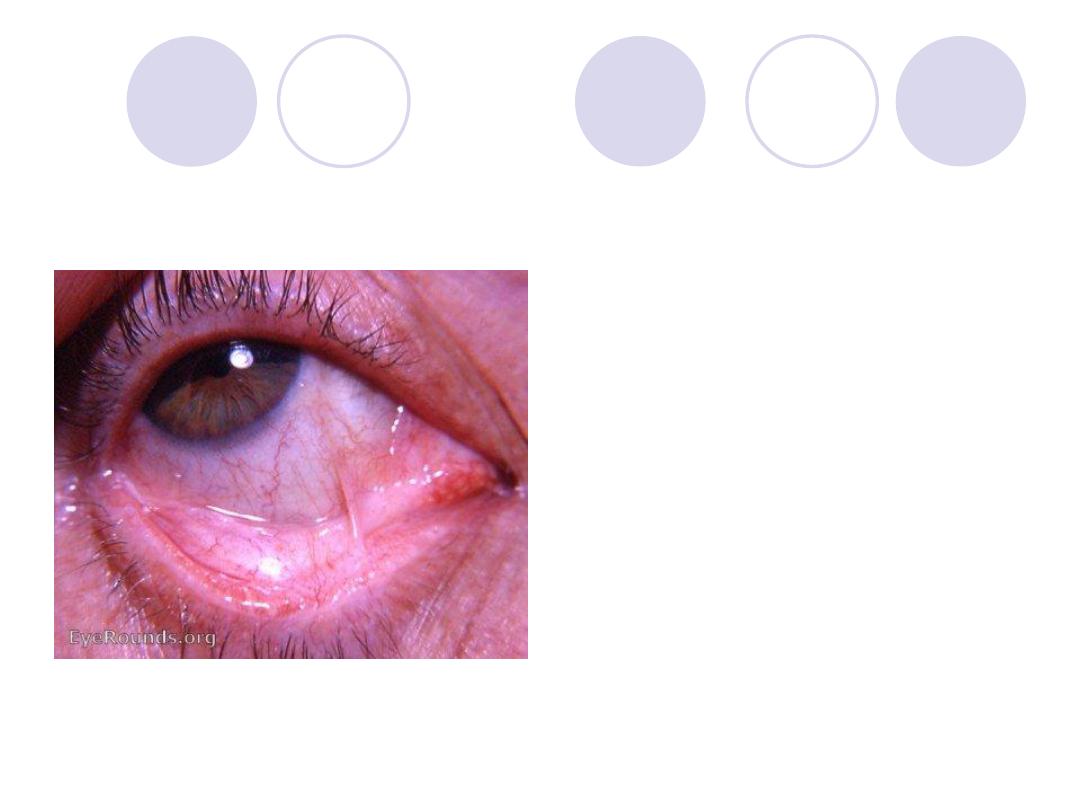
Diagnosis
3 causes
Answers
Diagnosis:
Symblepharon
Causes:
- Post-trachomatous
- Post-operative ( Pterygium
excision)
- Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
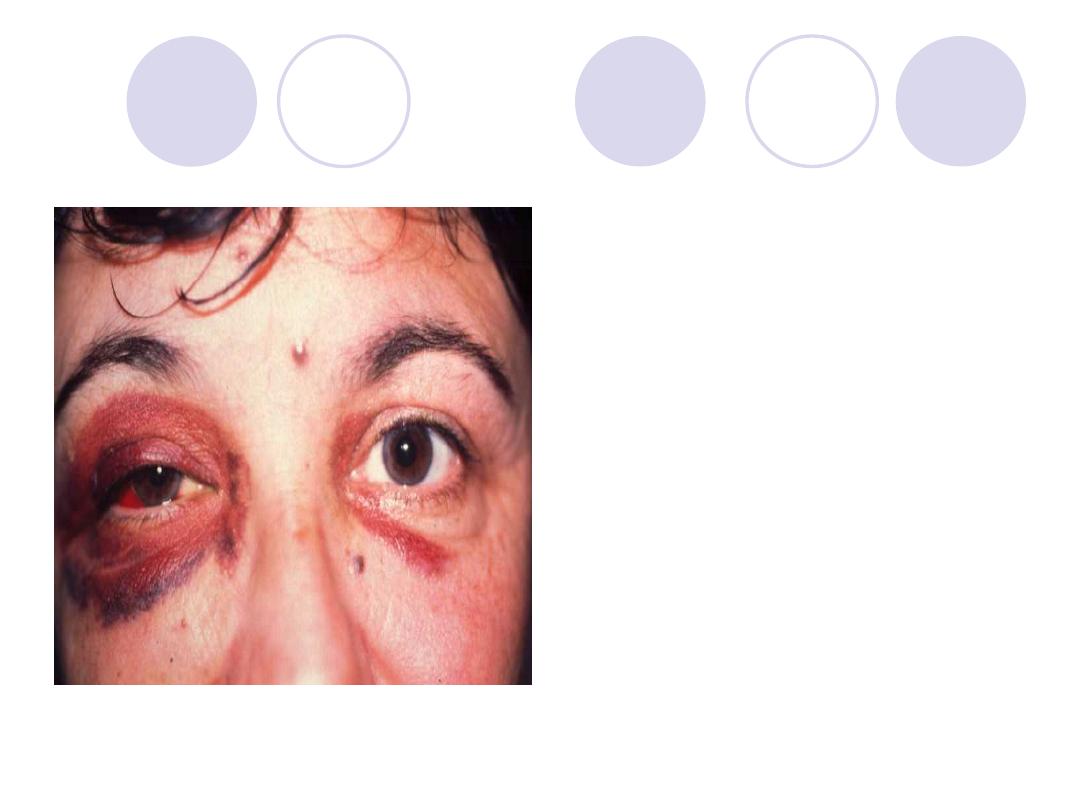
The eye lid & Conjunctiva
show
possible findings in the
crystalline lens
Answers
Comment :
Ecchymosis & subconjunctival
hemorrhage"
Possible findings:
(Concussion cataract "
Rosette-shaped" - Lens
subluxation or dislocation
)
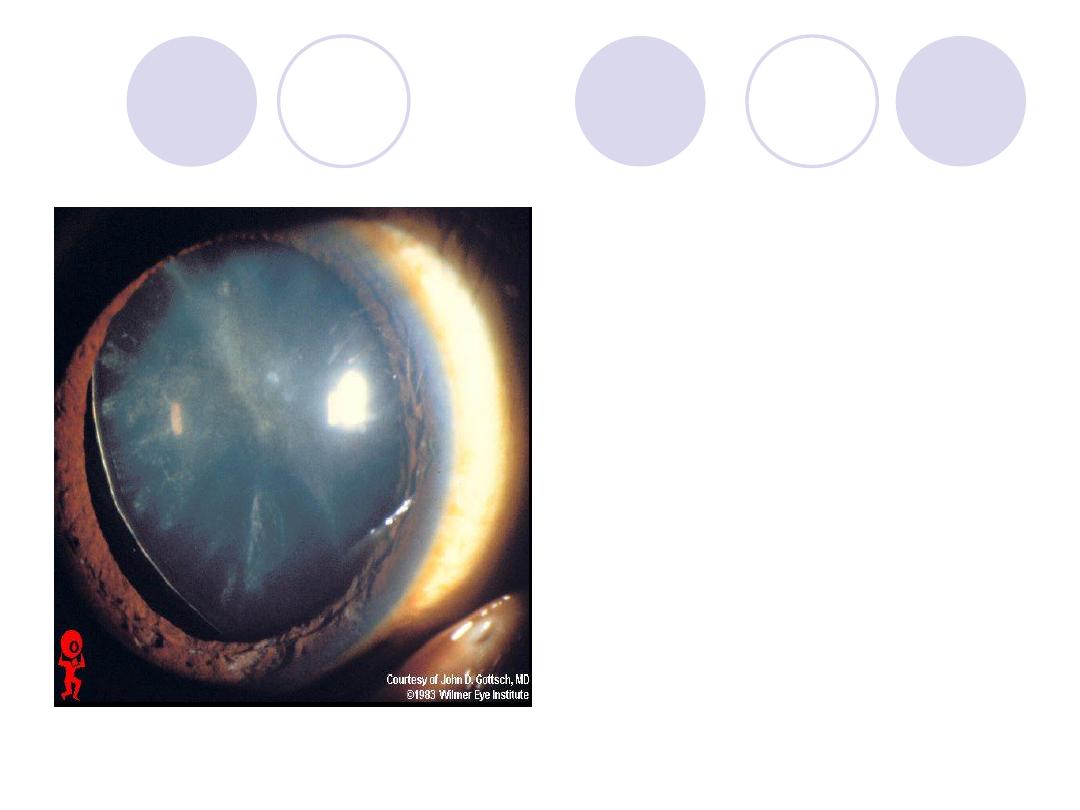
Diagnosis
2 causes
Answers:
Diagnosis :
Lens subluxation
Causes:
Marfan's syndrome
Homocystenuria &
Trauma
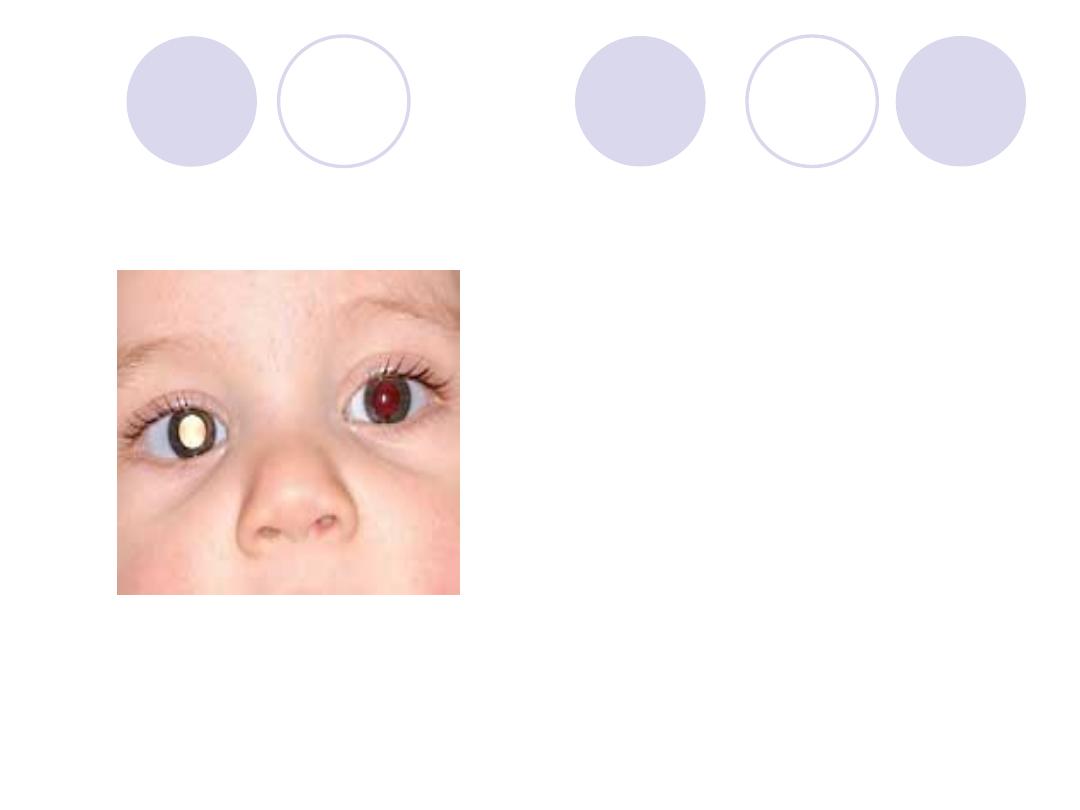
What's the sign called ?
3 possible causes
Answers
Sign :
Leukocoria
Causes :
Retinoblastoma
congenital cataract
Retinpathy of prematurity
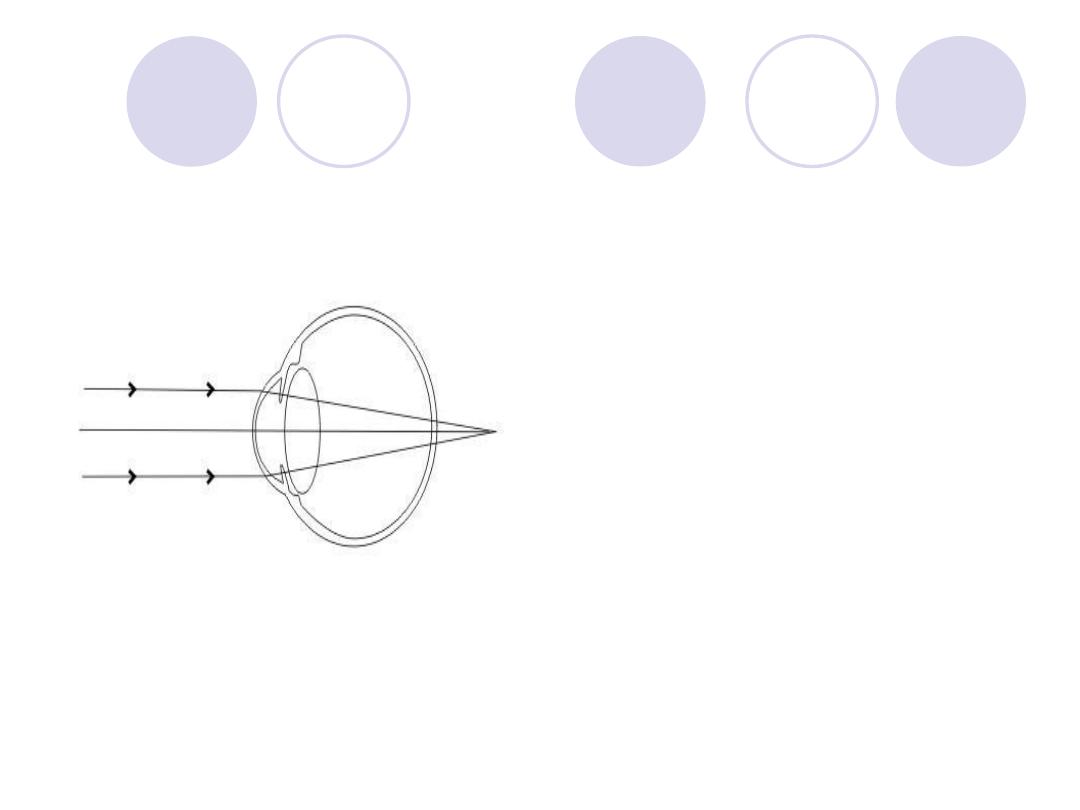
What is the error of
refraction ?
How to correct ?
Answers
Error of refraction:
Hypermetropia
Correction :
Spherical Convex "plus"
Lens
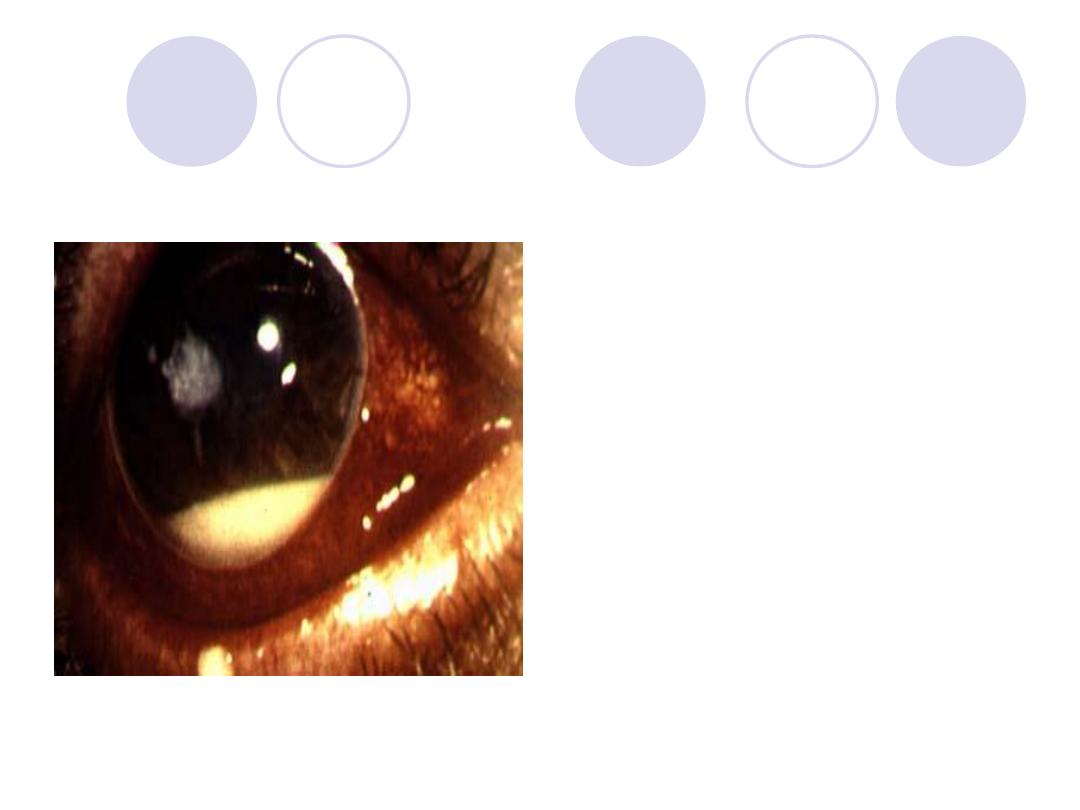
Diagnosis
mention caustive
organism
Answers:
Diagnosis :
Hypopyon corneal ulcer
Causative organism:
pneumococci
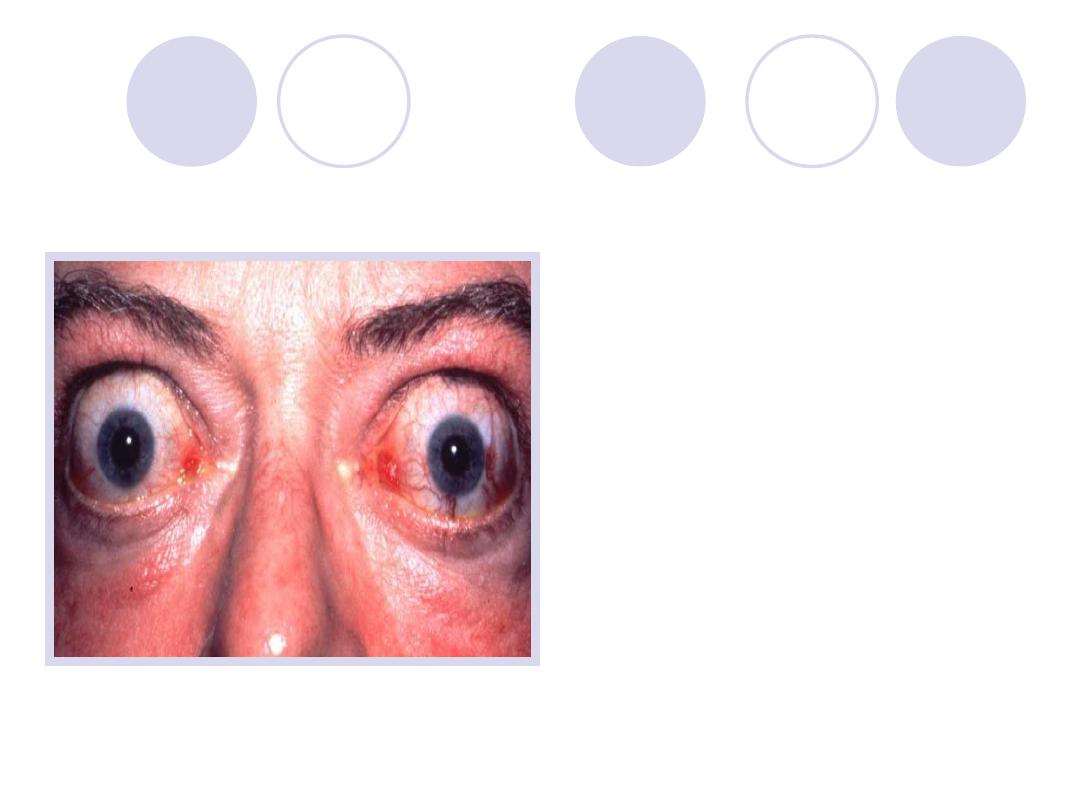
Diagnosis
Mention disease cause
this
Answers:
Diagnosis:
exophthalmos
Disease :
Hyperthyrodism
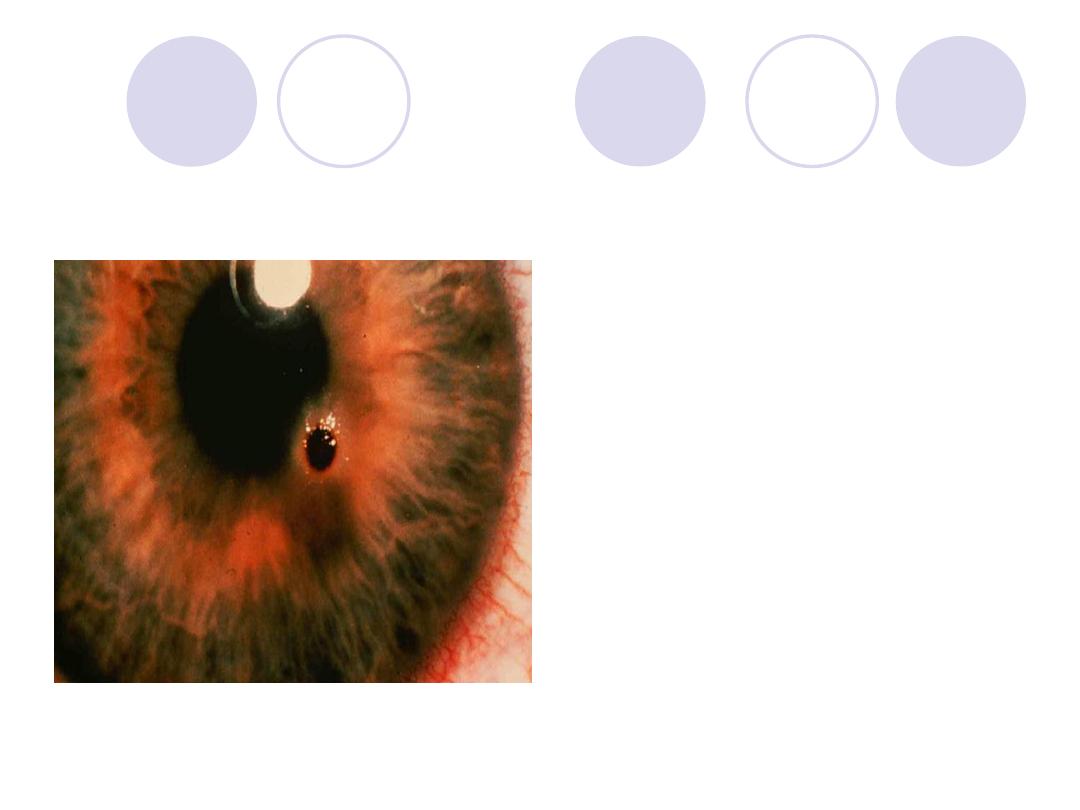

Diagnosis
treatment
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Corneal
foreign body
TTT:
Surgical removal

Diagnosis
mention muscle
affected and its nerve
supply
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Left upper lid
ptosis
Muscle affected :
levator palpebrae sup.
innervation:
oculomotor n.
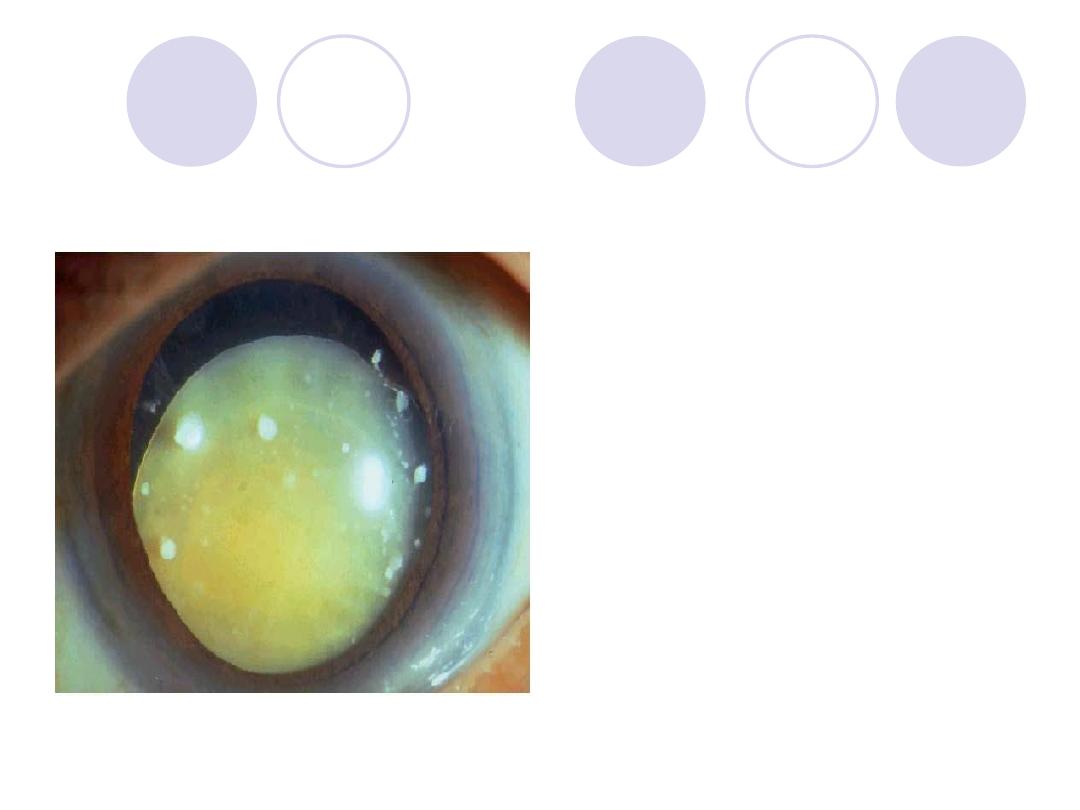
Diagnosis
Mention 2 complications
Answers:
Diagnosis
:
sublaxated &cataractous
lens
Complications
:
lens dislocation
2ry Glaucoma
Iridocyclitis
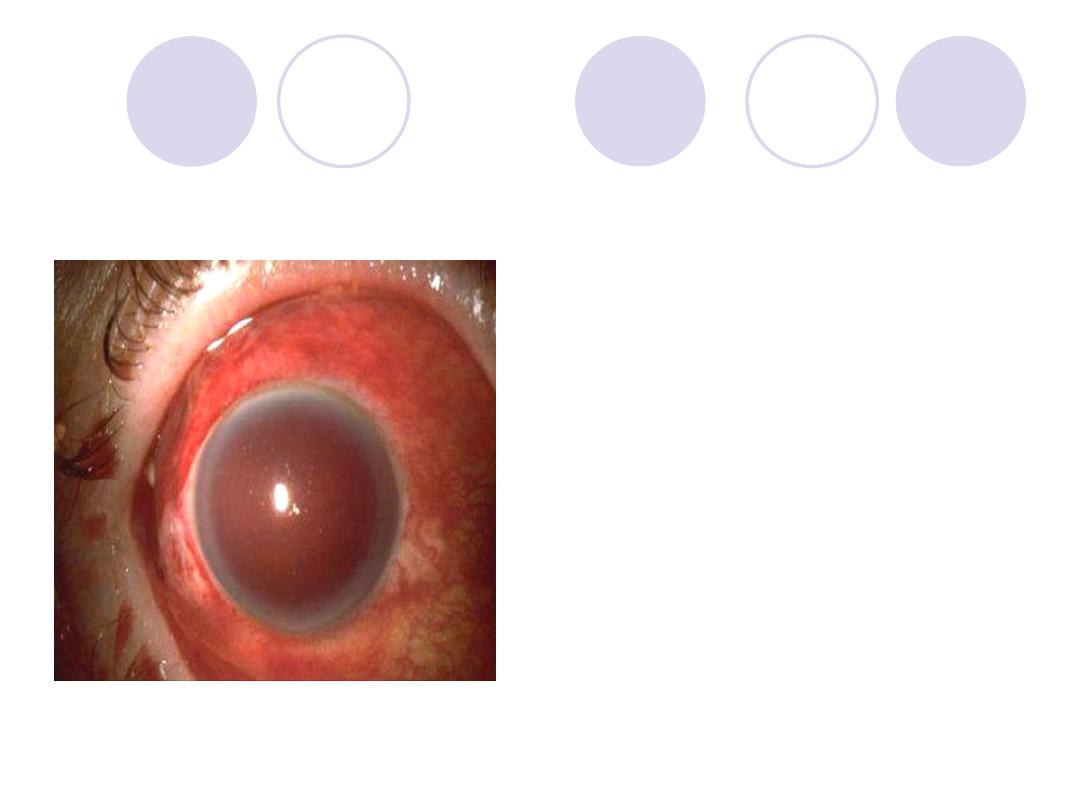
Diagnosis
Mention 2 complications
Answers:
Diagnosis:
Blood staining
of the cornea “total
hyphema or 8-ball
hyphema”
2Complications:
Elevation of IOP
Corneal staining
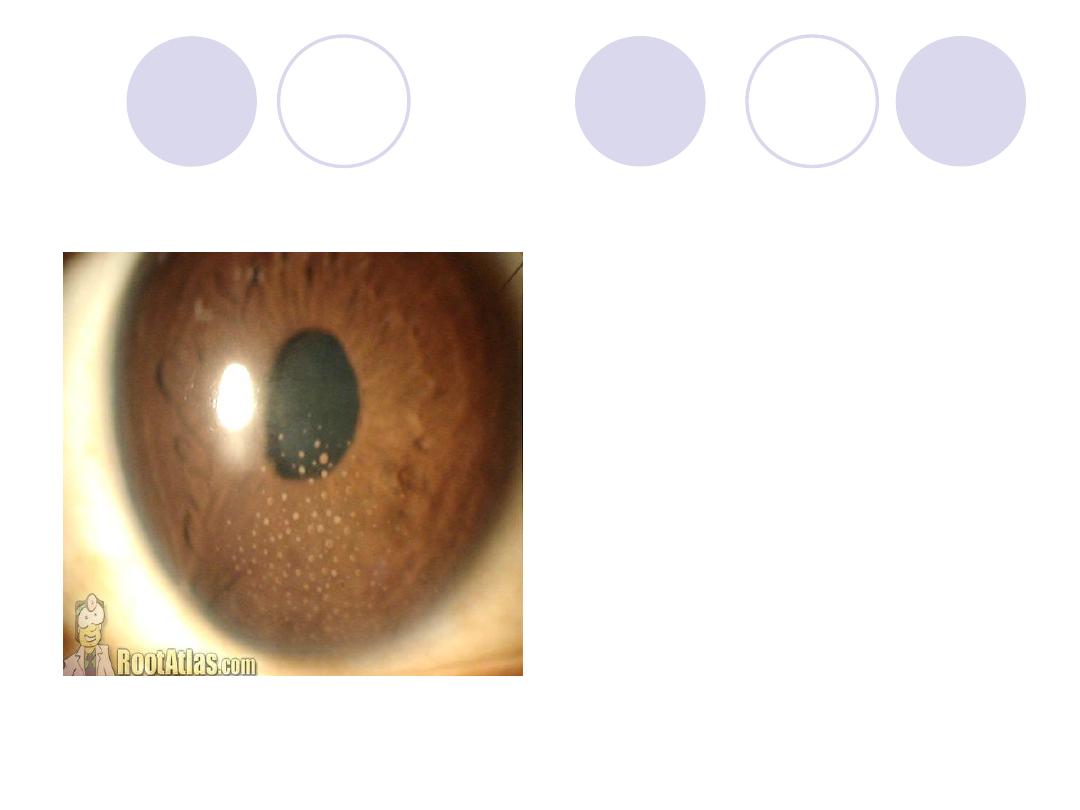
Diagnosis
Mention 2 ttt
Answers:
keartic precipitates
ttt :
Topical : Atropine sulfate
& corticosteroids.
Systemic: systemic
steroids (in severe
cases)
& Antibiotics (in infective
cases)

sederosis bulbi
Patient with foreign body in his eye
from one year
In picture you will see one eye normal
&other eye(black iris)
