Ophthalmology
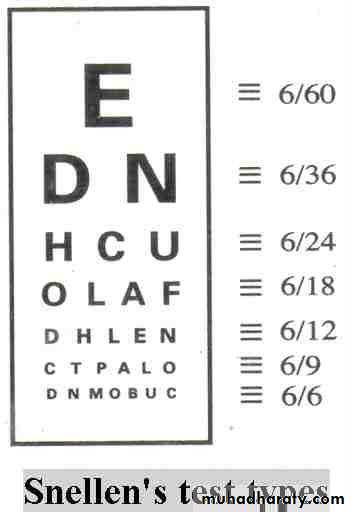
For assessment of visual acuity
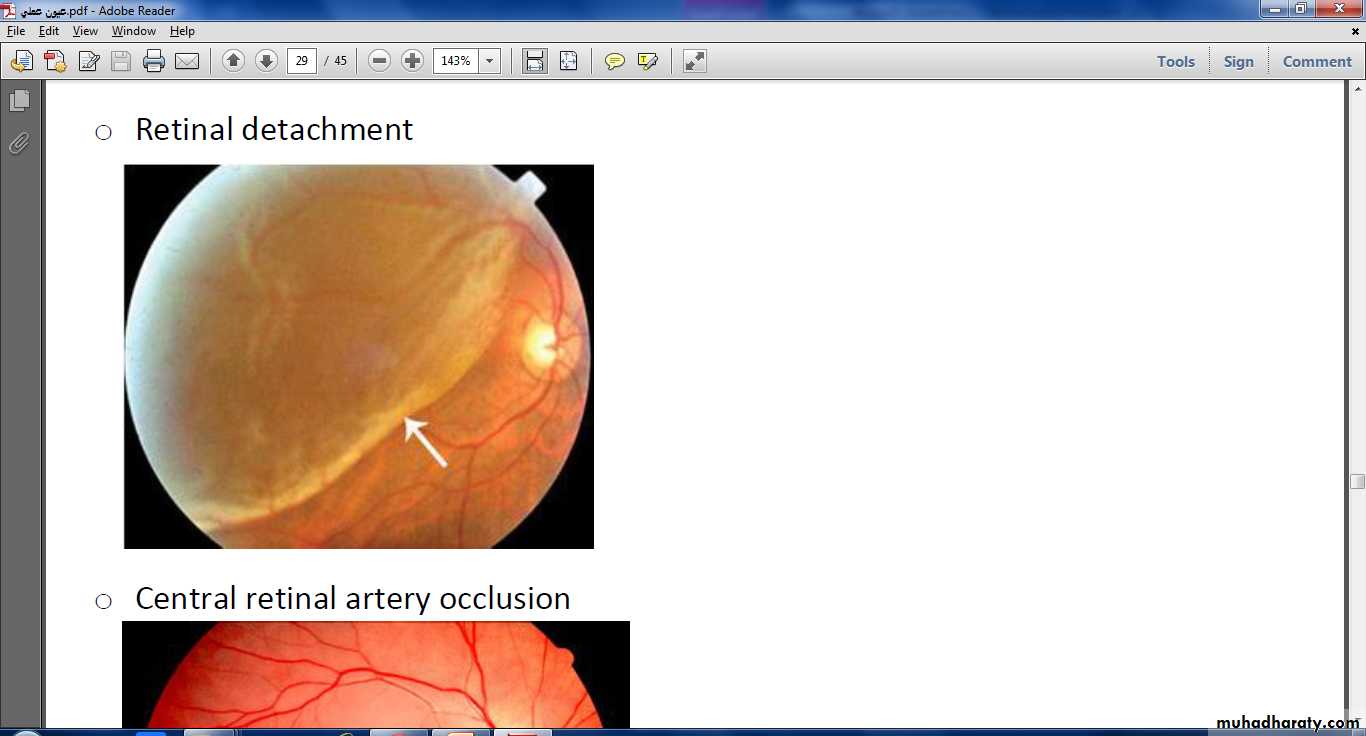
Direct ophthalmoscop:to examine fundus
Indirect ophthalomscope: to examine fundusCondensed lens:it is used with the slit lamp to examine fundus
Goldman 3 mirrors contact lens: it is used with the slit lamp to examine fundus
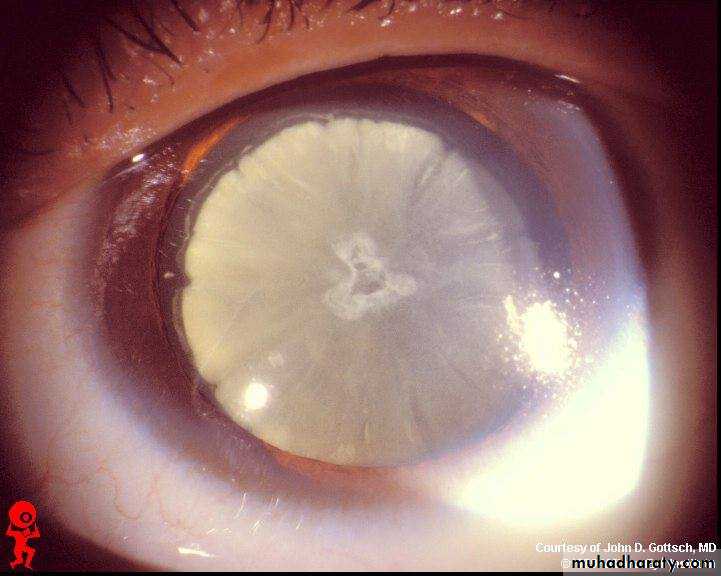
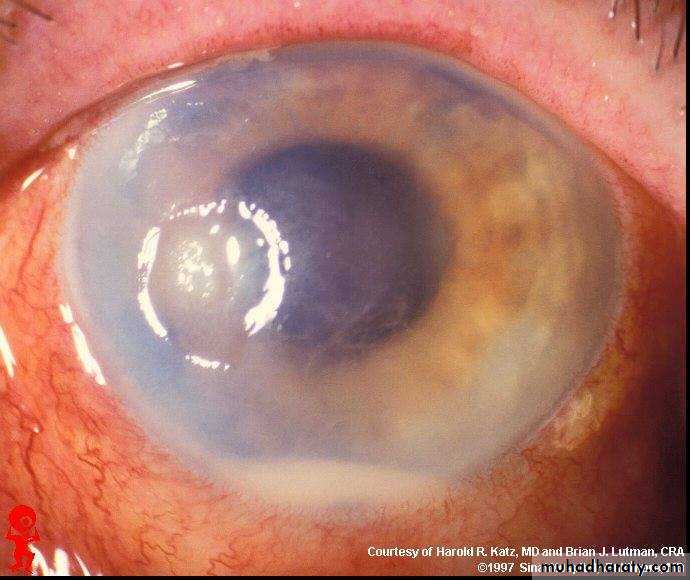
Dx :cataract+dilated pupil
Causes of cataract:1-age(commonest) 2-congenital 3-drugs like steriod 4-radiation 5-traumaCauses of dilated pupil:1-drugs 2-trauma 3- optic nerve damage 4- 3 nerve damage
Tx : surgery is the only tx for cataract
Assessment of patient:1-VA 2-light perception 3-pupillary reflex 4-color test through slit lamp 5- US to get idea about vitreous chamber and retian
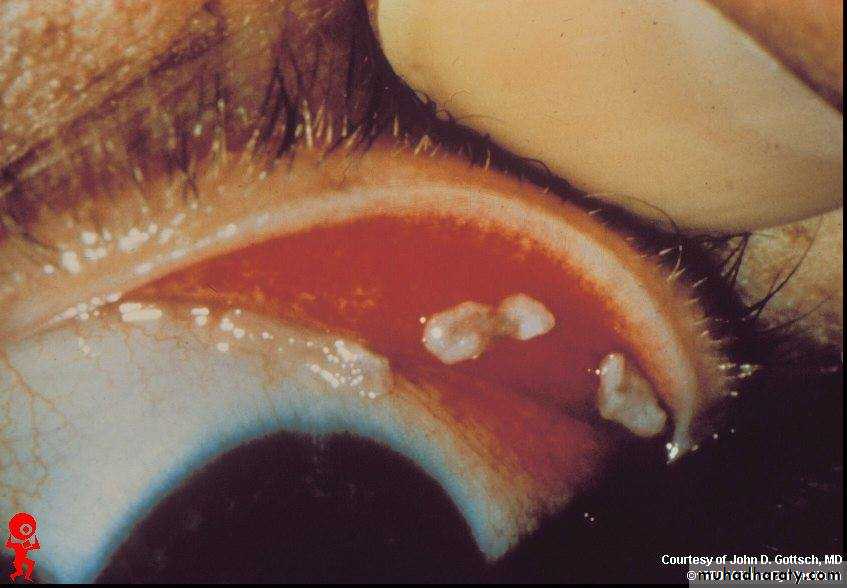
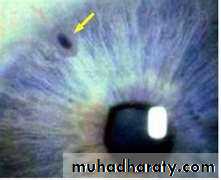
F.B. in the inner surface of upper lid
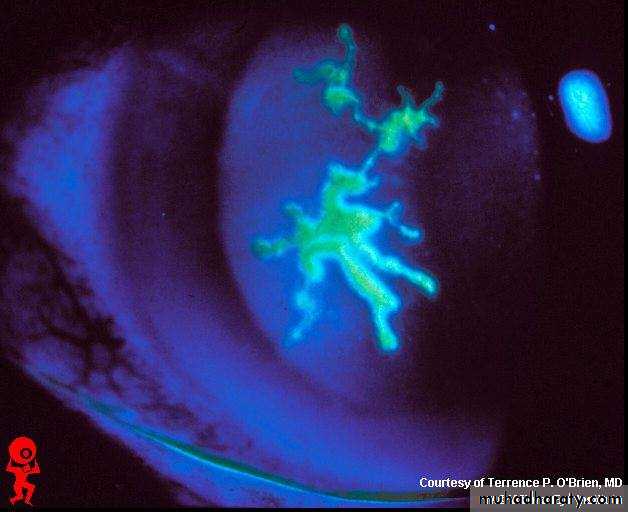
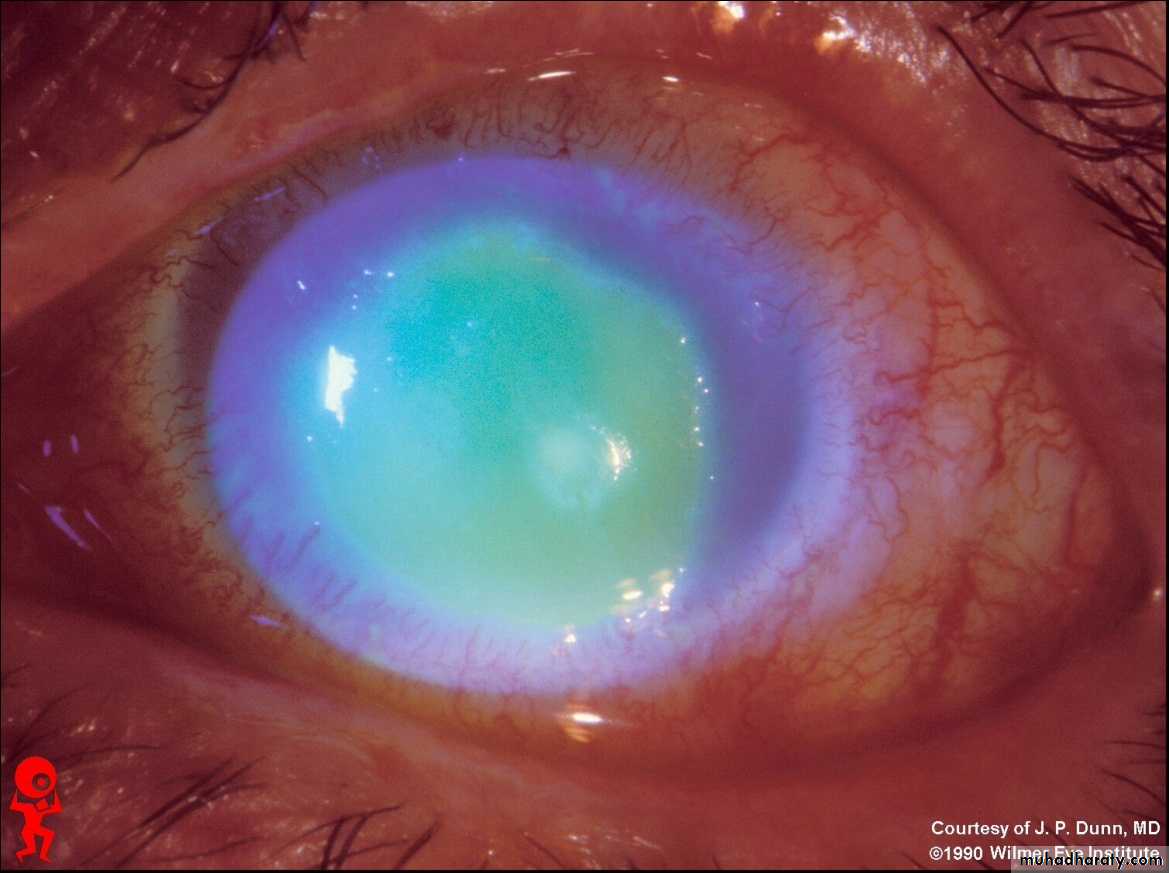
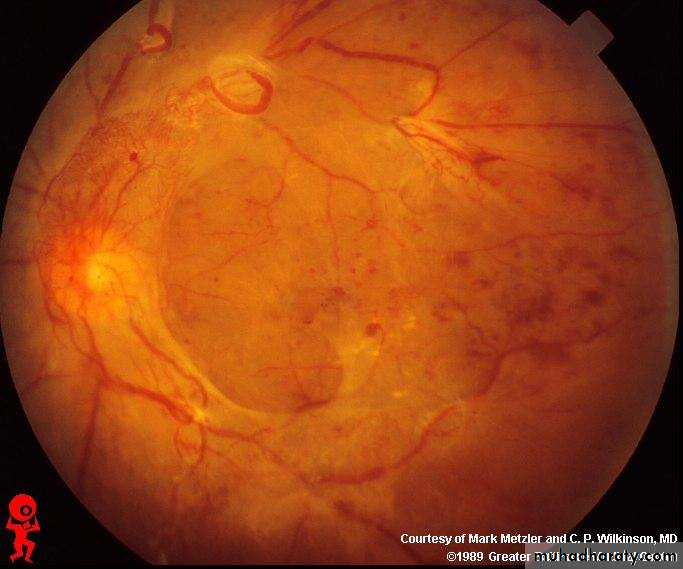
Flourescein stain showing ulcer in the retina(geographical ulcer)
Causes:1-steroids 2-chemical substances 3-bacterial infections 4-F.B. 5-trauma 6-contact lens usersTx : according to the cause
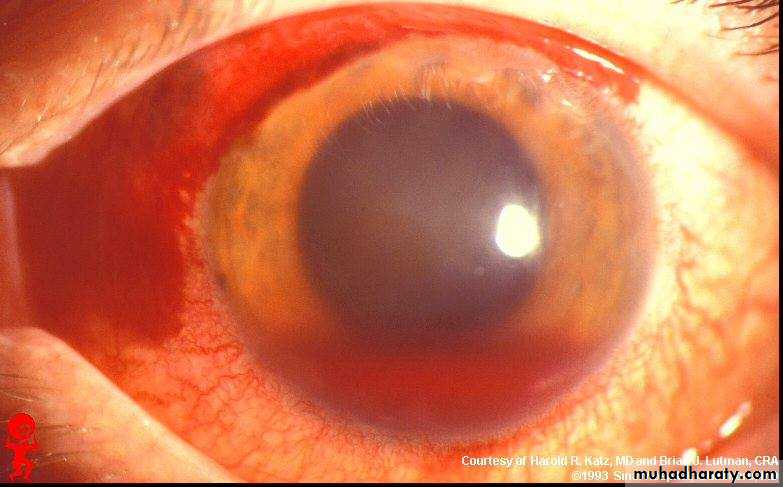
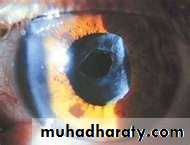
Hypopium (pus in the anterior chamber) with cloudy cornea +red eye
Causes of hypopium: 1-keratitis 2-iritisDx : subconjunctival hemorrhage+hyphema(blood in the anterior chamber)+dilated pupil
Possible cause: traumaNext step in assessment: assess IOP
Tx :1-bed rest with head elevated 2-anti-glucoma drugs if increased IOP
3-drainage of bllod if high amount
Fluorescein stain showing corneal ulceration
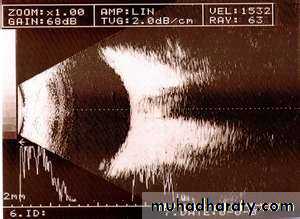
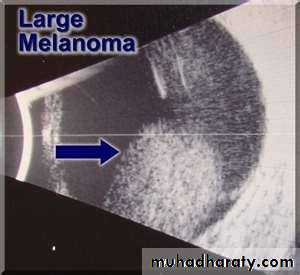
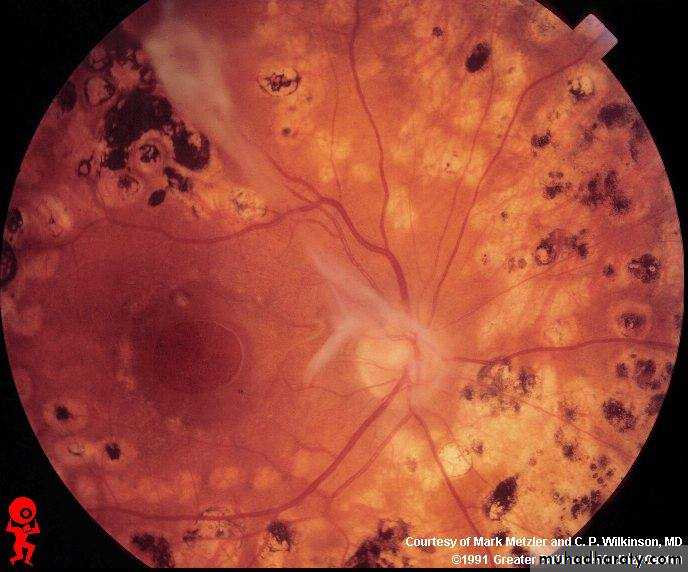
Same causes of any ulcersB scan sonography showing the vitreous cavity
Dx : peripheral laser iriditomy(YAG laser)
Ix : closure angle glucomaDx :Posterior capsule opacification
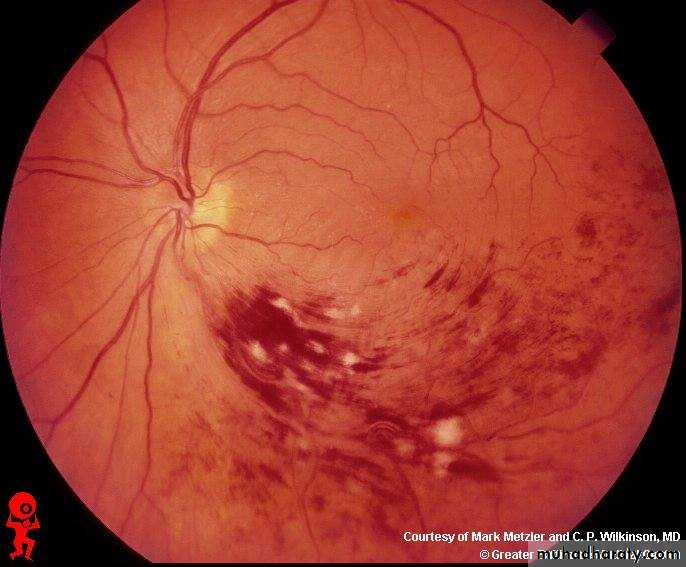
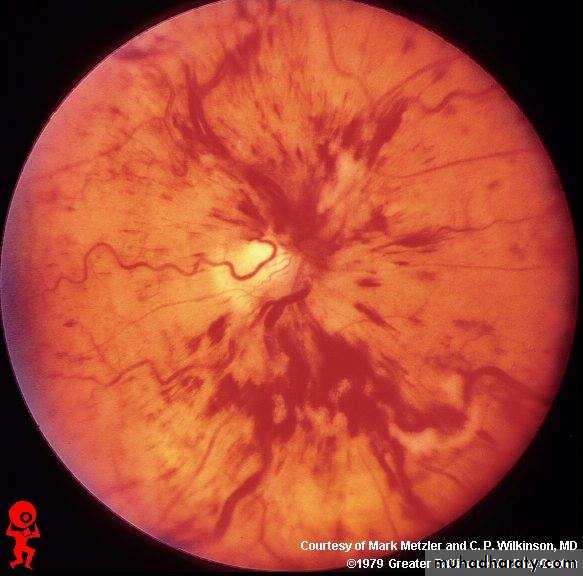
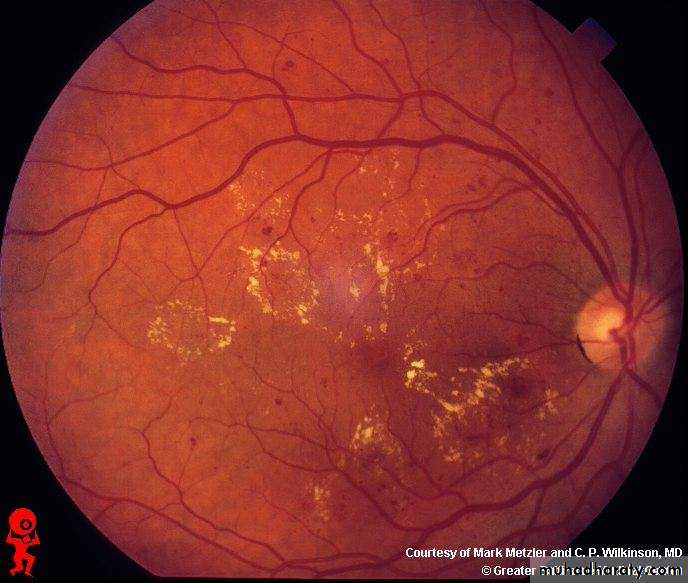
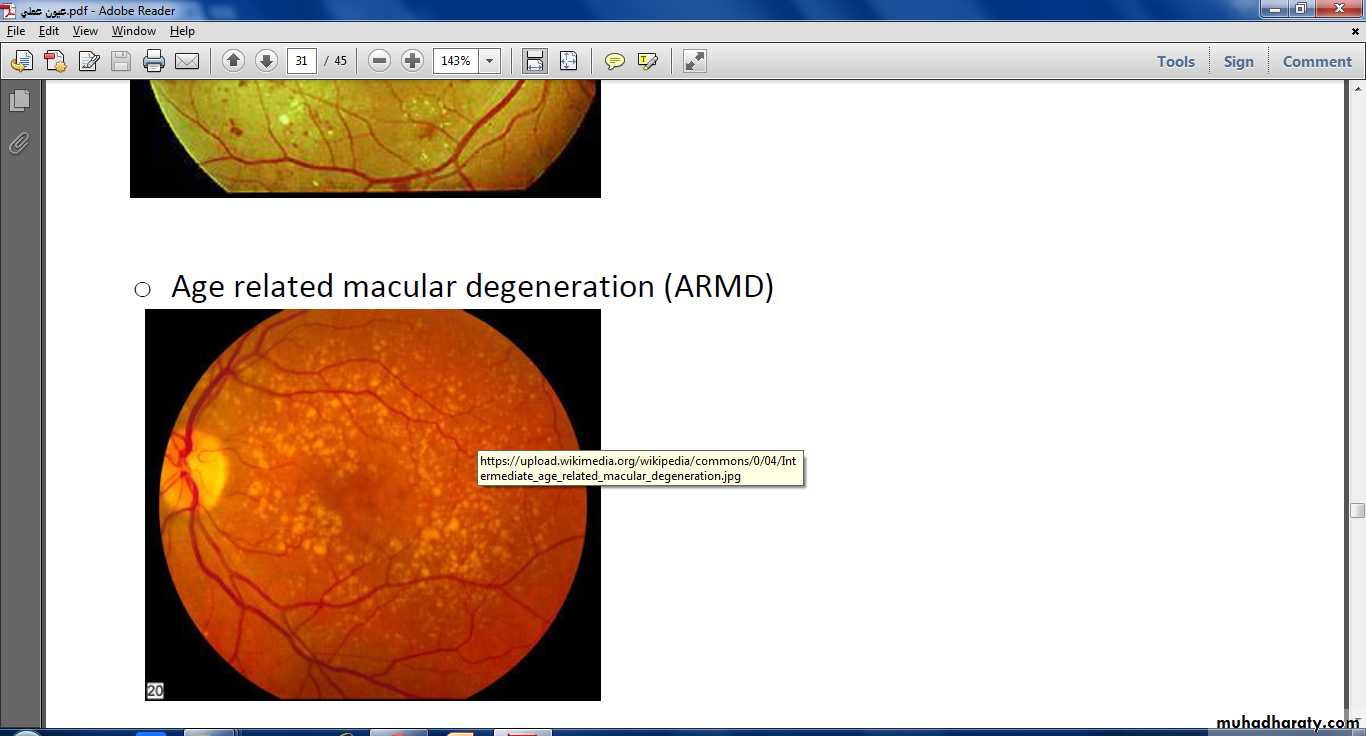
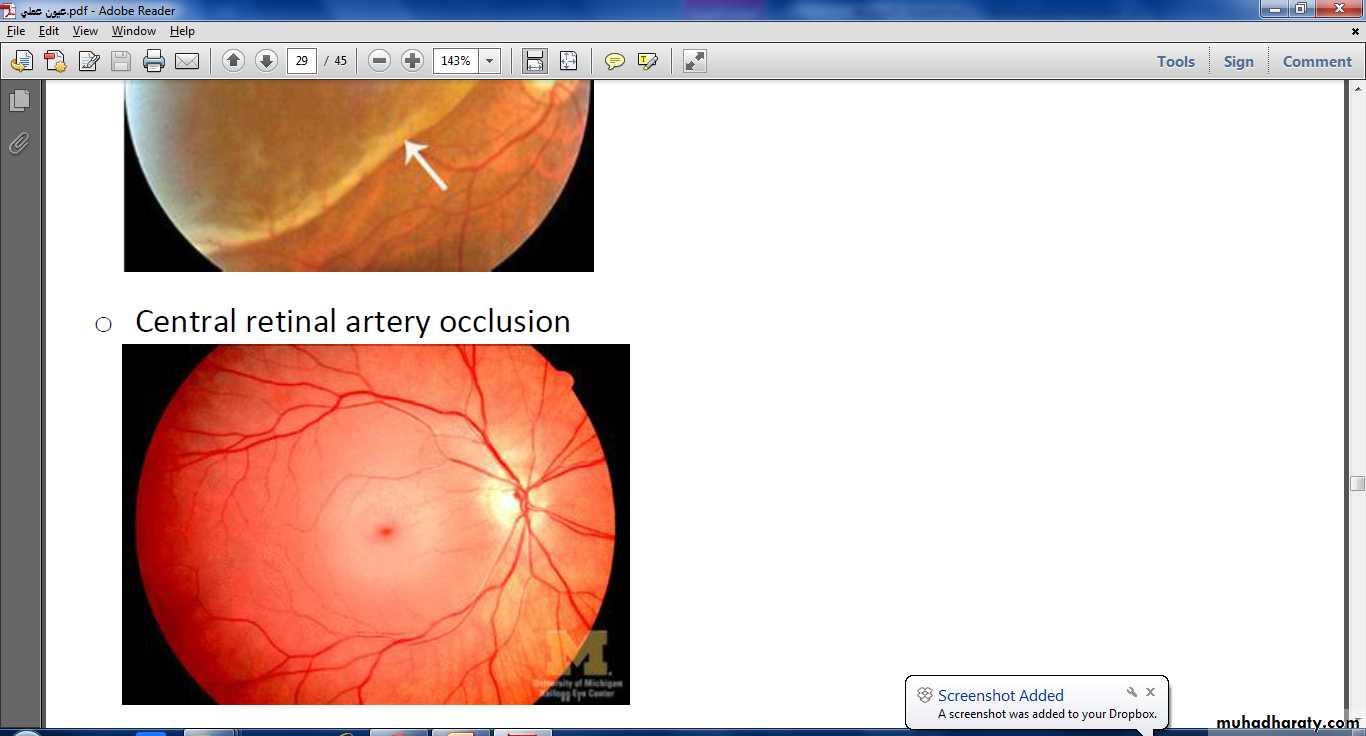
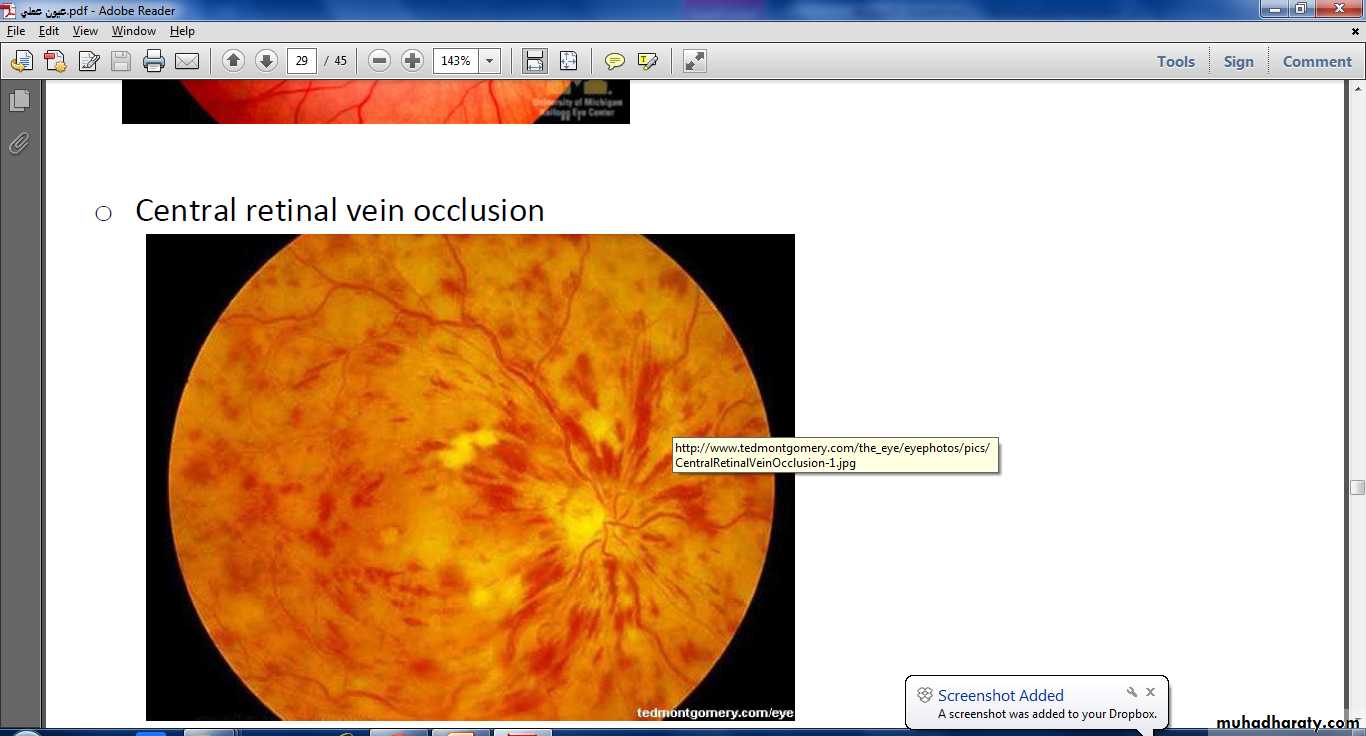
Tx :YAG laser capsulotomyOcclusion of the lower temporal branch of CRV marked by hemorrhage and multiple dots of ischemia in the lower temporal zone of retina