1
Fifth stage
Surgery
عملي
1
د.بسام
8/11/2015
Practical pediatric surgery
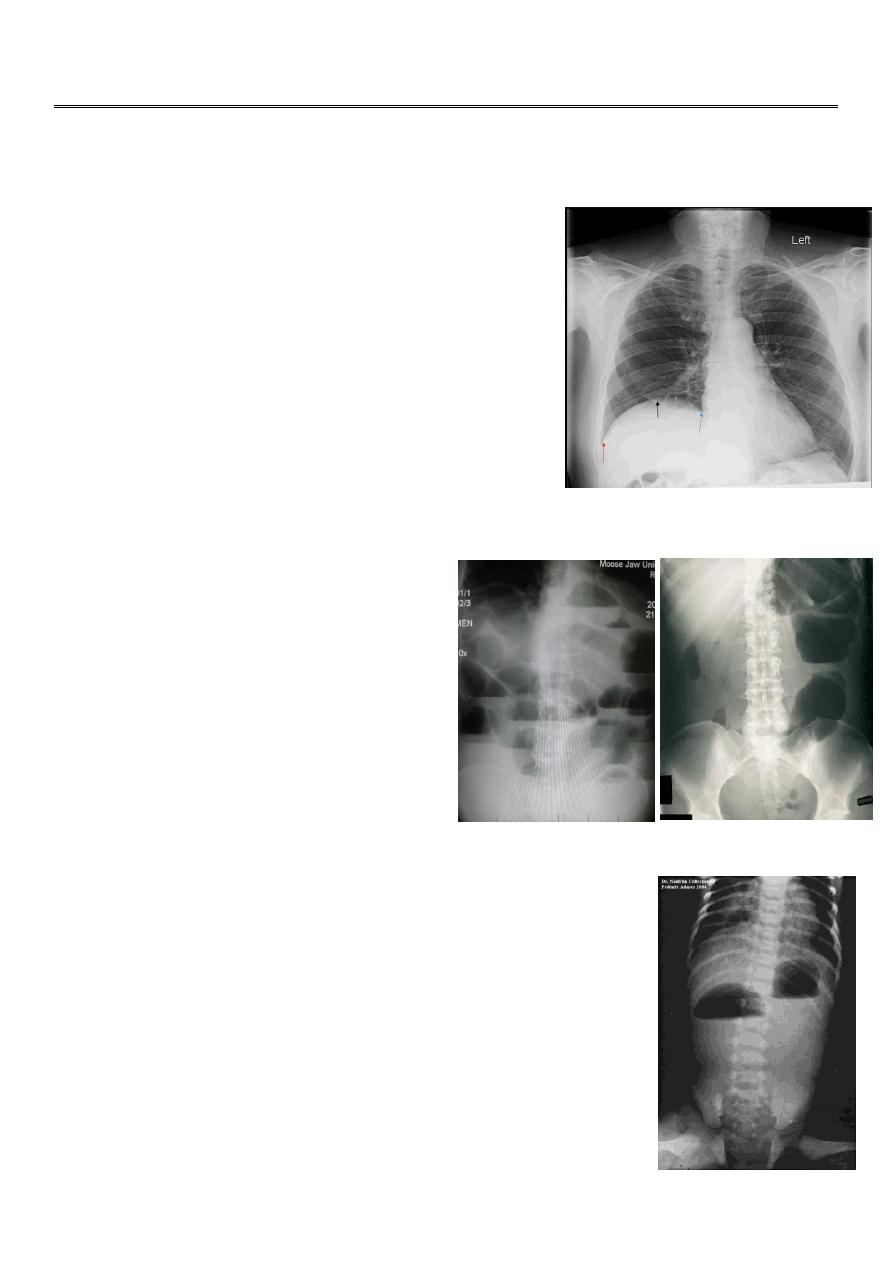
Elevation of the diaphragm:
It is due to paralysis of the diaphragm.
Patient is healthy.
No severe distress.
Present in 4-5 months.
X-ray
diaphragm is elevated, lung is present.
Treated by
diaphragmatic plication (reduction of
the diaphragm downward).
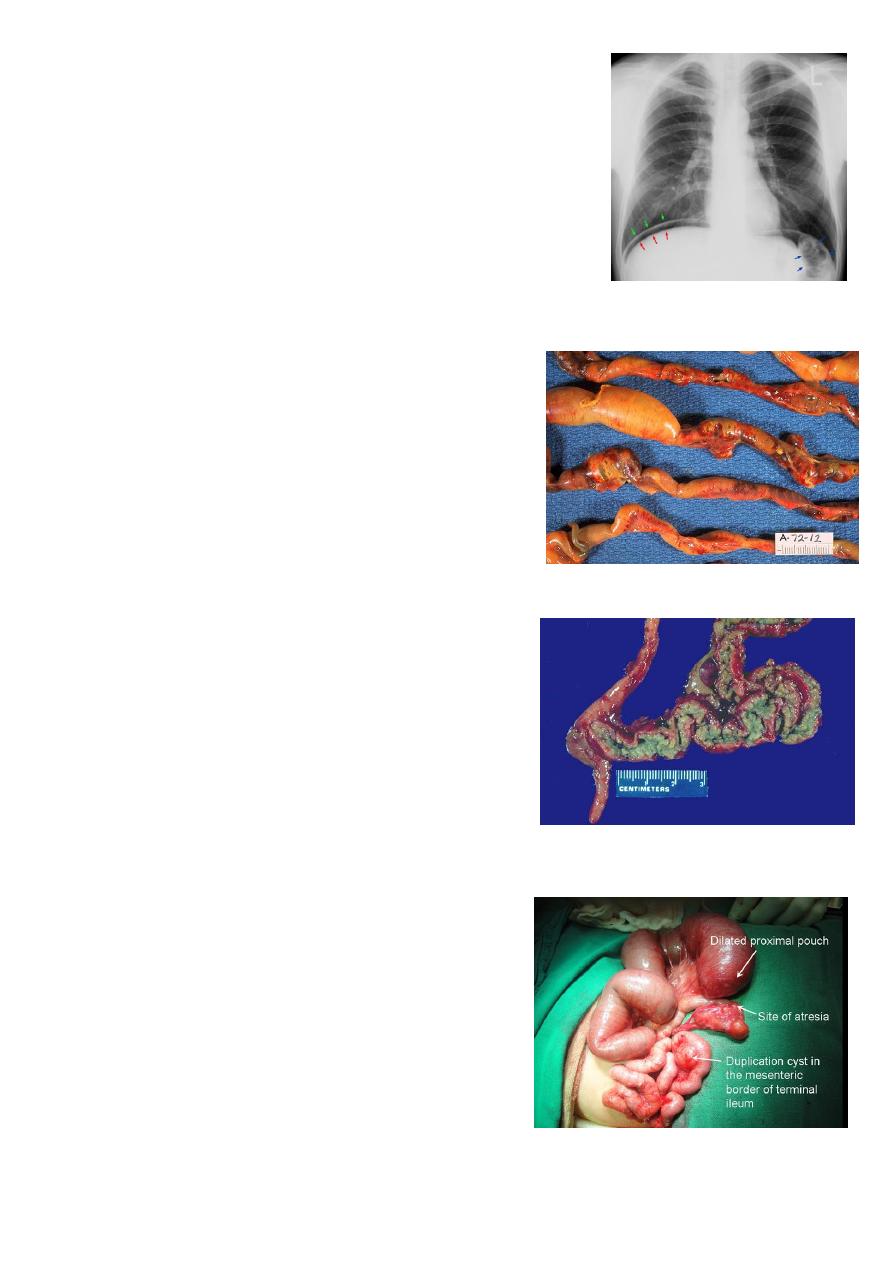
Bowel obstruction:
Upper obstruction above the
ligament of treitz.
Lower obstruction below the ligament
of treitz.
X-ray upper obstruction (multiple
small air/fluid level), lower obstruction
(few large air/fluid level).
Double bubble gas shadow:
It is sign of duodenal obstruction.
Causes of duodenal obstruction:
o Duodenal atresia.
o Annular pancreas.
o Stenosis.
o Mal-rotation.
2
Pneumoperitoneum:
It is air in the peritoneum.
Lead to distension of the abdomen.
Percussion tympanic.
Gastric perforation lead to massive Pneumoperitoneum.
X-ray saddle sign (air above and beside the liver).
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC):
Pneumatosis intestinalis sign presence of gas in
the wall of the bowel.
It is disease of pre-mature baby.
Treatment conservative (I.V fluid, antibiotics,
monitoring).
If complication occur do surgery.
Meconium ileus:
Presence of stick, thick, tenosius meconium.
Lead to bowel obstruction.
Cause abnormality in exocrine secretion (like
cystic fibrosis).
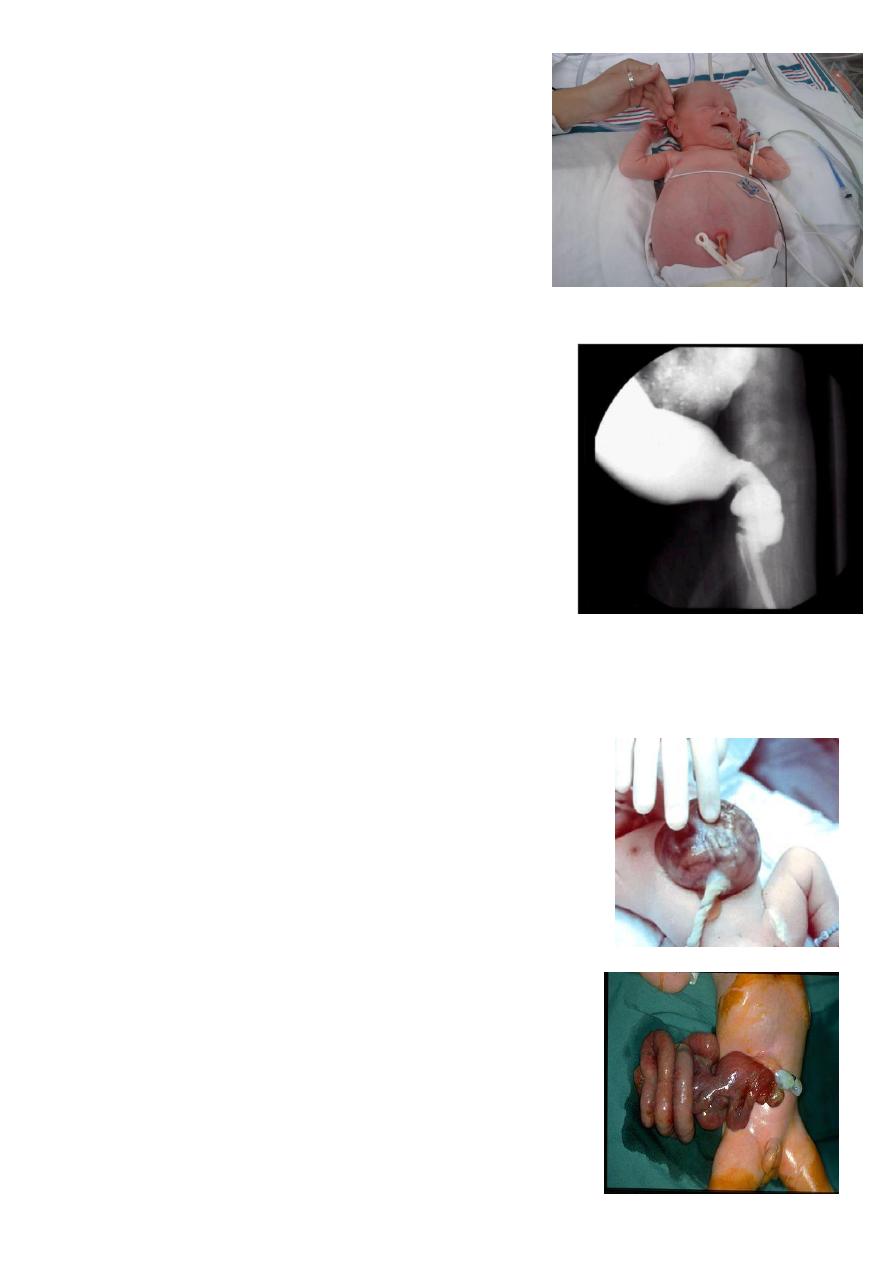
Bowel atresia:
Huge dilated bowel.
Blind end.
Distal part of the intestine is small in size.
Treatment surgery.
Presented as intestinal obstruction.
3
Cardinal signs of intestinal obstruction:
Bile stained vomiting.
Distension lower obstruction lead to more
dictation than upper obstruction.
Abdominal pain.
Failure to pass meconium complete obstruction.
Delay pass of meconium partial obstruction.
Hirschprunge disease:
Huge dilatation of the rectum.
It is due to absence of ganglia in the lower part of the
intestine.
Cone segment is the segment of transition between
ganglionic and aganglionic rejoins.
Presentation:
1- Delay to pass meconium (48 hours).
2- Signs of intestional obstruction (distension,
vomiting).
3- Chronic constipation (commonest presentation).
4- Complications enterocolitis lead to spurious diarrhea.
Surgery called pull-though (anal, abdominal, laparoscopic approaches).
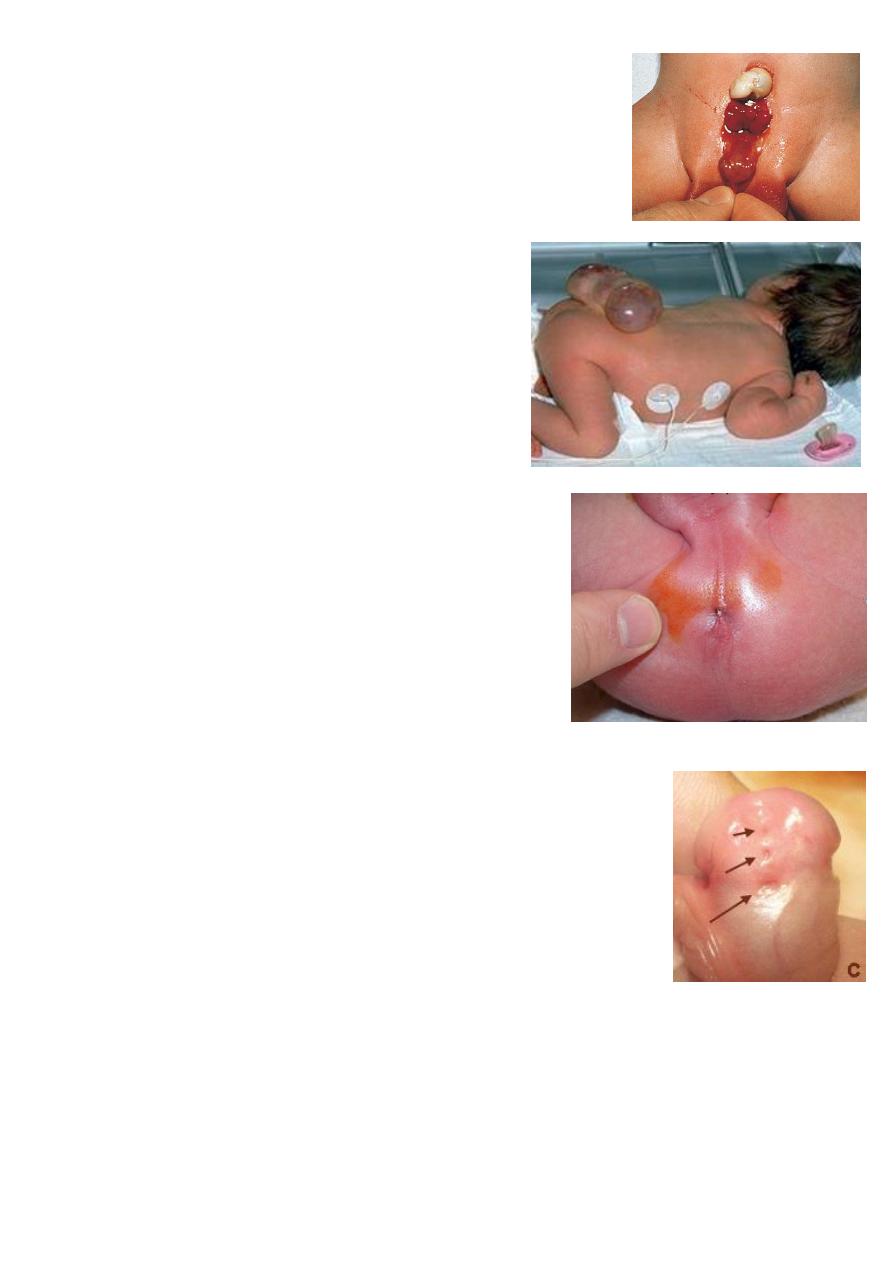
Omphalocele:
It is anterior abdominal wall defect.
Minor type: not contain liver.
Major type: contain liver.
Treated by surgery gradual reduction by silomish.
Gastroschizia:
No sac (omphalocele has sac).
Defect lateral to umbilicus (omphalocele in the umbilicus).
Has less congenital abnormalities (omphalocele more).
It is emergency so more dangerous (omphalocele less
dangerous).
4
Ectopia vesica:
It is anterior abdominal wall defect.
Lead to urine dripping and incontinence.
Treated by surgery.
Spina bifida:
Types (spinal dysraphism):
1- Meningeocele.
2- Meningomylocele.
3- Lipomeningomylocele.
Assoicated with hydrocephalus.
Lead to paralysis.
Imperforated anus:
Sometimes with fistula lead to pass of meconium
through urethra or skin (low type).
There is anal dimple.
In female single opening (chloaeca) or vestibular
fistula (opening in the vaginal vestibule).
Hypospadias:
Opening in the ventral aspect of the penis.
There are multiple types.
Lead to:
o Cosmetic problem.
o Sterility.
o UTI.
o Psychological problems.
Surgery before patient become aware for his genitalia.
5
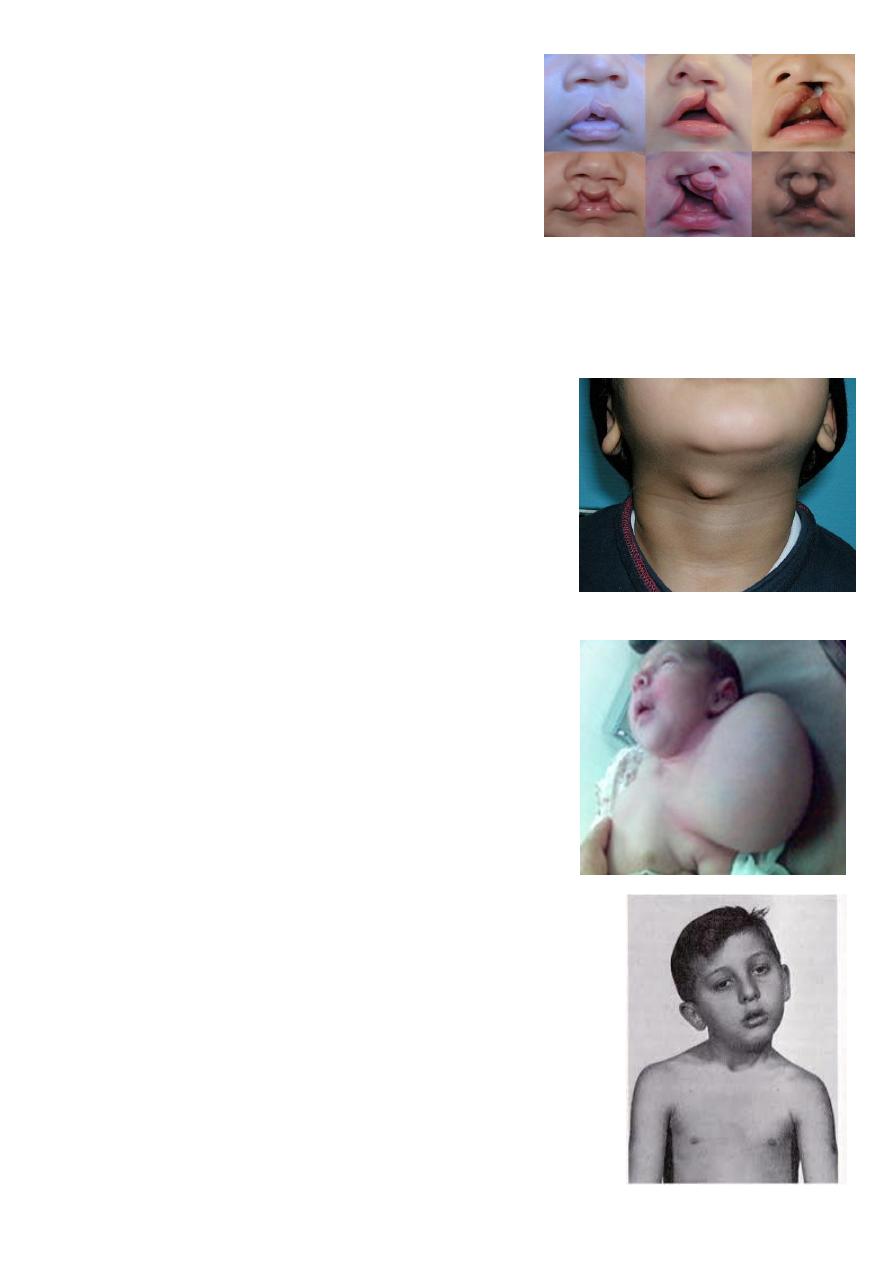
Cleft lip and palate:
Cleft palate lead to feeding problems, recurrent
otitis media, speech problems (nasal speech).
Do surgery in first year of life.
Cleft lip cosmetic problem do surgery before
3 months.
Types:
1- Complete or incomplete.
2- Bilateral or unilateral.
3- Lip + palate or only lip.
Thyroglossal cyst:
Lead to infection (fistula), cosmetic, may change to
cancer after 20 years.
Treated by surgery removed completely with
central part of the hyoid bone.
Cystic hygroma:
Arise from: neck, axilla, groin.
Treated by surgery.
Complication compression on structures, infection,
bleeding.
Sternocleidomastoid torticolus:
Called Sternocleidomastoid tumor.
It is due to trauma during delivery.
Physiotherapy if small age.
Lead to positional abnormality of the neck muscles.
Lead to mid-face hyperplasia.
Surgery cut the muscle and separate it.
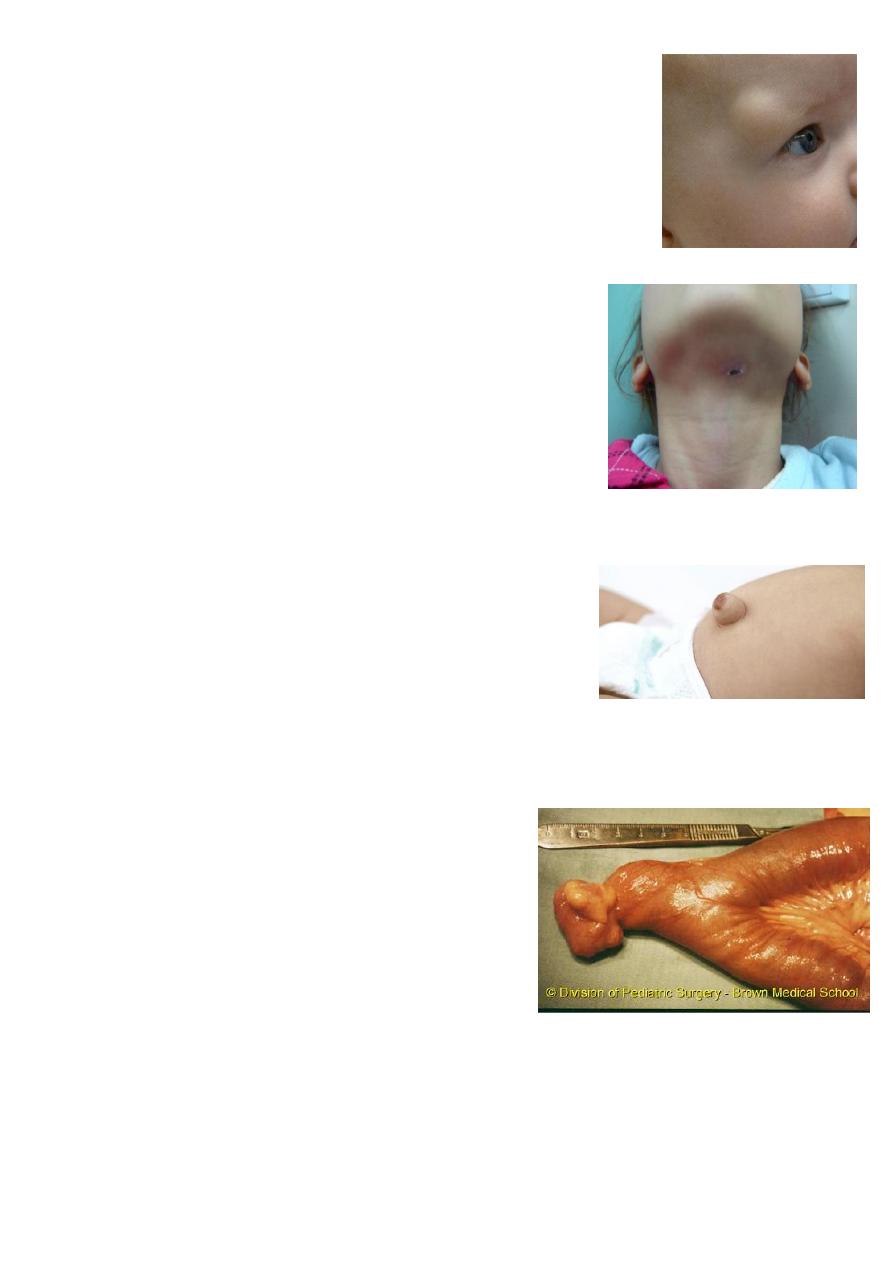
6
Dermoid:
Common site in pediatric above the eyebrow.
Lead to infection, liable to trauma (rapture).
Treated by excision (but not shave the hair).
Branchial cyst or fistula:
Open in the neck white sticky secretion.
It is remnant of second bronchial segment.
Have tract from the neck to the tonsils.
Lead to infection (abscess), malignancy.
Surgery remove the tract completely (be careful for
bifurcation of aorta and hypoglossal nerve).
Umbilical hernia:
May disappear with time.
Rarely have complications.
Do surgery if it still after 3 or 4 years or if it has
complications.
Patent vetilline duct connected to the umbilicus
infection, stool, odor do surgery.
Michel's diverticulum:
Presentation infection, melena, massive
bleeding per rectum (maroon color).
Diagnosed by isotope scan (there are hot spots) or
do laparoscopy (diagnostic and therapeutic).
Complications bleeding, intestinal obstruction,
intussusception.
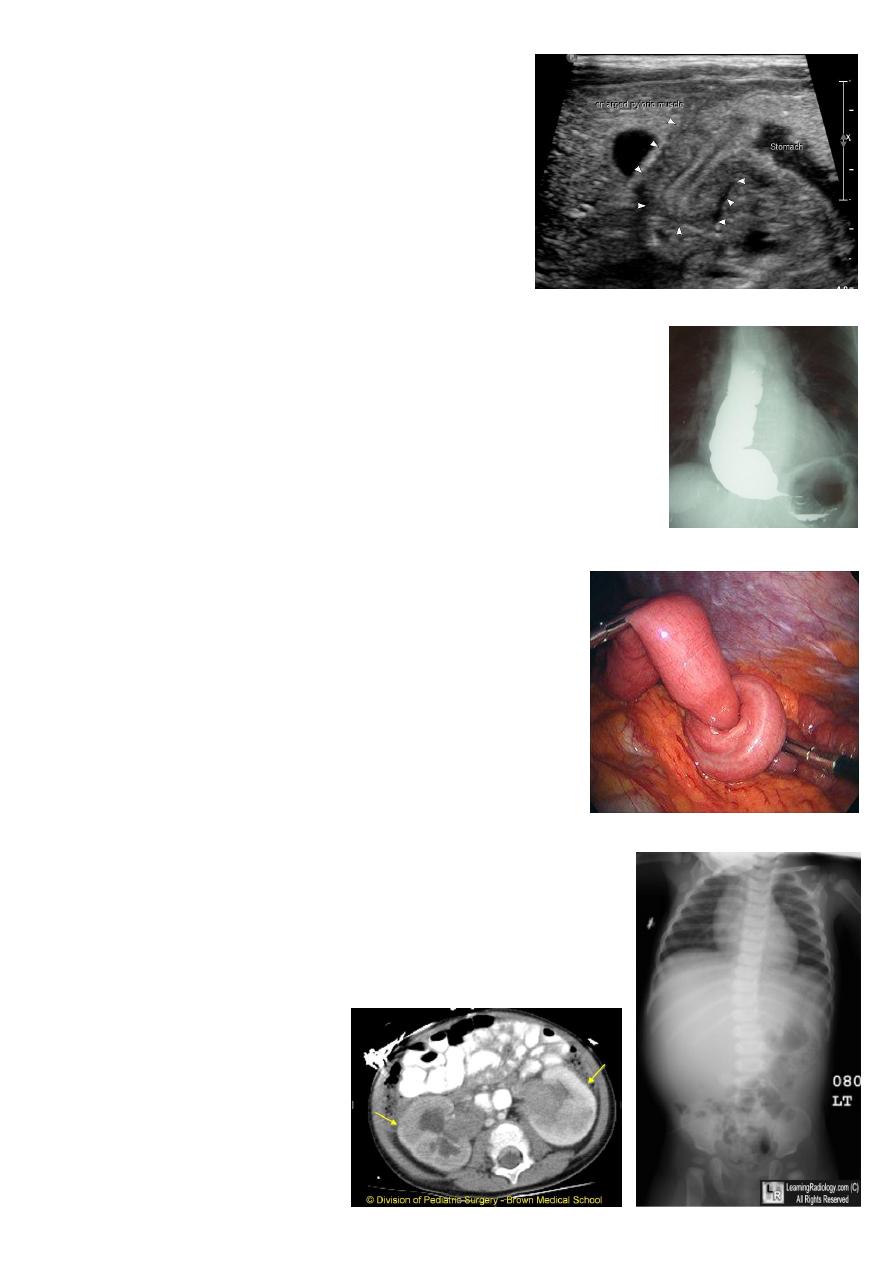
7
Pyloric stenosis:
Sings:
1- Projectile vomiting in the first month.
2- Olive mass in the abdomen.
3- Positive peristalsis (left to right).
4- Failure to thrive.
Can use ultrasound see delay emptying.
Treated by pyloric myotomy (don’t open the
lumen).
Achalasia cardia:
Could lead to halitosis.
Neurolgical symptoms.
Treatment surgery (cardiomyotomy).
Intussusception:
Primary (congenital) screaming, put his feet on his
abdomen, bleeding per-rectum (red current jelly stool),
sausage mass (big mass to the right of the umbilicus).
Secondary (in older children) due to tumor, mass,
bleeding, polyp.
Do Ultrasound and barium enema (spring coil sing).
Treatment: hydrostatic reduction by barium, pneumatic
reduction by air, surgery (push).
Wilms tumor:
It is the commonest tumor in pediatric.
Lead to abdominal pain, mass, hypertension.
Treated by chemotherapy and nephrectomy.
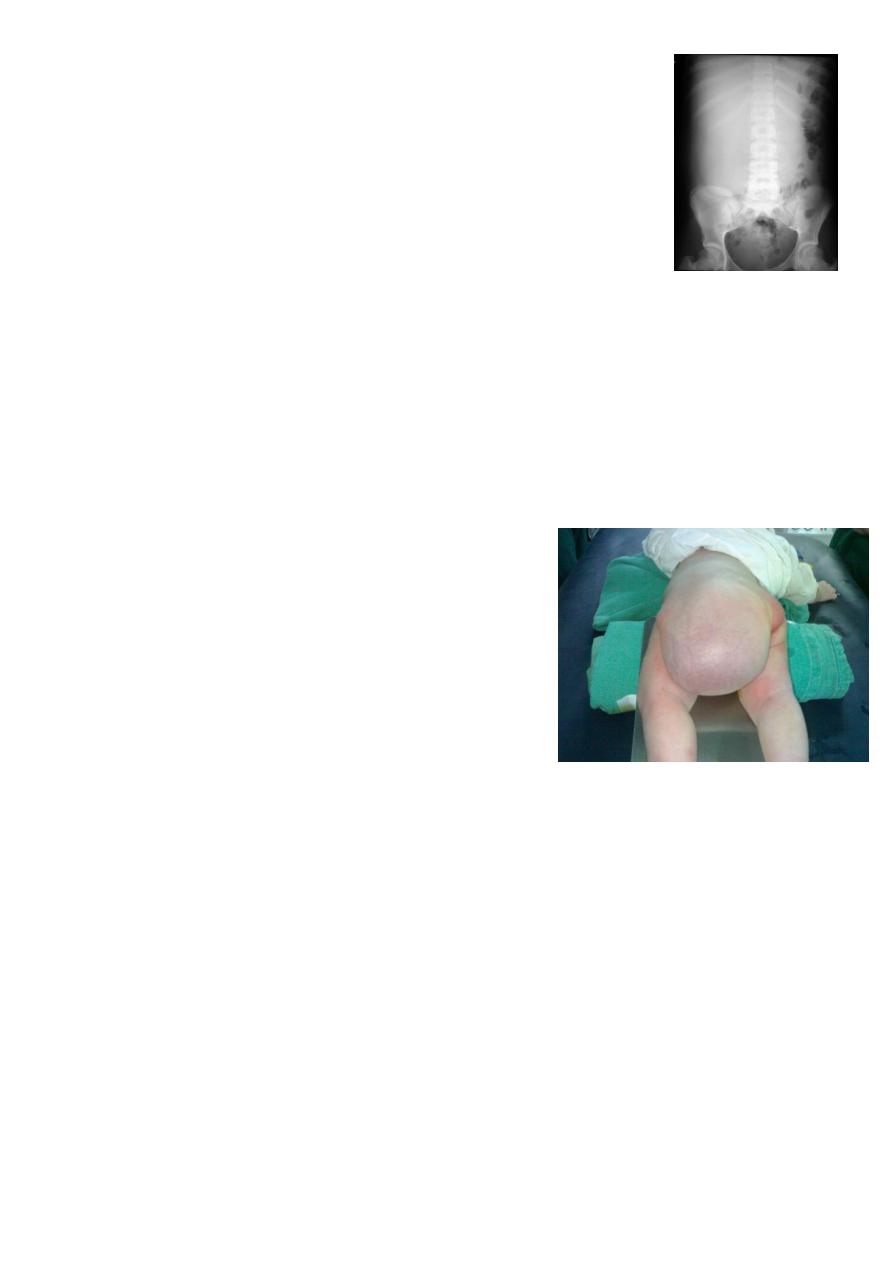
8
Nephroplastoma:
Second most common tumor in pediatric.
Arise form adrenal medulla.
Treated by surgery of chemotherapy.
Lymphoma:
Third most common tumor in pediatric.
Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin type.
Give chemotherapy better than surgery.
Sacrococcygeal teratoma:
Treatoma contain structures arise form
endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm.
Lead to obstructed labor, rapture bleeding
(cannot control it).
It is benign with 3 months could convert to
malignant.
Treatment surgery remove the mass, remove
the coccyx to prevent recurrence and prevent
malignancy.
