Renal system
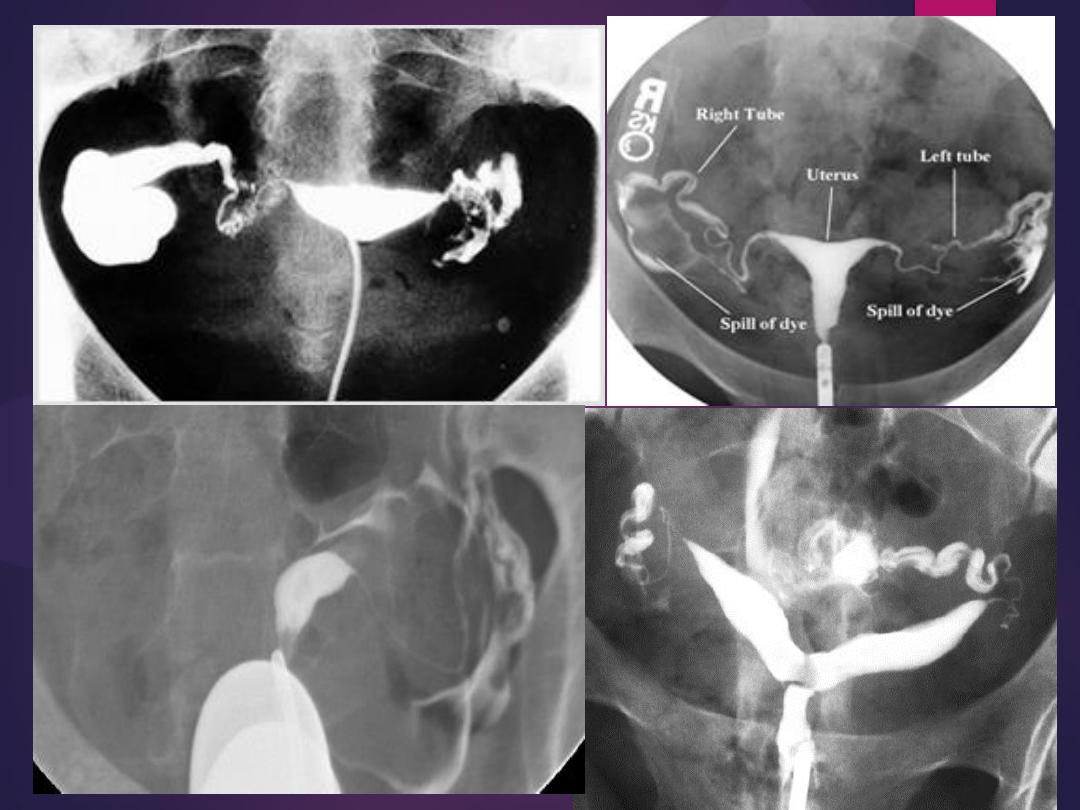
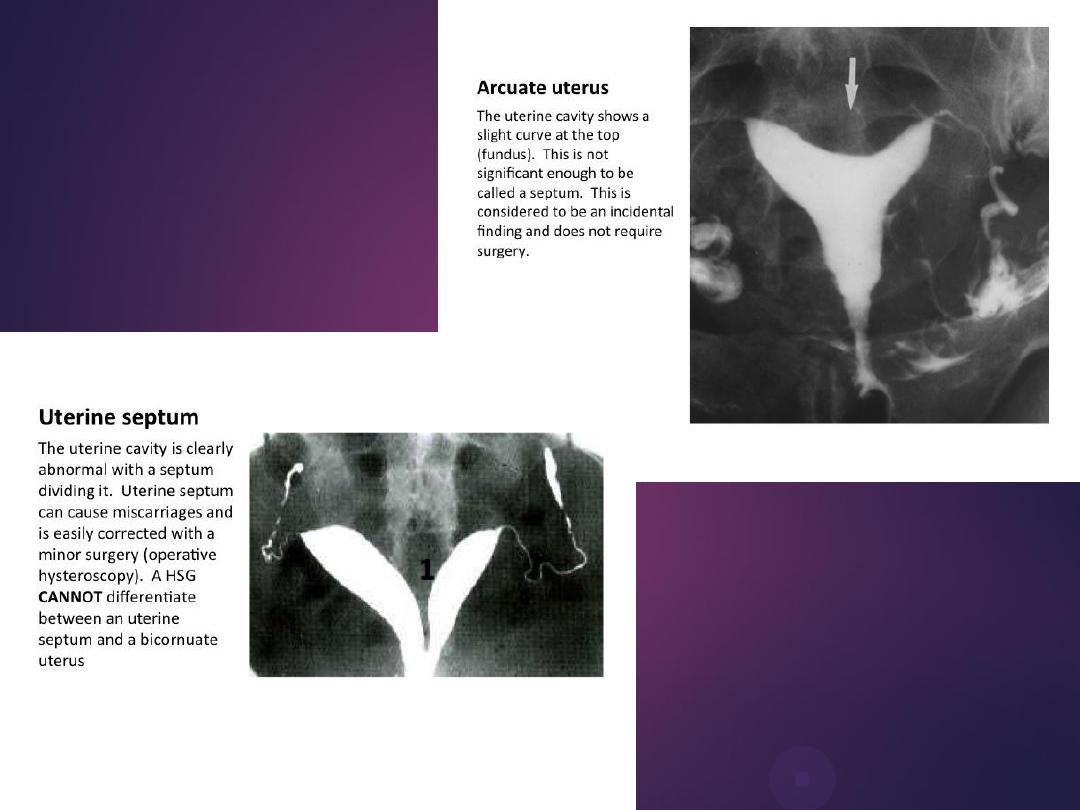
male &female reproductive
tracts
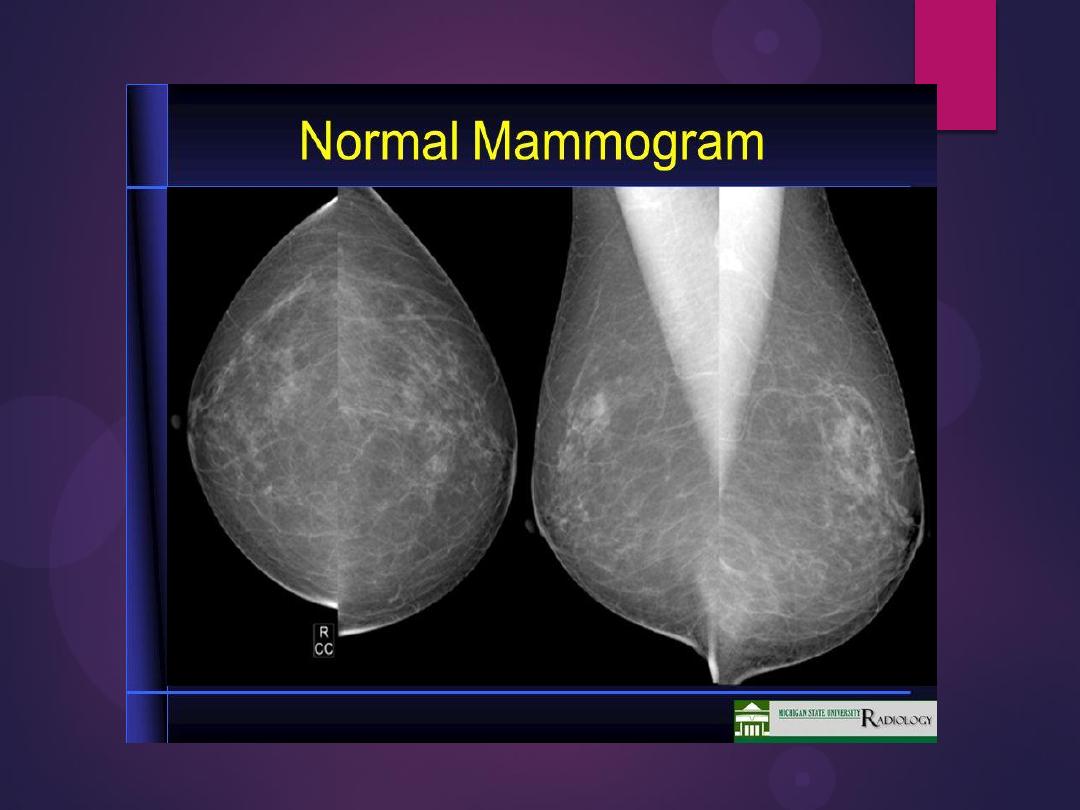
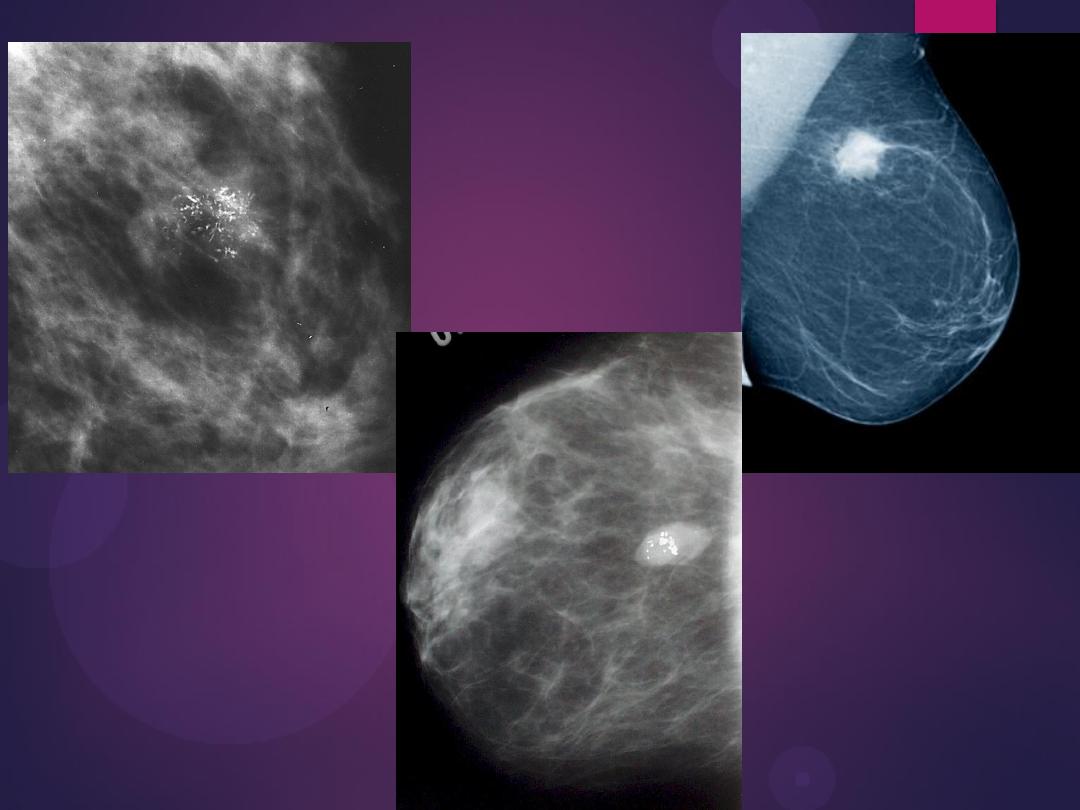
mammogram
DR.KHALEEL IBRAHEEM
DMRD,CABMS
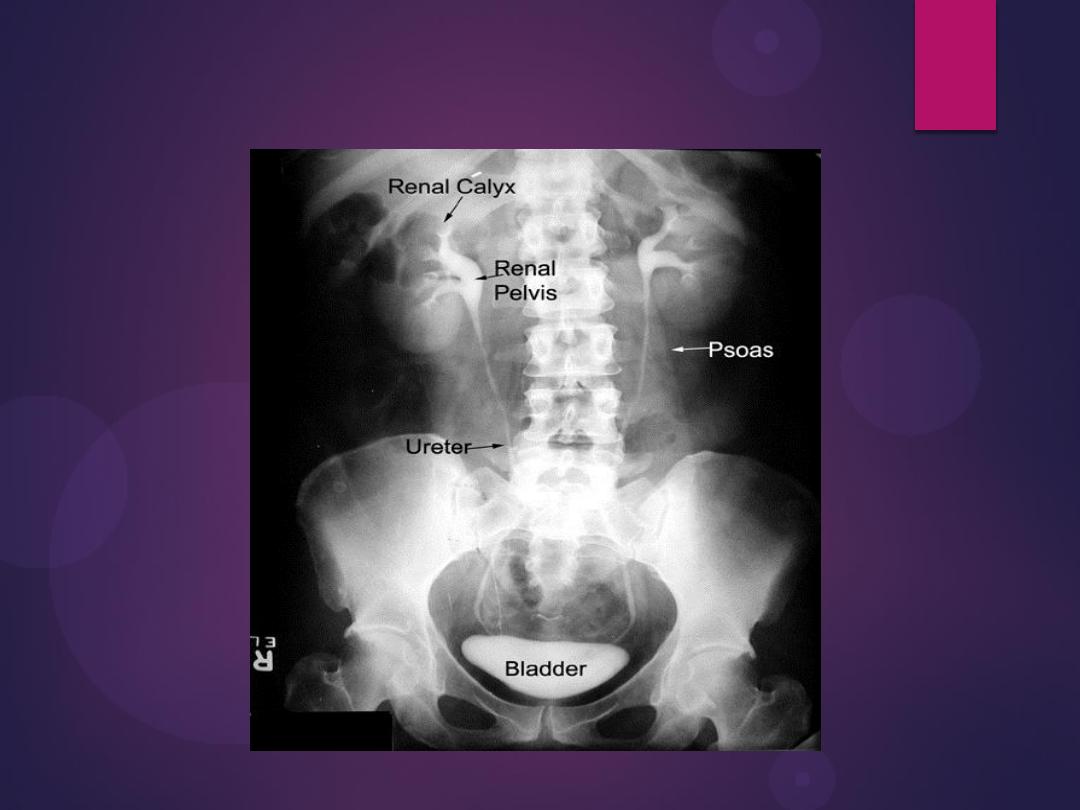
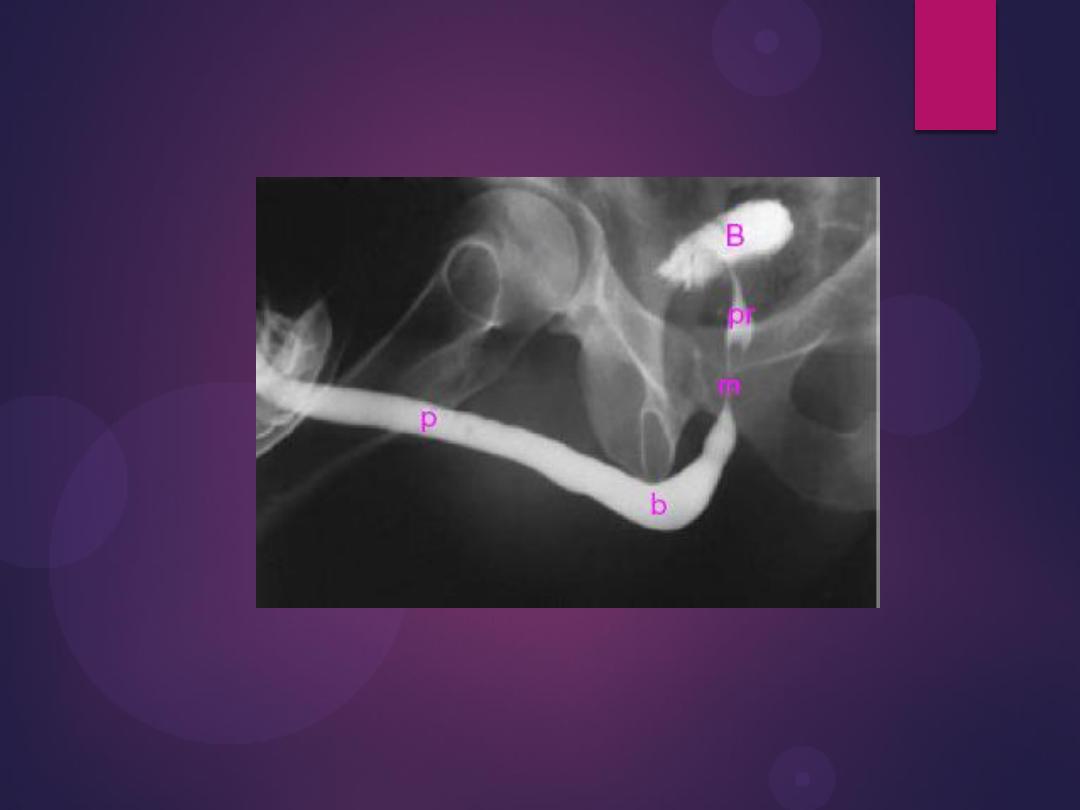
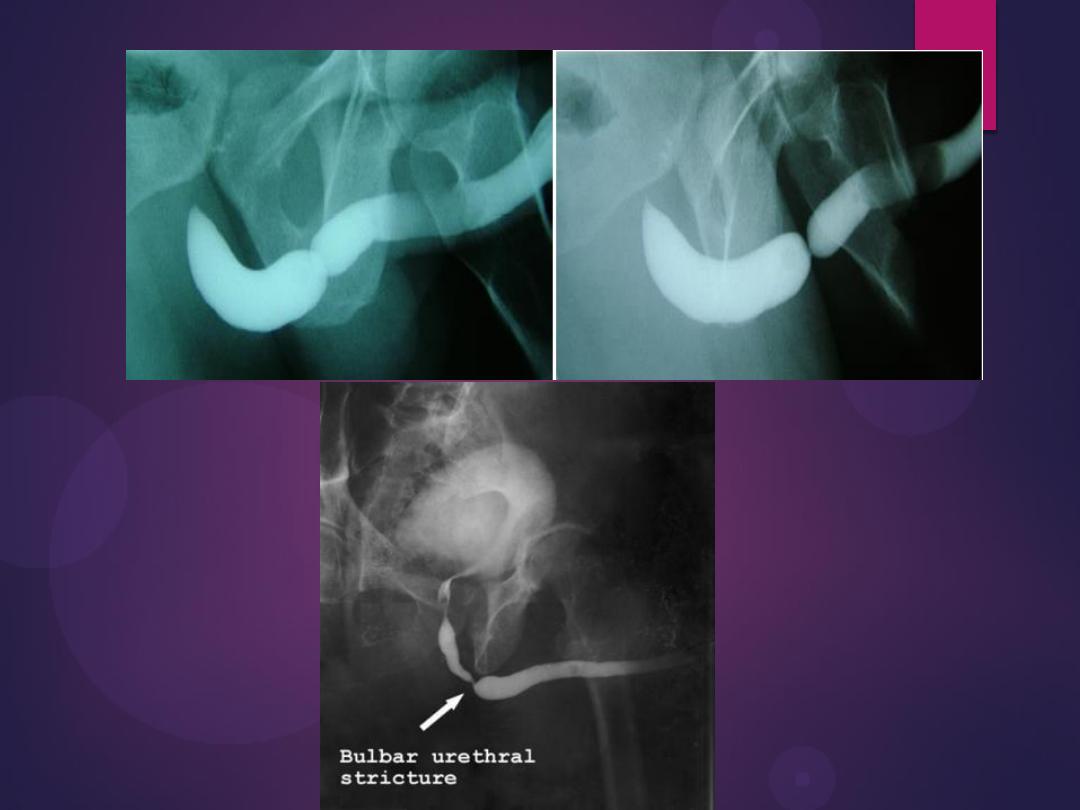
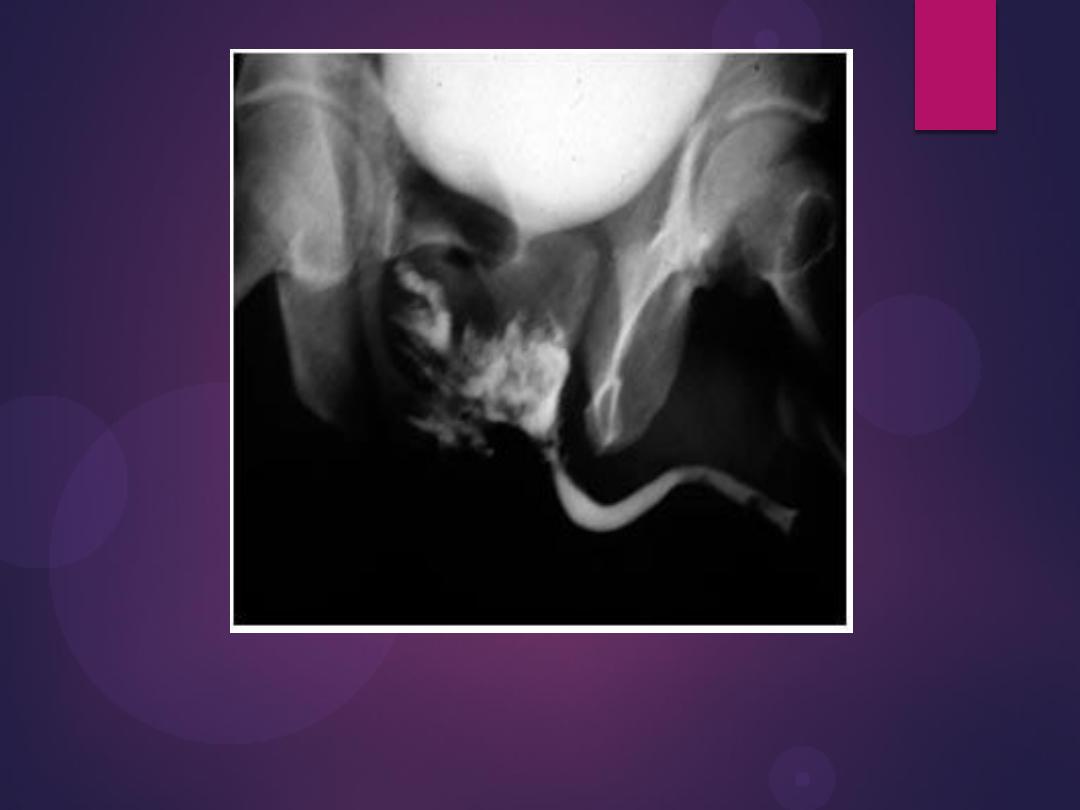
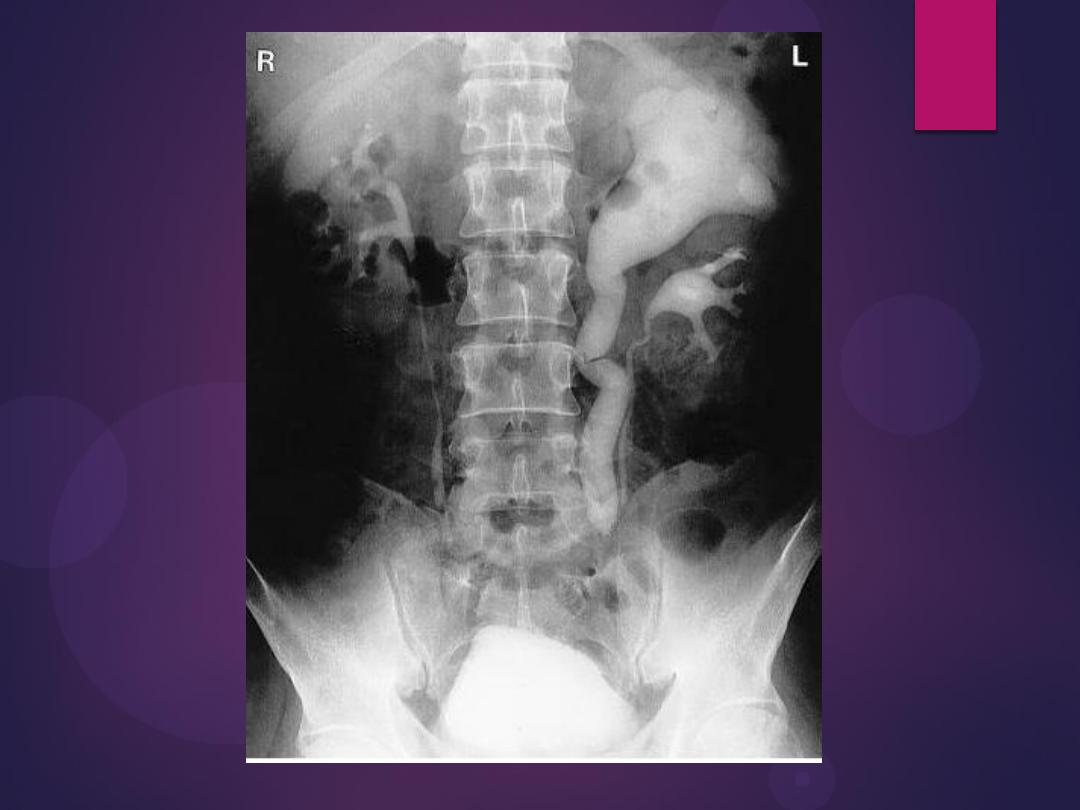
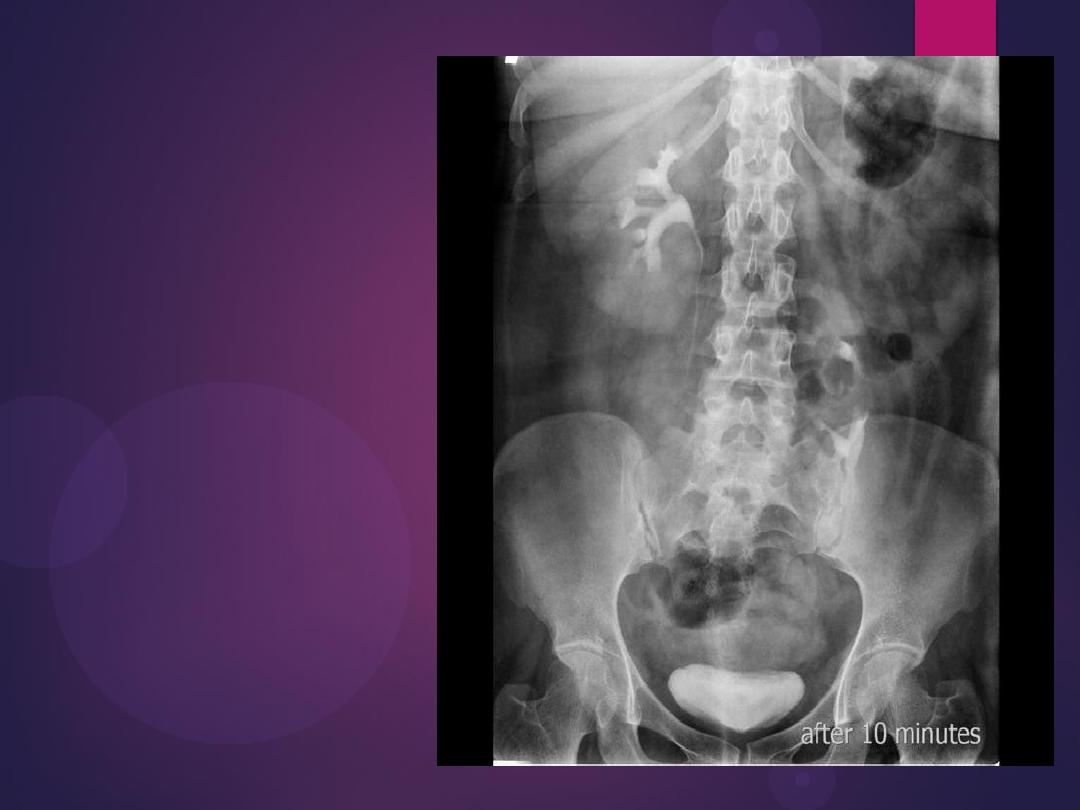
Normal IVU
Congenital renal disease
Renal agenesis
•absent kidney
•absent ipsilateral
•compensatory hypertrophy of the
contralateral (opposite) kidney
Horseshoe kidneys
The kidneys are also orientated with the
lower pole closest to the midline, which
is the reverse of normal
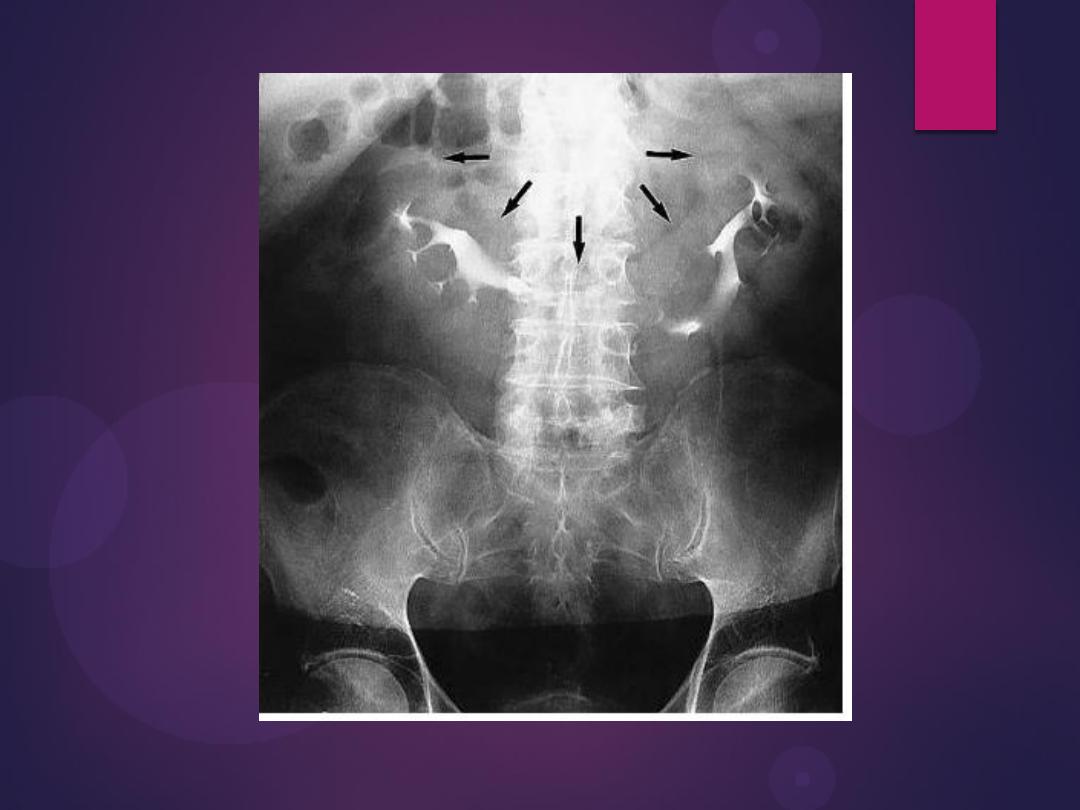
The anomaly is readily detected
on conventional urography. In
90% of crossed ectopy, there is at
least partial fusion of the kidneys
Crossed fused renal ectopia
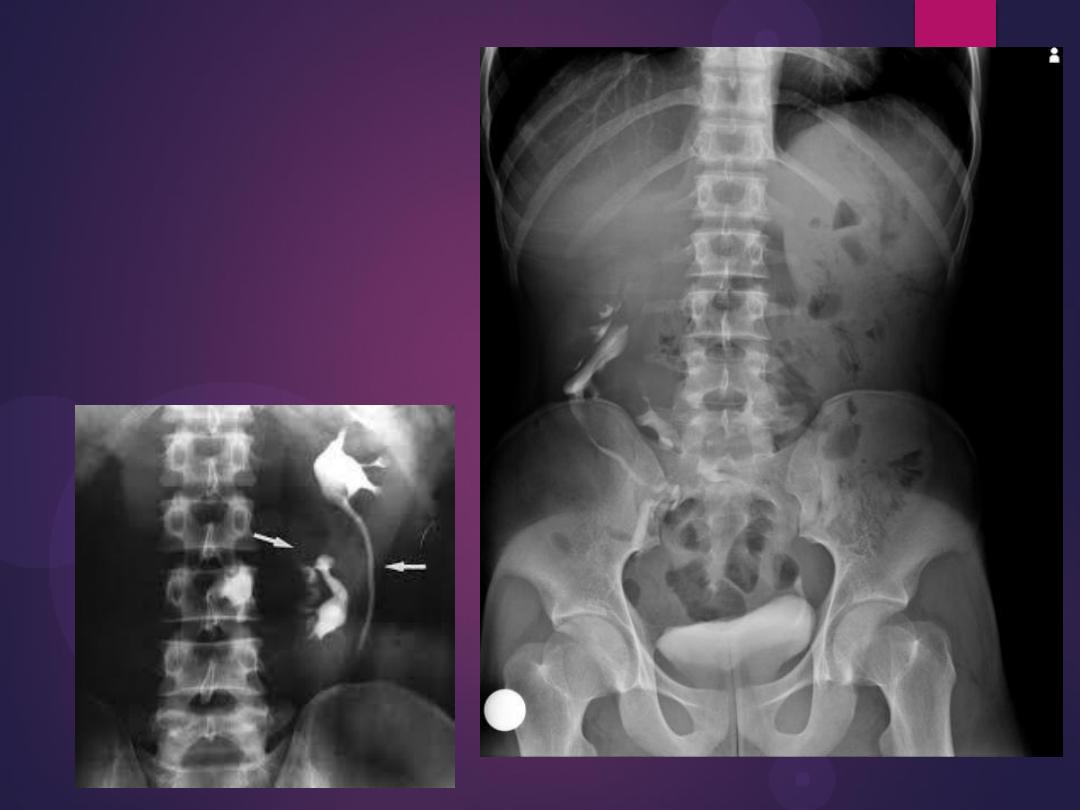
Left duplex system. The lower moiety
inserts into the bladder trigone
(not shown), whereas the upper moiety
ureter usually has an ectopic distal
insertion (see text).
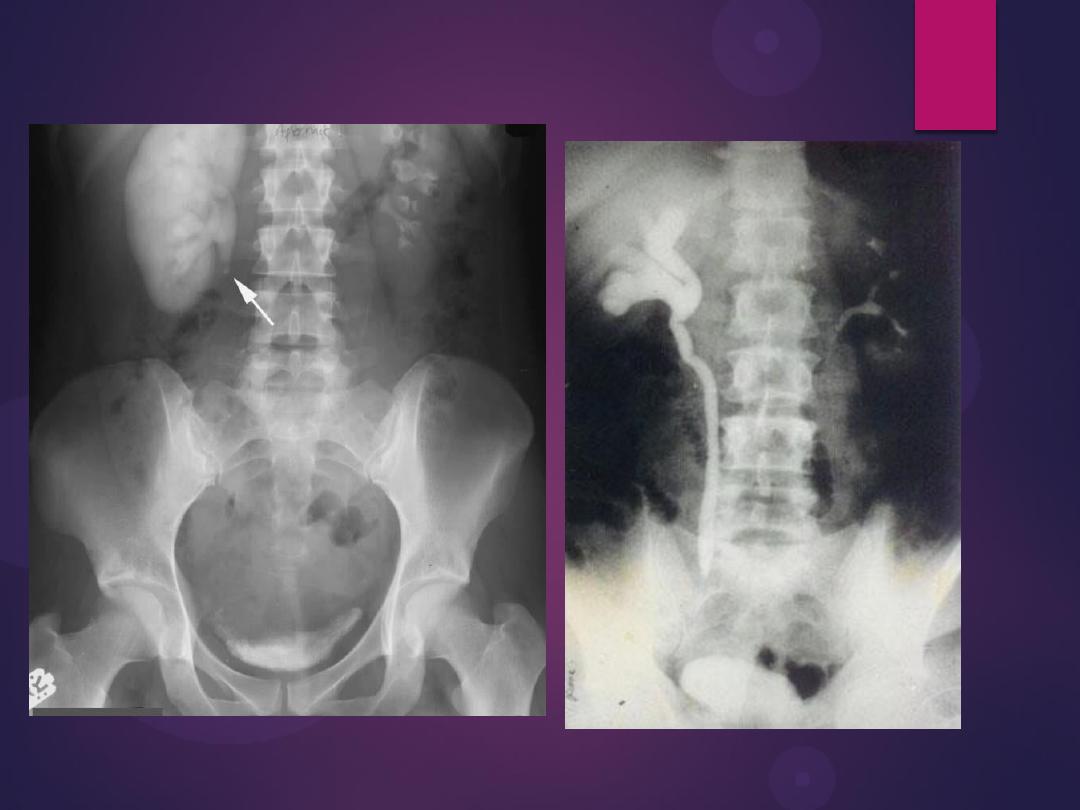
Pelvic kidney
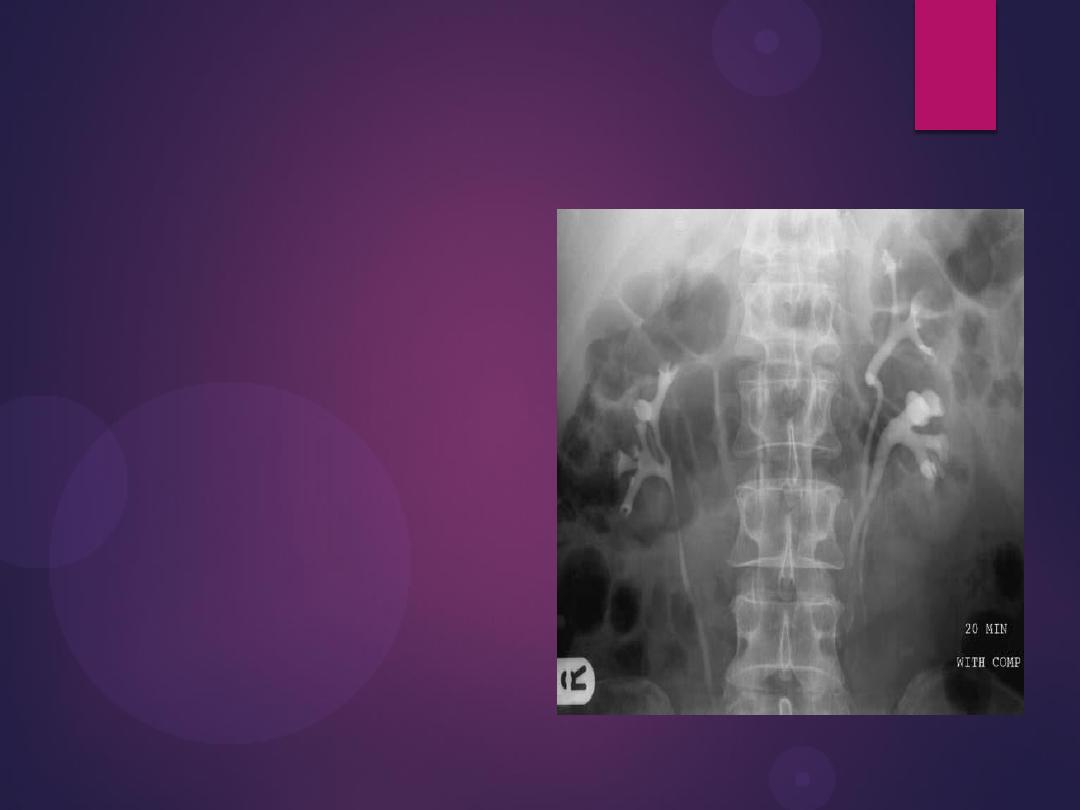
Pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction
Filling defects
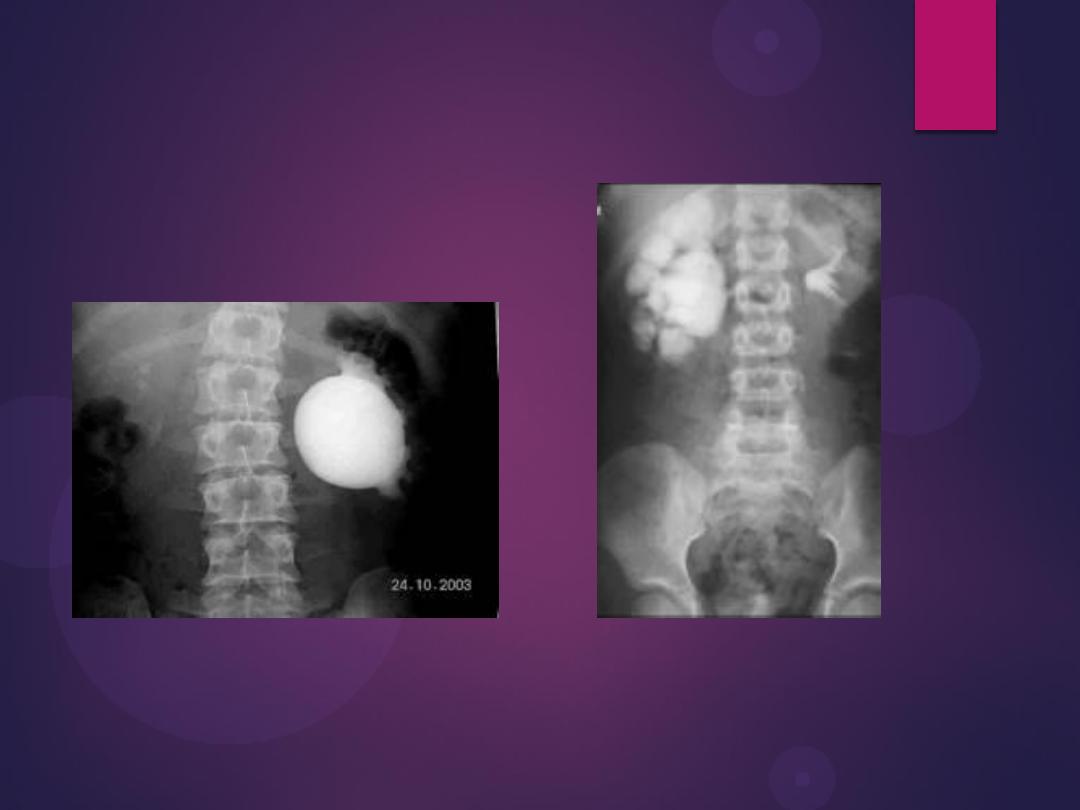
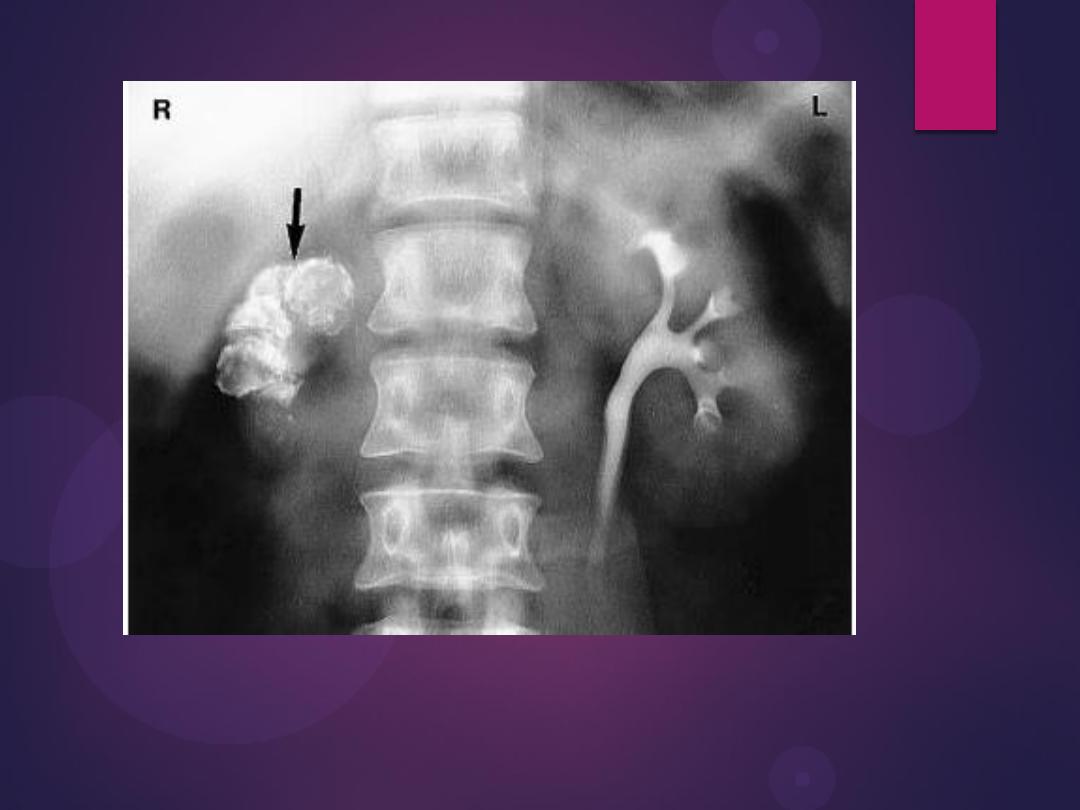
Multiple Calculi in the Renal Pelvis. A
retrograde pyelogram demonstrates
multiple filling defects

Radiograph from a retrograde pyelogram of the left kidney reveals a
multilobulated filling defect (arrow) in the left renal pelvis. Biopsy
confirmed transitional cell carcinoma.
Bladder
Bladder Wall Thickening
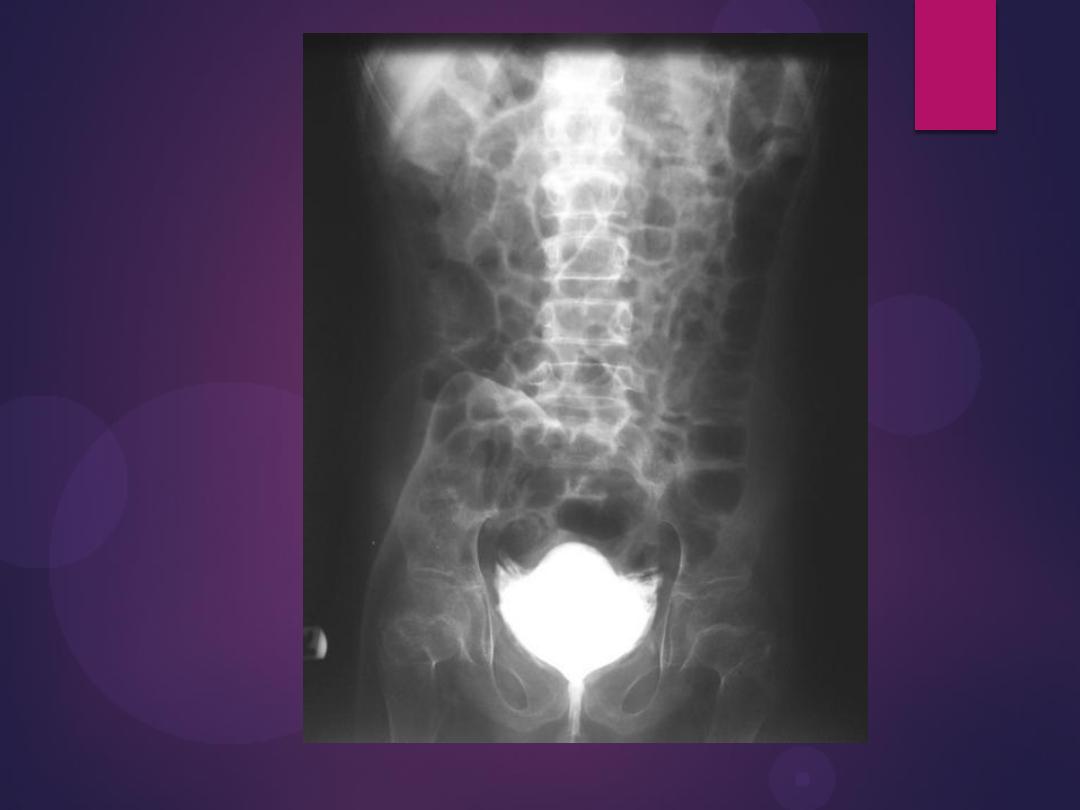
Bladder rupture. A cystogram done in a
patient after a motor vehicle accident
shows extravasation of contrast (arrows)
into the tissues surrounding the bladder, an
extraperitoneal bladder rupture
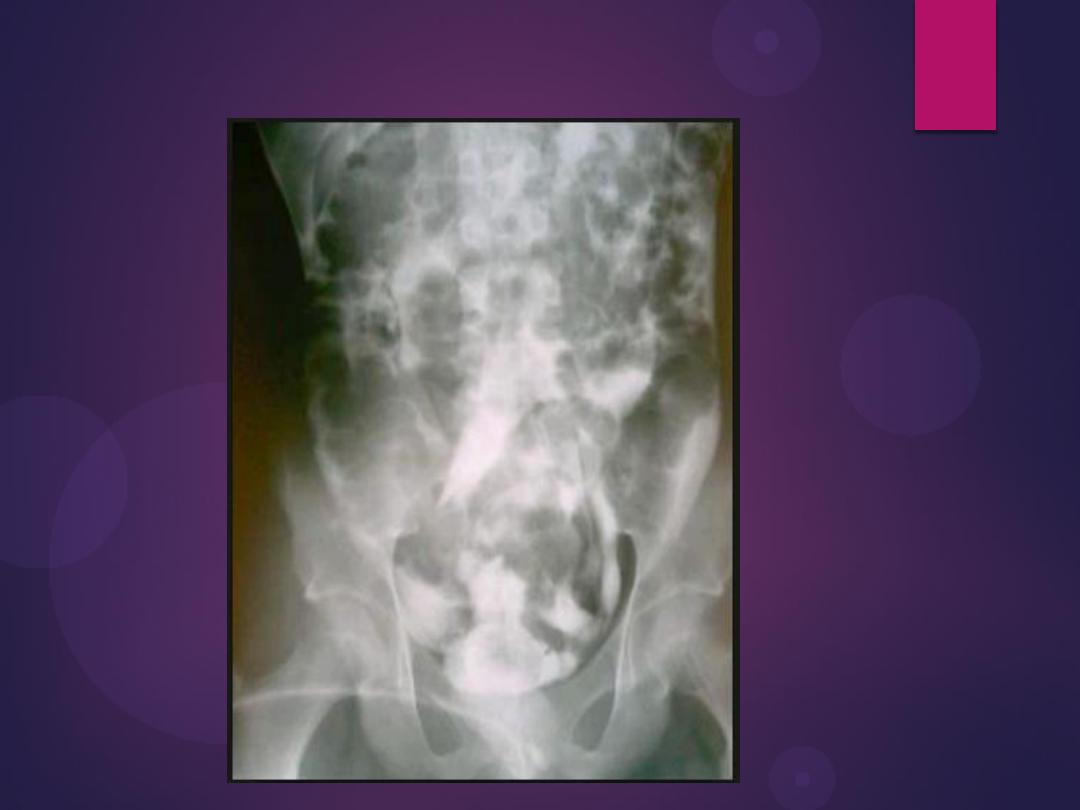
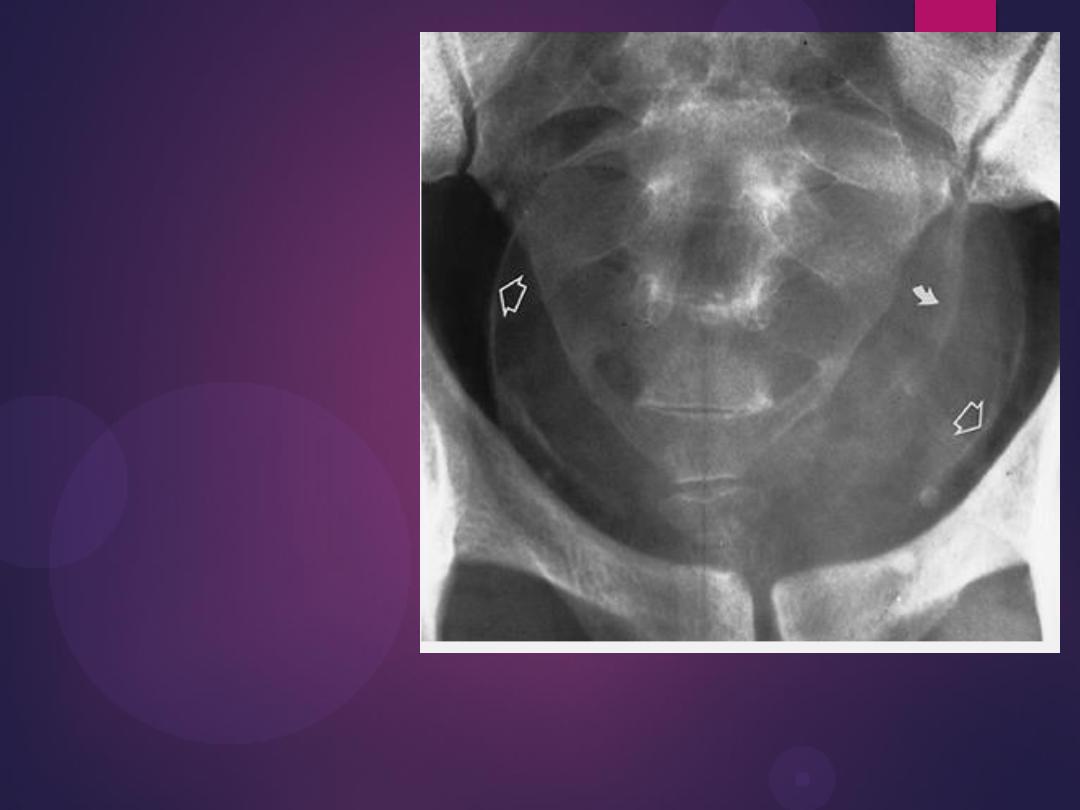
Infestation With Schistosoma haematobium. Plain radiograph
demonstrates calcification in the wall of the bladder (open arrows) and in
the wall of the left ureter (curved arrow). The bladder is filled with urine
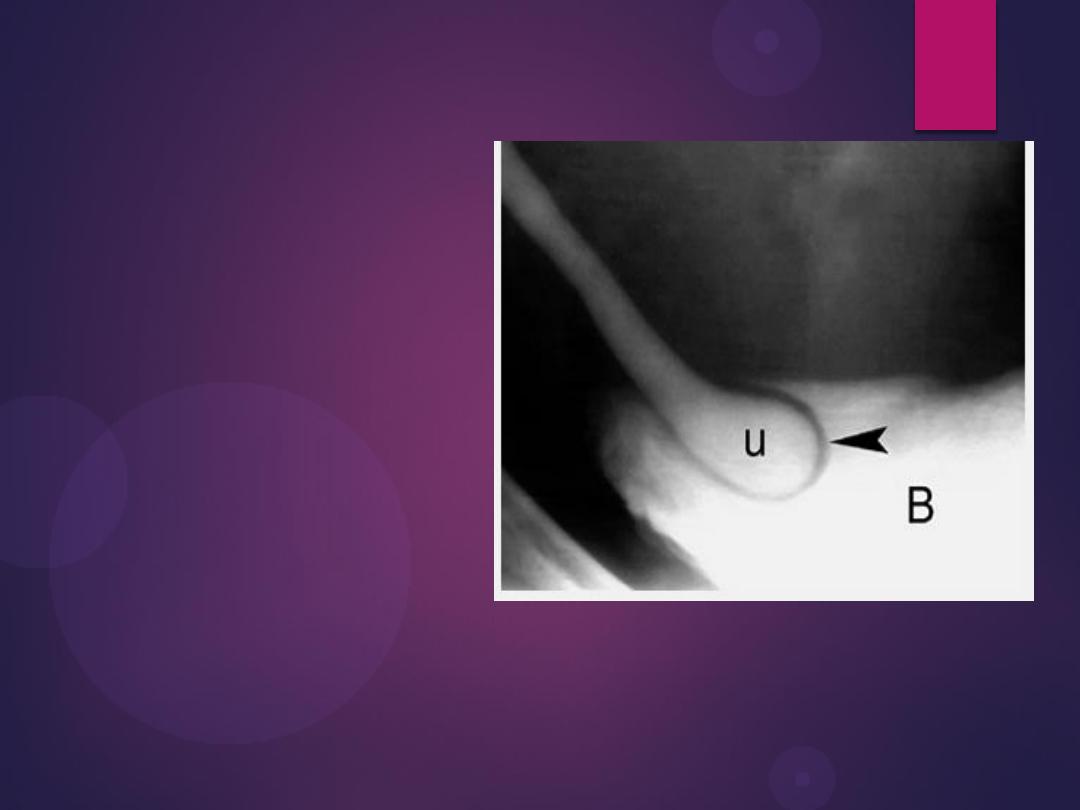
Filling defects
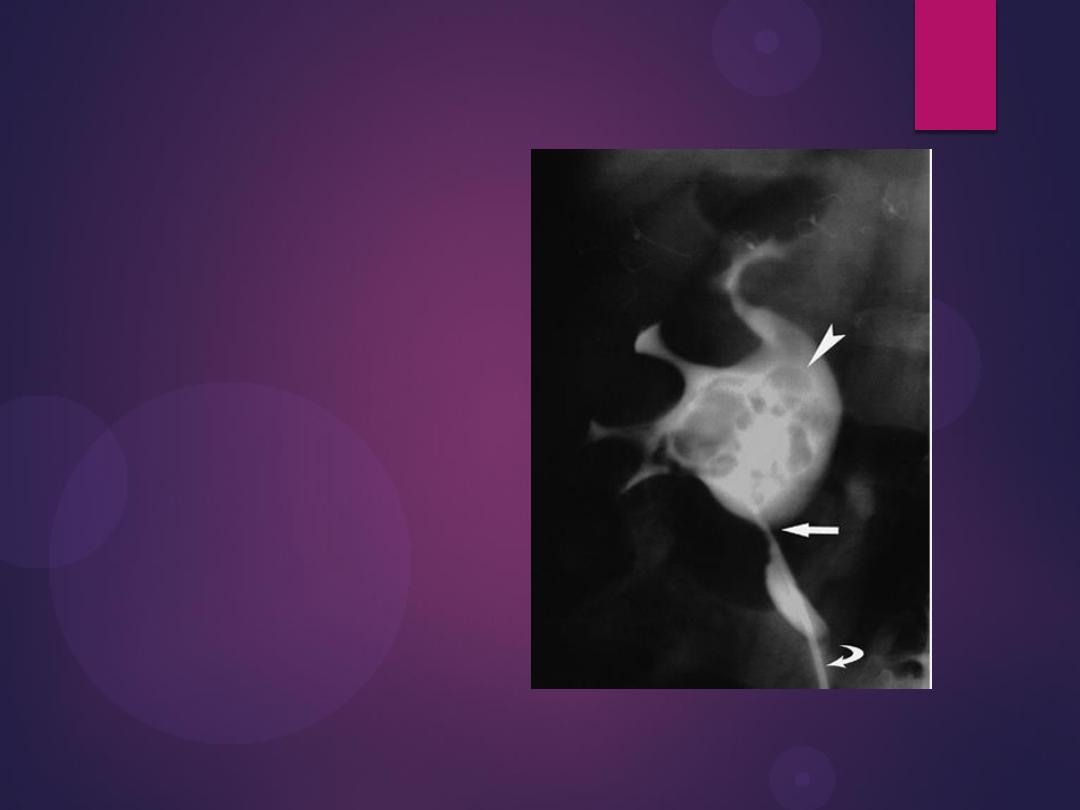
Radiograph from an excretory urogram demonstrates mild dilation of the
right ureter associated with a simple ureterocele (u) that protrudes into
the lumen of the bladder (B). The radiolucent wall of the ureterocele
(arrowhead) is outlined by contrast within the ureterocele and contrast
within the bladder lumen. The wall of the ureterocele is made up of the
wall of the ureter and the bladder mucosa.
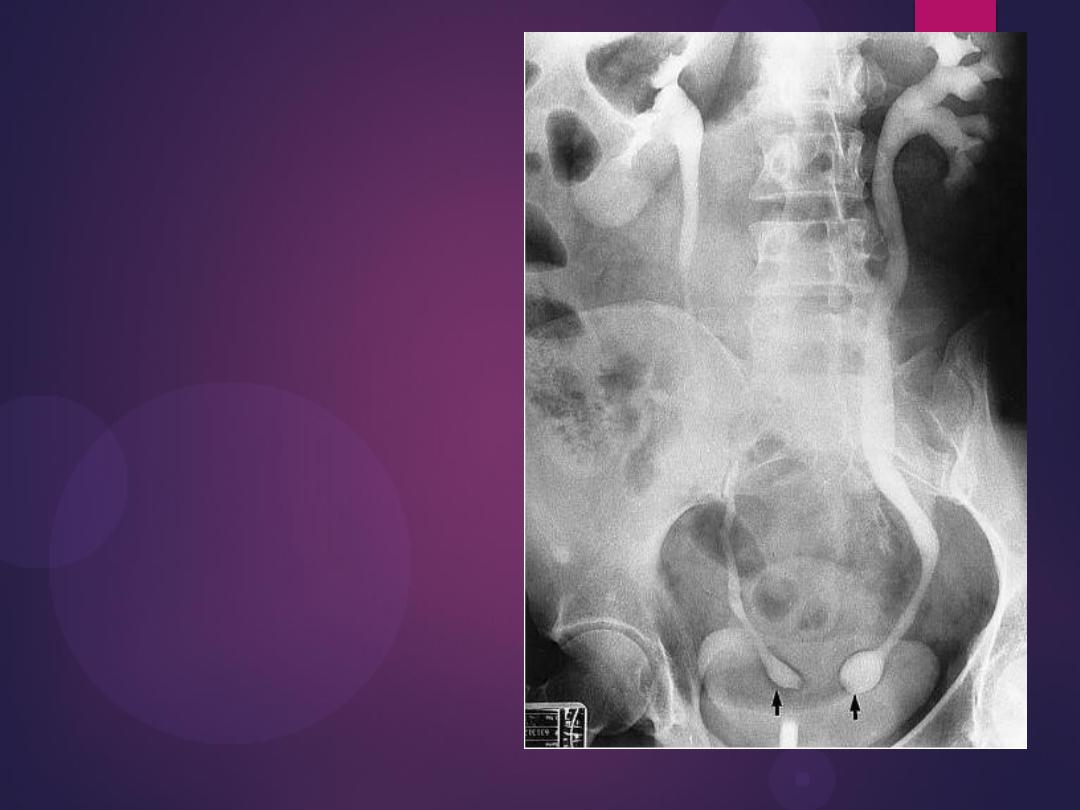
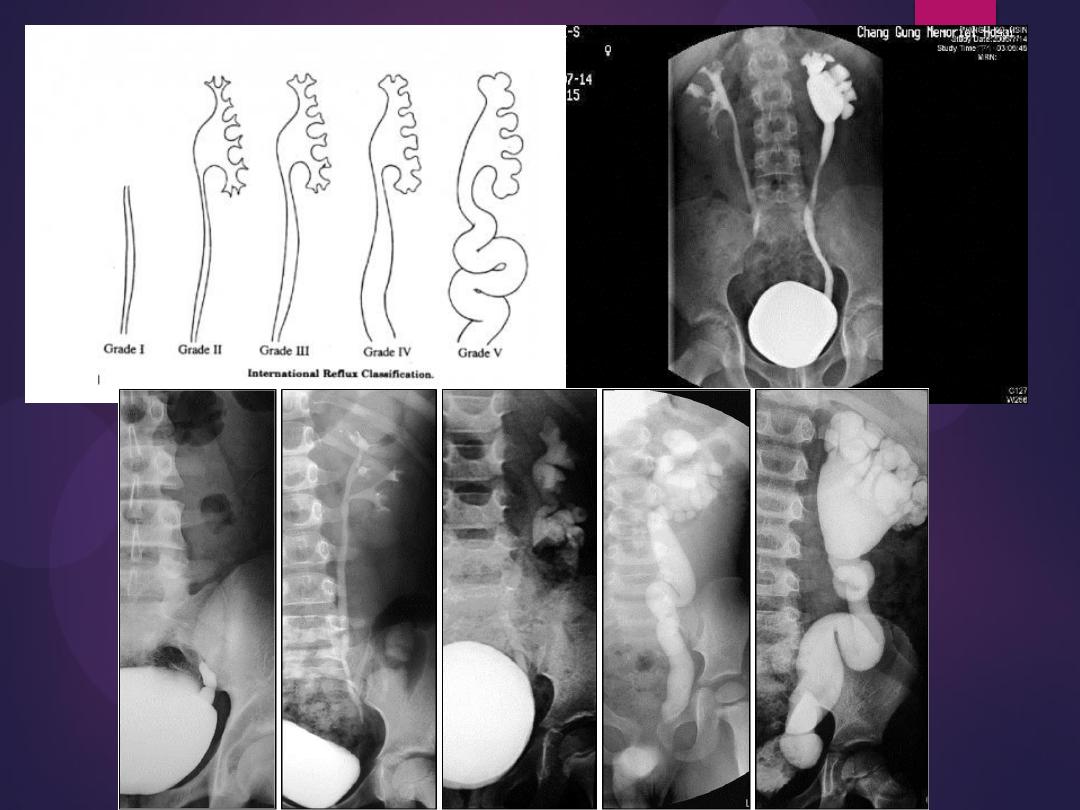
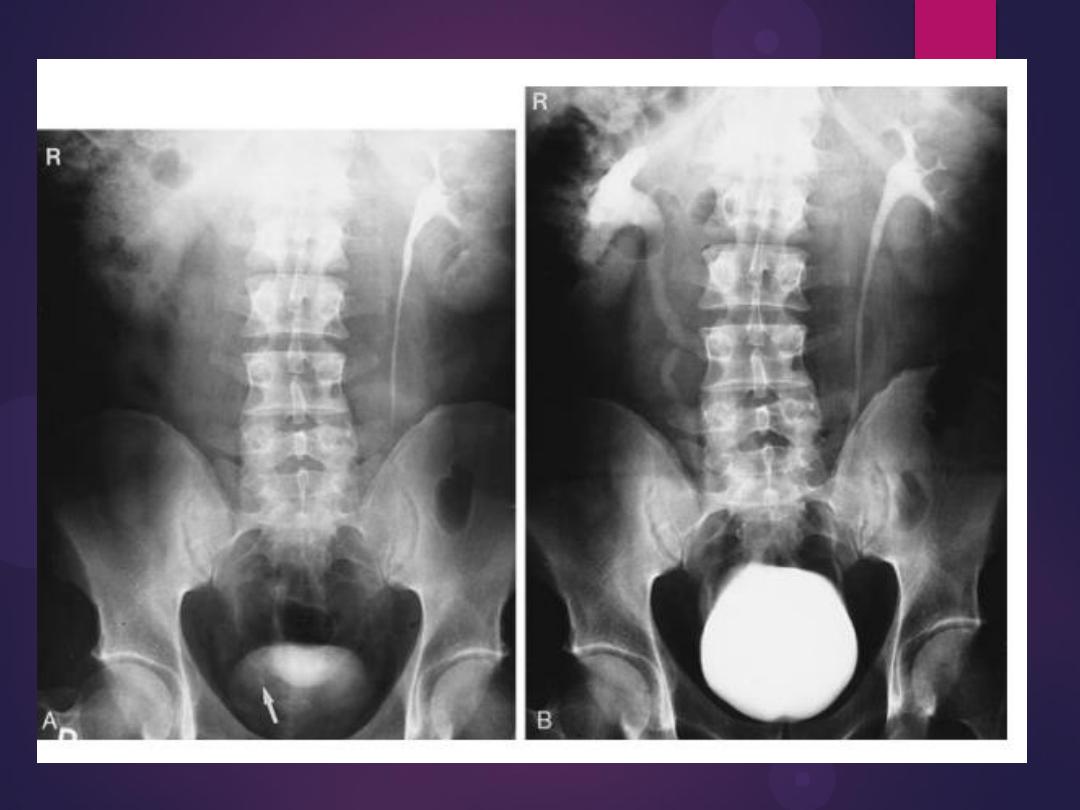
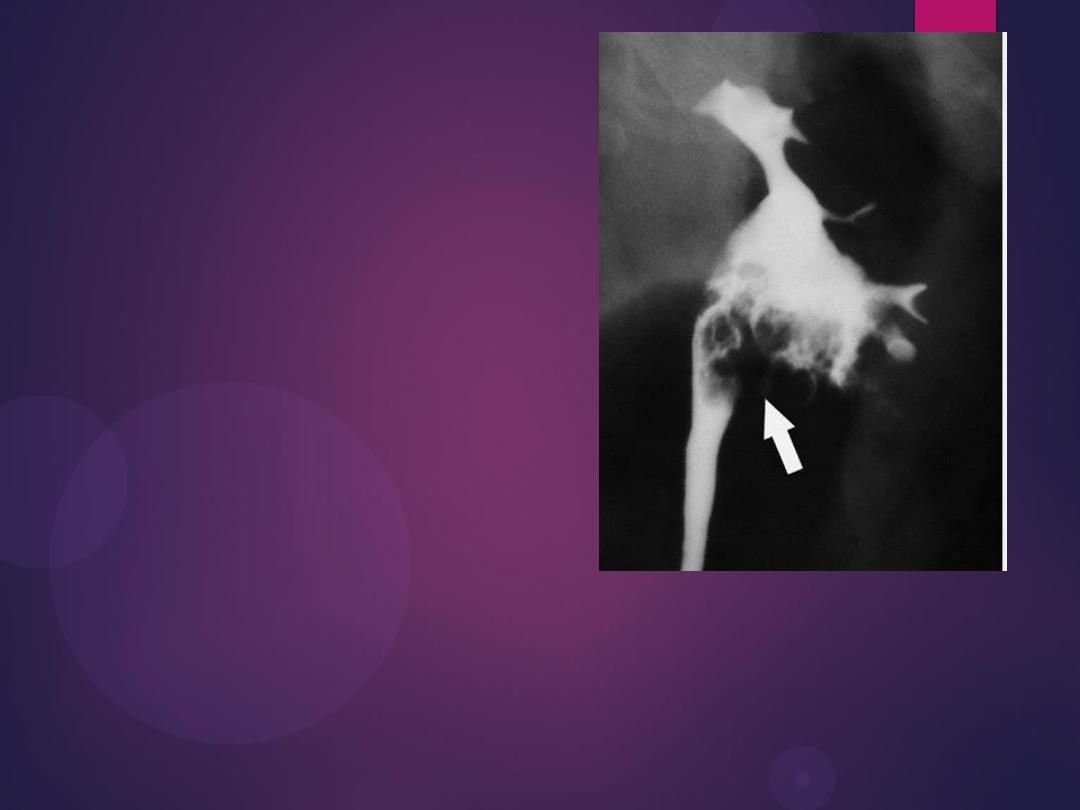
Bilateral ureteroceles. dilatation of the
distal ureter as it enters through the
bladder wall. This produces a typical
“cobra head” deformity (arrows.
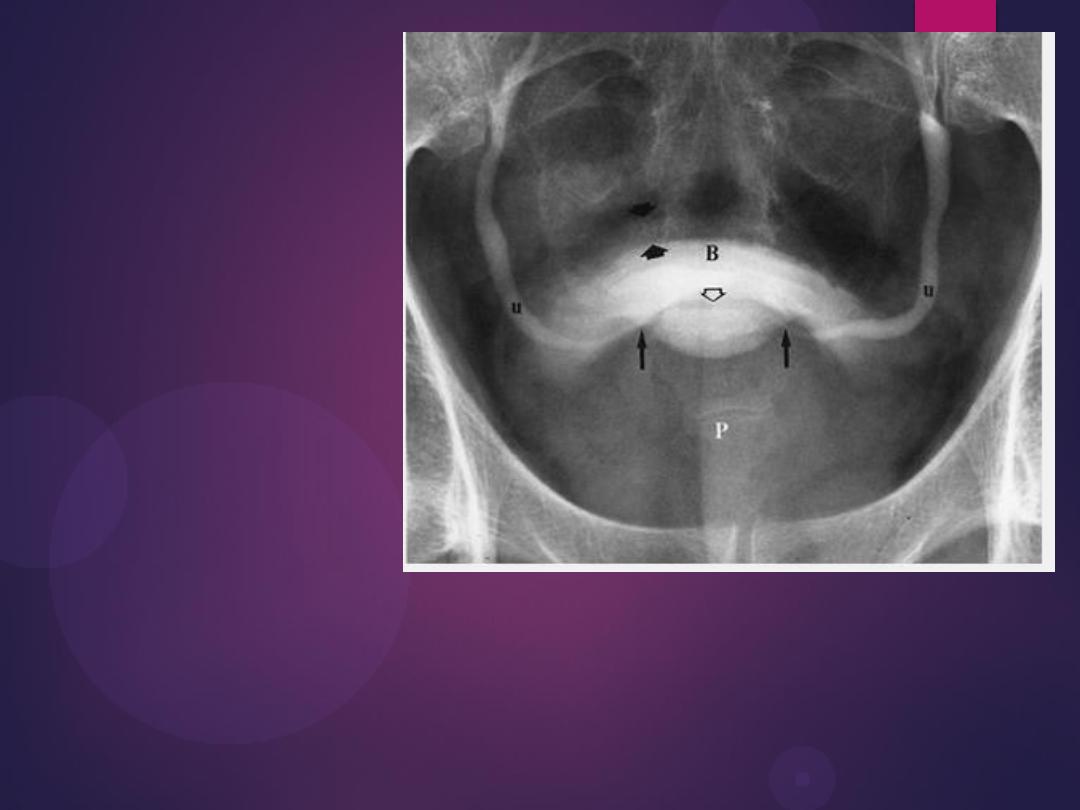
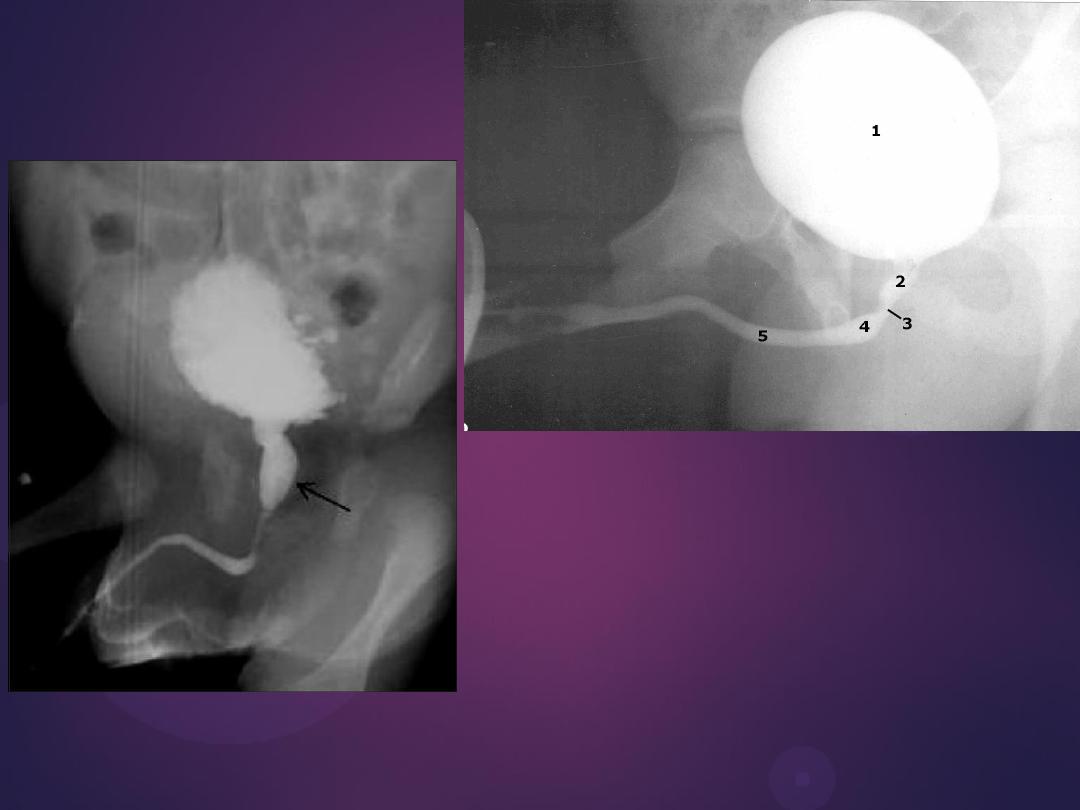
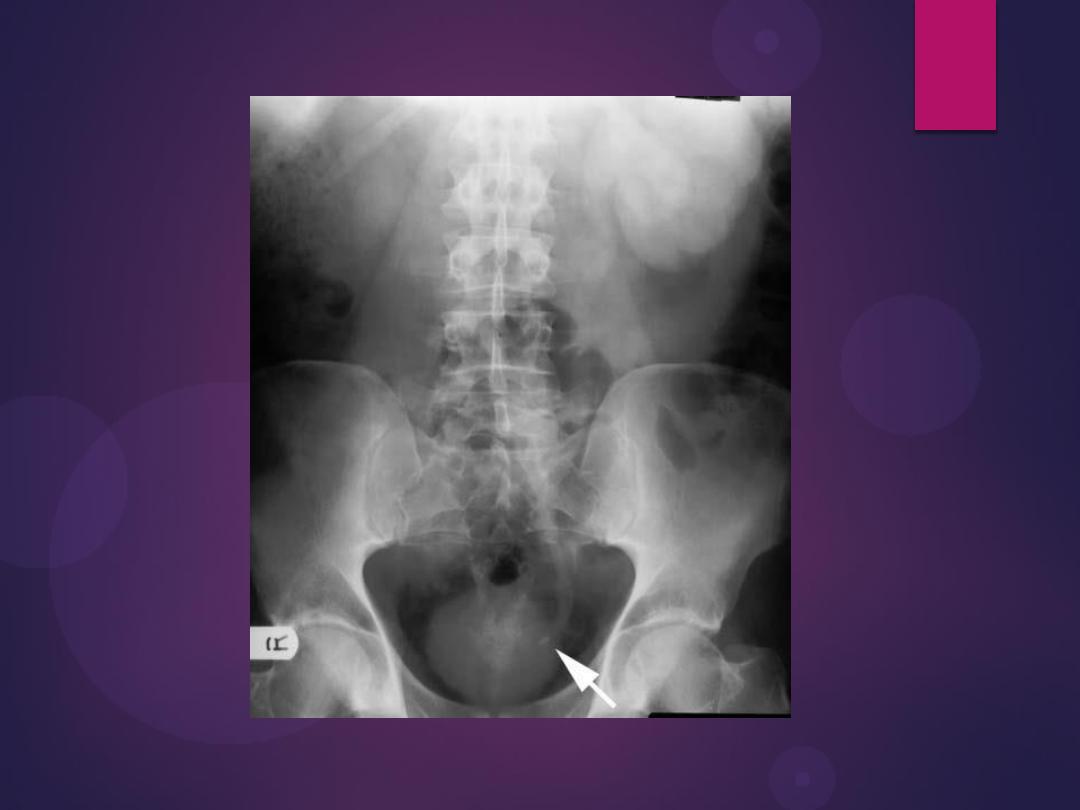
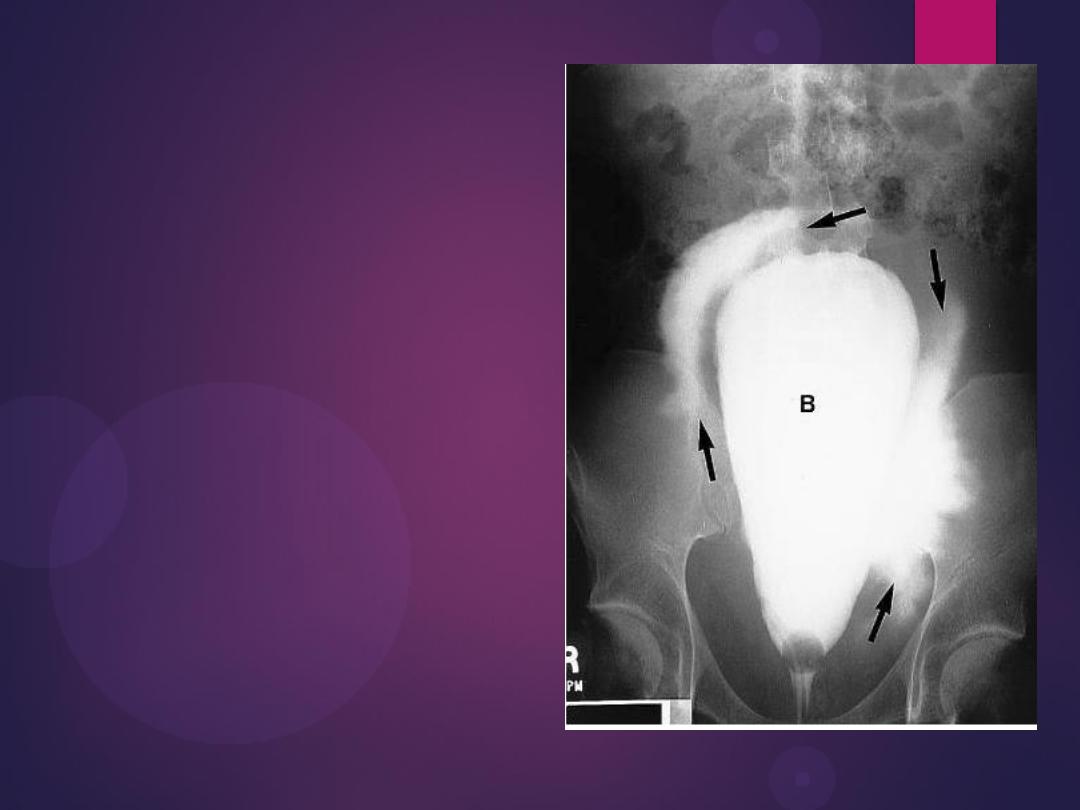
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy. A radiograph from an excretory urogram
shows marked uplifting of the bladder base because of massive
enlargement of the prostate (P). The trigone (open arrow) and ureteral
orifices (black arrows) are markedly elevated, resulting in a J-shaped
appearance to the distal ureters (u). The bladder wall is thickened
(between black arrowheads), and the bladder (B) mucosal pattern is
prominent.
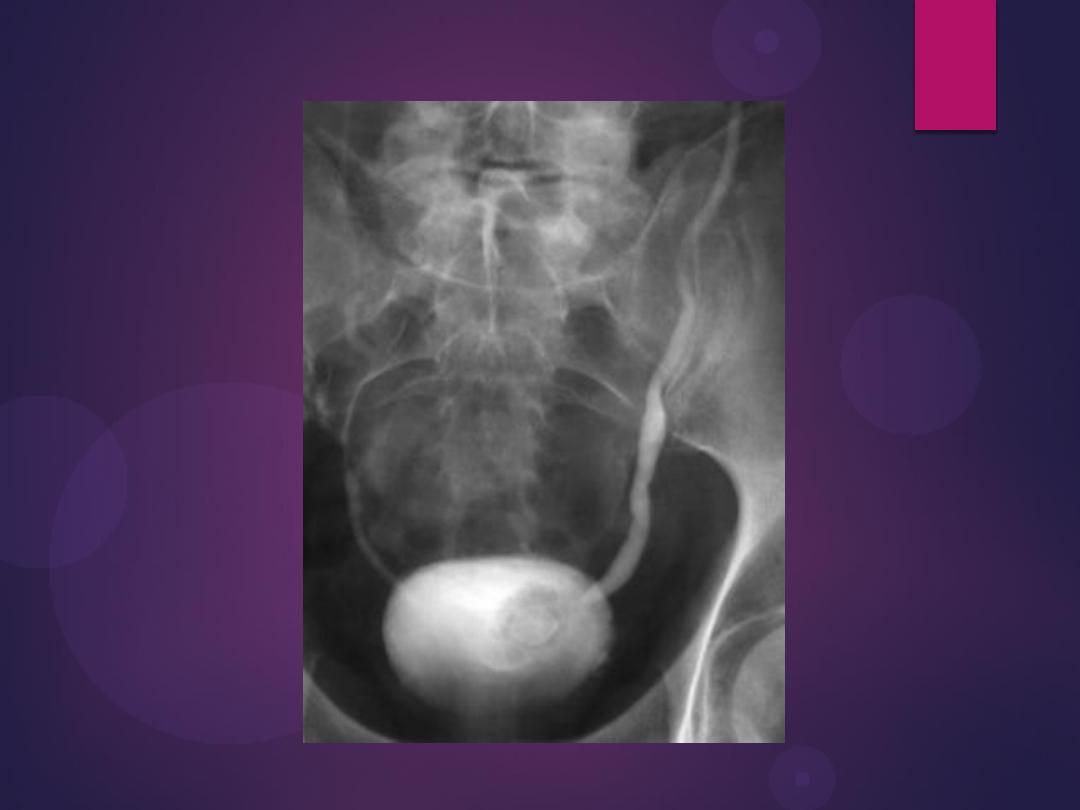
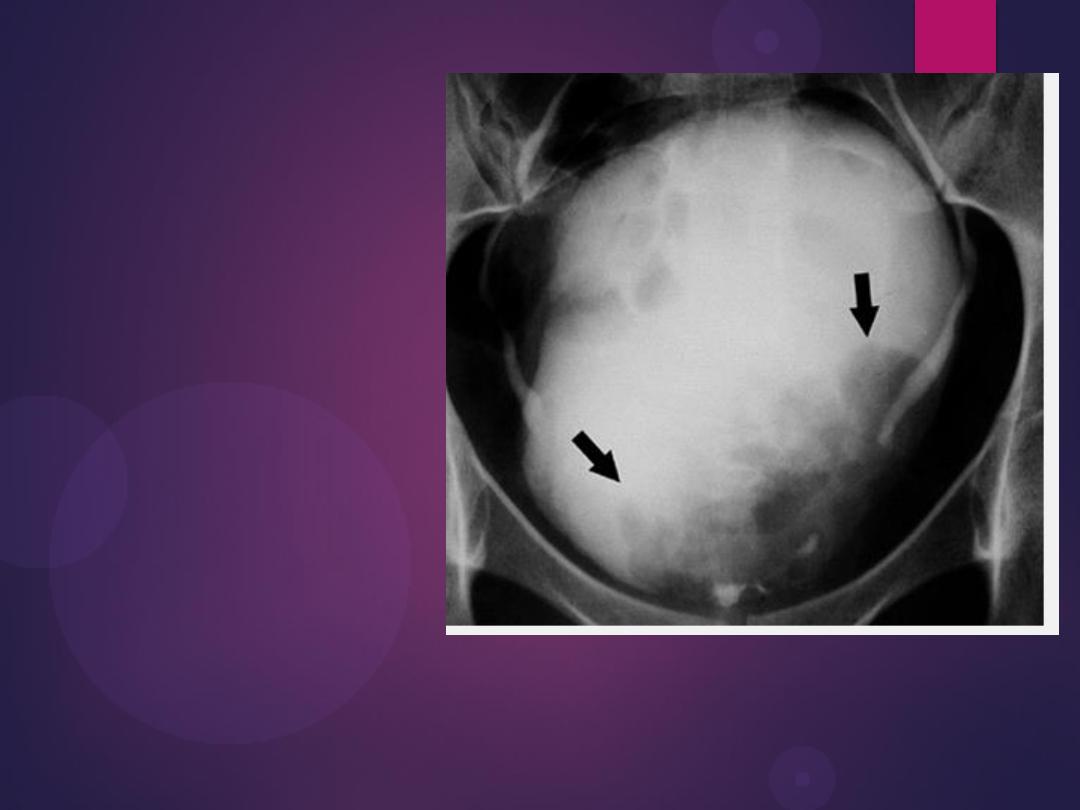
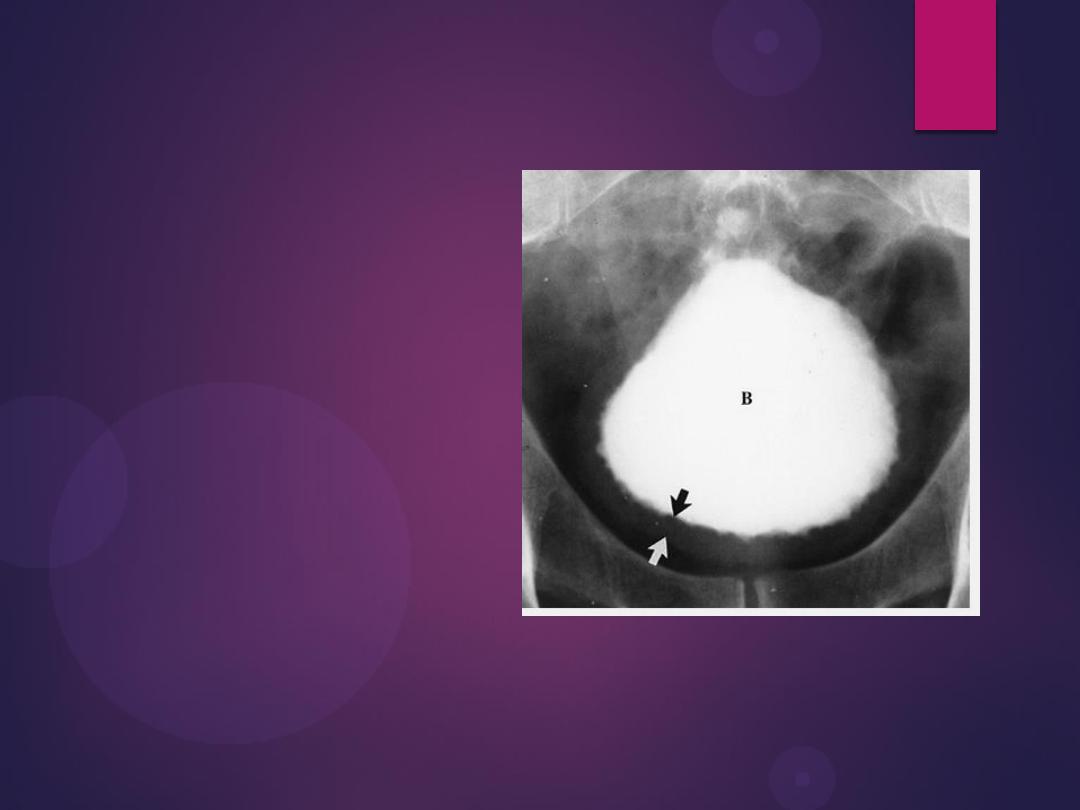
Transitional Cell Carcinoma. Radiograph from an excretory urogram
reveals a lobulated mass (arrows) causing a large filling defect in the base
of the bladder (B). Both ureters are visualized.
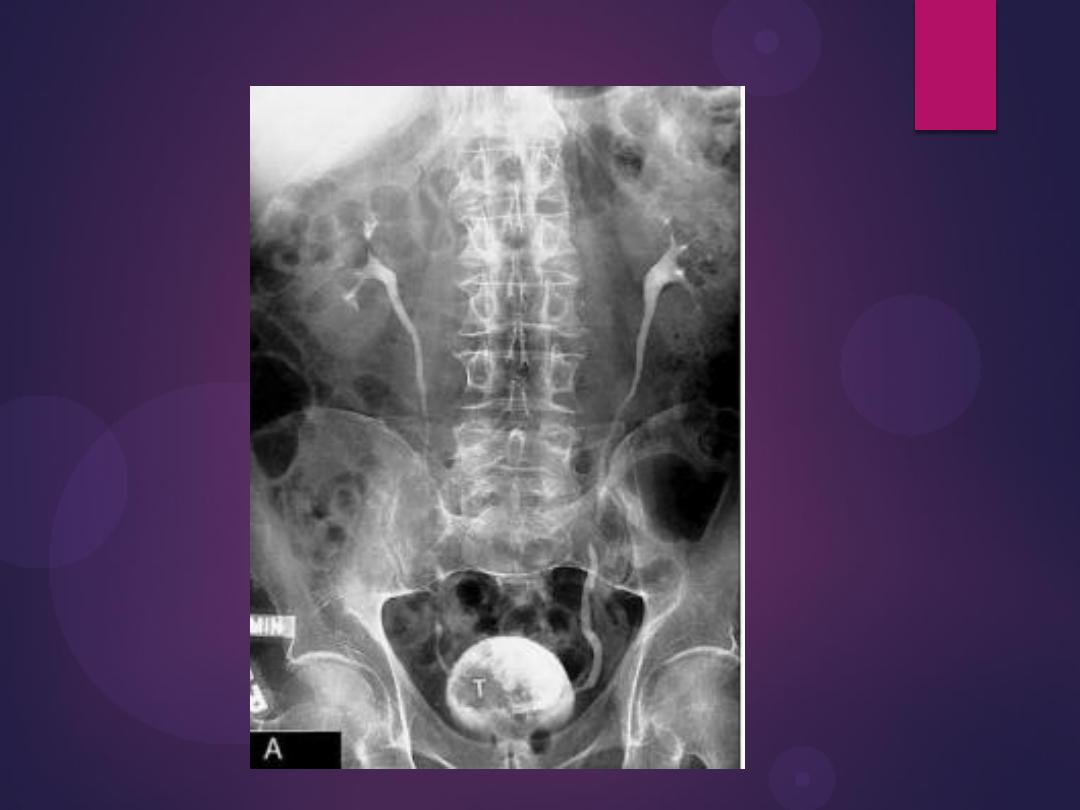
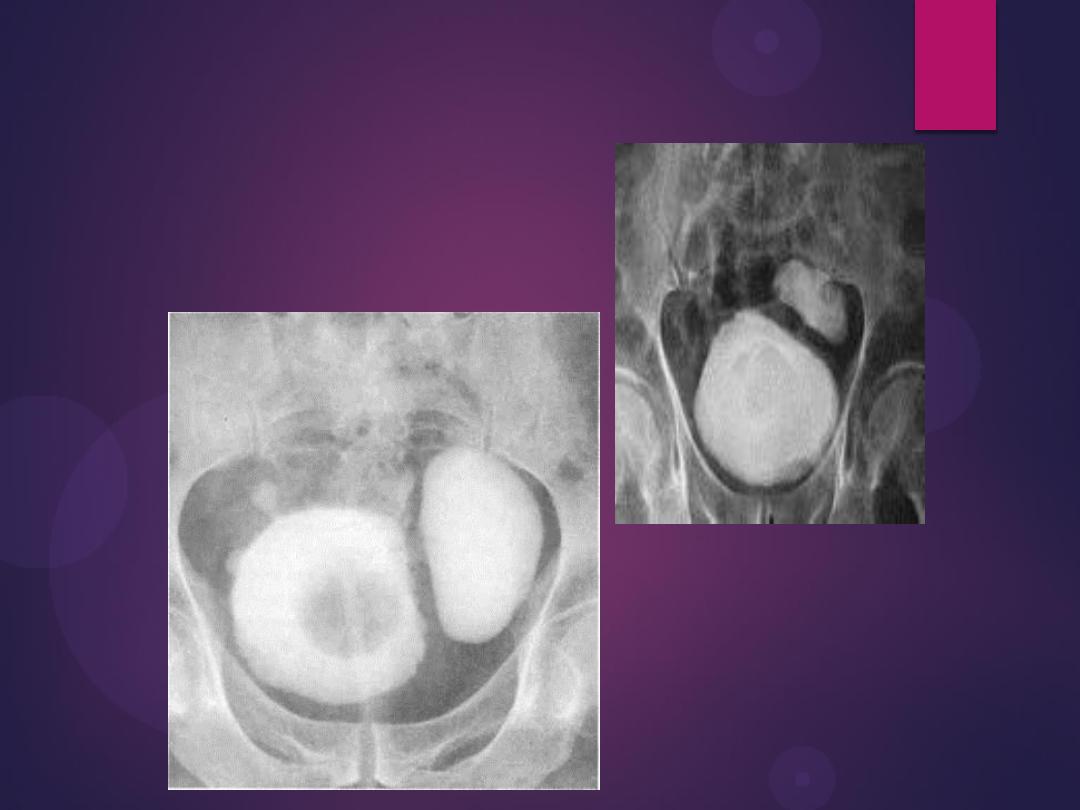
Urinary bladder diverticulum