Thoracic radiology
Dr.Khaleel IbraheemMBChB,DMRD,CABMS-rad
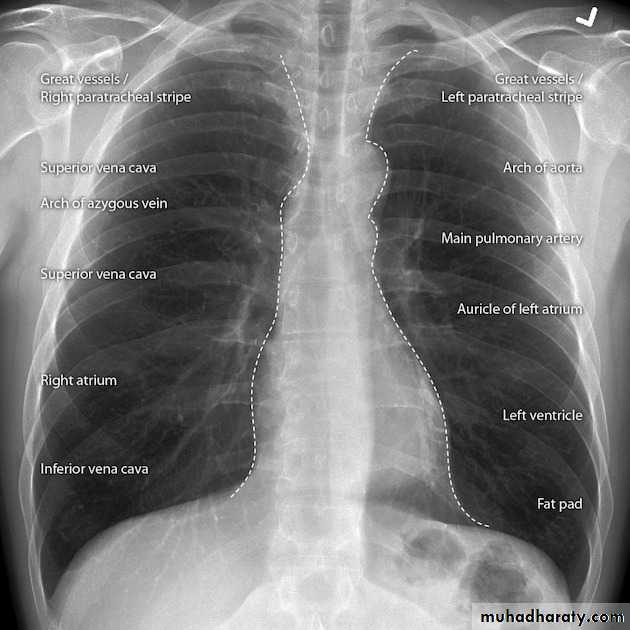
Approach to chest x ray
Chest consolidation
Diffuse lung lesions
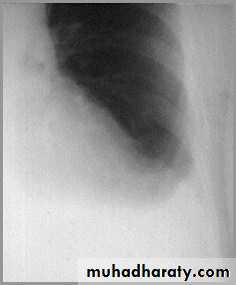
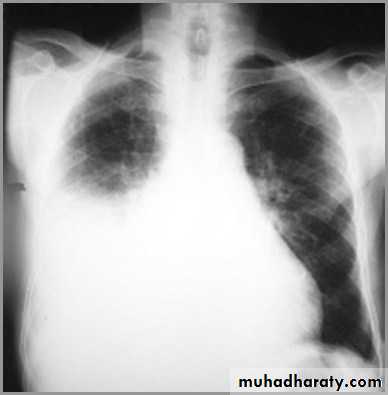
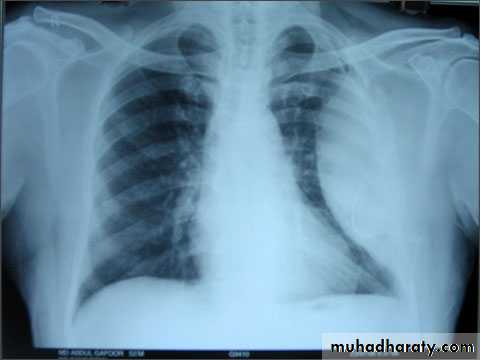
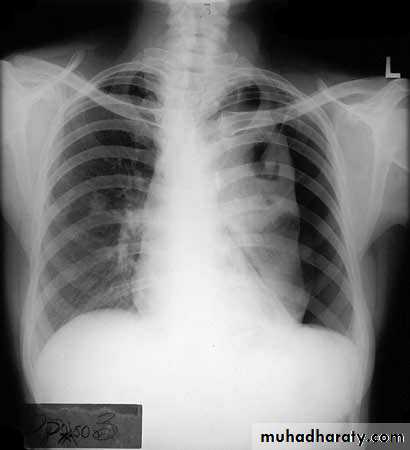
Differentiating the Causes of an Opacified Hemithorax
Atelectasis of an entire lungA large pleural effusion
Pneumonia of an entire lung
And a fourth cause: Post-pneumonectomy – removal of an entire lung
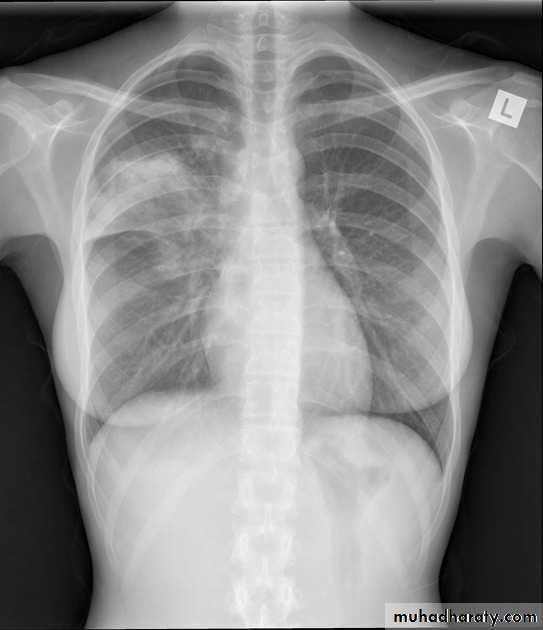
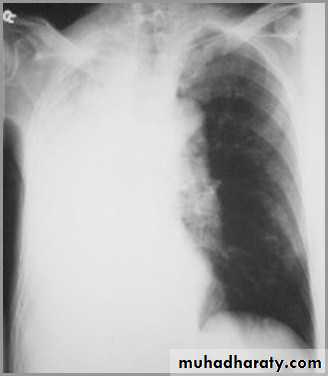
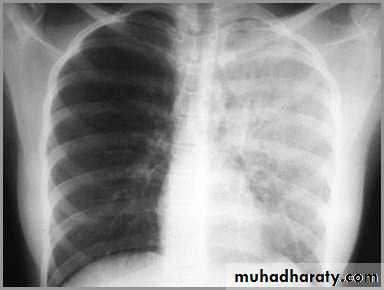
Atelectasis of the Lung
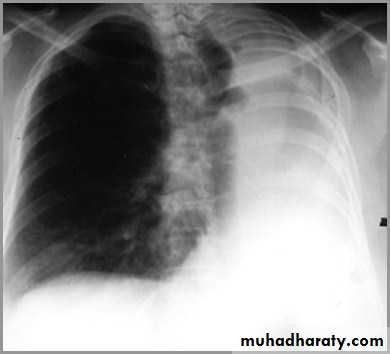
There is a shift of heart and hemidiaphragm toward side of opacification (toward side of volume loss)Pleural Effusion
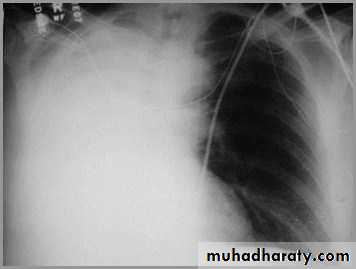
It acts like a massPushing the heart and trachea away from the side of opacification
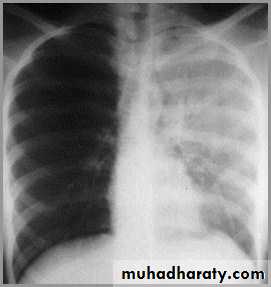
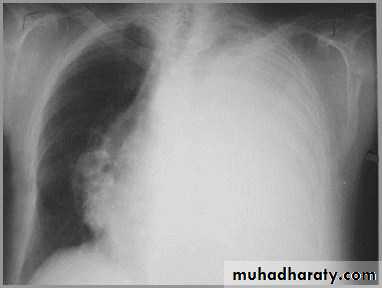
pneumonia
The hemithorax is opaque and there isno shift of the heart or tracheaThere may be an air bronchogram sign present
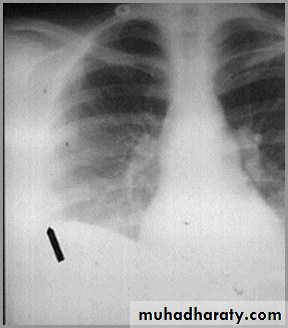
postpnemonectomy
The hemithorax eventually fibroses and becomes opaqueClues: There is frequently a resected fifth rib and/or surgical clips
quiz
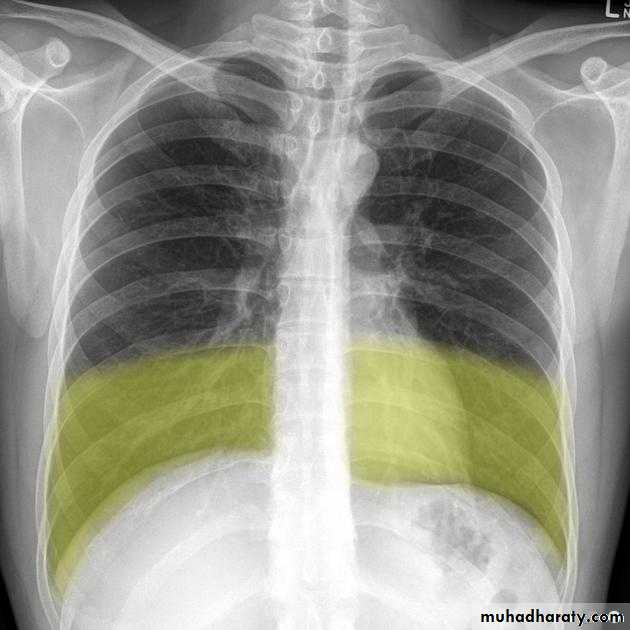
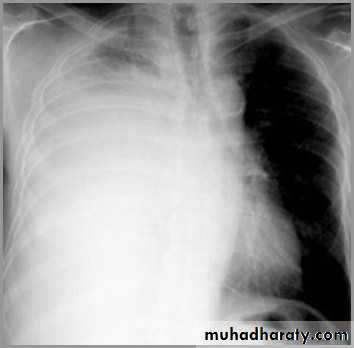
Pleural effusion
SubpulmonaryOn the frontal film, the highest point of the apparent right hemi diaphragm is displaced laterally (it is usually in the center).
Blunting of CP angle
Normally there are 2-10cc of fluid in the pleural spaceWhen >75cc accumulate, the posterior costophrenic (CP) sulci, seen on the lateral film, become blunted
When 200-300cc accumulate, the CP sulci on the frontal film become blunted
Meniscus sign
Pleural fluid tends to rise higher along its edge producing a meniscus shape medially and laterallyUsually only lateral meniscus can be seen
The meniscus is a good indicator of the presence of a pleural effusion
Loculated effusion
Occurs secondary to adhesions which form between visceral and parietal pleuraAdhesions more common with blood(hemothorax) and pus (empyema)
Loculated effusions have unusual shapes or positions in thorax
hydropneumothorax
If both a pneumothorax and a pleural effusion occur together, it is called a hydropneumothoraxA hydropneumothorax is usually due to trauma, surgery, bronchopleural fistula
It is characterized by an air-fluid level in the hemithorax
A straight edge,indicative of a fluid interface, in this case an air-fluid interface, is seen on the right.
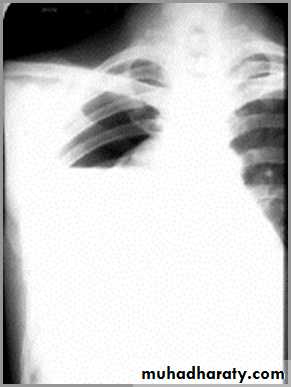
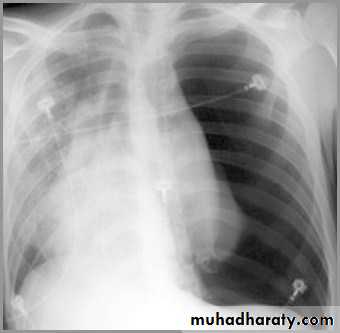
pneumothorax
When air enters the pleural space, the parietal and visceral pleura separate making the visceral pleura visibleThe thin white line of the visceral pleura is called the visceral pleural white line
You must see the visceral pleural white line to make diagnosis of pneumothorax!
Simple pneumothorax
In a simple pneumothorax, there is no shift of the heart or mediastinal structures (trachea)
Air in left hemithorax balances the air in the right hemithorax
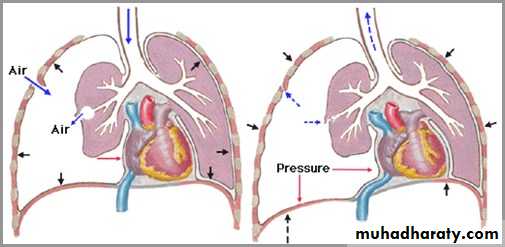
Tension pneumothorax
Progressive loss of air into pleural space causing a shift of the heart and mediastinal structures away from side of pneumothoraxOpposite lung is compressed
Respiratory function severely compromised