

Ba enema is the standard radiological examination. Double contrast
technique involve filling of part of the colon with barium then air is
blown to push barium & distend the colon so that the mucosa is
coated with barium. Preparation is required to rid the colon of fecal
material. Barium enema may miss rectal mucosal lesions.
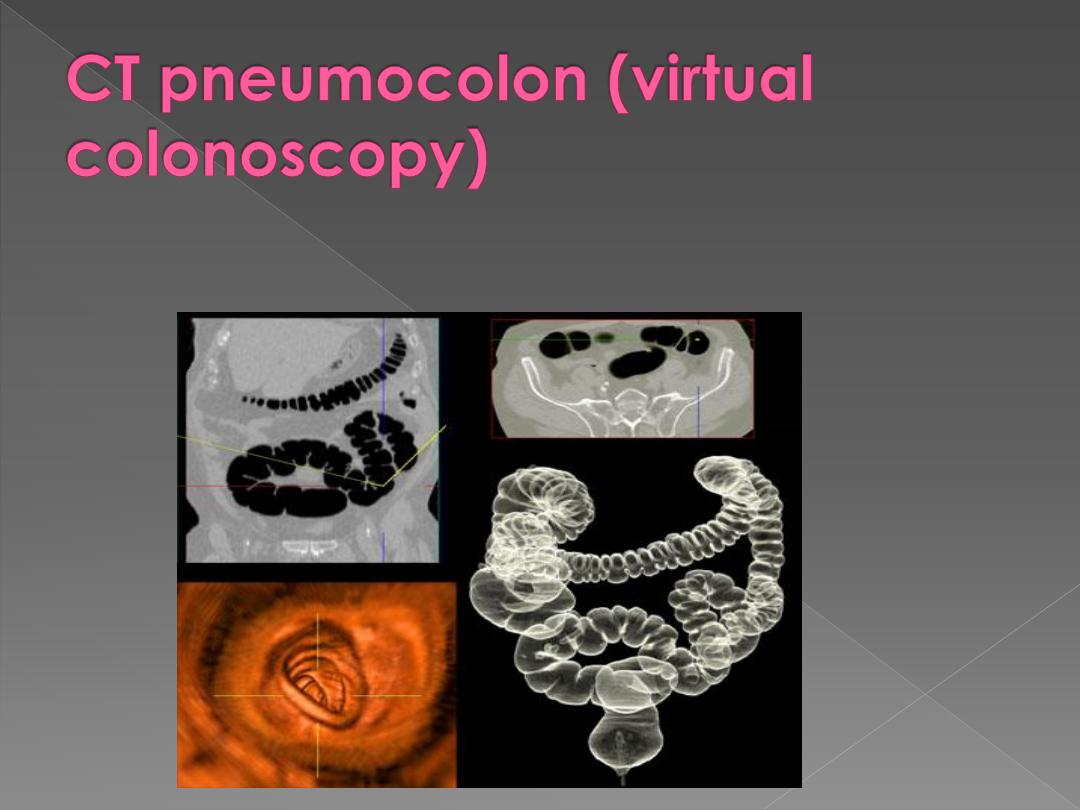
is new method to detect colonic carcinoma. Colonic preparation is
needed, no contrast for opacification of bowel but i.v. contrast is given,
and smooth muscle relaxant may be given.
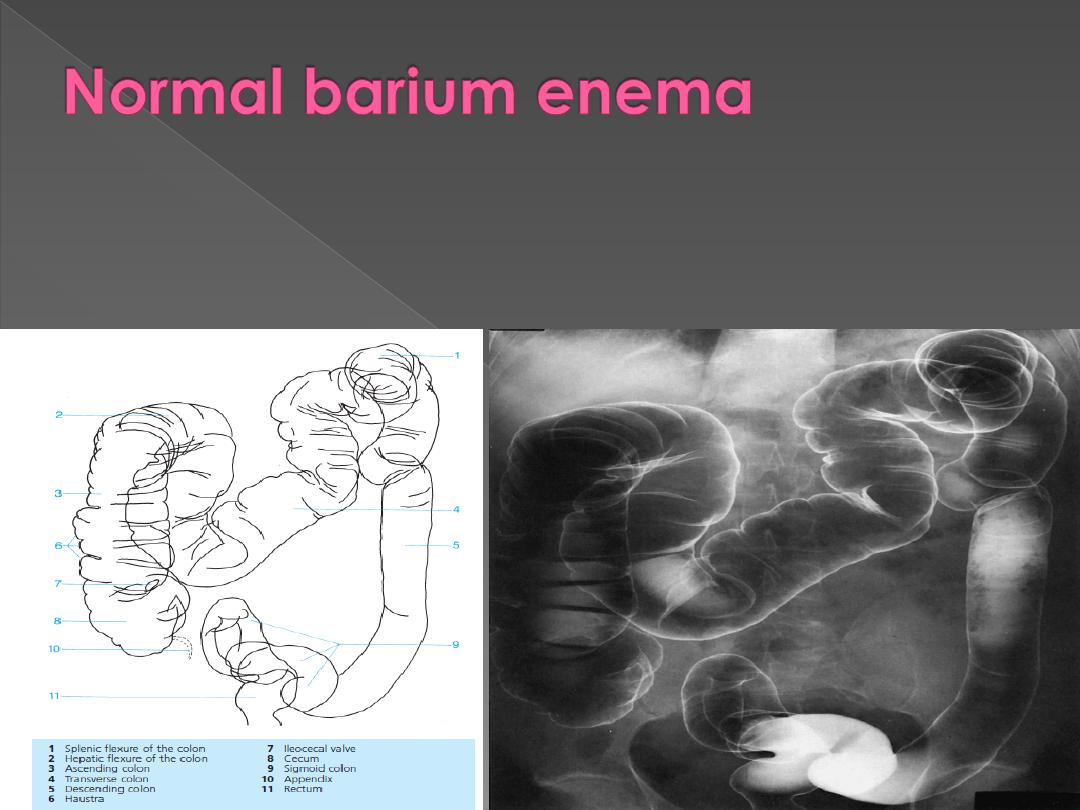
The colon has variable length. Sometimes there are redundant loops such as the sigmoid
and the transverse colon.
The caliber decreases from caecum to sigmoid.
Haustra may be absent in the descending & sigmoid region.
The outline of the colon is smooth
The caecum may be seen under the right hepatic lobe or even the center of abdomen.
The lips of the ileocecal valve may result in a filling defect that must not be mistaken for a
tumor.
The appendix & terminal ileum may fill but if not, there is no significance.

1. Narrowing:
Spasm seen in NORMAL people but may also seen in conjunction
with diverticulae disease & inflammatory diseases.

Strictures caused by
1carcinoma,
2diverticular disease,
3 Crohn's disease,
4 ischaemic colitis.
Rarer causes include TB, lymphogranuloma venereum, amebiasis &
radiation
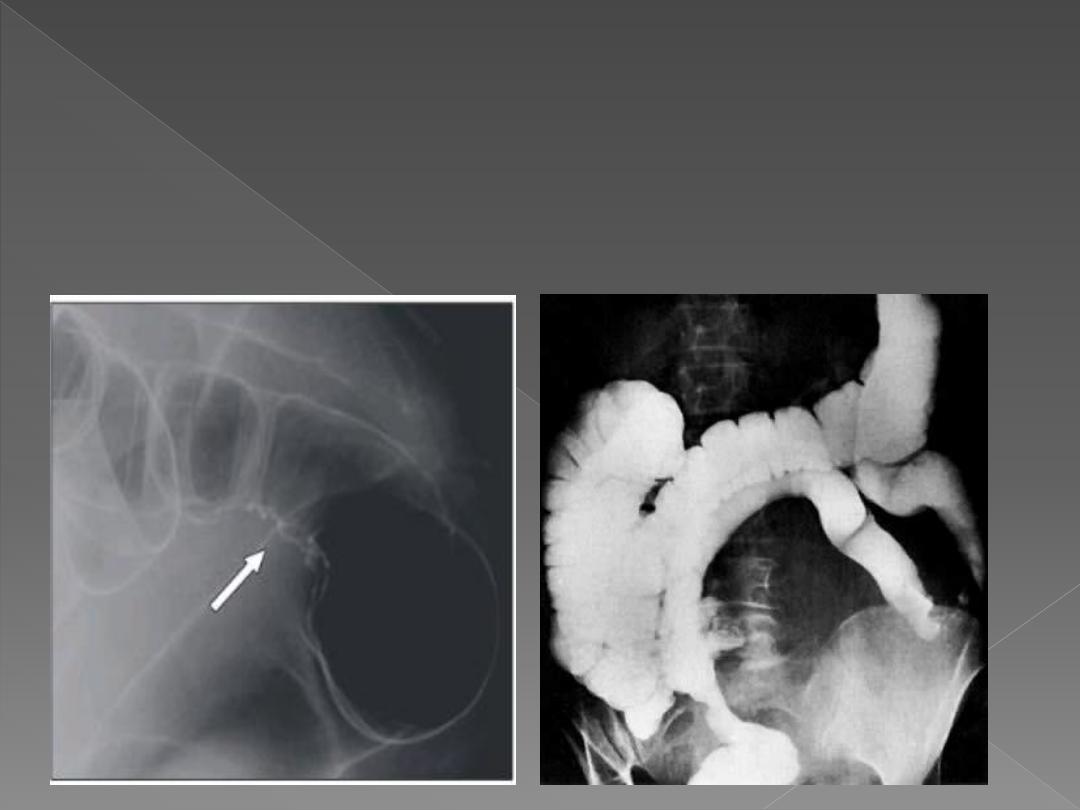
compression by extrinsic mass
Extrinsic compression causes a smooth narrowing of the colon
frequently from one side only & often displaces the colon. CT or US are
useful methods of confirming extrinsic compression & for assessing the
cause. E.g ovarian or uterine masses
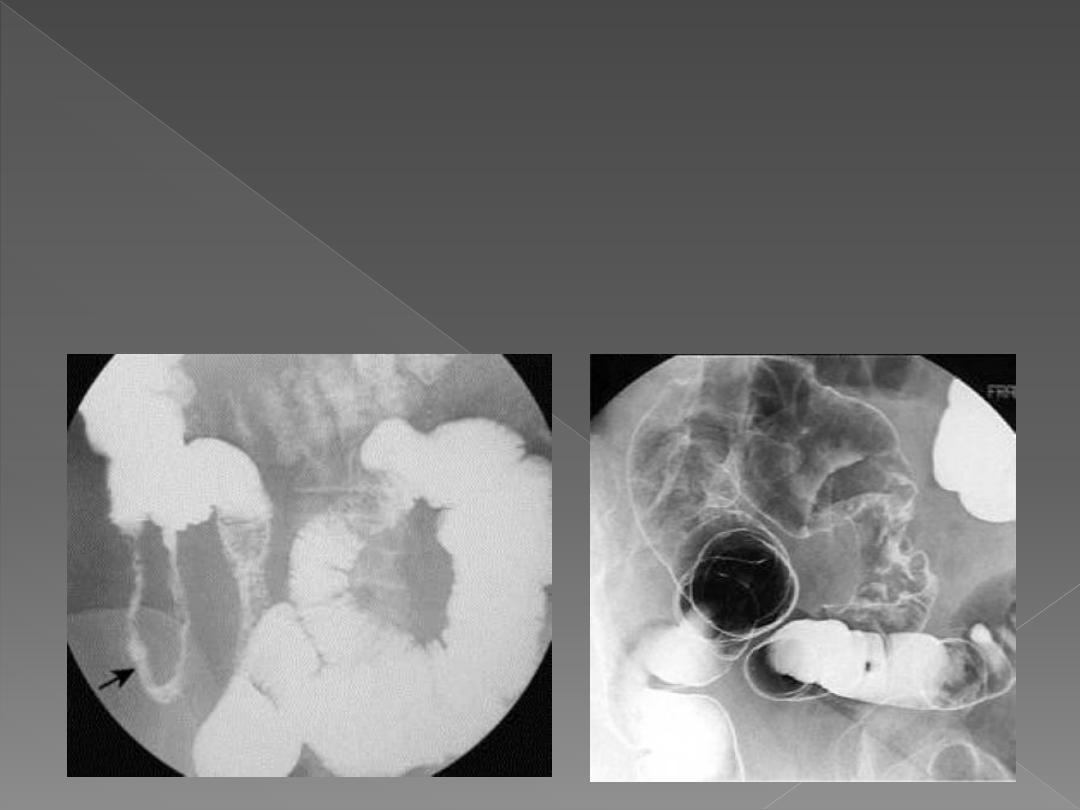
Points noted to reach the nature of a stricture:
Neoplastic
strictures have shouldered edges, irregular lumen & are rarely > 6
cm, While
benign
strictures have tapered ends, smooth outline & may be of
any length.
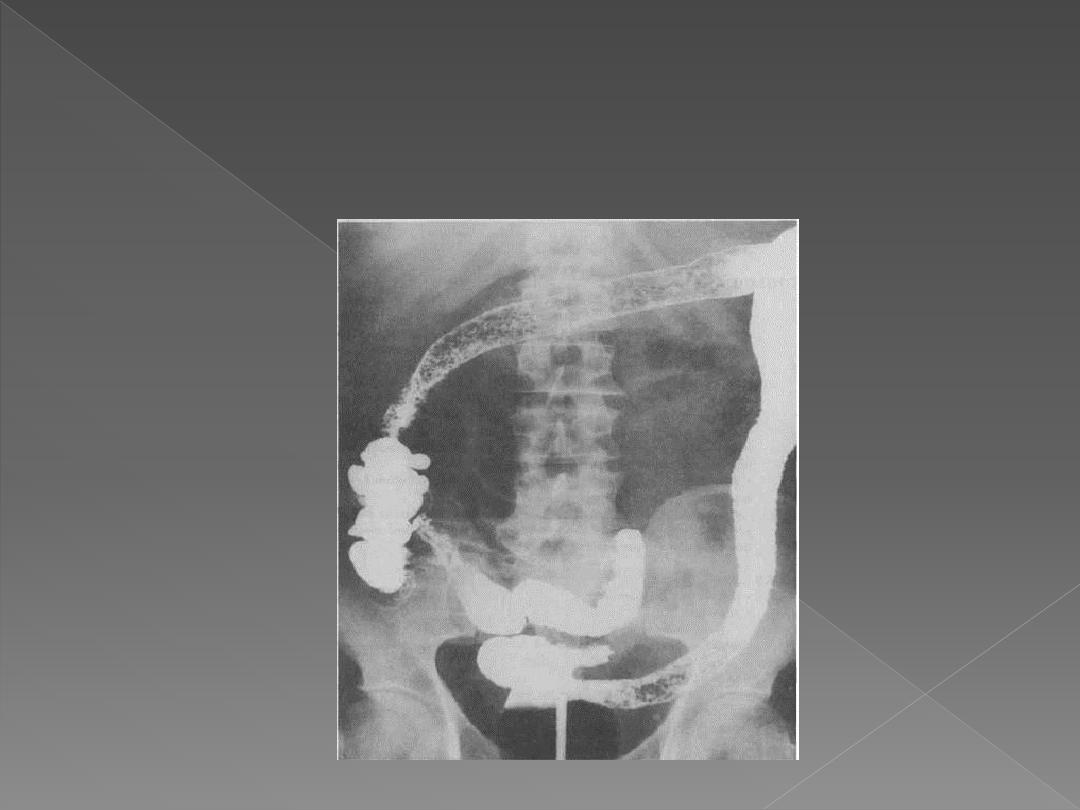
Ulceration may be seen in Crohn's
disease, while sacculation is a feature of
ischaemic colitis.
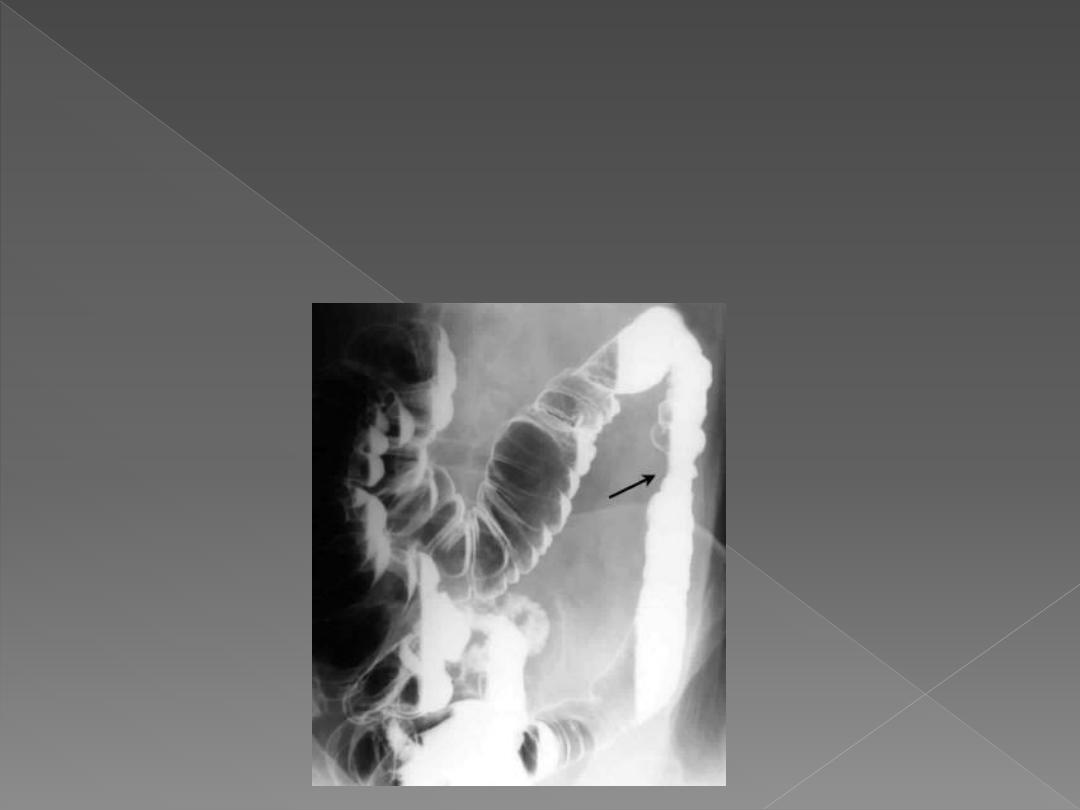
Narrowing in diverticular disease is accompanied by other
signs of diverticular disease & may appear similar to
neoplastic stricture.
Site of stricture can help in diagnosis. Diverticular disease is
usually confined to sigmoid. Ischaemic strictures are usually
centered between the splenic flexure & sigmoid. Crohn's
disease & TB have a predilection for the caecum.
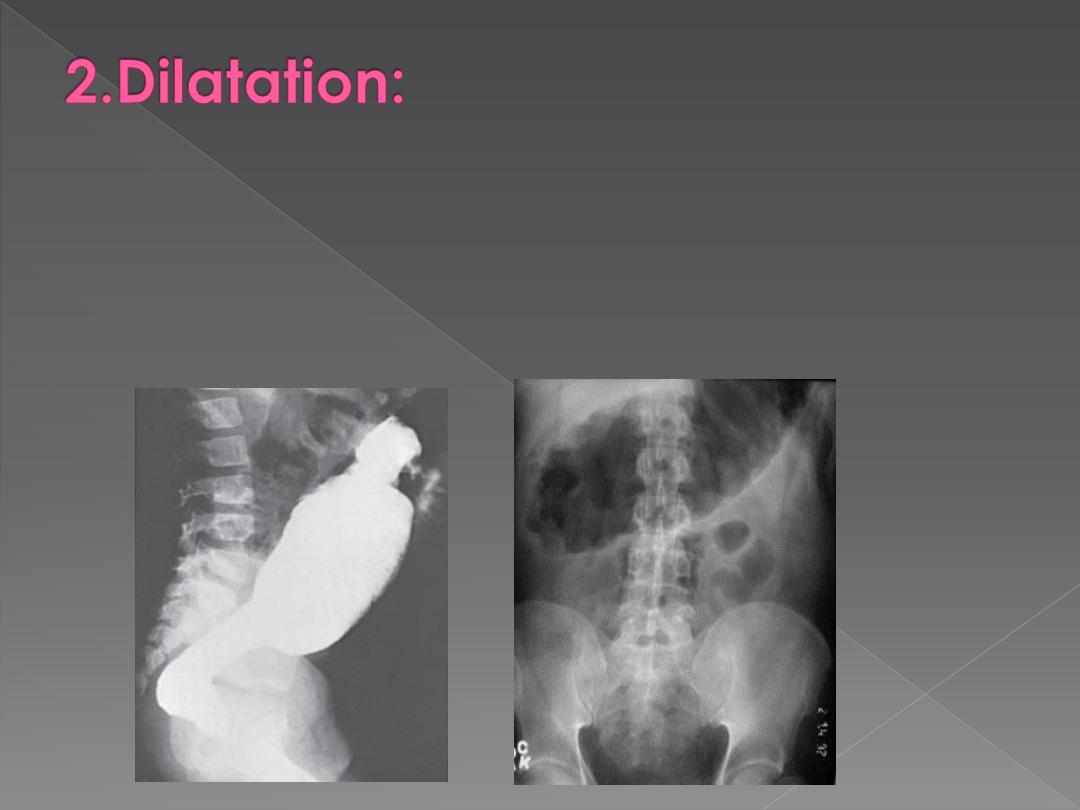
Is difficult to assess because double contrast examination involves distending the
colon.
Causes:
1. Obstruction: the most important consideration is the nature of obstructing lesion.
2. Paralytic ileus: diagnosed by clinical & plain film findings. Ba enema can be
undertaken in difficult cases (to be differentiated from mechanical obstruction). Ba
enema show dilated otherwise normal colon.
3. Volvulus.
4. Ulcerative colitis with toxic dilatation.
5. Hirschsprung's disease & megacolon.
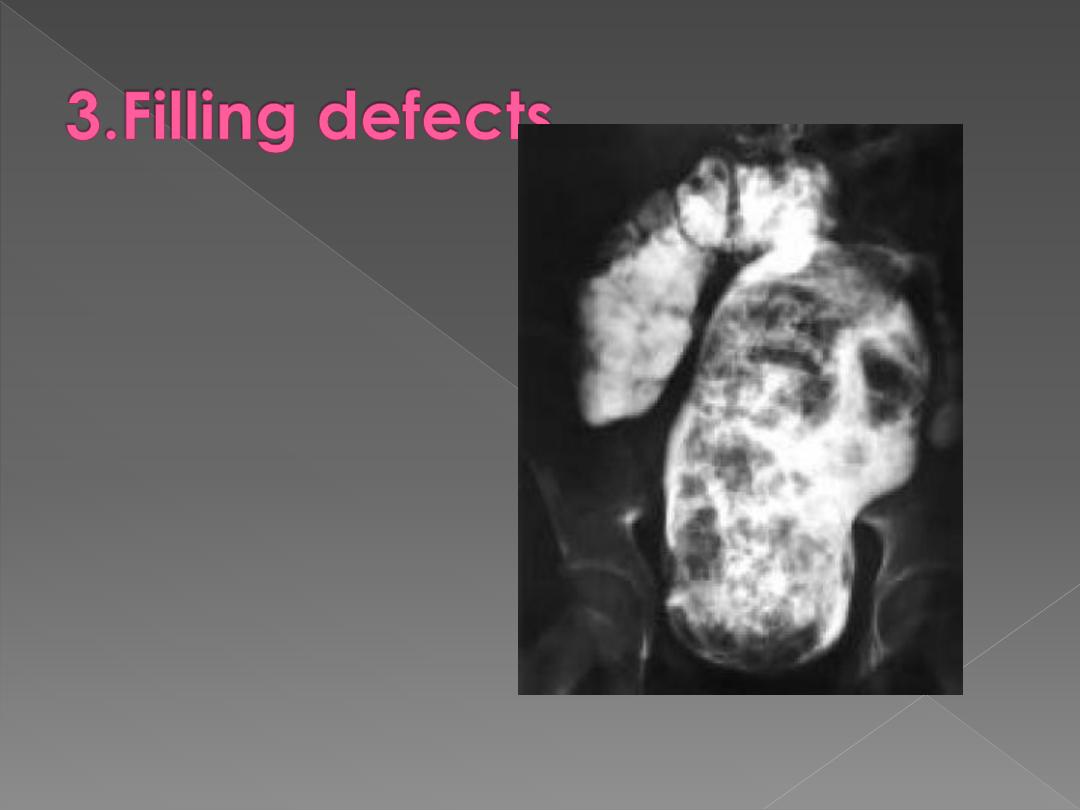
May be intraluminal, mural
or extrinsic. In clean colon, a
filling defect is likely to be a
polyp or a neoplasm. Feces
may cause filling defect with
no attachment to the wall &
completely surrounded by
barium & freely mobile.
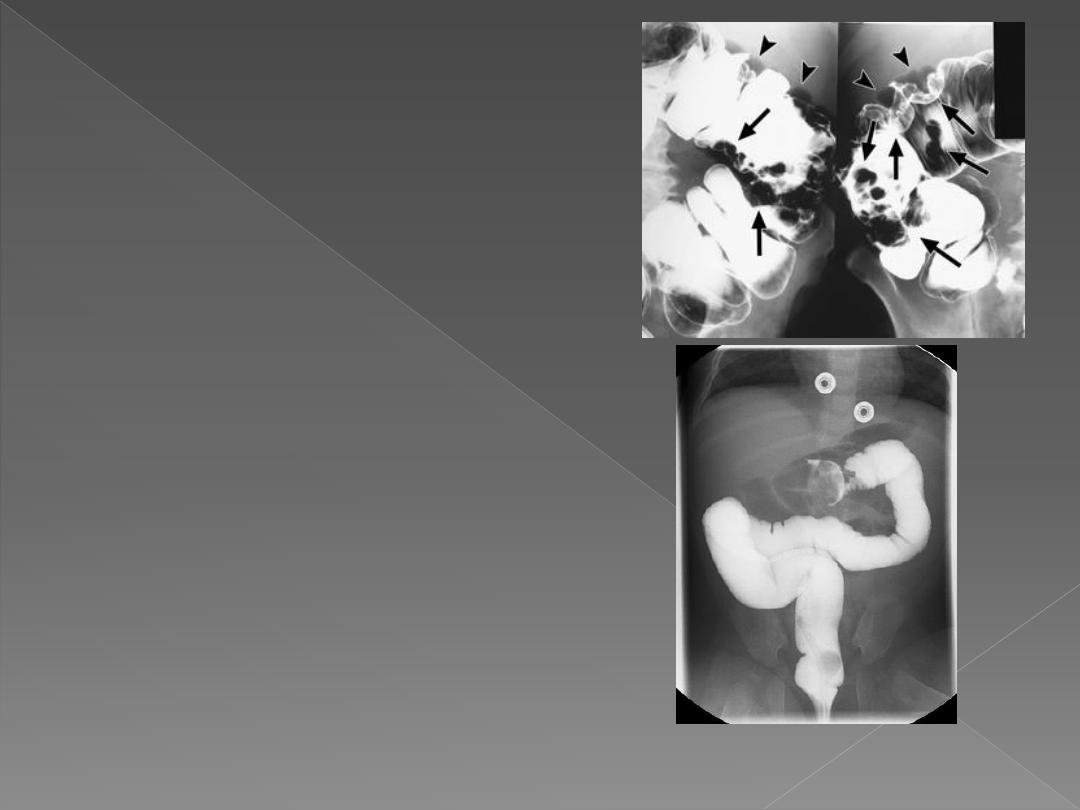
Intramural hemorrhage,
oedema or air in wall all
cause multiple smooth
defects arising from bowel
wall.
Intussusception causes a
unique filling defect..

4.Diverticula & muscle
hypertrophy:
Are seen with diverticular
disease.
5.Ulceration:
Recognized as small projections
from the lumen resulting in a
fuzzy or shaggy
appearance.
Causes:
1. Ulcerative colitis.
2. Crohn's disease.
3. TB.
4. Amoebic & bacillary
dysentery.
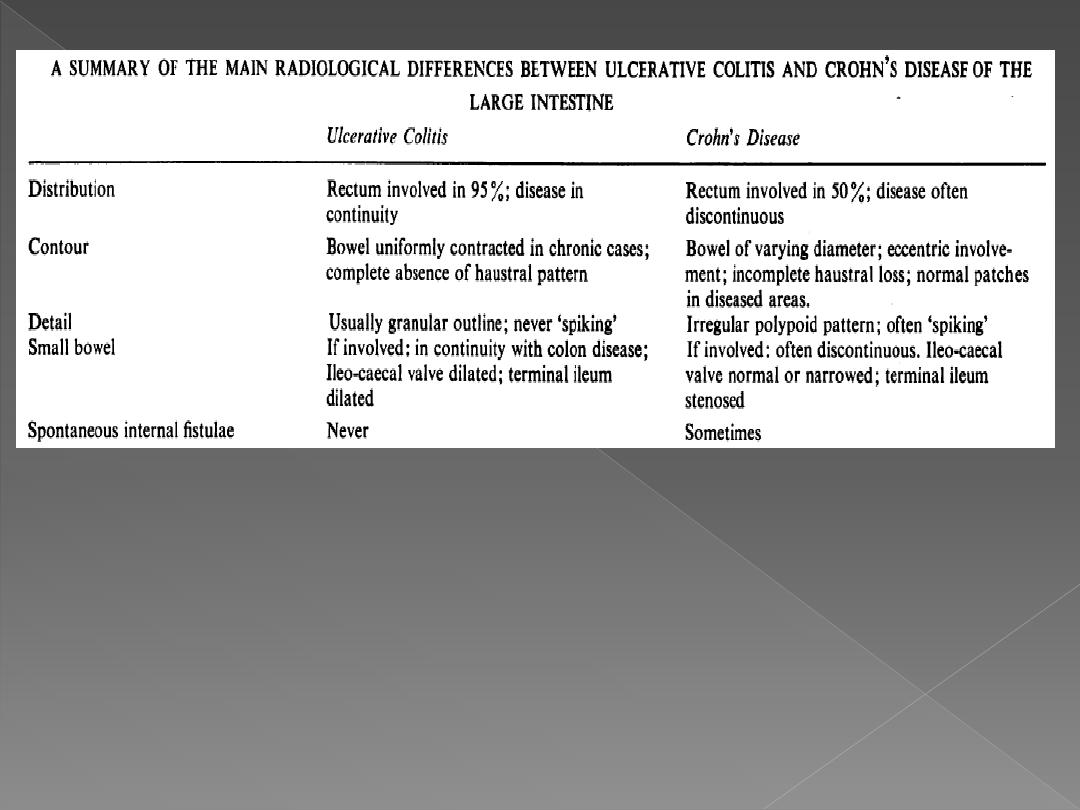
1. Ulcerative colitis & Crohn's
disease:
It may be difficult to distinguish
between them. Imaging can
be important for diagnosis,
assess the extent, severity &
complications of disease.
There is increased incidence
of carcinoma.
Ulcerative colitis
Always involves the rectum &
may extend in continuity
around the colon, sometimes
affecting the whole colon.
Ulcers
are usually shallow but in
severe cases may be deep.
In all but milder cases,
loss of
haustra
is noted.
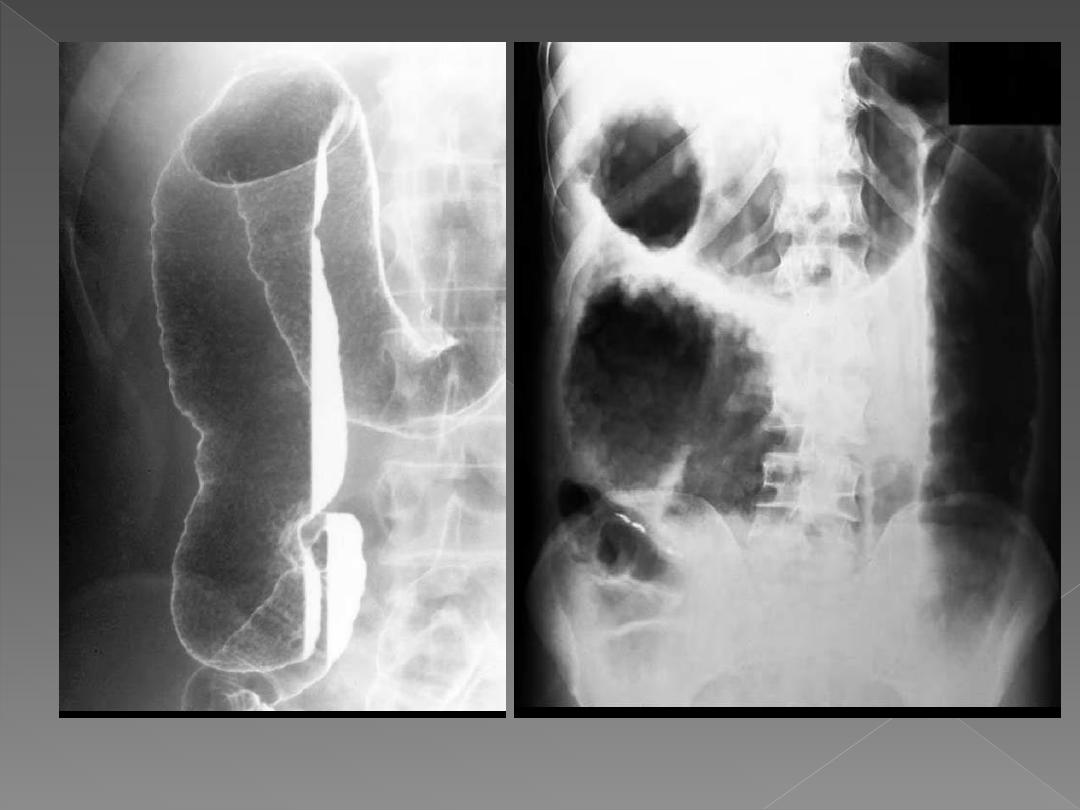
Double-contrast barium enema. Coarsely
granular mucosal ulcerations are visible in the
right colon
The colon is distended with gas and multiple polypoid
masses protrude into the colonic lumen
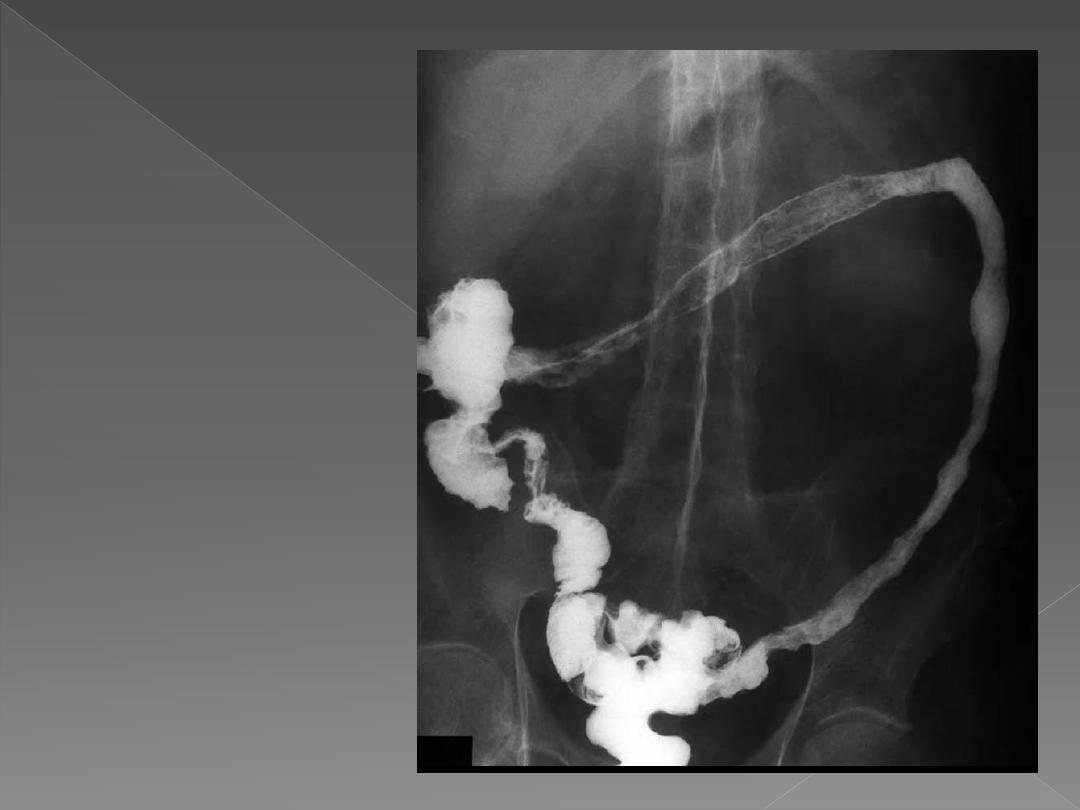
The colon is ahaustral and
shortened in Long-standing
ulcerative colitis
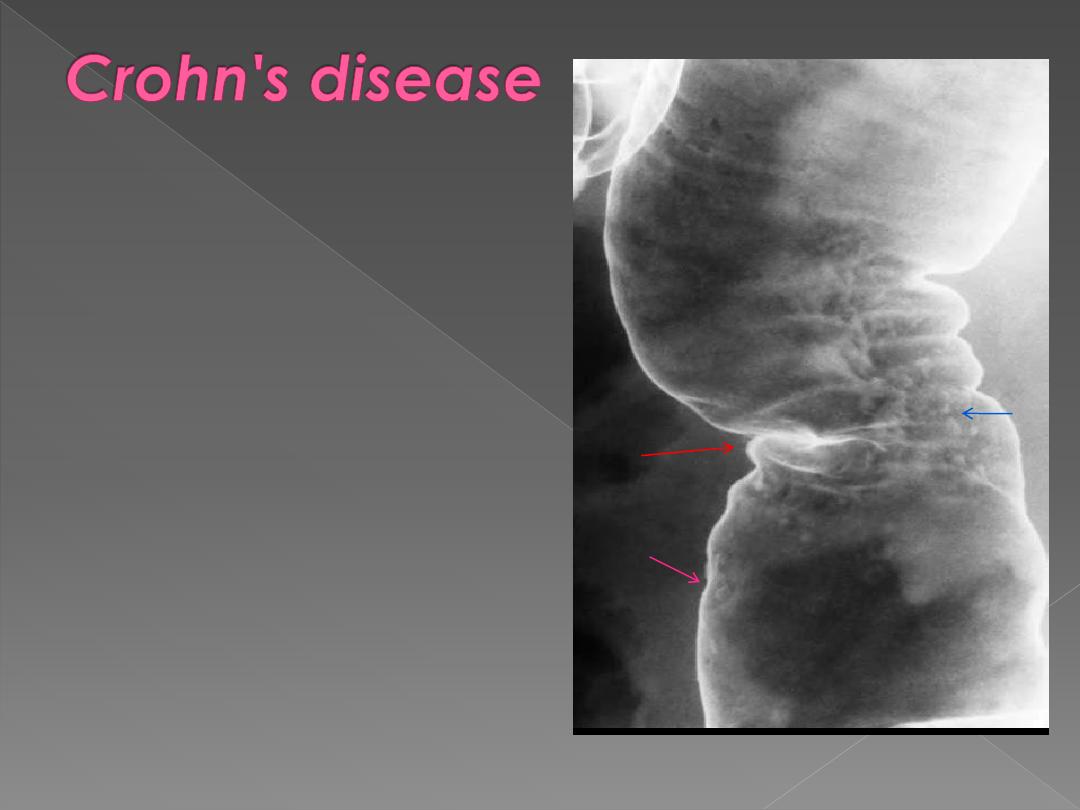
May affect any part of
GIT (mostly the lower
ileum & colon)
During the early stage:
1) Loss of haustra.
2)
Narrowing of lumen
3)
Shallow ulceration are
seen
.
4)
Mucosal edema and
ulceration give rise to
Cobblestone
appearance
.
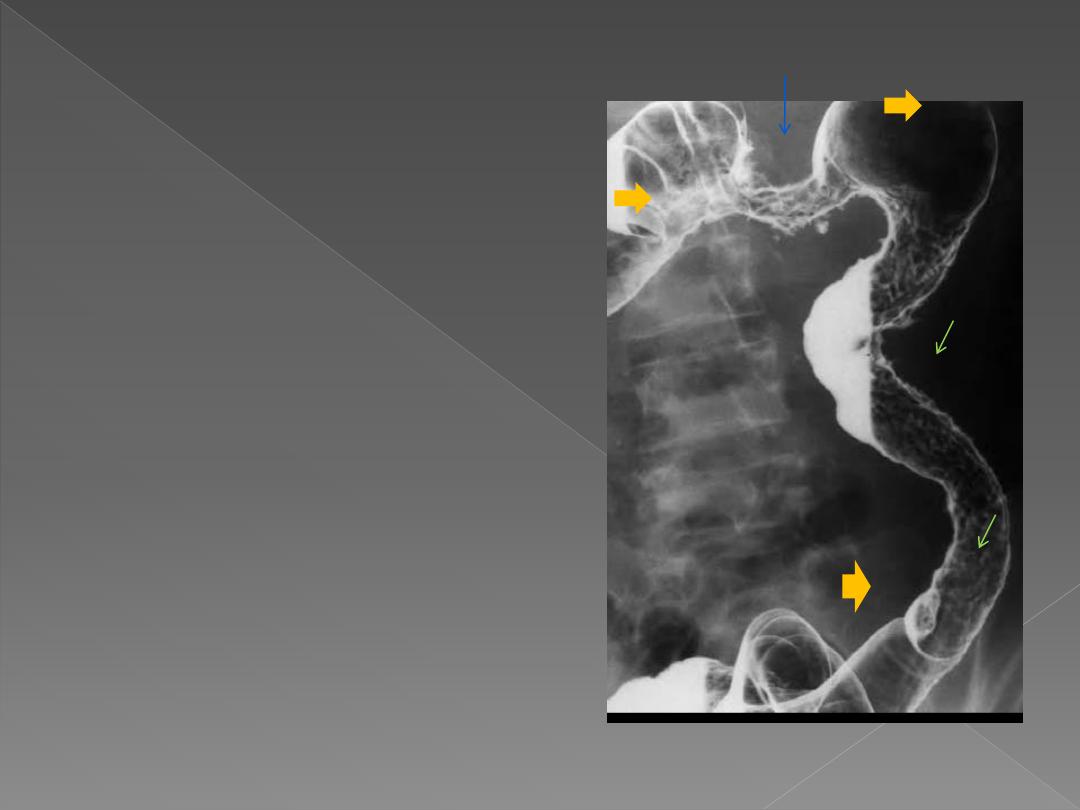
Later, the ulcers will become deeper
& may track in the submucosa.
The ulcer may be very deep,
penetrating muscle layer
(described as rose-thorn ulcers or
deep fissures).
Intra & extramural abscesses.
.
Strictures are common. They are
smooth & have tapered ends
.
When involved, the caecum is
usually contracted.
The disease may involve one
portion of the circumference of
the bowel.
Presence of skip lesions
diagnostic of Crohn's disease
.
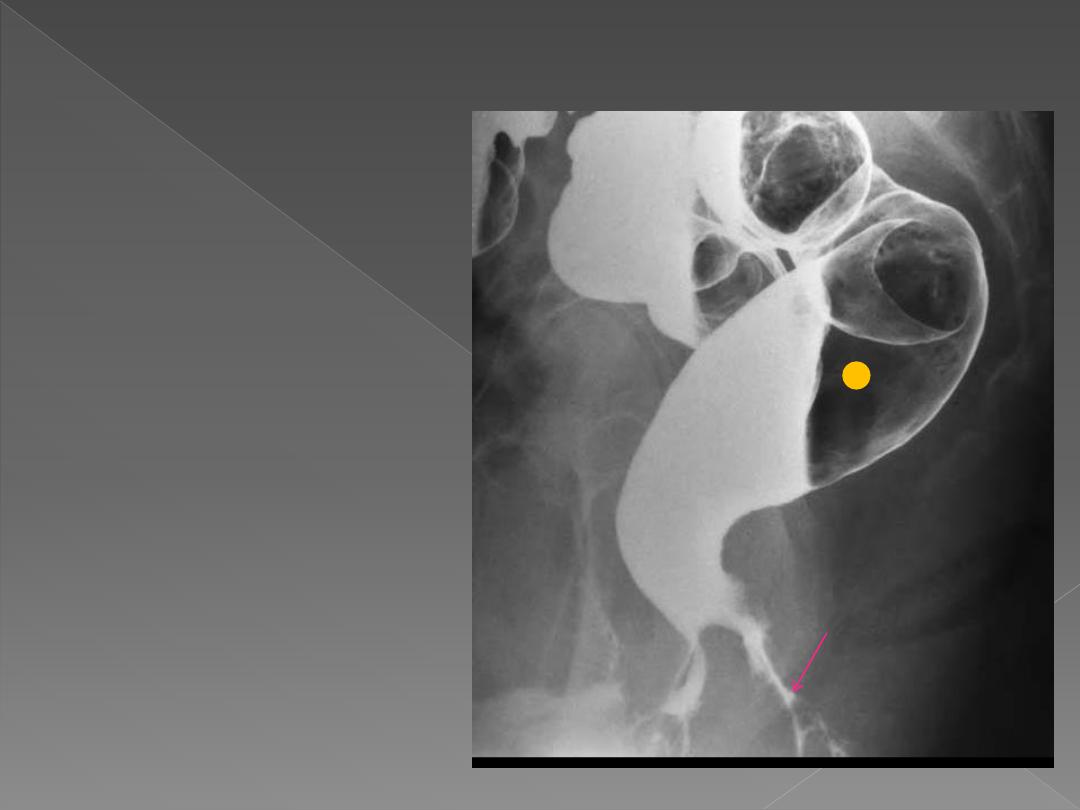
Fistulae
The rectum is often
spared.

Are out-pouchings of mucosa through the muscular layer &
are associated with hypertrophy of muscle layer.
It is more common in elderly & in sigmoid colon.
Diverticulitis is applied when there are symptoms of infection,
while diverticulosis when the condition is asymptomatic.
Diverticular disease covers both entities.
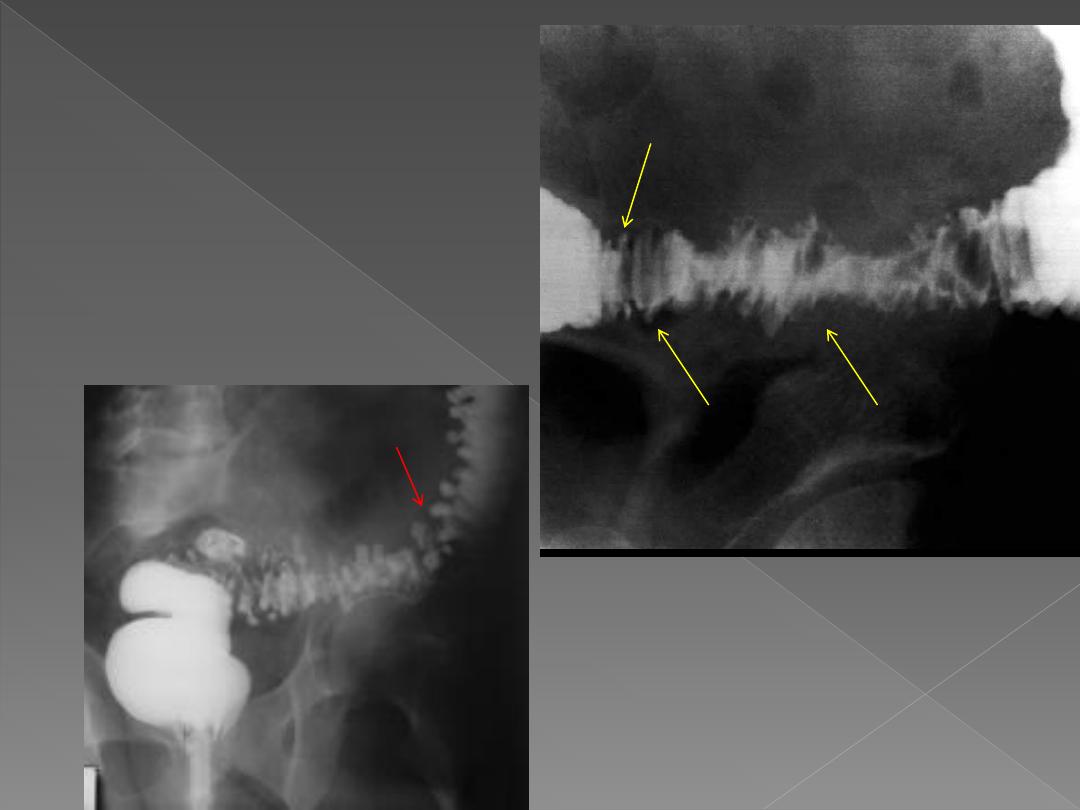
On Ba study They are seen as
spherical out-pouchings with
narrow neck
The colon may also show saw
tooth serrated appearance from
muscle hypertrophy
,
Sometimes, saw tooth
appearance may be seen in
isolation
When inflamed, diverticulae
may not fill.
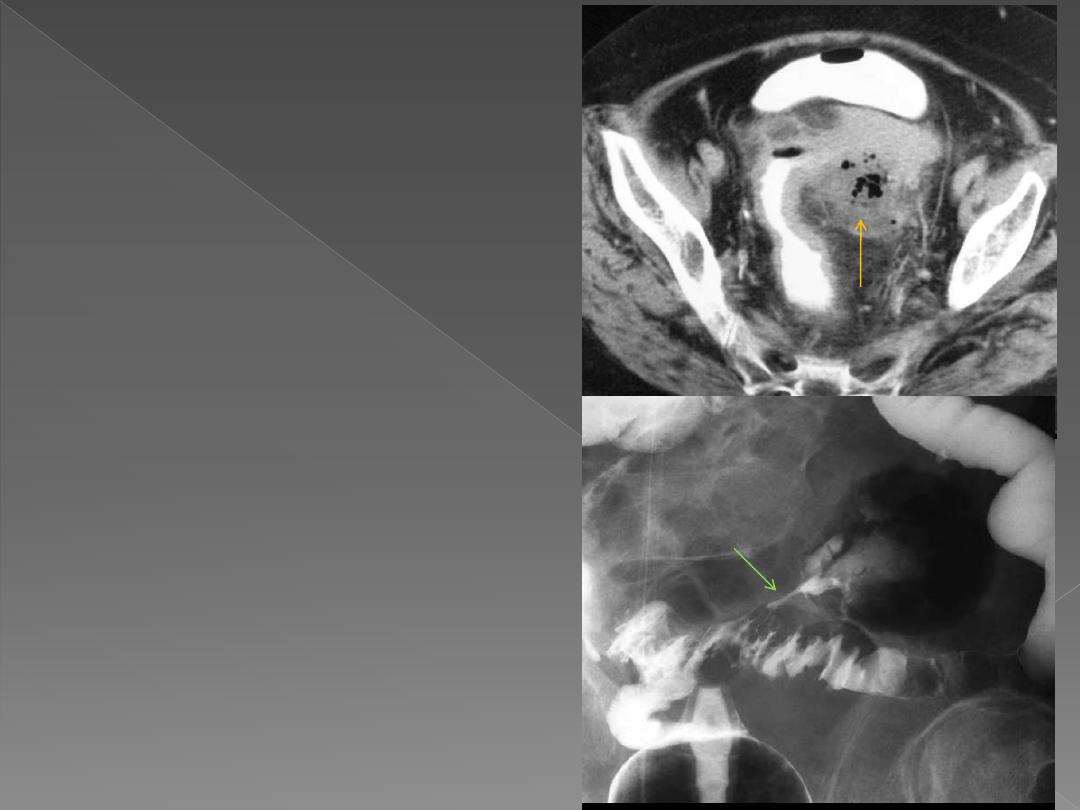
When perforated, it results in
pericolic abscess
(more readily
seen with CT) or a
fistula
into the
bladder, SB or vagina & in both
pericolic abscess & fistula, Ba is
noted outside the colon. It may
result in pneumoperitoneum
when perforation to the peritoneal
cavity.
A
stricture
may occur in an area
of recognizable diverticular
disease otherwise can't be
differentiated from Ca.
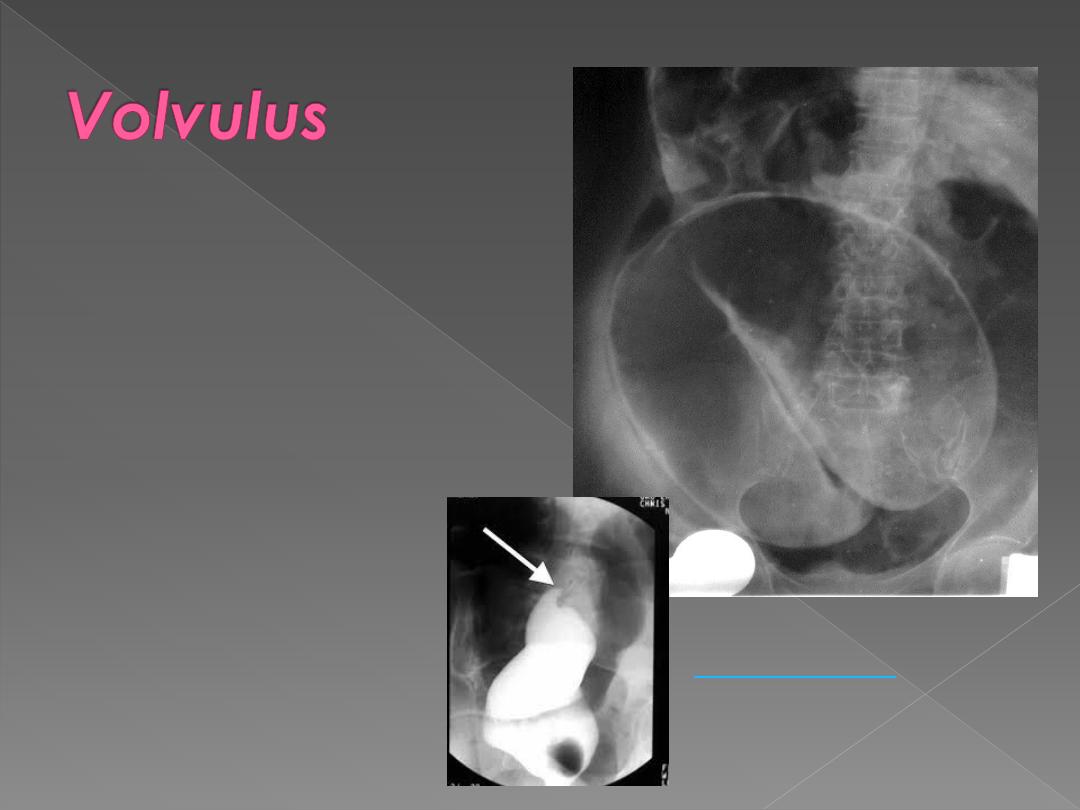
Frequently seen in sigmoid &
less often in caecum.
The twisted loop becomes
greatly distended &
proximal bowel dilatation
is noted.
The diagnosis can be made
from plain film.
Ba enema will show smooth
tapered narrowing with
marked dilatation of
proximal bowel.
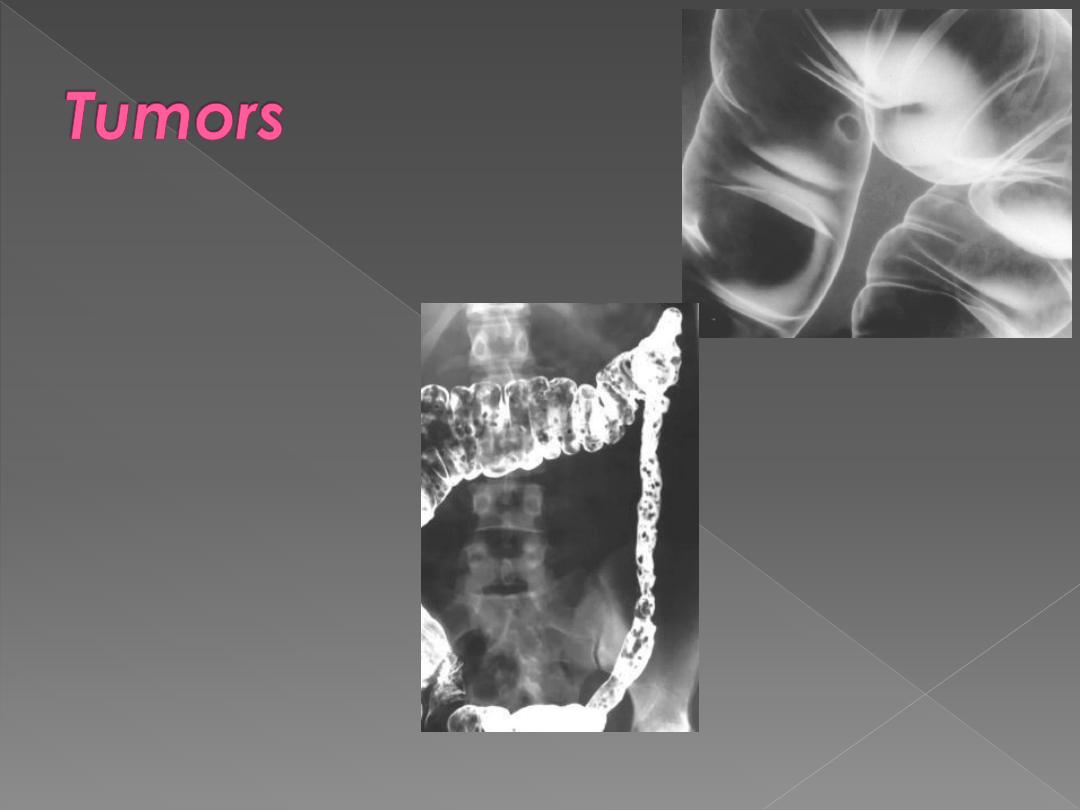
a. Polyps are best
evaluated by endoscopy
but may be found at Ba
enema.
They may be sessile or
on a stalk, single or
multiple.
It is impossible to
exclude malignancy in a
polyp by imaging,
however only tiny
minority of polyps less
than 1 cm in size & < 2
cm are cancers.
The features that
suggest malignancy are
a diameter of > 2 cm;
short thick stalk or an
irregular surface.
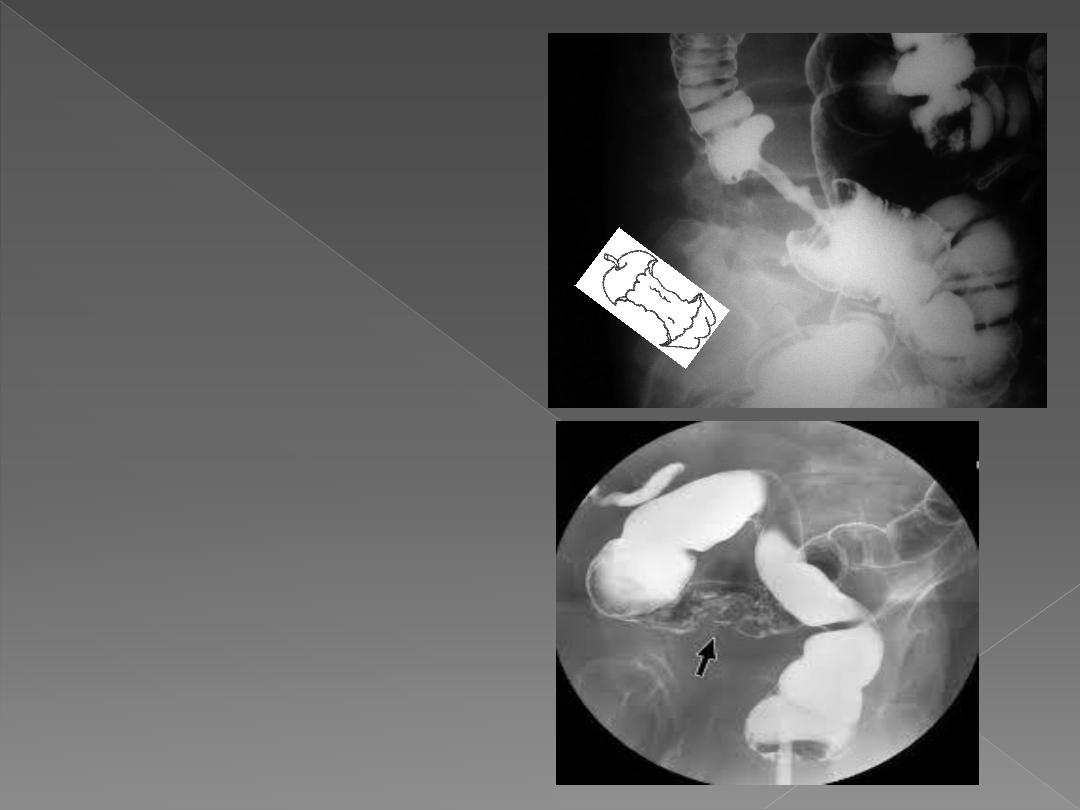
b. Carcinoma
May arise anywhere in colon but
commonest in rectosigmoid
& caecum. In rectosigmoid
region, it often has annular
obstructing stricture whereas
cecal carcinoma can
become large without
obstruction.
Ba enema shows
1. The annular carcinoma as an
irregular stricture with
shouldered edges, usually < 6
cm in length –apple core
sign-.
2. The Polypoid or fungating
carcinoma causes irregular
filling defect.
