Urinary tract infection
Dr.Nariman FahmiObjectives
Define Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Diagnosis of UTI
treatment for UTI
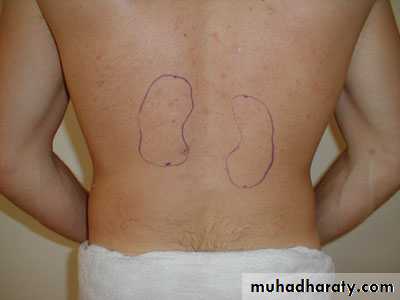
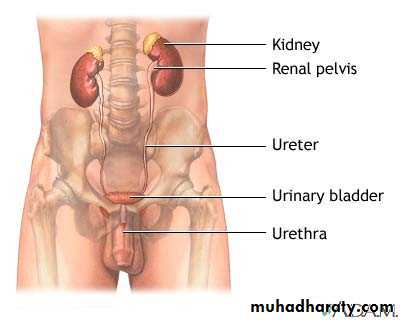
Relationship of the Kidneys to Vertebra and Ribs
Figure 23.1bThey are retroperitoneal and are located in the abdominal cavity.
They are at the level of T12 to L3, so they are at the costal margin, and the ribs protect them a little.
Even though they are protected by thoracic ribs, they are NOT in the thoracic cavity because they are below the diaphragm.
4
Case history
A 9 year old girl with a 2 days history of loin pain ,fever and vomiting, clinically she appears ill.a full blood count shows a Hb 12 mg/dl,
WBC of 14x10( cells/LYou send of a midstream urine sample for culture.
prescribed paracetol and ask the patient came next day. The next day you find that she has been reported urine culture of more than 100 000colonies of E-Coli.
What is the most probable diagnosis ??
Which part of renal tract is most likely infected and why??
What choice of antibiotics??
investigations that are needed
Urinary Tract Infections Yes, it is a bacteriuria
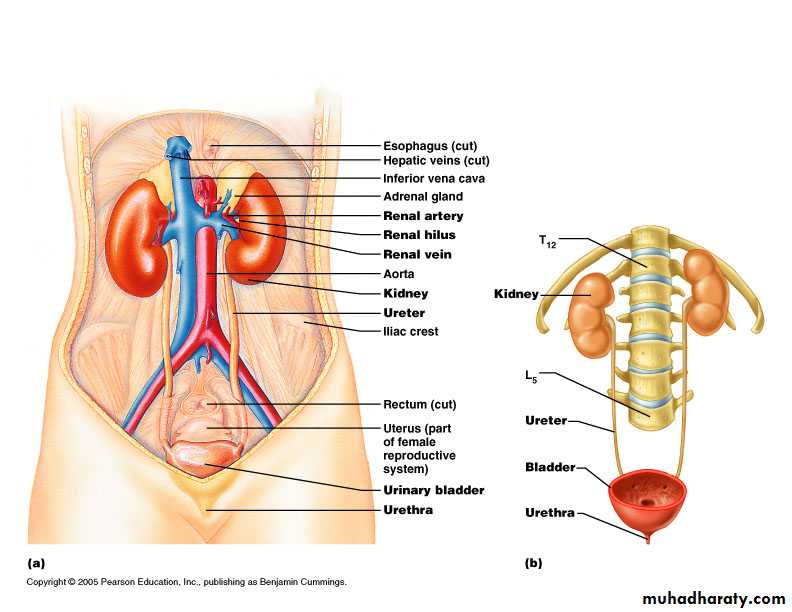
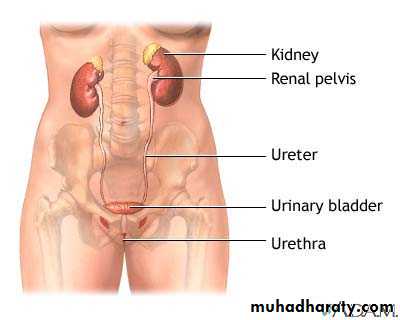
Urinary TractFemale Male
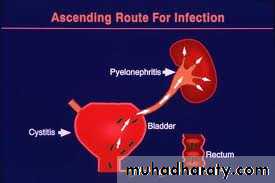
A UTI can happen anywhere along the urinary tract.
UTI have different names, depending on what part of the urinary tract is infected.Bladder -- an infection in the bladder is also called cystitis or a bladder infection
Kidneys -- an infection of one or both kidneys is called pyelonephritis or a kidney infection• Definition of UTI
Bacteriuria
Presence of bacteria in the urineDysuria
Pain or difficulty in urinating
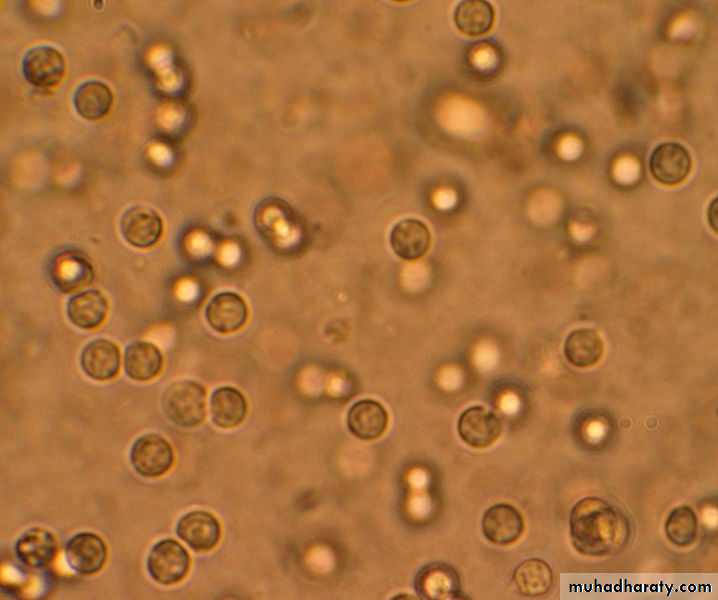
Pyuria
Presence of/increased numbers of white blood cells in the urineTerminology
Most UTIs are from ascending bacteria
E. coli (60-80%), Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterococcus, and coag. neg. staph.forms of UTI are
1-pyelonephritis2-Cystitis
3- urithritis
4- prostitis
Cystitis (bladder involvement )
clinical fatures
dysuria,
urgency,frequency,
suprapubic pain,
incontinence,
malodorous urine.
Cystitis does not cause fever and does not result in renal injury s
General urine exam
Microscopical exam
Pus cells in urineDIAGNOSIS
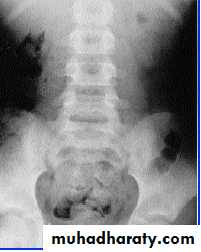
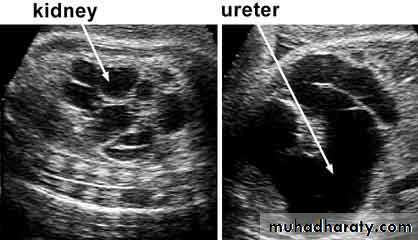
urine cultureImaging of the Renal tract
* Renal U/S* KUB
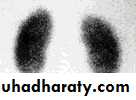
* DMSA
* IVU
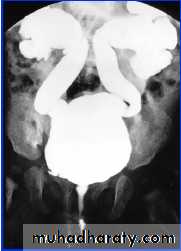
* Cystogram
VCUG/RNC
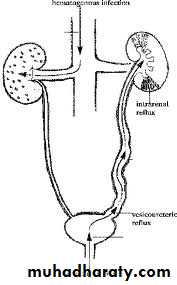
The goal of imaging studies in UTI is to identify
Anatomic abnormalities that predispose to infection and identify scarring
Reflux Seen on Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG) using transurethral contrast
Urinary Tract InfectionUpper urinary tract Infections:
Pyelonephritis
Lower urinary tract infections
Cystitis (“traditional” UTI)
Urethritis (often sexually-transmitted)
Prostatitis
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
HematuriaFever
Nausea/Vomiting (pyelonephritis)
Flank pain (pyelonephritis)
Findings on Exam in UTI
Physical Exam:Costo Vertebral Angle tenderness (pyelonephritis)
Urethral discharge (urethritis)
Tender prostate on PRE (prostatitis)
Suprapubic tenderness (cystitis)
Labs: Urinalysis
Positive + WBCs
Positive + RBCs
Culture in UTI
Positive Urine Culture = >105 CFU/mL
Most common pathogen for cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis:
Escherichia coli
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Proteus mirabilis
Klebsiella
Enterococcus
Most common pathogen for urethritis
Chlamydia trachomatis
Neisseria Gonorrhea
Pyelonephritis
Infection of the kidneyAssociated with constitutional symptoms – fever, nausea, vomiting, headache
Diagnosis:
Urinalysis, urine culture, CBC, Chemistry
Treatment:
2-weeks of Trimethroprim/sulfamethoxazole or fluoroquinolone ,cephalosporins
Hospitalization and Intravenous antibiotics if patient unable to take orally .
Question
A 24-year old woman presents with fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, flank pain and tenderness. Her temperature is 40°C, pulse rate is 120/min., and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg.
Question
What further studies do you want in this patient?How would you treat this patient?
What might you do if she does not improve after 3-4 days?