
Endodontic Diagnosis
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD
Diagnosis
Is the science of recognizing disease by means of
signs, symptoms and tests.
Effective treatments depends on an accurate
diagnosis.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Case History
The purpose of case history is to discover
whether patient has any general or local
condition that might alter the normal course of
treatment. It includes:
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Chief Complaint
It consists of information which promoted
patient to visit a clinician.
History of Present illness
Once the patient completes information about
the chief complaint, a report is made which
provides more descriptive analysis about this
initial information. It should include signs and
symptoms, duration, intensity of pain, relieving
and exaggerating factors.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Medical History
There are no medical conditions which
specifically contraindicate endodontic
treatment, but there are several which require
special care, for example anemia, bleeding
disorders, cardiorespiratory disorders, drug
treatment and allergies and likelihood of
pregnancy or pregnant itself.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Antibiotic prophylaxis
• Indications:
• Cardiac patients:
• Artificial heart valves
• History of infective endocarditis
• Congenital heart tissue defects and repairs
• Immunocompromised patients.
• Hemophiliacs
• Insulin dependent diabetics
• Patients who have a joint replacement in the past
2 years
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

regimens
• Adults: 2g amoxicillin 30-60 minutes before
treatment.
• Child: 50 mg/kg
• Penicillin sensitive patient: clindamycin 600mg
30-60 minutes before treatment.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Dental history
Past dental history: reveals information about
past dental problems and treatment. If patient
has difficulty tolerating certain types of
procedures or has encountered problems with
previous dental care, an alteration of the
treatment or environment may help to avoid
complication.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Present dental history
• The most common compliant that leads to
dental treatments is pain or swelling.
• Questions like when did you first notice this,
inception factors that improve or worsen the
condition.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD
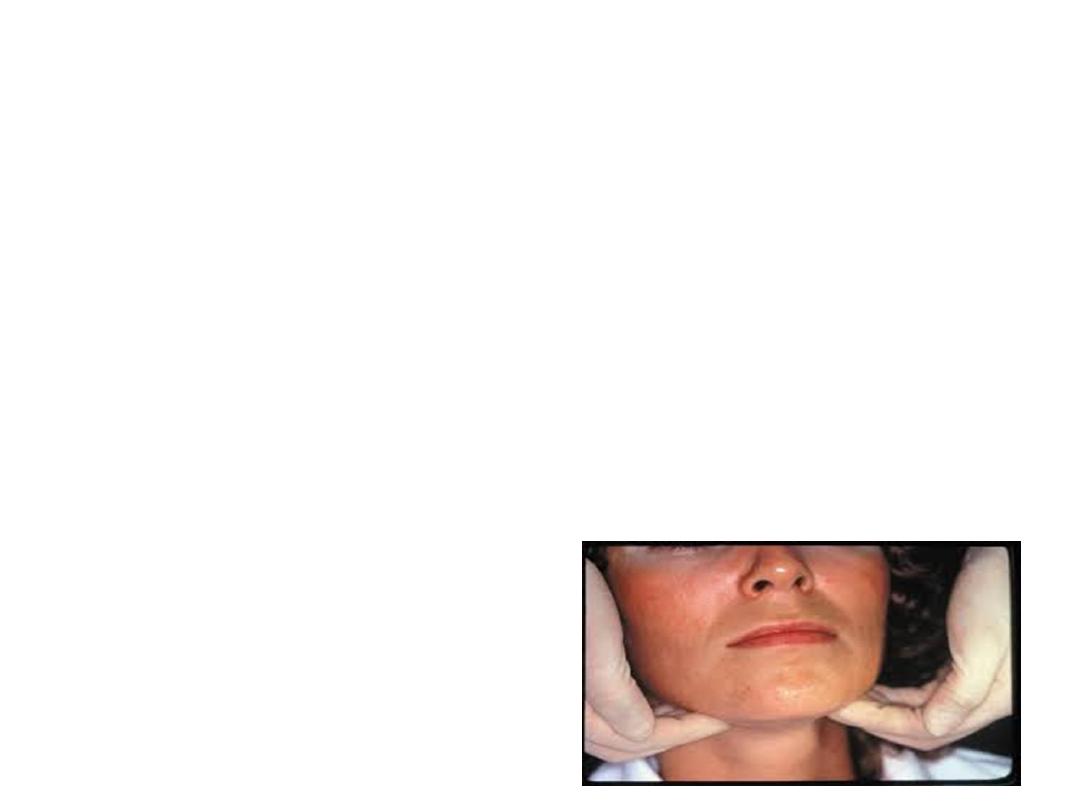
Clinical Examination
Extra oral Examination
Patient should be looked for any facial
asymmetry or distention of tissues. After extra
oral examination of head and neck region, one
should go for extra oral palpation. Palpation of
salivary glands should be done extra orally.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

• Palpation of TMJ can be done by standing in
front of the patient and placing the index
fingers in the pre auricular region to note any
restricted or deviation in movement, locking or
crepitus in TMJ.
• Palpation of lymph nodes should be done to
note any lymph node enlargement, tenderness,
mobility and consistency.
Dr. Emad farhan Al-khalidi
MSc, PhD

Intraoral Examination
During intraoral examination, look at the following structures
systematically:
1. The buccal, labial and alveolar mucosa
2. The hard and soft palate
3. The floor of the mouth and tongue.
After examining this, general dental state should be
recorded, which include:
a. Oral hygiene status
b. Amount and quality of restorative work
c. Prevalence of caries
d. Missing tooth
e. Periodontal status
f. Tooth wear and facets.
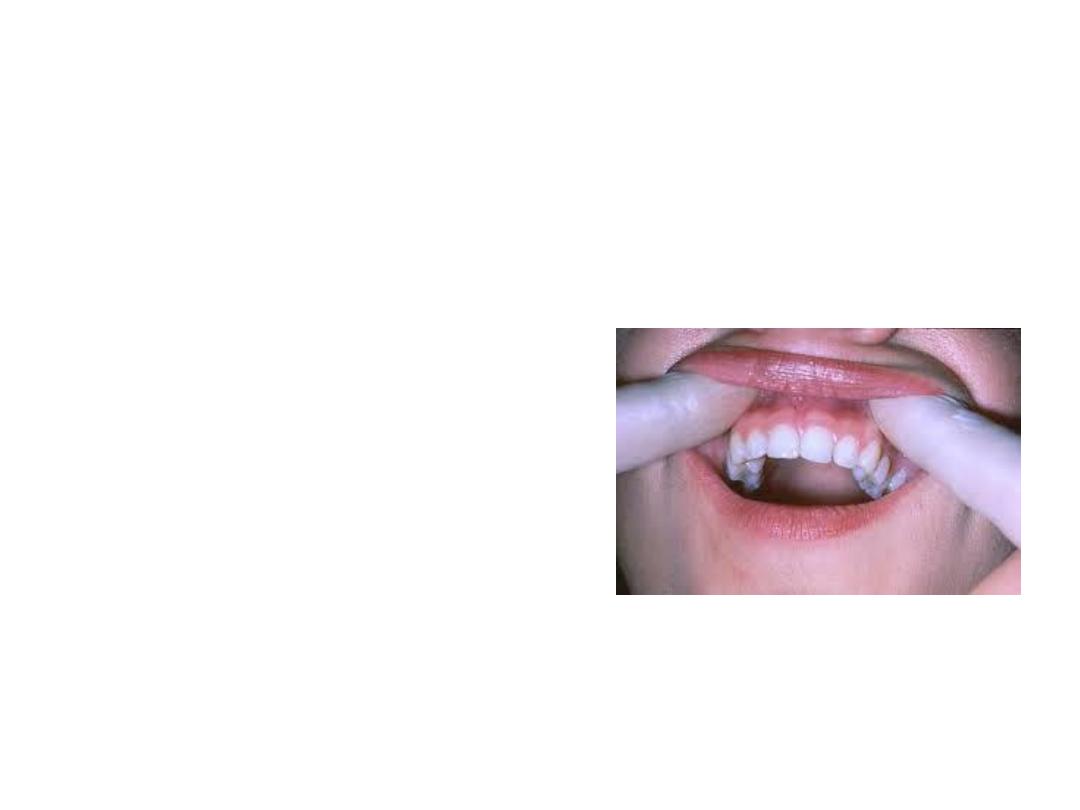
Palpation is done by pressure to check any
tenderness in soft tissue overlying suspected
tooth. Sensitivity may indicate inflammation in
periodontal ligament surrounding the affected
tooth.
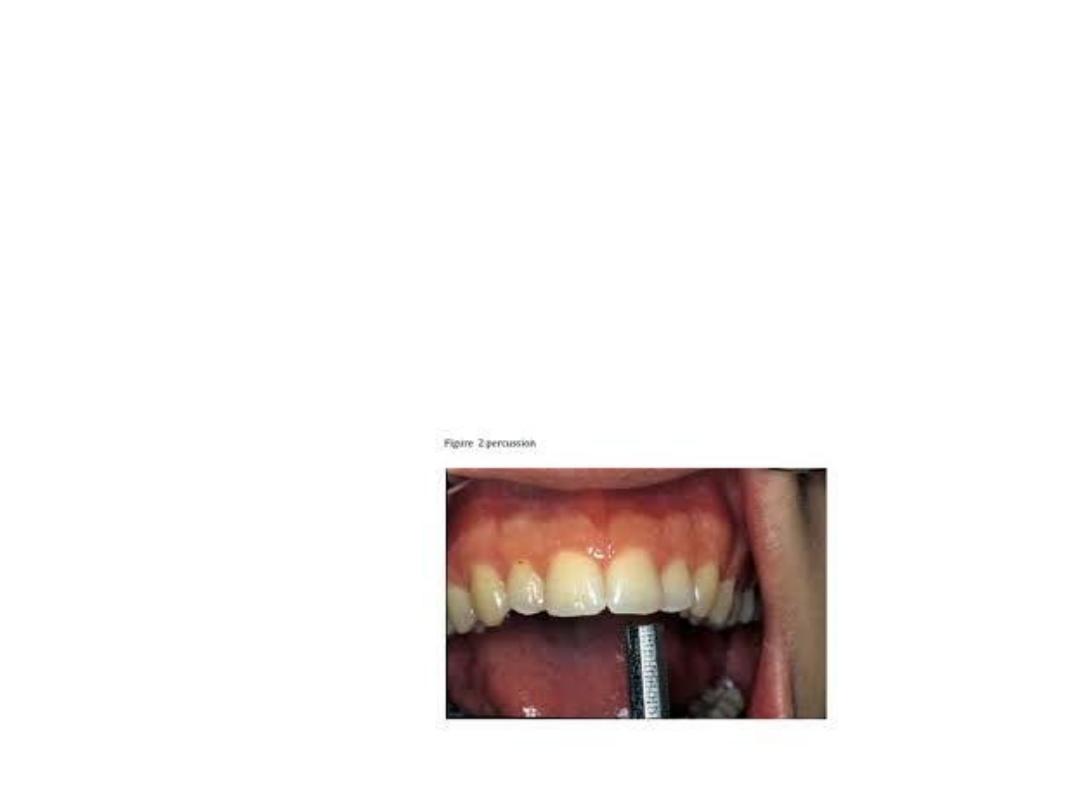
• Percussion of tooth indicates inflammation in
periodontal ligament which could be due to
trauma, sinusitis and/or PDL disease.
Percussion can be carried out by gentle
tapping with gloved finger or blunt handle of
mouth mirror.
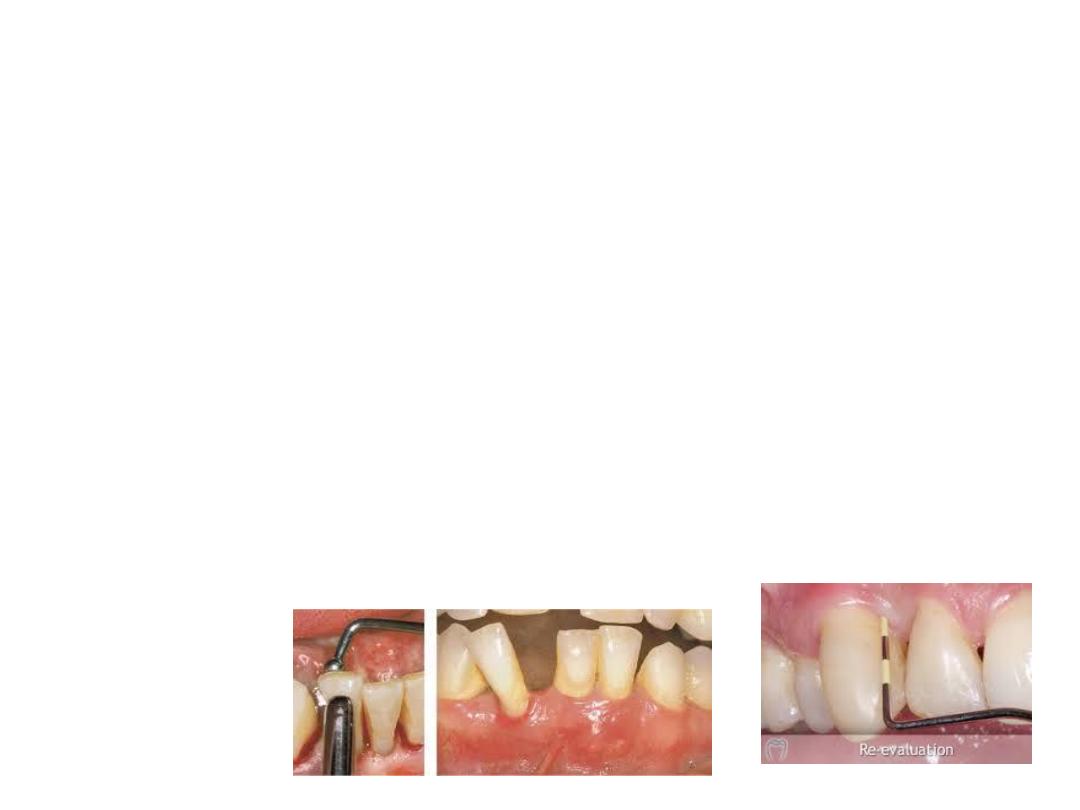
Periodontal evaluation can be assessed from palpation,
percussion, mobility of tooth and probing. The mobility
of a tooth is tested by placing a finger or blunt end of the
instrument on either side of the crown and pushing it
and assessing any movement.
Mobility can be graded as:
1. Slight (normal)
2. Moderate mobility within a range of 1 mm
3. Extensive movement (more than 1 mm) in mesiodistal
or lateral direction combined with vertical displacement
in alveolus.

Radiographs
• The radiograph is one of most important tools in
making a diagnosis. Without radiograph, case
selection, diagnosis and treatment would be
impossible as it helps examination of oral structure
that would otherwise be unseen by naked eye.
Generally, the periapical lesions of endodontic origin have
following characteristic features:
• Loss of lamina dura in the apical region
• Etiology of pulpal necrosis is generally apparent
• Radiolucency remains at the apex even if radiograph
is taken by changing the angle.

Radiographs help us in following ways:
a. Establishing diagnosis
b. Determining the prognosis of tooth
c. Disclosing the presence and extent of caries
d. Check the thickness of periodontal ligament
e. To see presence or absence of lamina dura
f. To look for any lesion associated with tooth
g. To see the number, shape, length and pattern of the
root canals
h. To check any obstructions present in the pulp space
i. To check any previous root canal treatment if done
j. To see any resorption present in the tooth.

Although the radiographs play an important role in
dentistry but they have a few shortcomings:
a. They are only two dimensional picture of a three
dimensional object.
b. Pathological changes in pulp are not visible in
Radiographs.
c. They don’t help in exact interpretation, for example
radiographic picture of an abscess, inflammation and
granuloma is almost same.
d. Radiographs can misinterpret the anatomical
structures like incisive and mental foramen with
periapical lesions
e. To know the exact status of multirooted teeth,
multiple radiographs are needed at different angles
which further increase the radiation exposure.

Pulp Vitality Tests
Pulp testing is often referred to as vitality testing. Pulp
vitality tests play an important role in diagnosis because
these tests not only determine the vitality of tooth but
also the pathological status of pulp.
Various types of pulp tests performed are:
1. Thermal test
a. Cold test
b. Heat test
2. Electrical pulp testing
3. Test cavity
4. Anesthesia testing
5. Bite test.
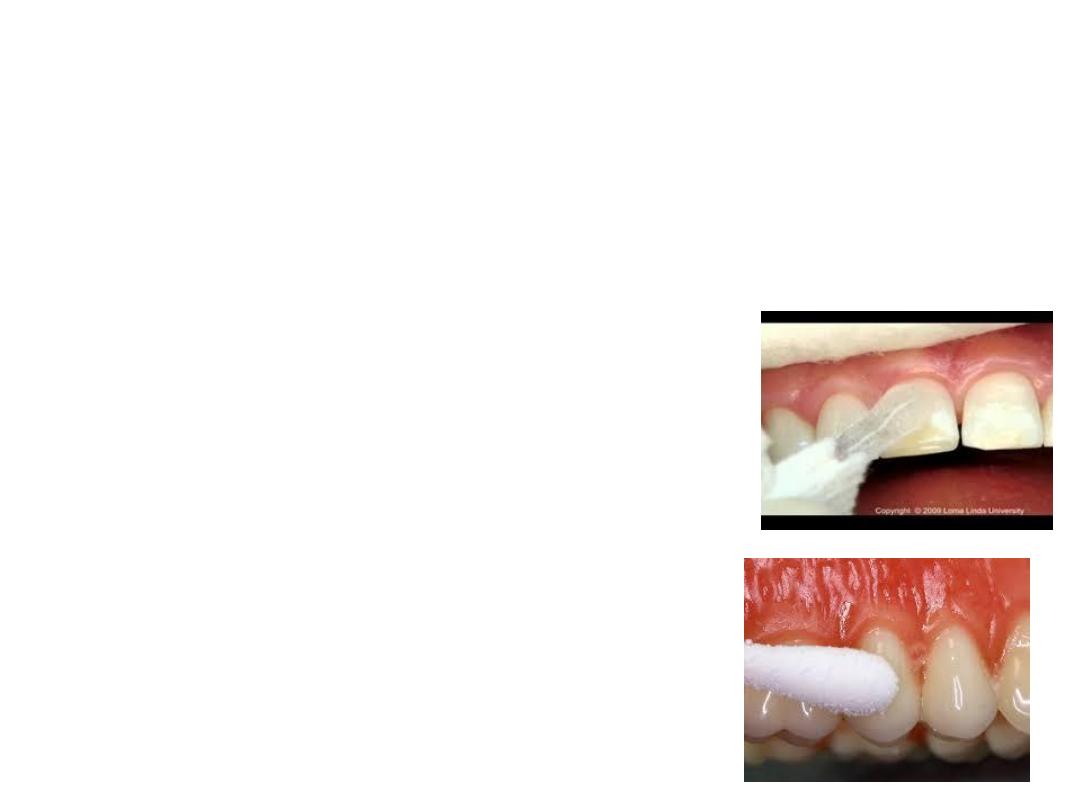
Thermal Test
In thermal test, the response of pulp to heat and cold is noted.
Cold test: It is the most commonly used test for assessing the vitality
of pulp. It can be done in a number of ways. The basic step of the pulp
testing, i.e. individually isolating the tooth with rubber dam is
mandatory with all types. Following methods are used for performing
cold tests:
1. Spray with cold air directed against the isolated tooth.
2. Application of cotton pellet saturated with ethyl
chloride.
3. The spray of ethyl chloride after isolating tooth.
4. The frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) is applied to the
facial surface of the tooth.
5. One of the easy methods for cold test is to wrap an
ice piece in the wet gauze and apply to the tooth.
6. Dichlorodifluoromethane (Freon) also
used as cold testing material.
Heat test: Heat test is most advantageous in the condition
where patient’s chief complaint is intense dental
painupon contact with any hot object or liquid. It can be
performed using different techniques like:
1. Direct the warm air to the exposed surface of tooth.
2. Use of heated stopping stick, hot burnisher, hot water,
etc.
3. Use of frictional heat produced by rotating polishing
rubber disc against the tooth surface.
4. Deliver warm water from a syringe on to the isolated
tooth.

[The preferred temperature for heat test is 150°F
(65.5°C)]
The patient may respond to heat or cold test in
following possible ways:
• Mild, transitory response to stimulation show
normal pulp.
• Absence of response in combination with other
tests indicates pulp necrosis.
• An exaggerated and lingering response indicates
irreversible pulpitis.

Conditions which can give false negative response:
1. Recently erupted teeth with immature apex
2. Recent trauma
3. Excessive calcifications may also interfere with the
nerve conduction.
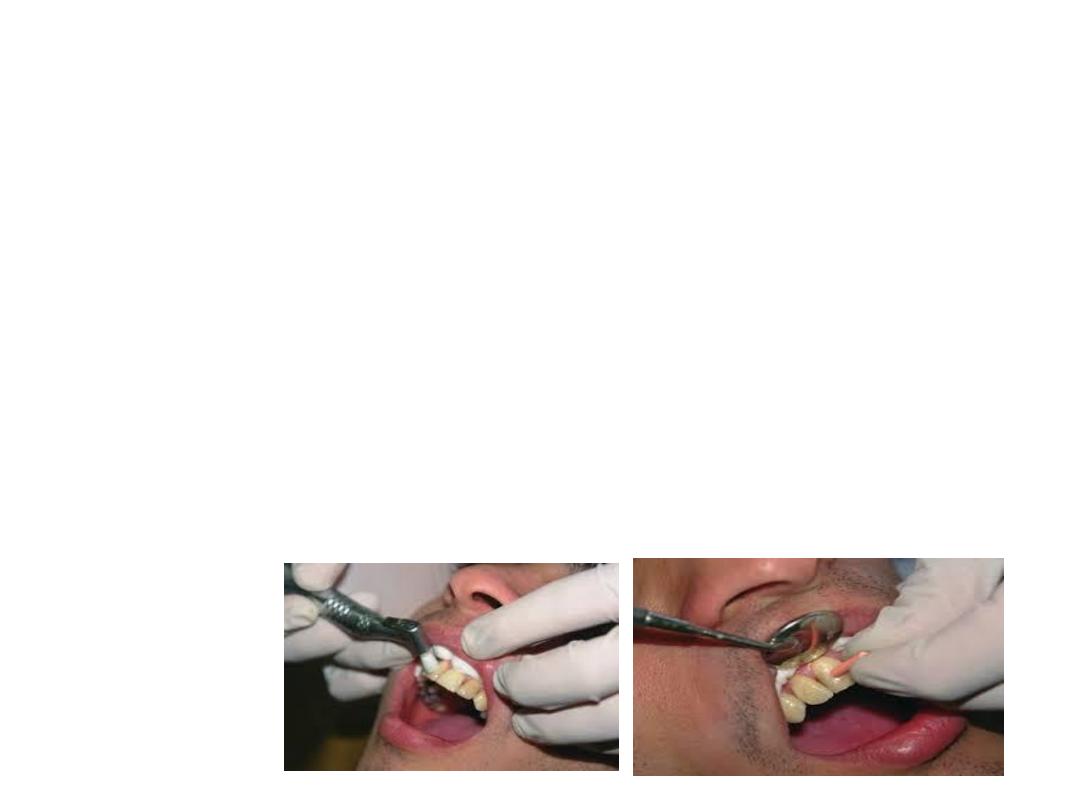
Electric Pulp Testing:
Electric pulp tester is used for evaluation of condition of
the pulp by electrical excitations of neural elements
within the pulp. A positive response indicates the vitality
of pulp. No response indicates nonvital pulp or pulpal
necrosis.
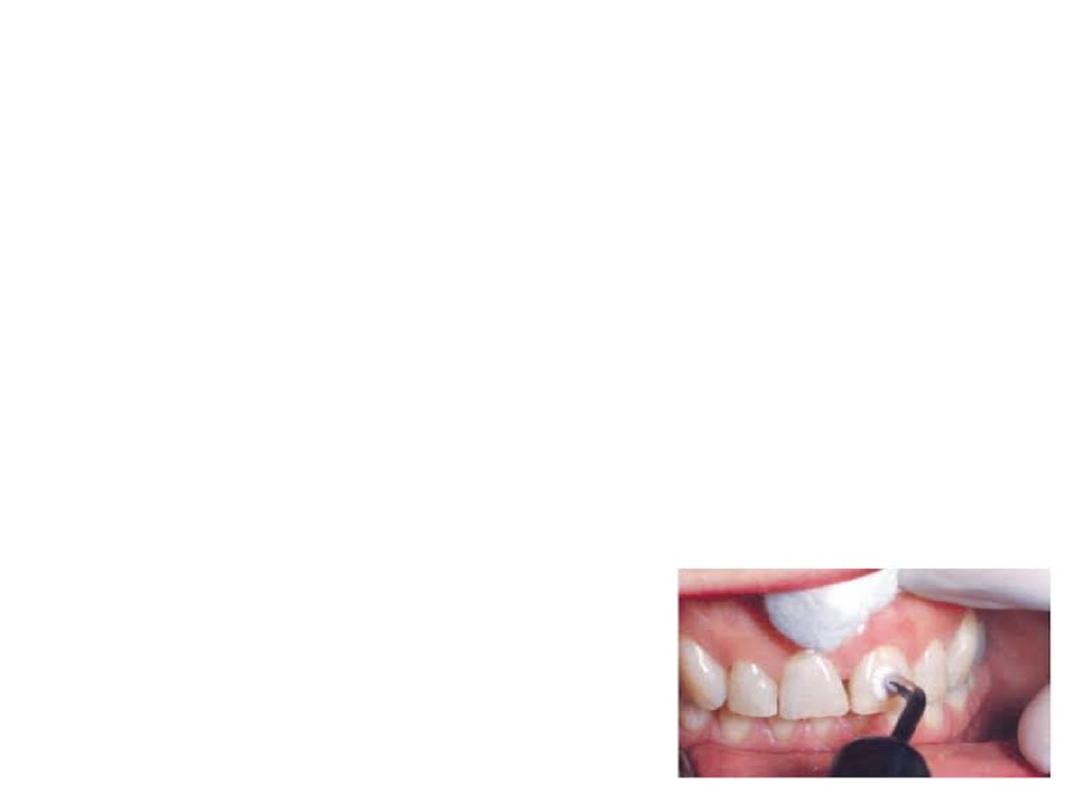
Procedure
1. Isolate the teeth to be tested.
2. Apply an electrolyte on the tooth electrode and place
it on the facial surface of tooth.
3. Once the circuit is complete, slowly increase the
current and ask the patient to point out when the
sensation occurs.
4. Each tooth should be tested 2 to 3 times and the
average reading is noted.
Disadvantages: Various conditions can give rise to wrong
results and thus misdiagnosis. These conditions can be
as follows:
1. When electrode may contact gingival tissue thus
giving the false positive response.

2. In multirooted teeth, pulp may be vital in one or more
root canals and necrosed in others, thus eliciting a
false positive response.
3. In certain conditions, it can give false negative
response for example:
a. Recently traumatized tooth
b. Recently erupted teeth with immature apex
c. Teeth with extensive restorations or pulp protecting
bases under restorations
d. Partial necrosis of pulp sometimes is indicated as
totally necrosis by electric pulp tester.
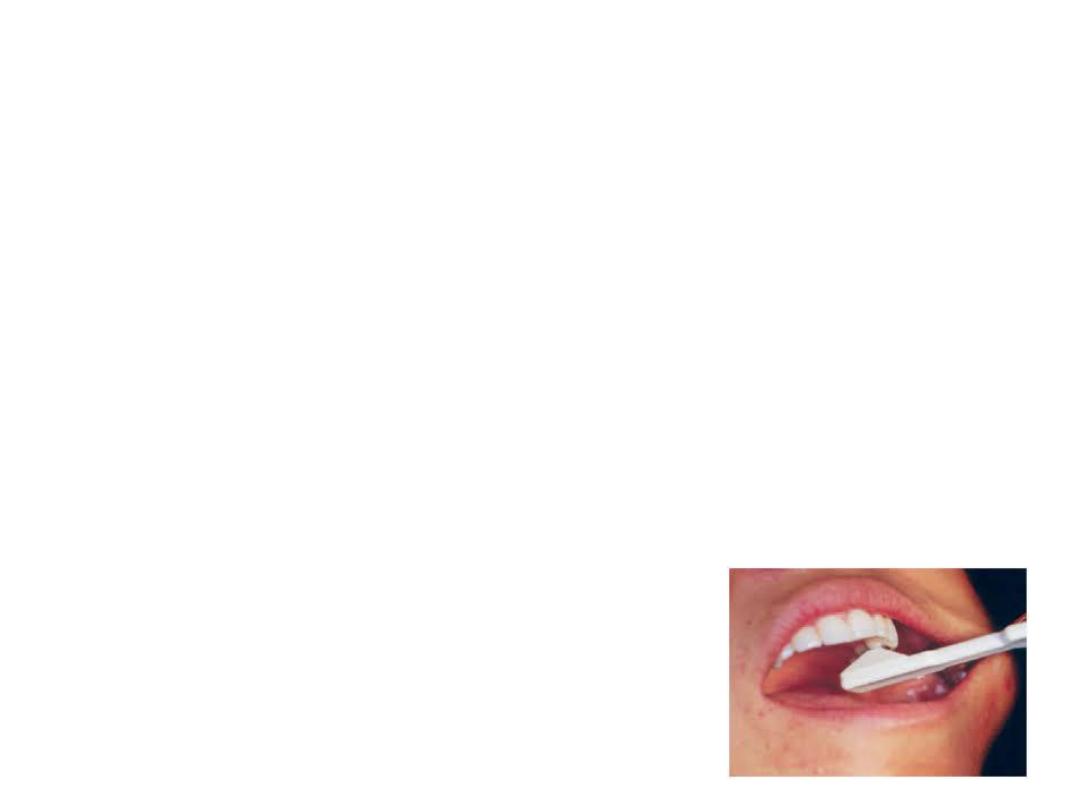
Test Cavity
This method should be used only when all other test methods are
inconclusive in results. Here a test cavity is made with high speed burs with
air and water coolant. The sensitivity or the pain felt by the patient indicates
pulp vitality.
Anesthesia Testing
The main objective of this test is to anesthetize a single tooth at a time until
the pain is eliminated. Injection is administered to the most posterior tooth in
the suspected quadrant. If the pain persists, even after tooth has been
fully anesthetized, then repeat the procedure to the next tooth mesial to it. It
is continued until the pain disappears.
Bite Test
This test helps if patient complains of pain on mastication. Tooth is sensitive
to biting if pulpal necrosis has extended to the periodontal ligament space or
if a crack is present in a tooth. In this patient is asked to bite on a hard object
such as cotton swab, tooth pick or orange wood stick.

Prognosis:
Predicting the likely out come of a
disease on condition of patient and action.
Differential diagnosis:
Is the list of most likely and possibly diagnosis based
on available information

RECENT ADVANCES IN PULP VITALITY
TESTING
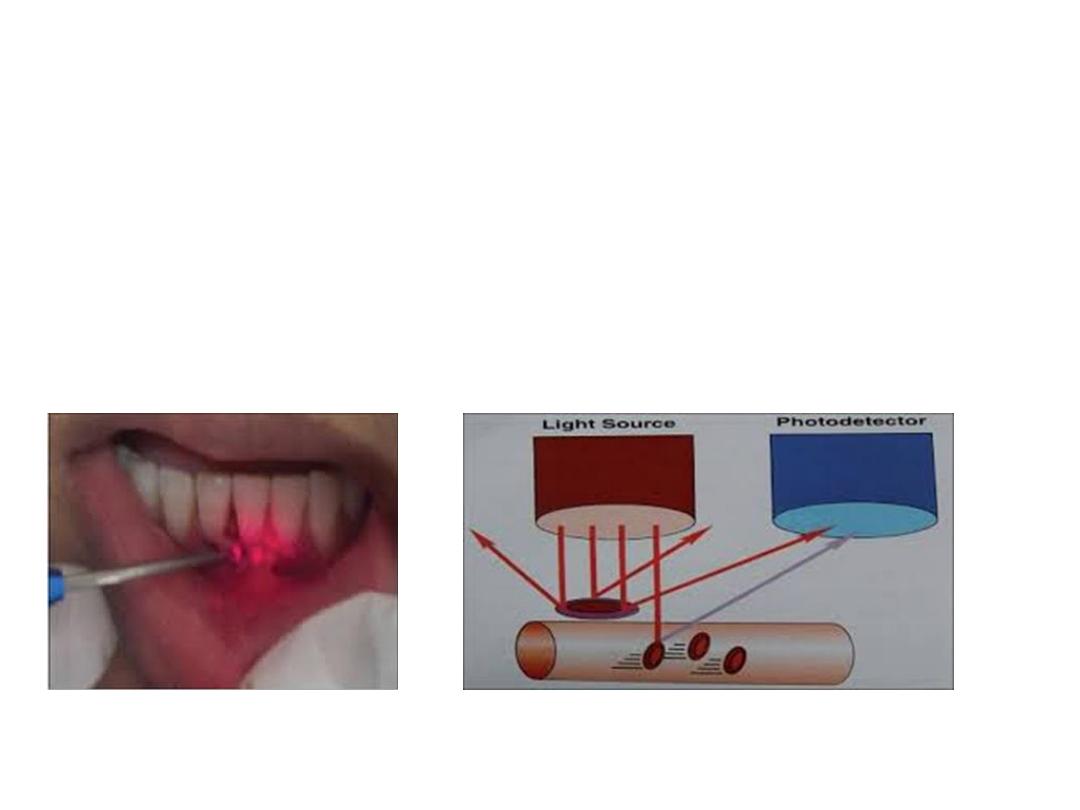
Laser Doppler Flowmetry (LDF)

Non invasive method to measure the blood flow
This technique uses laser beam that directed into the
tooth, Light that contacts a moving object is doppler
shifted and a signal is produced.
As red blood cells represents the majority of moving
objects within the tooth measurement of back scattered
light serves as an index of pulp blood flow
.

Advantages
• An objective test
• Accurate to check vitality.
Disadvantages
• Medications used in cardiovascular diseases
can affect the blood flow to pulp
• Requires higher technical skills to achieve
• Expensive.

Pulp Oximetry
Pulp oximetry is a non-invasive device for determining
pulp vitality. The probe of pulp oximeter consists of red
and infrared light-emitting diodes opposite a
photoelectric detector.
Pulp oximetry is especially helpful in cases of
traumatic injury to the teeth during which nerve supply
of the pulp may be injured, but the blood supply stays
intact.
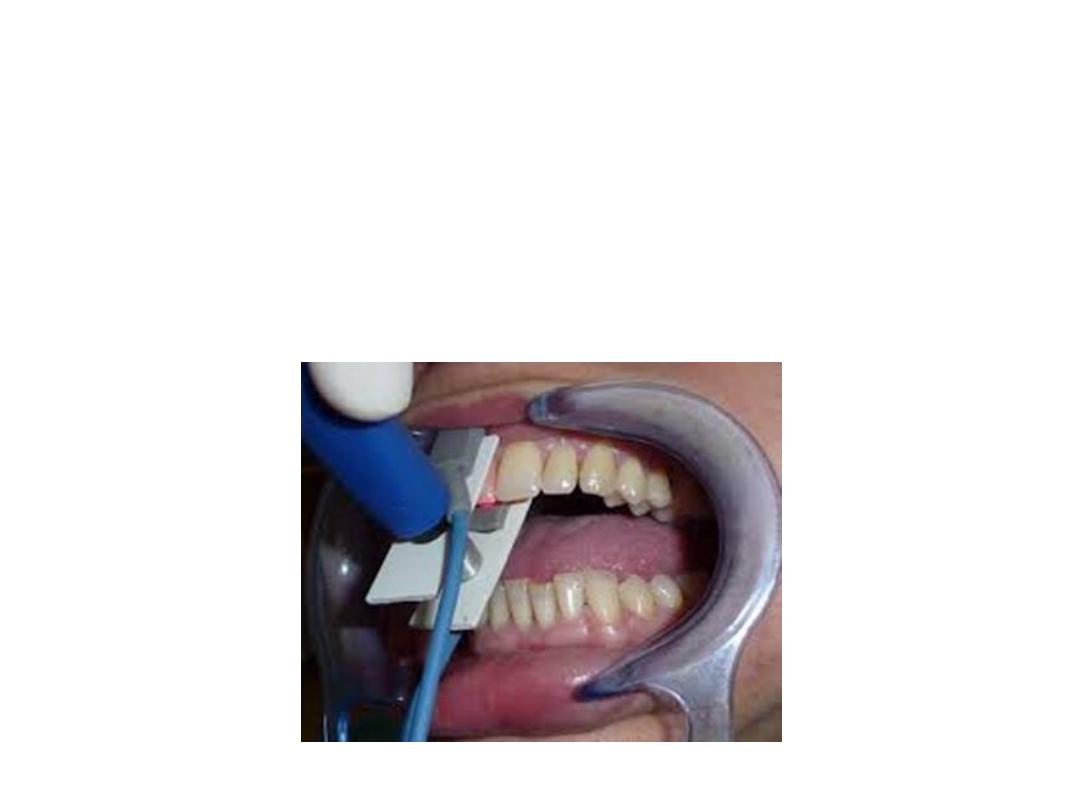
• Oximetry refers to determination of
percentage of oxygen saturation of circulation
arterial blood
• Well oxygenated blood appears bright red

Advantages
• Effective and objective method to evaluate
pulp vitality.
• Useful in cases of traumatic injuries where the
blood supply remains intact but nerve supply is
damaged.
• Easy to reproduce pulp pulse readings.
Disadvantage
Background absorption associated with venous
blood.

DIAGNOSE AND TREAT A CRACKED TOOTH
SYNDROME?
The crack tooth syndrome means incomplete
fracture of a tooth with vital pulp. The fracture
commonly involves enamel and dentin but
sometimes pulp and periodontal structure
may also get involved.

Diagnosis
The careful history of the patient, examination,
diagnosis tests, radiographs and sometimes
surgical exposure are needed for accurate
diagnosis of cracked tooth syndrome.
History of the Patient It includes:
a. A detailed history regarding dietary and
parafunctional habits.
b. History of any previous trauma.

Visual Examination
Look for any wear facets, steep cusps, cracked
restorations or unusual gaps between restorations and
tooth structure.
Tactile Examination
Pass the tip of sharp explore gently along the tooth
surface, it may catch the crack.
Bite Test
The pain during biting or chewing especially upon the
release of pressure is classic sign of cracked tooth
syndrome.
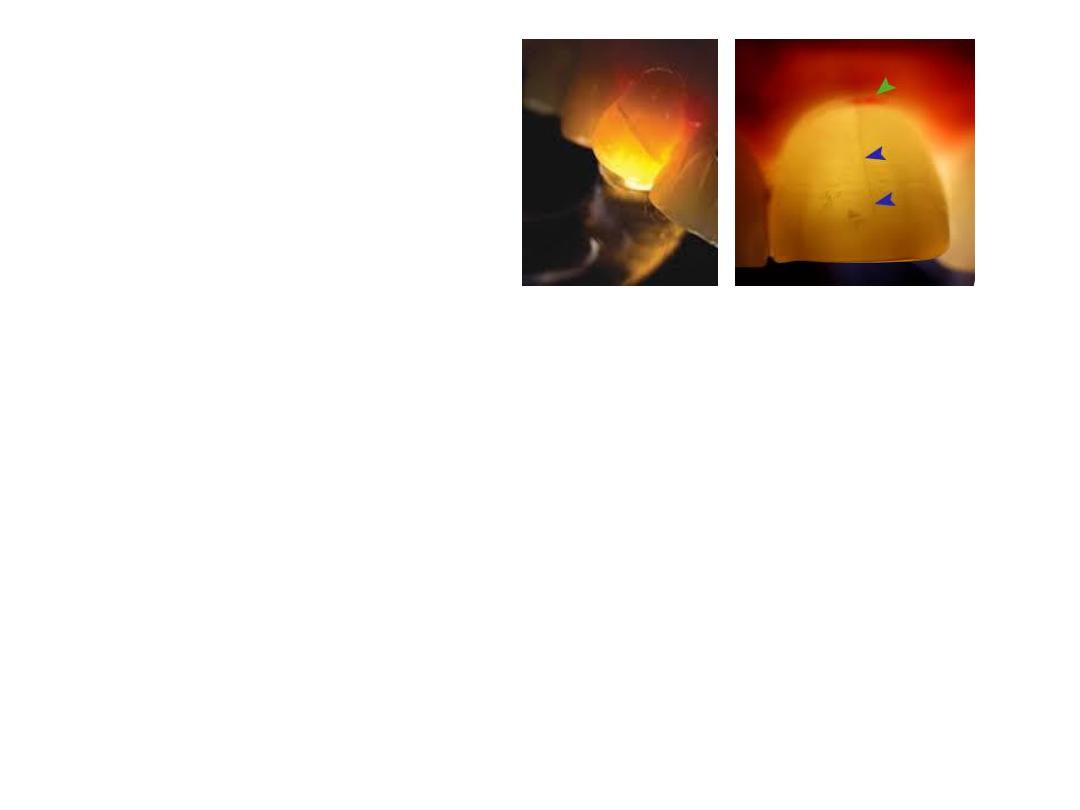

Transillumination
Use of Dyes
Staining of fractured teeth with a dye such as
methylene blue dye can aid in diagnosis. The dark
stain present on the fracture line helps in detecting
the fracture.
Radiographs
1. Taking radiographs from more than one angle can
help in locating the crack.

2. A thickened periodontal ligament space, a diffused
radiolucency especially with elliptical shape in apical
area may indicate crack.
Differential Diagnosis
There must be differentiation of a cracked tooth from a
fractured cusp. The tooth crack occurs more towards the
center of the occlusal surface as compared to the cusp
fracture which is more peripheral in position.
• If the crack has progressed to involve the pulp or
periodontium, patient may have thermal sensitivity
which lingers after removal of the stimulus or slight
to very severe spontaneous pain consistent with irreversible
pulpitis, pulp necrosis or apical periodontitis.

Treatment
The treatment plan for cracked teeth varies with location
and extent of the crack.
• Urgent care of the cracked tooth involves the occlusal
relief.
• Preserve the pulpal vitality by providing full occlusal
coverage for cusp protection.
• When crack involves the pulp, do endodontic
therapy.
• Apically extension and future migration of the crack
apically onto the root determines the prognosis.
Depending upon the treatment may involve
extractions, root resection, or hemisection.








