Haematology
Dr Khudhair Abass AliCollege of Medicine – Baghdad University
Objectives Lecture 5
Blood transfusion: A Safe blood transfusionBMT : types PRV ; A cause of polycythaemia.
Blood Products & transfusion
Donation :1.Whole Blood .
2. Apheresis e.g. platelets.
Blood components :
1.Red cell concentrate: (most of plasma removed ). ABO &Rh compatab. required.
Indication: Acute blood loss replac.& severe An.
2.Plat. Concentrate: ABO compatibility preferable.
Indication: Thrombocytopenia, Plat. Dysfunction.
3.FFP (150- 300 ml): ABO compat. recommended. Dose: 15 ml / Kg.
Indication.: Replacement. Of coagul. Fs def. , TTP .
4.Cryoprecipitate: (10-12ml pack): Contain fibrinogen(150-300mg) & coagulation
Fs. ( Each pack contain 80- 120u FVIII & VWF )
Indication: hypo- Fibrinogenemia , VWD ,Haemophelia.
Lecture (5)
Plasma Derivatives :
1.Coaguiation Fs : F VIII , F IX , recently: recombinant DNA technology.
2.Immunoglobulins : IV IgG (Ab.def., ITP, Gullian Bar. Synd.)
Prophylaxis of Varicella zooster.
Anti Rhesus D Ig
3.Human albumin :
5% :colloid fluid ( Crystalloid sol. Cheaper)
20% :Hypoprot. Odema (Nephrotic synd.), Ascitis in chr.
liver dis.
ABO Blood Groups :
Group Red cell A or B Ag Abs. in plasma % UKO None Anti A & B 46
A A Anti B 42
B B Anti A 9
AB A &B None 3
Donar Blood
Test for HIV ,HBV ,SYPHILIS ,ABO &RhRed cells FFP Pooled plat. --
Storage 40C - 30C 220 C
35 d 1 yr 5 d (agitated)
Adverse effects
Death: o.5/ 100 0001%: Symptoms e.g. fever , itch ,urticaria (repeated transfusions) .
Any symptoms or signs _take it seriously__WARNING !
1. ABO incompatibility :
Recep.IgM (Anti-A ,Anti-B or Anti AB + Transfused red cells
Activate complement system
intravascular haemolysis, hypotension, RF ,peribronchial edema & smooth muscle contraction2. Other immunological complication e.g. Transf. associated lung injury.
, 3. Infections: HBV, HCV, HIV, less than 1/1000 000,(bact. Contam. of plat.
Packs)
Conclusion: avoid unnecesary transfusion.
Signs & Symptoms of acute transfusion reaction :
(Fever, Chills, Tachycardia, Hyper or Hypotension, Collapse , Rigors, Flushing, Urticaria, bone, M., Chest & abd. Pain, SOB, Nausea , Resp.distress )Stop Transfusion
Temp, PR, BP, patient identity, Bl.pack, check compatibility form
1. Reaction only Fever or urticaria↓ ↓
FEVER URTICARIA
*Febrile Non Haemolytic Transf. Reaction * Mild Allergic Reaction
Treatment: Paracetamol Chlorpheneramine 10mg iv
Restart Transf. after 15-30min.at slower rate under observation if no more complications
Suspect ABO incompatibility
! Wrong Bl. Transfusion !YES NO
ABO incompat. Severe Allergic Reaction
Pack & giving set Blood Bank Bronch. Spasm,Angiodema,Abd.pain
i.v.Saline, Urine Output(catheter) Hypoten.
U.O.<100ml/h: give Frusemide ↓
Treat DIC NO YES
Bact. Contam. Stop Transf.
Pack & Giving Set back Chlorphen. 10 mg i.v.
to Bl.Bank, Bl.Culture, O2,Salbutamol Neb.
Repeat Bl.group & comp. Adrenaline 0.5 mg i.m. in
FBC, Coagul.screen ,Bioch. severe Hypot.or Bronchosp.
GUE. Send pack &giving set to Bl.
Broad spectrum antibiotics. Bank.
O2, Fluid.
.
No Bact. Contam.
If acute Dyspnoea. Hypot. Bl. Gases, CXR, CVP, Pul.cap. Pr.
↓ ↓
High CVP Normal CVP
Fluid Overload Transf. related Acute Lung Injury
O2, Frusemide 40-80 mg (Typically within 6h )
SOB, cough, CXR: bilat. nodular infilt.
Stop Transf. 100% O2 ,
Treat as RDS, Ventilation if necessary.
Bone Marrow & peripheral stem cell Transplant (BMT)
Allogenic :Stem cell from Donar, given i.v. to patient( previously conditionedby chemo ± radioth. → engraft into pt.BM (function 3-4 wks).
Sources :
1. Related (HLA identical siblings ).
2. Unrelated ( closely HLA matched Volunteer ) .
Indications :
1.Neoplastic disorders (Leukemia, AML, ALL, CML, MDS, Myelofibrosis )
2. Failure of haemostasis e.g.( Aplastic an.)
3.Inherited Defects e.g.( Thalassemia ) .
Complications : Mucositis, infection, bleeding, pneumonitis, infertility, Chr.GVHD.
secondary malignant dis.
20 yr. +HLA identical subling.> Best results : pt. with minimal residual dis. .Age
25 % die from procedure ,GVHD,
Long survival :50% for leukemia.
GVHD :
Aetiology: cytotoxic activity of donor T lymphocytes ,which become
sensitized to their new host,regarding it as foreign. This may cause
acute or chr. GVHD .
Acute: Ist 100 d, one third of pt. Mild – Lethal, → Skin rash, jaundice,
diarrhea.
Prevention: HLA matching + Immunosupp.drugs
Chronic :May follow acute or independent, later than acute, resemble CTD.
Reduced intensity BMT :↓ mortality
↓ Intensive conditioning
↓ Toxic , old pt.
↑ relapse ?
Autologous :
Pt. own stem cell, from Bl. Or BM ,harvested & frozen → conditioning→reinfuse .
Indications : Dis. do not primarily involving hematological Tissues, or
Pt. who had achieved good Remission.
e.g. AML CR2, Myeloma, poor –risk Hodgkin, High- grade Non-Hodgkin.
Marrow recovery : 2-3 wks .
No risk of GVHD.
↓ mortality .
↑ Recurrence .
Stem cells treated to remove any residual leukemic cells is still
investigated.
Polycythaemia
0.52 %< 180 g / L (18 g /dl) in M PCV < Hb
% 0.48 < 165 g/ L (16.5 g /dl) in F PCV
Classification : RBC Mass Plasma Vol
True Increased Normal
Relative Normal Decreased
Relative : e.g. Dehydration, Diuretics, Alcohol.
True : Primary Secondary Myeloprplif. Disorders ↑EPO (Hypoxia) Inappropriate ↑
( PRV) ↑ Altitude Renal dis.
Lung dis. CHD, Hepatoma
↑ Affinity Hb Bronchogenic Ca.
Uterine fibroid.
Phaeochromocytoma.
Cerebellar
haemangioblastoma
Polycythemia Rubra Vera
Age: more than 40y.Clinically :
1. Incidental.
2. Symptomatic :Hyperviscocity : Lassitude, loss of conc., headache, dizziness,
blackouts, pruritis (worse after hot bath) , epistaxis, peripheral arterial dis.
e.g. CVA (thrombosis) , venous thromboembolism,.
Peptic ulcer is common (sometimes bleeding ) .
Plethoric face , majority has palpable spleen .
Diagnosis: ↑ RC mass , ↑PCV , ↑ Plat.& Neutrophil (often) , JAK -2 Mut.(97%)
Hypercellular B.M. + Absence of secondary causes .
Treatment : ↓ risk of thrombosis : Venesection 400-500 ml (elderly less) every
5-7 wks → PCV 45%- & MAINTAIN AT THIS LEVEL .
Hydroxycarbamide ( Hydroxyurea), or ᾱ interferon → suppress marrow prolif.
& ↓ transform. Into myelofibrosis , control spleen size .
RA P 32 In old pt.
Prognosis : Survival 10- 20 y with Treatment. CVA & IHD 60%
Conversion to other myeloprolif. Dis. 15% , Acute leukemia ( RA P)
Summary
Blood Transfusion: Life saving proceedure,not always safe. has to be done properly, from right donor to the right recipient under medical supervision. .Most common side effects are febrile & urticarial reactions, which should be managed with suspension of transfusion for 15-30 minute, treat symptomaticaly & observation for progression of signs & symptoms. Restart if no progression.
BMT: Allogenic, Autologous.
PRV : Clonal disease , could be asymptomatic, or hyperviscocity
Symptoms.
Spleen palpable 50%
Lab: ↑ Hb, PCV., Red cell mass, WBC. Platelets
R: venesection
Hydroxyurea
Objectives:
WBC differential, functions,↑↓Lymphadenopathy.
Splenomegally
WBC DISORDERS
⁄ L * Normal Count : 4 –10 X 10 9 * Lecoerythroblastic picture : presence of immature WBC & ERYTHROBLASTin peripheral Bl.
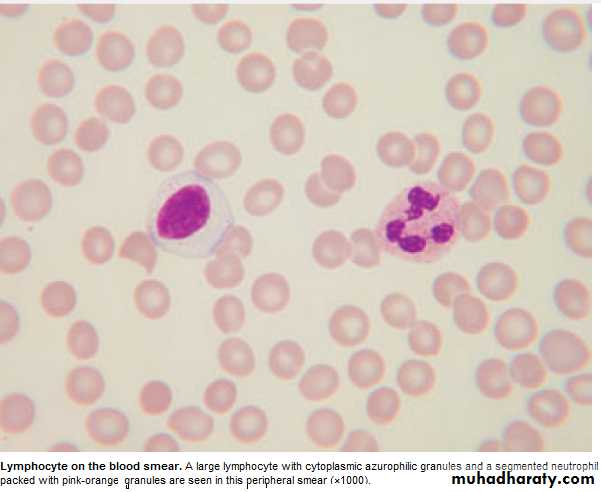
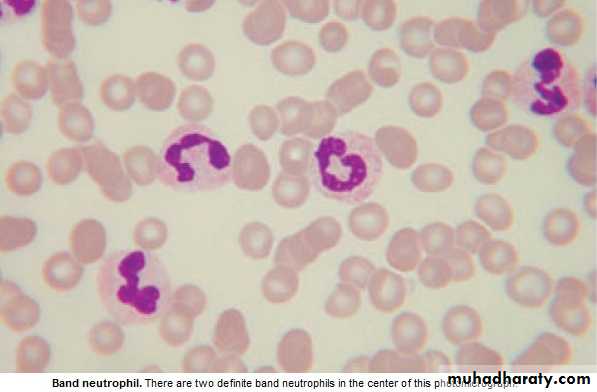
* Peripheral bl. Contain Neutrophils (N) ,Lymphocytes (L),Eosinophils (E),
Basophils (B) ,Monocytes(M) .
* Myelocytes & Metamyelocytes may appear in peripheral Bl. in infection.
* Leucocytosis : ↑ Total WBC or only one type of cell (differential) .
* Leucopenia : ↓ Total WBC or only one type of cell . NEUTROPHILS : 2---7 X 10 9 ∕ L
Recognize ,ingest & destroy foreign particles, spend 6-10 h in circul.→ removed by spleen .
* Neutropenia: < 1.5 x 10 9 ∕ L ( Asymptomatic –Sepsis )
If < o.5 x 10 9 / L – Critical , Fever sore throat ,perianal pain, skin inflam. → SHOCK if no antibiotics .
Lecture (6)
Neutrophelia Neutropenia,
Infection: Bacterial ,Fungal Viral ,Bacterial( TF) , Protozoal( malaria)Trauma: Surgery ,Burn . CTD, Alcohol.
Infarction: MI, PE ,Sickle C.Crises. BM infilt.: Leukemia, MDS,
Inflam.: Gout, R.arth.,U.C. Drugs
Malignant: Solid Tumors, Hodgkin's.
Myeloprolif.: PRV,CML.
Physiological: Exercise, Pregnancy.
Drugs causing Neutropenia
Analgesia,Anti-infl.: Gold,Penicillamine. Anti-Thyroid : Carbimazole.
AntiArrhythmics: Quinidine . AntiHypert.: Captopril, Nifedipine.
AntiDepres.: Amitryptylline. Anti-Malarial: Chloroquine.
AntiConvulsants: Phenytoin, Carbim.
Antibiotics: Sulphonamide,Penicillin, Chloramphenicol.
Miscellaneous: Cimetidine,Ranitidine,Chlorpropamide,Zidovudine
Lymphocytes : 1.5- 4 x 10 9 / L
T Lymphocytes : Mediate cell immunity.
B Lymphocytes : Mediate humeral immunity.
Lymphocytosis Lymphopenia
Infection :Viral, Bacterial (Pertussis) Inflam.: CTD.Lymphoprplif.: CLL, Lymphoma. Lymphoma , Post- splenectomy R.F., Steroids, Severe comb.im.def. Cytotoxics.
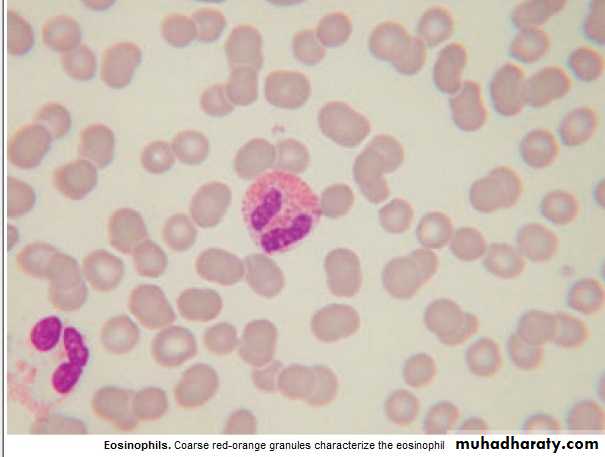
Eosinophils : 0.04 -0.4 X10 9 / L
1. Intracellular killing of Protozoa &Helminthes ., 2.Allergic reaction.Eosinophilia :
1. Allergy : Hay fever, asthma, eczema.
2.Infection ;Parasitic.
3.Drug hypersensitivity: gold,sulphonamide.
4:Skin dis.
5:CTD. Polyarteritis nodosa,Hypersensitivity.
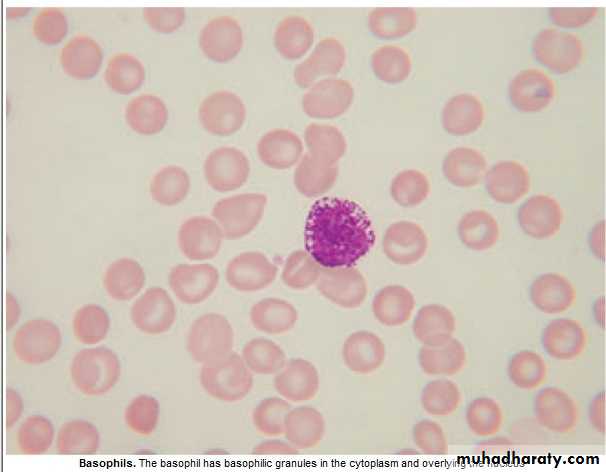
Basophils : 0.01 -0.1 x 10 9/ L
Involved in hypersensitivity reaction.Basophilia : 1. Myeloprolif.dis.: PRV, CML.
2. Inflam.: Acute hypersensitivity ,Ulcer. Colitis(UC).
3.Fe def. An.
Monocytes : 0.2 – 0.8 x 10 9 / L
Migrate into tissue → Macrophage .
Monocytosis : 1. Infection (TB).
2.Inflam. : CTD, UC.
3.Malig.: Solid tumors'.
Lymphadenopathy
Causes : Infection : 1.Bacterial : strep. ,TB, brucellosis. Typhoid fever.2.Viral ;EBV, HIV.
3.Protoz. :Toxoplasmosis.
4. :Fungal :Histoplasmosis.
Neoplastic : 1. Primary : Lymphoma, Leukemia
2.Secondary : lung, breast, thyroid, stomach. CTD :Rh. Arthritis,SLE.
Sarcoidosis,Amyloidosis.
Drugs :Phenytoin.
History :Speed of onset,Pain,Associated symptoms,Wt. loss,Night sweat., Itching.
Exam.: Site,Localised or Generalized.
Consistency: Hard,Soft,Rubbery.
Area of drainage, + General exam.
Investigations : CBP ( ↑ Neutrophils = Inflam. ,Haematological dis.), ESR, CXR, Biopsy.
Splenomegally
Causes : 1.Congestive: 4.Haematological:
a.Intrahep. Portal. HT. a. Red cell disorders
Cirrhosis,Hepatic V. Throm. Megalob. An.,Hemoglobinopat.
b.Extrahep.Portal HT. b.Autoimmune haemolytic An.
c.Cardiac:CHF, Const.peric. c.Myeloprolif.disorders :CML,PRV,
2.Infective: Myelofibrosis,ET.
a.Bact.:Endocarditis,Septicemia,TF, d.Neoplastic:Leukemia, Lymphom.
b.Viral :Hepatitis,EBV,Cytomegal. 5.Other Malignancies:Metast.(rare)
c.Protoz.:Malaria,Kala-azar. 6.Gauchers dis.
d.Fungal:Histoplasmosis. 7.Miscellan.:Cysts,Amyl.Thyrotoxico.
3.Inflammatory/Granulomatous:
Feltys syndrome,SLE,Sarcoidosis.
Clinically: + Liver → Lympho. Or Myeloprolif.dis.,Liver dis.,Amyloid.
+ LN → LymphoProlif.
Abdom. discomfort+ backache, splen. Infarc.→ severe abd. Pain., rupture ?
Investing.: FBC (Pancytopenia =Hypersplenism ?) ,Abd. US & CT ,CXR (Mediast. LN )
BM ,Splenectomy if all negative.
Summary
Lymphadenopathy:Most common cause is infection: painful ,tender,examine
drainage area.
Neoplastic cause is usually painless, examine other areas,
spleen and liver.
Send for CBP.
Splenomegally:
Most common cause is infection.
Check for lymphadenopathy and hepatomegally.
Send for CBP.